Practical Quiz - Chem 232 UMD
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
What lab is lab one?
Recrystallization of an impure solid
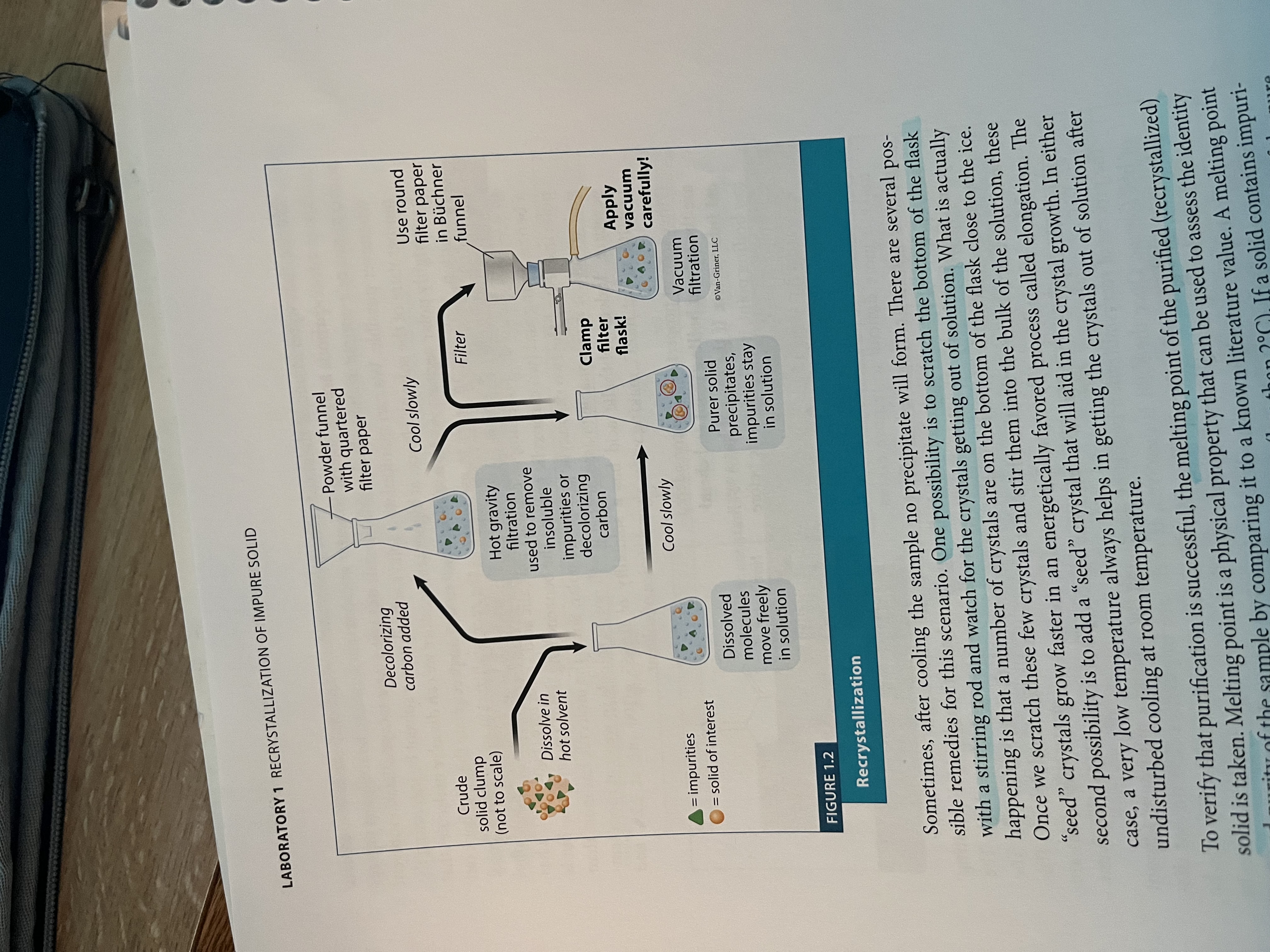
What is recrystallization of an impure solid?
a purification technique in which a crude solid is dissolved in minimum amount (volume) of hot solvent, and upon cooling, a purer solid precipitated from the solution
What is the most important consideration for good recrystallization?
Choosing a good solvent based on
Polarity
Differential solubility of solid in solvent
Solvent Bp
Chemical interaction between solid and solvent
Solubility of impurity in solvent
insoluble, soluble
The solid should be infinitely _____ at low temperatures and infinitely _____ at high temperatures
What can you do if there are purities that result that do not dissolve?
