Final Exam Flashcards Physics 2
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
mass defect
-The mass of a nucleus is always less than the sum of the masses of the individual protons and neutrons that make up the nucleus, where energy corresponding to the mass defect is equal to the nuclear binding energy
In atomic nucleus, the nuclear force binds
neutrons and protons together
delta 𝑚=
(sum of mass of protons+ sum of mass of neutrons)−mass of nucleus
Fission process
the total number of nuclei does not remain constant but the number of protons and neutrons does remain constant
in spontaneous fission reaction, the total mass of the products is ____ the mass of the original elements
less than
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
The uncertainty principle states that we cannot know both the position and speed of a particle,
A quark
building blocks of matter, combine to form particles like protons and neutrons, making up the nucleus of an atom
Hadrons
particles that interact through the strong force; baryons (made up of 3 quarks), mesons (1 quark and 1 antiquark)
leptons
fffundamental particle that does not feel strng nuclear force
Baryon number
Each baryon has B=+1, each antibaryon has B=−1, and non-baryons
have B=0
Conservation of Baryon Number
Experiments show that the total baryon number remains the same
before and after any process involving baryons.
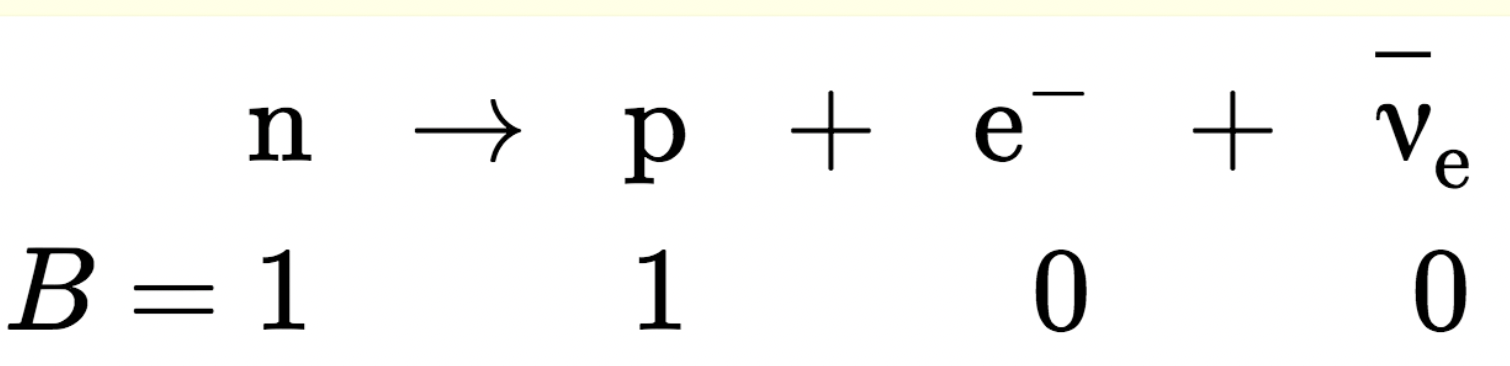
Lepton Number
Each lepton is assigned a lepton number L=+1, anti-leptons L=−1,
and non-leptonic particles L=0
Conservation of Lepton number:
