AQA GCSE Physics - ATOMIC STRUCTURE
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
Atoms are very small, having a radius of about
1x10-10 metres.
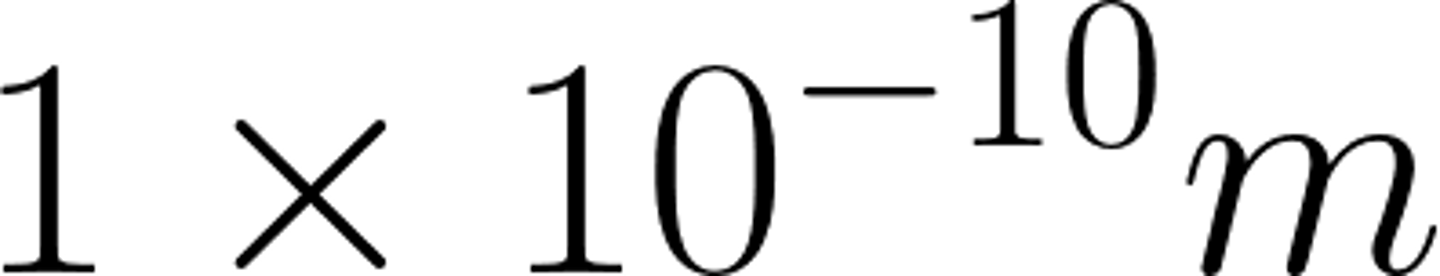
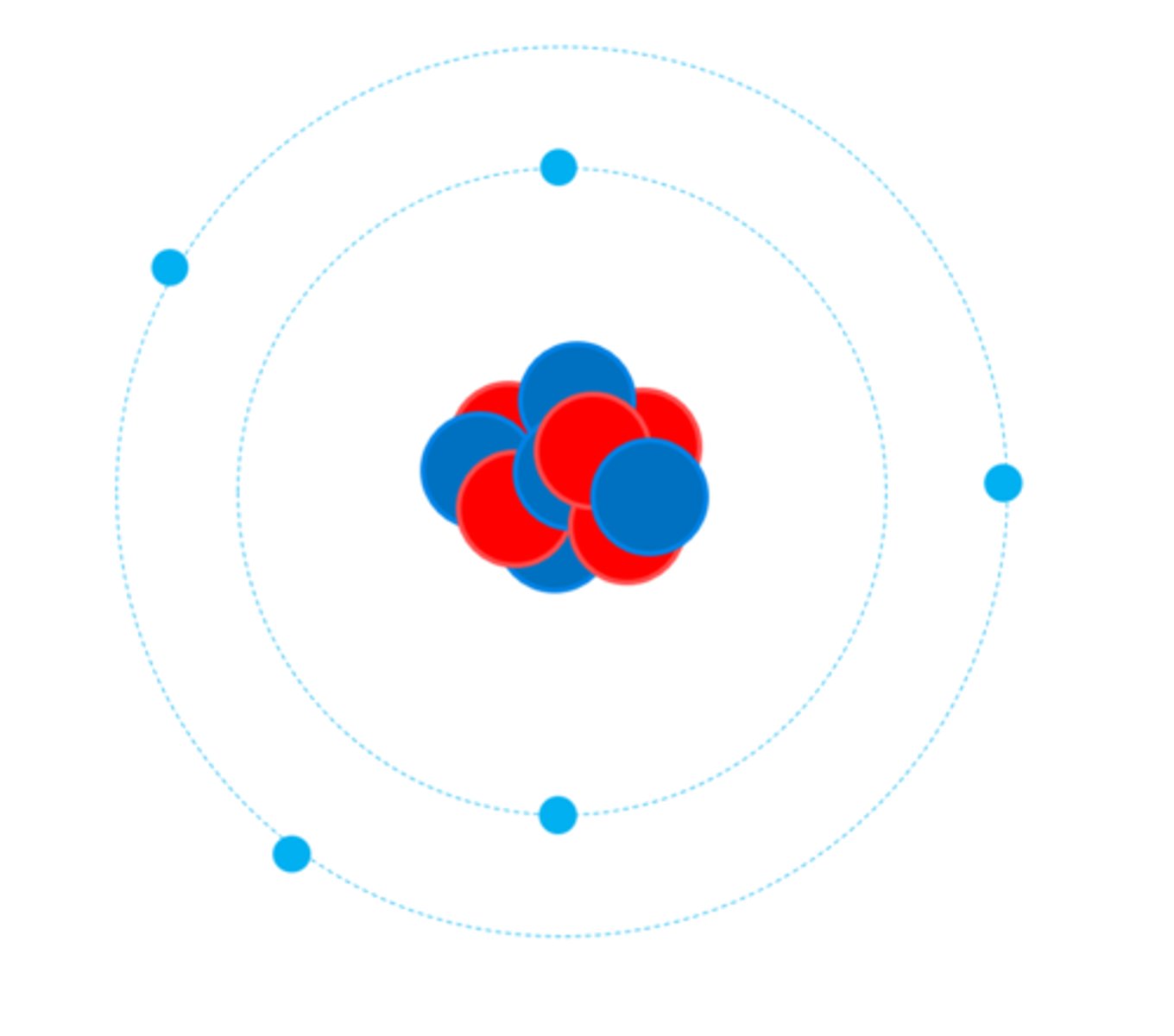
The nucleus of an atom is __________ charged
Positively

The nucleus contains 2 types of particle:
Protons and Neutrons
Protons are __________ charged
Positively
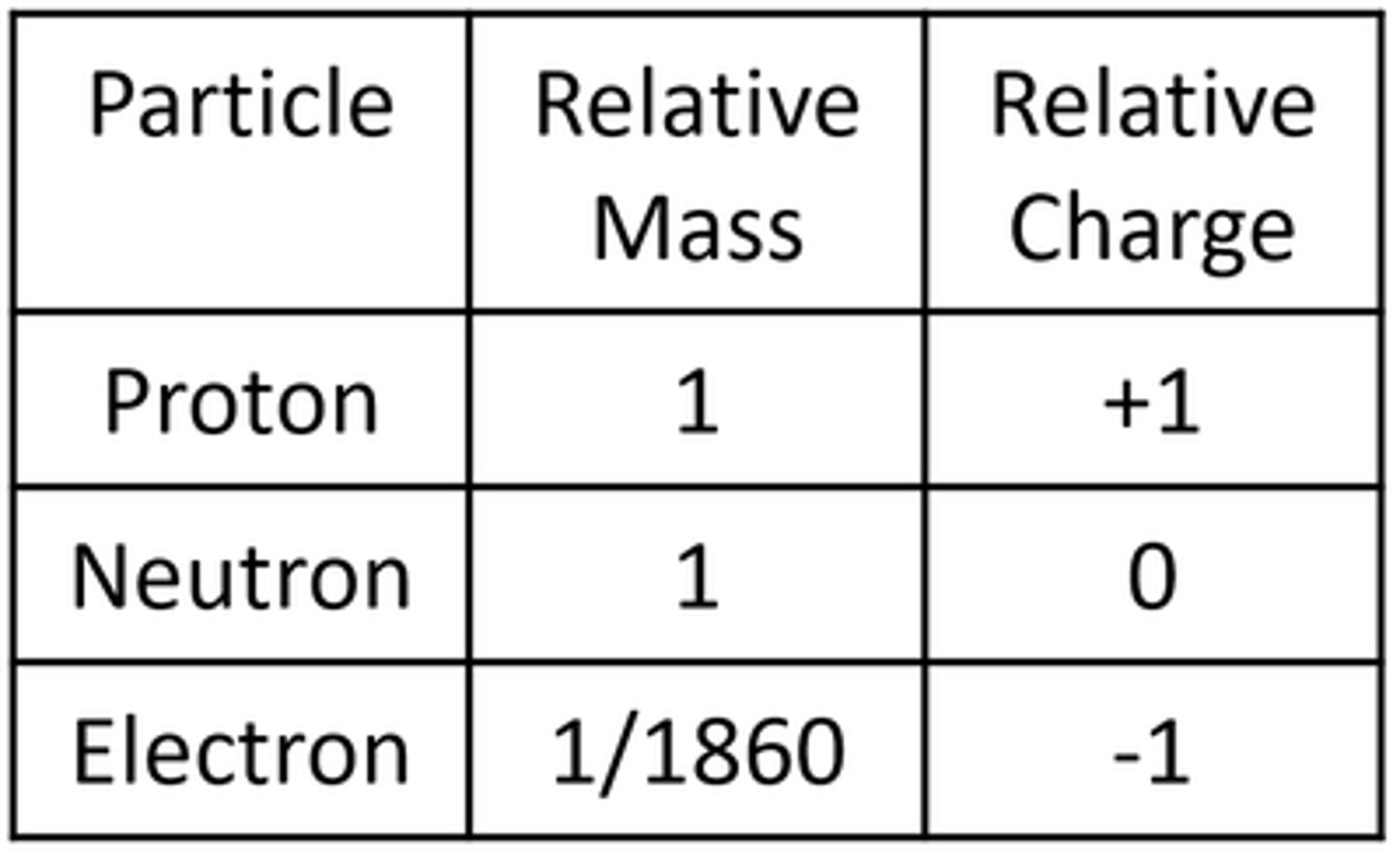
Neutrons have ____ charge
Zero
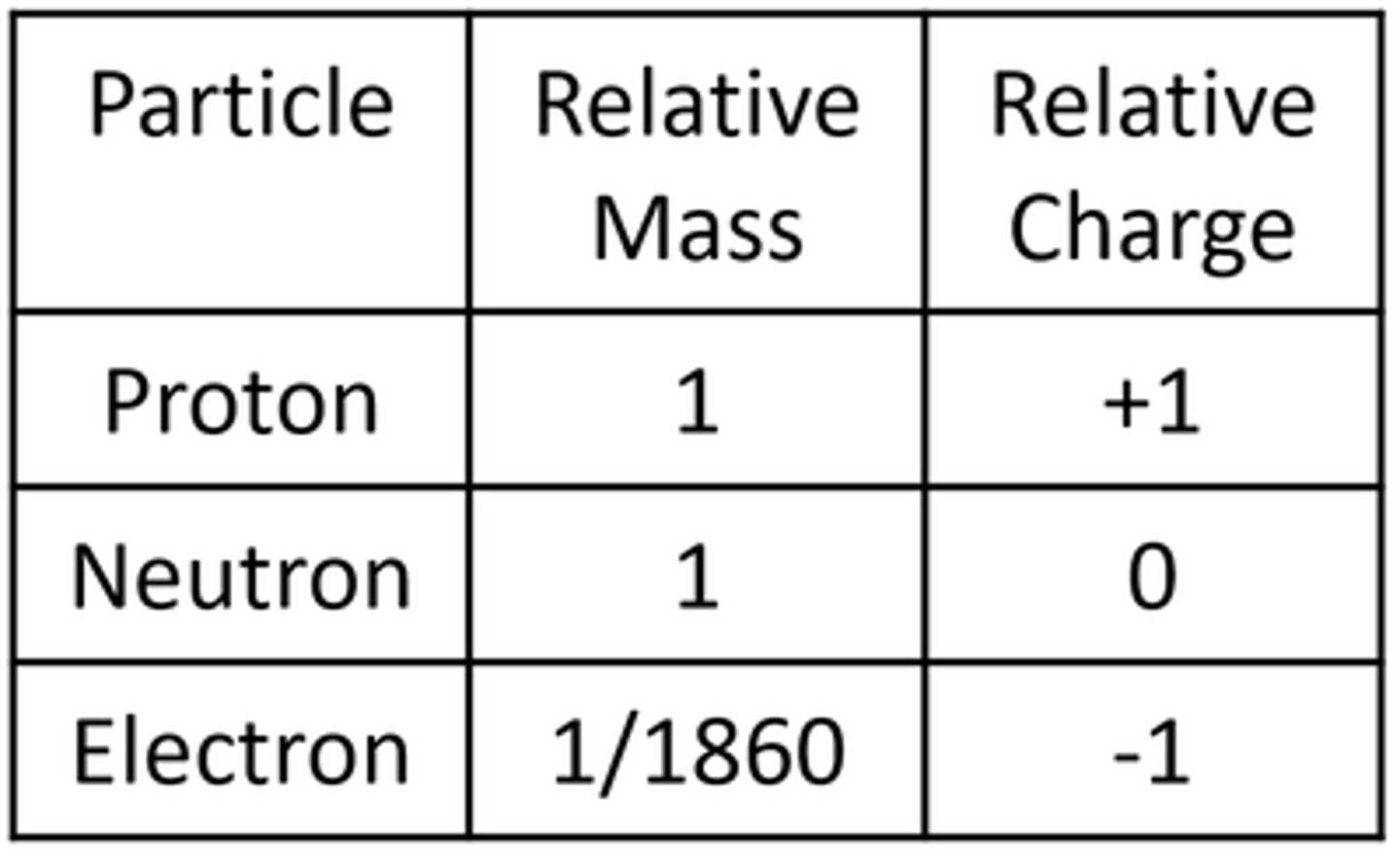
The nucleus is surrounded by _________
Electrons
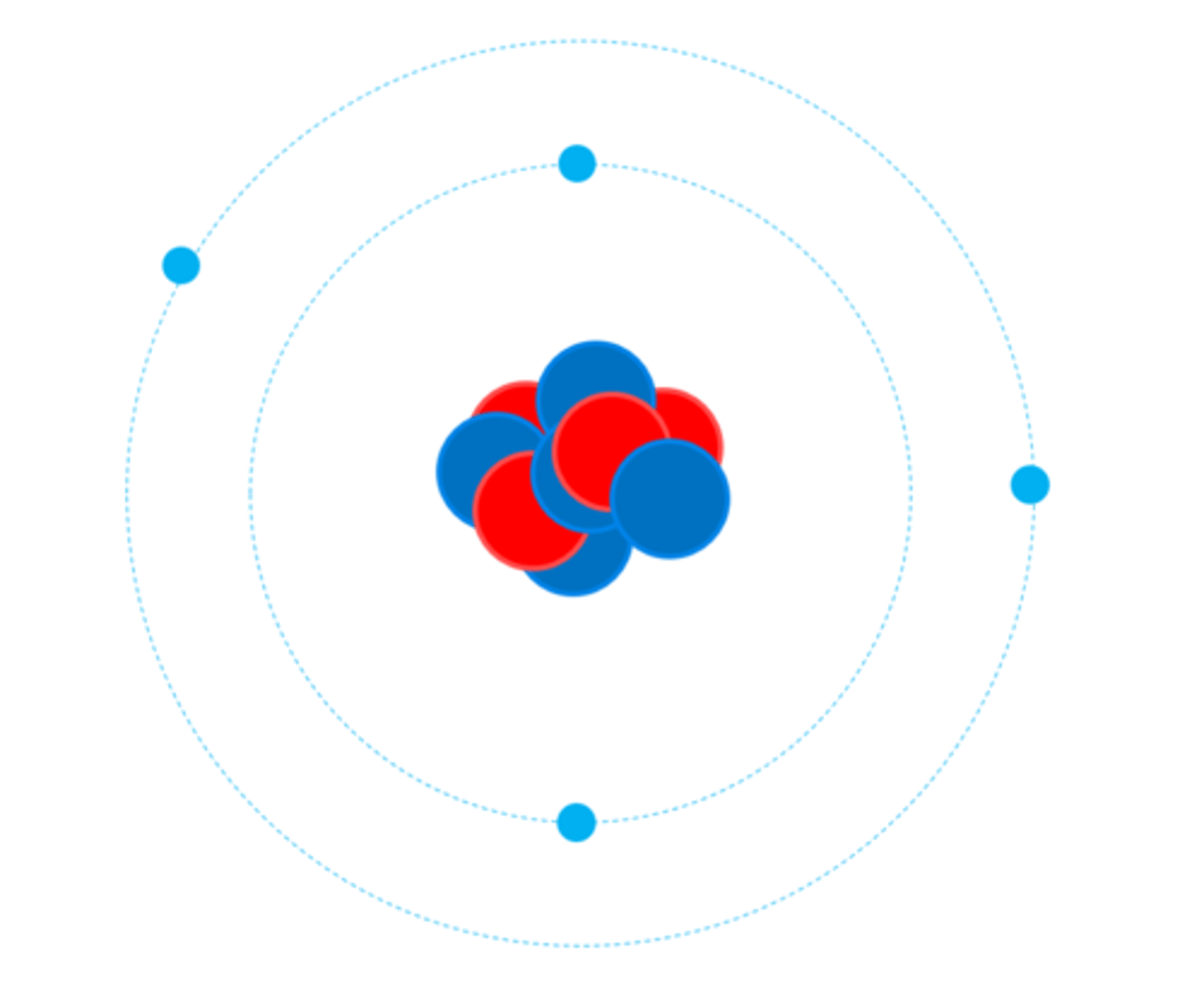
Electrons are __________ charged
Negatively
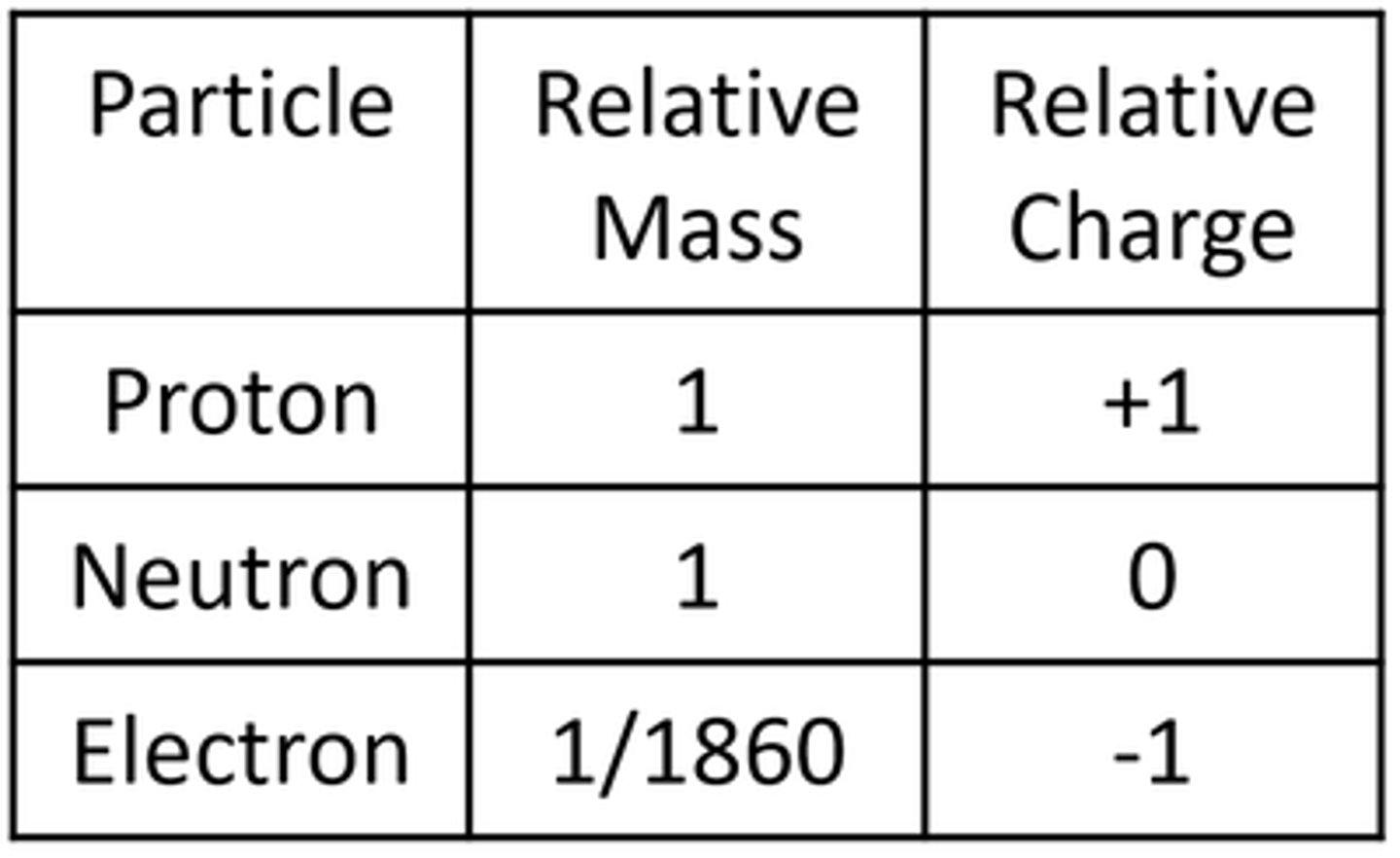
The radius of a nucleus is less than _______ of the radius of an atom
1/10,000
Most of the mass of an atom is concentrated in the _______
Nucleus
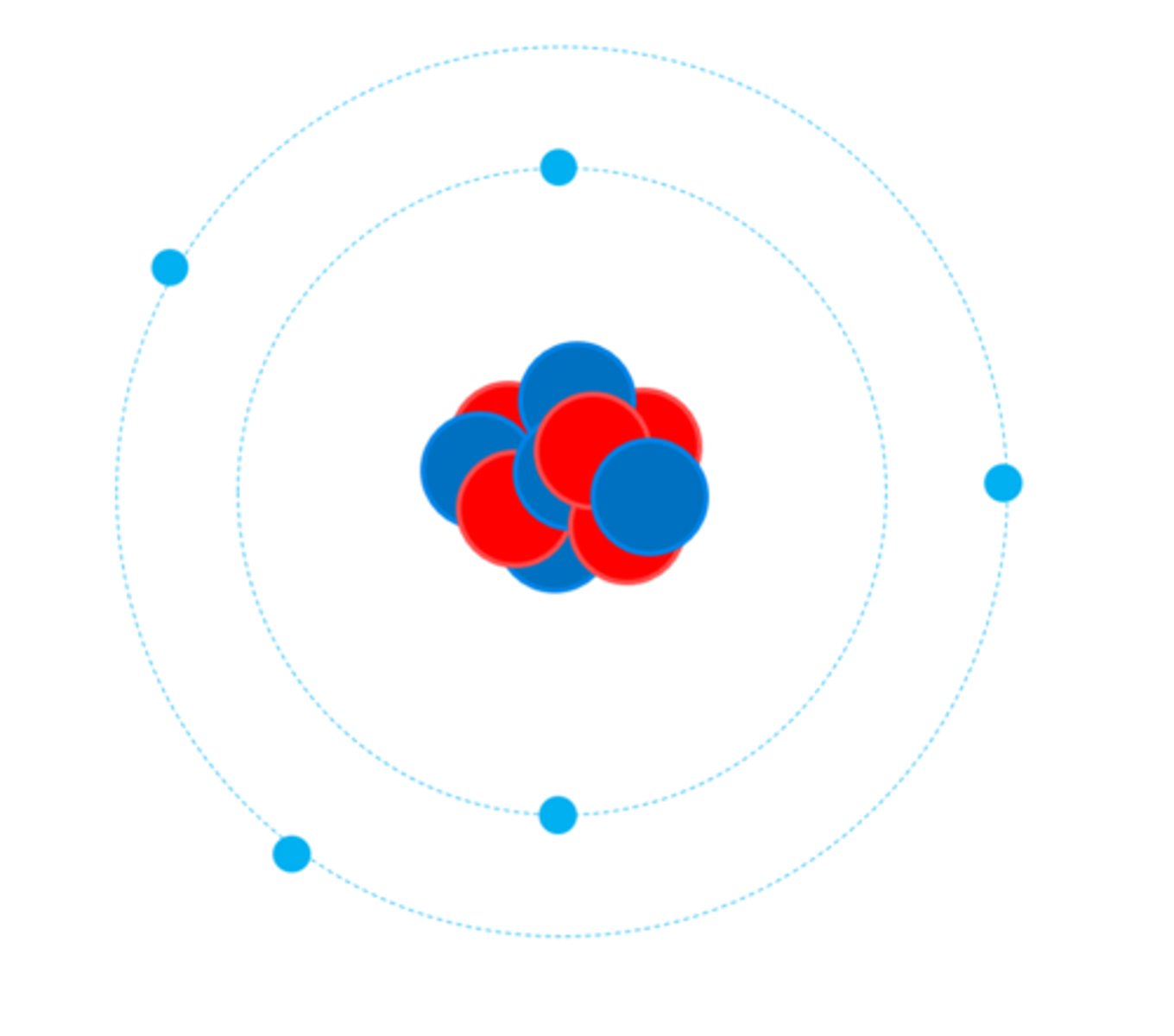
The electrons are arranged at different _________ from the nucleus
Distances (Energy Levels)
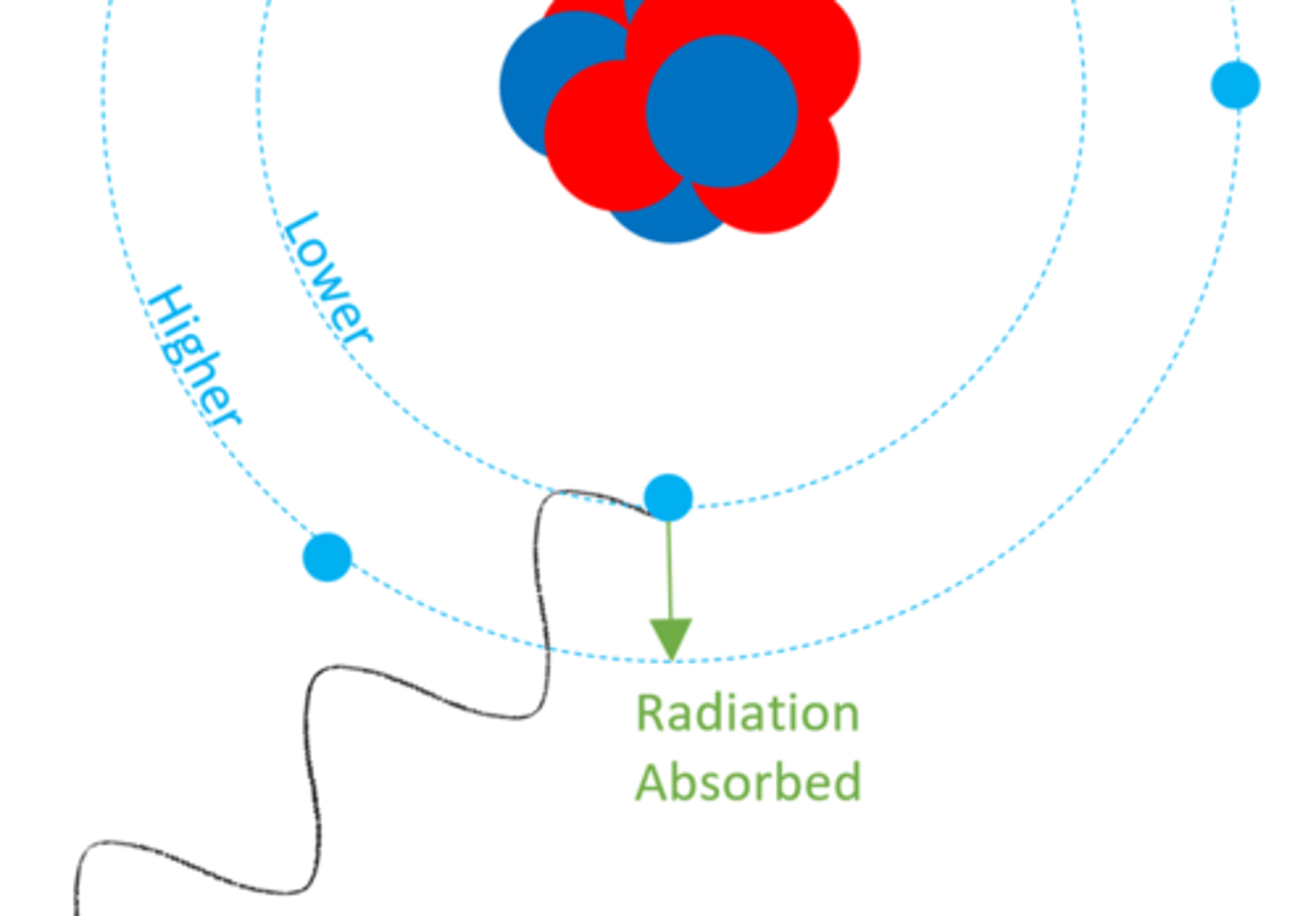
When an electron absorbs electromagnetic radiation it moves to a ______ energy level
Higher (further from nucleus)
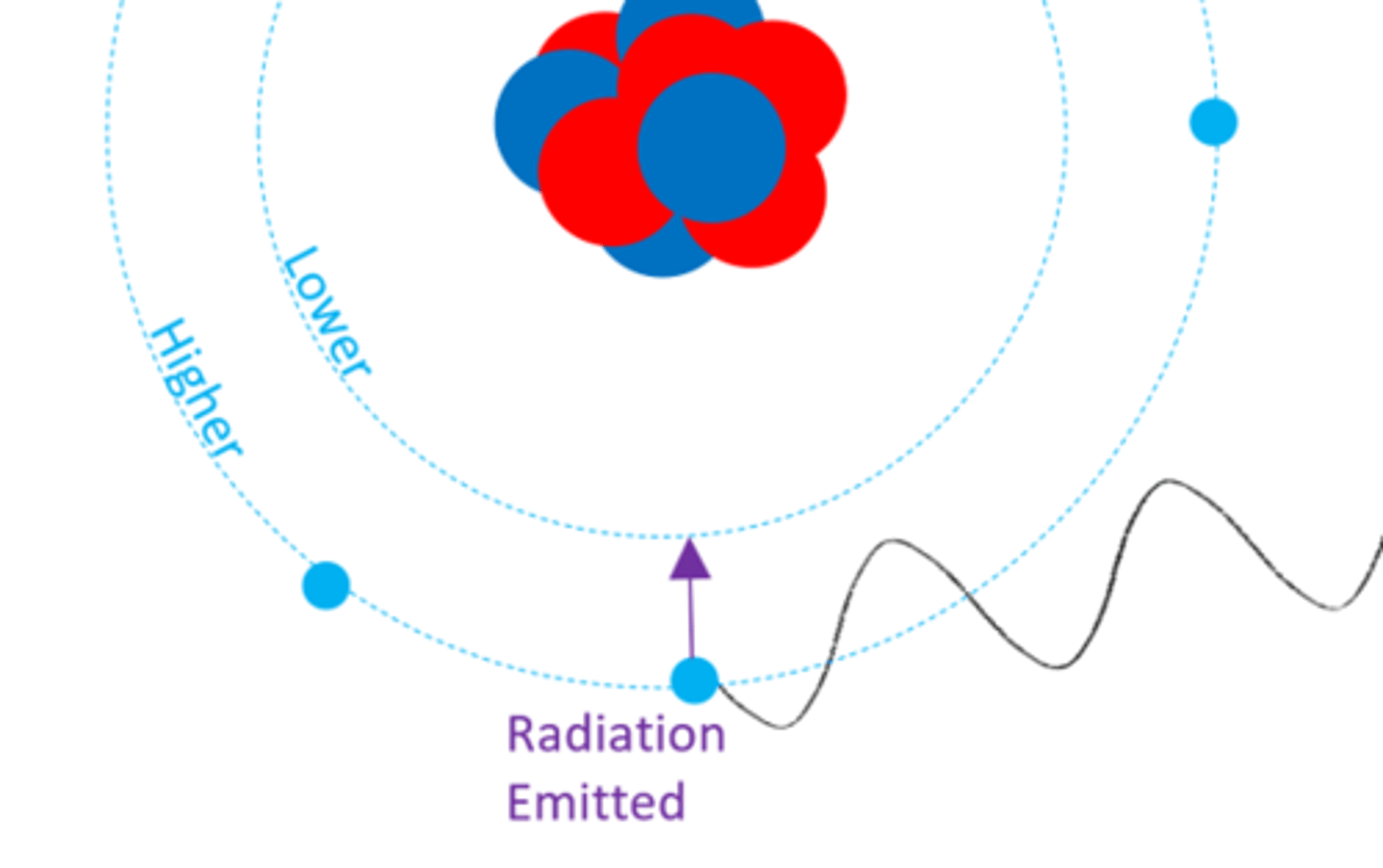