Use hot gravity filtration to filter them out, or a decolorizing agent
What is the experimental set-up for experiment 1?
four test tubes in a warm/hot water bath, then cooled to room temp, then finally in an ice bath, best solvent should be observed (which one is solid at cold and room temp but no precipitate at hot)
THERE MUST BE 4 TUBES, ONE FOR EACH SOLVENT
Then, for recrystallization, .40g of crude solid was placed in a 25 ml Erlenmeyer flask, best solvent was used, small magnetic stir bar was added, heated on hot plate until solid was completely dissolved
Cool to room temp, any insoluble are filtered out via gravity filtration
Recrystallized sample was collected via vacuum filtration using a Buchner funnel and filter flask
What is lab 3?
Extraction
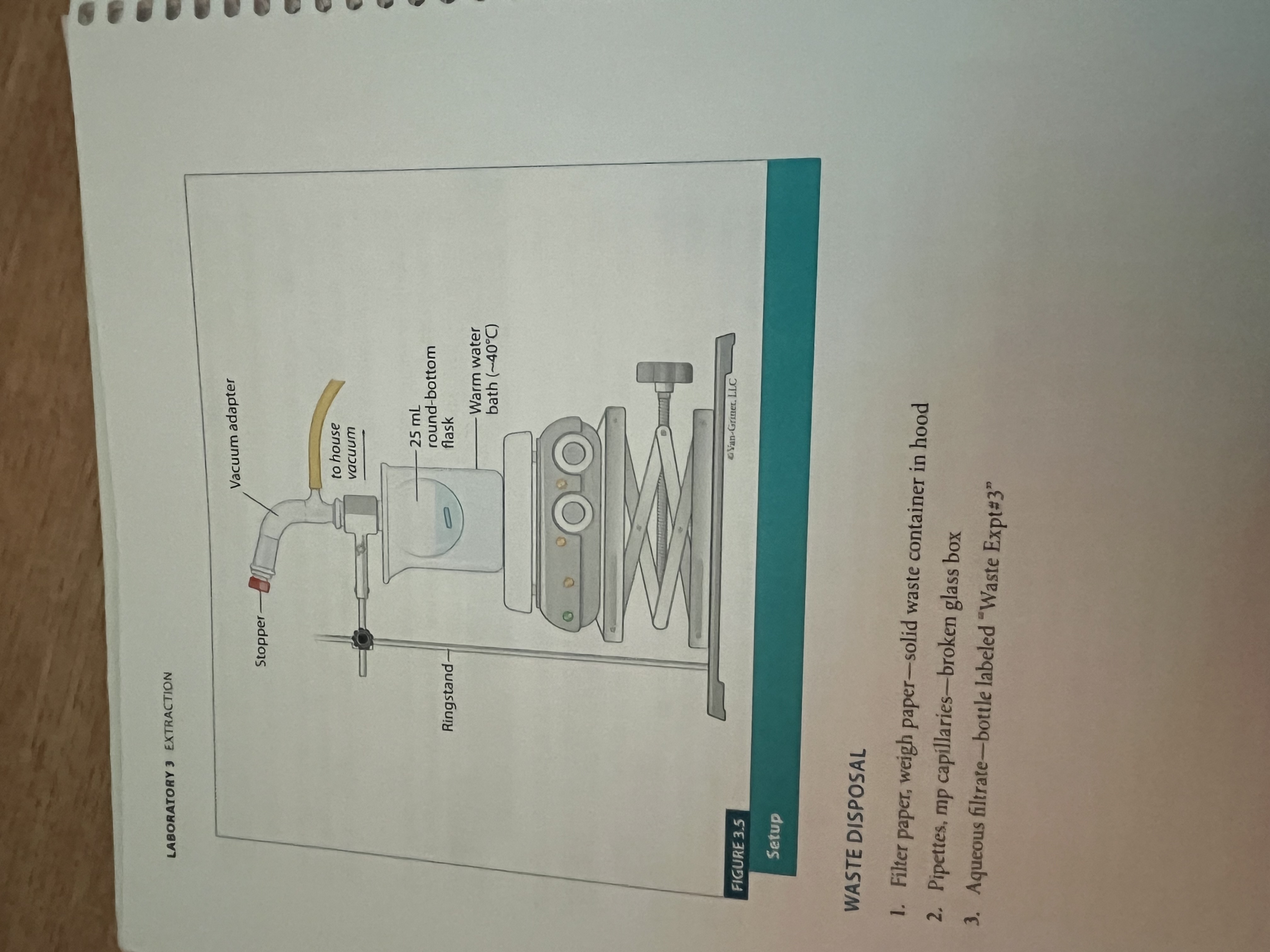
What is extraction?
A technique defined as transferring solute from one solvent to another
We match polarity as much as possible (like dissolves like)
We want something to be completely solvated at room temp, not partially precipitated at room temp like for experiment 1
Make sure the solvent has a high boiling point so we can remove it later
What is selectivity?