In any particle reaction or decay, the total lepton number before the
reaction equals the total lepton number after the reaction.
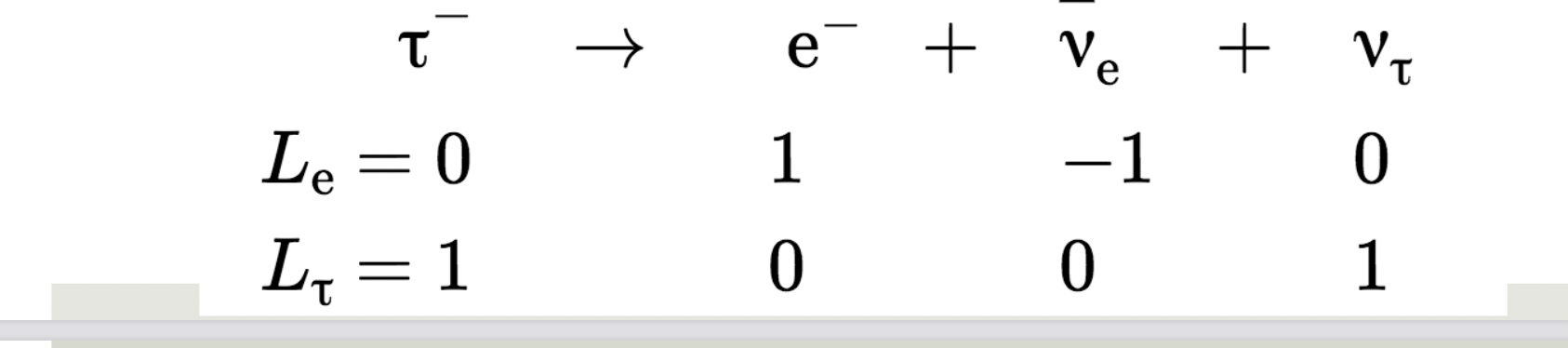
In Feynman diagrams, the electromagnetic force is
shown by the exchange of a photon, the particle that carries the electromagnetic interaction
In Feynman diagrams, the strong force is shown throughnteraction.
the exchange of gluons, the force-carrying particles of the strong interaction
The weak force is carried by the heavy W⁺, W⁻, and Z⁰ bosons.
In Feynman diagrams, weak interactions are shown t one of these bosons.
whenever
particles exchange or emit one of these bosons
Dark energy:
An unknown form of energy that
causes the universe’s expansion
to accelerate.
Dark matter:
It is a form of matter we cannot see
directly, and its properties are
different from all known particles in
the Standard Model.
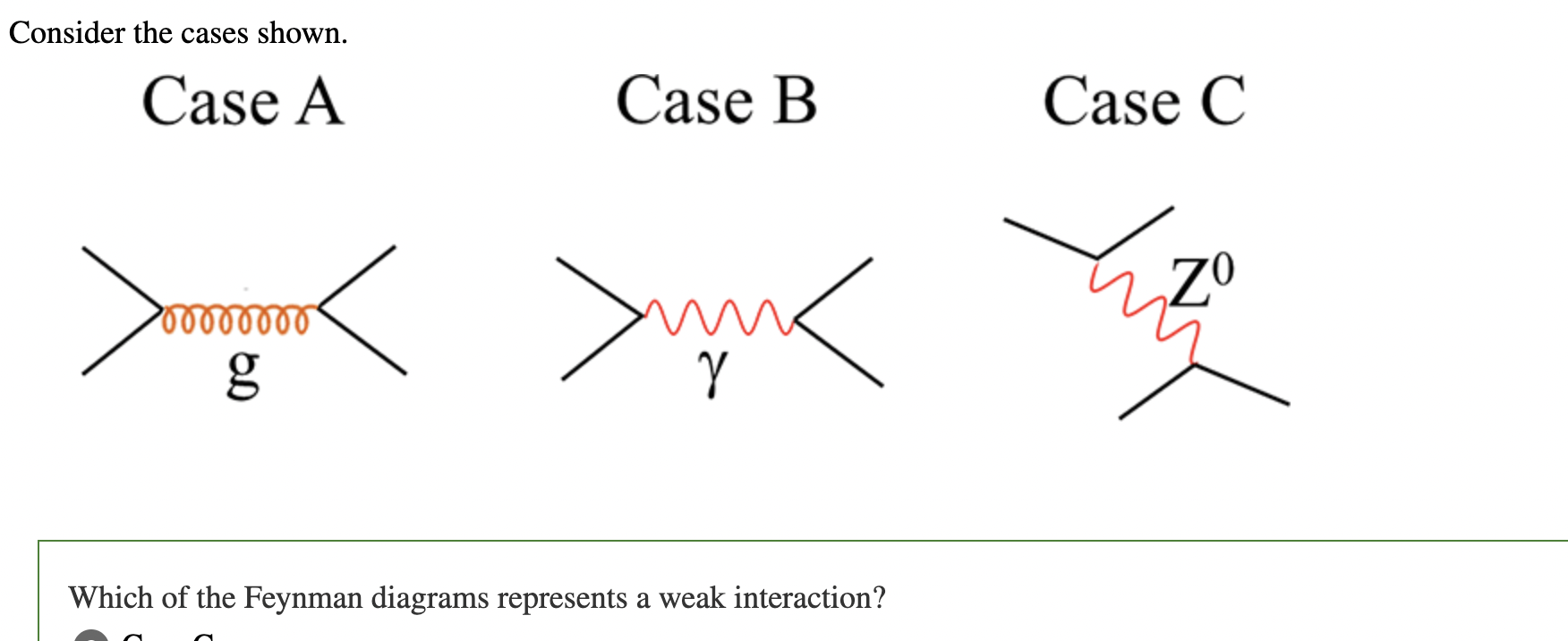

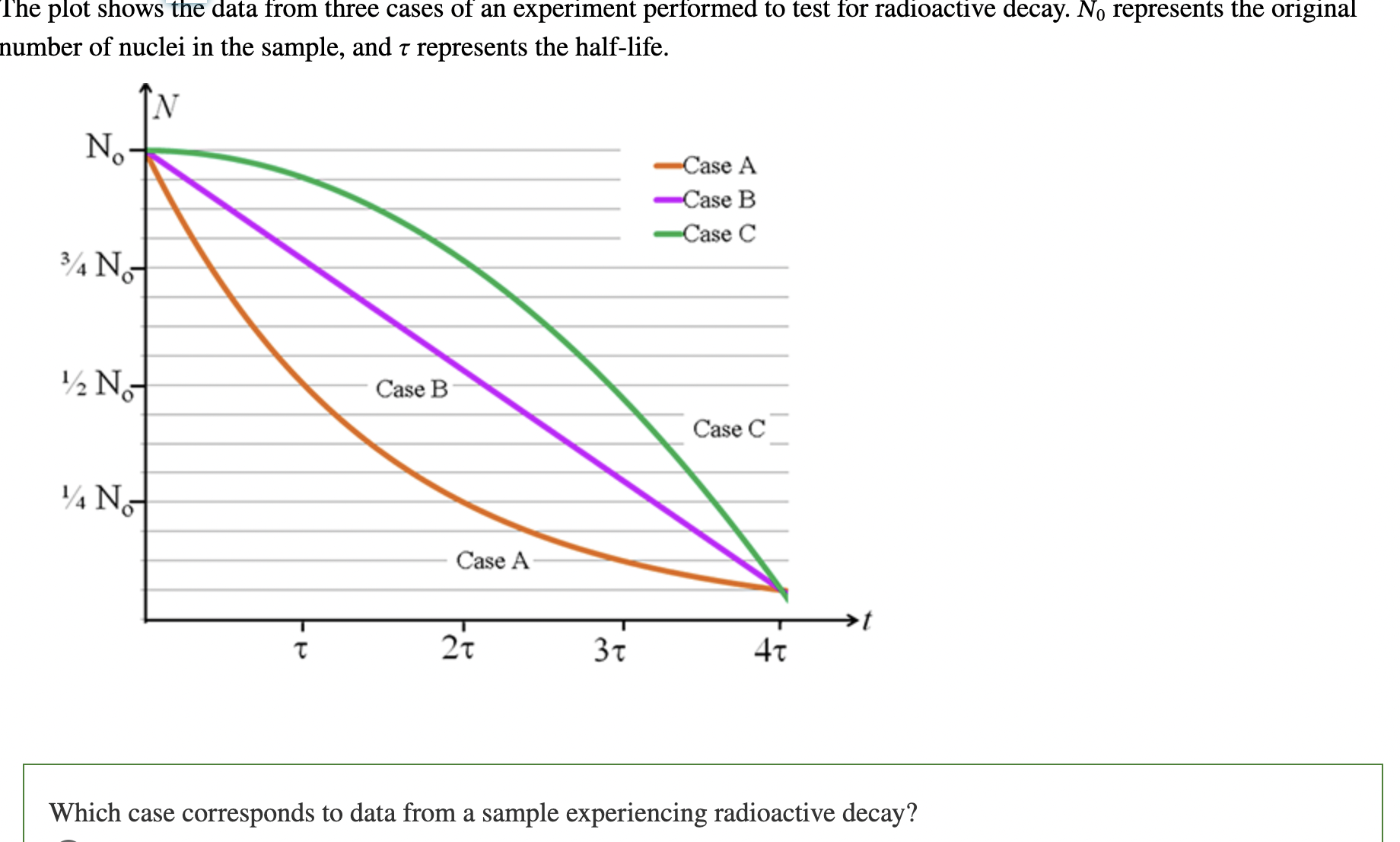
Case C

fission process:

total binding energy of fragments is less than the binding energy of the original nucleus
Fusion Process:
the kinetic energy of the fusing nuclei is large enough to overcome their mutual electrostatic repulsion
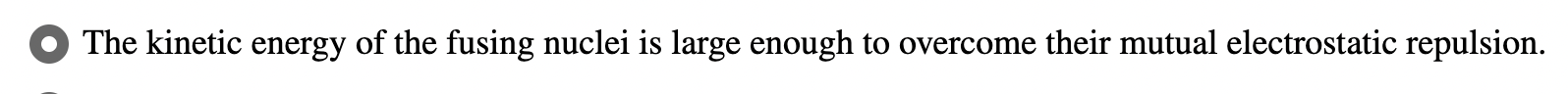
Case A
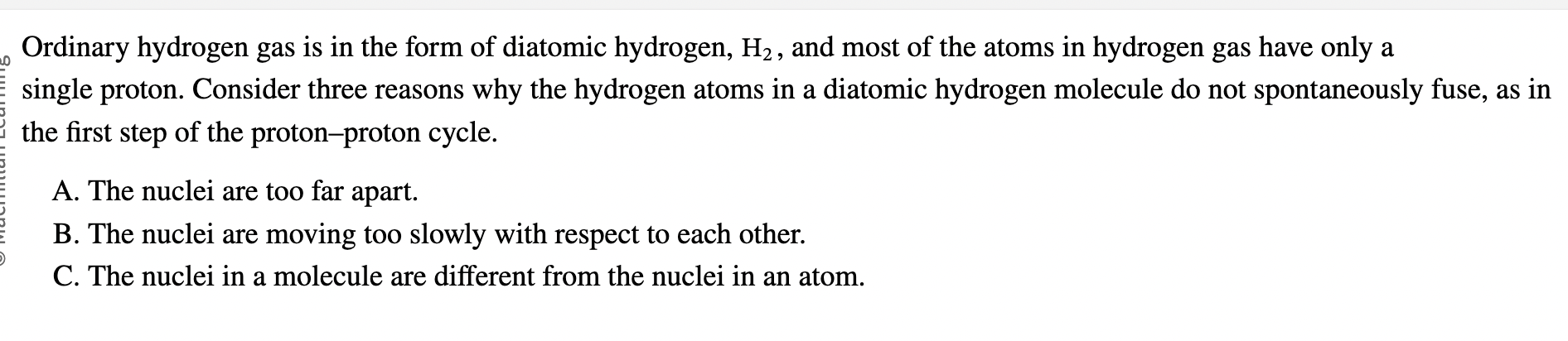
Why do Hydrogen proton-proton not spontaneously fuse?
Nuclei are too far apart and are moving too slowly
Coloumb force between two protons
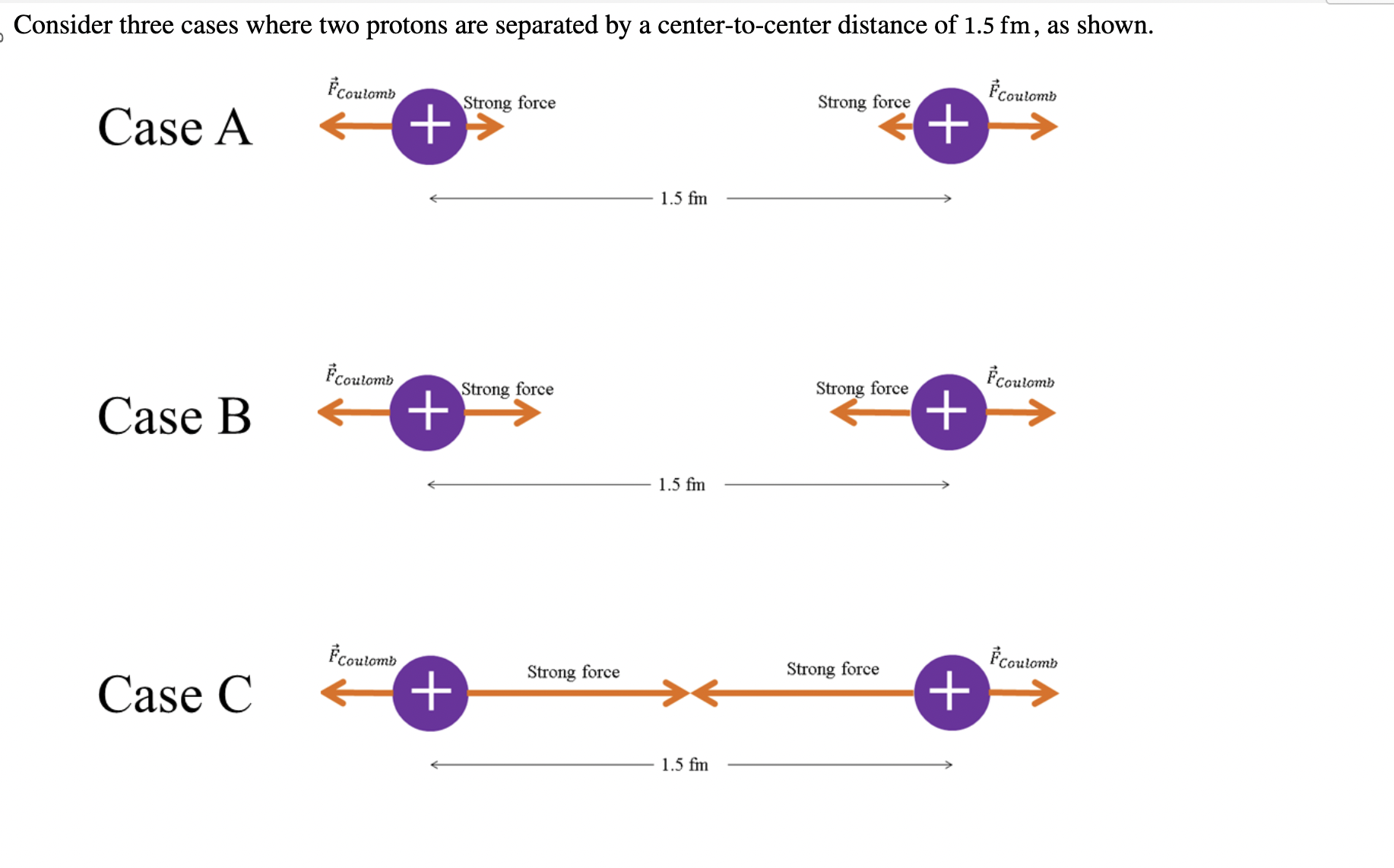
Case C

Nuclear Stability
determined by the binding energy per nucleon of the nucleus, which is the energy needed to separate a nucleon from the nucleus.