When an electron emits electromagnetic radiation it moves to a ______ energy level
Lower (closer to nucleus)
In an atom the number of electrons is equal to the number of _______ in the nucleus
Protons
Atoms have no overall electrical ______
Charge
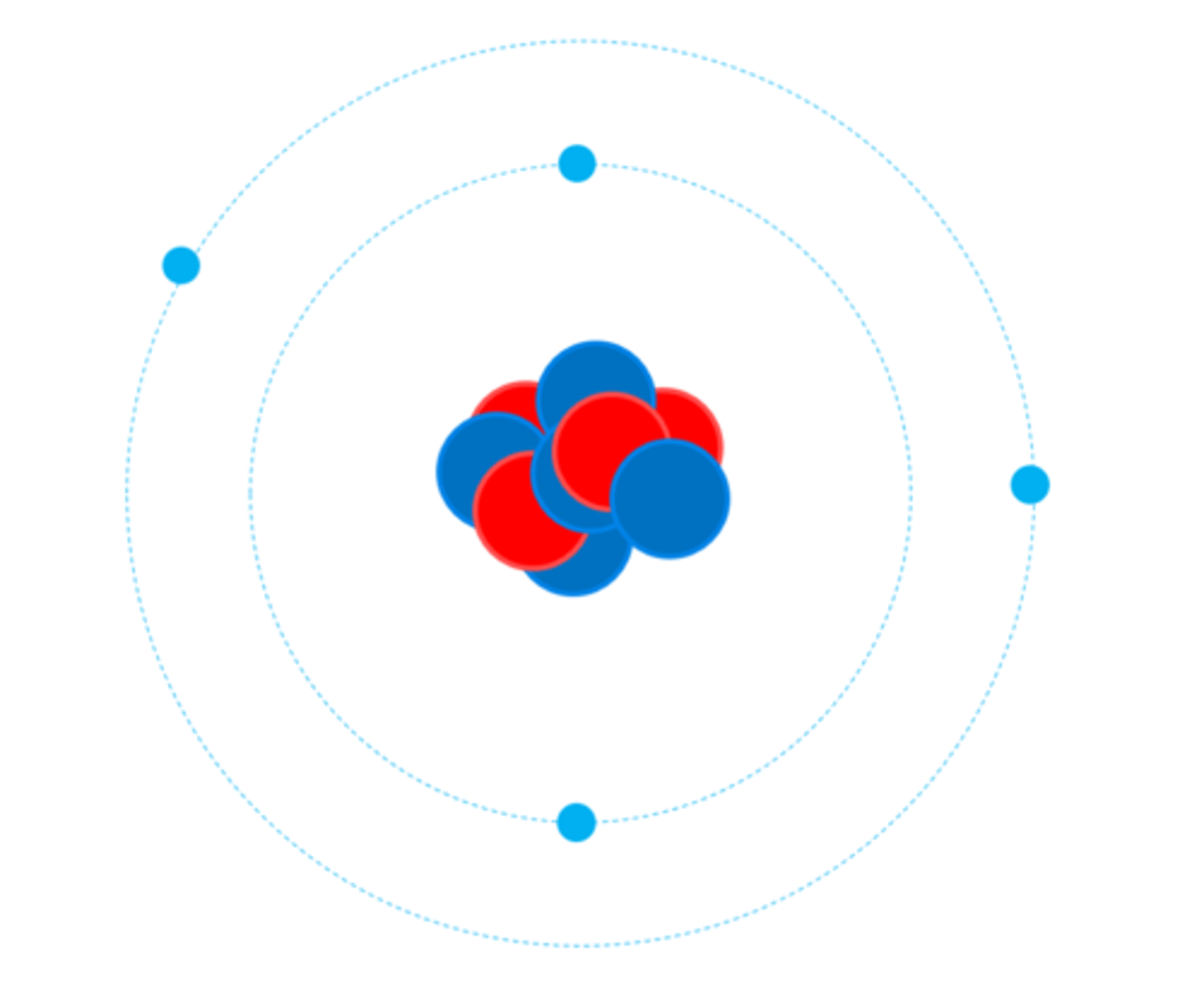
All atoms of a particular element have the same number of _______
Protons
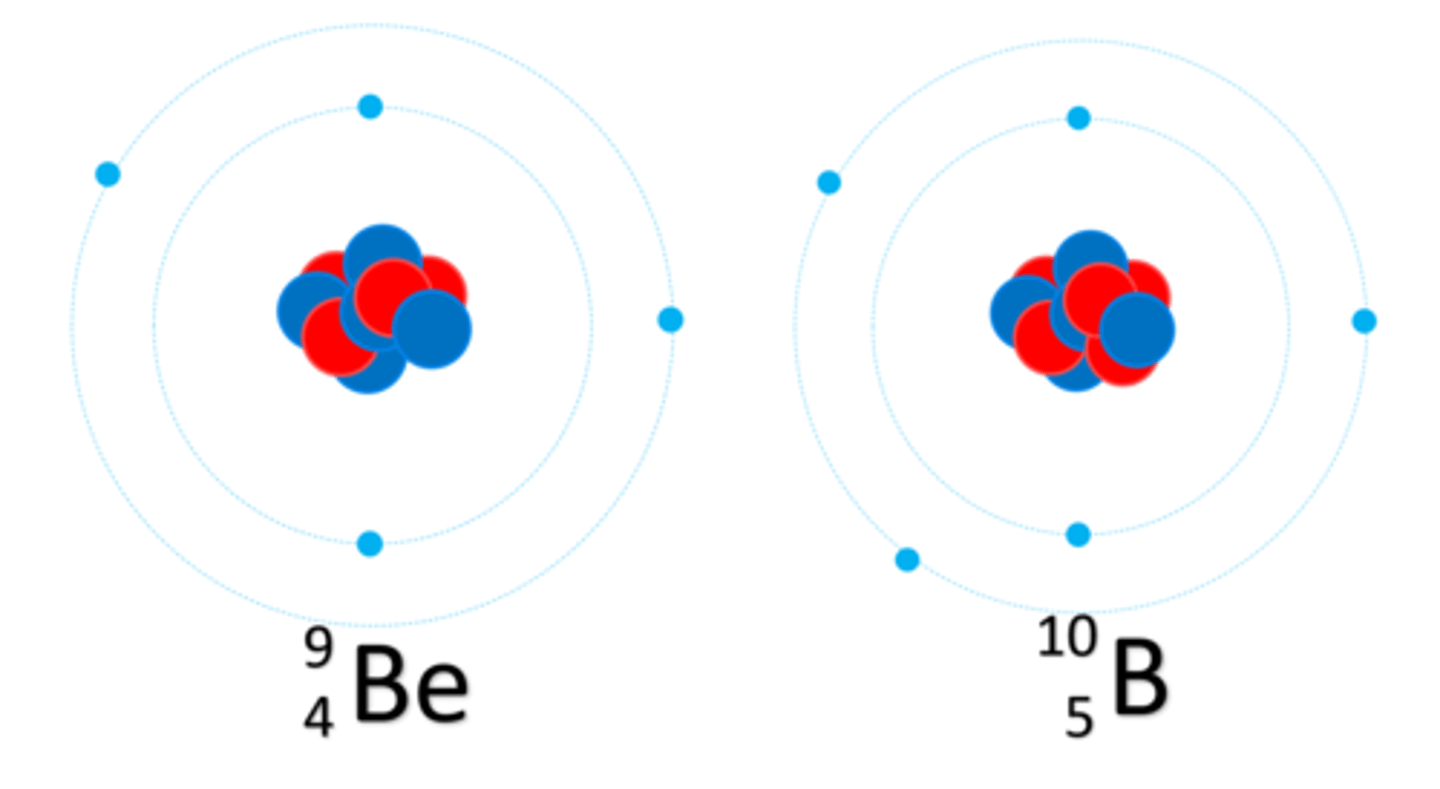
The number of protons in an atom of an element is called its ______ number
Atomic

The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom is called it's Atomic ____
Mass

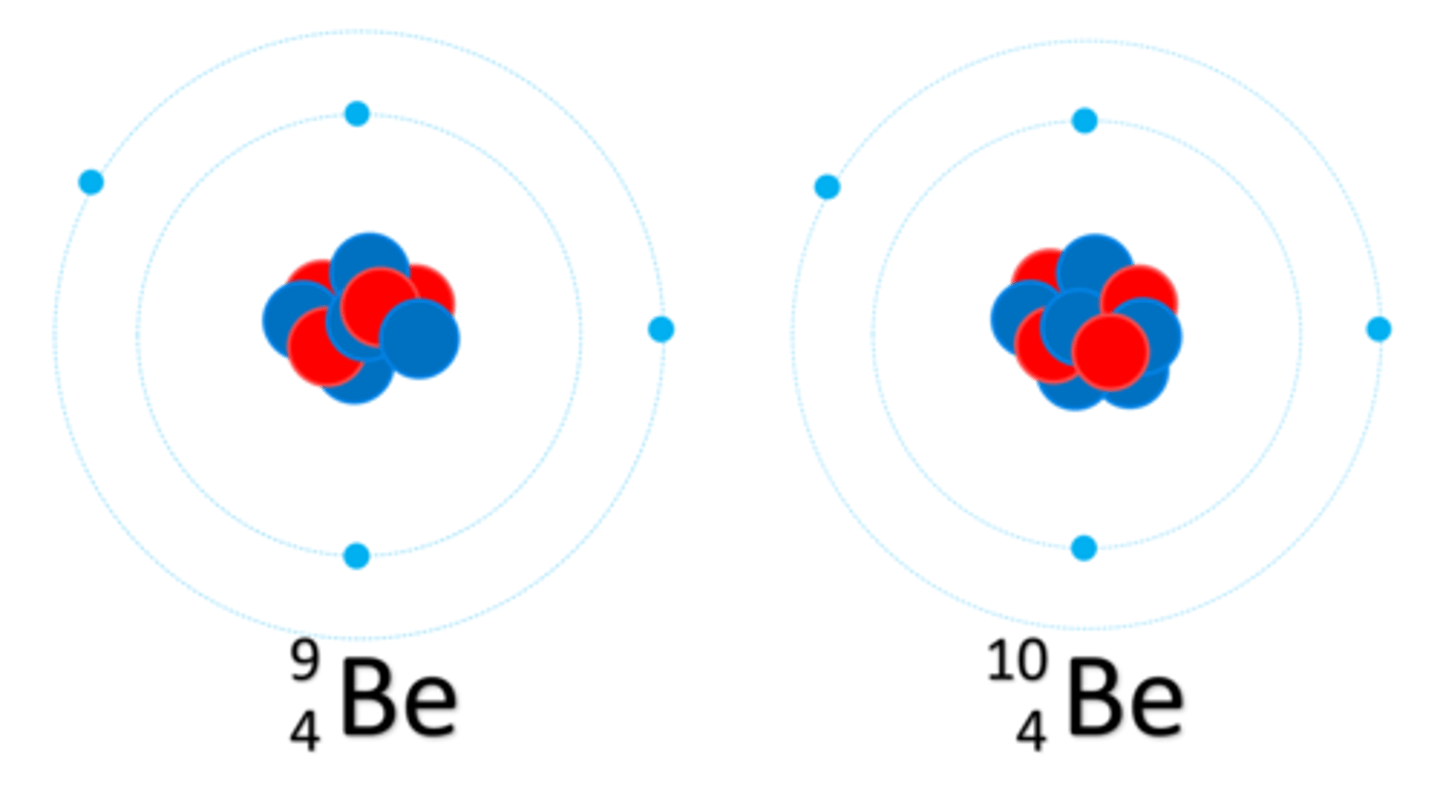
Isotopes are atoms with more or less ________
Neutrons
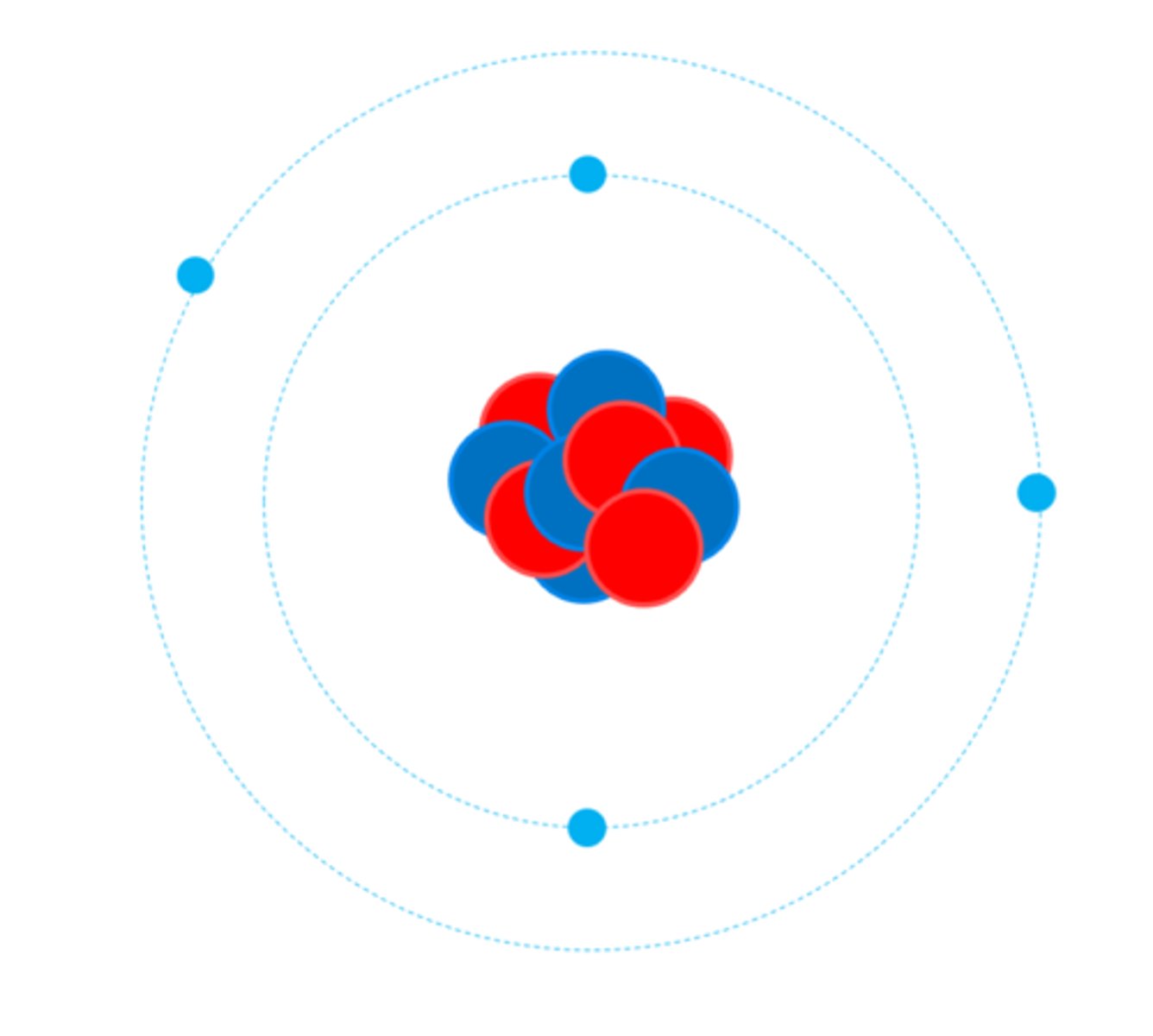
Atoms turn into positive ions if they lose one or more outer _________
Electrons
New experimental ________ may lead to a scientific model being changed or replaced
Evidence
Before the discovery of the ________, atoms were thought to be tiny spheres that could not be divided
Electron
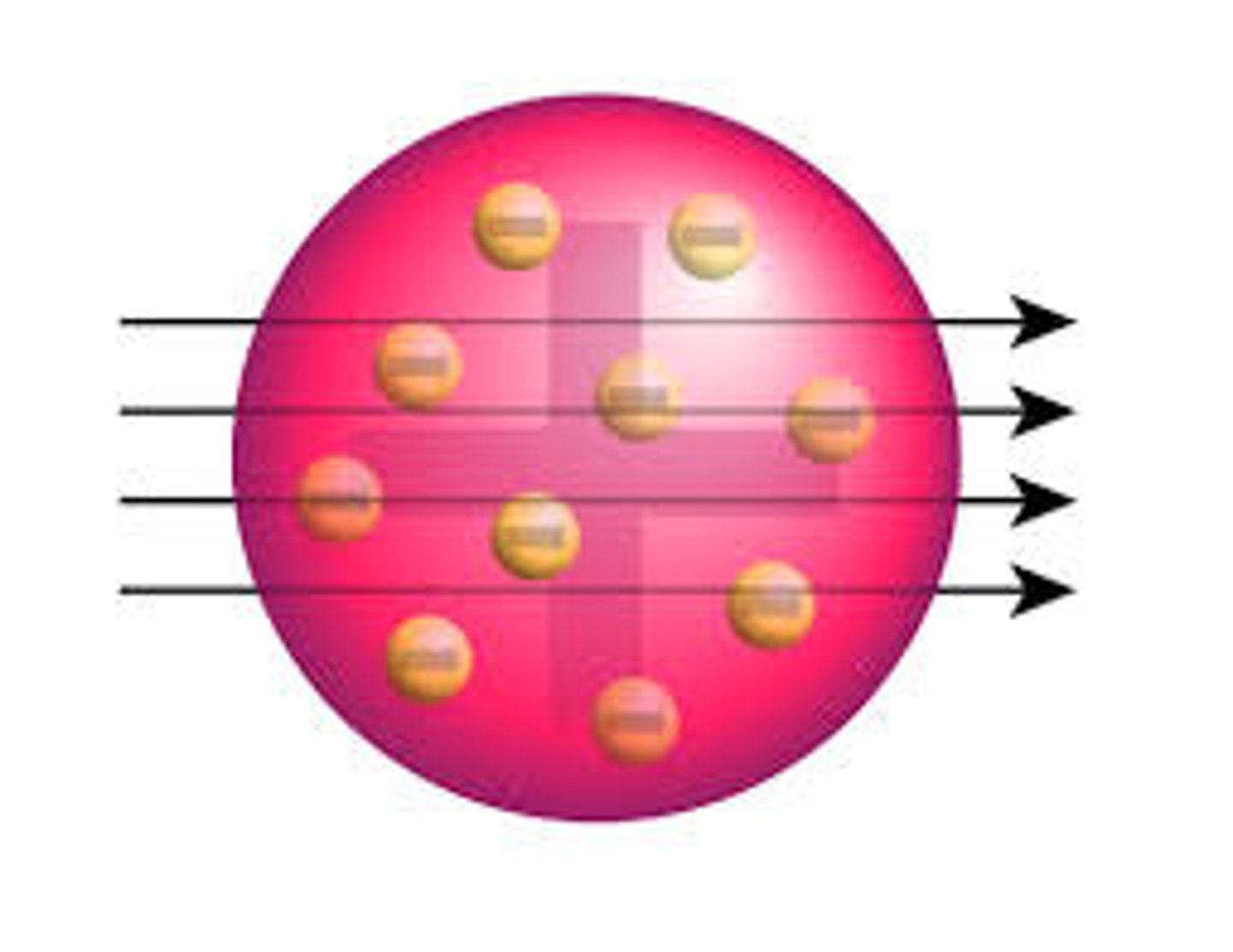
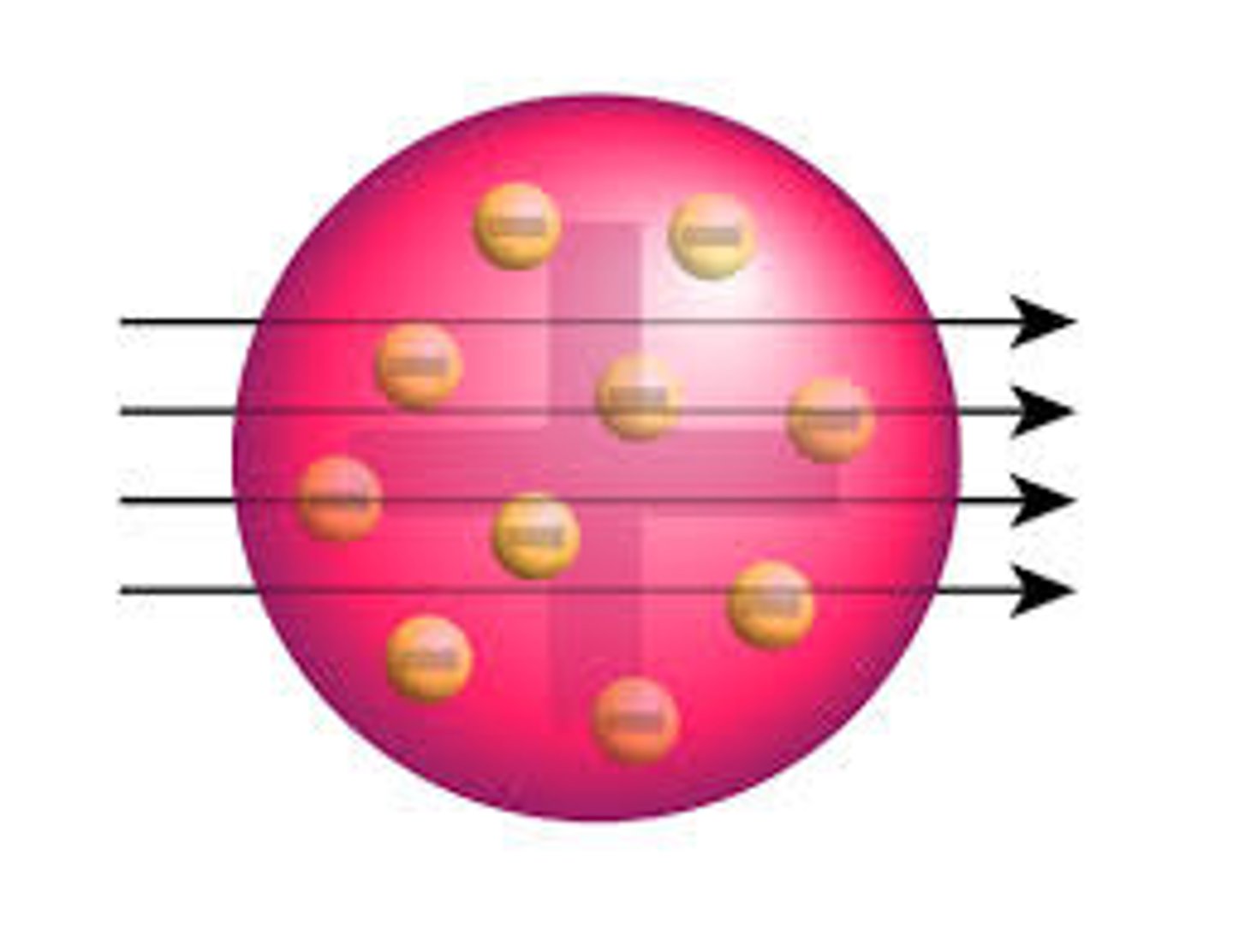
The discovery of the electron led to the ____ _______ model of the atom
Plum Pudding
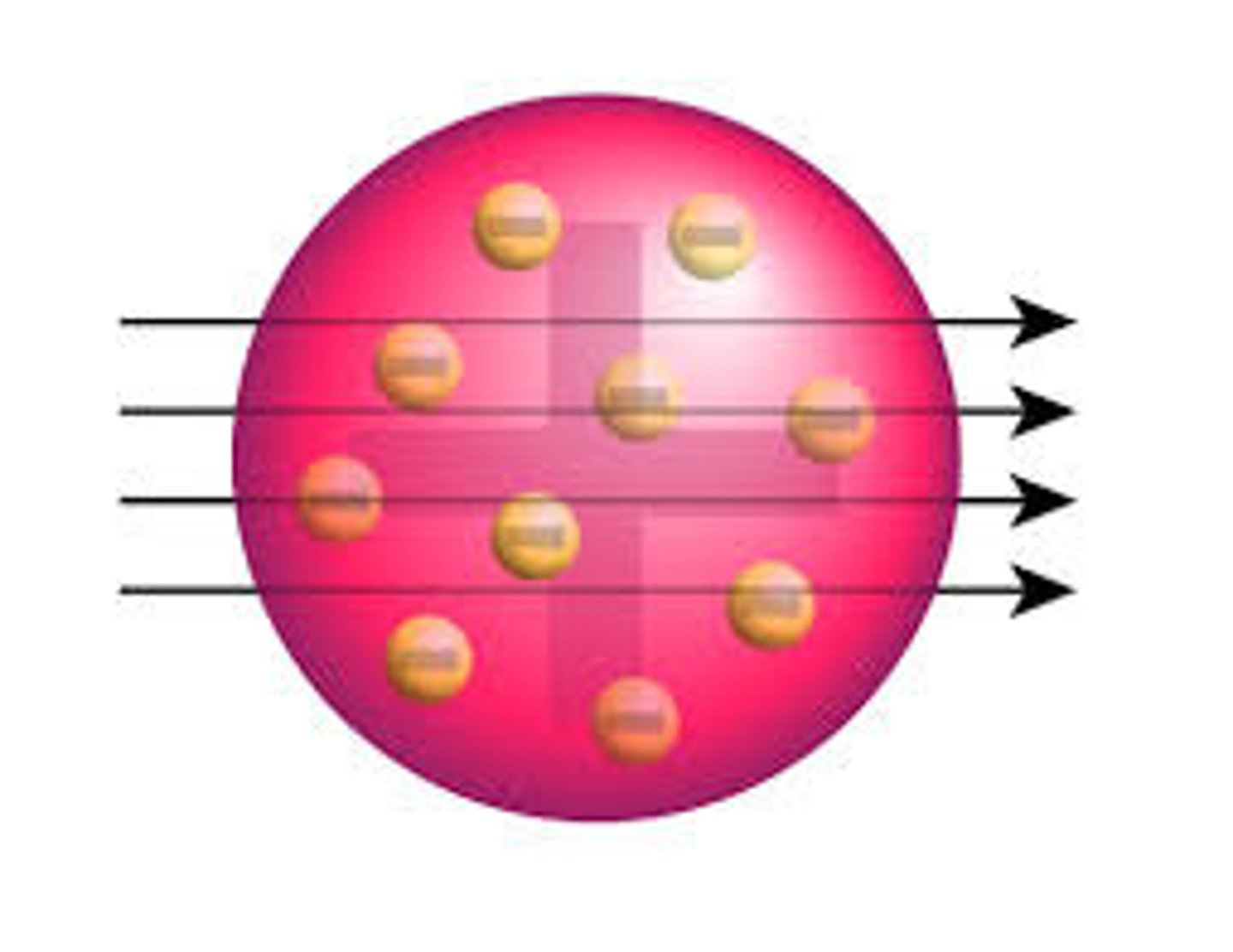
