EM E2 random questions
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
what are the physical findings due to neglect seen in infants?
diaper rash
alopecia
ribs showing
sunken
not meeting milestones
dirty
injuries
what are the physical findings due to neglect seen in school aged children?
stealing food
absent
emotionally withdrawn
poor eye contact
aggressive
poor dental health
fall asleep during school
dirty and unkempt
what are the findings of sexual abuse seen in children?
STDs
warts
ulcers
vesicles
store all evidence in paper bags !
what are the signs of physical abuse seen in children?
adult bite → 3 cm
cig burn → 5 mm
scald burns
skeletal injuries
abd/head injuries
what is mandatory in evaluation for Munchausen by proxy?
social services and psych eval
what are the s/sx of Munchausen by proxy?
bleeding
seizures
AMS
apnea
D/V
fever
rash
multiple organ involvement
MC biological mothers

what is the MC injured organ in blunt trauma?
liver then spleen***
what is the MC injured organ in penetrating trauma?
liver then small bowel
what is the gold standard tx for intra-abd injuries?
laparotomy
what is the etio of herpangina?
coxsackie virus
which Le Fort fracture involves only the maxilla at the level of the nasal fossa?***
1 → speak no evil
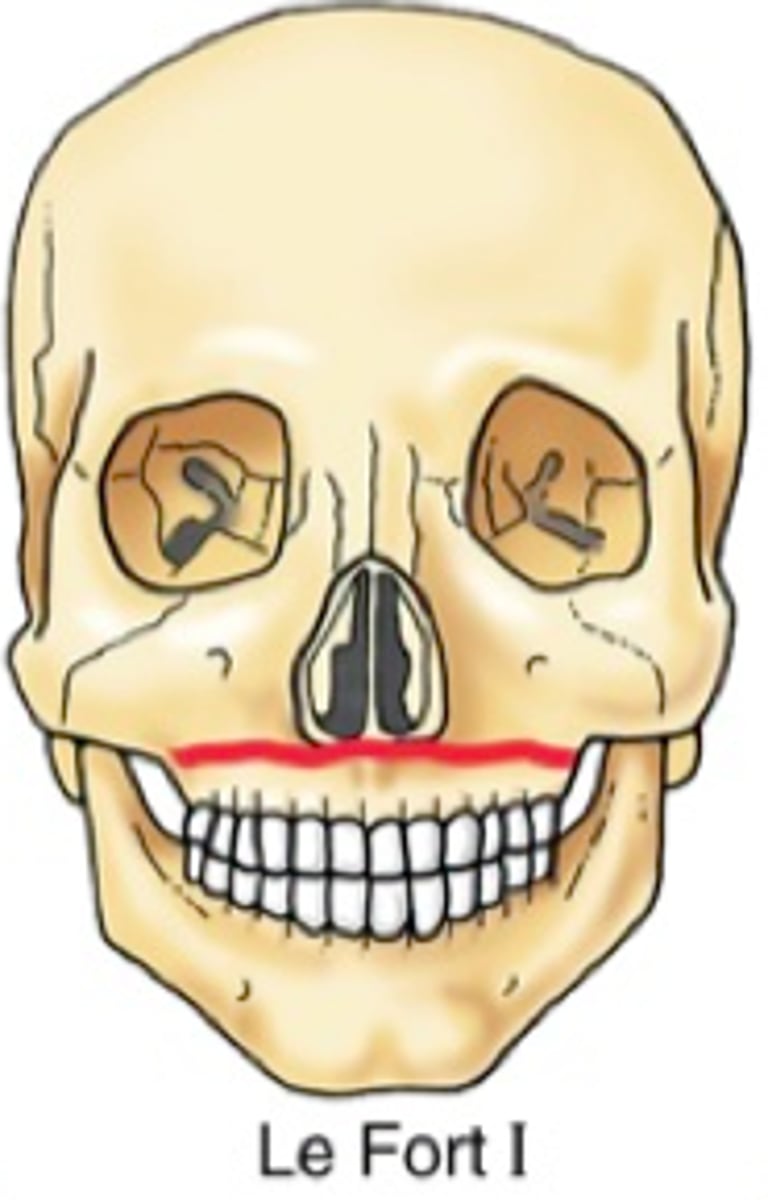
which Le Fort fracture involves the maxilla, nasal bones, and medial aspects of orbits?
2 → see no evil
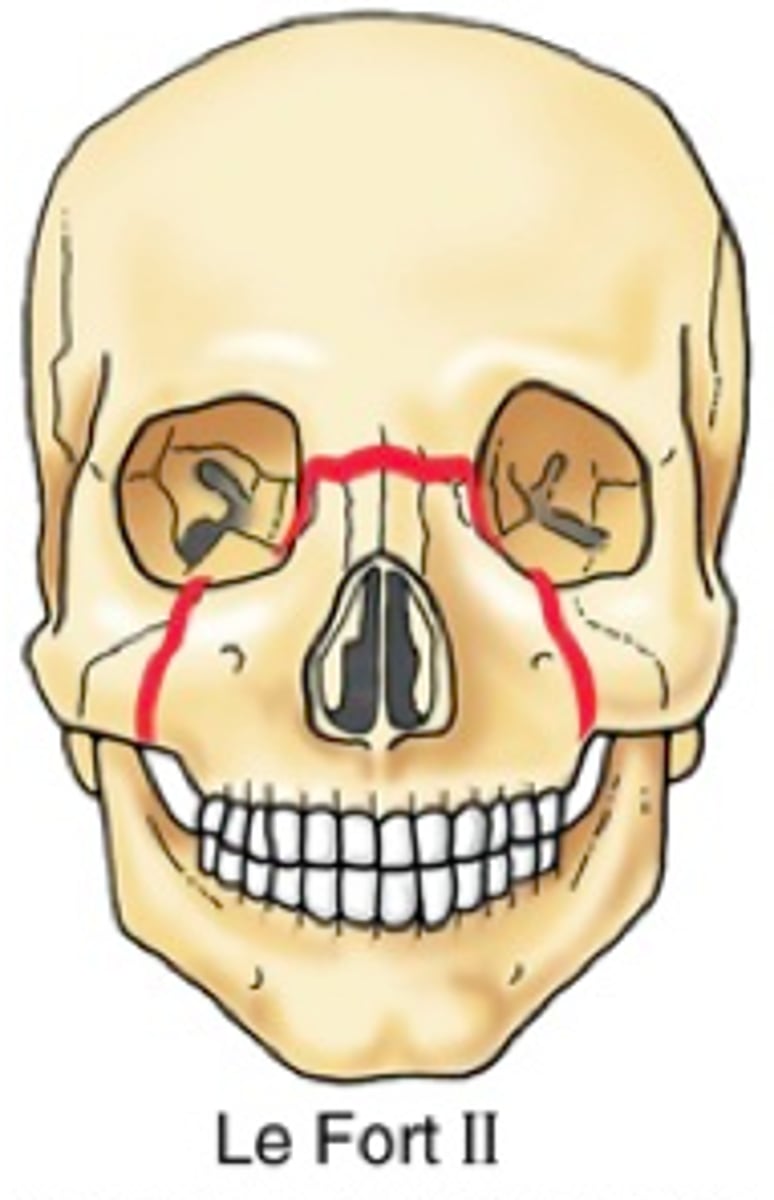
which Le Fort fracture involves the maxilla, zygomatic, nasal, ethmoid, and vomer and the lesser bones of the cranial base?
3 → hear no evil
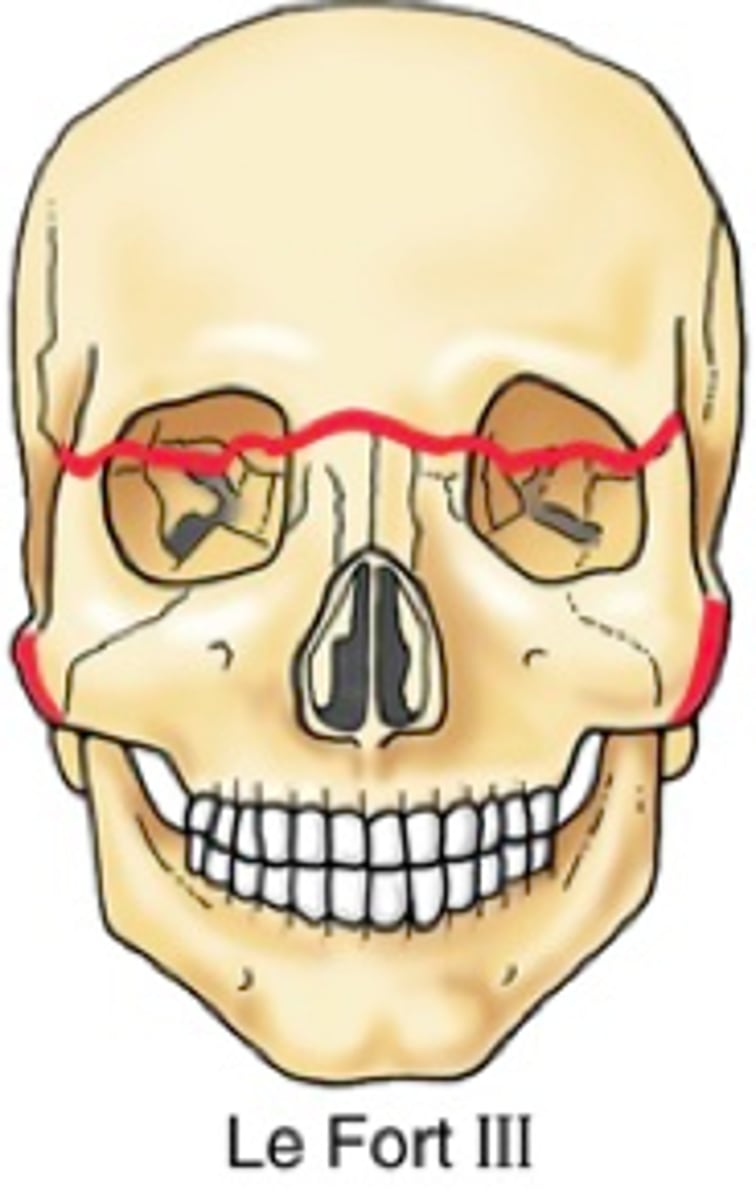
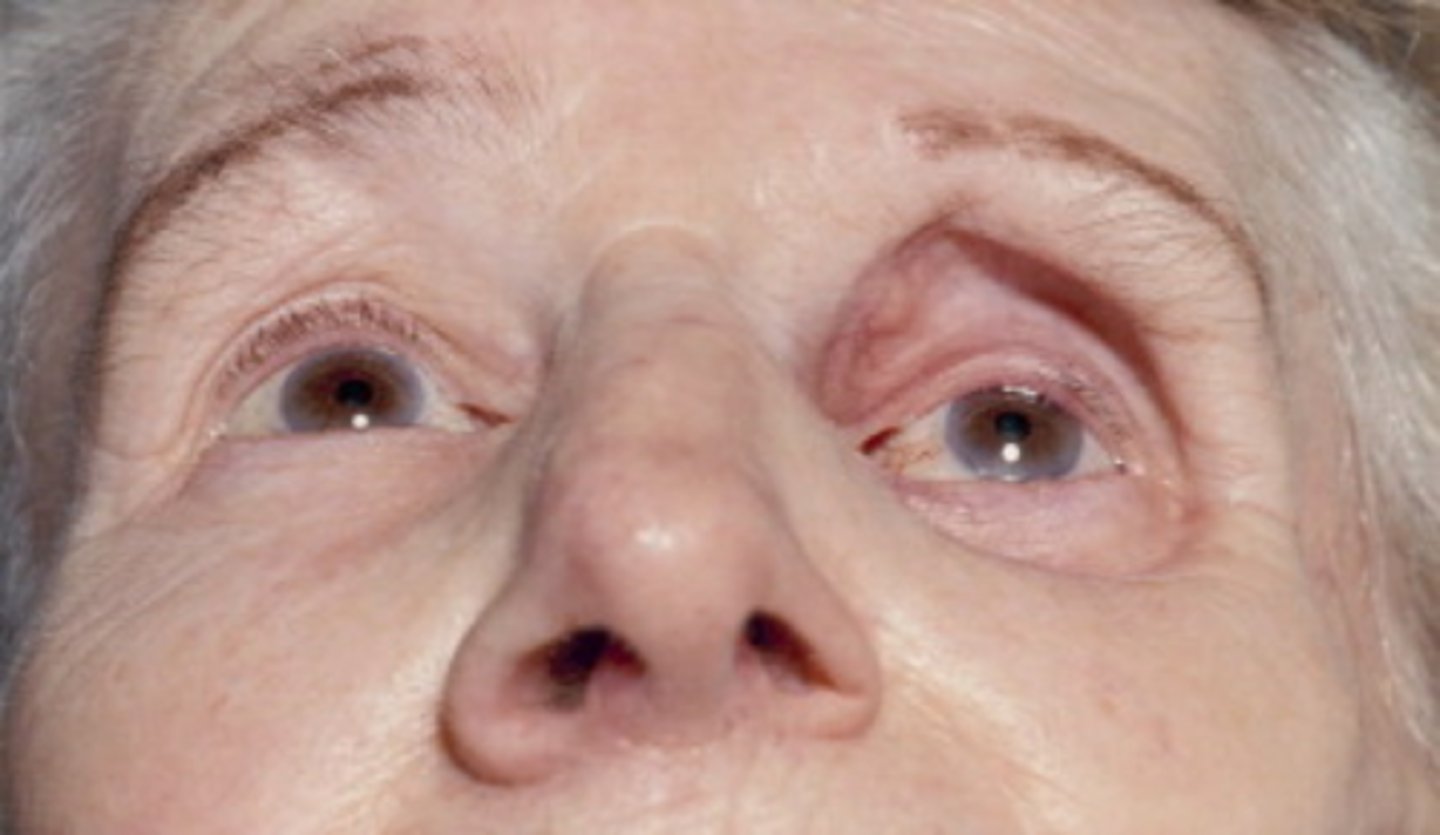
what is posterior displacement of the eye within the orbit? what other sx are seen?