A nucleus with a greater binding energy per nucleon is more stable than a nucleus that has less binding energy per nucleon.
Atomic Number Z =
the number of protons in the nucleus
Electron Family
Tau Family
Le:
- e-, ve=> +1
ve=> -1
anything else => 0
Lt:
T-, vt=> +1
Anti-tau neutrino => -1
anything else => 0
Neutron Number N =
= the number of neutrons in the nucleus
Mass Number A
= the number of neutron and proton in the nucleus
The isotopes of an element have the same _ but different _
Z value (# protons), different A and N values (sum of protons + neutrons, # of neutrons)
When electrostatic force and strong force are equal..
a stable nucleus
is created!


Nuclear Stability: Neutrons add without _
attractive force, without repulsion
Binding energy
the energy required to hold the
nucleus together, coming from the strong nuclear force
Binding Energy Formulas
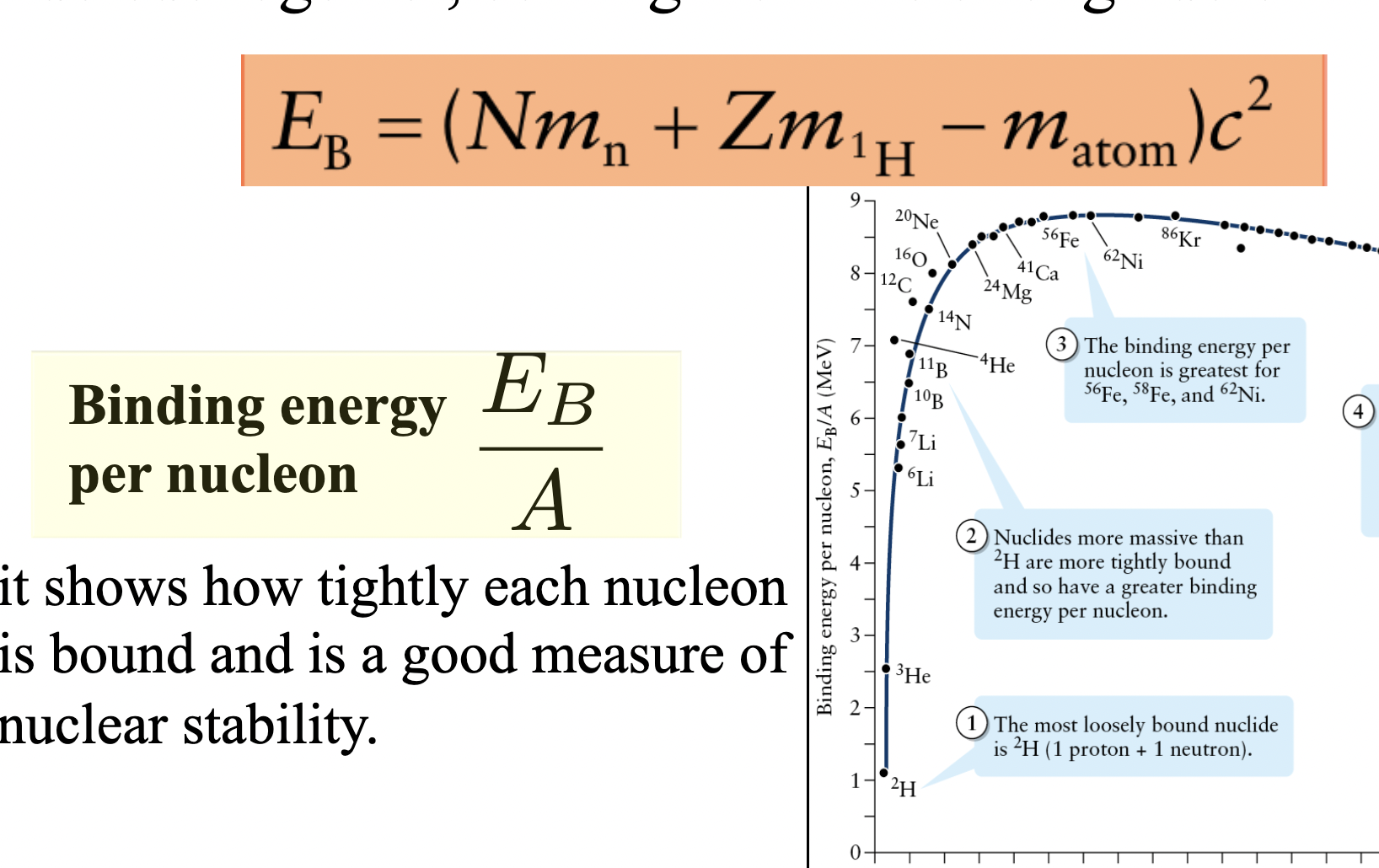

Nuclear Fusion
occurs when light nuclei combine into a heavier one, releasing energy because some mass is lost in the process.
Nucelar Fission
For nuclei with A>60, the binding energy per nucleon decreases, so splitting a large nucleus into smaller ones (fission) creates
more stable nuclei.
Energy is released in fission because the fragments have far more kinetic energygy than the original neutron and nucleus.
Fission releases energy from ___ nuclei, while fusion releases energy from _____ nuclei.
large, small
For A<60:
Fusion will ____ energy.
Fission will ____ energy.
release, consume
For A>60:
Fusion will ____ energy.
Fission will ____ energy.nergy.
consume, release
Half-life is _____ proportional to the decay constant
inversely
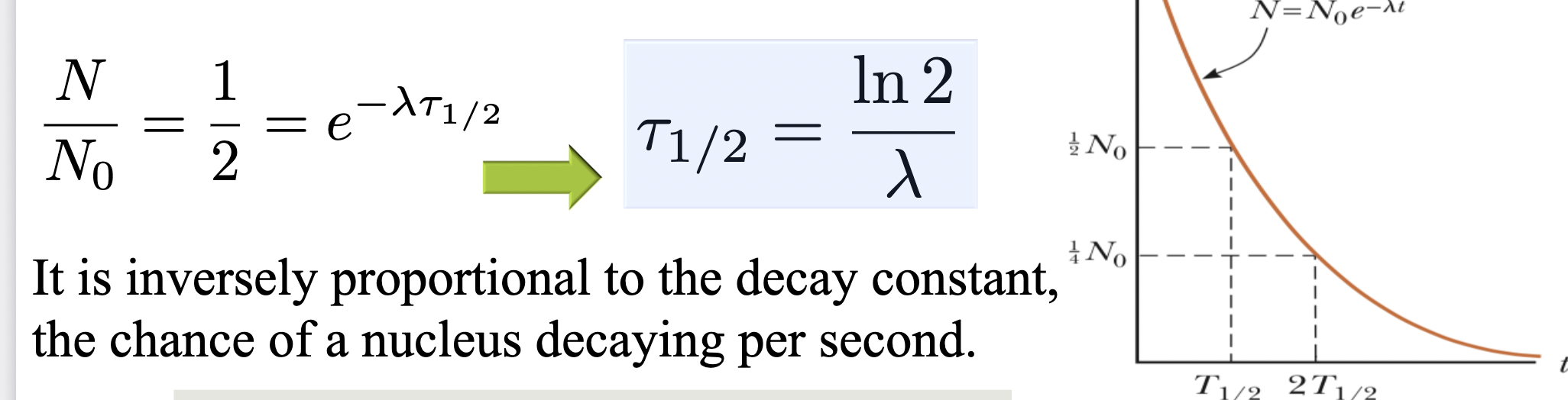
The decay rate____
also decreases exponentially over time, meaning a radioactive sample produces fewer and fewer decays per second
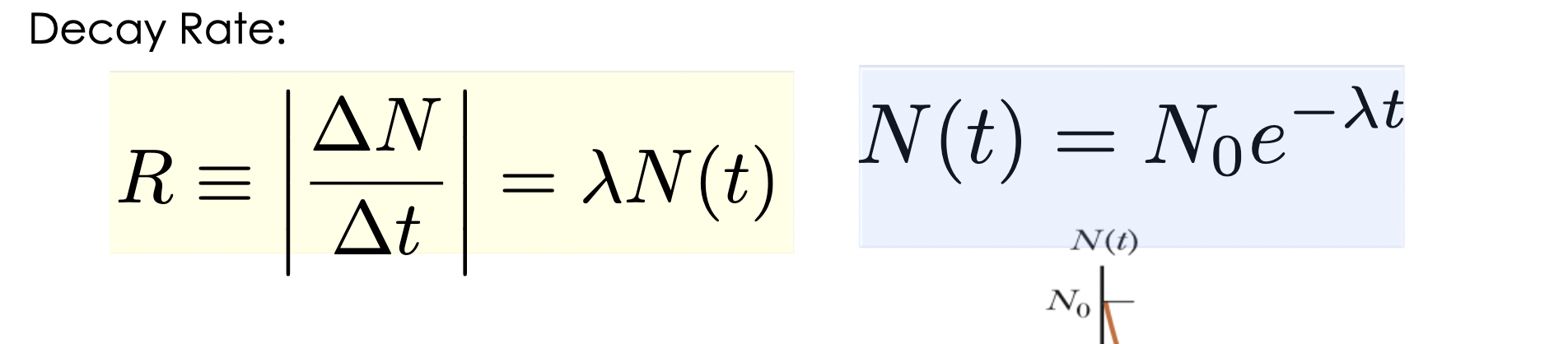
Alpha decay
a type of radioactive decay in which an unstable nucleus releases an alpha particle to become more stable.