The solvent extracts only our compound of interest and not other components
typically achieved by experience and trial and error
In order to extract the max amount of solute into the solvent, we help the process along b raising the temperature, grinding the solid, and mixing well
What kind of extraction did we use?
Liquid-liquid extraction - use two immiscible solvents to separate a mixture of solids (must have different densities, refractive indices)
MOST ORGANIC COMPOUNDS ARE NOT WATER SOLUABLE
In order to separate the mixed solutes, we increase the solubility of one solid in water and “pull” it to the aqueous phase, thus separating it from the other organic solids in the mixture
The process is repeated (take advantage of the acidity/basicity of the solution
What bases are used for what compounds experiment 3?
Strong acids, like carboxylic acids, use weak bases (NaHCO3) to deprotonate it
Weak acids, like phenol, require strong bases like NaOH
Amines are protonated with strong acids like HCl
What reagents are used for experiment 1?
Benzoic acid, p-toluic acid, acetanilide, and benzyl
What solvents are used in experiment 1?
Hexanes, acetone, ethanol, and water
What reagents are used in experiment 3?
3-nitrobenzoic acid, 2-napthol, and 1,4-dimethyoxybenzene
What are the solvents used in experiment 3?
NaHCO3, NaOH, and HCl
What is experiment 4?
Thin layer chromatography of spinach
What is chromatography?
separation and purification technique
thin layer chromatography is based on partitioning the sample between two phases, the mobile and stationary
Planar version
Stationary phase is the silica paper, and the mobile phase is capillary action
Separates based on polarity (silica plate is polar, so the more polar a substance, the less distance it will travel.
What are the pigments that we plan to extract in experiment 4?
Chlorophyll-a, lutein (xanthophyll) and B-carotene.
What is experiment 5?
Column chromatography of spinach
What is column chromatography?
Another common technique for separation of liquids - we use a stationary phase and mobile phase
Is quantitative
Column is the Pasteur pipet
Stationary phase (silica) is packed and the mobile phase (organic solvents) is applied at the top, traveling down the column
GRAVITY IS A HUGE COMPONENT HERE
How does polarity relate to column chromatography?