The ____ _______ model suggested that the atom is a ball of positive charge with negative electrons embedded in it
Plum Pudding
The Plum Pudding model was replaced by the Nuclear Model of the atom using evidence from the _____ __________ experiment
Alpha Scattering
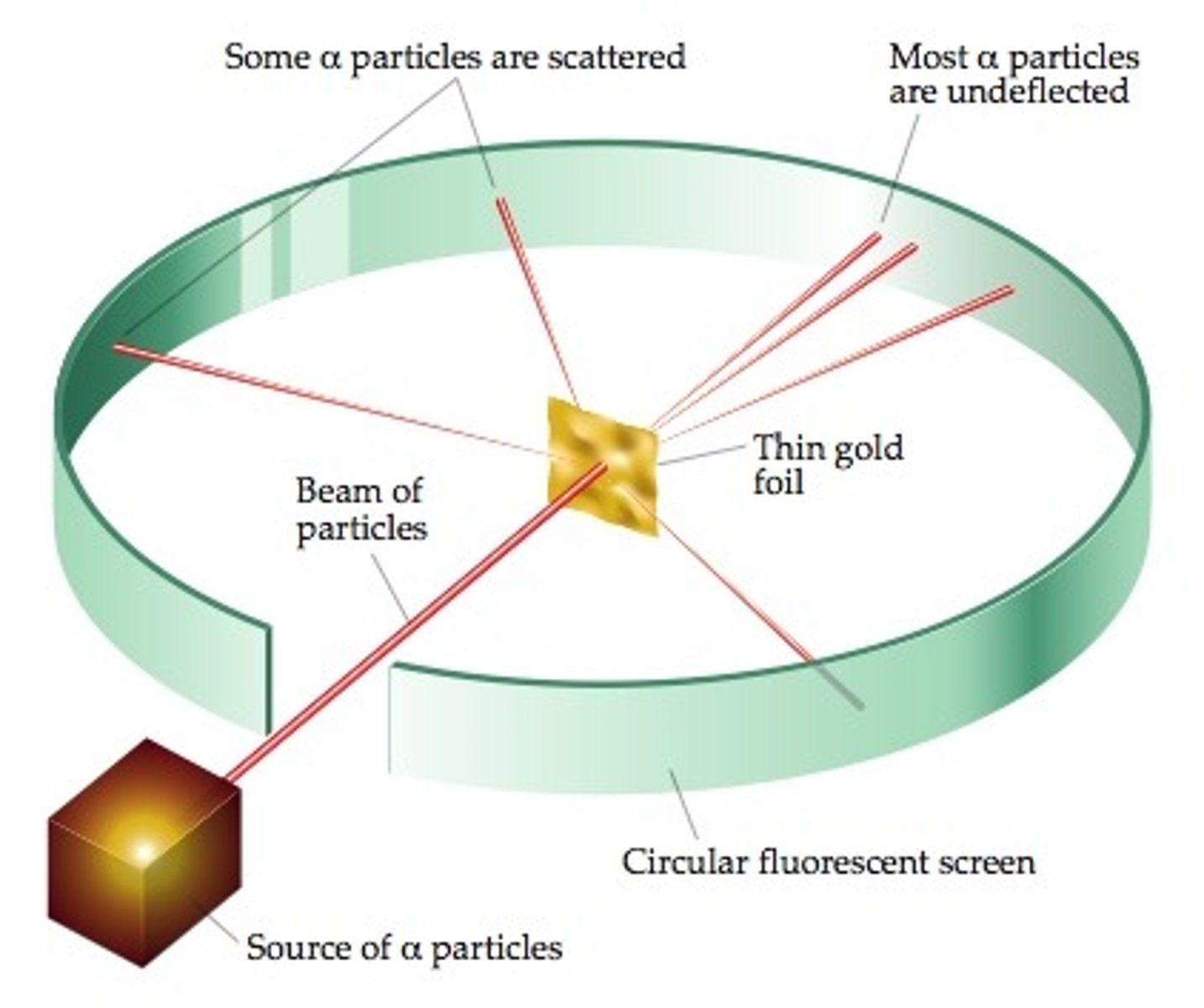
The Alpha Scattering experiment concluded that the ____ of an atom was concentrated in the Centre (Nucleus)
Mass
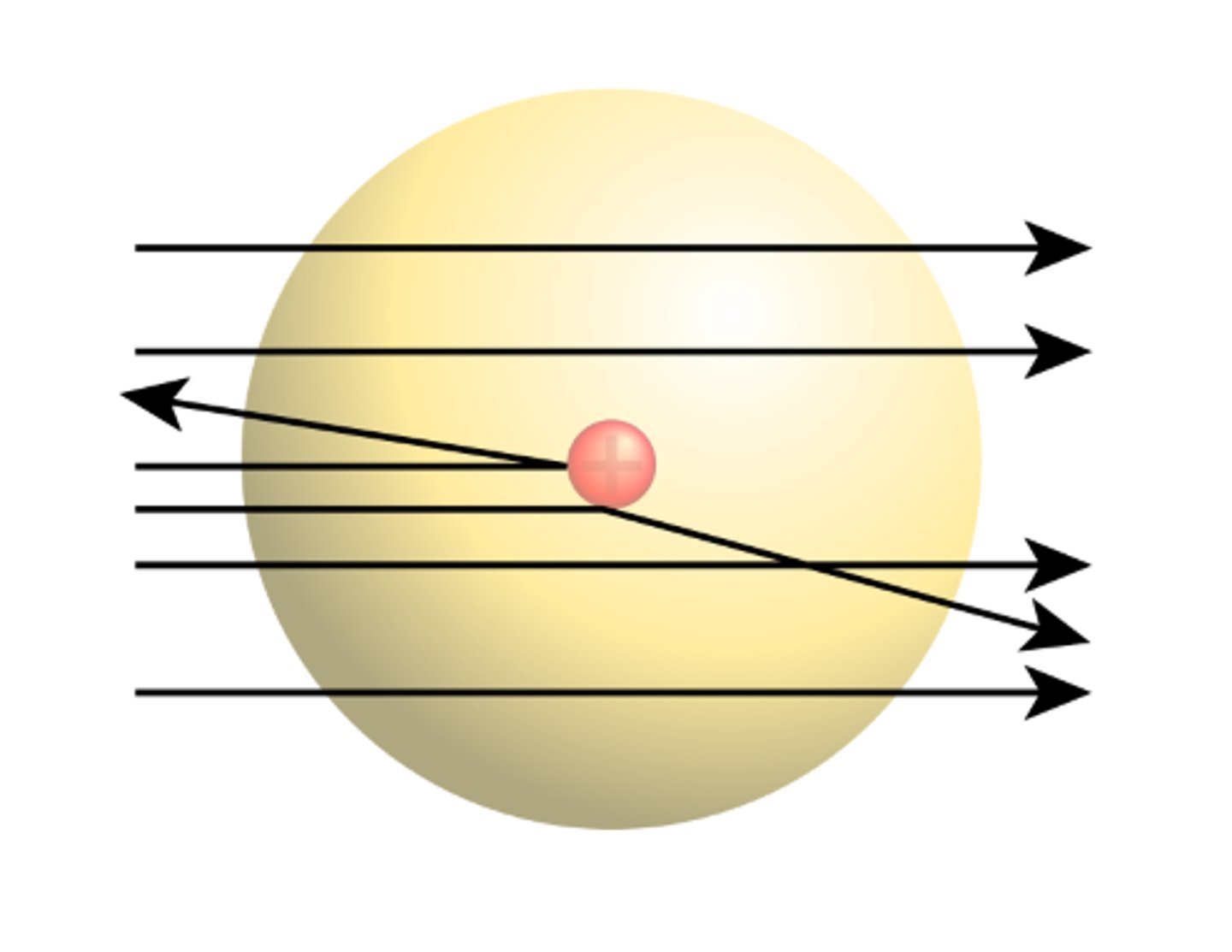
The Alpha Scattering experiment also concluded that the nucleus of the atom was _______
Charged

Niels Bohr adapted the nuclear model by suggesting that electrons _____ the nucleus at specific distances
Orbit
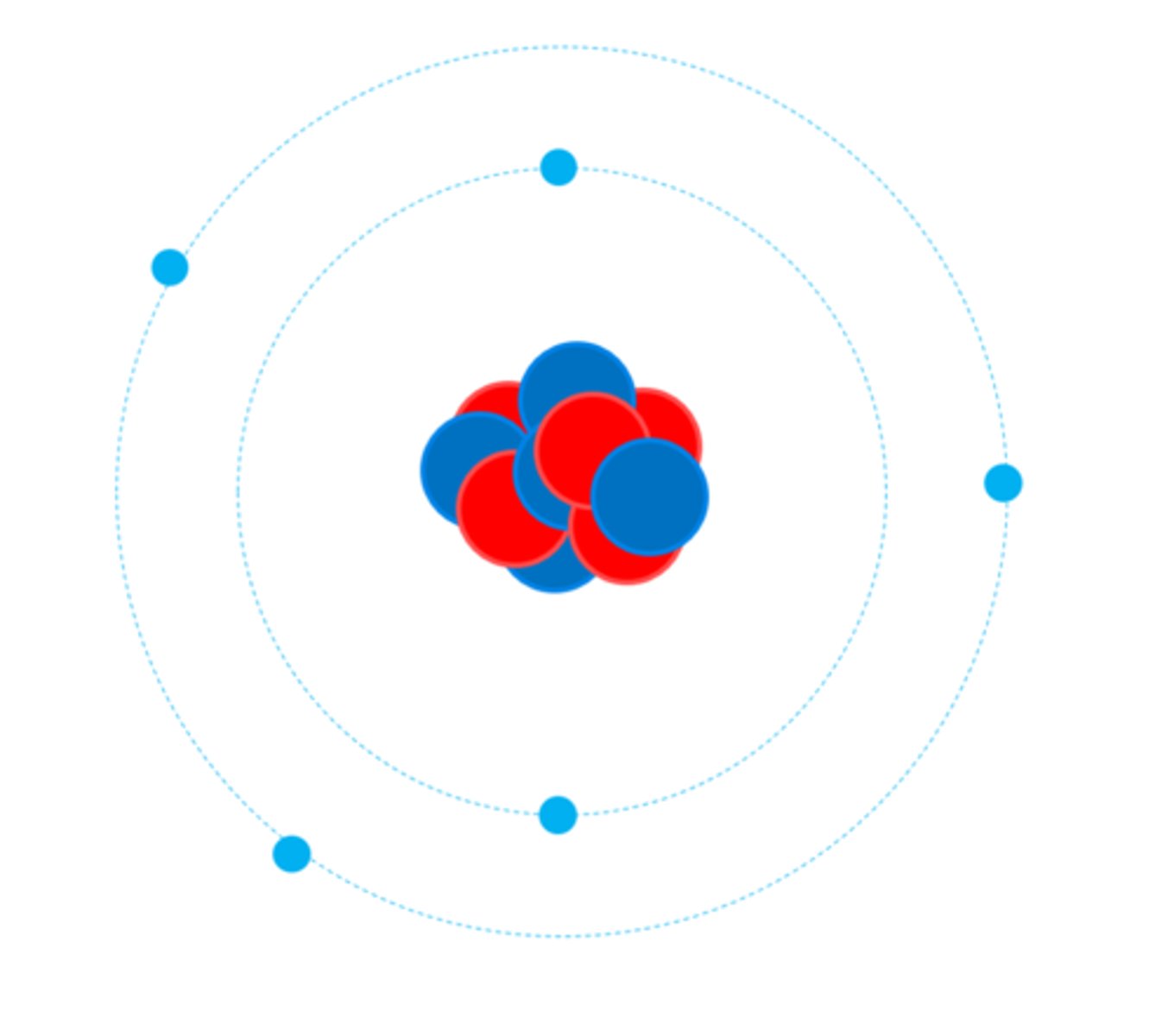
The theoretical calculations of Bohr ______ with experimental observations
Agreed
Later experiments found that the positive charge of a nucleus could be divided into a whole number of smaller particles, the name ______ was given to these particles
Proton
About 20 years after the nucleus became an accepted scientific idea, James Chadwick provided the evidence to show the existence of ________
Neutrons
Some atomic nuclei are ________
Unstable