enophthalmos*** → impaired ocular motility, diplopia, infraorbital hypesthesia
clouding of the maxillary sinus on the side of trauma is ____________ ___________ until proven otherwise***
orbital fracture
emphysema of orbit is a sx of which dx?
orbital blowout fracture
what is the MC ligamentous injury of the hand?
PIP → via axial load and hyperextension
which elbow dislocation is MC?
posterior
what does a fat pad sign indicate?
bleeding into soft tissue or pathological fracture
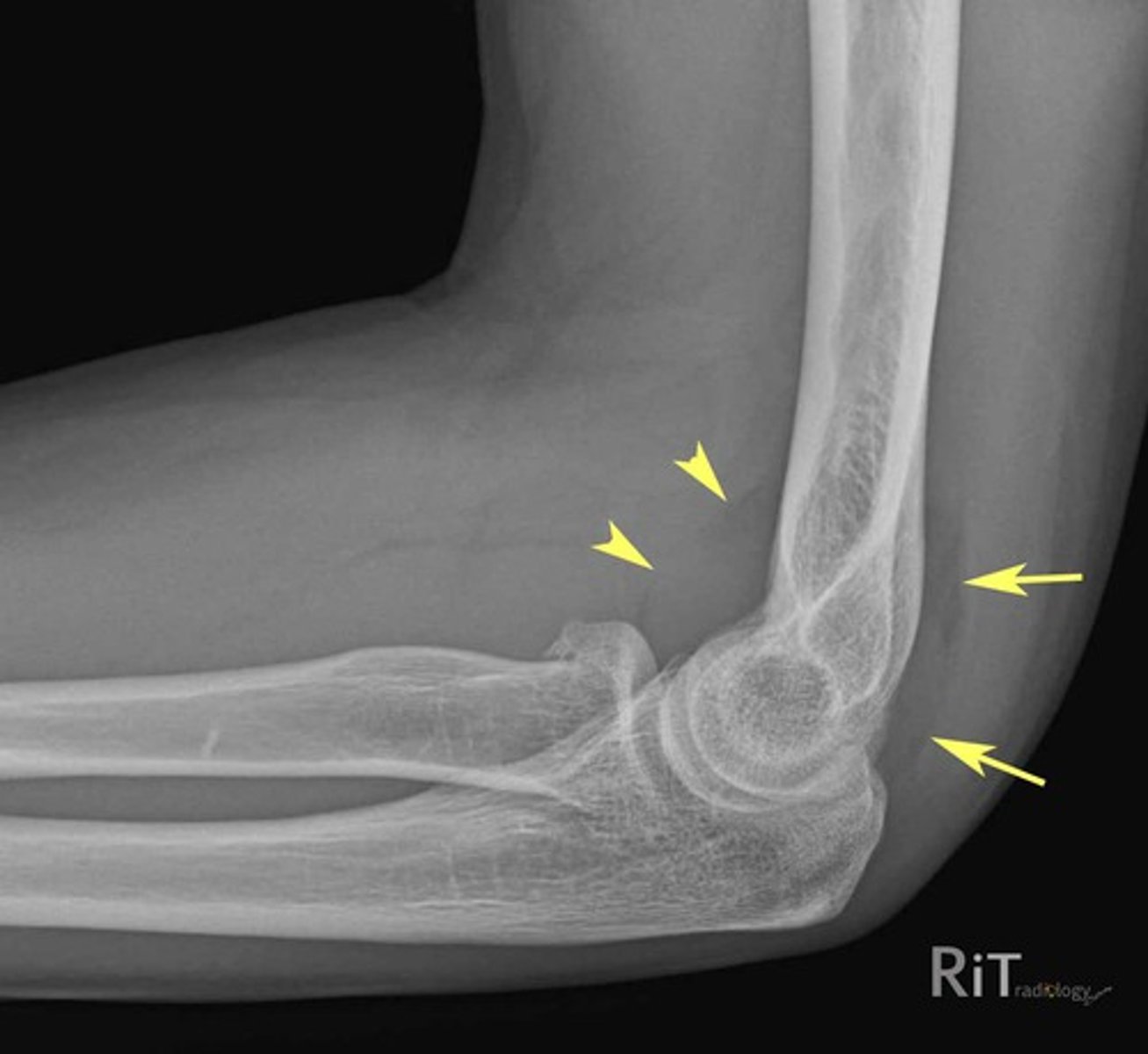
which shoulder dislocation is MC?
anterior
which odontoid fracture: fracture of the upper part of the odontoid peg?
1
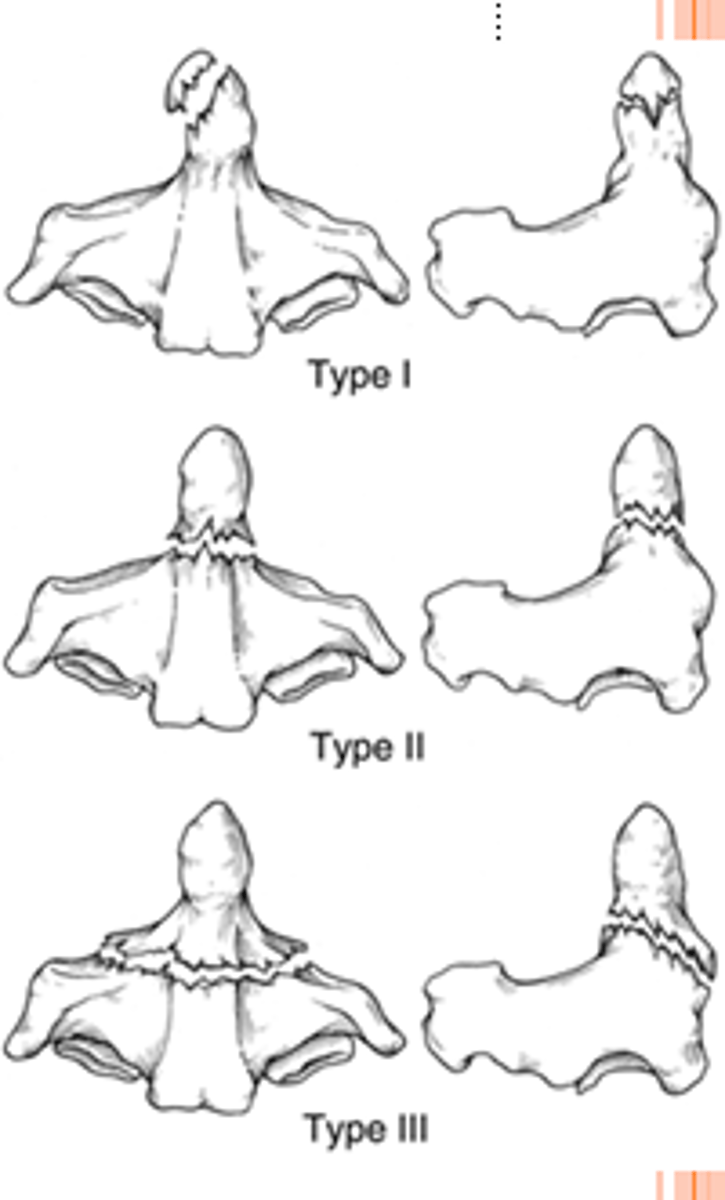
which odontoid fracture: fx of the base?
2
which odontoid fracture: through the odontoid and into the lateral masses of c2?
3 → best prognosis

what is the MC hip dislocation?
posterior → force applied to flexed knee
what are the complications of a posterior hip dislocation?
sciatic nerve injury
AVN
which hip fx: abducted, externally rotated, flexed?***
anterior
which hip fx: adducted, internally rotated, shortened?***
posterior
what are the precipitating factors for DKA?
