biological rhythms - 20.01.24
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Biological rhythms
Predictable patterns in physiological processes.
Adaptive significance
Advantage of anticipating environmental rhythmic events.
Exogenous rhythms
Rhythms generated by external environmental processes.
Endogenous rhythms
Rhythms generated by internal physiological processes.
Circadian rhythm
Daily biological cycle lasting approximately 24 hours.
Circalunar rhythm
Biological cycle aligned with lunar phases.
Circannual rhythm
Seasonal biological cycle over a year.
Locomotor activity
Common circadian rhythm related to movement.
Free-running rhythm
Oscillation unaffected by external time cues.
Entrainment
Adjustment of biological rhythms to environmental cues.
Melanopsin cells
Retinal cells involved in circadian light detection.
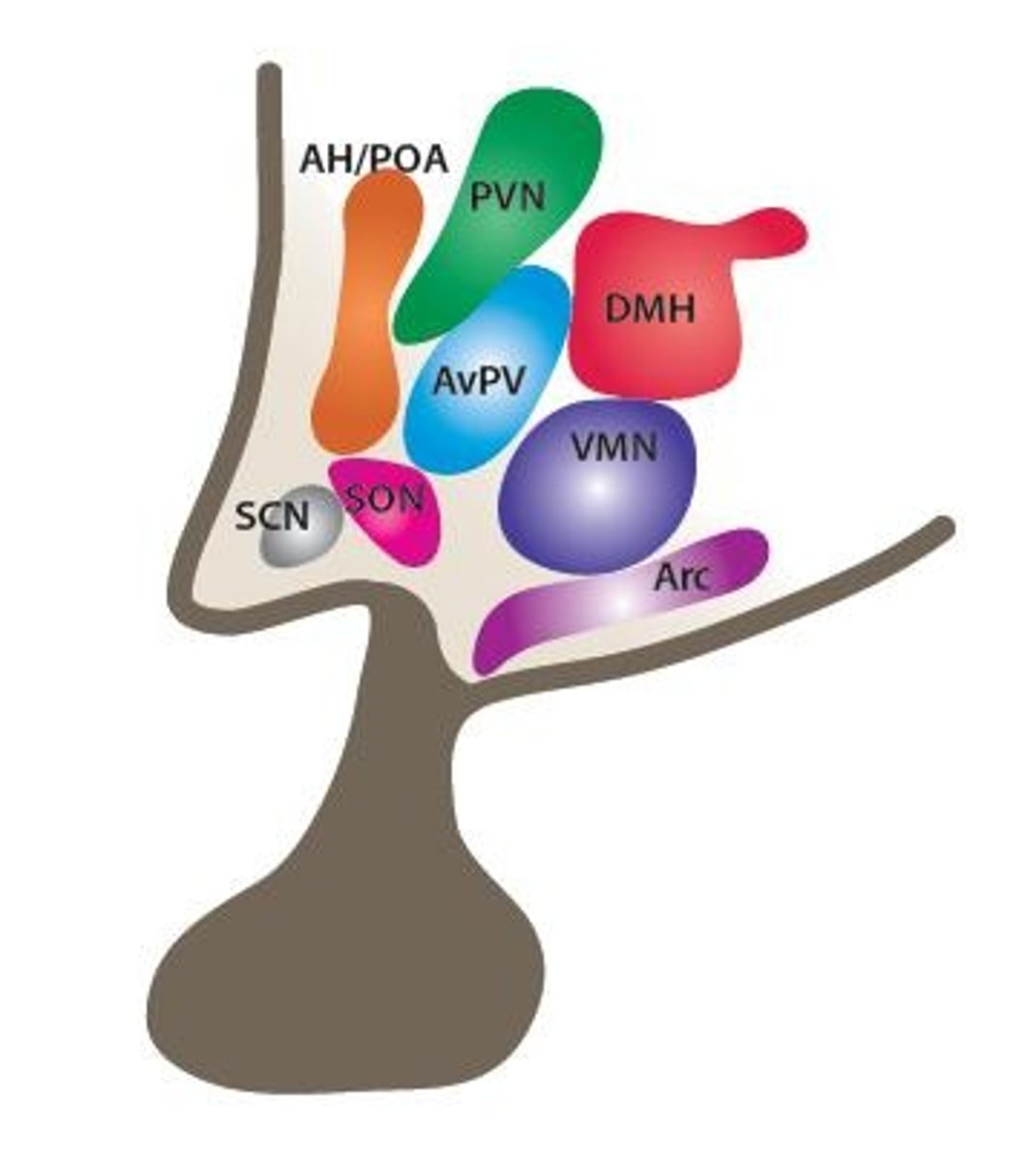
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN)
Master pacemaker regulating circadian rhythms.
Circadian-dependent change
Daily variations in hormone levels post-food intake.
Food Entrainable Oscillator (FEO)
Oscillator regulating feeding rhythms independent of SCN.
Clock genes
Genes controlling circadian rhythms in tissues.