Compounds that are more polar tend to stick to the stationary phase and lag behind, while less polar compounds interact with the mobile phase more and travel faster down the column with the mobile phase
What is retention time?
Time it takes for a compound to travel down the column and be collected
What must you push into the pipette before adding the sand and MgSO4?
A small piece of cotton
After your pigments are extracted using column chromatography, what do you do?
A TLC plate with one “control” and blot the pigments next to the control to see how well the extraction was
You’re extractions should match up with the pigment results on the sample.
What is experiment 6?
Distillation
What is distillation?
A process in which a liquid is heated to its boiling point and the resulting vapor phase is conducted to and condensed in a different container.
Separation and purification technique for mixture of liquids that have different boiling points
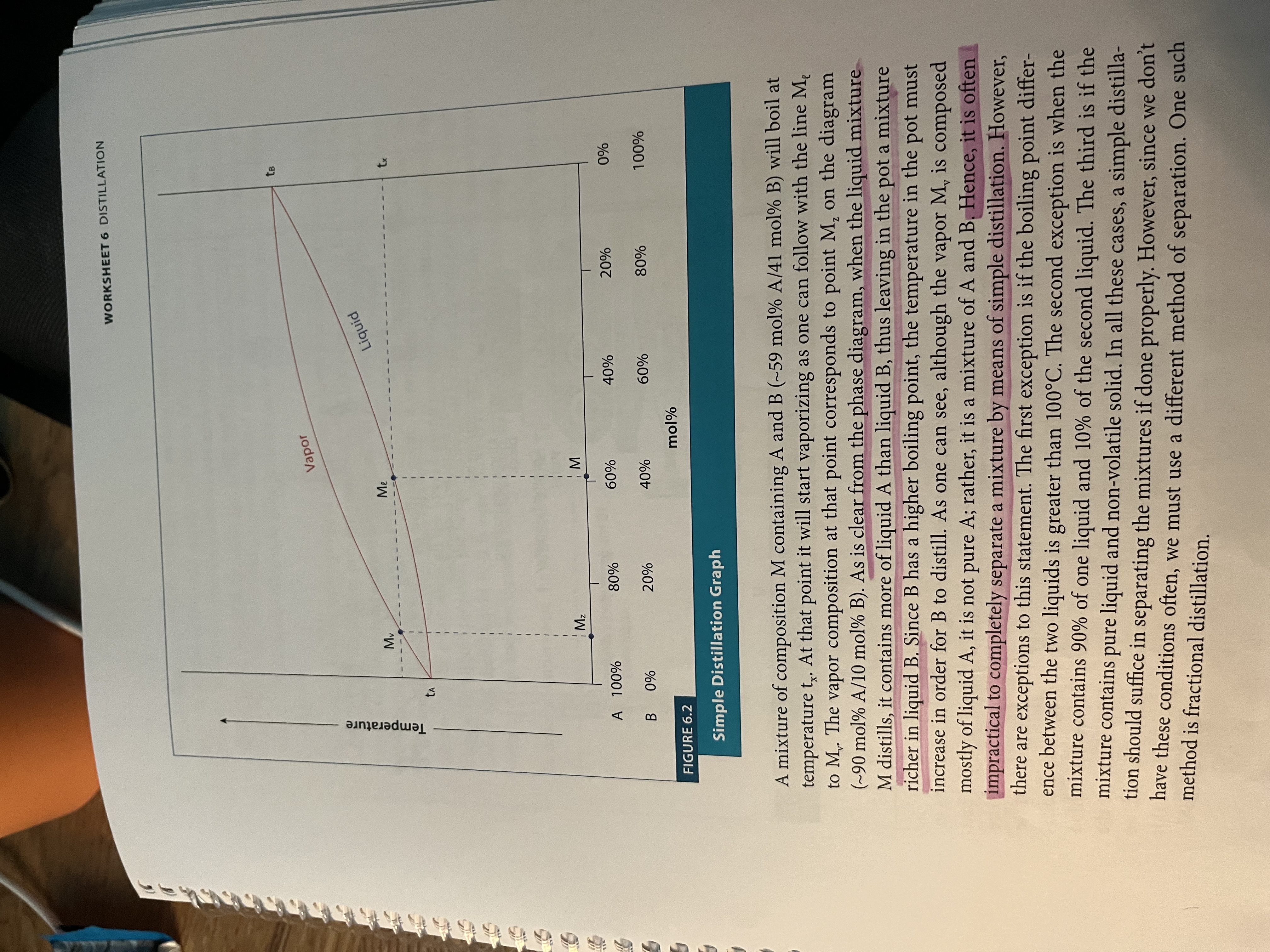
What are the two kinds of distillation?
Simple distillation - a useful technique when the liquids in the mixture have ~50 degrees Celsius difference in their boiling point
Temperature often rises as distillation occurs because the flask is having more and more of the high temperature solvent
Fractional Distillation - simple distillation but using a fractionating column to repeat the processes of distillation so that it is a more pure distillate that results
More surface area for distillation = more accurate results (repeated cycles of evaporation and condensation as the liquid moves up the tube)
Make sure that you have a temperature gradient so that there is no reflux back into the RB flask
What is important to note about the speed of distillation?
It must occur not too fast and not too slow in order collect pure distillate
Heat setting on 2-3 stir bar
Distill no longer than an hour
Collect at 2mL and 7 mL (don’t collect more than 7mL)
What is experiment 7?
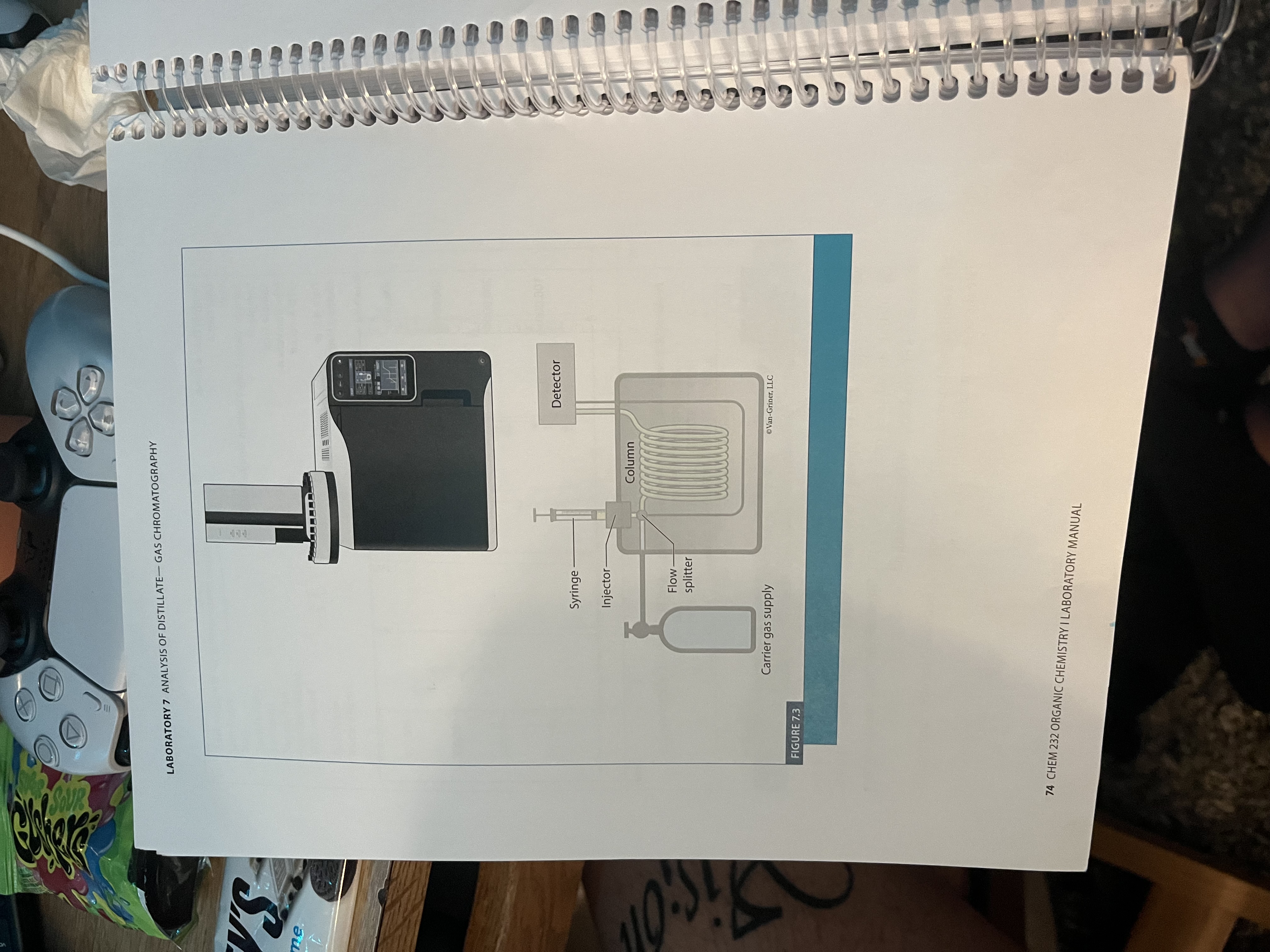
Analysis of distillate - gas chromatography
What is Gas Chromatography?
is an analytical technique of separation and analysis
separation in the GC is based on volatility or boiling point
Used as an analytical tool rather than a preparatory one
