SCIENCE TEST
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Prokaryotic
Simple organism composed of one cell with no nucleus, simple, contains no organelles
Eukaryotic
Larger organisms made of one or more cells with a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
Autotrophic
Creates their on energy, either from the sun or chemical reactions
Heterotrpic
Gets energy from consuming other organisms
Derived characteristics
a trait that arose in the most recent common ancestor of a particular lineage and was passed along to its descendants.
Node
The point on a cladogram where the lines intersect, indicates the location of the last common ancestor
Clade
a group of ALL the organisms believed to have evolved from a common ancestor
Common ancestor
An organism or group of organisms that is shared by multiple lineages
Microbiology
A field of science that studies small organisms
Pathogen
Anything that makes you sick
Flagella
A long whip like appendage that allows single celled organisms to move
Antibiotics
A medication that treats bacteria infections
Caspid
The outside shell of a bacteria
Virus
A small non living infectious particle, containing some kind of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) and surrounded by a protein coat
Lytic cycle
One of the reproductive cycles of a virus, where a virus injects its DNA into a host cell but DOES NOT make more copies
Lysogenic cycle
One of the reproductive cycles of a virus, where the viral DNA in a host cell is activated to create more viruses
Vaccine
A method of preventing viral illness.
Levels of classification from browsing to most specific
Broadest Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Specific Species
Human scientific name
Homo sapien or homo sapien
Chimpanzee scientific name
Pan troglodytes
Bonobo scientific name
Pan paniscus
African Wild Dogs (Lycaon pictus), are in the family Canidae. Do you think they are more closely related to Arctic Foxes or Dogs based on what you know about them? (Try to think of how else we might sort these based physical/geographical characteristics)
Since they share the same Family name for both foxes and dogs, and neither have the same genus name we would have to rely on other traits such as physical or geographical indicators. Since dogs are more closely related in size, shape and location to african wild dogs, they likely are more closely related.
Eubacteria
Prokaryotic |
Uni |
Yes, contains peptidoglycan |
Both |
asexual |
Mostly sessile, some motile |
Can make us sick, most abundant kingdom |
EXAMPLES: STAPH, MRSA, Streptococcus |
Archaebacteria
prokaryotic |
Uni |
contains uncommon lipids, lack peptidoglycan |
Both |
Asexual |
Mostly sessile, some motile |
Extremophiles, cannot make us sick |
EXAMPLE methanobacteria |
Protista
Eukaryotic |
mostly unicellular |
Cellulose or other sugars, or none |
Both |
Both |
motile/sessile |
Catch all category |
Example: Euglena |
Fungus
Eukaryotic |
mostly multicellular |
Yes, contains Chitin |
Heterotroph (Decomposers) |
Both |
Sessile |
Mostly land based, can reproduce using spores |
EXAMPLES: Mushrooms, yeast |
Plant
Eukaryotic |
Multi |
Yes, contains Cellulose |
Autotrophs |
sexual/asexual |
Sessile |
Cannot move, mostly green (Chlorophyll) |
EXAMPLES: Trees, flowers |
Animal
Eukaryotic |
Multi |
NO |
heterotroph |
Both (Primarily sexual |
Motile |
All motile, live on both land and in the water |
EXAMPLES Us, Dogs, Fish, Insects |
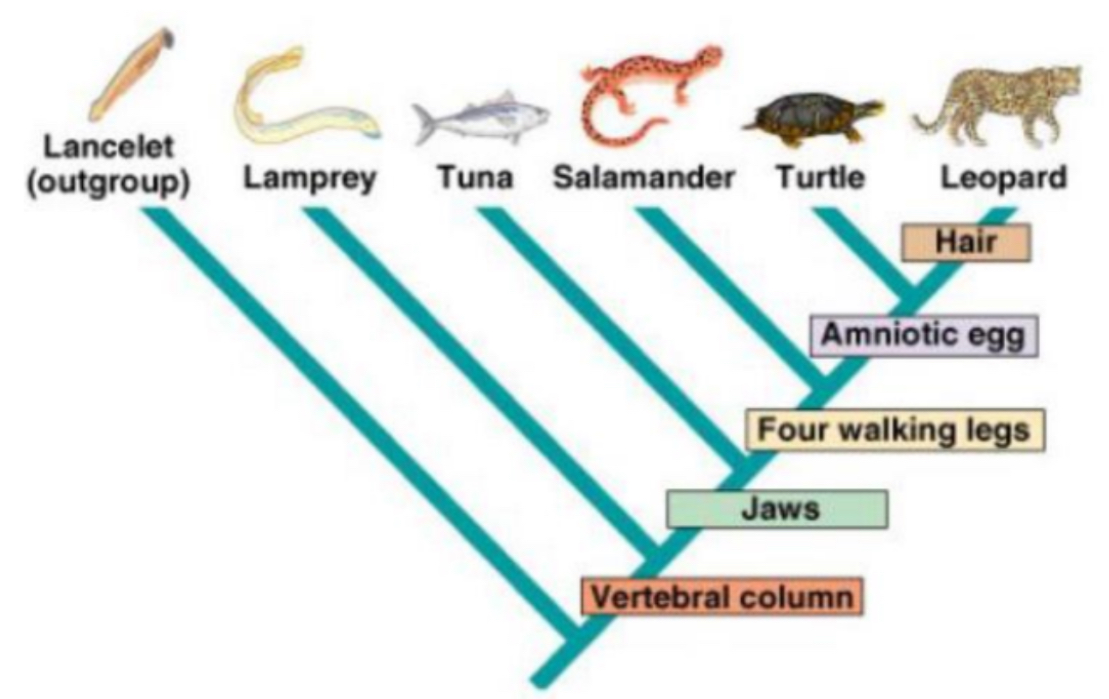
What traits separates lampreys from tuna on this cladogran?