- T1DM
- poor insulin compliance
- stress
- infection/UTI → klebsiella
what are the s/sx of DKA?
dehydration
hypotension
AMS
N/V
kussmaul breaths
fruity breath
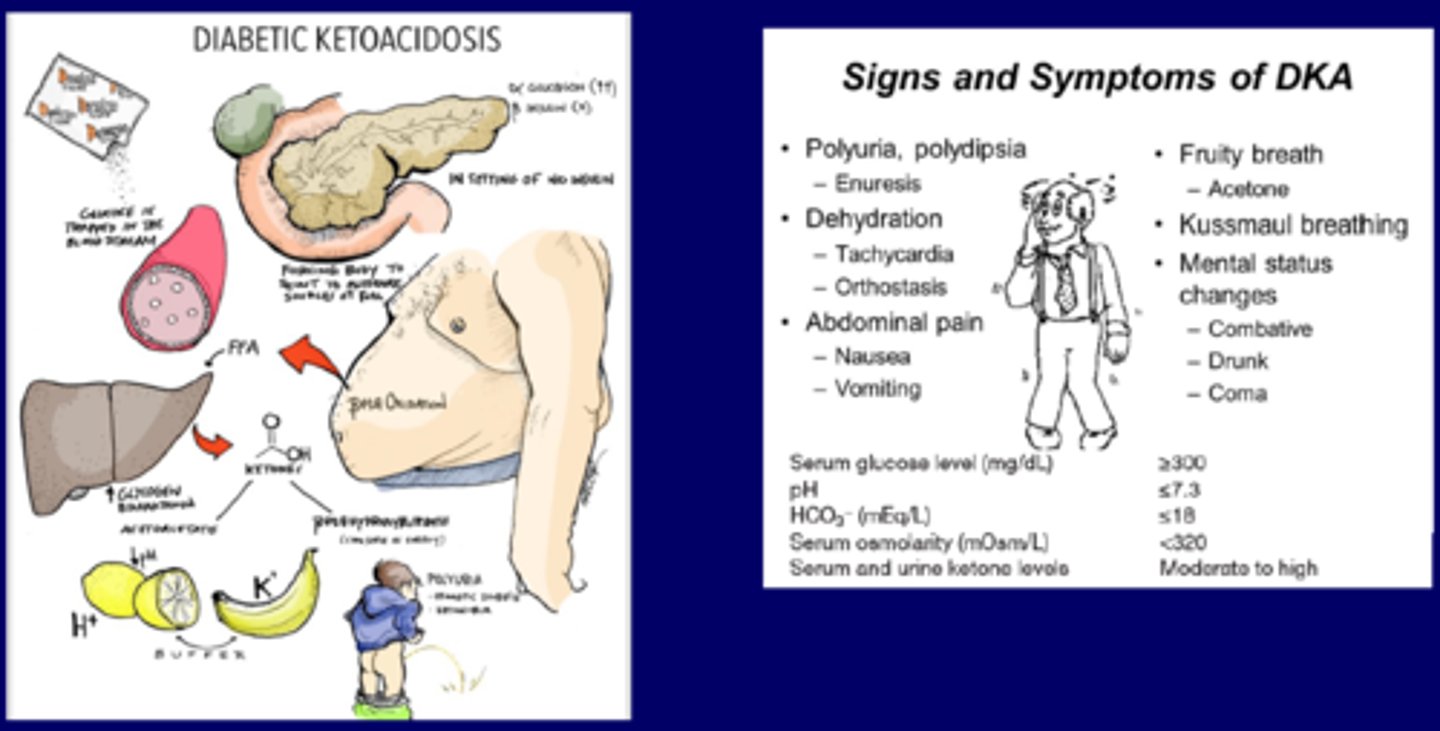
what are the complications related to tx of DKA?
1. hypoglycemia, hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia (gradually correct to avoid this)
2. cerebral/pulm edema
3. ARDS (from aggressive fluid tx, shift of fluid across pulm capillary membrane)
what do labs look like in DKA?
serum ketones > 5
blood glucose > 250
bicarb < 18
pH < 7.2 (HAGMA)
HYPOkalemia
ketonuria
glucosuria
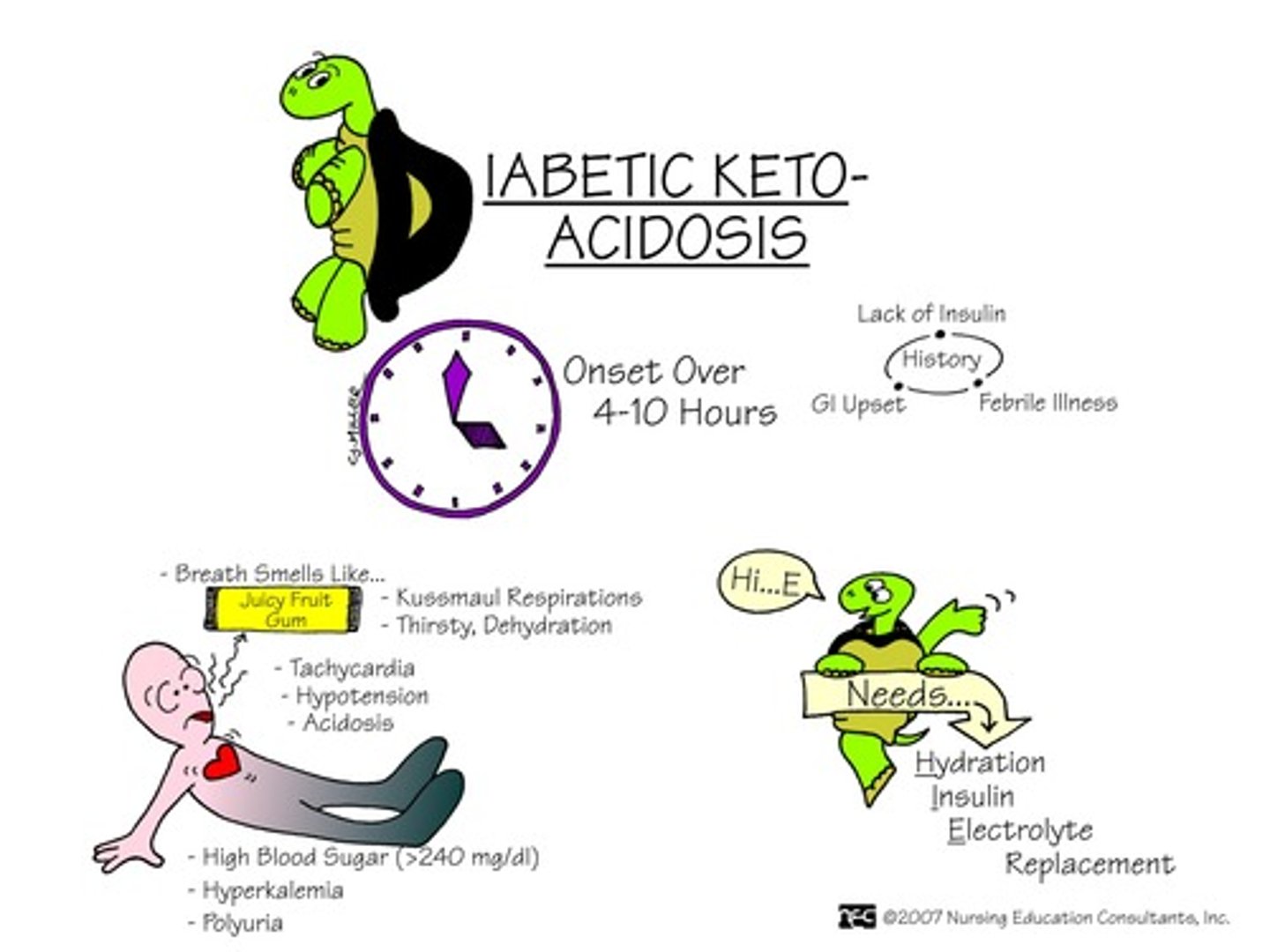
what is the treatment for DKA in ORDER?
1. fluids → 1-3 L of NS in the first hr
2. insulin and/or potassium (after labs)
3. phosphate, magnesium, bicarb
what NIHSS score indicates a severe stroke?***
REALLY HIGH = REALLY BAD
dont need to know numbers
what are the sx of cluster HA?***
severe unilateral orbital/supraorbital/temporal pain lasting 15-180 mins with at least one of the following:
- ipsilateral conjunctival injection
- lacrimation
- nasal congestion
- rhinorrhea
- facial swelling
- miosis
- ptosis
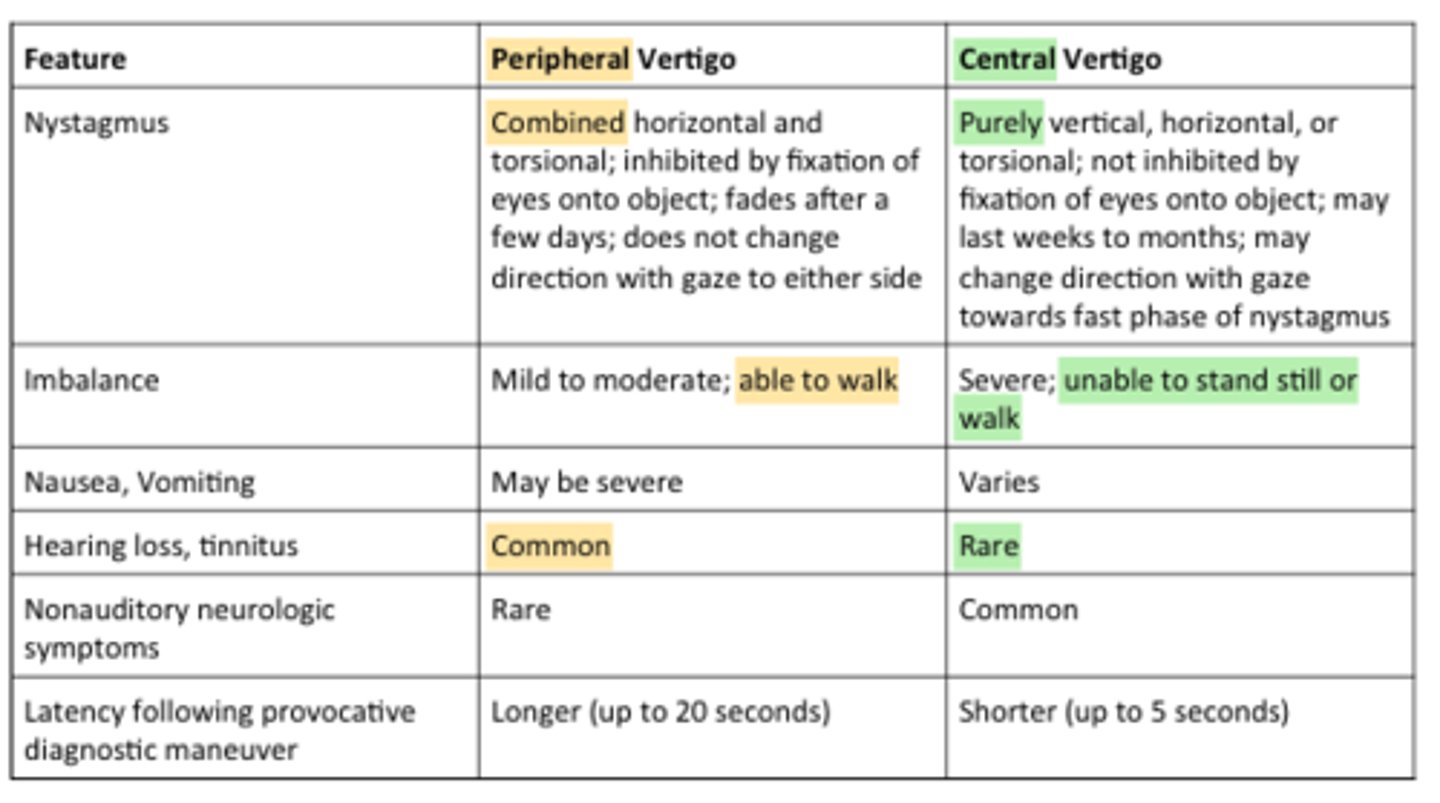
peripheral or central vertigo: sudden onset, horizontal nystagmus, hearing loss, fatigue of s/sx?***
peripheral →paroxysmal, intense spinning, rotary vertical or horizontal nystagmus, frequent nausea/sweating, aggravated by movement, hearing loss/tinnitus, ABSENT CNS s/sx
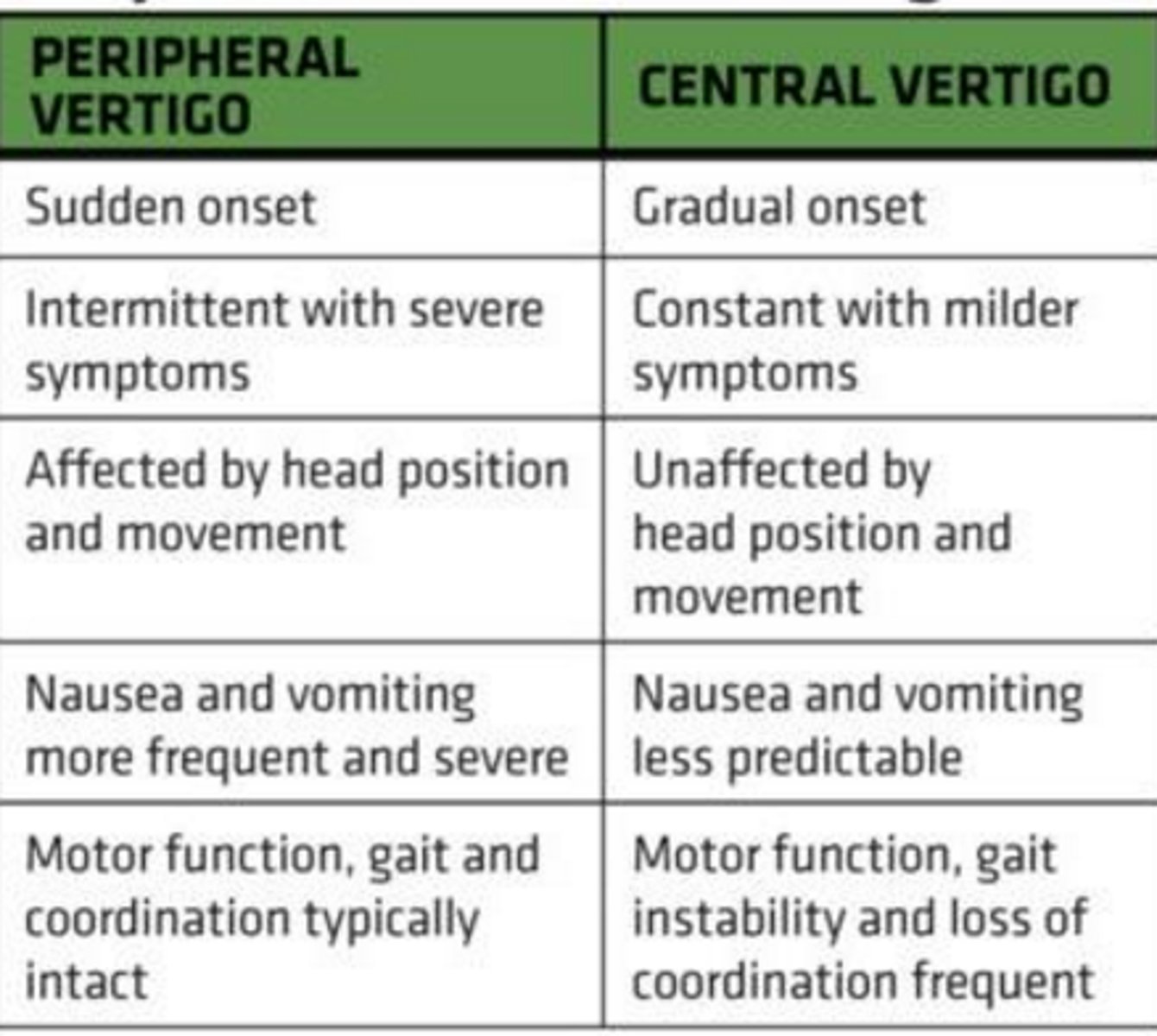
peripheral or central vertigo: constant, vertical nystagmus, CNS symptoms?***
central → sudden/slow onset, less intense vertigo, constant pattern, vertical nystagmus, no fatiguing of symptoms, no hearing loss/tinnitus, no abnormal TM, CNS sx present
what is the MC etio of toxic shock syndrome (TSS) in women aged 15-24?
staph
what is the MC etio of TSS in women aged 20-50?
strep
what are the s/sx of TSS?
- female w retained tampon
- high fever
- chills
- body aches
- erythematous desquamating rash → palms and soles!!
what is the tx for TSS?
inpatient → vanco + clinda
what is the difference between periorbital cellulitis and orbital cellulitis?