An unstable _______ gives out radiation as it changes to become more stable
Nucleus
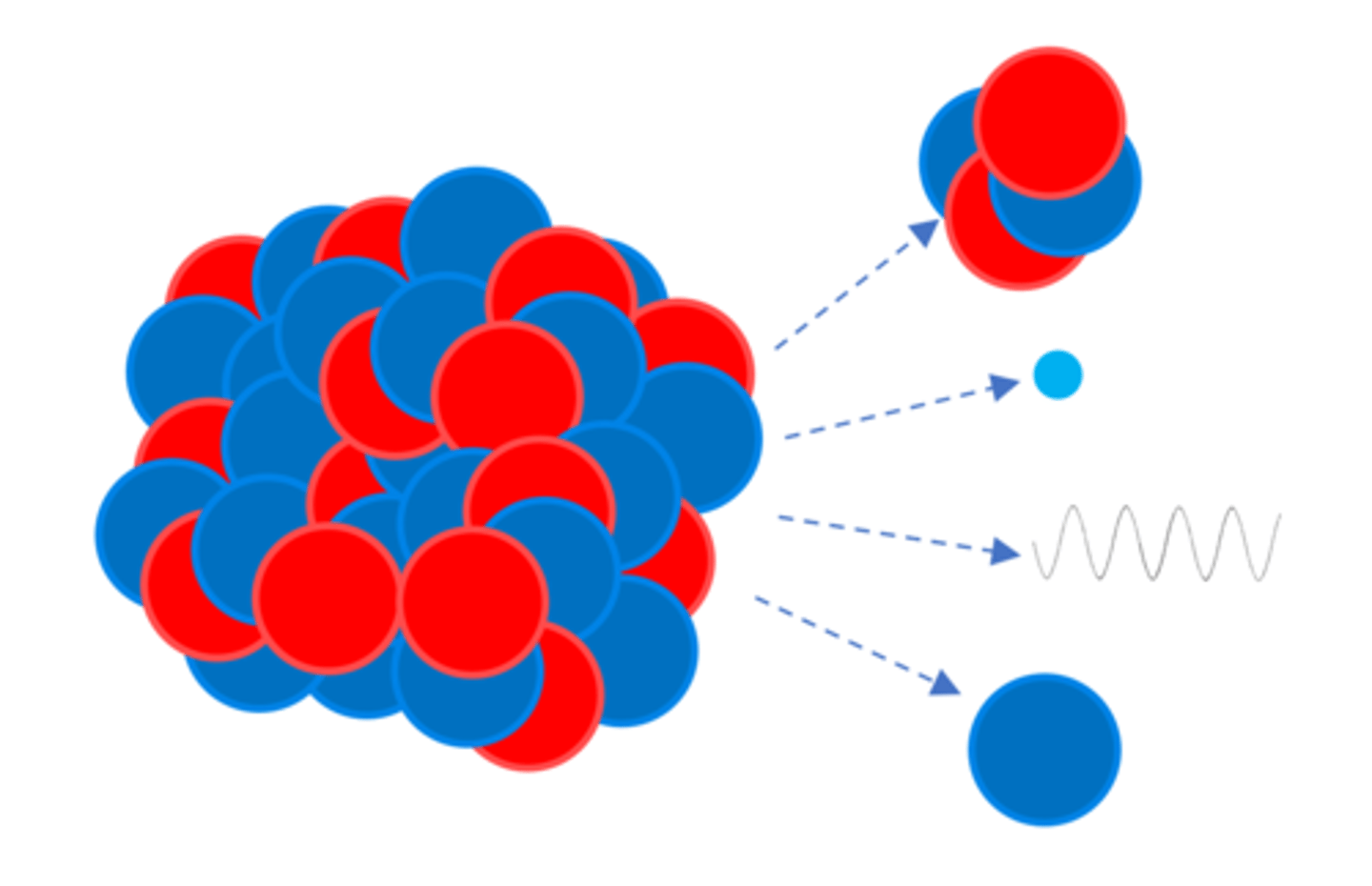
Radioactive _____ is a random process
Decay
________ measures how quickly unstable nuclei decay
Activity
Activity is measured in _________
Becquerel (Bq)
_____-____ is the number of decays recorded each second by a detector (eg Geiger-Muller tube)
Count-rate
An alpha particle (α) consists of two ________ and two protons
Neutrons

An alpha particle (α) is the same as a helium _______
Nucleus
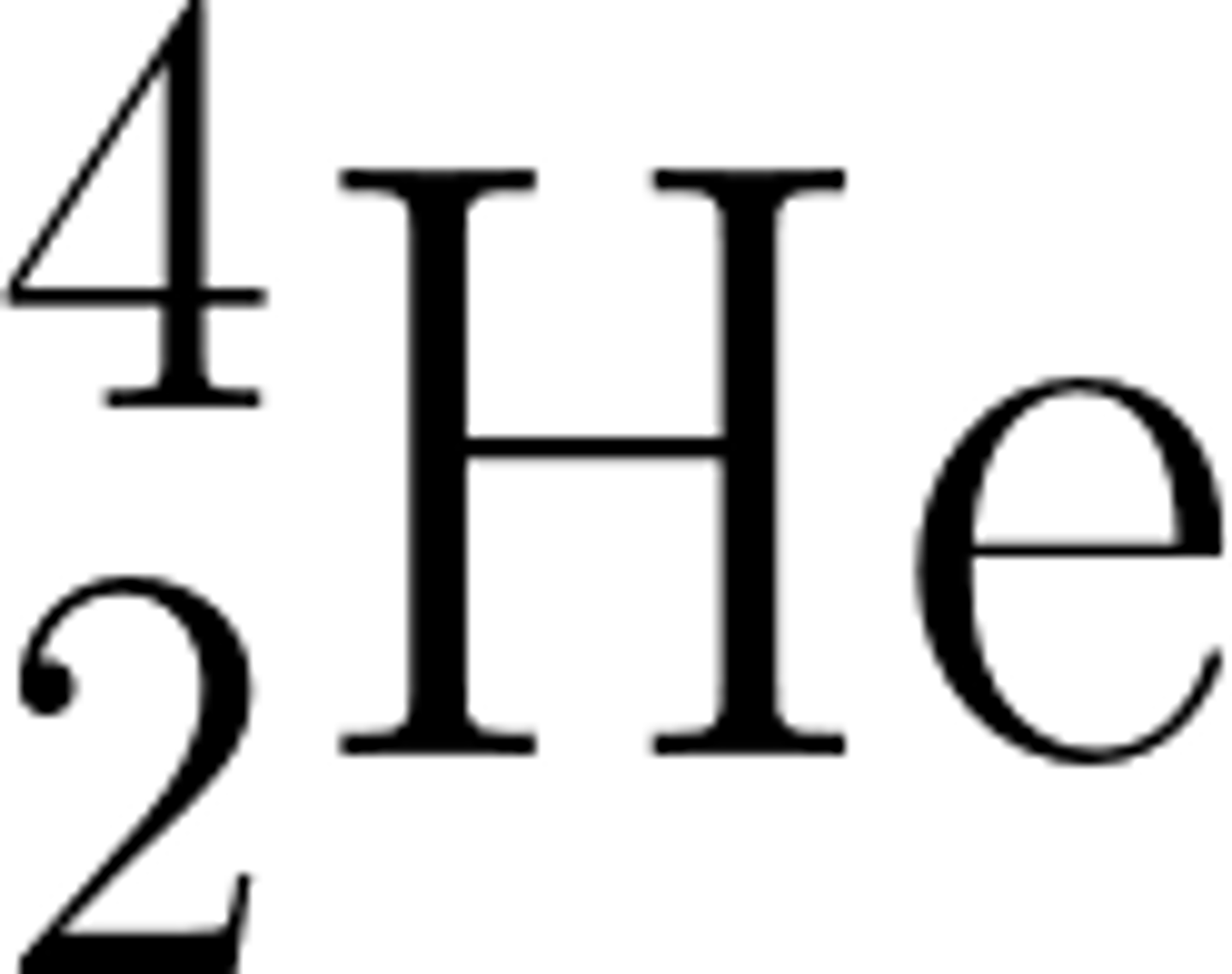
A beta particle (β) - a high speed ________ ejected from the nucleus
Electron
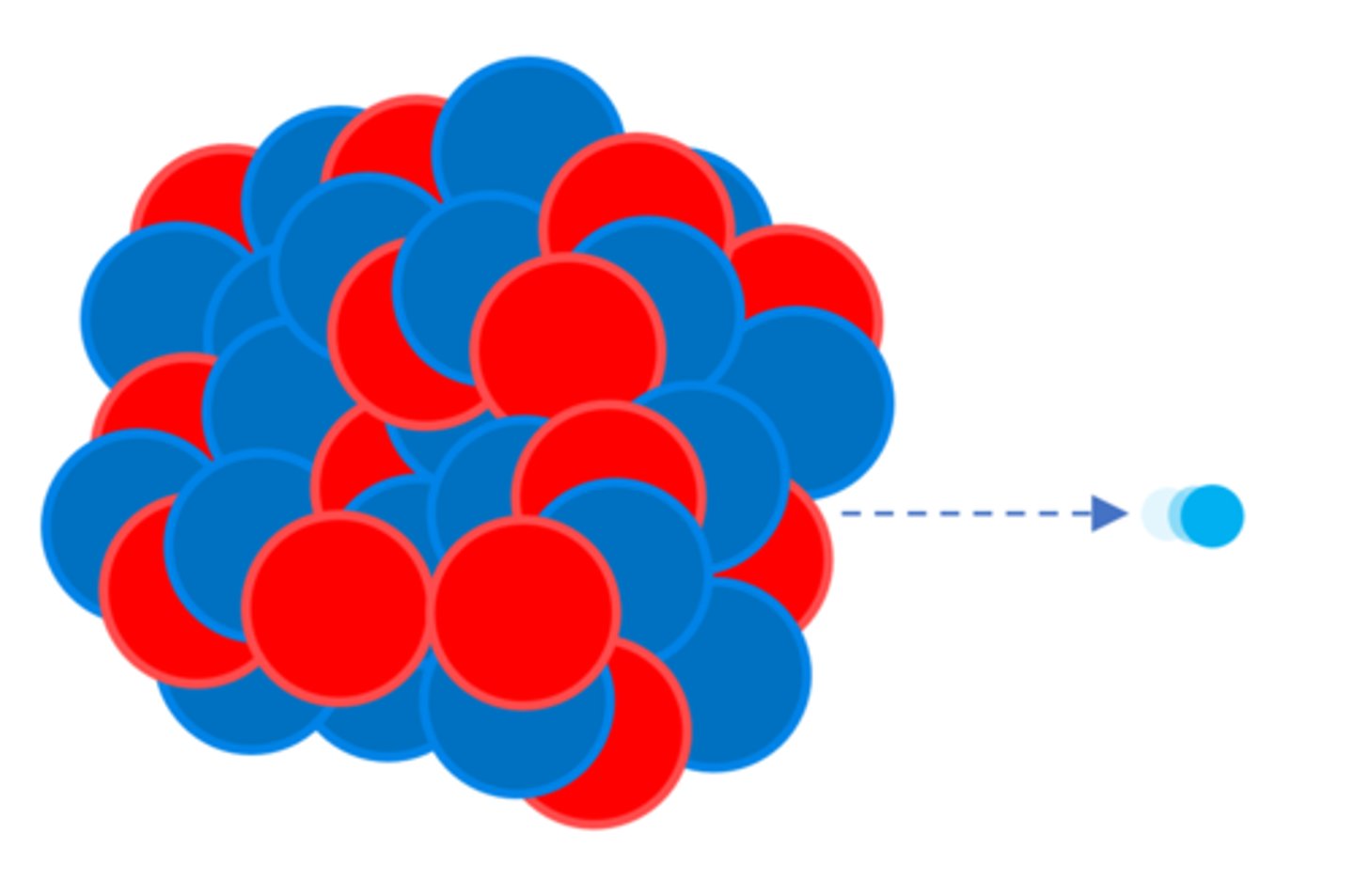
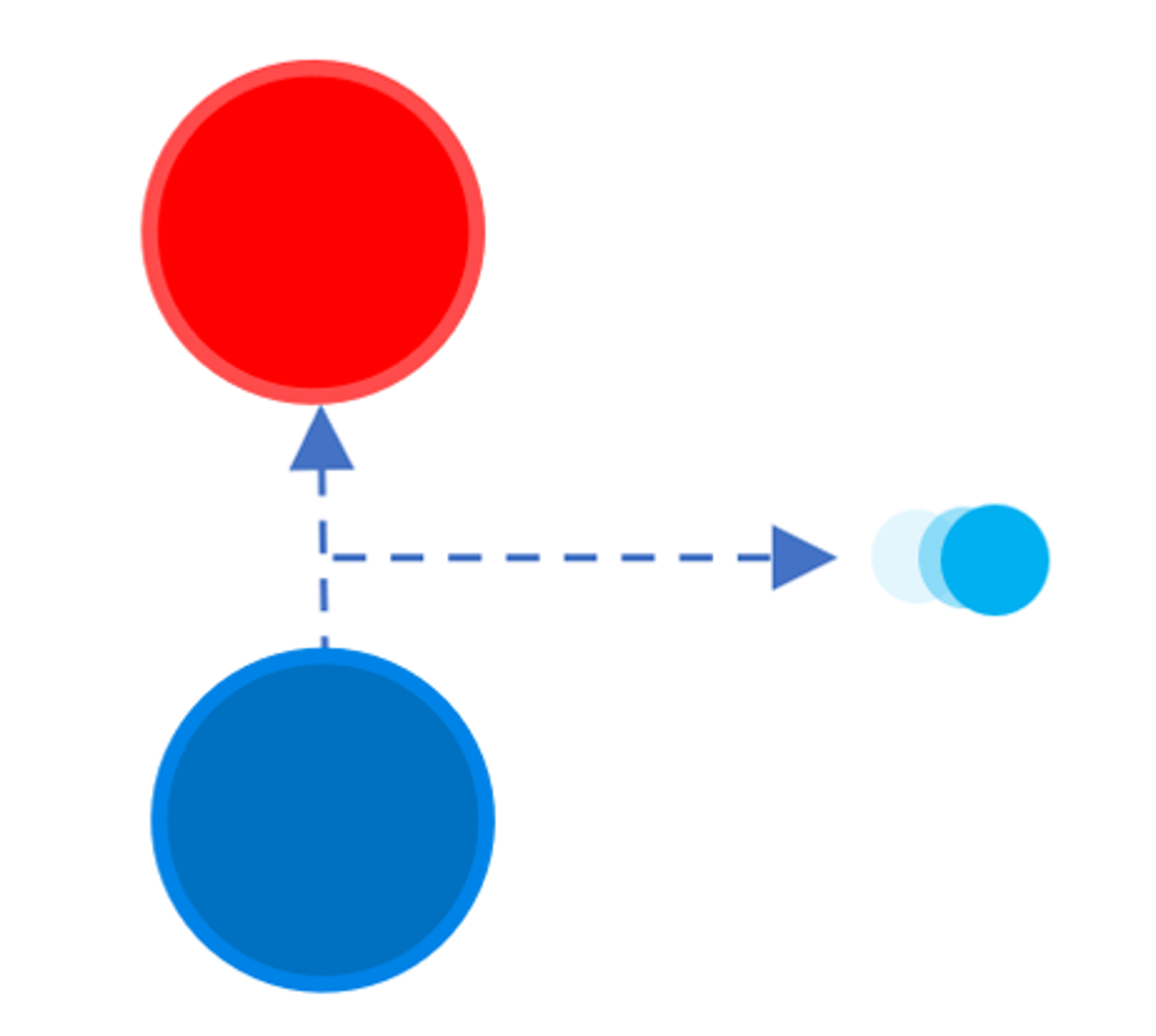
A beta particle (β) is emitted when a neutron turns into a ______
Proton
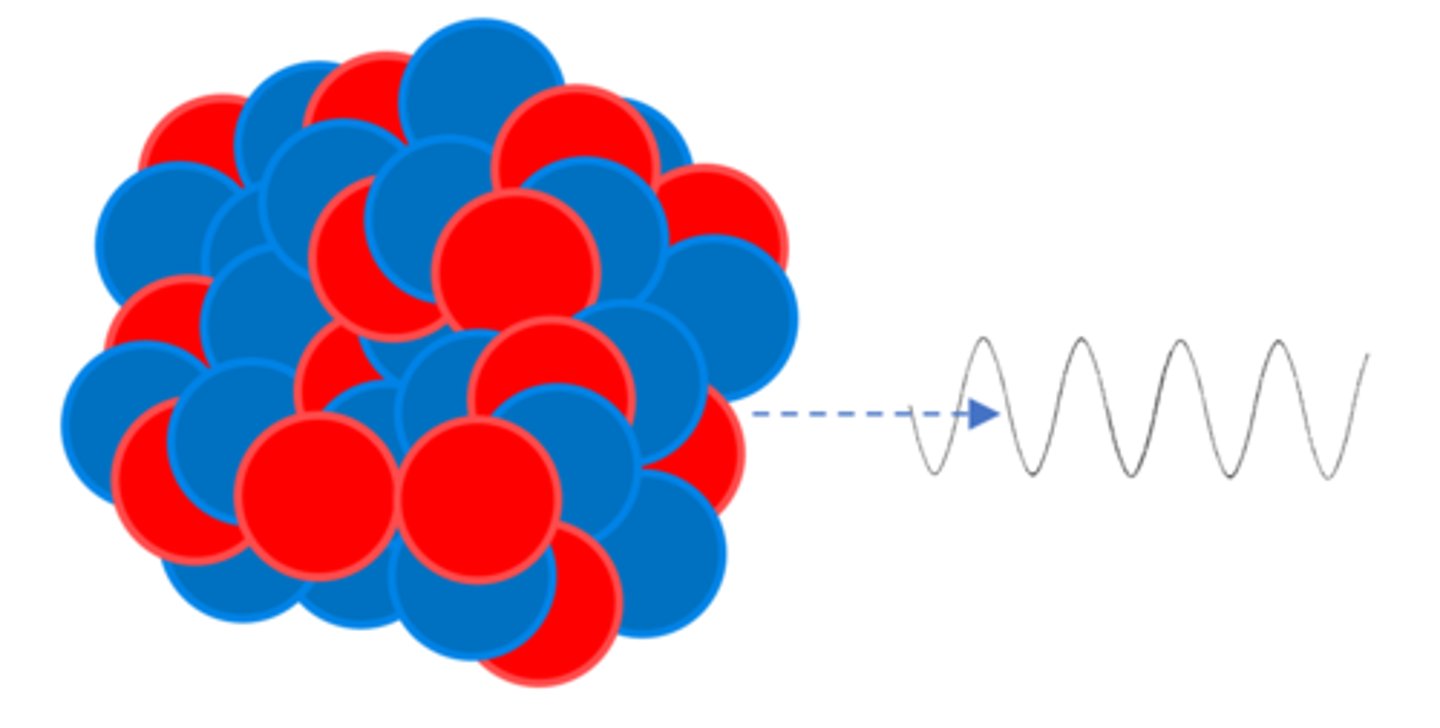
A gamma ray (γ) is electromagnetic radiation from the _______
Nucleus
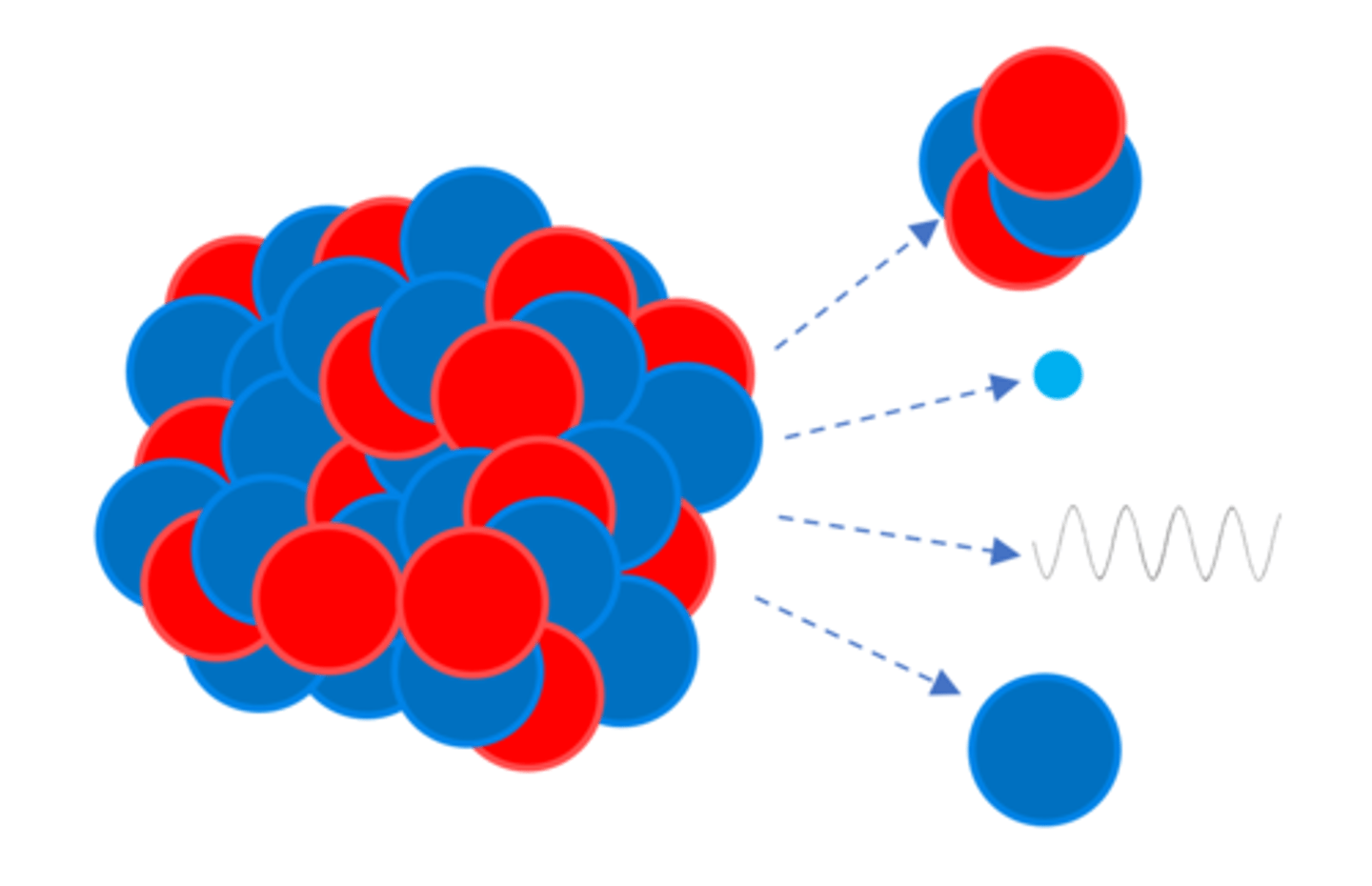
An unstable nucleus may emit an alpha, beta, gamma or a _______
Neutron (n)
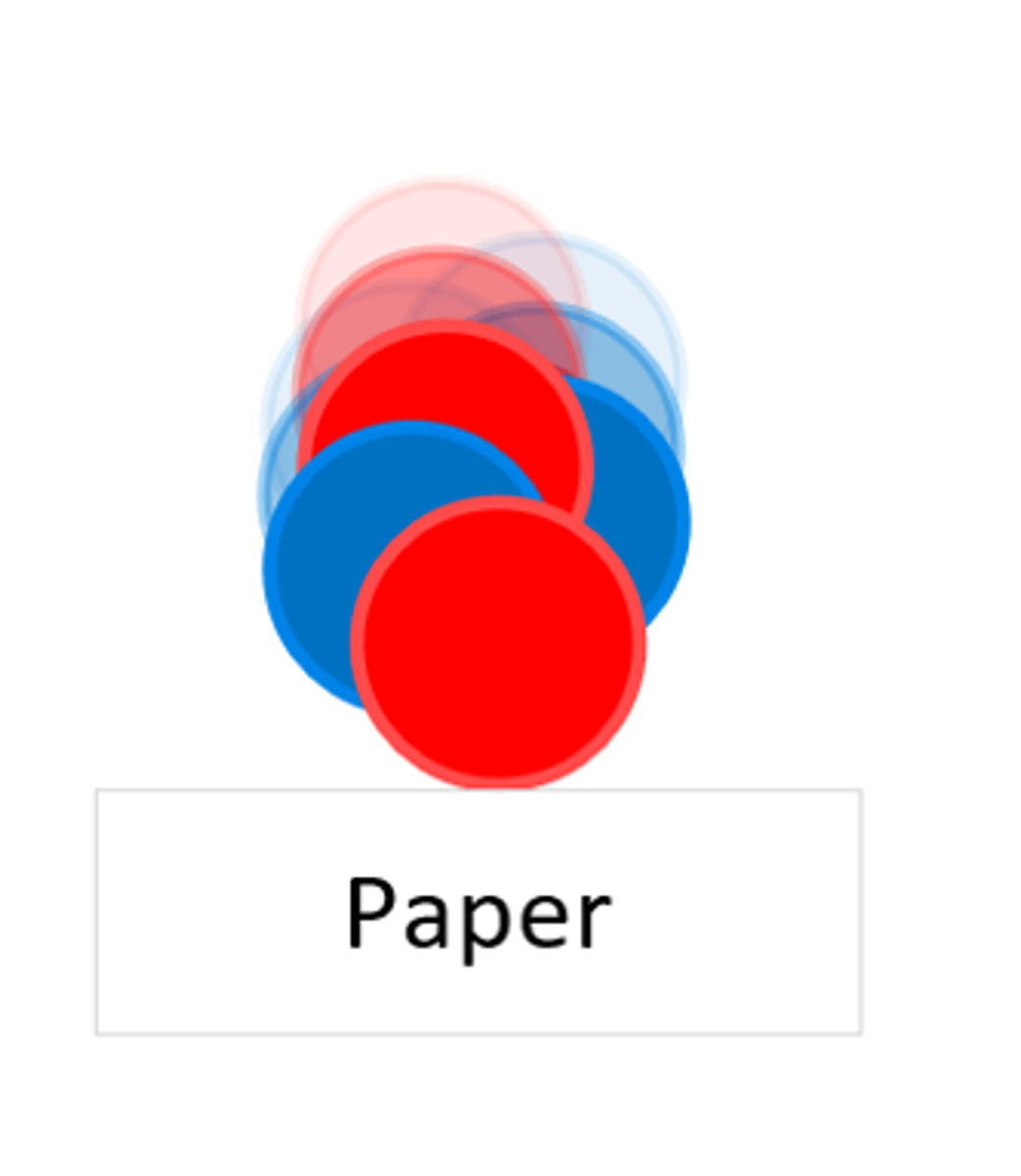
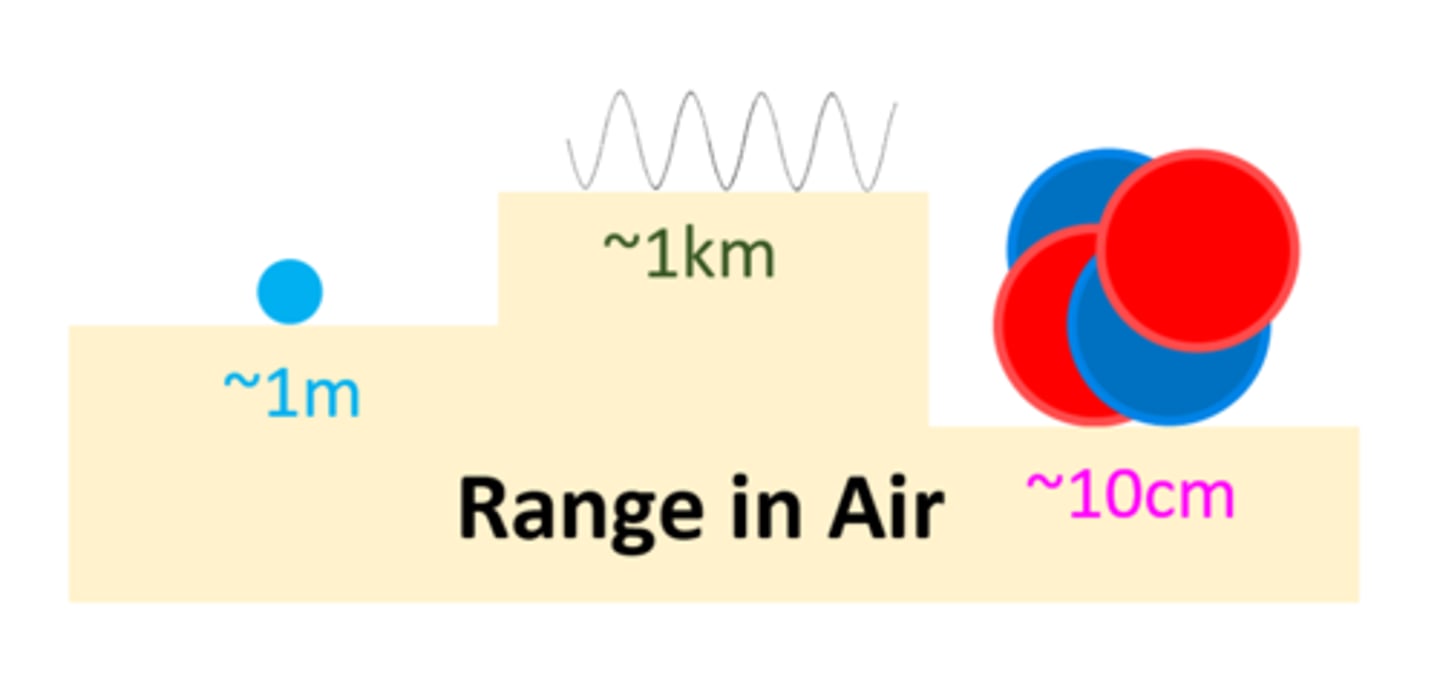
An alpha particle can be stopped by _____
Paper

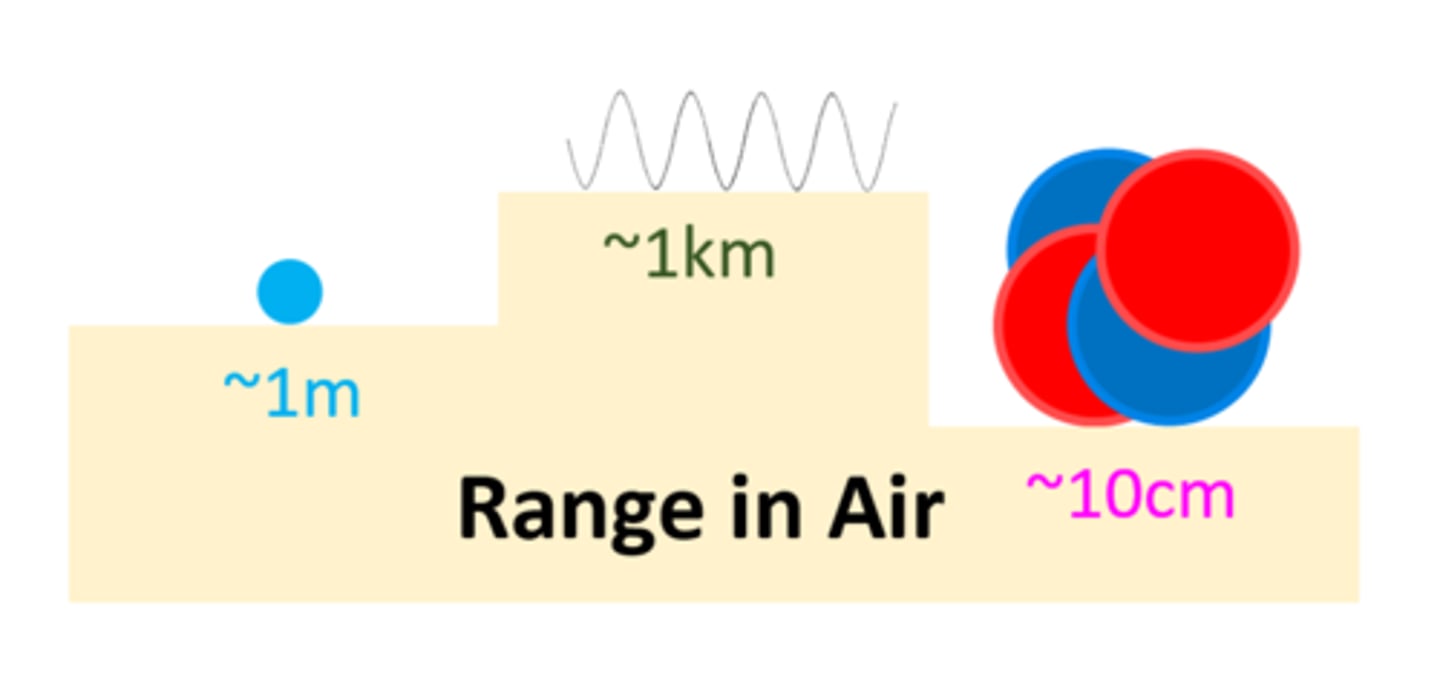