Used as a identification tool by comparing an unknown with a known standard using the retention times under the same conditions preferably on the exact same instrument
What are the stationary phase and mobile phases of the GC?
Stationary phase - very thin coating of viscous liquid on a long capillary tube (VERY HIGH BP, generally non-polar)
Mobile phase - inert gas (hydrogen or nitrogen)
What is important to know about GC’s?
The solvent that you use - tells us which peak is the solvent peak so we can ignore it when looking to the chromatogram
Where the solvent peak will be will be based on its boiling point (if you have a mix of two solutions that have high bps, use a low bp solvent, and if you have a mix with low bps, use a high bp solvent like xylenes)
What is the GC detector?
Flame ionization detector - sample is burned in hydrogen flame, producing ions that conduct electricity and can be used by the GC.
How to identify peaks on the chromatograms?
Lowest retention time = lowest BP
To confirm, we use pure solutions of the two solutions in our mixture to get a baseline for the retention time of the liquid before we make a final judgement
What is the response factor?
What we get when we divide the area of the lower bp liquid by the higher bp liquid
We apply this number to every molar ratio by multiplying the higher bp liquid by this number to get the adjusted molar ratio
What is experiment 8?
Free radical halogenation of alkanes
What are we doing during free radical halogenation of alkanes?
Comparing the relative rate of free radical halogenation of six hydrocarbons under three different conditions
Red/orange bromine color allows bromination reaction to be easily followed (color disappearing = fully reacted)
What are the three steps in free radical halogenation?
Initiation - X2 → 2X
Propagation - R-H +X → HX + R radical
R radical + X = X → RX + X radical
Overall reaction - R-H +X2 → R-X +HX
What hydrocarbons do we study?
Toluene, ethylbenzene, isopropyl benzene, t-butyl benzene, cyclohexane, methyl-cyclohexane
What is the lab set up for Bromination?
At room temp: Label 6 test tubes with the name of the solution on it, add the 1M bromine solution to each of the test tubes, watch for the color to disappear for 20 minutes
At elevated temperature, add the test tubes to a warm water bath
For bromination with irradiation, add a lamp
What is lab 9?