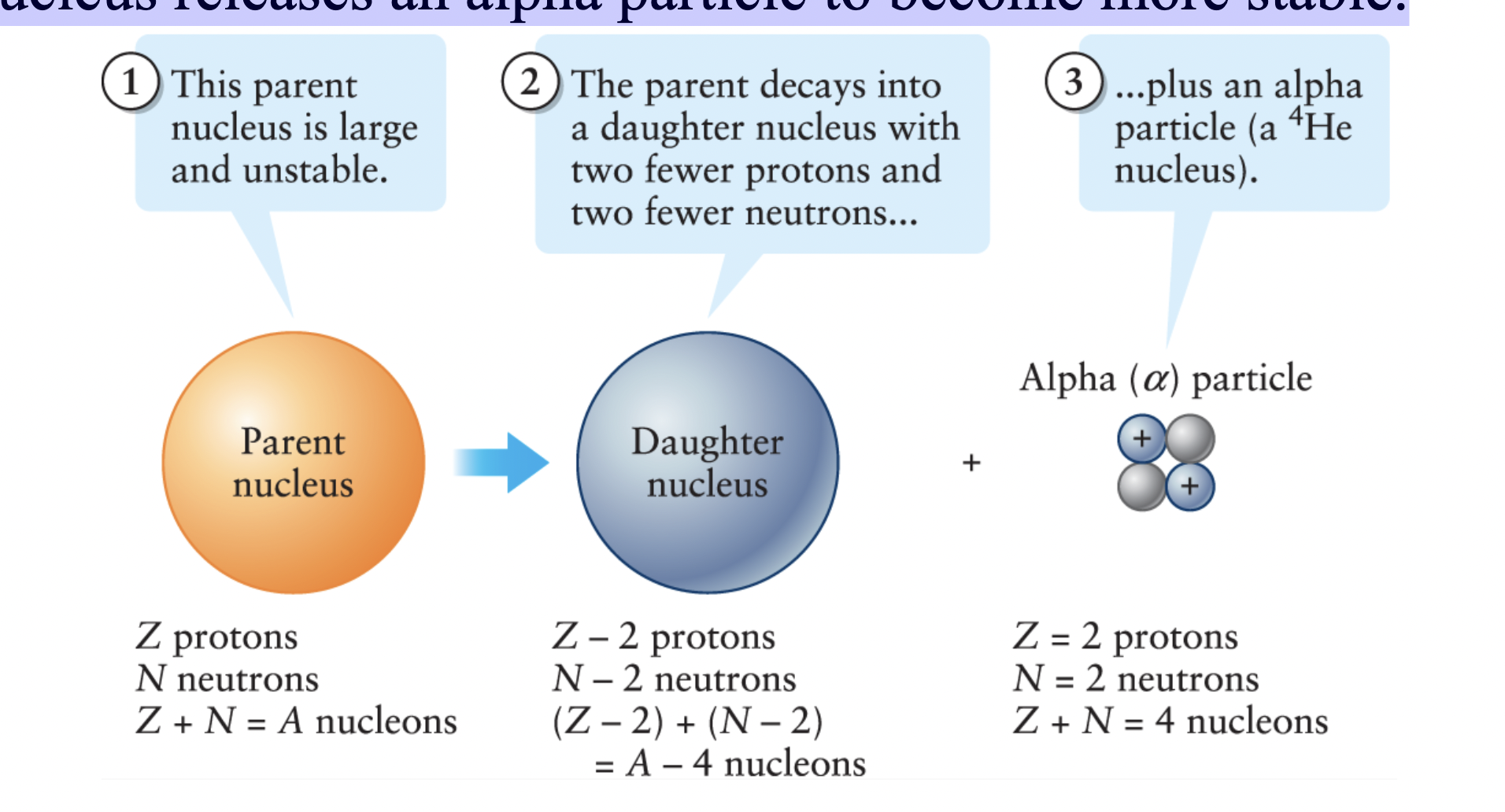
Beta decay
when a nucleus changes a neutron or proton
and emits an electron or positron.
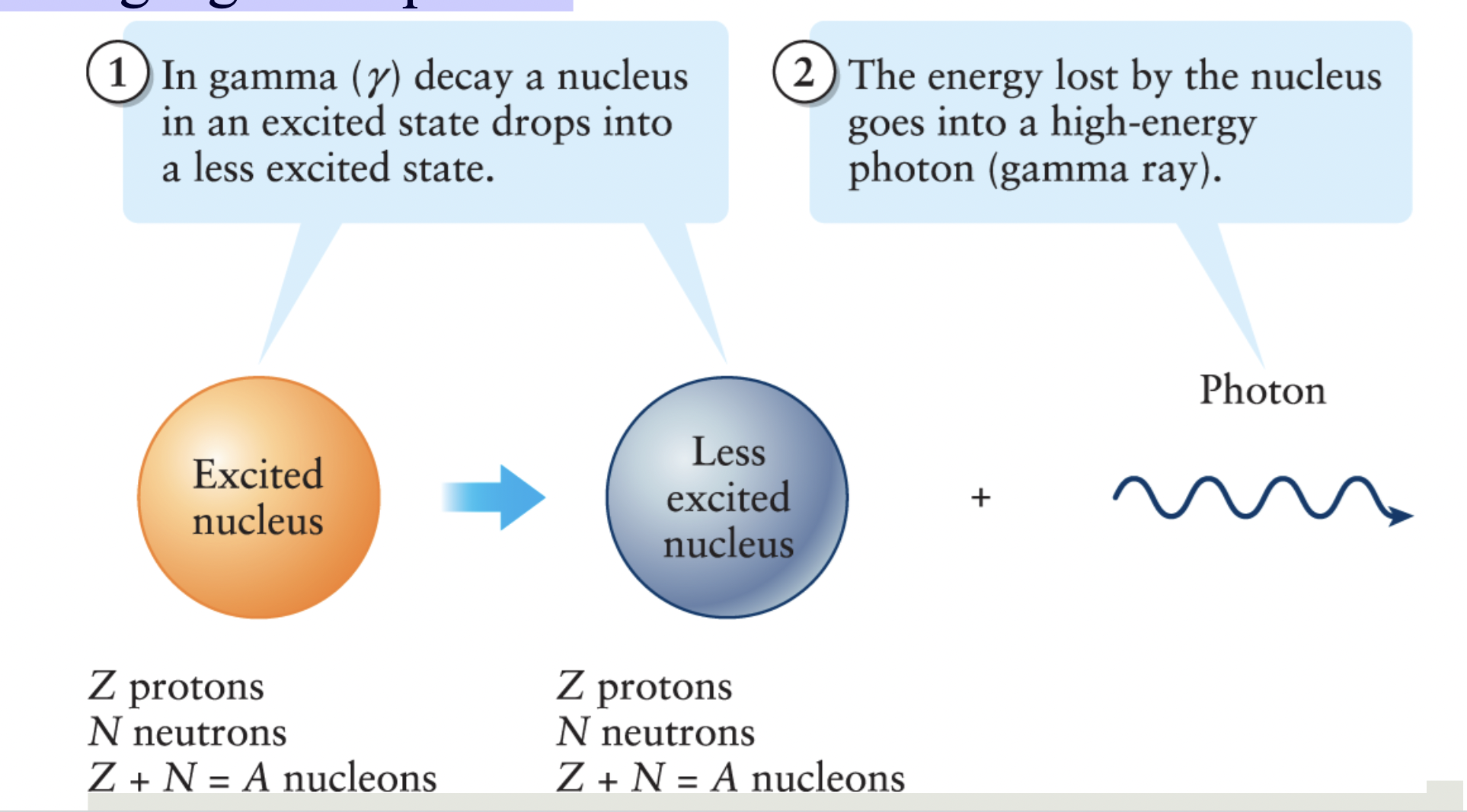
Gamma decay
when an excited nucleus releases energy by
emitting a gamma photon
Wave-particle duality
Electrons and photons can
sometimes behave like particles
and sometimes like waves
Quantization:
certain physical properties can only
take on specific discrete values instead
of any value in between
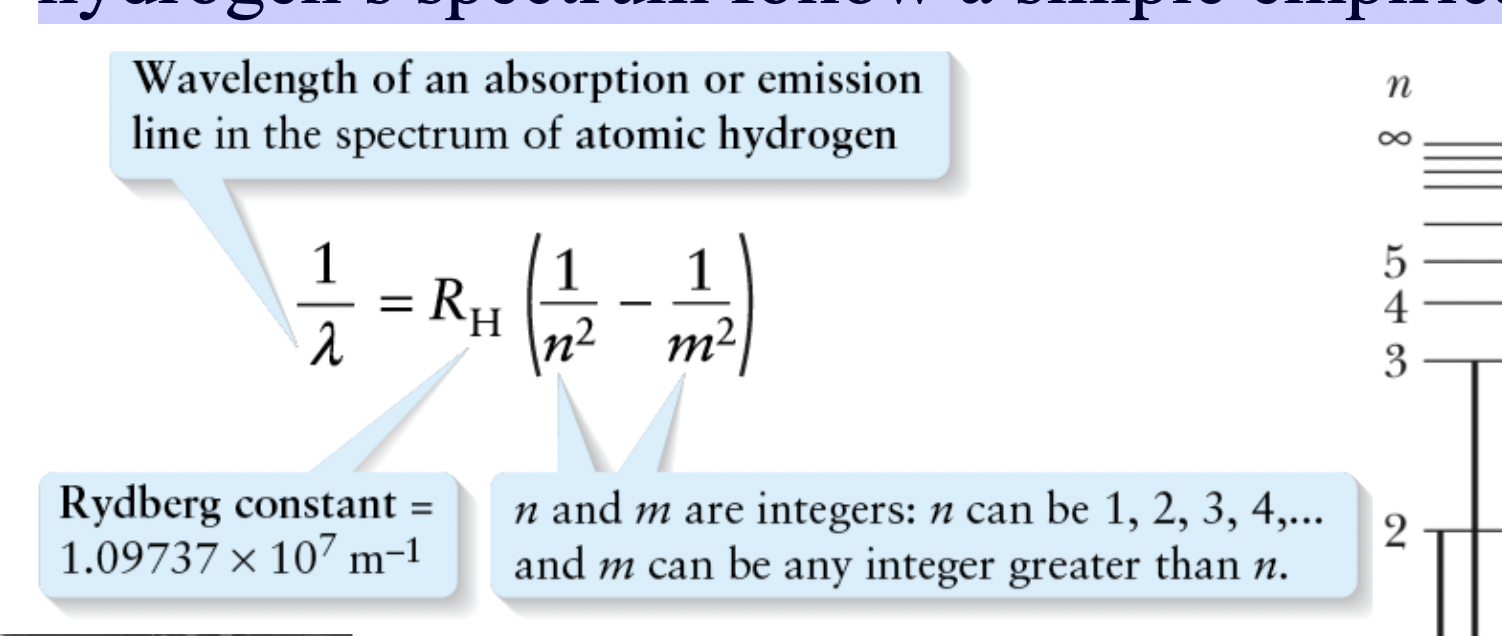
Rydberg Formula
the wavelengths in hydrogen’s spectrum follow a simple empirical formula
Light absorbed when ___. Light is released when ____.