An alpha particle can travel _ ___ ___ through air
A few cms

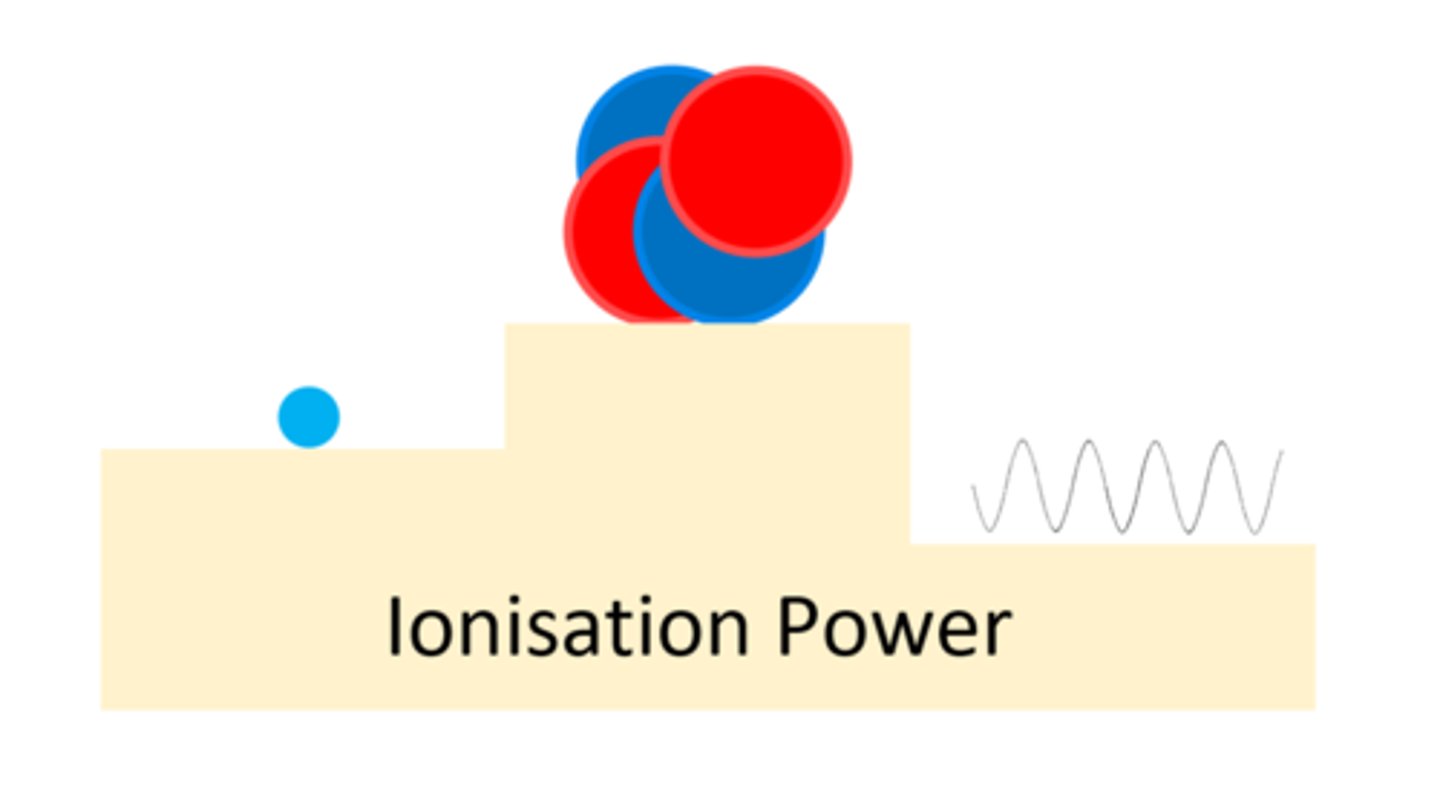
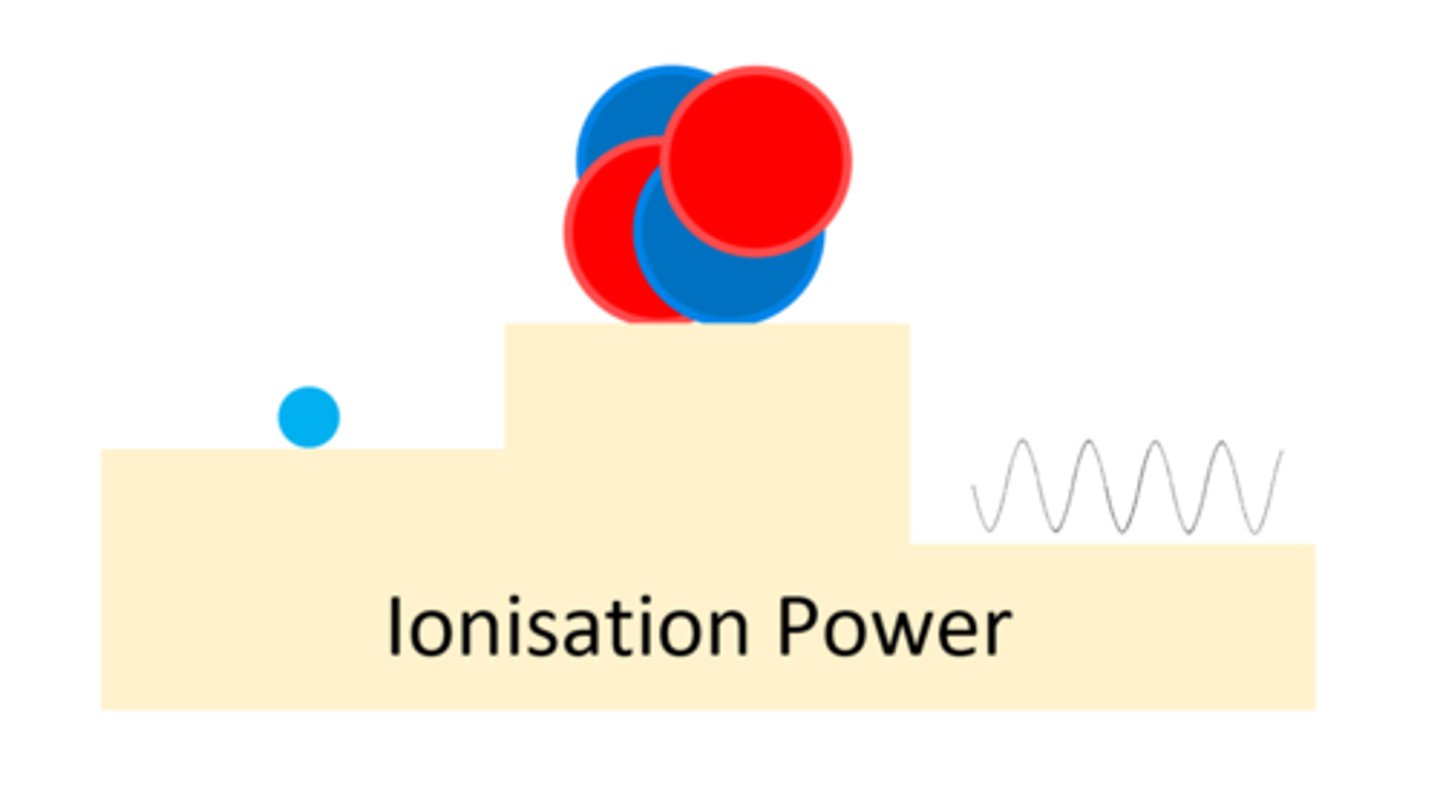
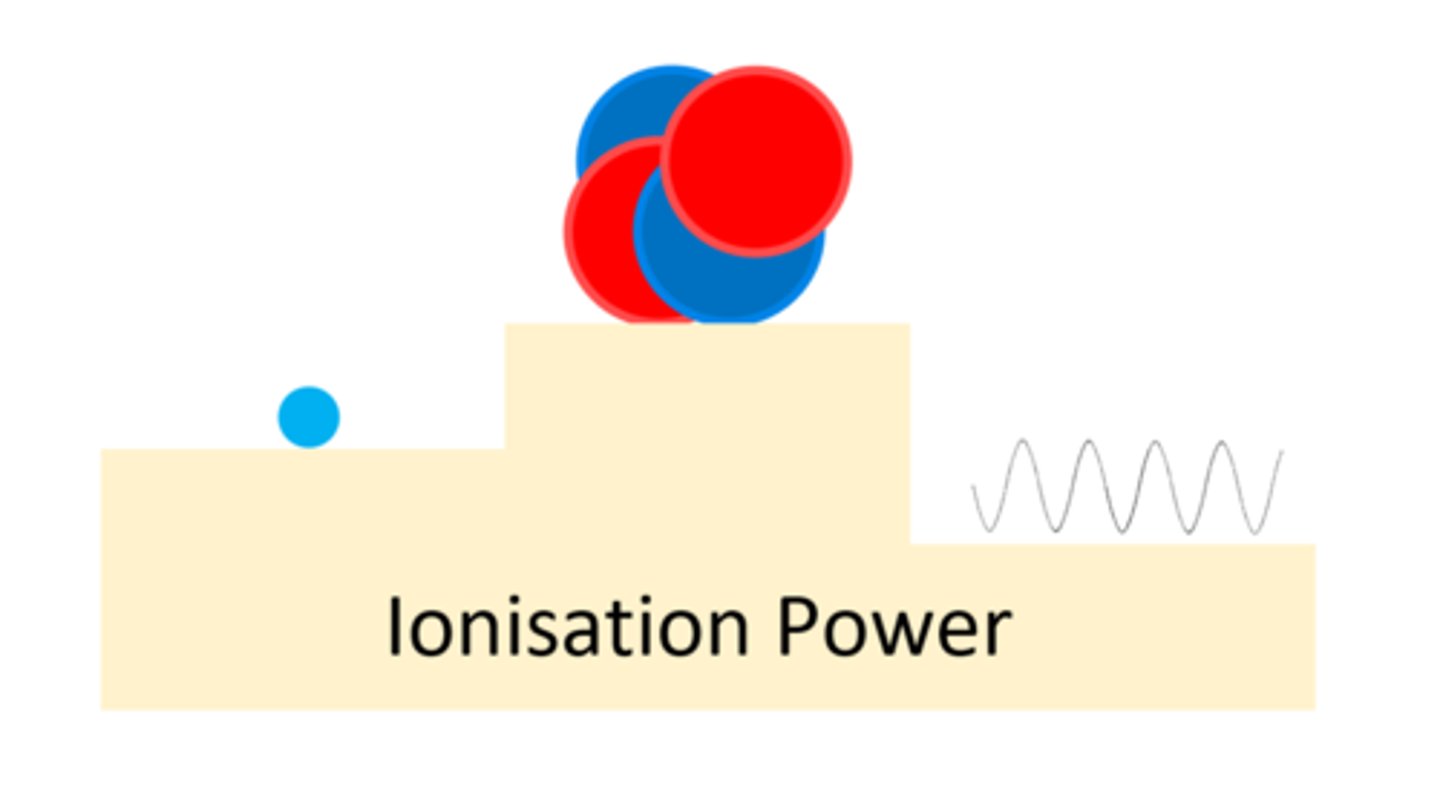
An alpha particle has a ____ ionising power
High
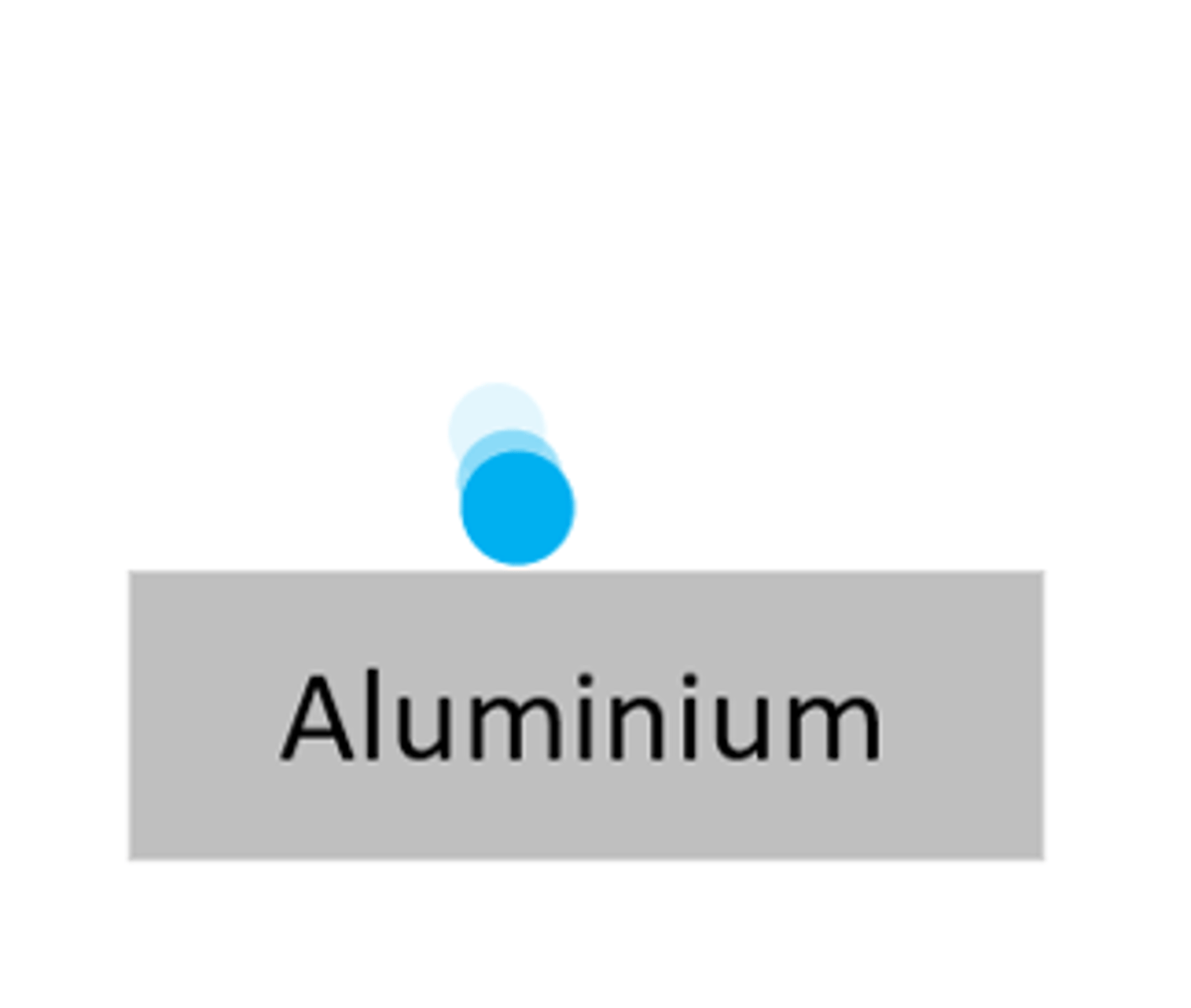
A beta particle can be stopped by ____ _________
thin aluminium
A beta particle can travel _ _____ through air
1 Meter
A beta particle has a _____ ionising power than alpha
Lower
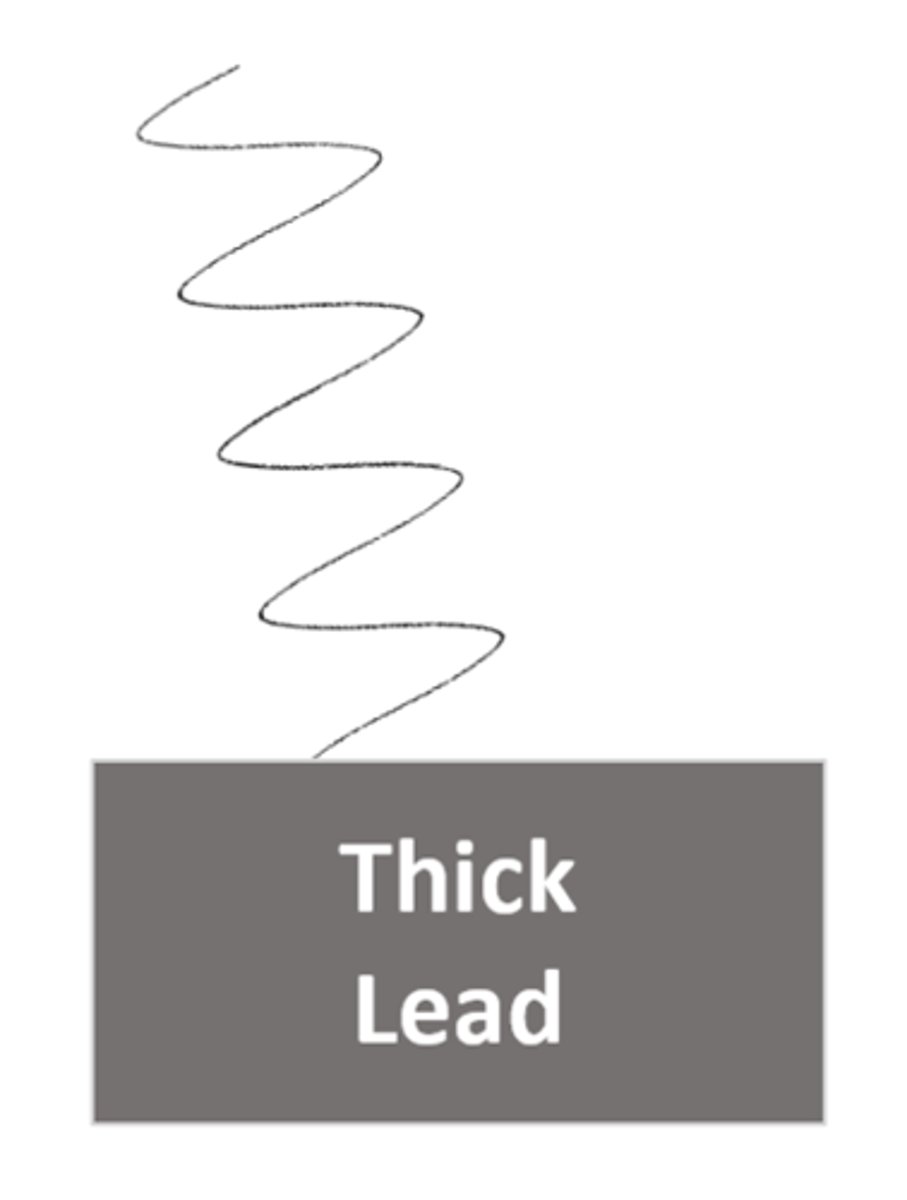
A gamma ray can be slowed by _____ ____
Thick Lead
A gamma ray can travel _ __ through air
1 km
A gamma ray has a ____ ___ ionising power
Very Low
A ___ ionising power means that healthy cells are not harmed during radiotherapy
Low
A ____ penetration power means that radiation can be detected through thick materials
High
A _____ half-life means the substance won't be radioactive for very long
short
In a nuclear equation an alpha particle may be represented by the symbol:
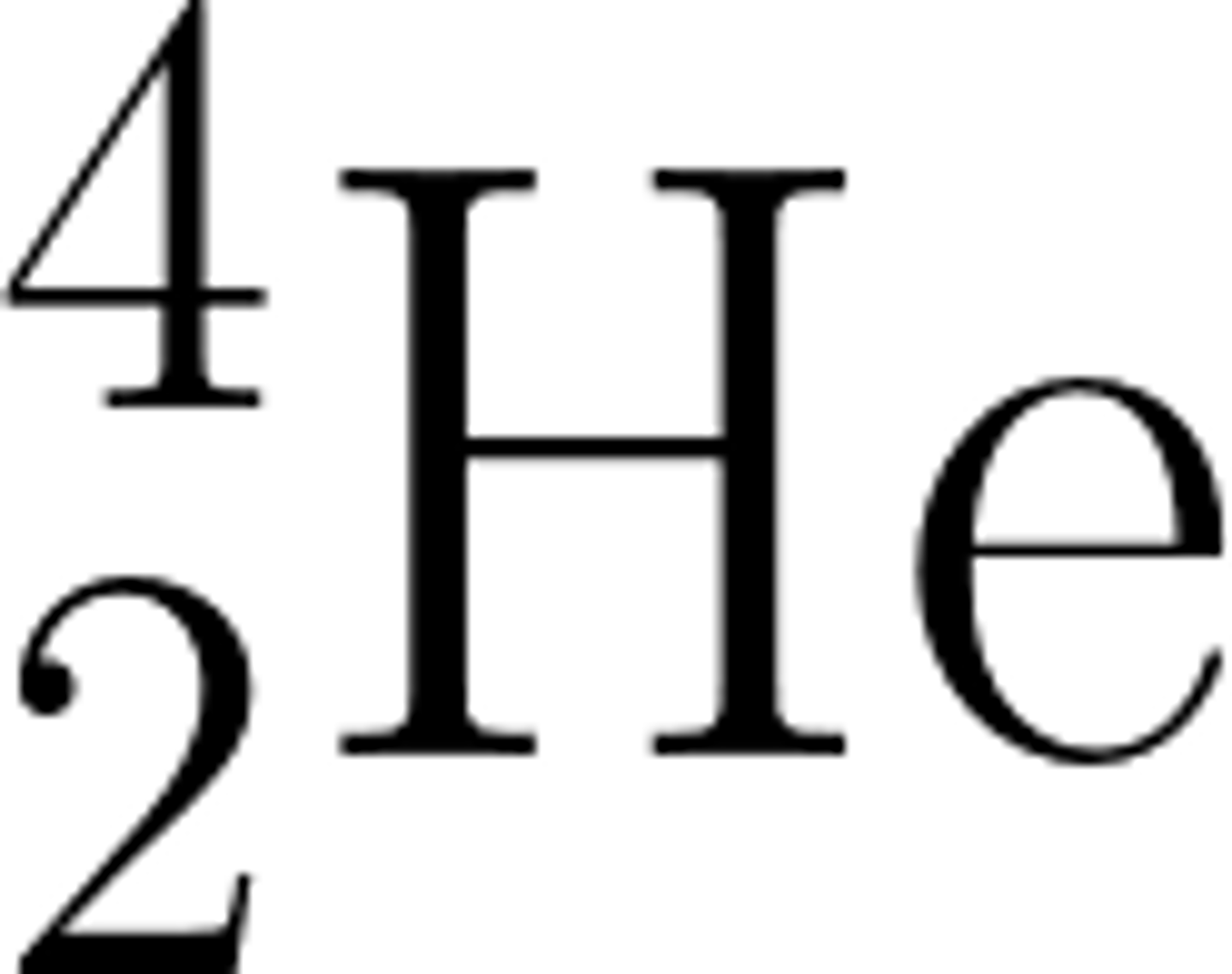
In a nuclear equation a beta particle may be represented by the symbol:
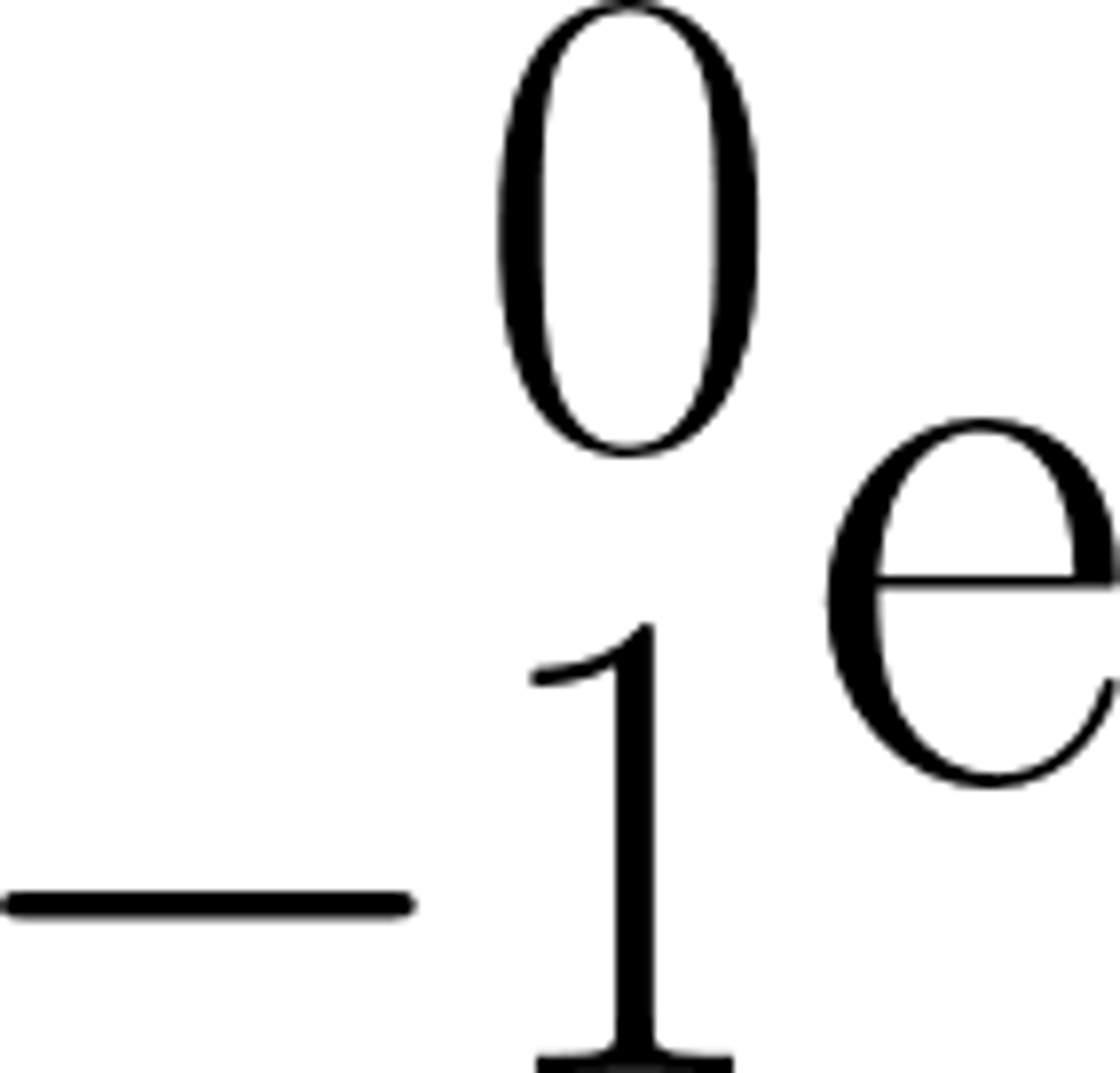
The emission of different types of nuclear radiation may cause a change in the mass and/or the ______ of the nucleus