EOMs are PRESERVED in PERIorbital and IMPAIRED in orbital
Peri = preserved
what is the tx for periorbital cellulitis?
mild/mod → augmentin
severe → rocephin + vanco IV
what is the tx for orbital cellulitis?
vanco + rocephin
get contrast CT of orbits + paranasal sinus
pt presents with unilateral facial paralysis, peripheral vertigo, and hearing loss with vesicles in their ear canal. what is the dx?
Ramsay hunt → reactivation of VZV → affects CN 7

what formula is used to calculate fluid replacement for burn patients?***
Parkland Bourne
(4ml x body wt (kg) x BSA %) / 1000 = L over 24 hrs
half given in 8 hrs, second half in 16 hrs
pt presents with burns across the abdomen, chest, left arm and left hand. pt weighs 71 kg. what volume of IV fluids should be given in the first 8 hrs of treatment?
(4 x 71 x 28)/1000 = 8 L in 24 hrs
4 L in first 8 hrs
what is the MC fish envenomation cause?
stingrays → tx with hot water soak

what is the MC cause of nonbacterial fish poisoning?
Ciguatera → N/V/D, abd pain, body chills, itching, HA, perspiration, dizziness, muscle pain, weakness/cramps, tingling, numbness
which dx has pathognomonic symptom of reversal of hot and cold tactile perception?
ciguatera → tx with IV mannitol and benadryl
pt presents to the ER from the beach with multiple linear, very painful "whiplike" urticarial lesions. what is the tx?***
portuguese man-of-war attack → sea water, acetic acid (vinegar), remove nematodes
NOT HOT WATER
pt presents with morbilliform pruritic dermatitis after returning from beach vacation. the rash is present in areas covered by her bathing suit and her itching is worse at night. what is the dx?
sea bathers eruption → tx with benadryl, calamine lotion, hydrocortisone
what tis the MCC of death via envenomation?
hymenoptera stings (bees, wasps, ants)
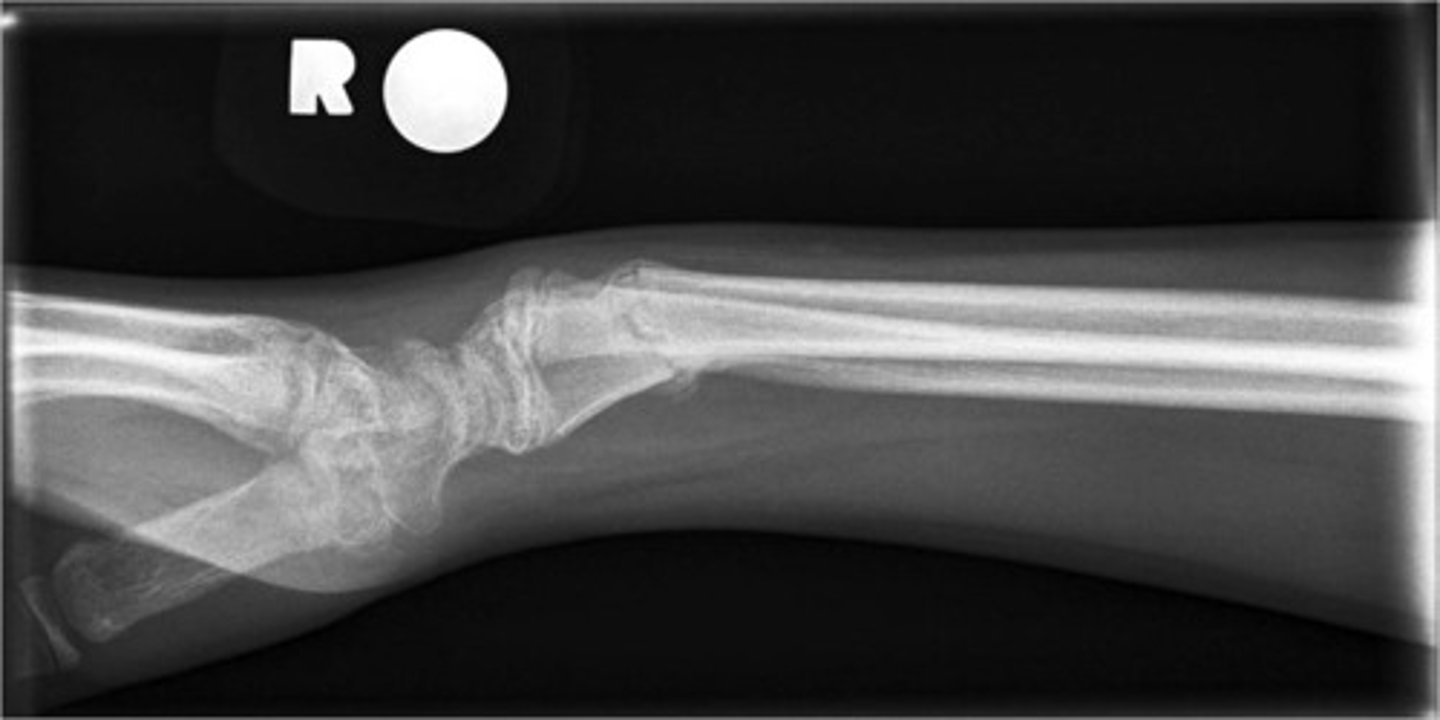
which fracture: distal radial metaphysis fracture that is DORSALLY angulated?***
Colles → the FRAGMENT moves dorsally (back of the hand) (not the shaft) → dinner fork deformity
know imaging
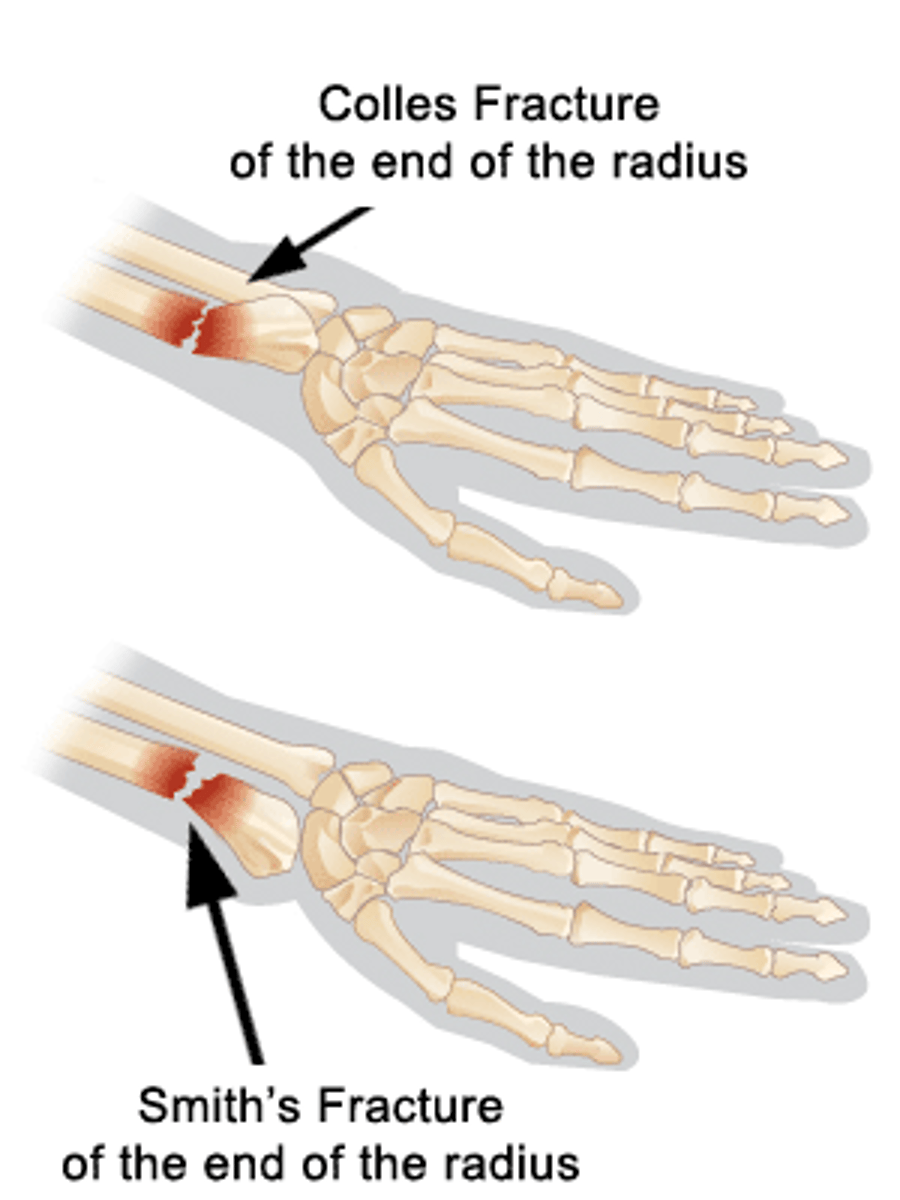
which fracture: volar/VENTRAL angulated fracture of the distal radius?***
smith → fragment moves towards the PALM
know imaging!!!
