
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
WHO IS A CONSUMER?
One who identifies a need or desire acquires a product, and then disposes of the product
• Many people may be involved in this sequence of events. (all are consumers)
• Influencer / Decision Maker / Purchaser / User
• Consumers may take the form of organizations or groups
Consumer behavior
applied social science that focuses on how consumers make decisions, interact with and understand products.
It refers to the entire process of how consumers choose, buy, use, and dispose of products, services, ideas, or experiences to meet their needs and wants.
Acquiring
Buying, leasing, trading, borrowing, gift-giving, finding, stealing
Using
Functional
Symbolic
Disposing
Throw away
Give away
Recycle
Ebay
Offering
A product, service, activity, or idea offered by a marketing organization to consumers
Managers
strategic marketing plans are consumer-focused
Ethicists
advocacy groups, co-ops
Public policy makers
FDA, nutrition information, investigation of misleading ads
Common Mistake: Use of Intuition, Common Sense
— Easier, more vivid than collecting & analyzing
data
Problems w/this approach:
― Make decisions based on few observations
― Biases
― People infer causality from correlation
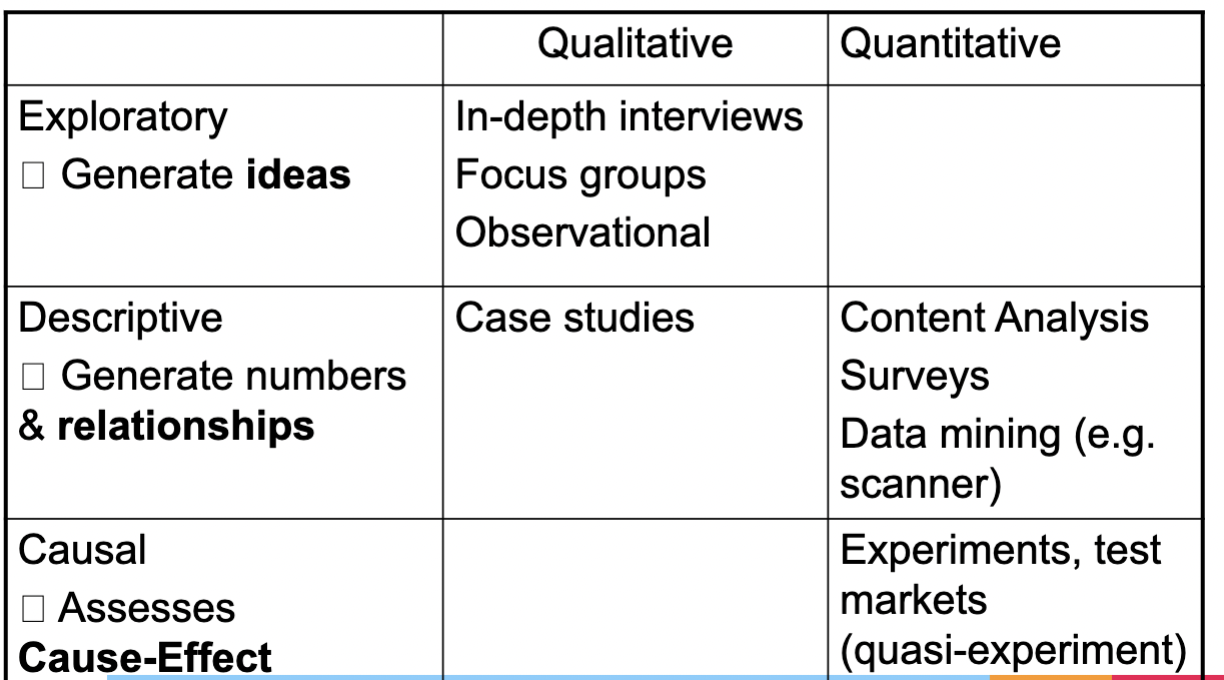
Types of research projects
○ Basic research
■ Research to understand consumer behavior or marketing in general
■ Academic research
○ Applied research
■ Research directed at a specific problem at a specific organization
■ Corporate Research
Primary Data
○ Collected specifically for current purpose
○ Could be internal or external
■ Experiments (lab studies)
■ Quasi-experiments (test markets, coupon studies)
■ Non-experiments (focus groups, observation, projective techniques)
Secondary Data
○ Collected for some other purpose
■ External (Gallup polls, Nielsen, census, etc. )
■ Internal (company records)
*Collect this before primary
*Disadvantages: could be outdated, not what you’re looking for, not specific enough
Focus Group
A group of 6-10 people discuss a marketing issue by sharing their thoughts and reactions. A trained moderator guides the discussion on a product or marketing idea but does not participate.
Observational Research
▷ A technique in which researchers
observe how consumers behave in
real-world surroundings
▷ Most useful when investigating
complex social settings; less useful
for studying well-defined hypotheses
under specific conditions
Test Market
Studies the effectiveness of
one or more elements of the
marketing mix evaluating
sales of the product in an
actual market
Experiements
▷ Consumers randomly assigned to
receive different “treatments”
Elements of Experiments
▷ Requirements to establish
causality:
control/manipulate the cause
(independent variable) and hold
“everything else” constant
the cause has to precede the effect
(dependent variable)
random assignment - makes
experimental groups statistically
equivalent
What tools do we have to collect primary data?
Survey Types
Personal interview surveys
mail survey + phone survey
online survey
Types of Questions
open-ended
close-ended:
■ Yes/No
■ Semantic Differential Scale
■ Likert Scale
Correlation
relationship between two
variables
Causation
one variable producing an effect in
another variable
3 factors necessary for causation
▷ Correlation
▷ Temporal Antecedence (one thing needs to come before the other)
▷ There is no third factor driving both
Spurious Correlation
▷ Spurious = artificial, fake
▷ Danger of data mining
▷ Lots of things are correlated, but not really related
What drives consumer purchase?