Charge
Alpha decay causes both the mass and charge of the nucleus to ________
Decrease
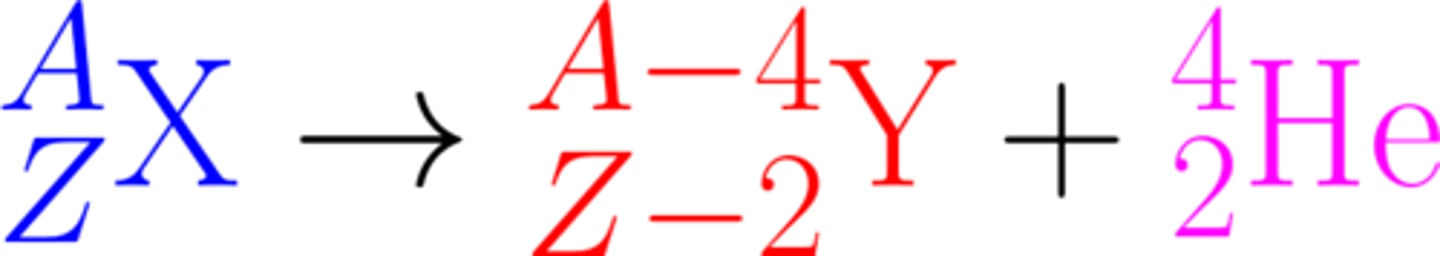
Beta decay does not cause the ____ of the nucleus to change
Mass

Beta decay causes the charge of the nucleus to ________
Increase

The emission of a _____ ___ does not cause the mass or the charge of the nucleus to change
Gamma Ray
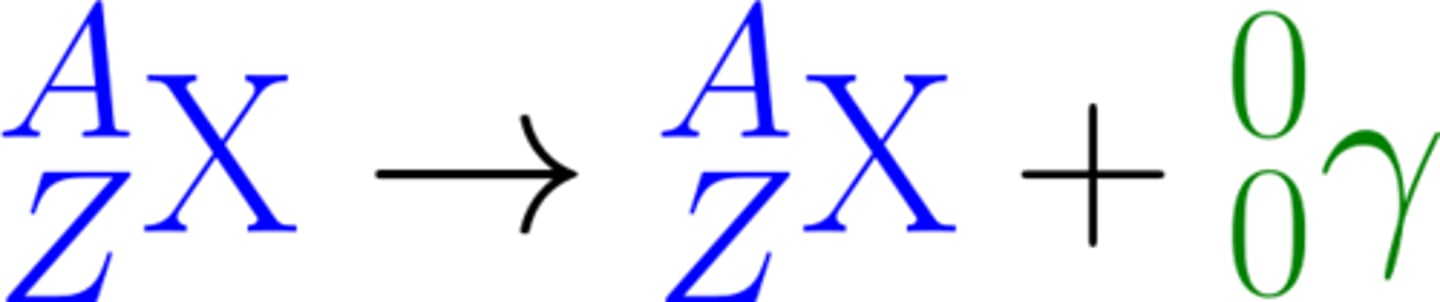
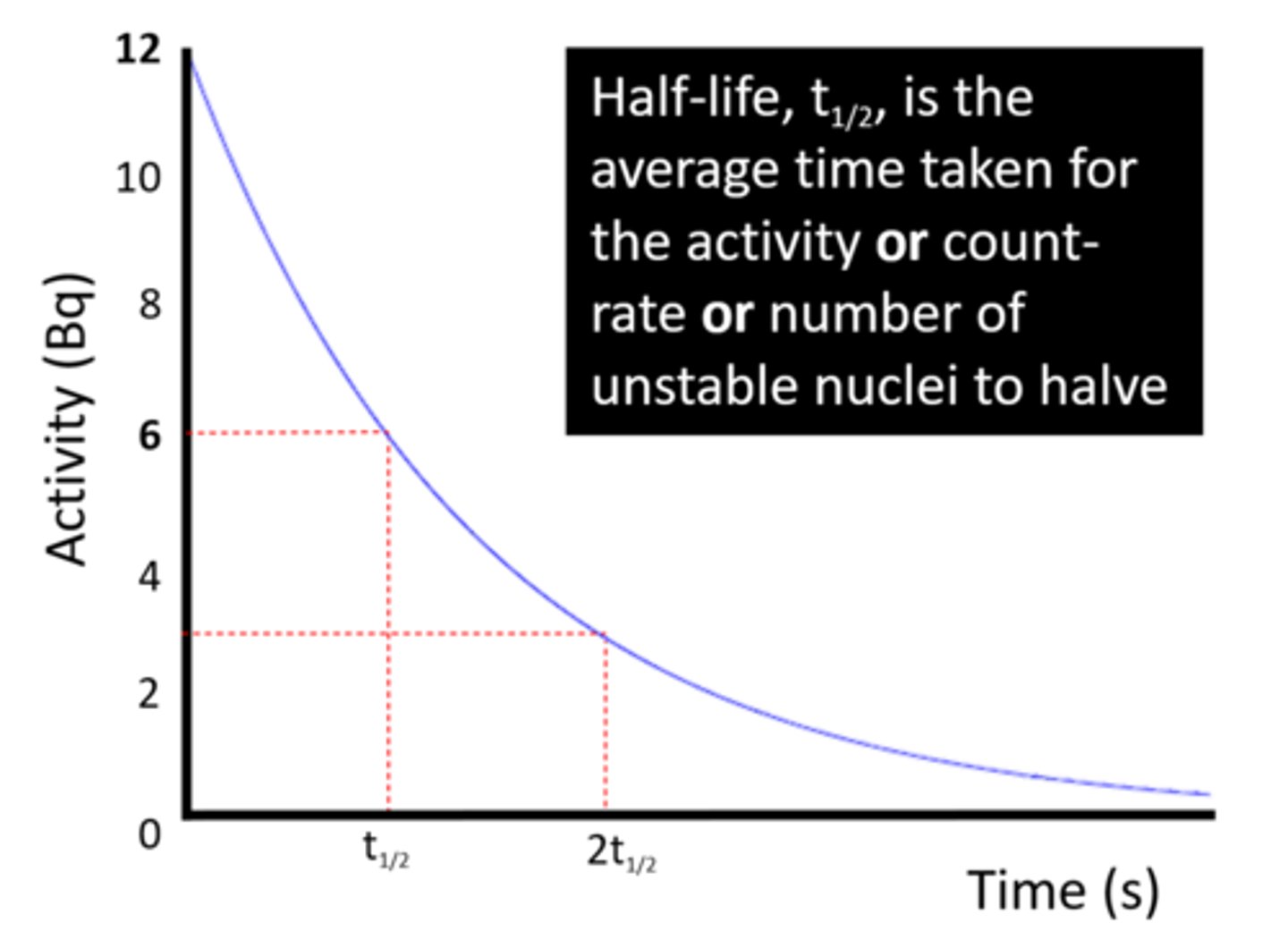
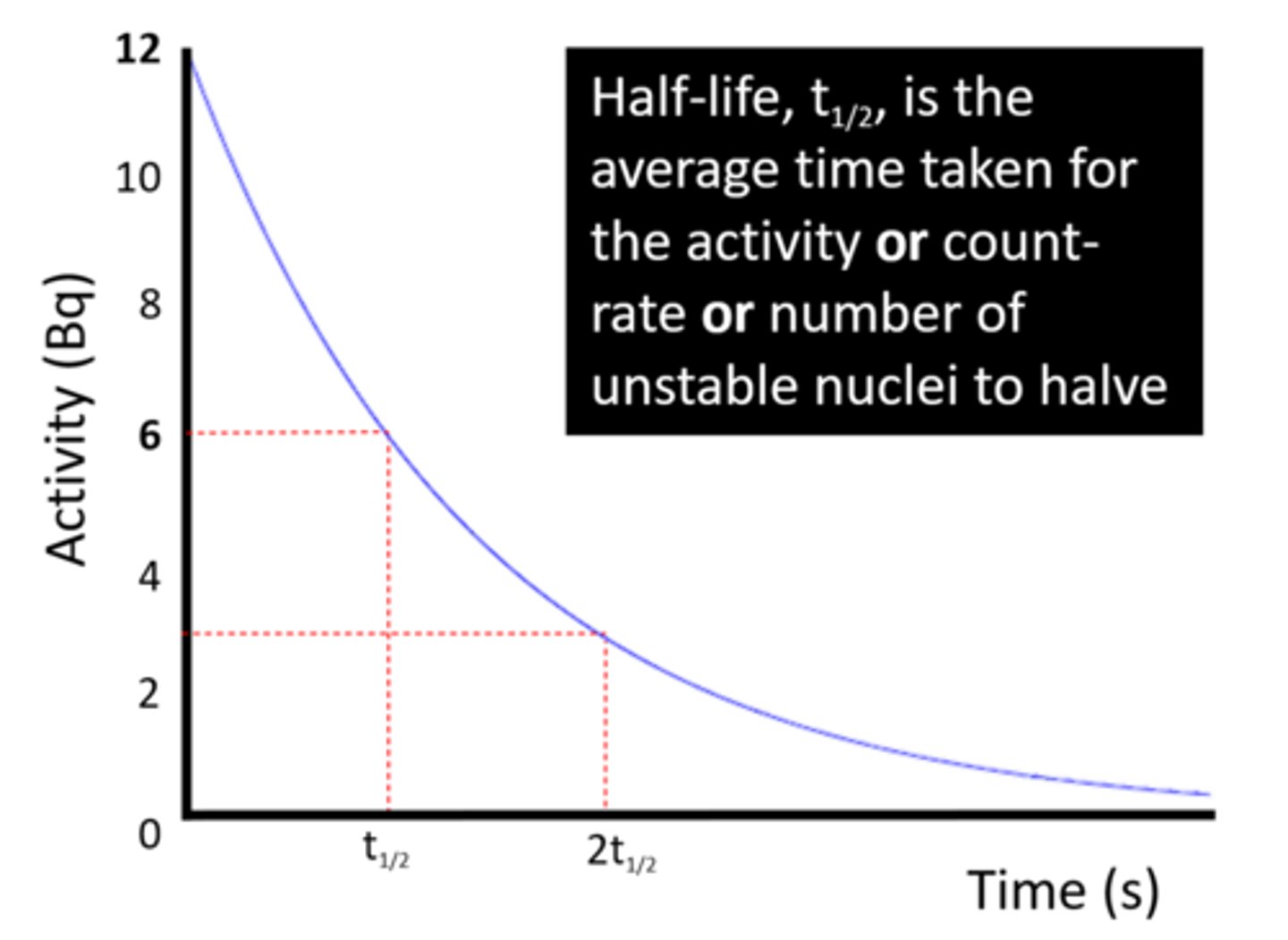
The half-life of a radioactive isotope is the time it takes for the number of unstable nuclei in a sample to _____
Halve

The half-life of a radioactive isotope is the time it takes for the count rate (or activity) from a sample to fall to ____ its initial level
Half
Radioactive _____________ is the unwanted presence of materials containing radioactive atoms on other materials
Contamination
The hazard from contamination is due to the decay of the contaminating _____
Atoms
Contaminating atoms which emit gamma rays are more hazardous at _____ distances
Large
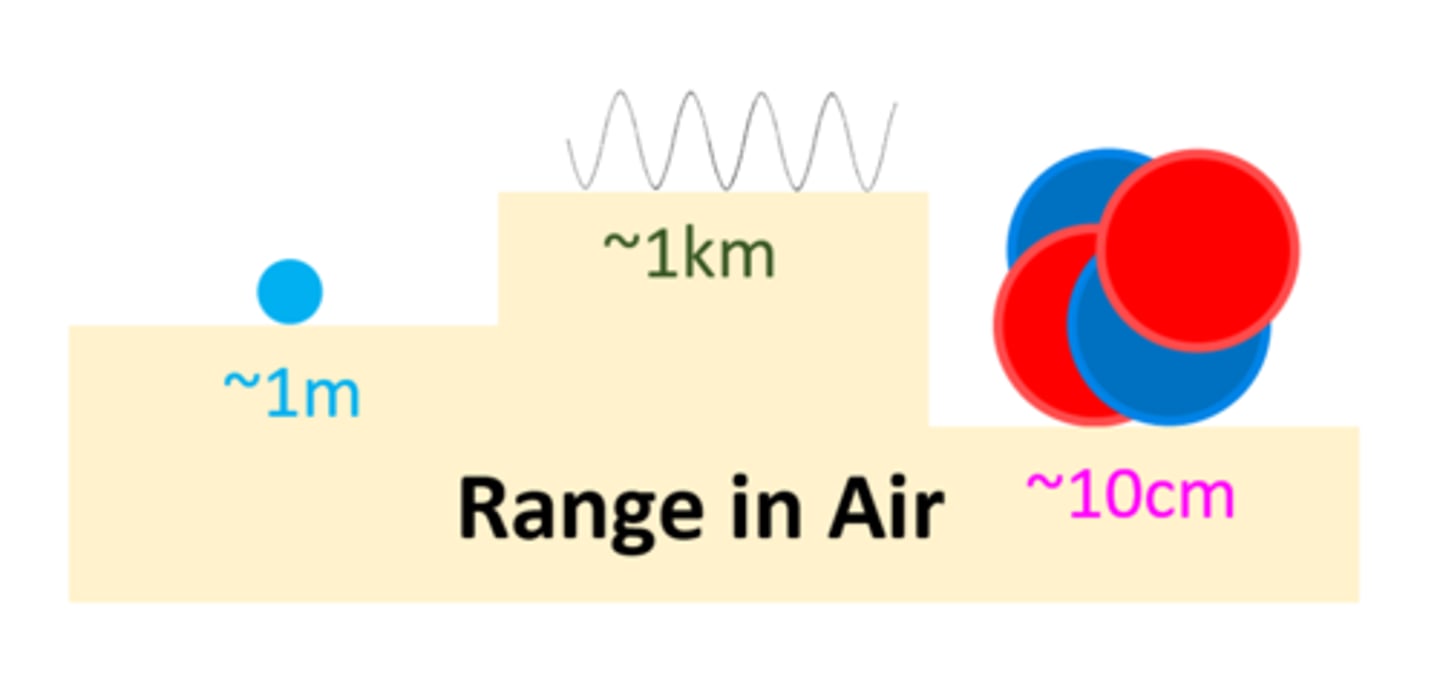
Contaminating atoms which emit alpha particles are very hazardous at _____ distances
