Antigens, MHC, and Antibodies
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What type of molecules are the best immunogens because of their large size and high complexity?
proteins
A(n) (alloantigen/heteroantigen) is an antigen from another member of the host’s species.
alloagntigen
A(n) (alloantigen/heteroantigen) is an antigen from another species.
heteroantigen
Small molecules that need to be coupled with a carrier protein to become immunogenic are called what?
haptens
Lymphocytes can only recognize specific binding sites on antigens called:
epitopes
What dose MHC stand for?
major histocompatibility complex
What is the function of MHC?
present antigens on the surface of infected cells for T-cell recognition
Class I MHC is located in what 3 regions on chromosome 6?
A
B
C
MHC class (I/II) molecules process endogenous (originating inside the cell) antigens.
class I
Class II MHC is located in what 3 regions on chromosome 6?
D
MHC class (I/II) molecules process exogenous (originating outside the cell) antigens.
class II
The B27 HLA allele is associated with what disease?
ankylosing spondylitis
celiac disease
rheumatoid arthritis
type 1 diabetes
ankylosing spondylitis
The DQ2 (strong) and DQ8 (weak) with + HLA alleles are associated with what disease?
ankylosing spondylitis
celiac disease
rheumatoid arthritis
type 1 diabetes
celiac disease
The DR4 HLA allele is associated with what disease?
ankylosing spondylitis
celiac disease
rheumatoid arthritis
type 1 diabetes
rheumatoid arthritis
The DQ2 (weak) and DQ8 (strong) HLA alleles are associated with what disease?
ankylosing spondylitis
celiac disease
rheumatoid arthritis
type 1 diabetes
type 1 diabetes
What are adjuvants?
enhance antigenicity of vaccines
MHC testing is preformed for what type of transplant?
tissue grafts
What cell produces antibodies?
plasma cells (B cells)
What is the primary function of an antibody?
protecting host by binding to antigens
The (fab/Fc) portion of an antibody includes the bindings sites and hinge region.
fab
The (fab/Fc) portion of an antibody can activate complement sequence or bind to cell receptors.
Fc
What are the 2 types of light chains?
Kappa
Lambda

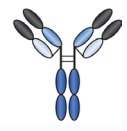
What is part A?
variable light VL
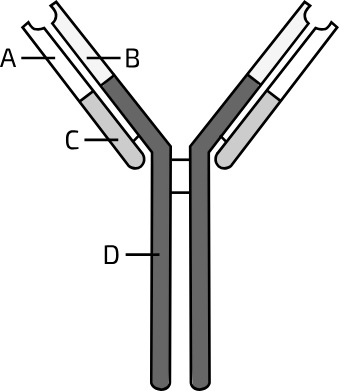
What is part B?
variable heavy VH
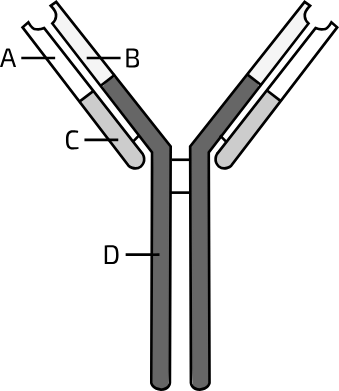
What is part C?
constant light CL
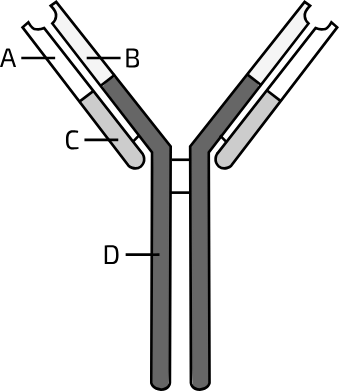
What is part D?
constant heavy CH
(Inter/Intra)-chain disulfide bonds hold the 4 polypeptide chains together to form a complete antibody.
inter-chain
(Inter/Intra)-chain disulfide bonds hold the the light and heavy chains together.
intra-chain
Unique heavy chain in the antibody class.
isotype
allotype
idiotype
isotype

The genetic variation in the constant regions.
isotype
allotype
idiotype
allotype
Variations in the variable regions that cause antibody specificity.
isotype
allotype
idiotype
idiotype
(Papain/Pepsin) cleaves the antibody to produce 1 Fc fragment and 2 Fab fragments.
papain
(Papain/Pepsin) chops up the Fc region to produce 1 whole Fab fragment
pepsin
(IgG/IgM) is pentameter with 10 binding sites.
IgM
(IgG/IgM) has the same response time in primary and secondary antigen exposures.
IgM
How long does it take for IgM antibodies to be detectable in the body after primary/secondary antigen exposure?
5-7 days
(IgG/IgM) is a monomer with 2 binding sites.
IgG
IgG has a shorter lag phase in the (primary/secondary) antigen exposure response.
secondary
How long does it take for IgG antibodies to be detectable in the body after secondary antigen exposure?
24-48 hours
(IgG/IgM) has memory cells.
IgG
(Avidity/Affinity) is the strength of the bond.
avidity
(Avidity/Affinity) is the initial attraction between antigen and antibody.
affinity