3.3.4.1 Mass Transport in Animals PART 2
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
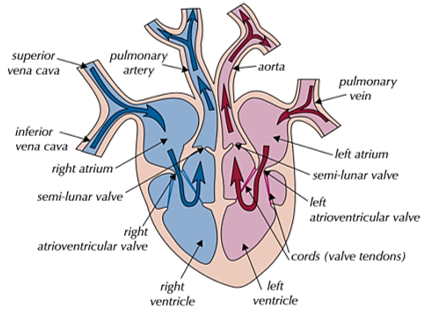
structure of the HEART
left = pulmonary vein, left atrium, atrioventricular bicuspid valve, left ventricle, semi-lunar aortic valve, aorta - oxygenated blood
right = vena cava, right atrium, atrioventricular tricuspid valve, right ventricle, pulmonary artery - deoxygenated blood
structure of the CHAMBERS
atria = thin-walled and elastic so can stretch when filled with blood
ventricles = thick muscular walls to pump blood under high pressure
-left ventricle = has thicker, muscular walls as it needs to pump blood around the whole body
-right ventricle = thinner wall as it only needs to pump blood to the lungs nearby
function of VALVES
maintain a unidirectional flow of blood
-atrioventricular = stop blood flowing back into the atria when ventricles contract
-semi-lunar = stop blood flowing back into the ventricle after the ventricles contract
structure + function of VESSELS -arteries + arterioles
-arteries = carry blood from the heart
thick, muscular walls - handle high pressure without tearing, have elastic tissue - control blood flow, small lumen
-arterioles = arteries divide into these smaller vessels
constrict when muscle contracts - control blood flow, when muscle relaxes - dilates blood vessel so increases blood flow
structure + function of VESSELS -veins + capillaries
-veins = take blood back into the heart
thin walls due to lower pressure, have valves - ensure blood does not flow backwards, larger lumen
-capillaries = arterioles branch into these + where gas exchange occurs
selectively permeable - allow diffusion of substances, one cell thick walls - short diffusion pathway, large number of them - increases surface area
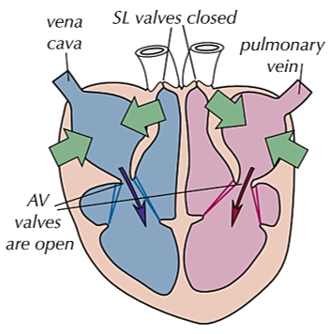
THE CARDIAC CYCLE (right side) 1) atria to ventricles
atria contract and ventricles relax
-atrioventricular valves are open
-as the atria contract, the volume decreases and the pressure increases - atrial pressure is higher than ventricle pressure as blood is flowing in
-this forces blood into the ventricles so the pressure there increases slightly as they receive the atrial blood
-semi-lunar valves are closed
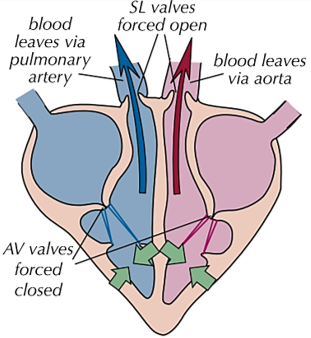
THE CARDIAC CYCLE (right side) 2) ventricles to SL valves
ventricles contract and atria relax
-as ventricles contract, the pressure increases
-pressure of ventricles becomes higher than pressure in atria so forces atrioventricular valves shut to prevent backflow
-pressure in ventricles becomes higher than pressure in aorta + pulmonary artery which forces semi-lunar valves to open
-so blood is forced out into arteries
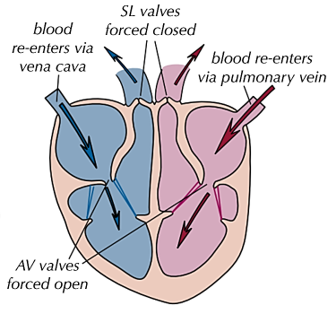
THE CARDIAC CYCLE (right side) 3) SL valves to body/lungs
atria and ventricles relax
-as ventricles relax, the pressure becomes higher in aorta and pulmonary artery so semi-lunar valves close to prevent backflow
-blood flows into the atria as there is higher pressure in vena cava and pulmonary vein so pressure of atria increases
-as ventricles continue to relax, their pressure falls below atrial pressure so atrioventricular valves open
-so blood flows into ventricles passively
cardiac output EQUATION
cardiac output = heart rate x volume
cm3min-1 = bpm x cm3
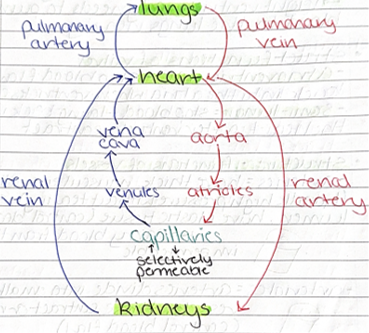
circulatory system in mammals -DRAW
coronary artery - supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle
coronary vein - carry deoxygenated blood away from heart muscle
tissue fluid
supplies glucose, amino acids, oxygen and other nutrients to cells and also removes waste materials
FORMATION of tissue fluid
1) blood is pumped by the heart by the contraction of ventricles which produces high hydrostatic pressure
2) the hydrostatic pressure in capillaries is greater than the hydrostatic pressure in tissue fluid
3) difference in hydrostatic pressure forces water + some dissolved substances out of the blood capillaries forming tissue fluid so the net loss of fluid decreases pressure in capillaries
tissue fluid re-entering
-the hydrostatic pressure lowers in capillaries so tissue fluid is forced back into capillaries by high hydrostatic pressure around
-plasma has lost water but still contains proteins so has lower water potential than tissue fluid
-so water leaves tissue and enters capillaries by osmosis
-so water returns to blood by lymphatic system
lymphatic system
excess tissue fluid is absorbed/drained into this
‘Explain why a lack of protein in the blood causes a build up of tissue fluid’
-the water potential in capillary is higher than normal
-so less water is absorbed into capillary by osmosis (remains in the tissue)
-so more tissue fluid forms
lymph
old tissue fluid that contains CO2, waste materials from tissues, lower levels of useful material