what should be ordered if SAH is suspected?
lumbar puncture
what should be ordered for CVA/stroke pts?
- CT non contrast
- EKG
- CXR
- 3 Ps → PT, PLT, PTT
- MRI (after CT)
- cerebral angiography
which HA: bilateral, non-pulsating, not worse with exertion, no N/V?
tension
which HA: N/V, photophobia, phonophobia, lightheadedness?
migrane
which HA: worse HA of your life?
SAH
MC caused by berry aneurysm
which dx presents with severe unilateral pain in the trigeminal nerve lasting only seconds?
Tic Douloureux → tx w carbamazepine
what is the imaging of choice for sternoclavicular dislocation?
CT
what is the tx for trichomonas vaginialis?***
flagyl → avoid alcohol!!***
what are the s/sx of trich?***
strawberry cervix → erythematous with petechial hemorrhages
what are the tx for gonorrhea, chlamydia, syphilis, HSV, granuloma inguinale?
gonorrhea = rocephin
chlamydia = doxy
syphilis = pen G
HSV = antivirals (any)
granuloma inguinale = azithro
which nerve is compressed in colles fracture resulting in paresthesias?
median nerve
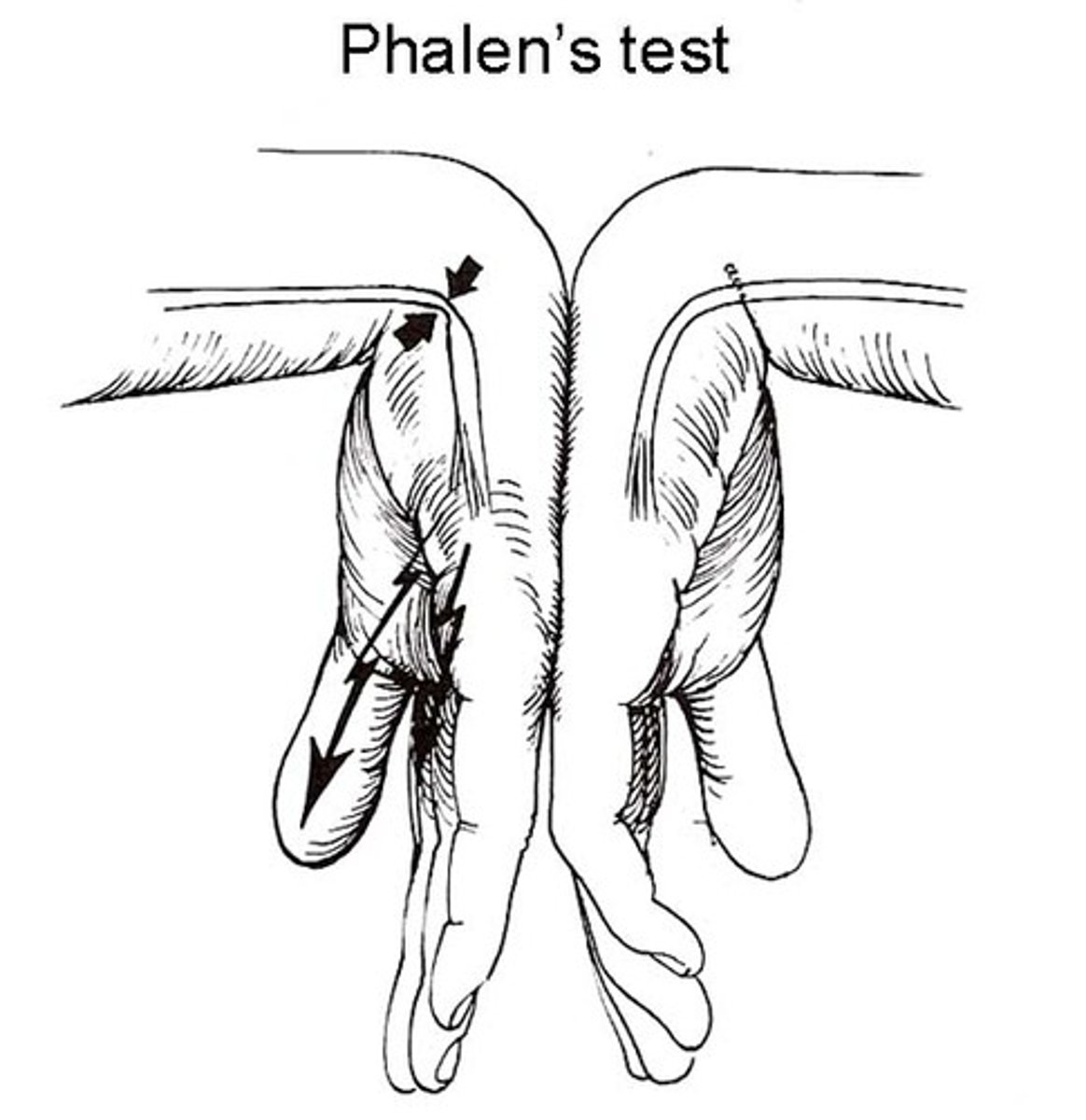
pt presents with pain and numbness in thumb and first 2 fingers that is worse at night. what special tests can be used for diangosis?
carpal tunnel → Tinels and phalens
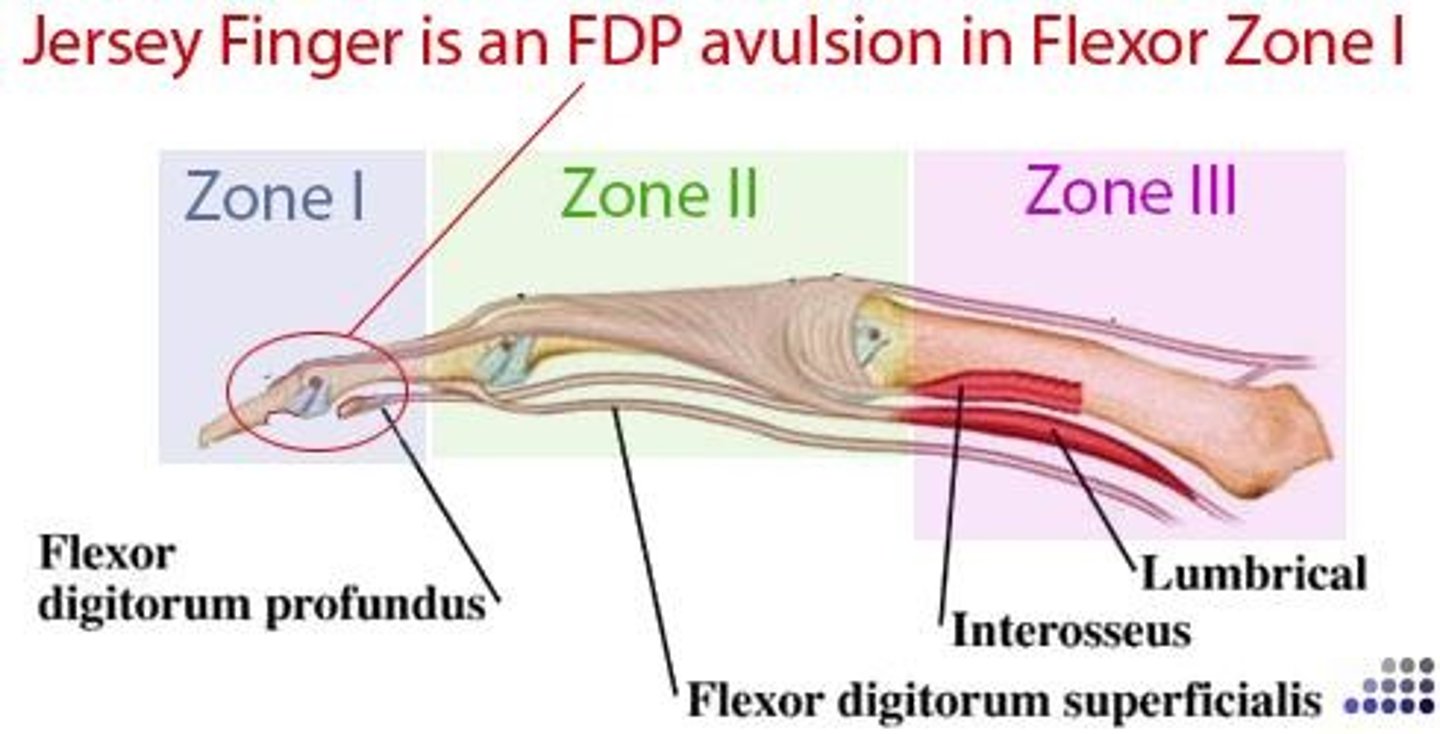
what is an avulsion fracture of FDP from its insertion?
