W4L9: Part 1: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution SN2
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Nucleophilic substitutions
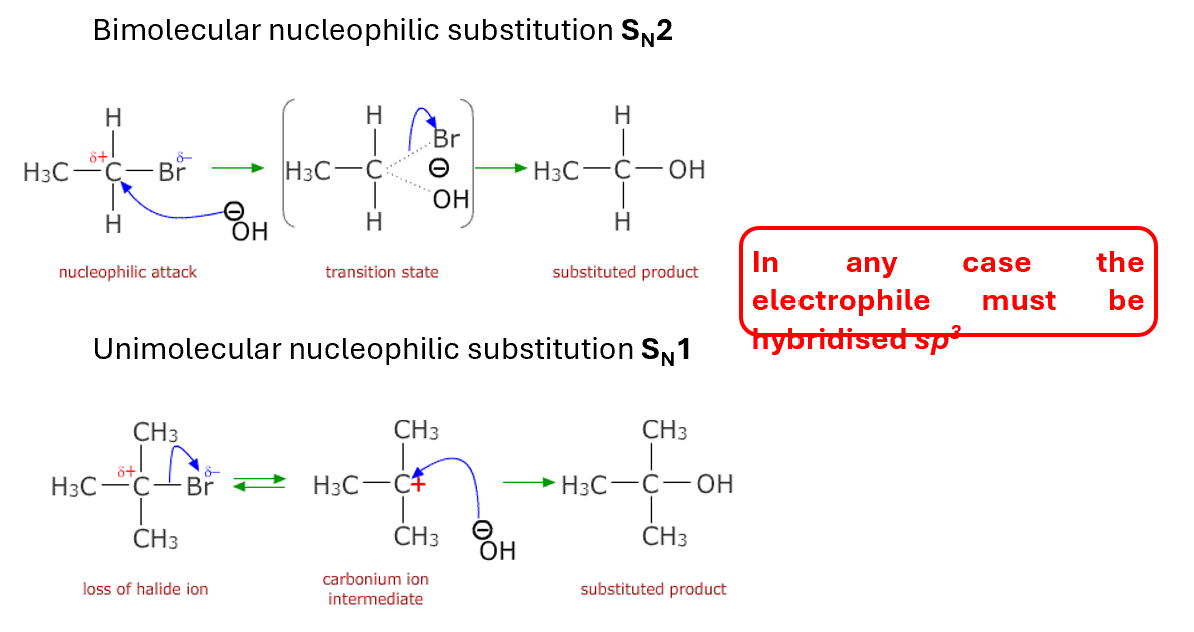
Two mechanisms are possible for substitution at a saturated carbon
Molecularity determined by the number of species in RDS
Tertiary more stable and can stay for a long time
For any nucleophilic substitution we need to keep into consideration:
Structure of the reagent (halogeno-alkanes are very common)