Nucleophilic substitution reactions
What is the conductivity probe (experiment 9)
used to measure the solutions ability to conduct electric current between two electrodes
Strength of the current is directly proportional to the concentration of ions in the solution, so a higher concentration of ions will give higher conductivity values
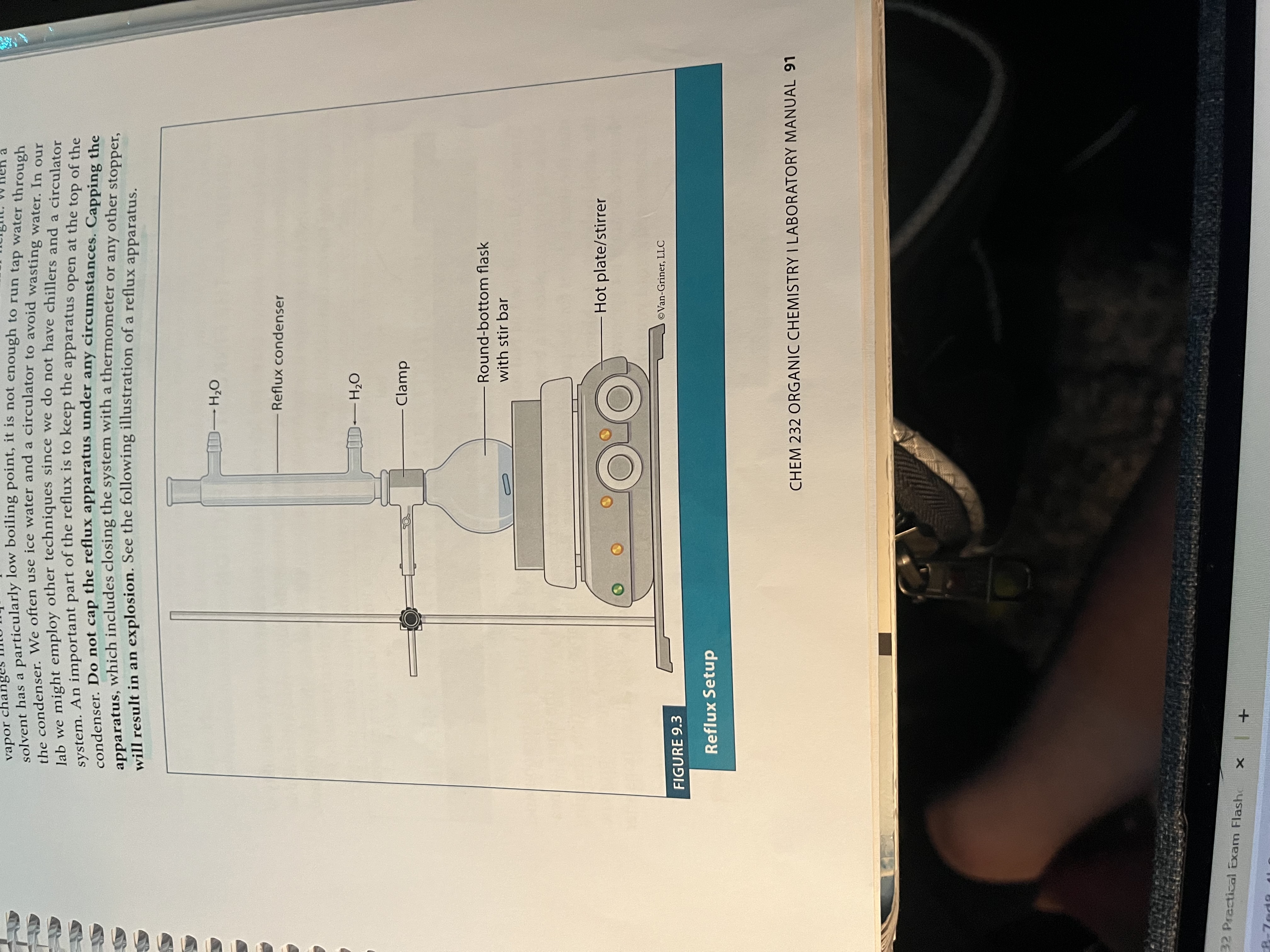
What is reflux (experiment 9)?
Allows us to run the reaction at the solvent’s BP without boiling it off
Drips back into the reaction flask when it is heated
DO NOT CAP THE SETUP BECAUSE ITLL EXPLODE
What are the solvents and procedure used for experiment 9?
NaI for the Finkelstein reaction (SN2) with 1-bromobutane, 1-chloro-butane, 2-bromobutane, and 1-bromo-2-methylpropane
Add a stir bar and place beaker on stir 3-4, timing when precipitate appears (stop after 25)
Sub or elim for 3-bromopropyl benzene with sodium methoxide in methanol
Use reflux apparatus then use the separatory funnel to separate the two layers you form
Repeat with room temp and see what happens
Substitution - methanol and 2-bromo-2-methylpropane, 2-chloro-2 methylpropane, 2-bromobutane and 2-chloro-butane
USE CONDUCTIVITY PROBE
What is experiment 10?