▷ Consumers care less about products than you
think they do.
▷ They care about the consequences that the
products enable, which are aligned with
specific underlying motivations
▷ Acquiring a product is a tool that
consumers use to achieve some
goal, value or need.
What is Motivation?
Inner state of arousal, this aroused energy
is directed to achieving a goal
Motivation is enhanced when…
something is personally relevant
▷ Personal relevance is increased when:
○ Consistent with values, goals and needs
○ Increase of consequences in your life
○ Influences self-concept
Types of Needs
▷ Biogenic Needs
▷ Psychogenic Needs
▷ Need for Affiliation
▷ Need for Power/Control
▷ Need for Uniqueness
▷ Utilitarian and Hedonic Needs
▷ Social/Anti-Social/Non-Social Needs
Characteristics of needs
▷ Dynamic! – ever evolving
▷ Exist in hierarchy
▷ Internally or externally aroused
▷ Not always congruent – ○ can conflict
Goal-relevant behavior:
▷ We get motivated for a purpose and
take actions to reach that goal
▷ Goal directed arousal
Motivation is also enhanced when:
▷ Discrepancy between
present state & ideal
state
o Discrepancy creates
tension
o Drive: the larger the
discrepancy, the more
urgency felt, the more
motivation experienced
Needs vs. wants
○ Want: particular form of consumption used to
satisfy a need
■ Need: hunger, thirst, warmth, belonging
■ Want: Dunkin Donuts (vs. food), Coke (vs.
water), Columbia down jacket (vs. a coat),
TikTok (vs. being in person with friends)
Goal Valence
Positively-valued
goal: approach (weight
loss)
○ Negatively-valued
goal: avoid (odor)
■ Deodorants &
mouthwash
Measuring Needs
Attributes > Consequences > Values
A means-ends chain is a knowledge
structure that links consumers’
knowledge about product attributes with
their knowledge about consequences and
values
Perceived Risk
The extent to which a consumer is uncertain about
the consequences of buying, using or disposing of an
offering
Ability to Act – depends on:
▷ Knowledge/Experience
▷ Cognitive Style
▷ Intelligence
▷ Education
▷ Age
▷ Money
Opportunity is determined by:
▷ Time
▷ Distractions
▷ Complexity of Information
▷ Amount of Information
▷ Repetition of Information
Marketing Implications
motivation
ability
opportunity
*Advertisers leverage Motivation, Ability and Opportunity (MAO)
to involve and engage target customers
Affective responses
Emotional responses are key to effective marketing. Emotions are deeply rooted and influence decision-making at every stage, making their impact more complex than just liking or disliking an ad
Arousal
our moods gives us a cue of when to be motivated
Mere exposure effect
when people develop a preference for something just because they see or experience it repeatedly.
Benefits of Repetition
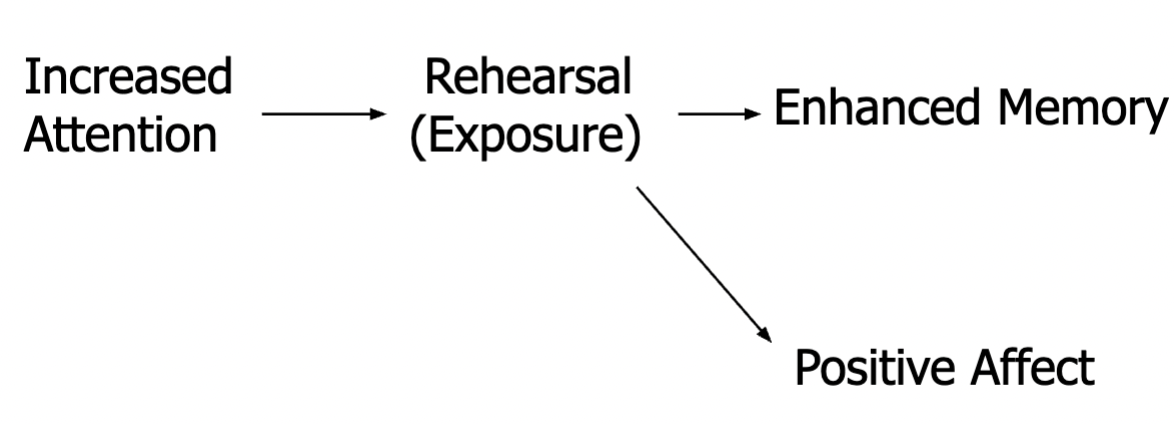
Exposure
The process by which the consumer comes into physical
contact with a stimulus – we have the possibility of noticing
the information
Selective Exposure
marketers control when/where consumers encounter the brand
What gets our attention?
● Prominence (size)
● Color
● Position
● Novelty (surprising, unexpected)
● Loud
● In general: stimuli that contrast with what’s around them
Perception
• Process of developing an interpretation of a stimulus
🡪 Deciding what a stimulus means
• Registration of stimuli by one of the 5 senses
• How we select, organize and interpret (abstract) data
• In essence, how we view the world
Methods of Perception
Vision – size and color
Hearing – Muzak as a stimulus, jingles
Taste –clear individual and cultural differences,
subjective
Smell – Smells affect moods, can be a mktg tool
(e.g., Cinnabon, Candles at Anthropolgoie, etc.)
Touch - can stimulate or relax customers; people
want to touch products before they buy