Type of solvent (polar aprotic, polar protic…)
Strength of the nucleophile
Number of molecules involved in the transition state (Rate of the reaction)
Leaving group (LG)
Stereochemistry of the substitution
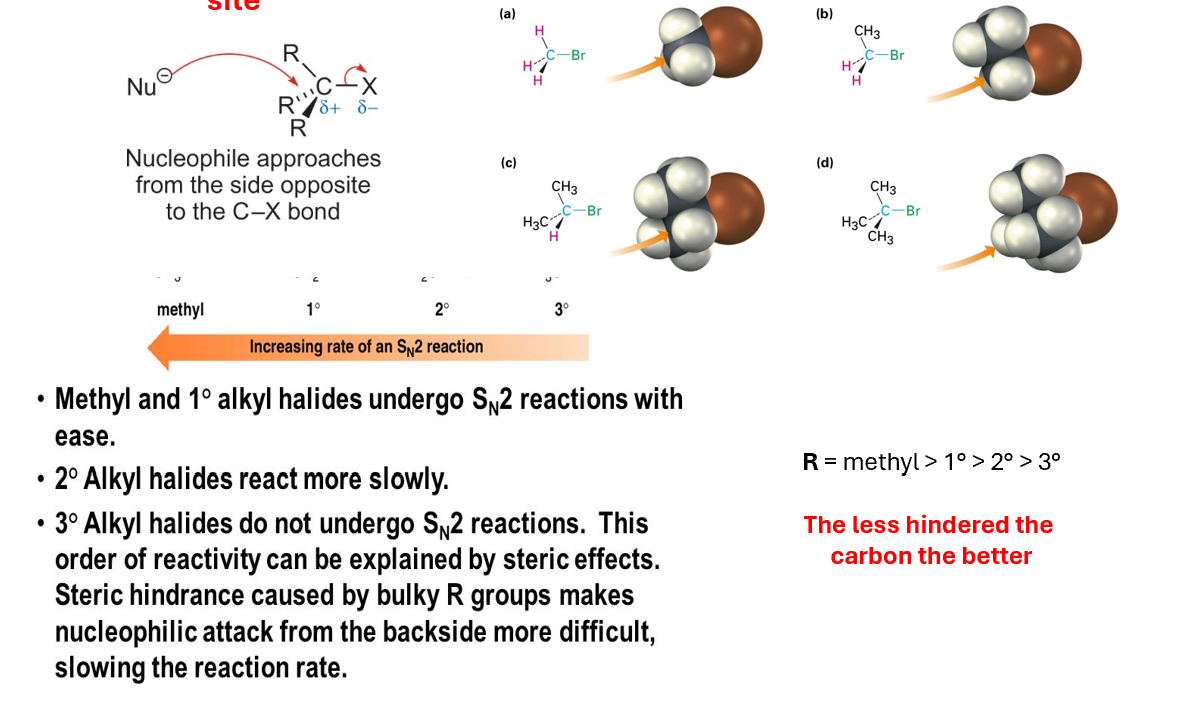
Structure of reagent influencing SN2
The reagent must not be hindered at the electrophilic site
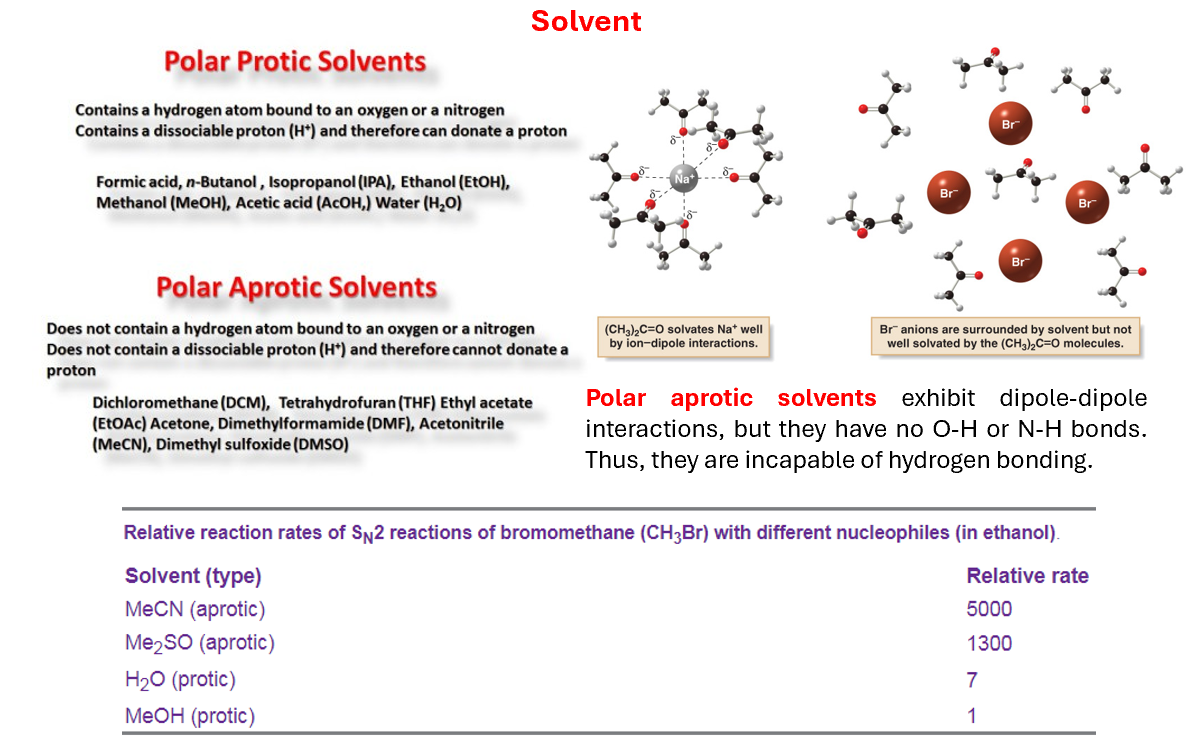
Solvent influencing SN2