Elimination of alkyl halides (e1 and e2)
What are we doing exactly in experiment 10?
exploring the effect of the base structure on the distribution of elimination productions
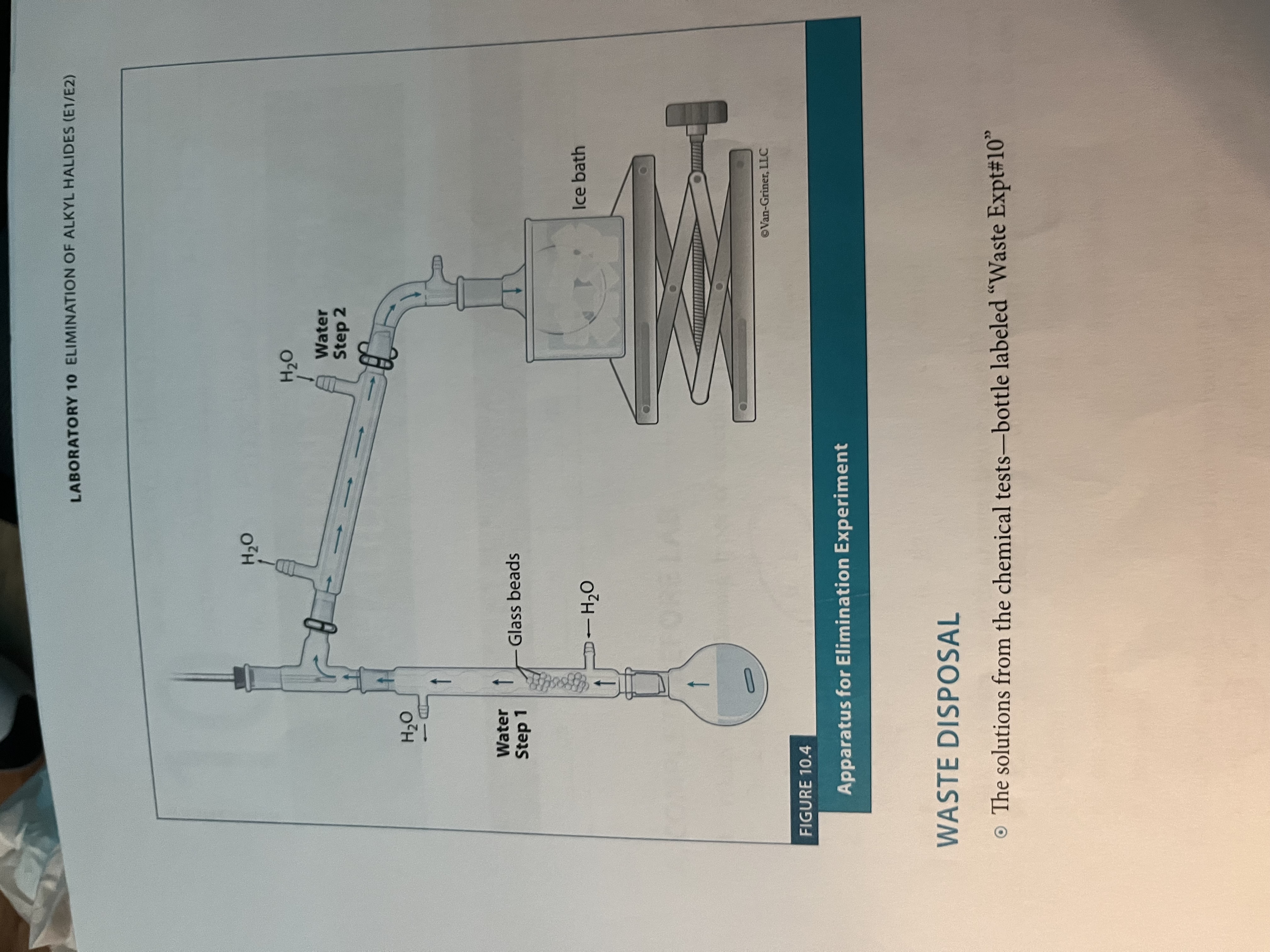
What is the set-up for experiment 10?
Similar to fractional distillation but grease the joints of the column prior to assembly
What are the solvents./bases/nucleophiles for experiment 10?
KOH, KoTBu,1-propanol, 1-butanol
What tests do you perform to each of the solvents that you used after elimination has supposedly taken place?
Bromine in dichloromethane - place a few drops of .1 M bromine in dichloromethane and then add to your test tube, watching for the brown color to change to colorless
Bayer test - place two drops of product in a test tube and add 0.1M KMnO4 drops, watching for the purple color to turn to a brown precipitate
What is experiment 11?
GC analysis of elimination
What is the objective for experiment 11?
