MOD 3 - Pre and Post-processing
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Pre-processing
correction of "raw" image data done by the computer software
minor faults: cleans any dust, scratches, reduces noise, adjusts for small defects in the receptor
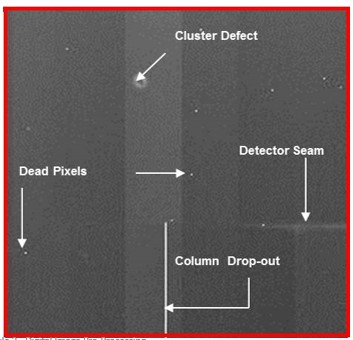
Dead Pixels
what
correction
pixels that don’t respond to radiation and appear as small dots prior to pre-processing
fixed through pixel calibration: interpolation, assigning a digital value from the average of the surrounding 8 pixels
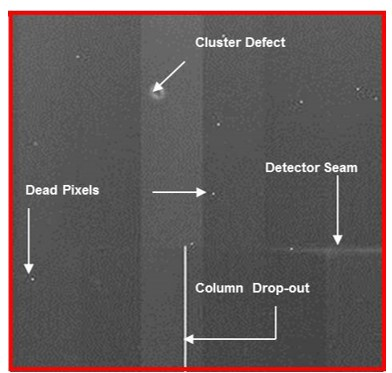
Row or Column Drop-Out
what
correction
when an entire row or column of pixels don't work, appearing as vertical white lines
interpolation, assigned the average value of neighbouring columns
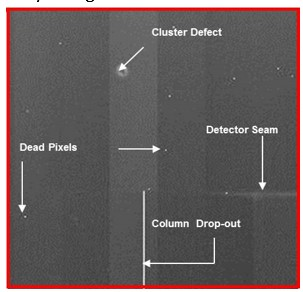
Detector Seam
what
correction
inherent flaw where two detector parts meet leading to a slight variation in IQ
correction is interpolation, however wont work if too severe
Cluster Defect
what
correction
when many pixels in a small area are defective, creating a uniform white cluster
correction is interpolation
Flat-Field Uniformity
A component of the pre-processing stage where the electronic noise within the system is evened out (eg. anode heel effect)

Detector Calibration
purpose
types
calibration allows our system to recognize where dead pixels are and allows for flat fielding levels to be determined
types:
Offset calibration
Gain calibration
Pixel calibration
Offset Calibration
to reduce the intrinsic noise caused by current running within the detector, as it interferes with the diagnostic quality of our images
machine will do this automatically from once to several times a day
Gain Calibration
Flat Field Testing
used to compensate for sensitivity variations that can occur across the detector
looks for defective pixels, image wide gradient differences and variations in the signal
Pixel Calibration
performed to ensure that all DELs are displaying uniformly and fixed through interpolation
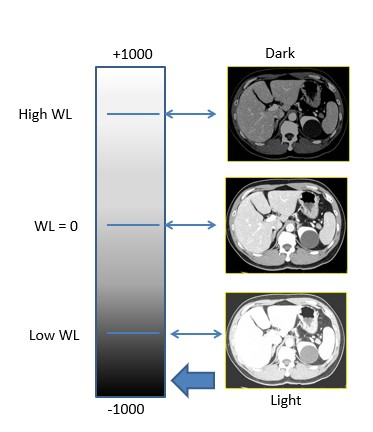
Windowing (Grayscale Processing)
used to adjust the contrast and brightness of the image
window level = controls brightness, the center of window range
window width = controls contrast
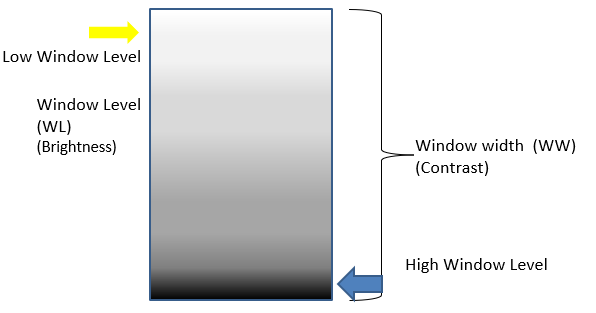
wide window width =
low contrast bc of more grey shades
increased window level =
darker image (window tint analogy)