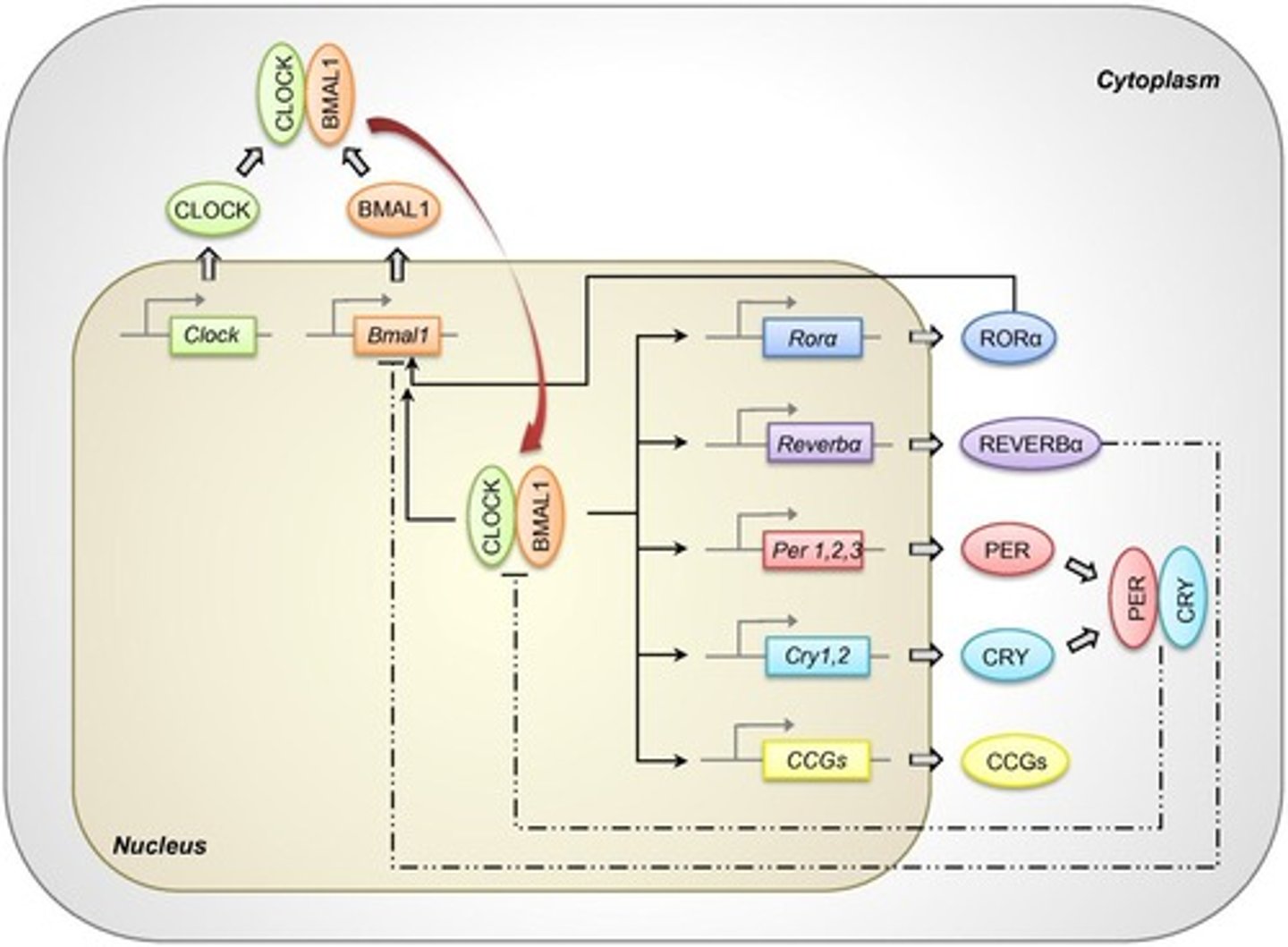
Per1 signaling
Regulation of circadian rhythms in liver metabolism.
Clock KO mice
Mice lacking clock genes exhibit metabolic deficits.

Aberrant light exposure
Disruption of circadian rhythms due to unnatural light.
Constant light (LL)
Continuous light exposure affecting body mass.
Food timing impact
Timing of food intake influences body weight.
Night shift work
Work schedule disrupting normal circadian rhythms.
Metabolic dysfunction
Impaired metabolic processes linked to circadian disruption.
Diurnal mRNA rhythms
Daily fluctuations in mRNA levels across conditions.
Obesity association
Link between clock gene polymorphisms and obesity.
Dampened rhythms
Reduced rhythmicity in physiological processes during diseases.
ACTH
Adrenocorticotropic hormone, deals with stress responses including increased cortisol and fight or flight response
hormones
A chemical messenger that is released into the bloodstream or tissue fluid system that affects the function of target cells some distance from the source.
neurohormone
a hormone produced by neurons
neuropeptide
a peptide hormone produced by a neuron
neurosteroid
a steroid hormone produced by a neuron
neurotransmitter
a chemical messenger that acts across the neural synapse
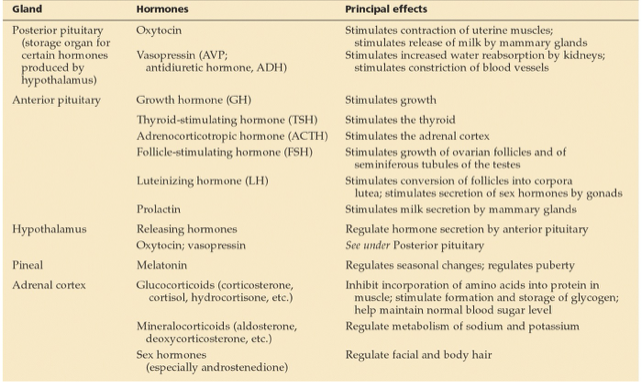
summary of hormones
aromatase
aromatase levels and distribution governs most sex differences
examples of animal daily rhythms
Sleep
Mental performance
Autonomic nervous system
Hormone secretion
Blood pressure
Occurrence of disease symptoms & mortality (e.g. morning heart attacks)