To analyze the product the students obtained from elimination experiments and compare the distributions to see which one of the two was favored over the other
NO RESPONSE FACTOR
Same set-up to GC of distillate experiment, except we use xylenes as our solvent (high BP) since our products have low BPs.
Run 3 standards - 2-bromo-2methylbutane, 2-methyl-2-butene and 2-methyl-1-butene
2-butene will be zaitzev, other will be hoffman (lower bp)
Recrystallization set up
Extraction set up
How to use the separtory funnel

Extraction flow chart


What the TLC plate should look like

How column chromatography is set up

How simple distillation is set up

Phase diagram for simple distillation
Phase diagram for fractional distillation
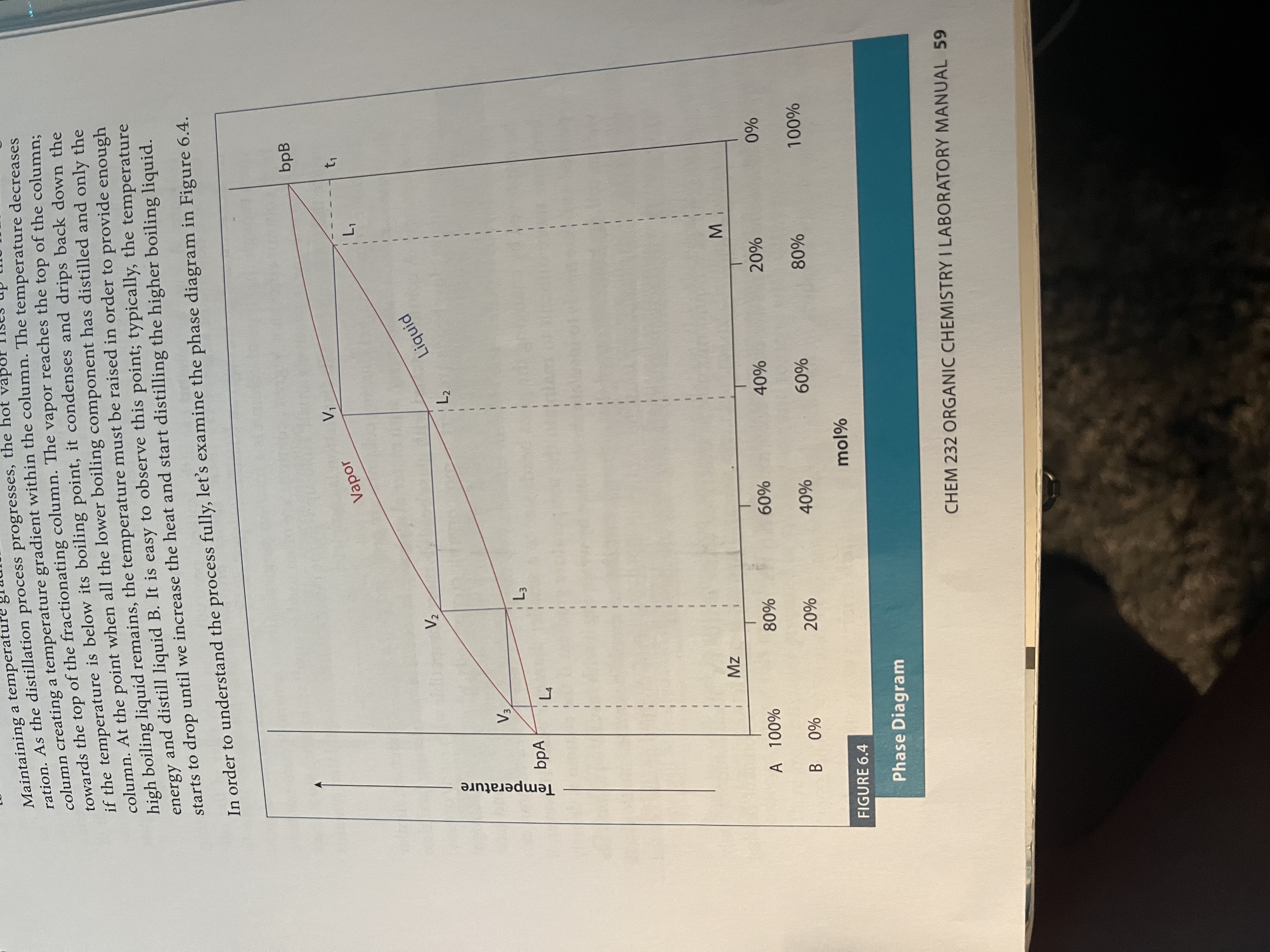
Setup for fractional distillation

Setup for reflux
Set up for elimination
Conductivity probe

GC machine