Jaws
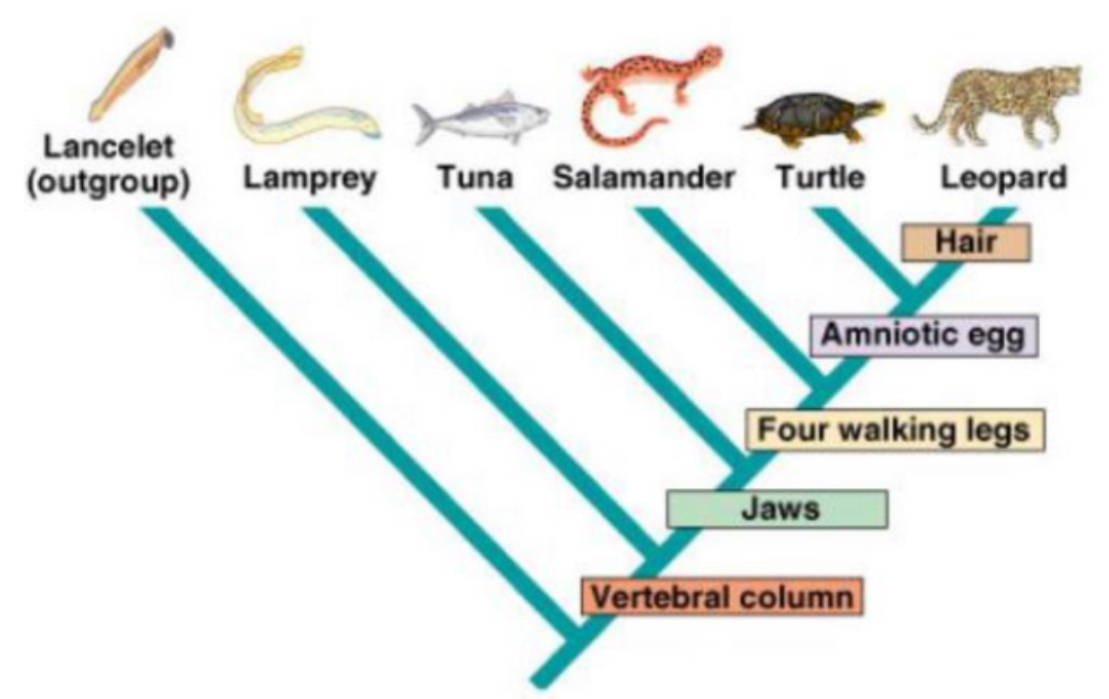
What separates a salamander from a turtle?