Polar aprotic solvent cannot solvate the “naked” negative ion, so it becomes more active in the substitution, whereas the polar protic solvent can solvate both ions via hydrogen bonding, making the nucleophile less available
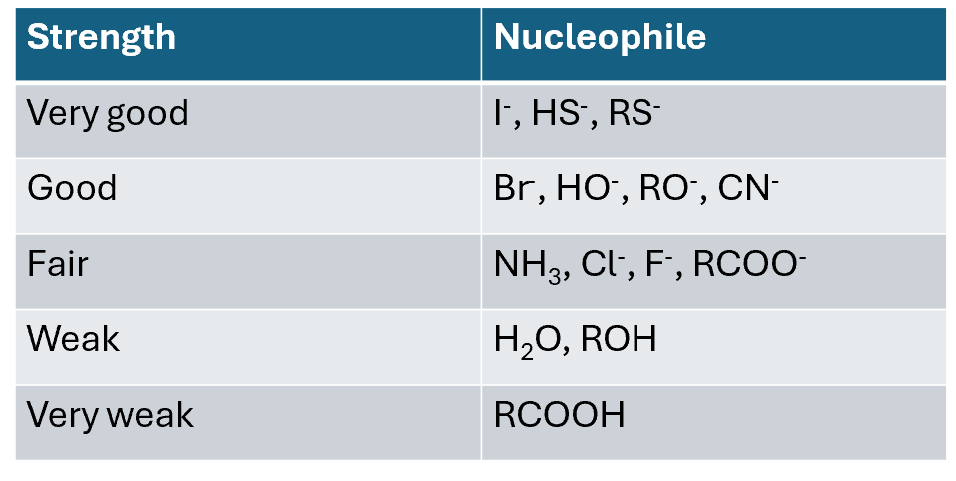
Nucleophile strength influencing SN2
Stronger nucleophiles react faster in SN2 and strong bases are generally good nucleophiles, but not all strong nucleophiles are necessarily strong bases
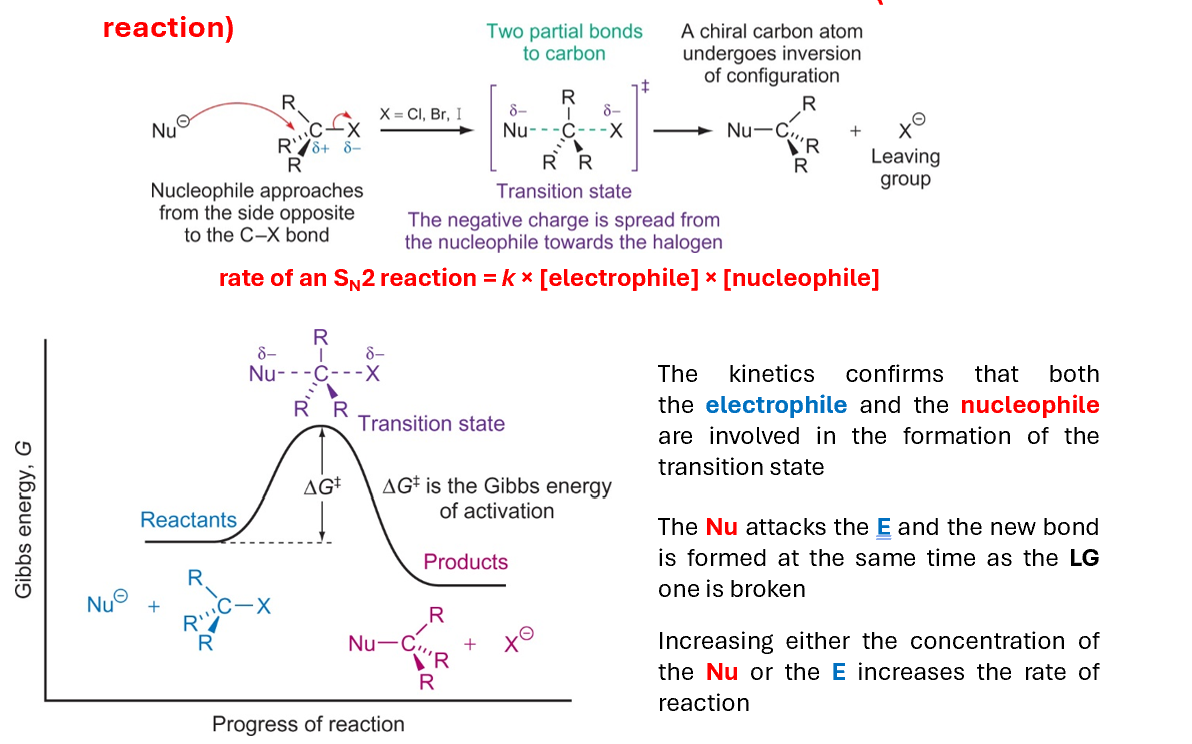
Molecules in transition state influencing SN2