low energy orbit→high energy orbit
high energy orbit→low energy orbit
Bohr Model
Bohr Model Assumptions:
1. Electrons travel in fixed circular orbits.
2. Only certain stable orbits are allowed, with no energy loss.
3. Light is emitted or absorbed when electrons change orbits.
4. Each orbit’s circumference equals an integer multiple of the
electron’s de Broglie wavelength
Bohr radius
For Hydrogen, the orbit with the smallest radius (n=1)

At rest, the total energy of an electron is the sum of ___
kinetic and potential energy
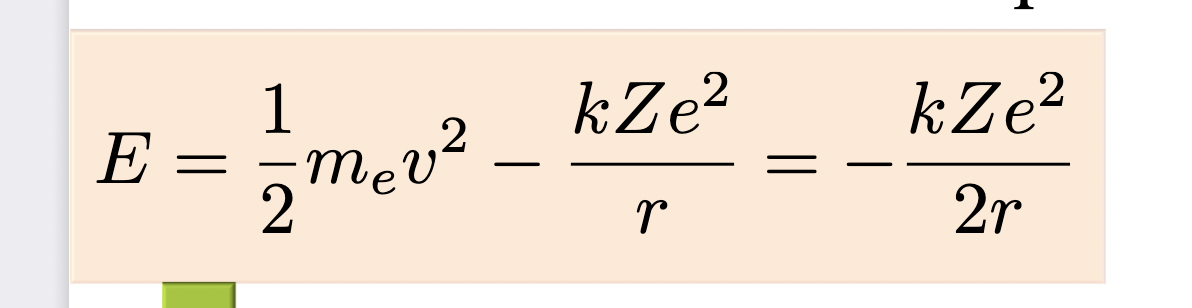
____ is emitted or absorbed whenever an electron transitions between allowed energy levels in an atom
Light
Uncertainty Principle
It is physically impossible to measure simultaneously the exact position and exact linear momentum of a
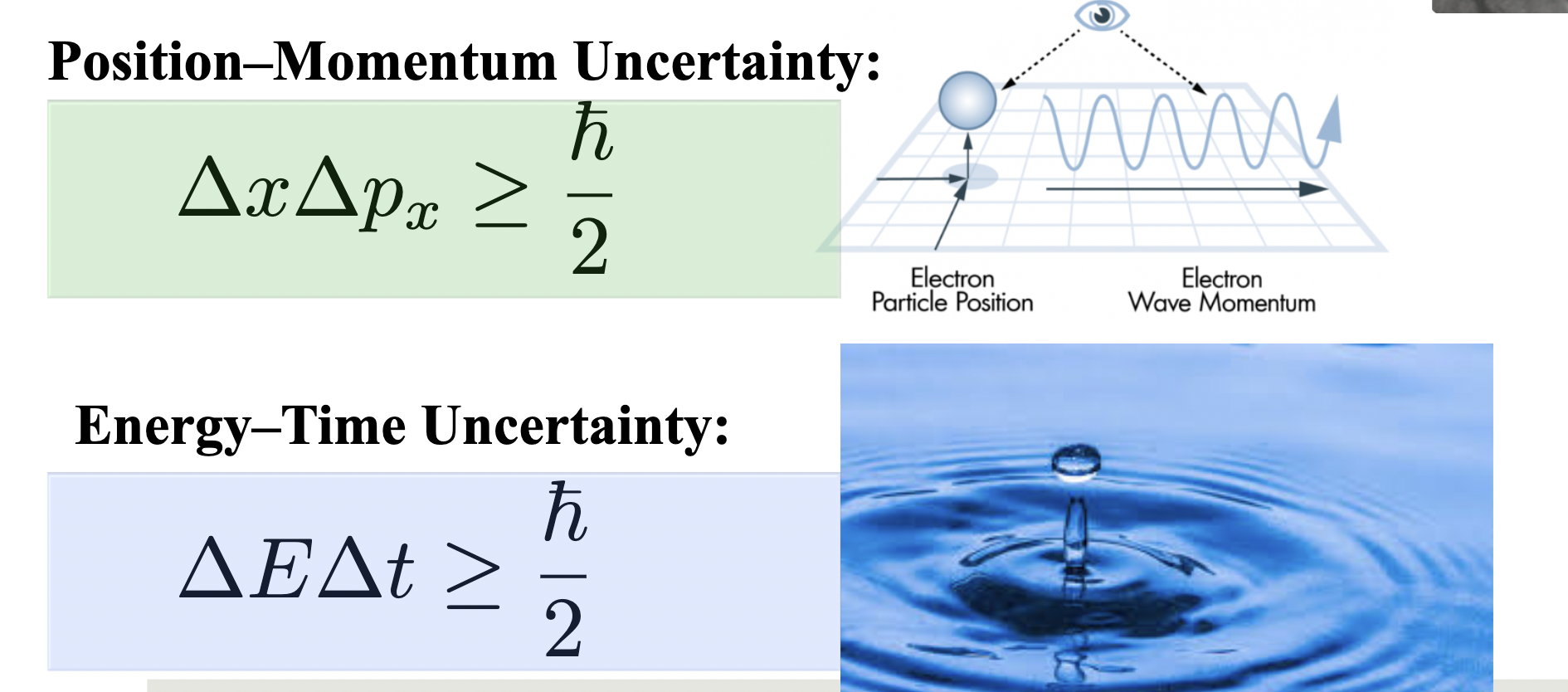
particle
Quantum tunneling:
The particle has a nonzero
probability of being foun
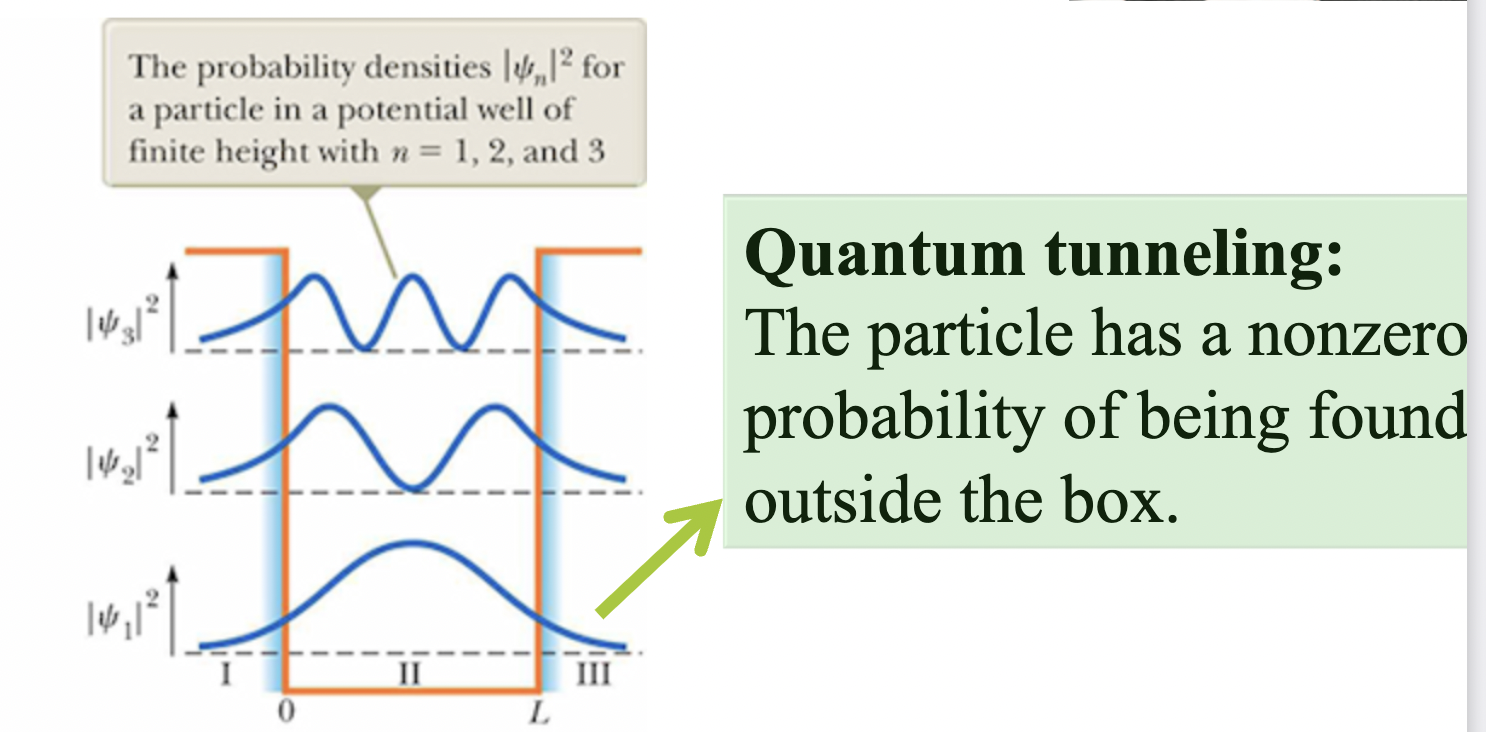
d
outside the box.