Amniotic Egg
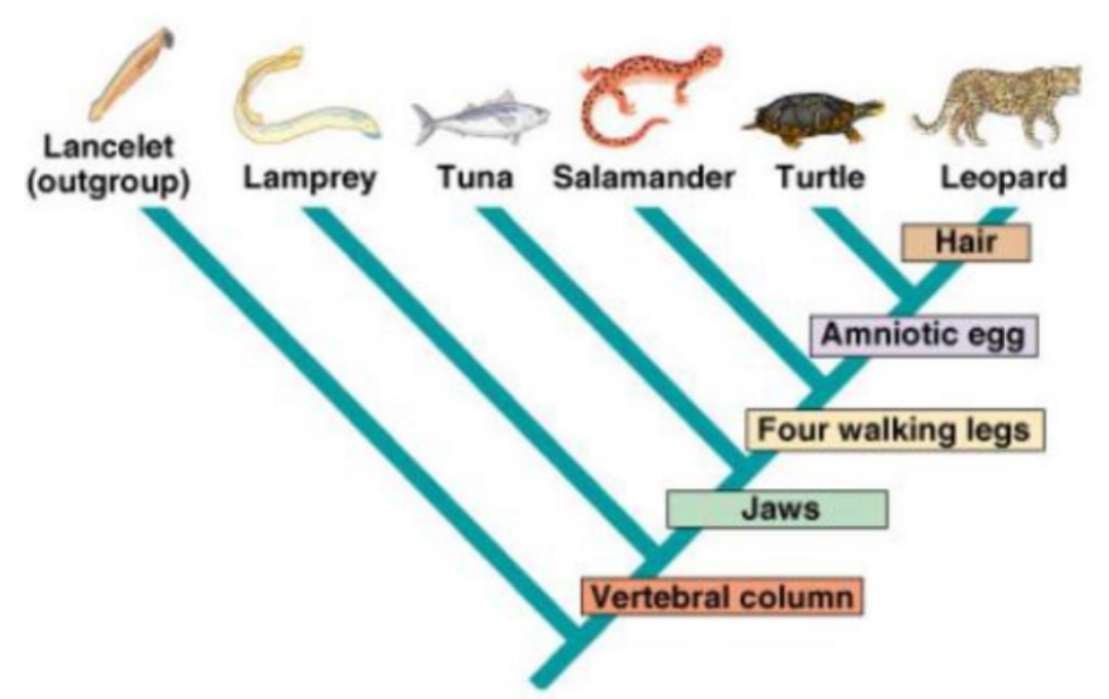
Which organism is most related to the leopard?
Turtles
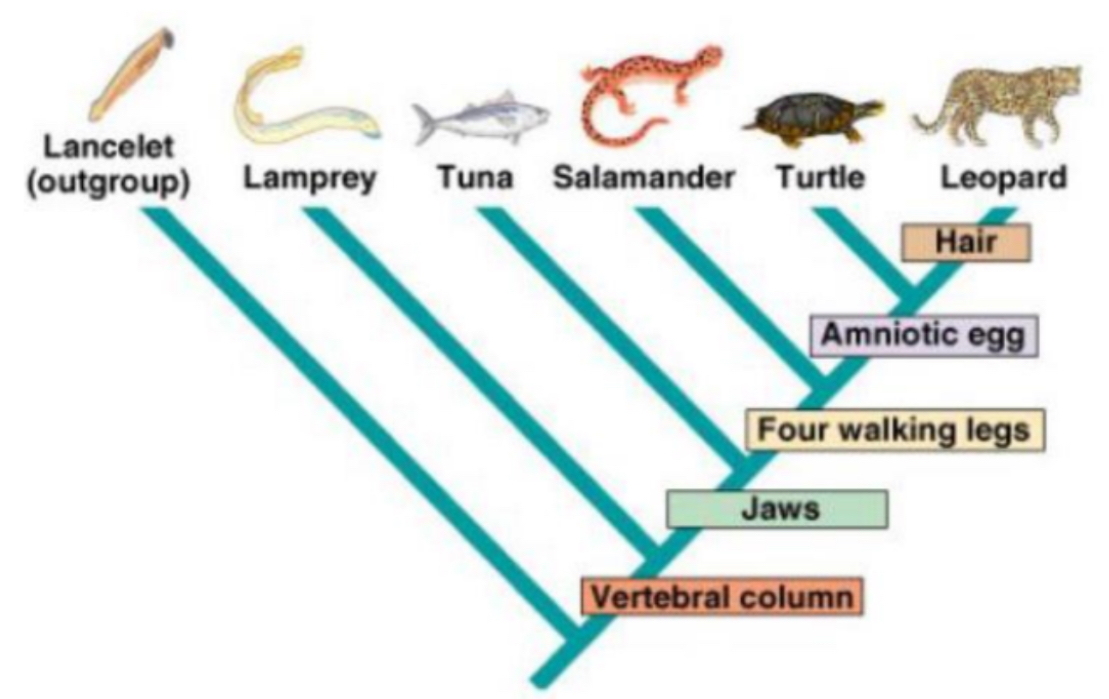
Which organisms DNA will differ the most from the leopard and why?