Short
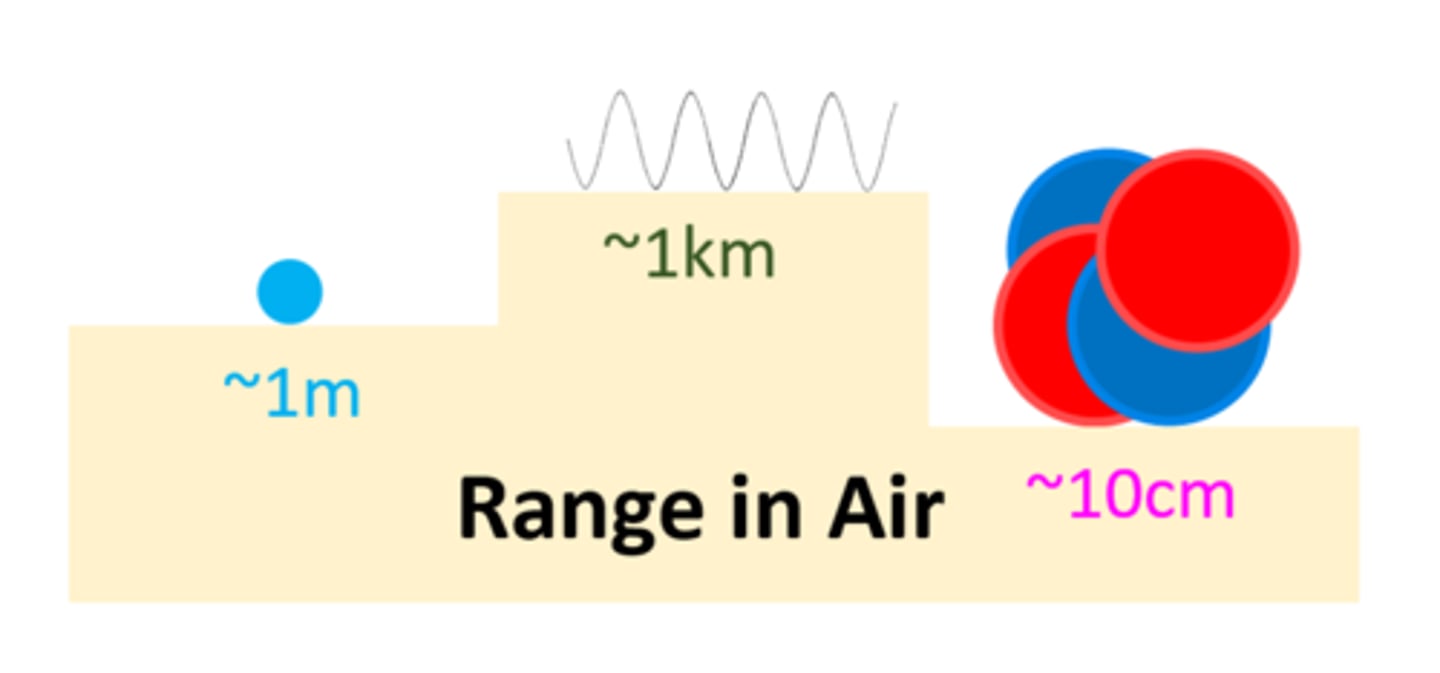
At short distances, contaminating atoms which emit beta particles are ____ hazardous than alpha particles
Less
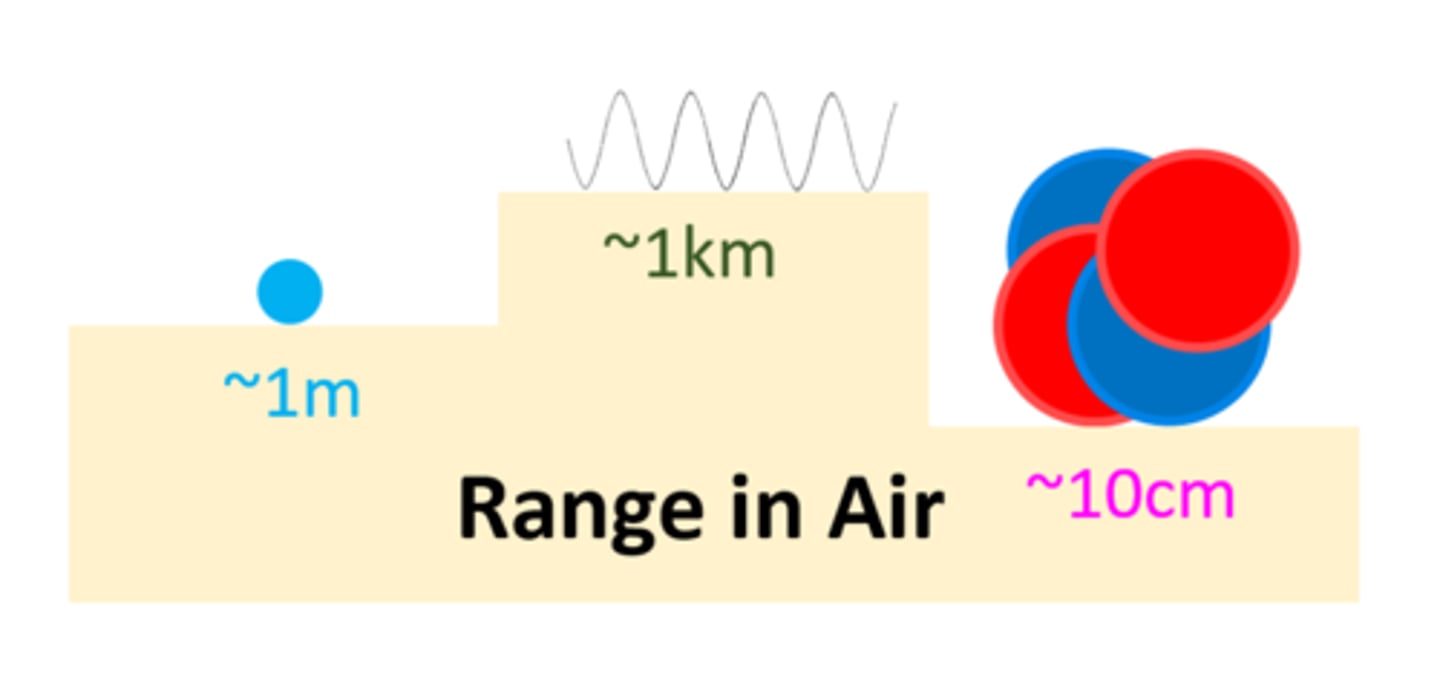
___________ is the process of exposing an object to nuclear radiation
Irradiation
An __________ object does not become radioactive
Irradiated
It is important for the findings of studies into the effects of radiation on humans to be published so that the findings can be checked by ____ ______
Peer Review
The peer review process allows information to be critiqued by- and ______ with other scientists
Shared
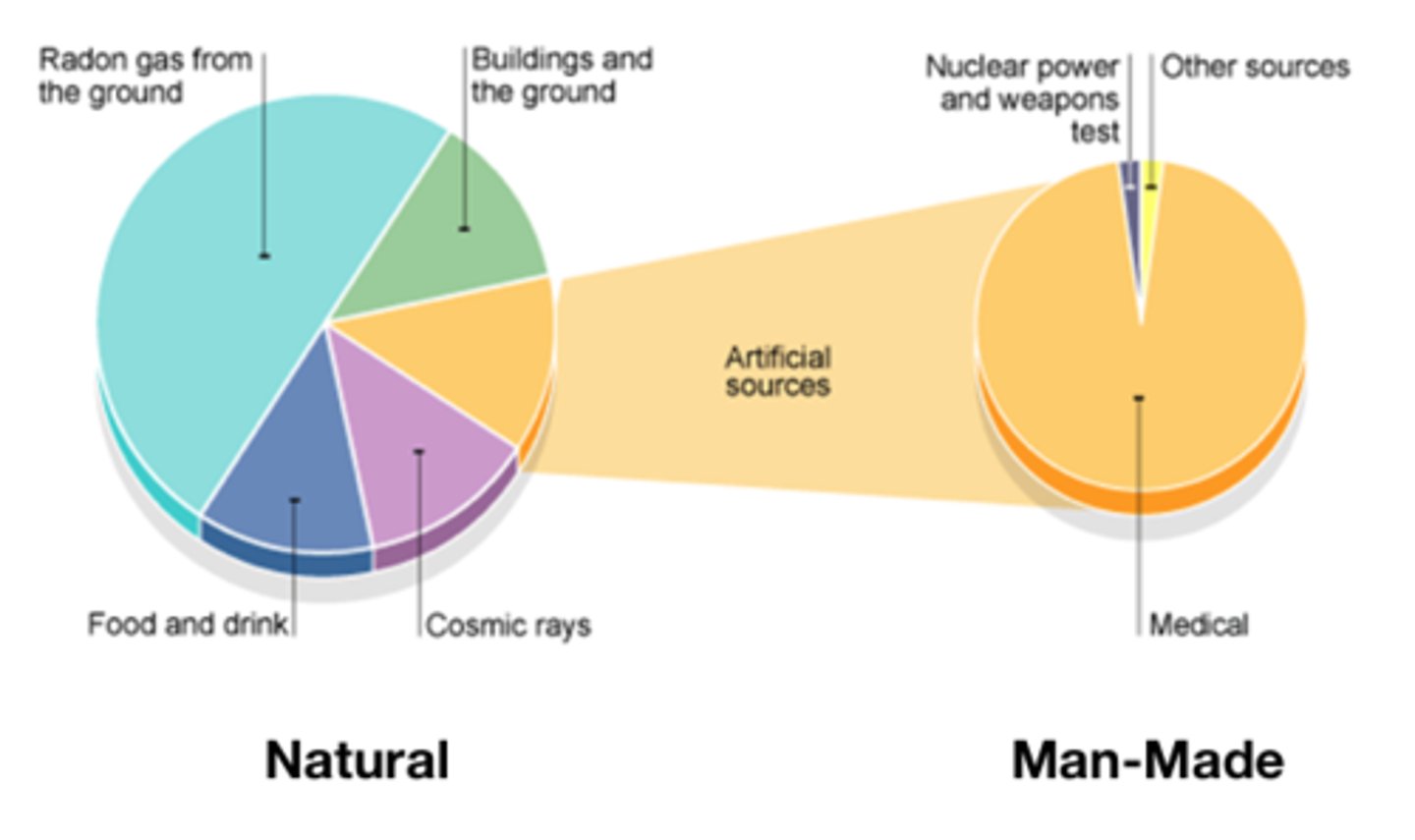
__________ radiation is around us all of the time
Background
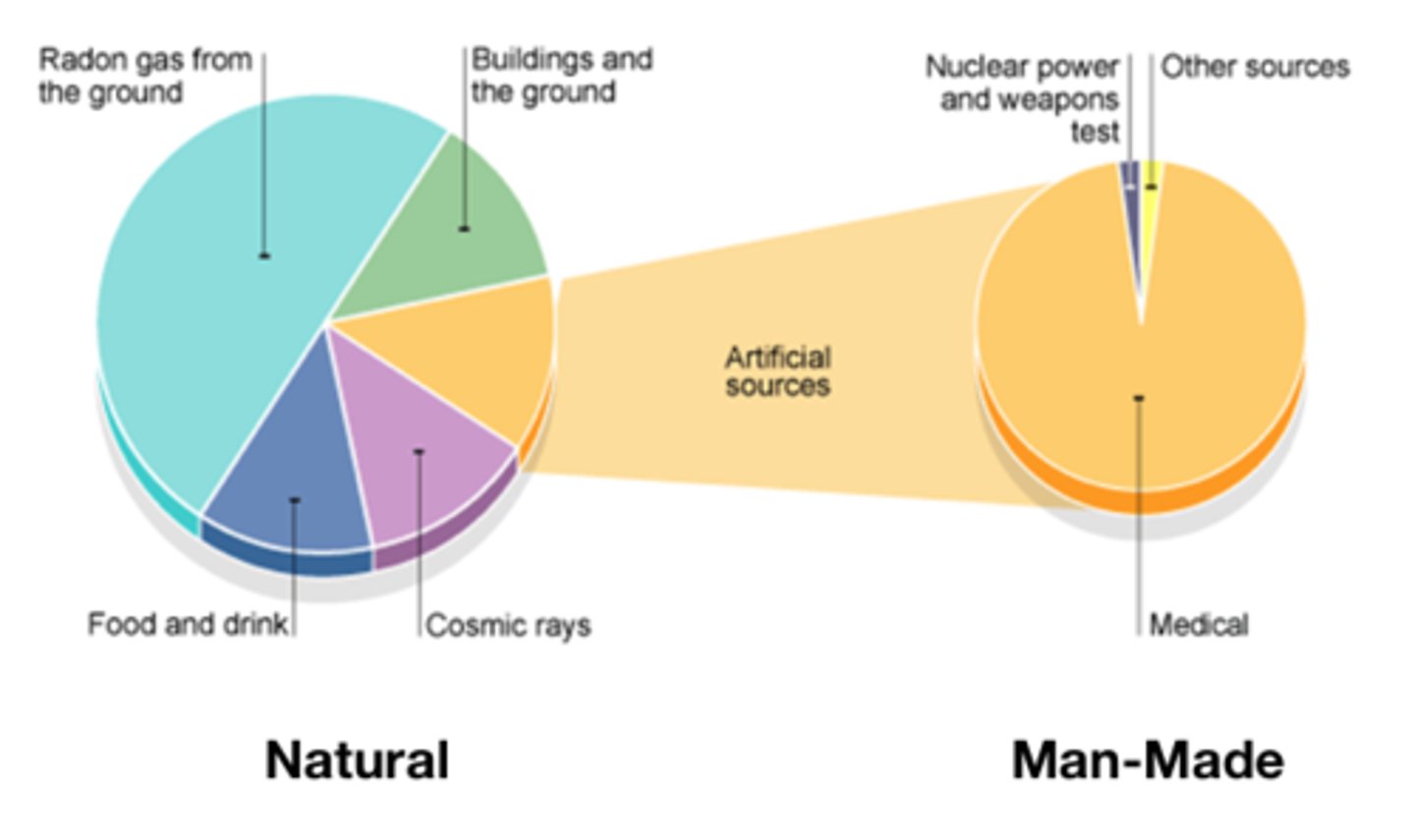
_______ background radiation sources include rocks and cosmic rays from space
Natural
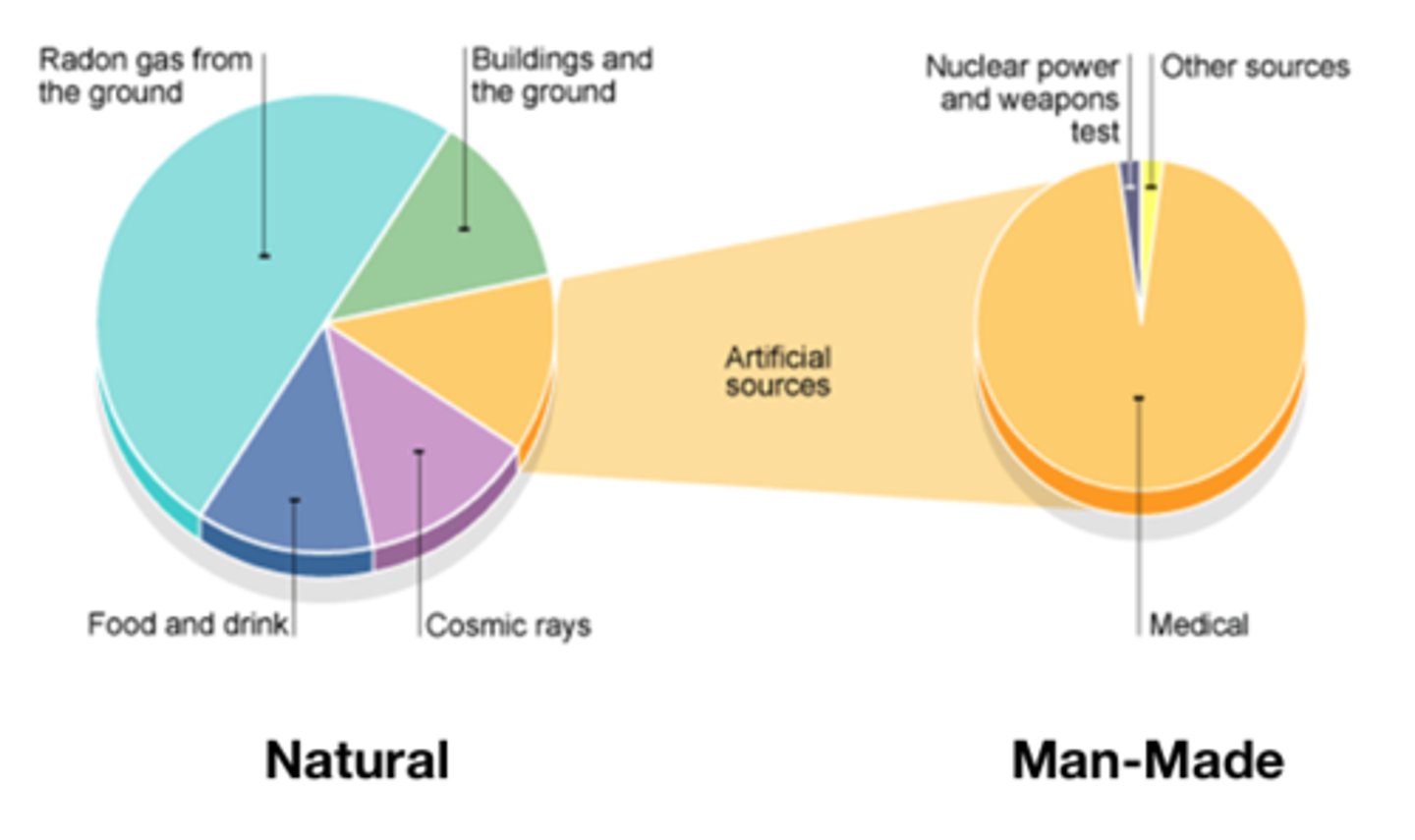
___-____ background radiation sources include the fallout from nuclear weapons testing and nuclear accidents
Man-made
The level of background radiation and radiation ____ you are exposed to may be affected by occupation and/or location
Dose
Radiation dose is measured in...