When an electron jumps from a higher to a lower atomic orbit, the atom emits a photon with an energy 𝐸photon that equals the electron energy 𝐸𝑚 of the higher orbit minus the electron energy 𝐸𝑛 of the lower orbit, where 𝑚 and 𝑛 are positive integers with 𝑚>𝑛
𝐸photon=𝐸𝑚−𝐸𝑛
The energy of a photon 𝐸photon equals the product of Plank's constant ℎ and the speed of light 𝑐 , divided by the photon's wavelength 𝜆 .
𝐸photon=ℎ𝑐/𝜆
Combine the two photon energy equations, then solve for the wavelength.
𝜆=ℎ𝑐/(𝐸𝑚−𝐸𝑛)
𝜆=ℎ𝑐/(𝐸𝑚−𝐸𝑛)
Because there is an inverse relationship between the emitted photon wavelength and the energy lost by the atom during the transition, the longest wavelength photon is emitted from the ____ energy transition
smallest
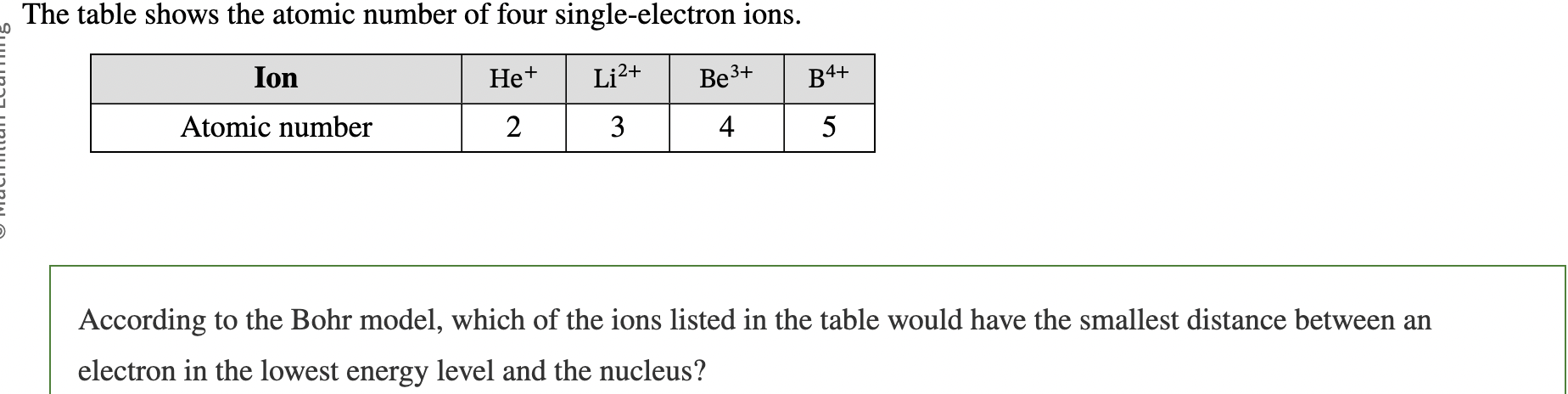
B4+
Wave Evidence of Light
-Double-slit interference pattern
-Diffraction through narrow slits
-Reflection and refraction in optics
Particle Evidence of Light
Blackbody radiation
Photoelectric effect
Compton Scattering
Momentum of a Photon
p = E/c = h/λ
de Broglie wave- length of a particle
λ= h/p = h/mv
Wien’s displacement law
λmax T = 0.289 × 10^-2 m · K
pPhotoelectric effect
is the emission of electrons from a
material when it is hit by light.
It takes energy from light to liberate an electron from the surface of a material
the maximum kinetic energy for these liberated photoelectrons
KEmax = hf - work function
Work function
the minimum energy with which an
electron is bound in the metal
Energy of photon
E= hf
Momentum of a photon
p= hf/c = h/ λ
Compton Scattering
photon’s collision with other
particles is similar to a collision between two billiard balls, causing change in wavelength and evidence that light exhibits particle behavior
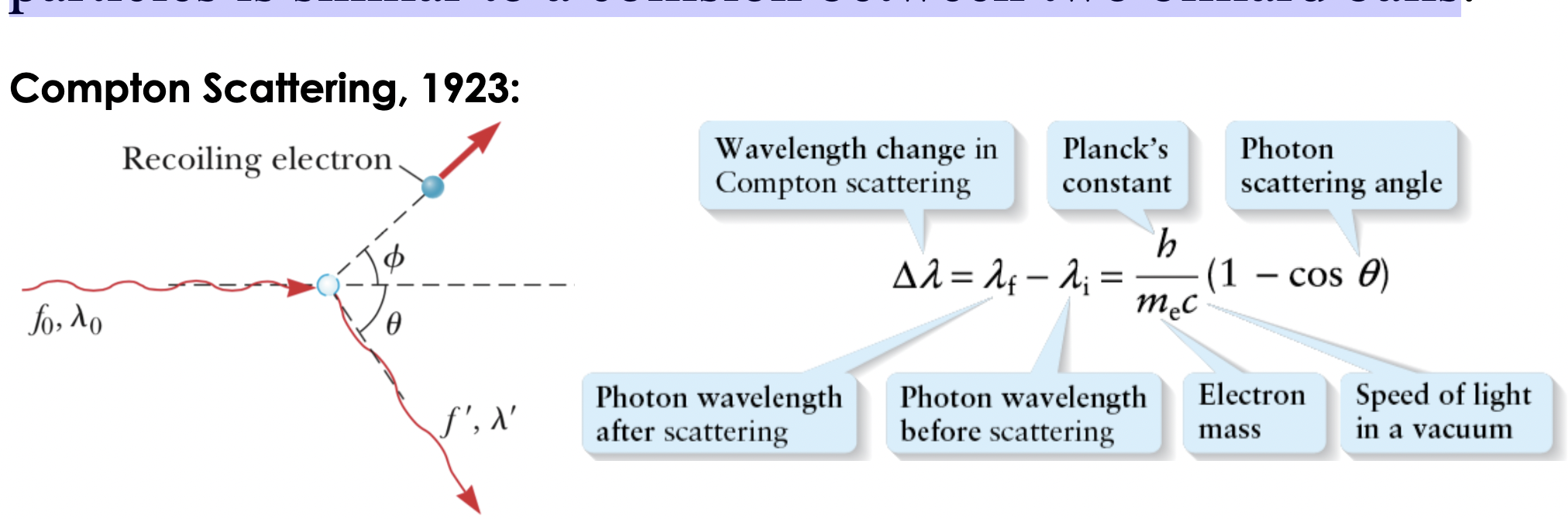

Rank de Broglie wavelength from smallest to longest
B< A<D<C
After a collision, a photon's wavelength is always____ than its wavelength before the collision because of momentum transfer
longer
Michelson-Morley Experiment
showed that the speed of light is the same in all directions
Principle of relativity
All the laws of physics are the same in all
inertial frames
The constancy of the speed of light
the speed of light in a vacuum is constant in
all inertial frames, regardless of the source or
observer’s motion.