Lancelet, farthest away on the cladogram
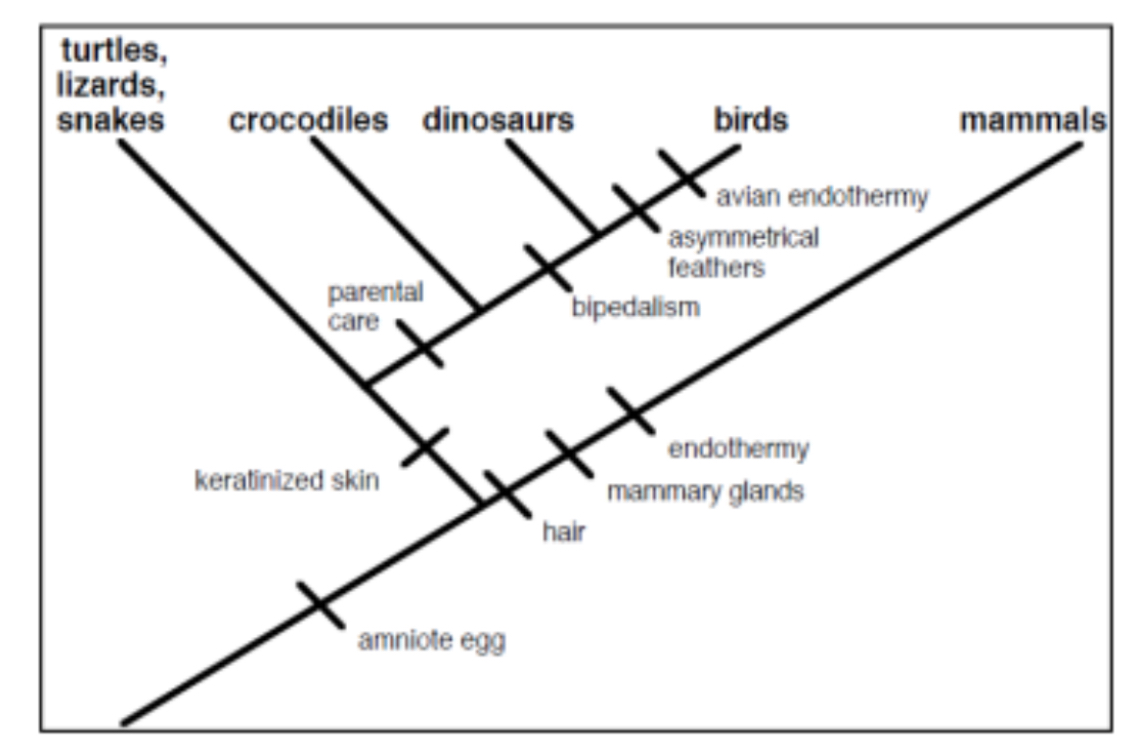
Name five derived traits possessed by birds?
Amniotic Egg, Keratinized skin, parental care, bipedalism, asymmetrical feathers
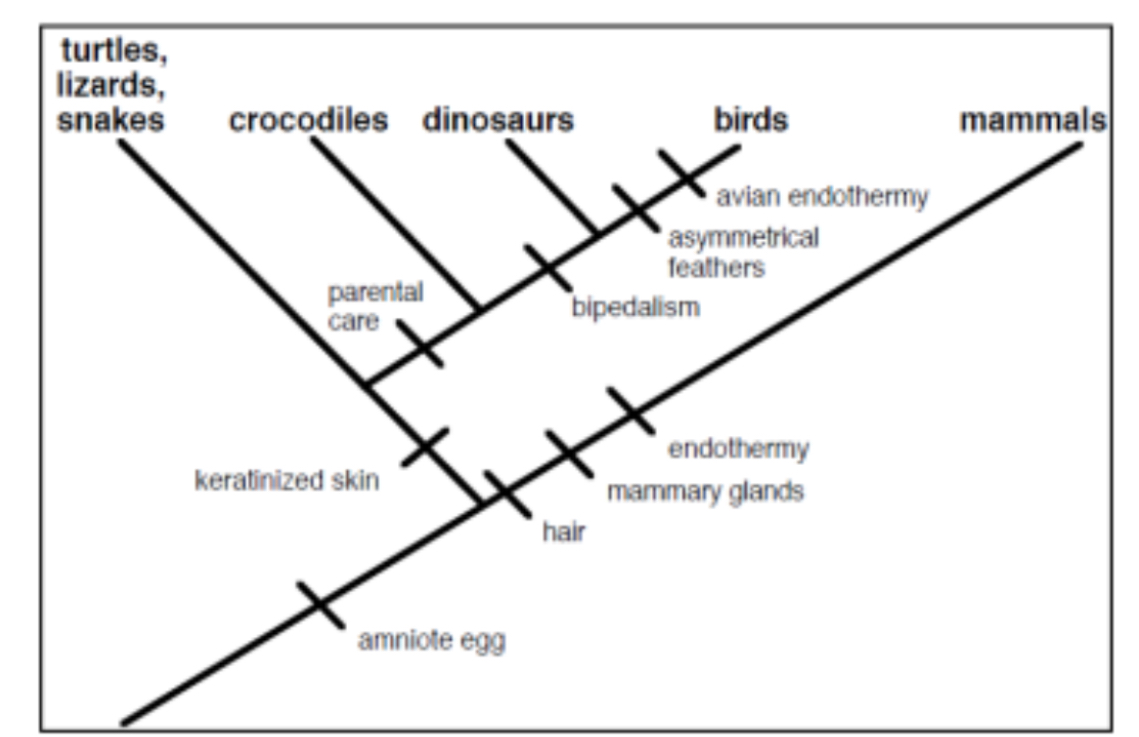