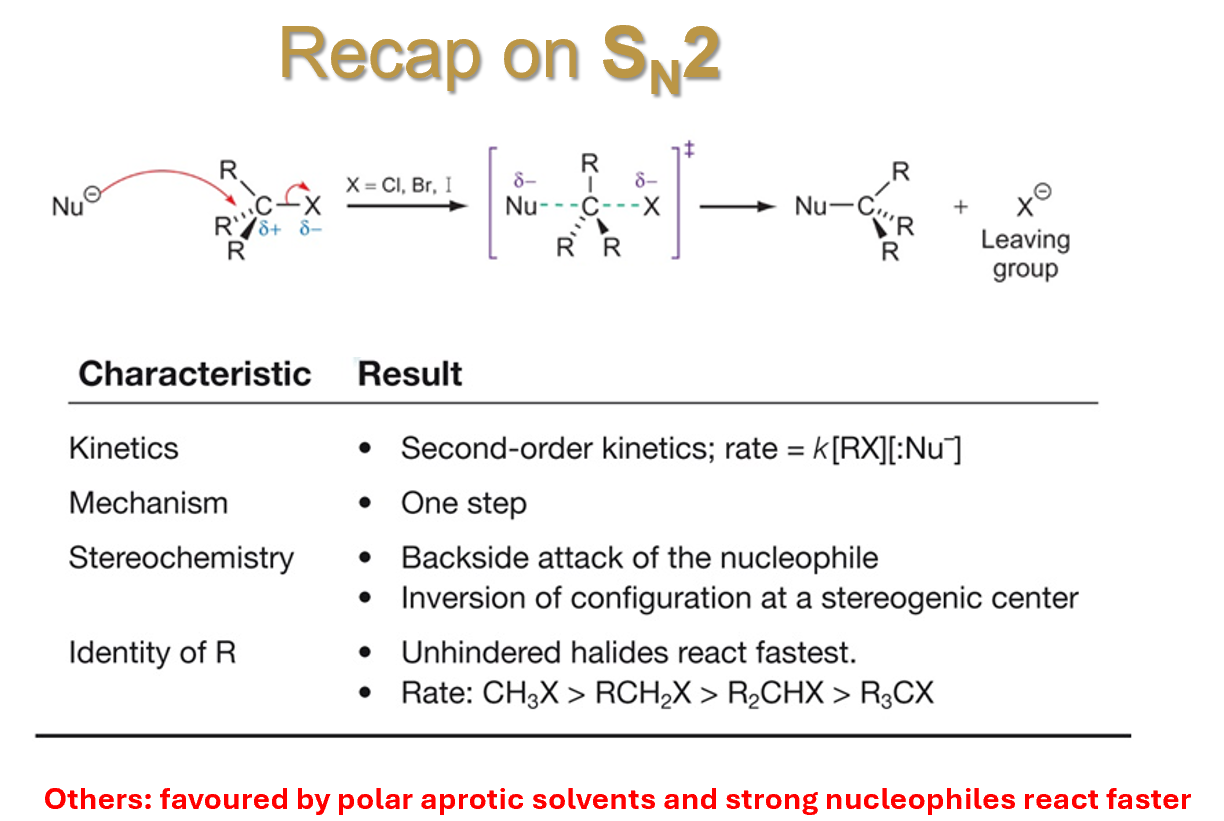
The reaction mechanism proceeds through a transition state in which both the nucleophile and leaving group are present. It means that the rate of the reaction is influenced by the concentration of both nucleophile and electrophile
The kinetics confirms that both the electrophile and the nucleophile are involved in the formation of the transition state
The Nu attacks the E and the new bond is formed at the same time as the LG one is broken