In relativistic mechanics there is no such thing
as absolute length or absolute time
Proper Time
the interval between two events measured by an observer for whom the events occur at the same place.
time dilation
t proper = 2d/c
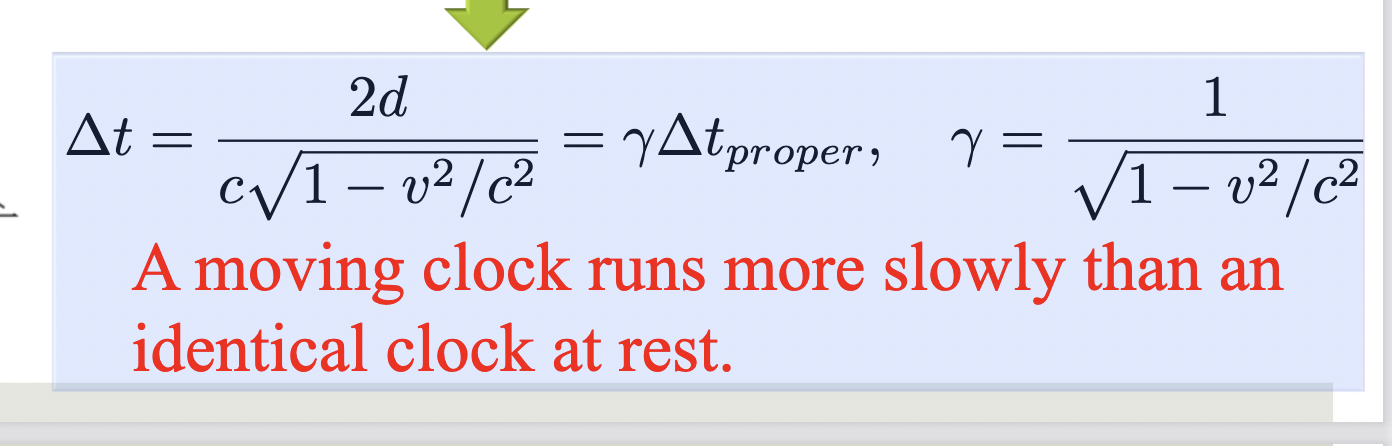
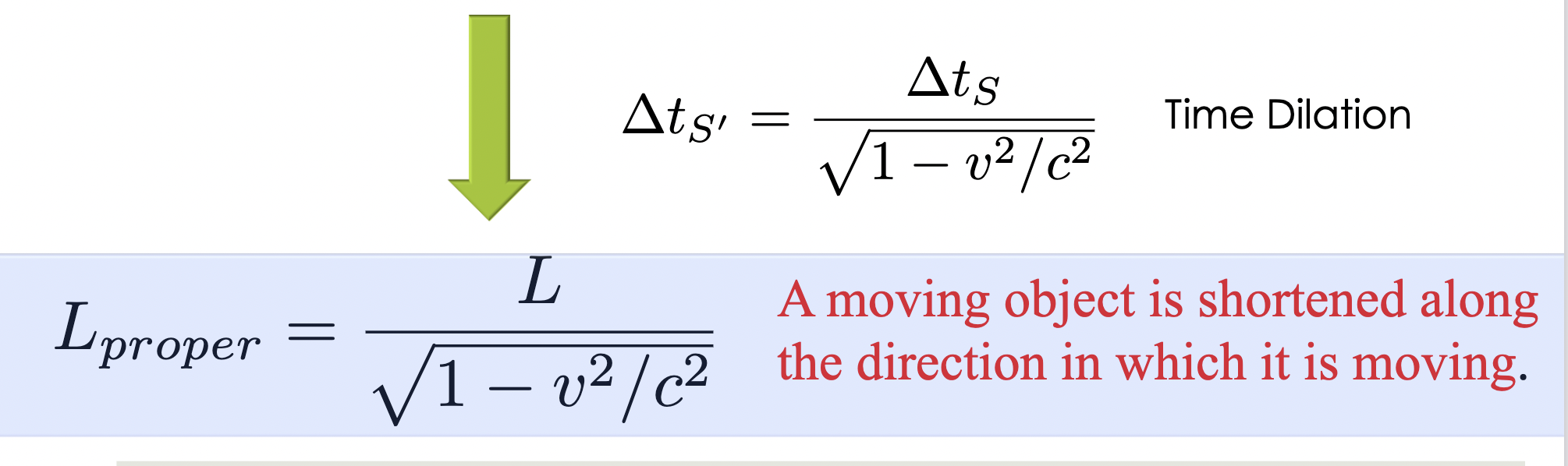
Length Contraction
The length of an object measured in a reference frame that is moving with respect to the object is always less than the proper length
Lorentz Transformation
connects space and time between
moving reference frames, ensuring that the speed of light remains constant for all observers.
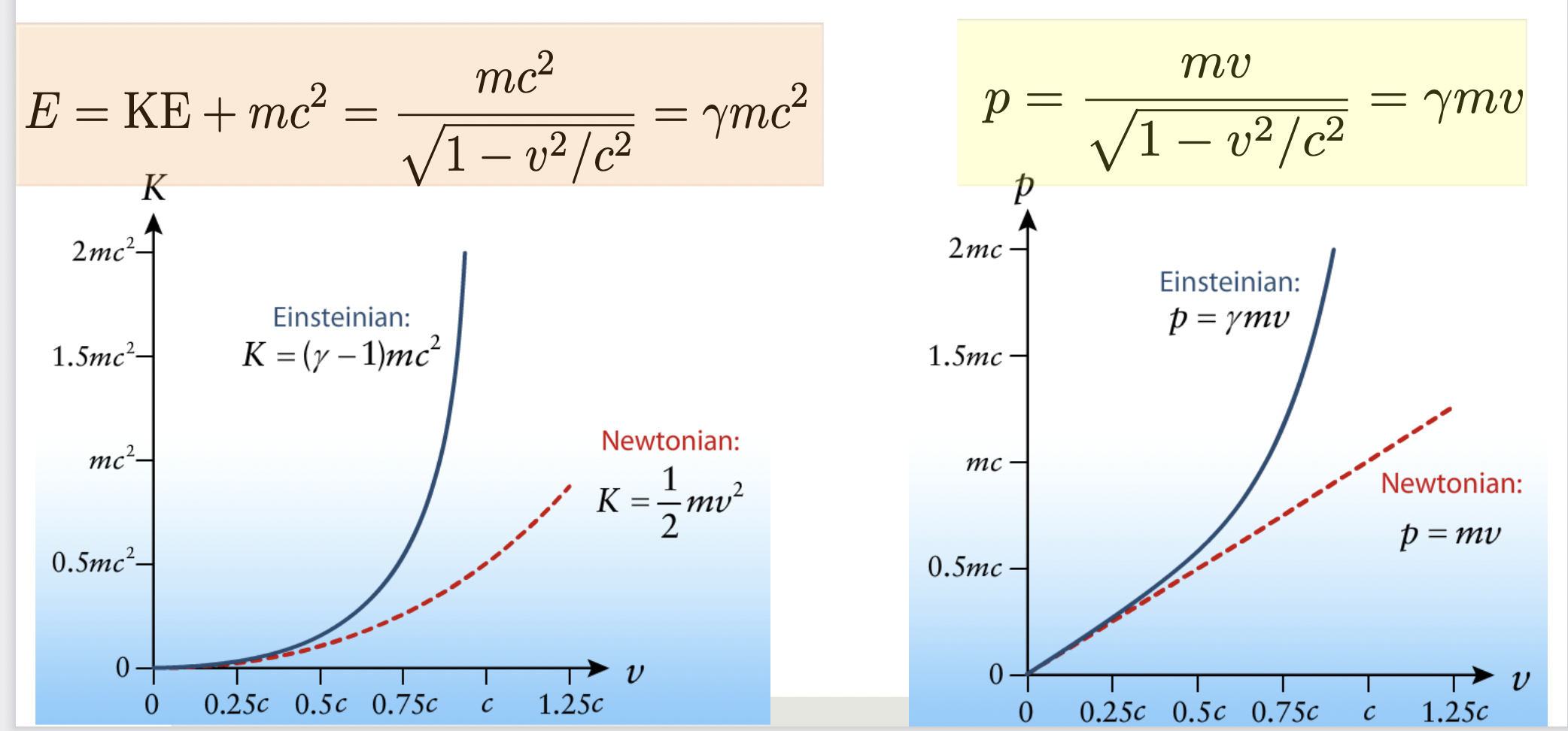
Momentum and energy
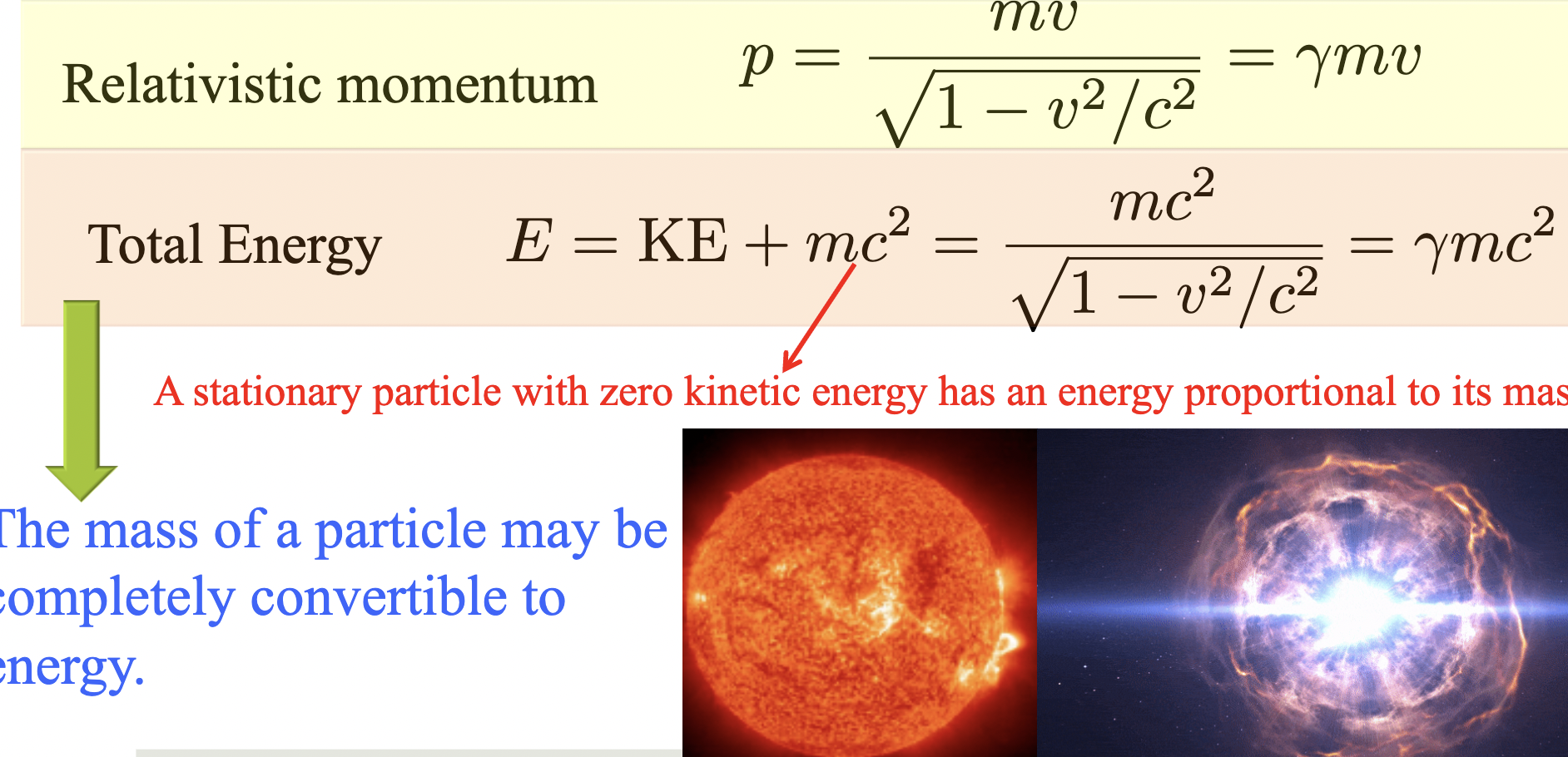
When the velocity is much smaller than the speed of light v≪c,
the relativistic momentum and kinetic energy reduce to their
Newtonian forms
General relativity
All the laws of nature have the
same form for observers in any
frame of reference, accelerated or
not.