Name derived traits possessed by reptiles/birds (the group comprised of turtles, lizards, snakes + crocodiles + dinosaurs + birds; including their common ancestors)
Amniotic egg, keratinized skin
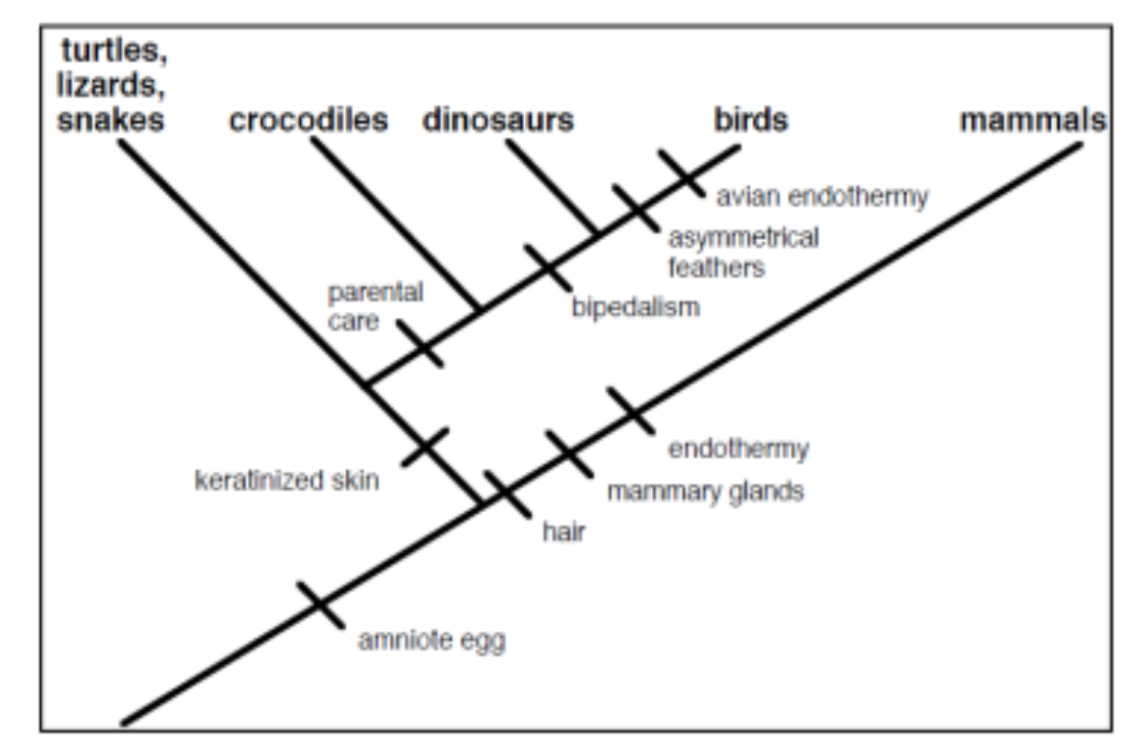
True or False: On their own, crocodiles, dinosaurs, and birds form a clade.