Sieverts (Sv)
____ millisieverts (mSv) = 1 sievert (Sv)
1,000
The ____-_____ of radioactive isotopes can be very short or very long
Half-lives
Medical radioactive isotopes with a long half-life pose a ____ risk to the patient
High
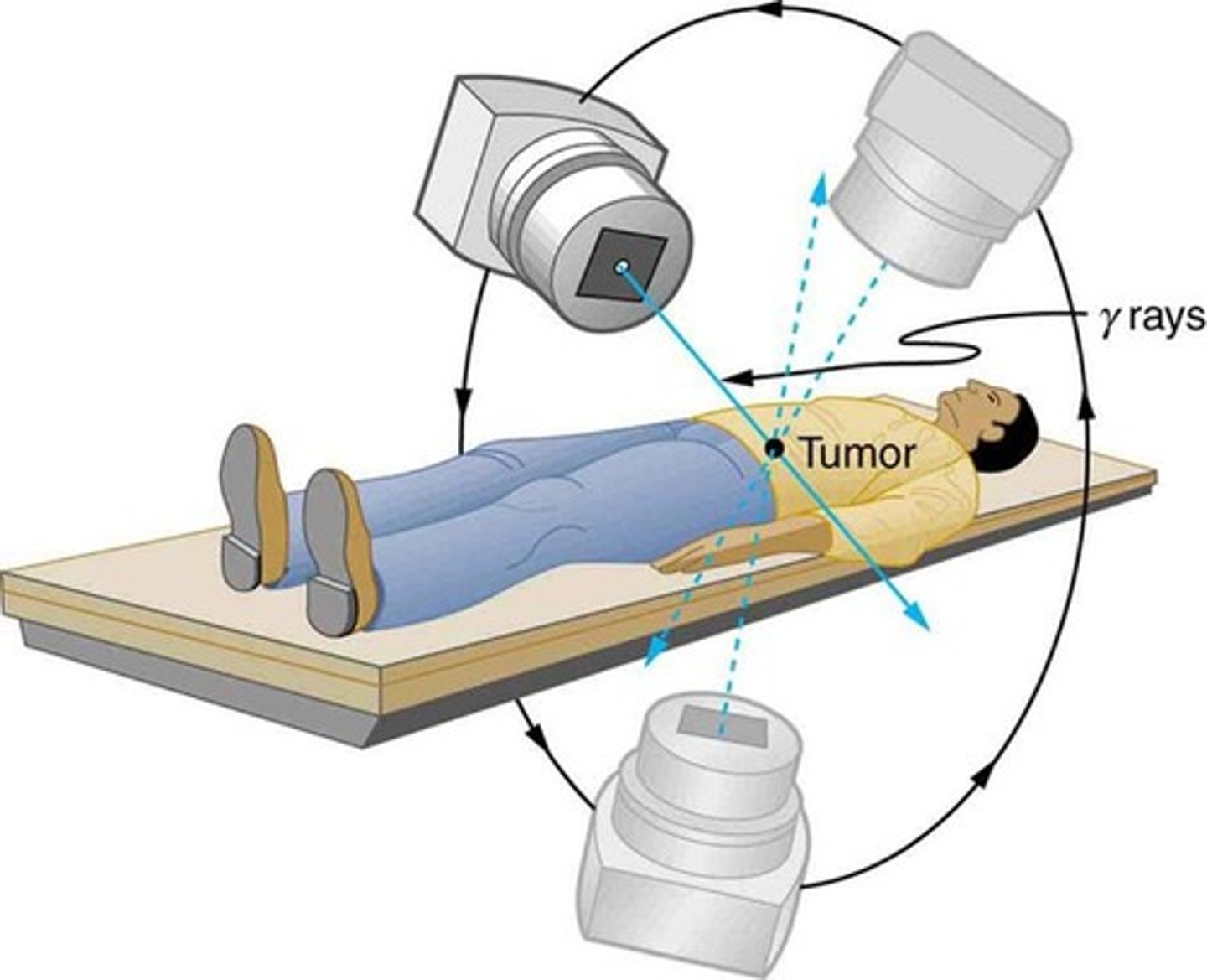
Nuclear radiations are used in ________ for the exploration of internal organs or destruction of unwanted tissue
Medicine
Nuclear _______ is the splitting of a large, unstable nucleus
Fission
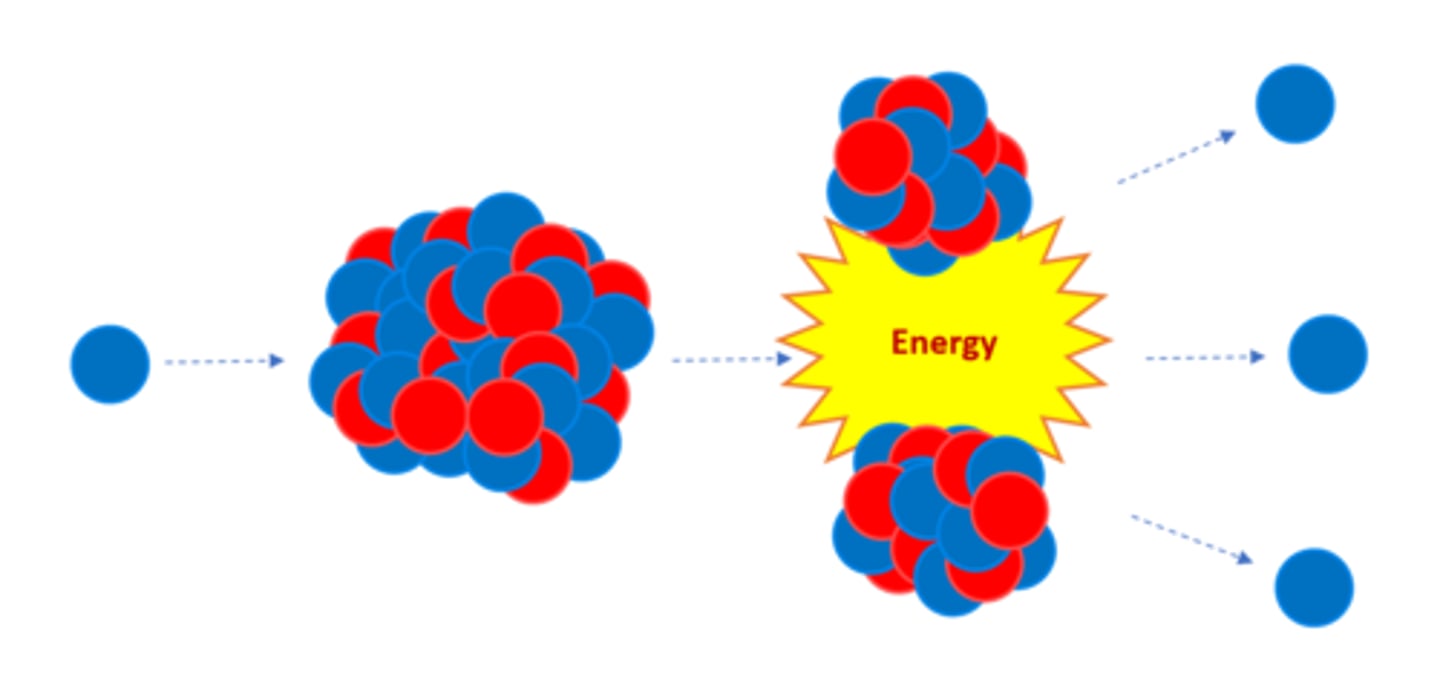
For fission to occur the unstable nucleus must first absorb a _______
Neutron
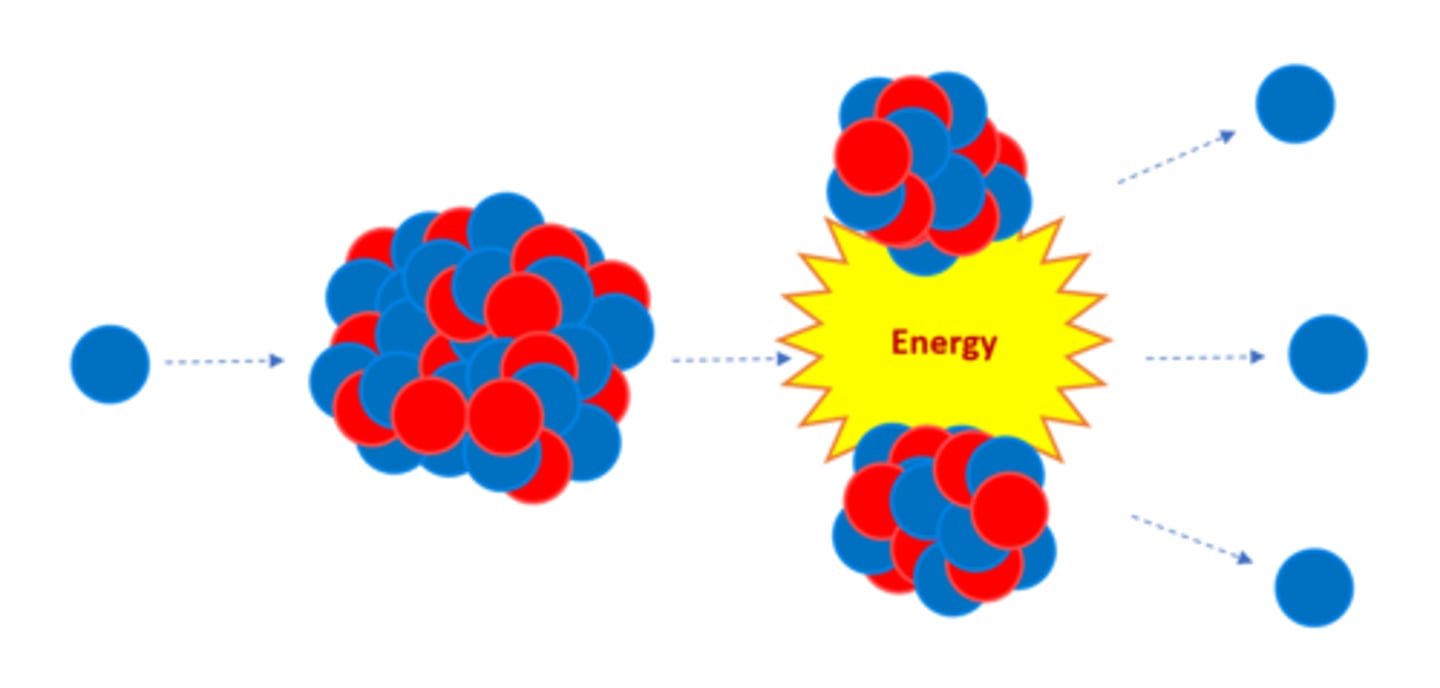
A nucleus undergoing fission splits into two _______ nuclei
Smaller
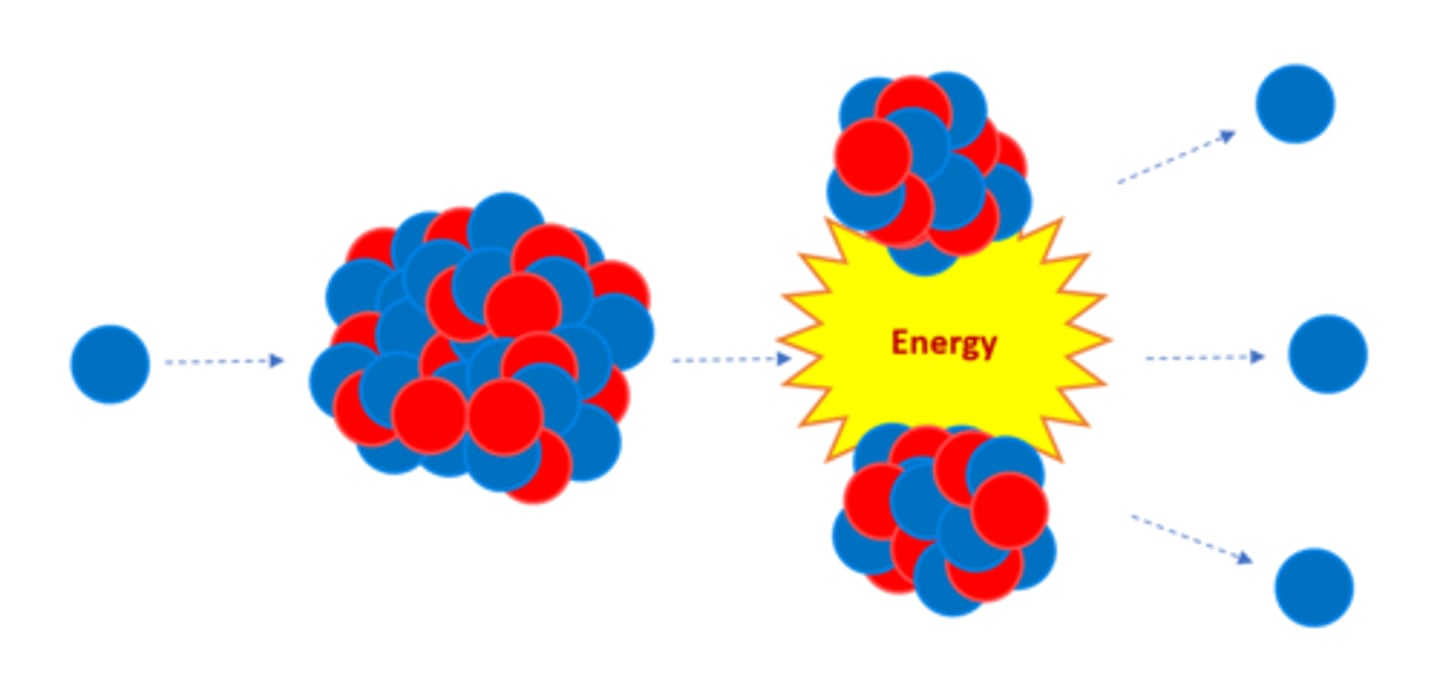
A nucleus undergoing fission splits in two AND emits two or three ________ plus energy
Neutrons
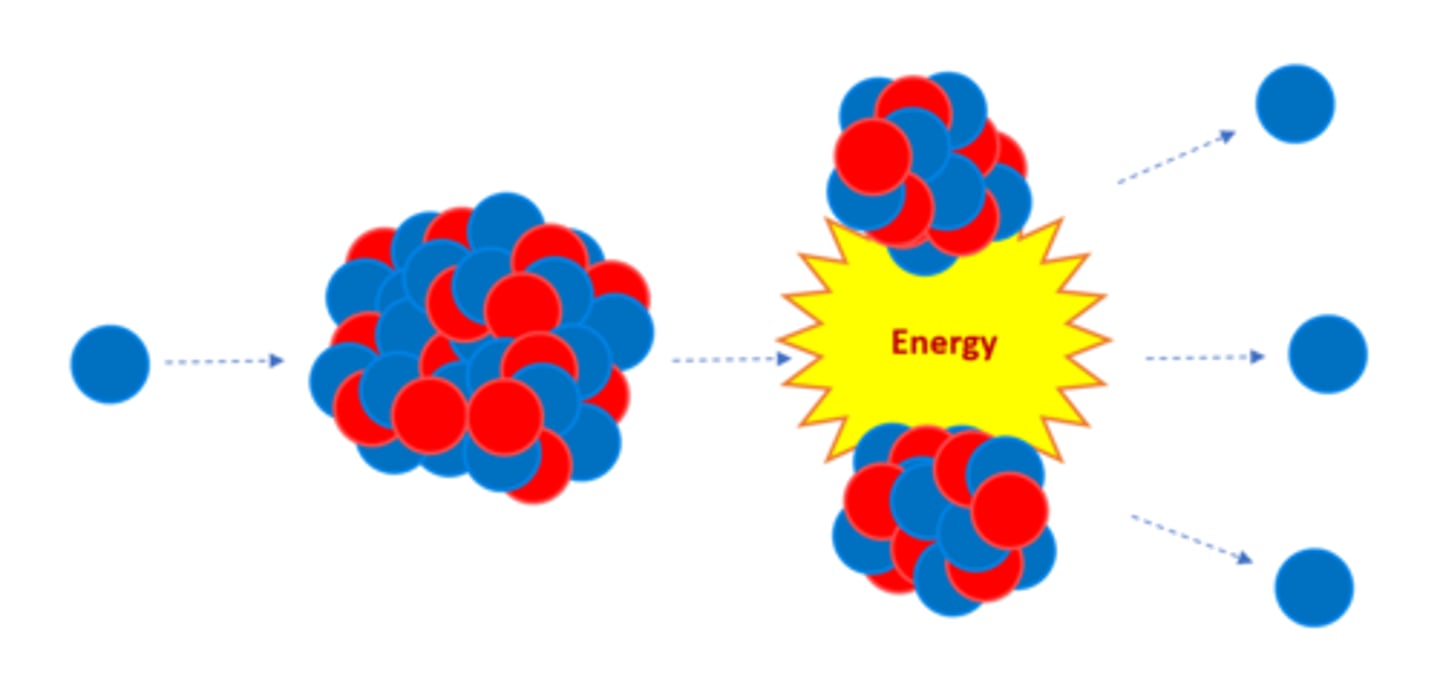
All of the fission products have _______ energy
Kinetic
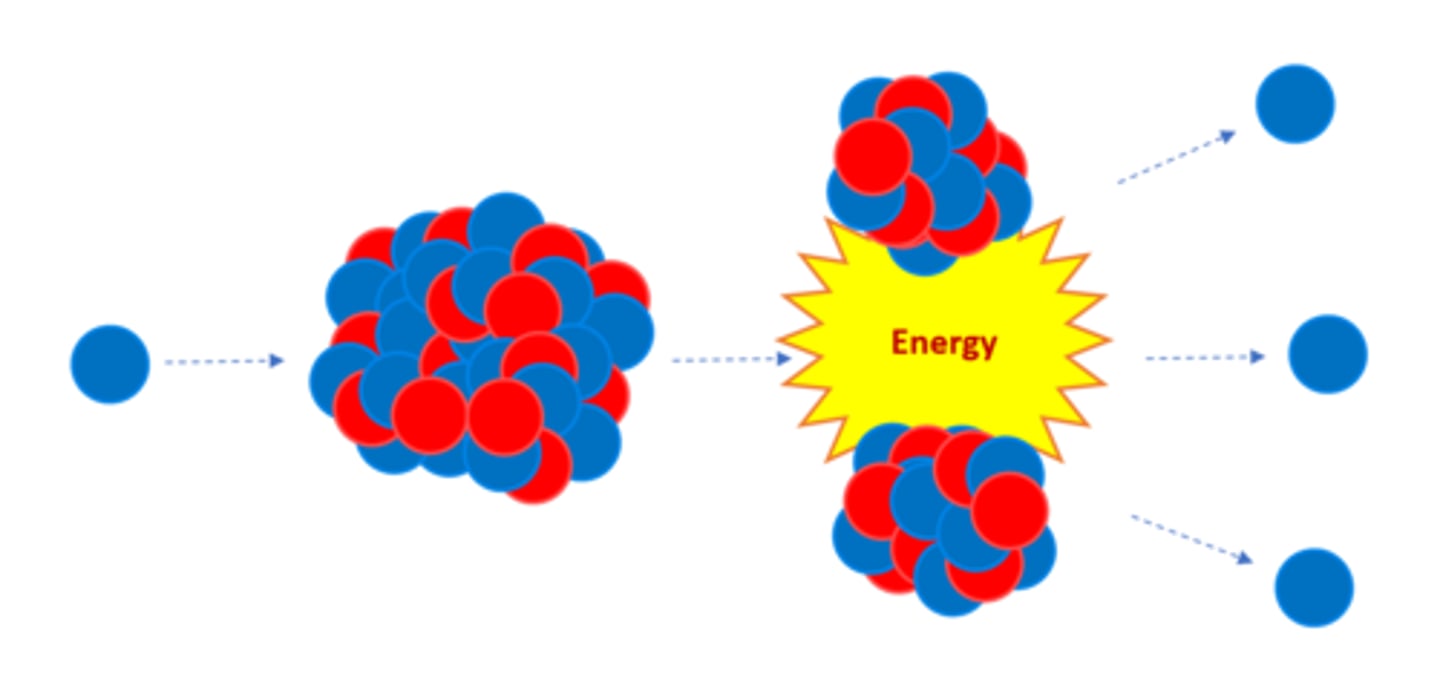
The neutrons emitted by a splitting nucleus in nuclear fission may go on to start a _____ ________
Chain Reaction
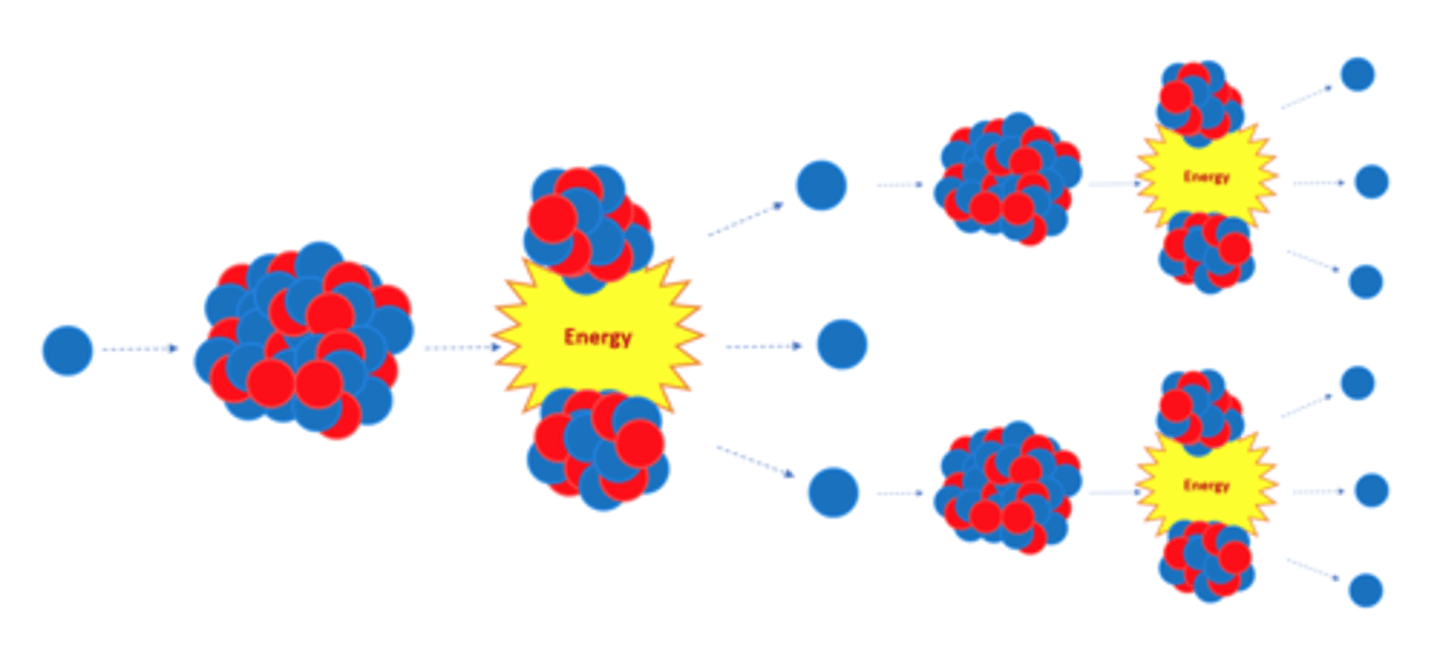
The chain reaction in nuclear fission is controlled in a nuclear reactor to control the ______ released
Energy
The explosion caused by a nuclear weapon is caused by an uncontrolled _____ ________
Chain Reaction
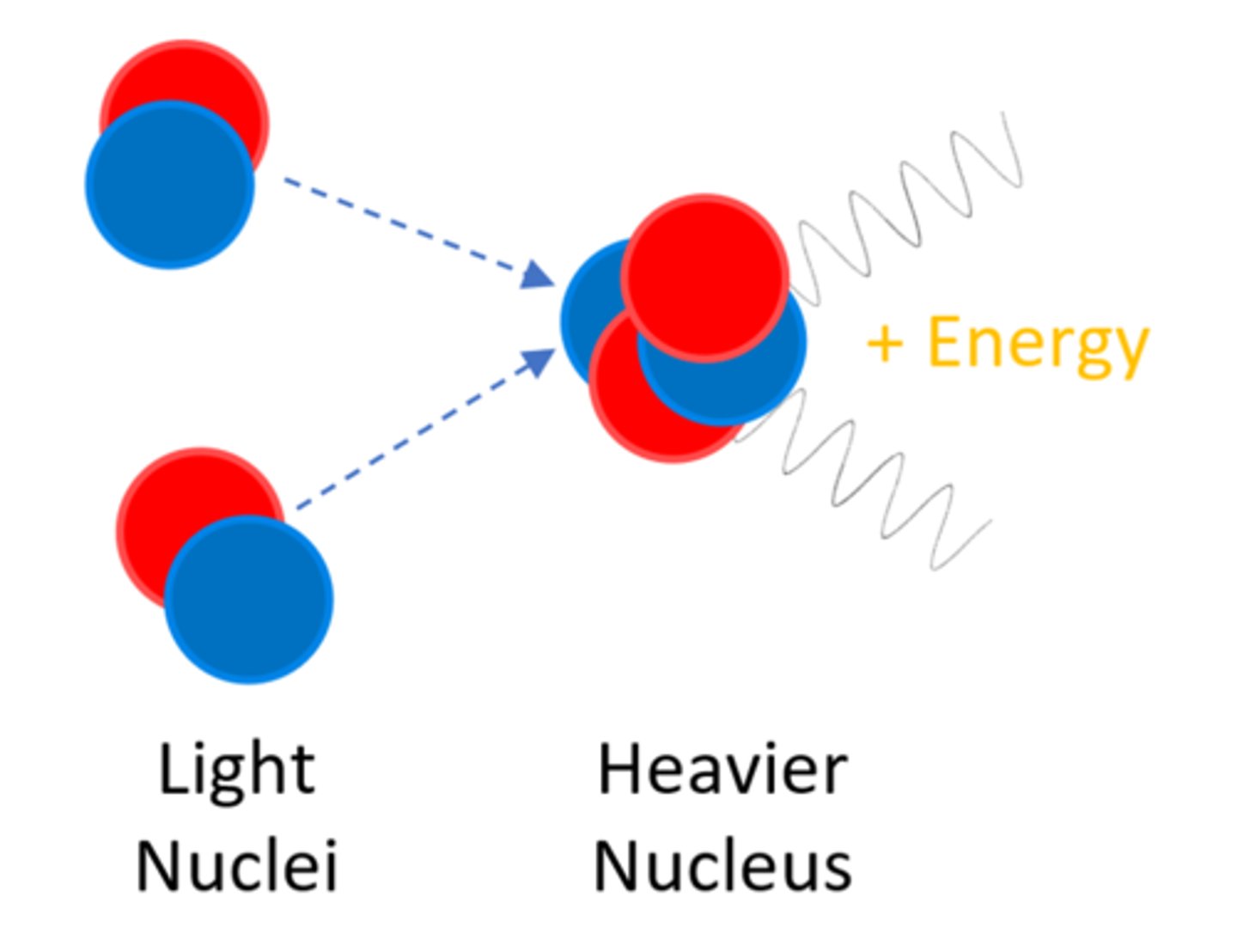
Nuclear ______ is the joining of two light nuclei to form a heavier nucleus
Fusion
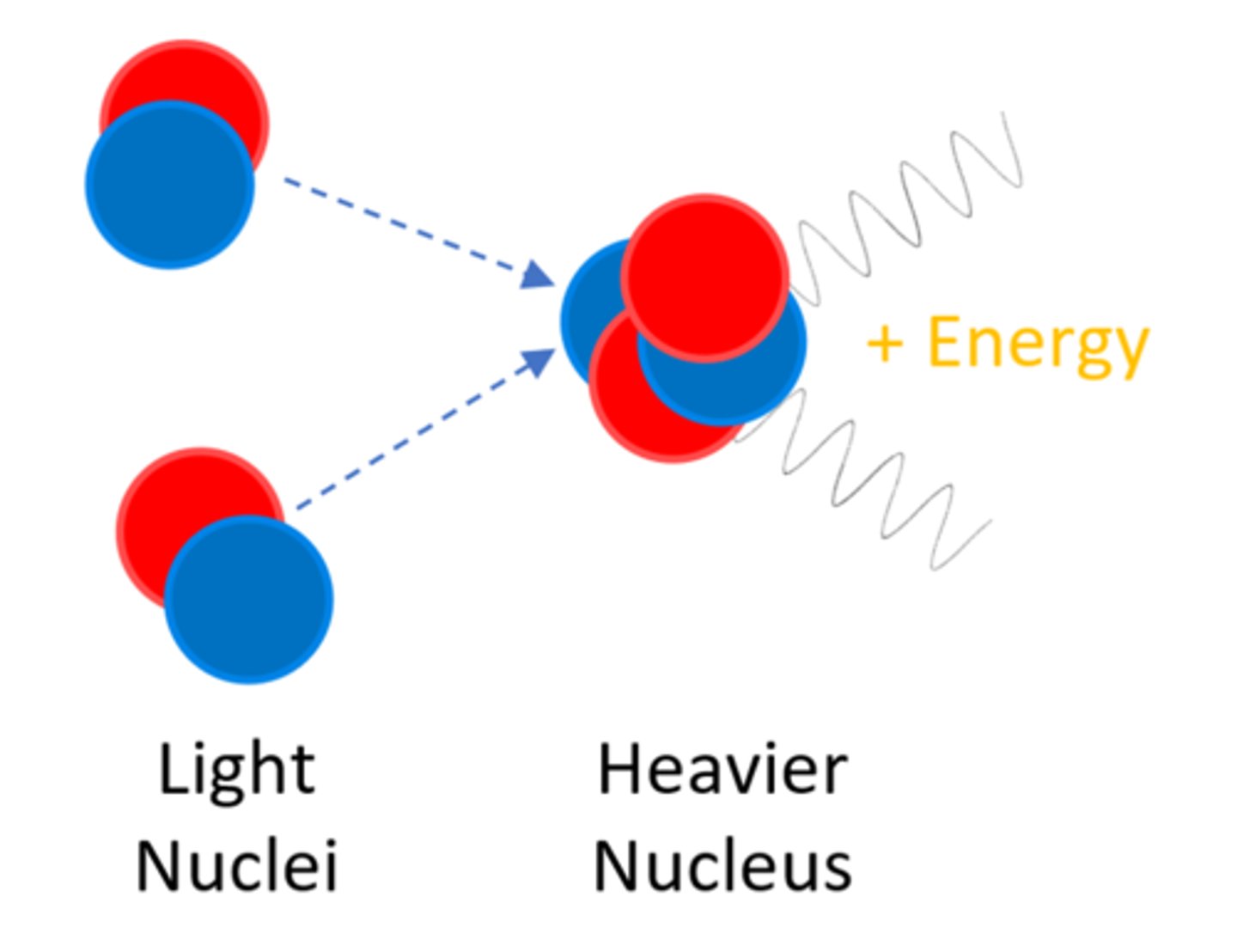
In nuclear fusion some of the mass may be converted into ______
Energy