mammalogy- control systems and biological rhythyms
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
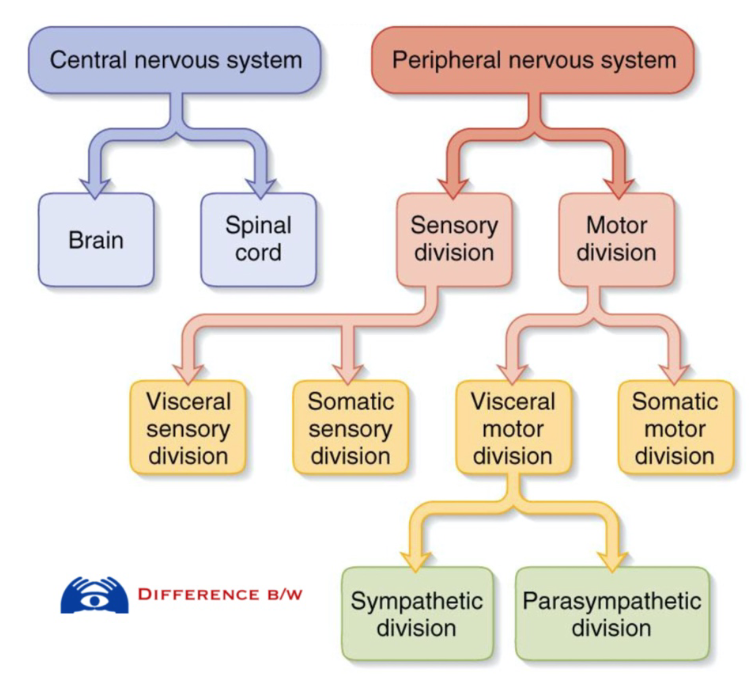
CNS develops from
dorsal, hollow nerve cord that differentiates during development into a brain and spinal cord.
the CNS contains
all of interneurons and most of the perikarya. contains many sensory and motor neurons
the PNS contains
only sensory and motor neurons traveling to/from the CNS
PNS divisions
sensory(afferent) and motor(efferent)
spinal cord
connects the PNS to brain. nerves enter/exit vertebral canal by intervertebral foramina. where reflex arcs occur. begins at the medulla oblongata.
conus medullaris
the end of the spinal cord. a tapering structure with numerous spinal nerves that form the cauda equina.
medulla oblongata
caudalmost portion of brain. part of brain stem. contains perikarya of posterior cranial nerves, ganglia for rigin auto controlled behaviors.
cerebellum and pons
cerebellum responsible for coordination of somatic motor activities.
pons contains perikarya of certain cranial nerves, ganglia for auto controlled behaviors, and axons
midbrain
contains perikarya of certain cranial nerves, ganglia for rigid auto controlled behaviors, axons.
reticular formation
made up of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. responsible for rigid auto controlled behaviors
diencephalon subdivisions(3)
thalamus- main relay center between cerebrum and CNS.
epithalamus- dorsal to thalamus, has endocrine organ (pineal gland).
hypothalamus- ventral to thalamus, main visceral control center.
forebrain
made up on diencephalon and cerebrum
hypothalamus functions
control of ANS.
regulation of body temp.
monitors hunger and thirst.
circadian rhythyms.
control of endocrine system
cerebrum
shows the greatest degree of variation between species. has white and grey matter
cerebral white matter
cerebrum component- inner core. has clusters of grey matter within it called basal nuclei (ex-amygdala).
neocortex/ cerebral cortex
cerebrum component- grey matter. outer. highly convoluted. arranged into domains by function. shows somatotrophy
light entering the eye, steps
light passes through the cornea. it refracts and bends the light. light then passes through the lens. it focuses light on to the retina.
tapetum lucideum
for nocturnal animals. composed of guanine crystals that reflect light back into retina to increase photic stimulation. pupils larger in these animals.
photoreceptors
in the retina. convert light into a nervous signal. respond to specific wavelengths.
rods and cones
photoreceptors.
rods- dim light, lower resolution.
cones- color vision, fovea, higher resolution
the outer ear
collects sound, directs them inward. in order- pinna(unique to mammals), external auditory canal, tympanic membrane
middle ear
in the temporal bone. receives sound waves from tympanic membrane. ossicles in order- malleus, incus, stapes
inner ear
the cochlea. spiral shaped. sound waves converted into nerve signals.
cochlear duct- middle canal, houses sensory structure responsible for hearing (organ of corti)
limbic system
olfaction is hard wired into brain via the limbic system
vomeronasal organ
evagination of ventral olfactory mucosa that becomes isolated from nasal cavity during development. chemoreceptive.
horomones
secreted into blood stream which carries them to site of action.
control structure of endocrine system
hypothalamus. connected to pituitary organ, which secretes a variety of horomones including tropic horomones.
hypothalamus
well vascularized. monitors blood chemistry. causes increase/decrease in release of horomones
pituitary portions(2)
posterior- produces ADH and oxytocin.
anterior- produces GH, TSH, ACTH, LH, FSH, PRL, MSH.
pituitary plays role on physiology
thyroid endocrine organ
in thoracic cavity, produces calcitonin and thyroxine
parathyroid endocrine organs
in the thyroid, produces PTH, an antagonist of calcitonin
adrenal gland endocrine organ
adrenal medulla- central portion, sympathetic ganglion priming body for emergencies.
adrenal cortex- outer portion, produces hormones such as hydrocortisone.
entrainment
occurs when behavioral events match their period and phase of that of an environmental oscillation
to be called circadian, there are 3 criteria
rhythm has endogenous free-running period of ~24 hours.
it is entrainable.
it exhibits temperature compensation
ultraradian rhythms
period shorter than 24 hours. (blinking)
infraradian rhythms
periods longer than 24 hours. (seasonal)
circalunal rhythms
lunar months
are ultradian and infradian rhythms entrainable
yes
do smaller or larger mammals experience greater variation to rhythms
smaller