True but should include their common ancestors as well
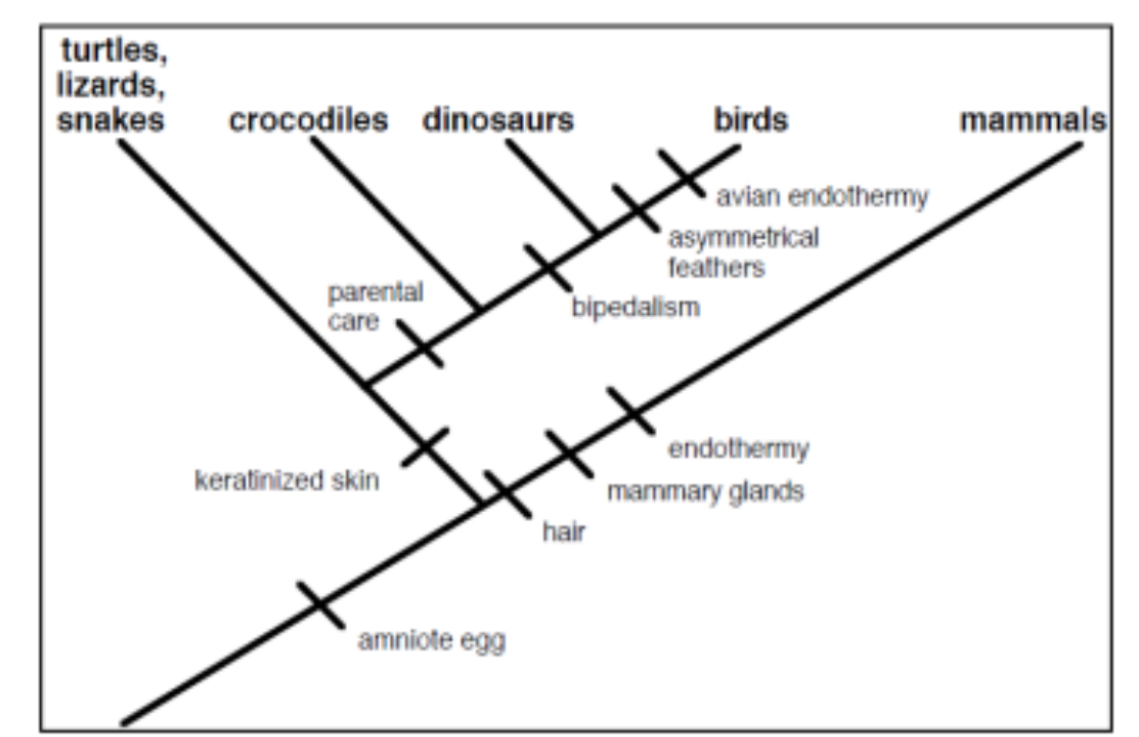
True or False: On their own, turtles, lizards, snakes, crocodiles, and dinosaurs form a clade.
False
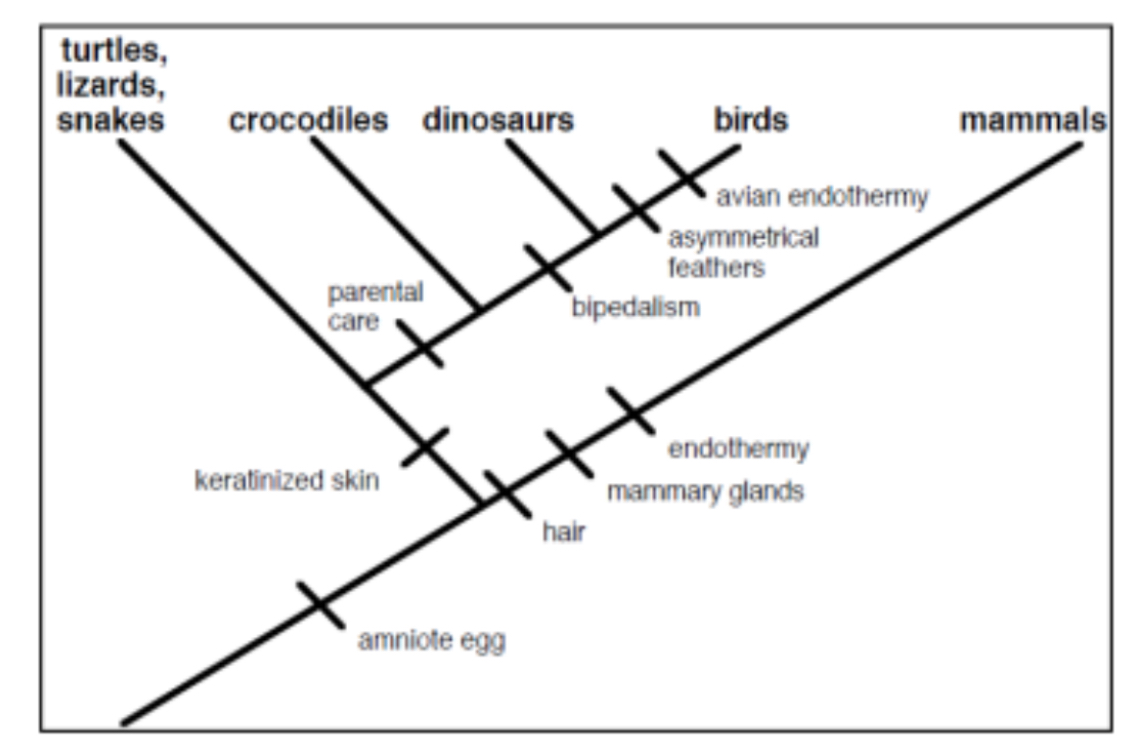
According to the cladogram, which character evolved first: the amniote egg or hair?
