Chemistry Midterm
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
Chemistry
The study of matter and the changes it undergoes
Organic Chemistry
Study of compounds containing carbon
Inorganic chemistry
Study of compounds not containing carbon
Biochemistry
Study of the processes that take place in living organisms
Analytical Chemistry
Study of the composition of matter
Physical chemistry
Study of reaction mechanisms (rates and energy transfer occurring in a reaction)
Pure Chemistry
Pursuit of chemical knowledge for its own sake
Ex. sticky notes
Applied chemistry
research directed toward a practical goal
Steps of Scientific Method
Observation
hypothesis
controlled experiment
theory (explanation for what happened)
scientific law (summary of the results of many observations)
collaborate and communicate
steps of numeric problem solving
Analyze
calculate
evaluate
accuracy
a measure of how close a measurement is to the actual, true, or theoretical value
precision
a measure of how close a series of measurements are to one another
error
experimental - accepted
percent error
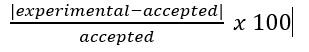
sig figs when looking at a physical measurement
all known digits + 1 estimated digit
adding or subtracting sig figs
sum/difference rounded to the same number of decimal points as the number with the least number of decimal points in the equation
International System of Units (SI)
Standards of measurement used in science based on the metric system
SI Base Units
Length: meter (m)
Mass: kilogram (kg)
temp: kelvin (K)
time: seconds (s)
Amount of a substance: mole (mol)
luminous intensity: candela (cd)
Electric current: ampere (A)
1 Liter
1 dm³, 1000 cm³
energy
force (N) x distance (m)
force

acceleration
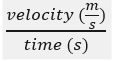
velocity
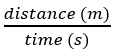
Joule
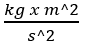
Newton
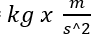
Calorie
non-SI unit for energy
quantity of heat that raises one gram of pure water by 1 C
1 cal = 4.184 J
Celsius
Uses freezing point of water (0 C) and boiling point of water (100 C)
C = 5/9(F-32)
Kelvin
aka absolute scale
freezing point of water: 273.15 K
boiling point of water: 373.15 K
degree sign is not used
K = C + 273.15
No negative temps
Density
D = g/cm³
D = g/mL
extensive properties
a property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample
Intensive properties
properties that depend on the type of matter, not how much
Pure substance
matter that has uniform and definite composition
physical property
quality or condition of a substance that can be observed without changing the composition of a substance
solid
definite shape and volume, incompressible
liquid
indefinite shape, definite volume, particles not rigid or orderly but flow past each other
gas
indefinite shape and volume, particles flow past each other, compressible
fluid
any substance that has particles able to flow past each other
vapor
the gaseous state of a substance that is generally a liquid or solid at room temperature
physical change
properties of a material change but the composition does not, reversible or irreversible
heterogenous mixture
a mixture in which the composition is not uniform throughout
homogenous mixture
a mixture in which the composition is uniform throughout, also called a solution
phase
describes any part of a sample within uniform composition and properties
filtration
separated solid from liquid due to particle size
distillation
separates two liquids due to their volatility (readiness to become gas)
chromatography
separates a mixture due to phase mobility
centrifuge and separation funnels
separates mixtures based on density
chemical change
produces matter with different composition than its original
2 ways to break down compounds
Heating and electrolysis
distinguishing substances and mixtures
if the composition of a material is fixed, it is a substance. If the composition can vary, it is a mixture
atomic number
# of protons, unique to each element
period
horizontal row on a periodic table
properties differ from one to the next
7
group
vertical column
properties similar
18
metals
80% of the periodic table
generally good heat and electricity conductors
high sheen or luster (reflect light)
solid at room temp (except Hg)
ductile (can be drawn into a wir3e)
malleable (can be formed into foil)
like to form cations (atoms with a positive charge)
metallic character increases from top right to bottom left on the periodic table, with exceptions
nonmetals
located in the top-right corner of the periodic table, except for H
most are gases at room temp, some solids, 1 liquid (Br)
poor conductors, good insulators
solids are brittle
like to form anions (atoms with a negative charge)
metalloids
staircase that borders metals and nonmetals on the periodic table
semi-conductors (conduct heat and electricity efficiently between a metal and nonmetal)
solid at room temp
chemical properties
the ability of a substance to undergo a specific chemical change
can only be observed when going through a chemical change
chemical reaction
when one or more substances change into one or more new substances
reactant
substance present at the start of a reaction
product
substance formed during the reaction