Jersey finger
what is the MC site of tendon injuries?
extensor tendons
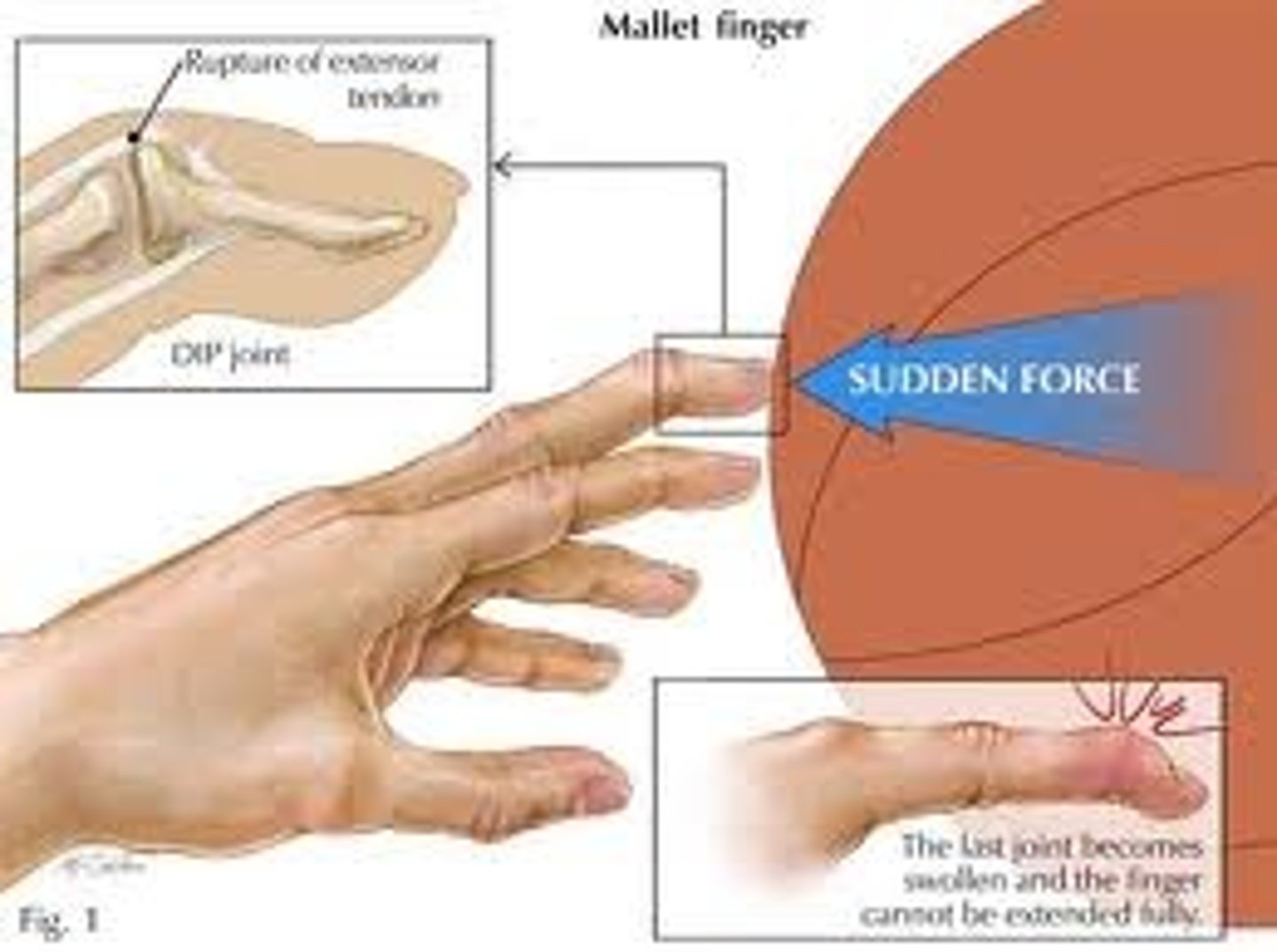
mallet finger may develop a _______ _______ deformity?
swan neck → flexed DIP and extended PIP
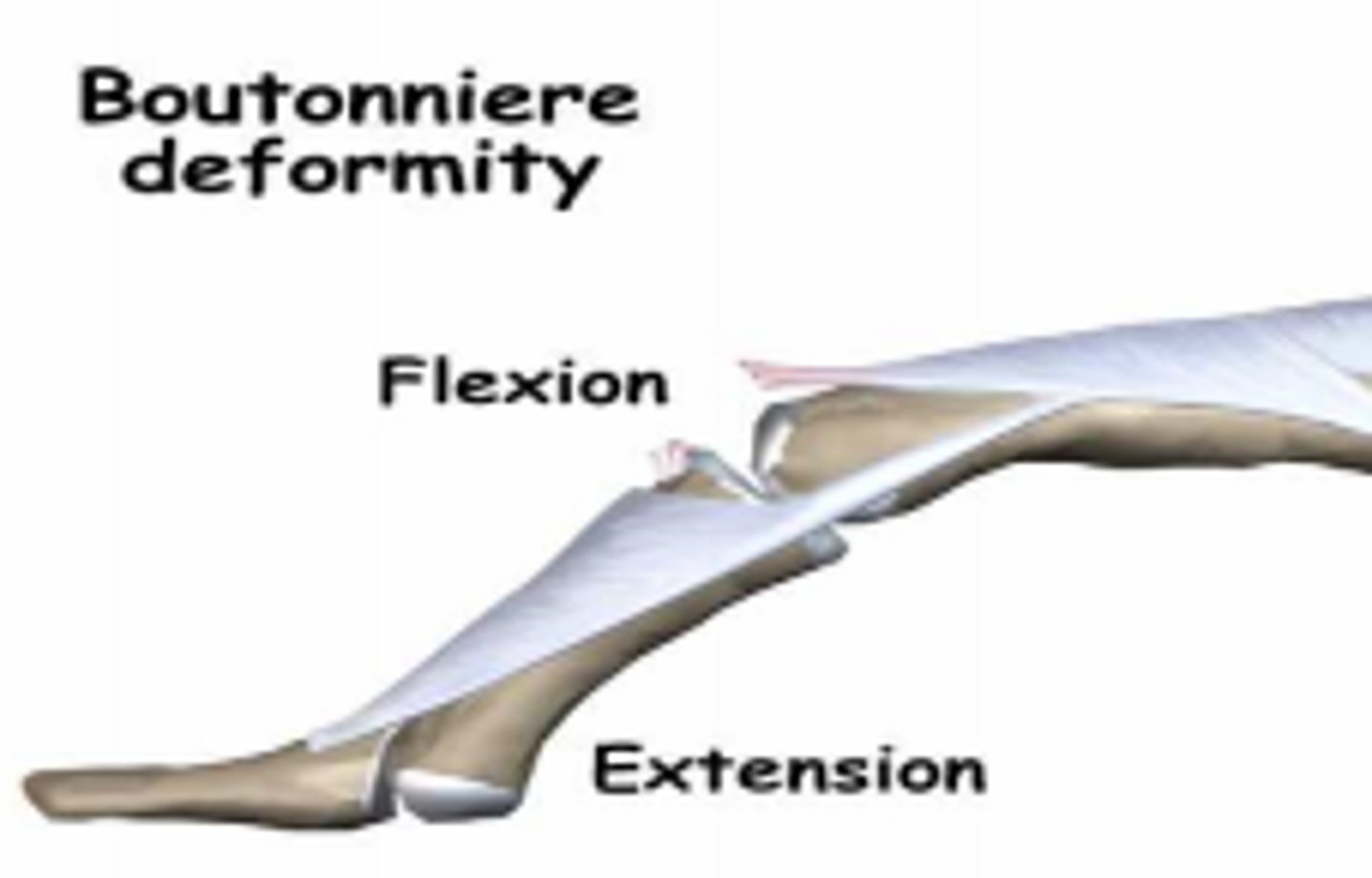
which deformity is caused by a flexed PIP and extended DIP?
boutonniere
what are the hallmark findings of heat stroke?***
- cerebral dysfunction with impaired consciousness
- high fever
- absence of sweating
SALTER HARRIS FRACTURES!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
........................................... :|
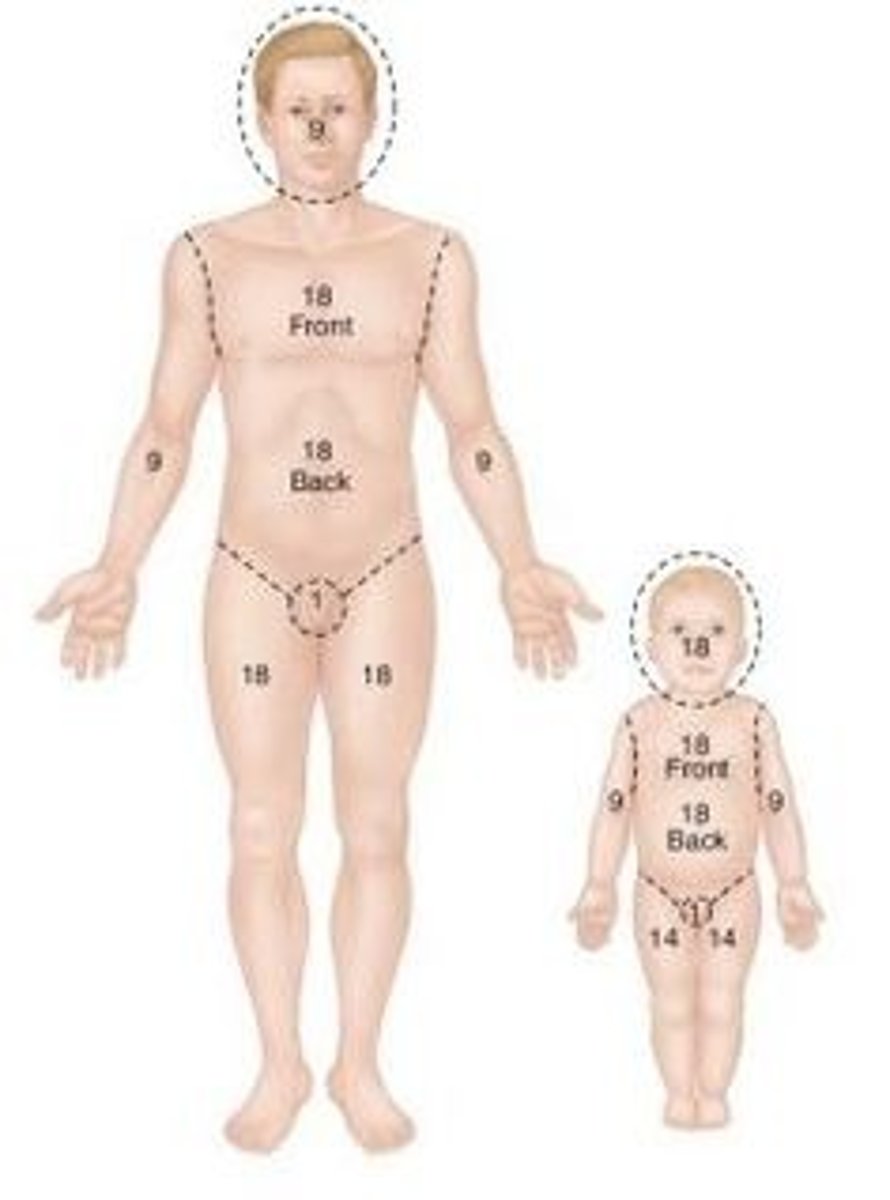
rule of 9s***
Head and neck = 9%
Upper Ex = 9% each
Lower Ex = 18% each
Front trunk = 18%
Back trunk = 18%
Groin, hands = 1%
burns to which body parts warrant admission?
hands
feet
face
perineum
what is the tx for tylenol toxicity?
mucomyst
activated charcoal within 1 hr
what is the tx for aspirin toxicity?
charcoal within 1 hr
bicarb if acidotic
dialysis for severe
what is the tx for anticholinergic toxicity?