In the vicinity of any given point, a
gravitational field is equivalent to
an accelerated frame of reference
without a gravitational field.
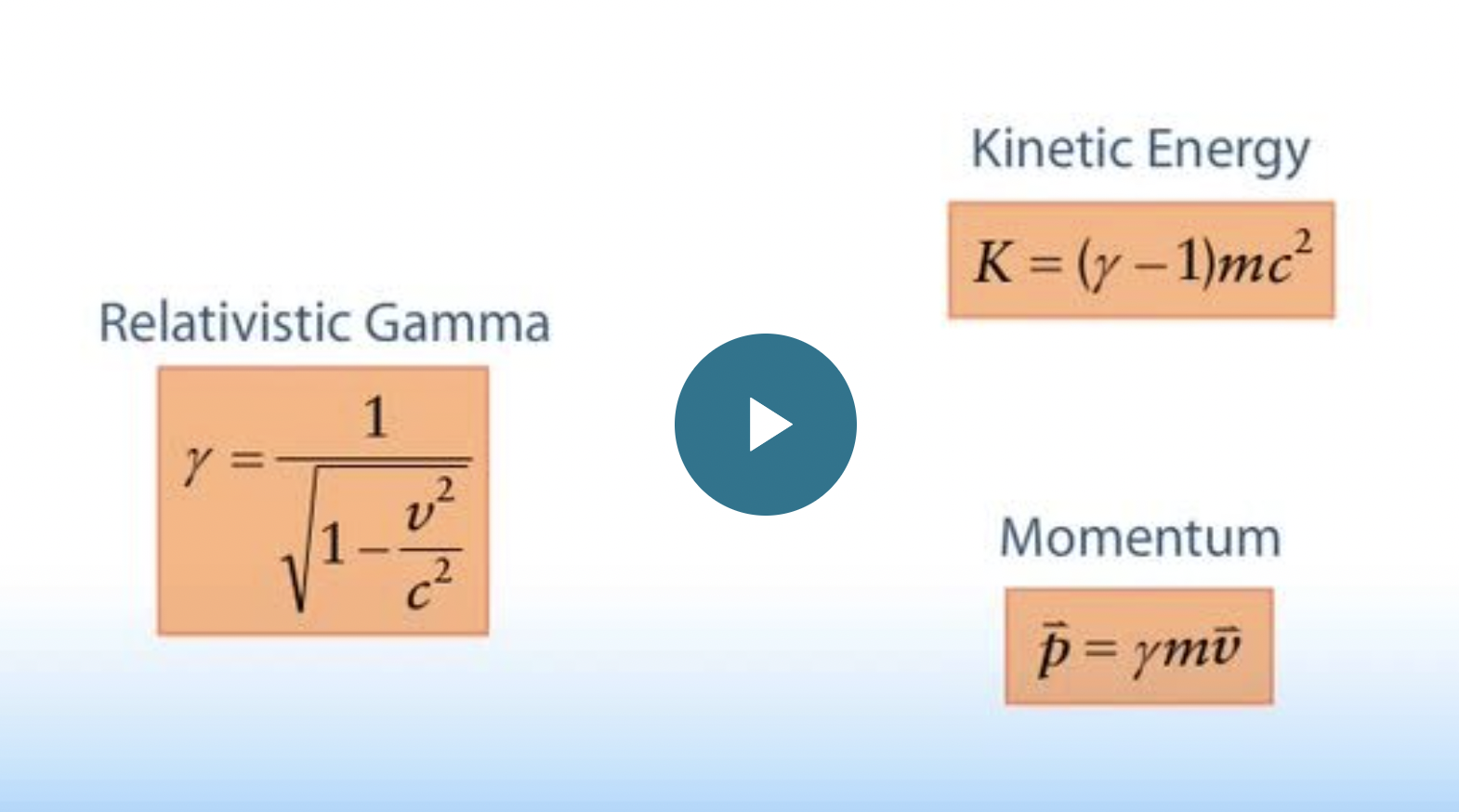
Relativistic gamma, kinetic energy, and momentum formulas
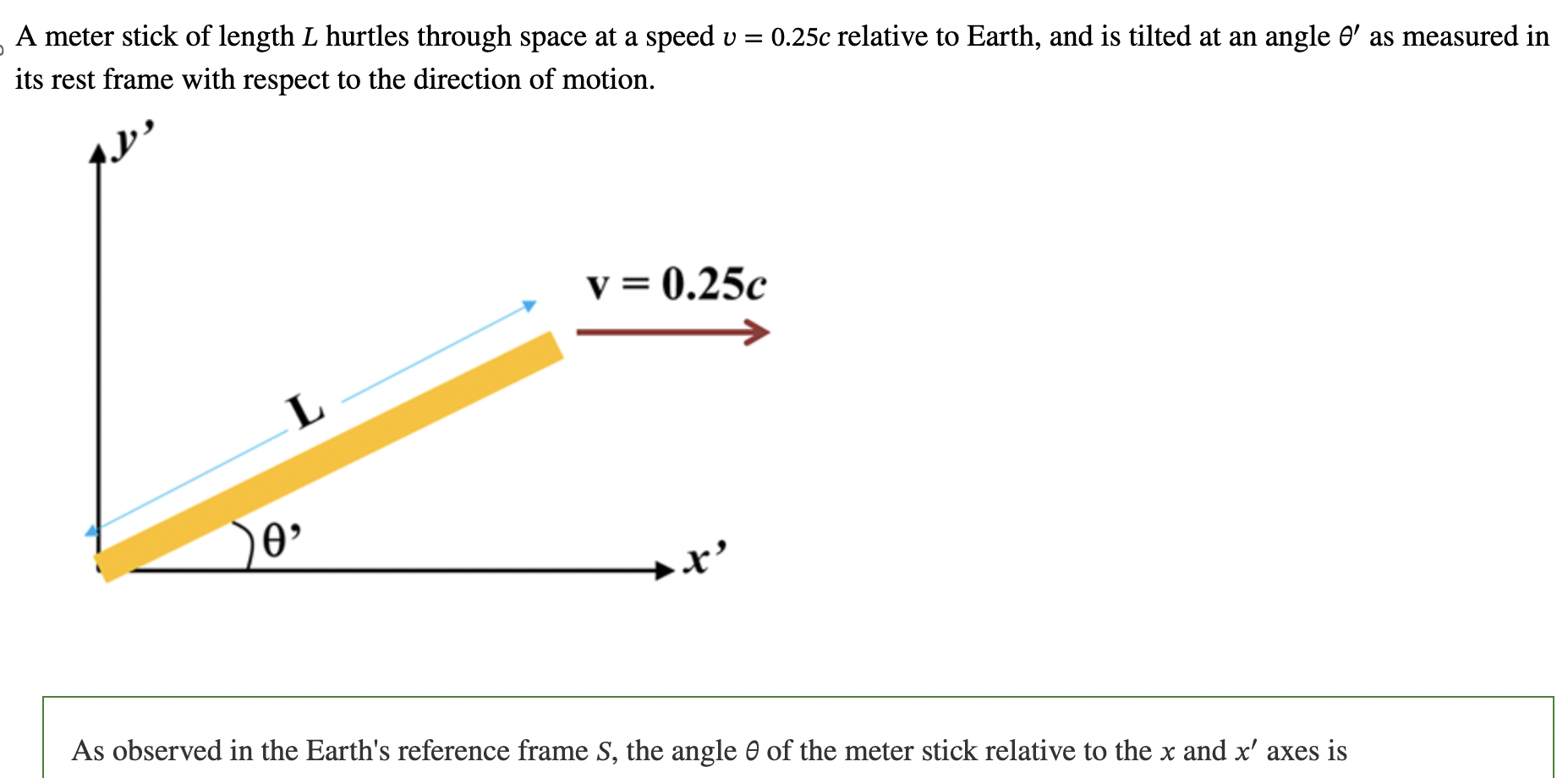
angle > angle prime