4 clues of a chemical change
transfer of energy: energy used or produced in the form of light or heat
change in color
formation of a gas
precipitate forms: a solid that forms and settles out of a liquid mixture
model
representation of a theory using words, diagrams, or mathematical expressions
atom
the smallest particle of an element that retains its identity and properties in a chemical reaction
Democritus
said everything is made form indivisible and indestructible particles (atoms)
no experimental support
Dalton
Turned Democritus’s ideas into scientific theory by studying ratios in which elements combine in chemical reactions
Dalton’s first postulate
all elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. (Not valid)
Dalton’s second postulate
atoms of the same element are identical. (Not valid)
Dalton’s third postulate
Atoms of different elements can be physically mixed together or chemically combined in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. (Valid)
Dalton’s fourth postulate
Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated from each other, joined, or rearranged in different combinations. Atoms of one element cannot change into atoms of another element as a result of a chemical reaction. (Valid)
Size of Atom
Radius of an atom ranges from 5 × 10^-11 m to 2 × 10^-10 m
observing atoms
through scanning electron microscopes. A beam of electrons is focused on the sample
Dalton’s model of an atom
a dense sphere
Cathode Ray Experiment
Conducted by JJ Thompson
Cathode ray is a glowing beam that travels from the cathode to the anode
Cathode is a negatively charged electrode
Anode is positively charged electrode
Thomspon took most of the pressure out of the system and ran the Cathode Ray
Measured the mass to charge ratio of the tiny negative particles in the ray using a magnetic field and the beam deflected a lot
Cathode Ray conclusions
All substances contain negatively charged particles (capusuls/electrons) because the beam was always attracted to the positive side of the magnetic field
particles must have a very great charge, be very small, or both
Robert Millikan
Oil drop experiment to find the charge of an electron
Suspended negatively charged oil droplets between two charged plates
Adjusted the voltage to see how the oil fell
Discovered the charge of an electron
charge of an electron
1.60 × 10^-19 coulomb
Eugene Goldstein
anode ray experiment
discovered the proton
anode ray deflected much less than cathode ray
James Chadwick
Realized that the mass of an atom was much larger than the mass of protons and electrons
called the extra particle a neutron
Mass of an electron
9.11 × 10^-31 kg
mass of a proton
1.67 × 10^-27 kg
Ernest Rutherford
Conducted an experiment using gold foil. According to Thompson, alpha particles (helium atoms without their electrons) should pass straight through the foil, but 1 in 20,000 shot back at him. So, he proposed that the atom is mostly empty space with a nucleus containing the protons and neutrons. Called this the nuclear atom.
Atomic number
number of protons, gives elements unique properties.
mass number
protons + neutrons
hydrogen isotopes
Hydrogen-1
Hydrogen-2 (Deuterium)
Hydrogen-3 (Tritium)
Mass spectrometer
allows us to calculate the masses of atoms
relative mass
one AMU is 1/12 the mass of a Carbon-12 atom.
Weighted atomic mass
(mass x abundance) + (mass x abundance)
nuclear atom
protons and neutrons are in the positively charged nucleus, electrons distributed around the nucleus.
Bohr Atom model
Planetary model
electrons exist in specific paths called energy levels
predicted the behavior of hydrogen
didn’t account for repulsion between electrons
quantum
the amount of energy needed to climb an energy level
explains why elements emit different colors
atomic emission spectrum
different frequencies of light emitted by different elements
photoelectric effect
the phenomenon that when light shines on metal, electrons are emitted from the metal if there is sufficient energy. discovered by Einstein
spectroscopy
measurements of spectra produced when radiation from the electromagnetic spectrum interacts with matter
matter absorbs and emits electromagnetic radiation
Wavelength and frequency relation
inversely proportional
frequency and energy relation
directly proportional through Planck’s constant
Energy when a photon is absorbed or emitted
when a photon is absorbed or emitted by an atom or molecule, energy is increased or decreased by the amount equal to the energy of the photon
quantum mechanical model
Erwin Schrodinger worked from Bohr’s planetary model to develop equations to determine the properties of an electron as a wave and particle
Photoelectric effect + Heisenberg uncertainty principle = quantum mechanical model
determined allowed regions where electrons could exist (probabilities)
no specific paths or orbits in this model
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
it is impossible to know the position and momentum (trajectory) of quantum particles
electron cloud
the darker the cloud, the higher the probability an electron is there
atomic orbital
the region of space with the highest probability of finding an electron
Principle energy levels (n)
Bohr’s energy levels