Amniotic egg
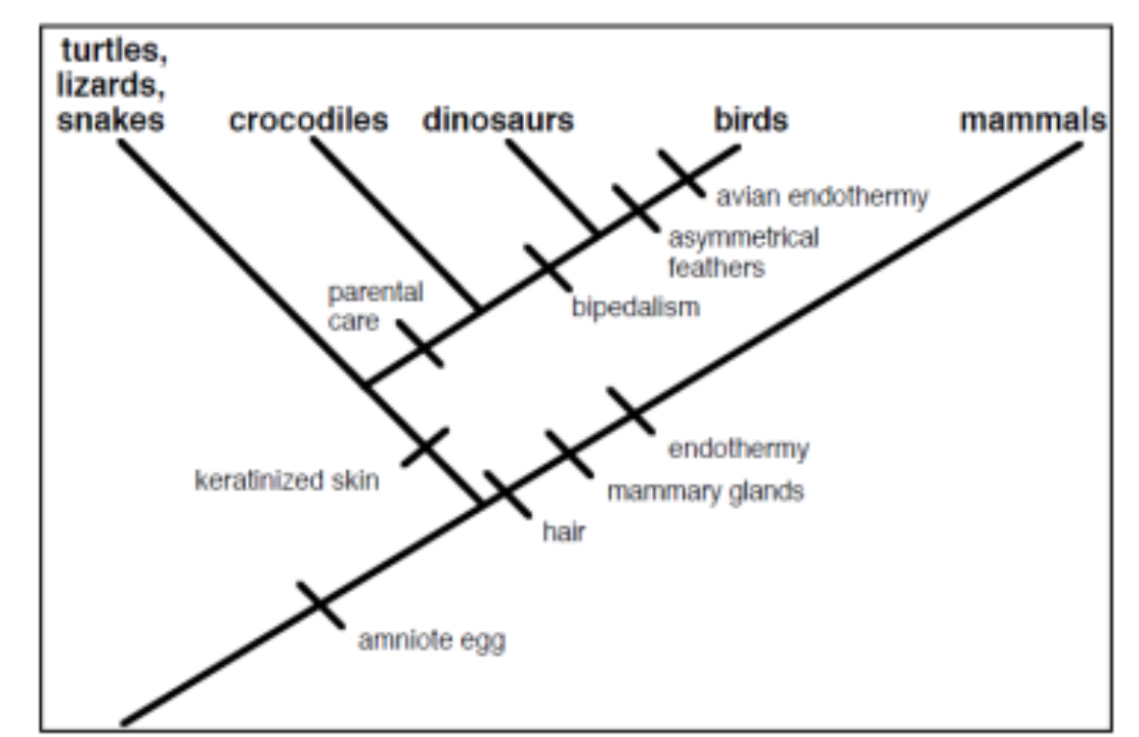
According to the cladogram, which character evolved first: keratinized skin or bipedalism
Keratinized skin
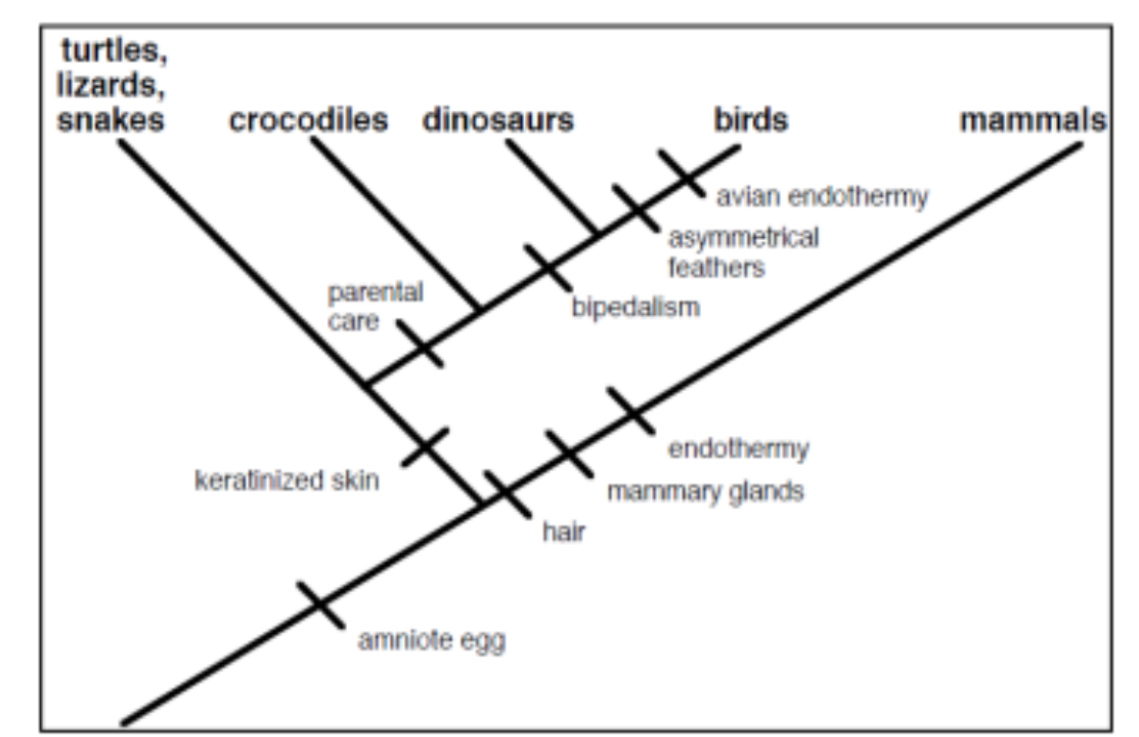
On the cladogram, where is the point (i.e. node) that represents the most recent common ancestor of crocodiles, dinosaurs and birds. (indicate by stating the derived characteristics on either side of the node).
Between parental care and bipedalism
Bacteria characteristics
Nucleus? |
How do they reproduce? |
Can it cause disease? |
What is its structure? Aka what is it made of |
Living or non-living? |
Size? |
Beneficial? |
How can it be treated? |
No |
Asexually through binary fission, can also do conjugation |
Yes |
Prokaryotic Cell, has an outside capsid |
Living |
Small for cell |
Yes |
Antibiotics |
Viruses characteristics
Nucleus? |
How do they reproduce? |
Can it cause disease? |
What is its structure? Aka what is it made of |
Living or non-living? |
Size? |
Beneficial? |
How can it be treated? |
No |
By infecting a host cell that builds more viruses for them |
Yes |
Nucleic acids surrounded by a protein coat |
Non Living |
Even smaller than a cell |
Somewhat, can help drive evolution |
Vaccines are preventative, anti virals can prevent replication |
Explain in simple terms how viruses infect host organisms (you should describe both the lytic and lysogenic cycle)
Example answer: A virus would begin by attaching to a host cell, it would then inject its genetic material into the host. Once in the cell it would likely enter the lysogenic cycle, where its DNA is added to the host's DNA. The DNA is then replicated everytime the cell replicates. At some point the viral DNA is triggered on and thus the cell enters the lytic cycle. During the Lytic cycle the cell builds more viruses using the hidden viral DNA. These viruses then eventually cause the cell to rupture, thus releasing more viruses in the environment.
Are viruses living or nonliving? What evidence do you have to support your answer?
Example answer: Non Living, they lack several characteristics of life such as being made of cells, maintaining homeostasis, using energy.
How do any of the experiments we discussed regarding germ theory (aka, Koch or Pasteur) help support the principles of the scientific method?
They demonstrate that through testing we can disprove previously accepted theories like spontaneous generation and instead develop new and changing ideas.