Physostigmine
charcoal within 2 hrs
pt presents to the ED with reports of overdose but can't remember which drug. they report yellow vision and EKG shows ST-T changes. what is the antidote?
digoxin toxicity → digibind
what are the sx of BB toxicity?
bronchospasm
bradycardia
hypoglycemia
what are the sx of CCB toxicity?
hypotension
bradyarrhythmia
hyperglycemia
what are the sx of nitrate/nitrite tox?
orthostatic hypotension
lightheaded
syncope
tachy
diaphoresis
tx with methylene blue
toxic levels of which class of drugs can cause prolonged PR, QRS, and QT interval?
TCAs
what is the tx for tox of insecticides?
cholestyramine
what is the mainstay of tx for iron toxicity?
deferoxamine chelation
what does activated charcoal not bind to?
alcohols
what is the tx for seizures?
benzos first
phenytoin for pts who continue to seize despite benzos!!
which findings help confirm that a patient had a seizure prior to presenting to the ED?
tonic clonic movements
urinary/bowel incontinence
post-ictal confusion
tongue biting
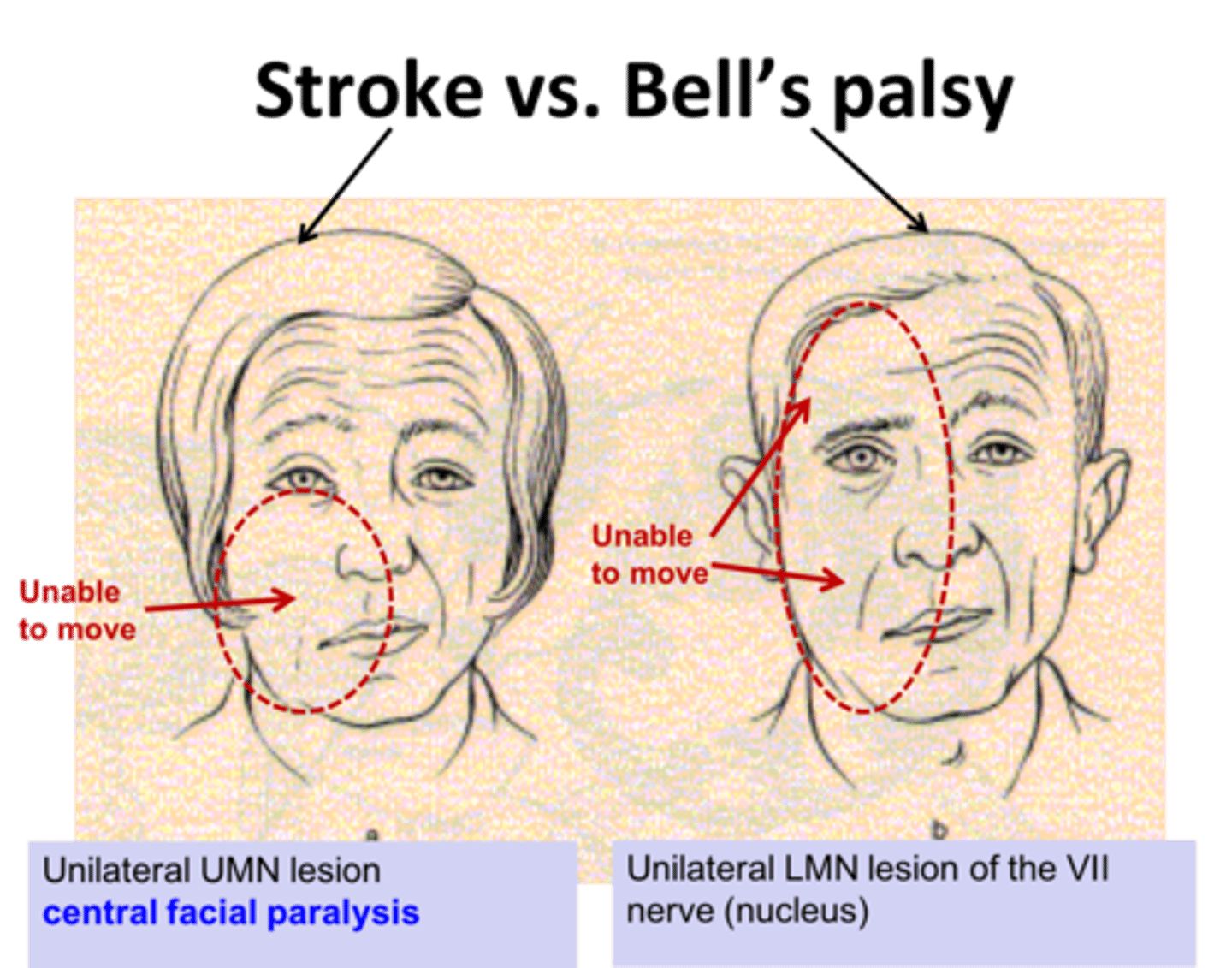
bells palsy or stroke: unilateral facial weakness. patient is unable to lift eyebrows
bells palsy!!!! → includes forehead
stroke spares forehead → able to lift brows and have forehead wrinkling
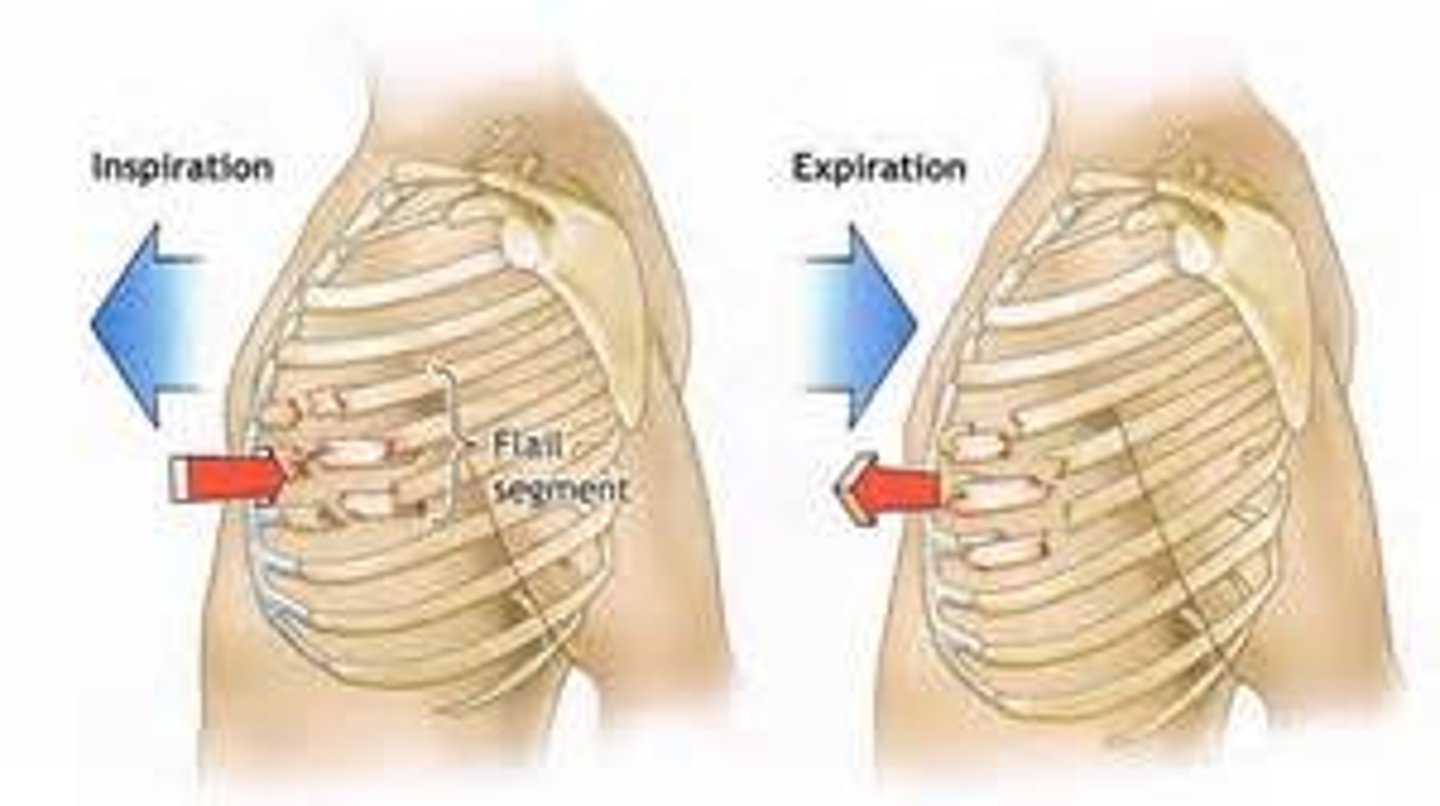
how many ribs are broken to cause flail chest?
2 or more contiguous rib fractures with 2+ breaks PER rib
what is the test of choice for eval of blunt neck trauma?
CT angiogram
what is the tx for carbon monoxide poisoning?