Increasing either the concentration of the Nu or the E increases the rate of reaction
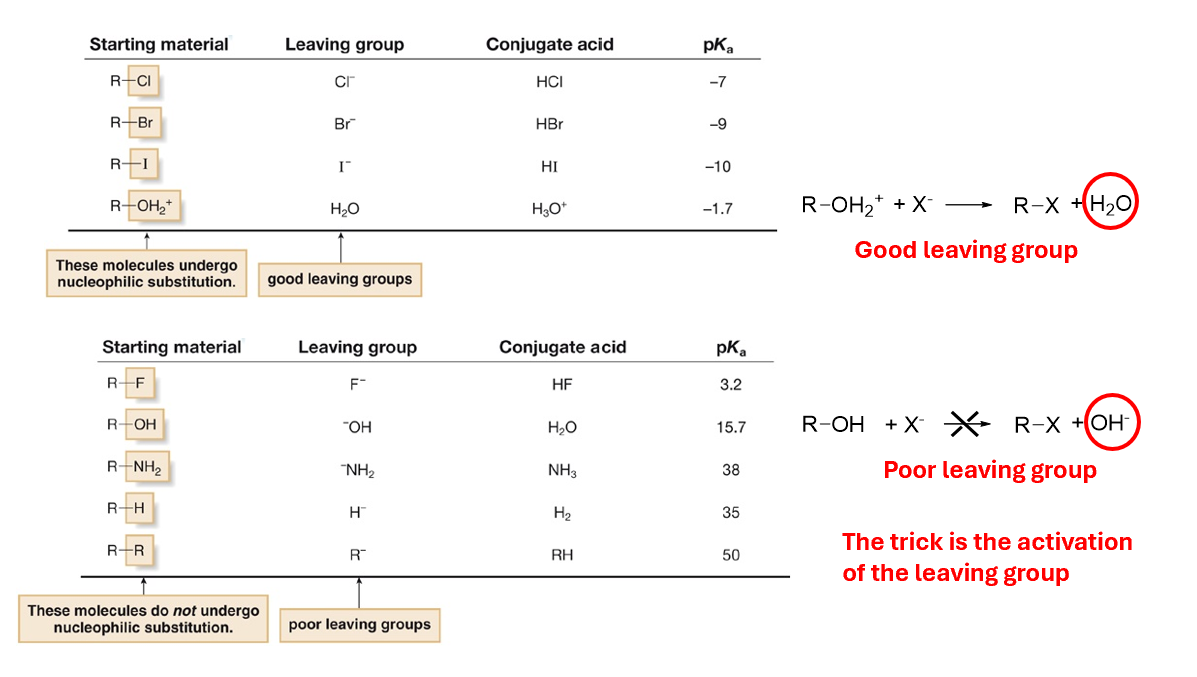
LG influencing SN2
The effect of the pka of the conjugated acid is very important
low pKa leaving group undergo nucleophilic substition
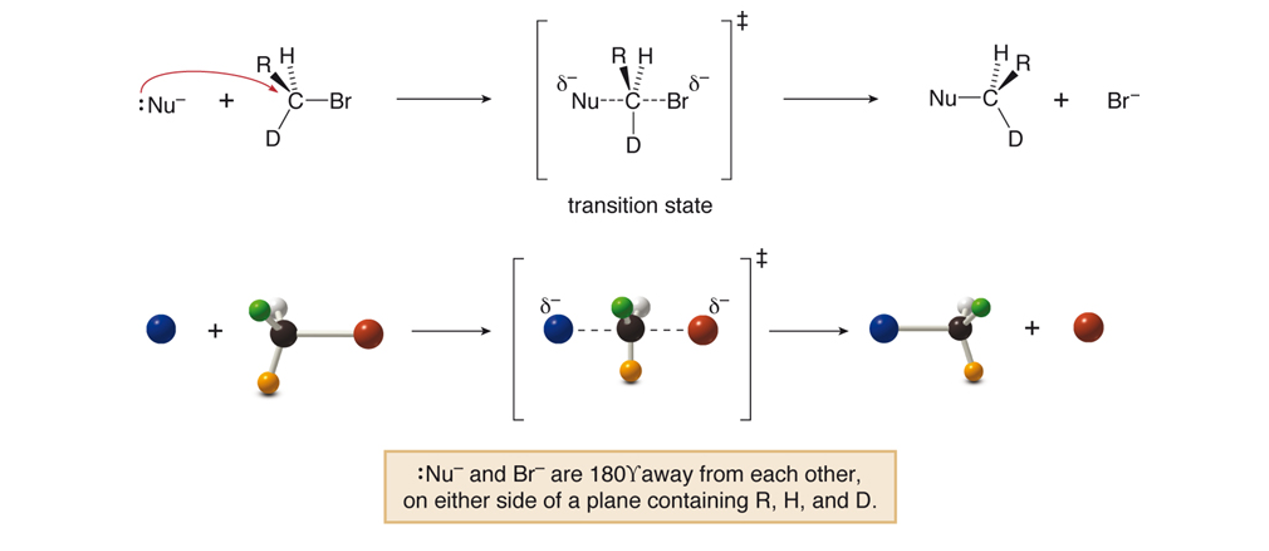
Stereochemistry of the substitution - influencing SN2
All SN2 reactions proceed with backside attack of the nucleophile, resulting in inversion of configuration at a stereogenic center.