O2
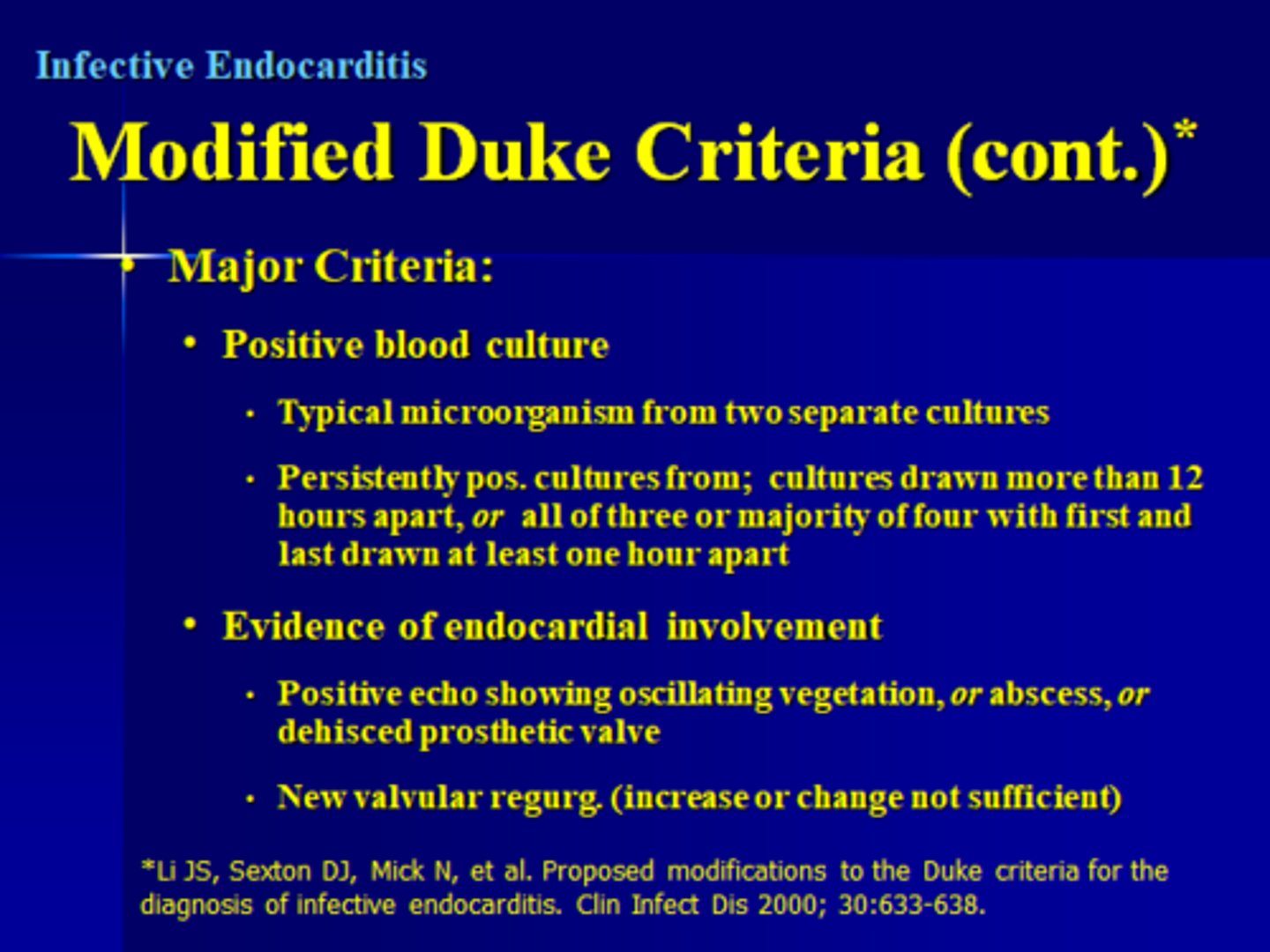
what is the major Duke criteria?***
blood cultures positive
endocardial involvement
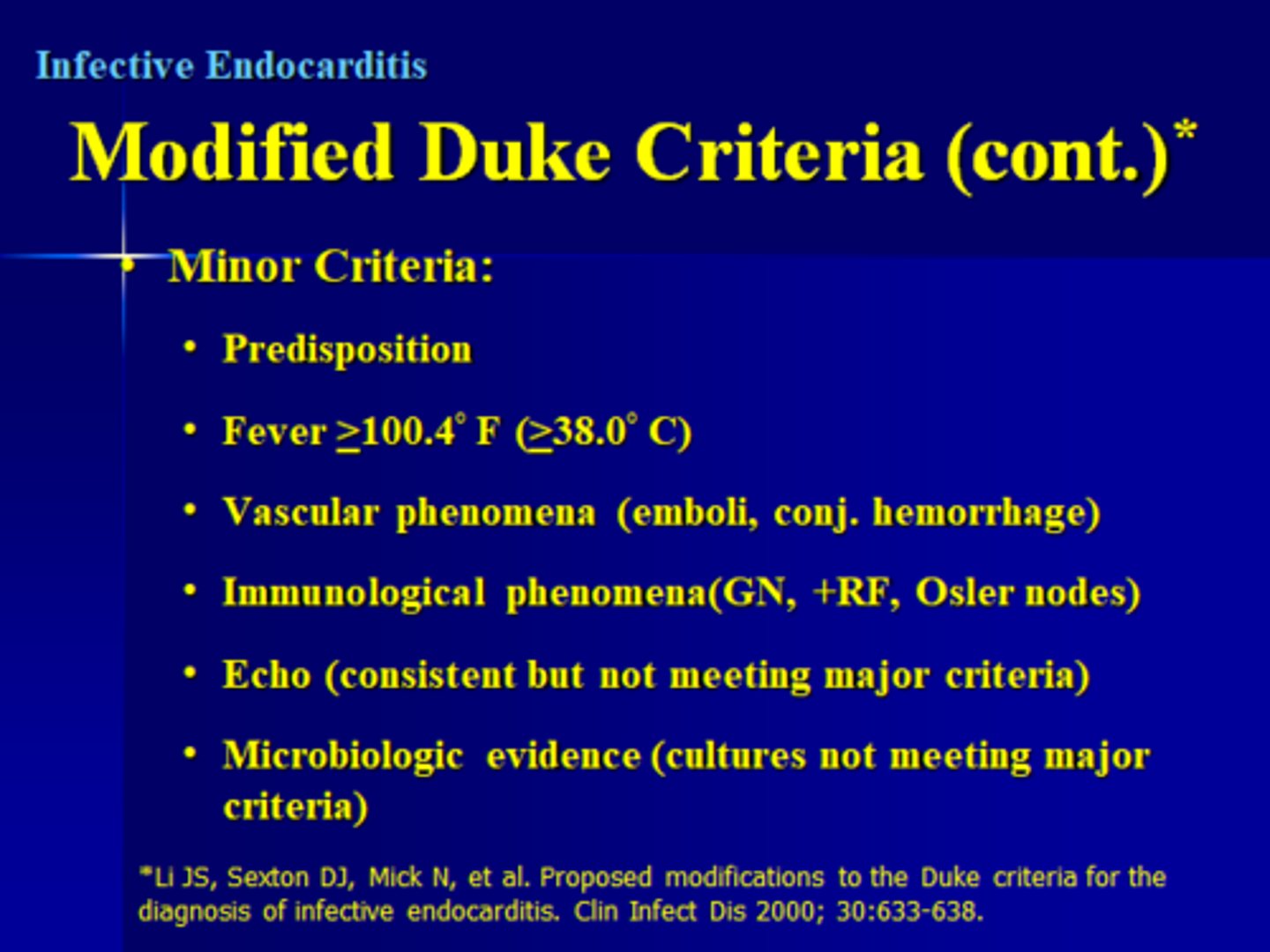
what is the minor Duke criteria?***
predisposing factors
temp >38 C
vascular phenomena
immunologic phenomena
microbio evidence
what is the required Duke criteria for dx of IE?
2 major
OR
1 major + 3 minor
OR
5 minor
for tx of infective endocarditis, you should draw ___ blood cultures then begin abx
3***
what are the sx of sickle cell pain crisis?
- pain in abd, bones, joints, soft tissues
- acute chest pain syndrome
- infection (bc of spleen)
- sus stroke
- PAIN is the MC → opioids mainstay of tx***
retic would be elevated***
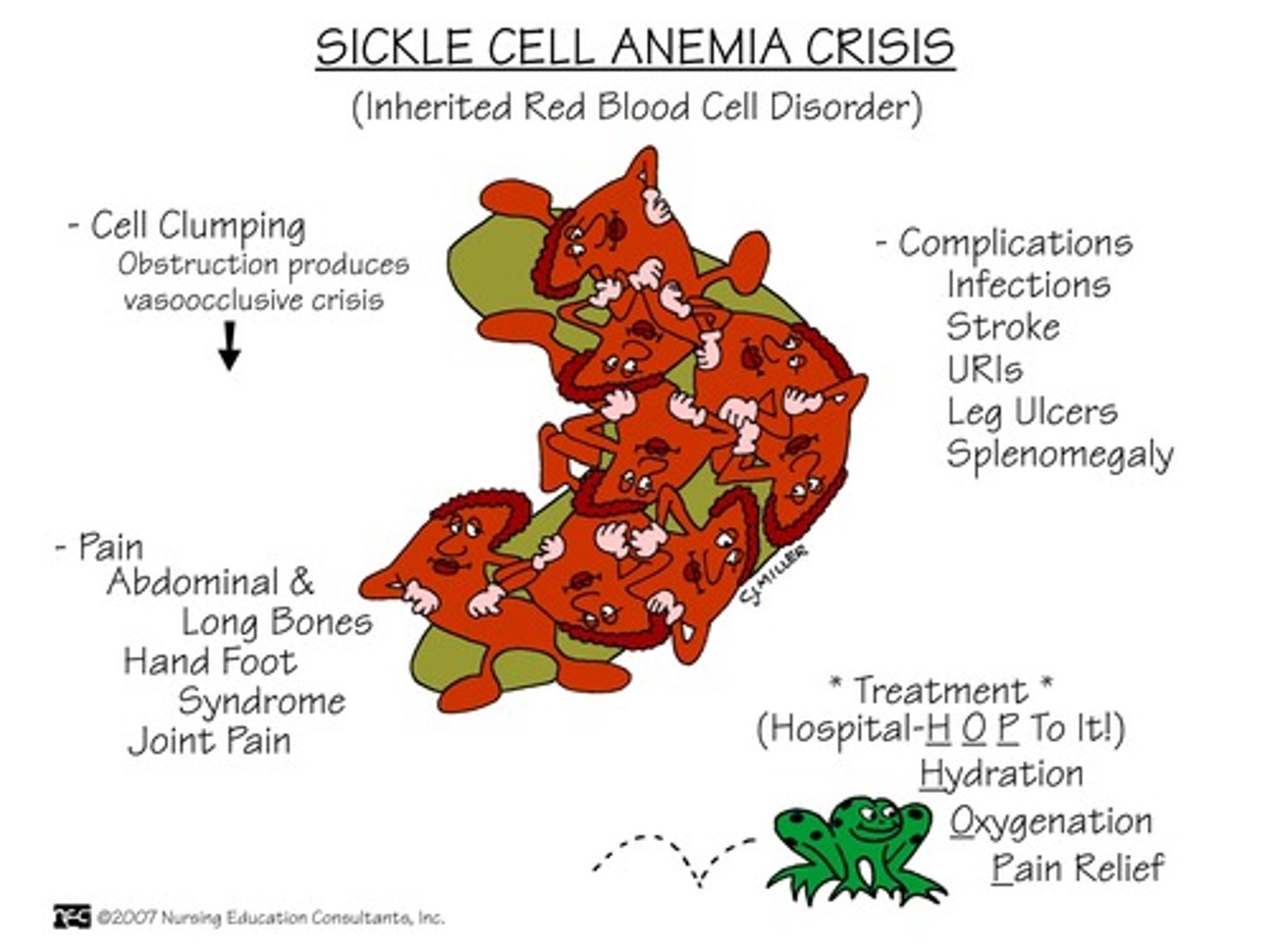
platelet count of what indicates transfusion therapy?
<5000
low speed acceleration-deceleration MVAs are causes of _________ injury?
C-spine
high speed, high-energy crash cause what type of injury?
structural damage to spine
what are the s/sx of central cord syndrome?
- decreased strength
- milder decreased pain/temp sensation
- spastic paraparesis
- spastic quadriparesis
- loss of fine motor skills