Biological molecules - enzymes, DNA, water, ATP
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
what do enzymes do?
lower the activation energy required to drive a reaction, enabling conditions to be met
how do enzymes lower activation energy?
they form an enzyme-substrate complex
why are enzymes necessary?
molecules must combine with sufficient energy for the reaction to happen so the bonds are put under sufficient strain
intracellular enzymes
work inside cells eg DNA polymerase
extracellular enzymes
secreted by cells and work outisde cells eg amylase
anabolic reactions
enzymes bring the substrate molecules together to build up molecules, reducing repulsion between molecules
catabolic reactions
enzyme active site affects/strains the bonds in substrate so they’re easier to break
how do enzyme bonds work?
substrate forms temporary bonds with amino acids in active site
what is the active site determined by?
the enzymes tertiary structure
lock and key mechanism
substrate molecules bind with active site as a consequence of complementary shapes and the enzyme produces environment necessary but remains unchanged
lock and key limitation
when other molecules bind to the enzyme at other places than the active site, the activity of the enzyme is altered
induced fit hypothesis
enzymes have 3d flexibility
binding of substrate induces enzyme to change shape
so no exact fit when substrate is bound
as it changes shape, enzyme puts strain on substrate
strain distorts particular bonds in substrate
as temperature increases what happens to rate of reaction?
it increases because there is more kinetic energy and so more collisions and more enzyme-substrate complexes
what happens when temperature is too high?
enzymes denature because bonds that stabilise the tertiary structure are broken and protein unravels and loses shape so the active site changes
what happens when pH is too high or too low?
H+ and OH founds in acids and alkalis can disrupt ionic and hydrogen bonds that hold tertiary shape so denatures
substrate concentration?
as it increases, rate of reaction increases until excess of substrate concentration where maximum reaction rate is maintained
what is the limiting factor for substrate concentration?
enzyme concentration
enzyme concentration?
rate of reaction is directly proportional
competitive inhibitors
molecule competes with normal substrate for active site
what happens if the substrate concentration increases with a competitive inhibitor?
the inhibitors are overcome due to competition and maximum rate is reached
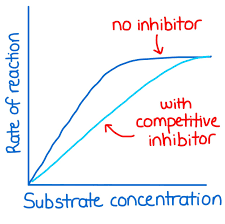
non competitive inhibitors
attach away from the active site and the inhibitor changes the shape of active site preventing induced fit
what happens if the substrate concentration increases with a non competitive inhibitor?
effect of inhibitor is not overcome and there is no change
what does RNA do in all living cells?
transfers genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes
what are ribosomes formed from?
RNA and proteins
examples of polymers of nucleotides
RNA and DNA
what are the components of DNA?
deoxyribose, a phosphate group and an organic base
what are the 4 organic bases in DNA?
adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine
what are the components of RNA?
ribose, a phosphate group and an organic base
what are the 4 organic bases in RNA?
adenine, cytosine, guanine and uracil
what does a condensation reaction between 2 nucleotides form?
a phosphodiester bond
whats a nucleotide made up of?
phosphate, pentose sugar and nitrogen containing base
how do nucleotides run?
antiparallel - look in notes about 3 prime stuff
4 ways RNA differs from DNA
sugar is ribose sugar
uracil replaces thymine as a base (pairing with adenine)
nucleotides form a single polynucleotide strand
RNA strands are much shorter
why did scientists doubt that DNA held the genetic code?
it has a relatively simple composition
why does DNA replicate?
before cell division so that each new cell has full amount of DNA
what is the method of DNA replication called?
semi-conservative replication
what does enzyme DNA helicase do in the first step?
break the hydrogen bonds between bases on the two polynucleotide DNA strands making the helix unwind to form 2 single strands
what do the original strands do in step 2?
act as template for new strand with complementary base pairings meaning that free floating DNA nucleotides are attracted to their complementary exposed bases on original template strand
what catalyses the condensation reactions which join the nucleotides of the new strand together and what forms?
DNA polymerase and hydrogen bonds are formed between the bases on the original and new strands
why is the new strand made in a 5’ to 3’ direction?
the active site of DNA polymerase is only complementary t the 3’ end of the new strand
who’s experiment validated the semi conservative theory?
Meselson and Stahl
what isotopes were used in the experiment?
nitrogen (as DNA contains it) , heavy ^15N and light ^14N
how was the experiment prepared?
2 samples of bacteria were grown for many generations, one in a nutrient broth containing light and one heavy nitrogen
as the bacteria reproduced they took up nitrogen to help make nucleotides so it gradually became part of bacteria’s DNA
then spun in centrifuge and heavy settled low
then bacteria grown in heavy taken out and placed in light for one round of DNA replication
results of experiment (pic)
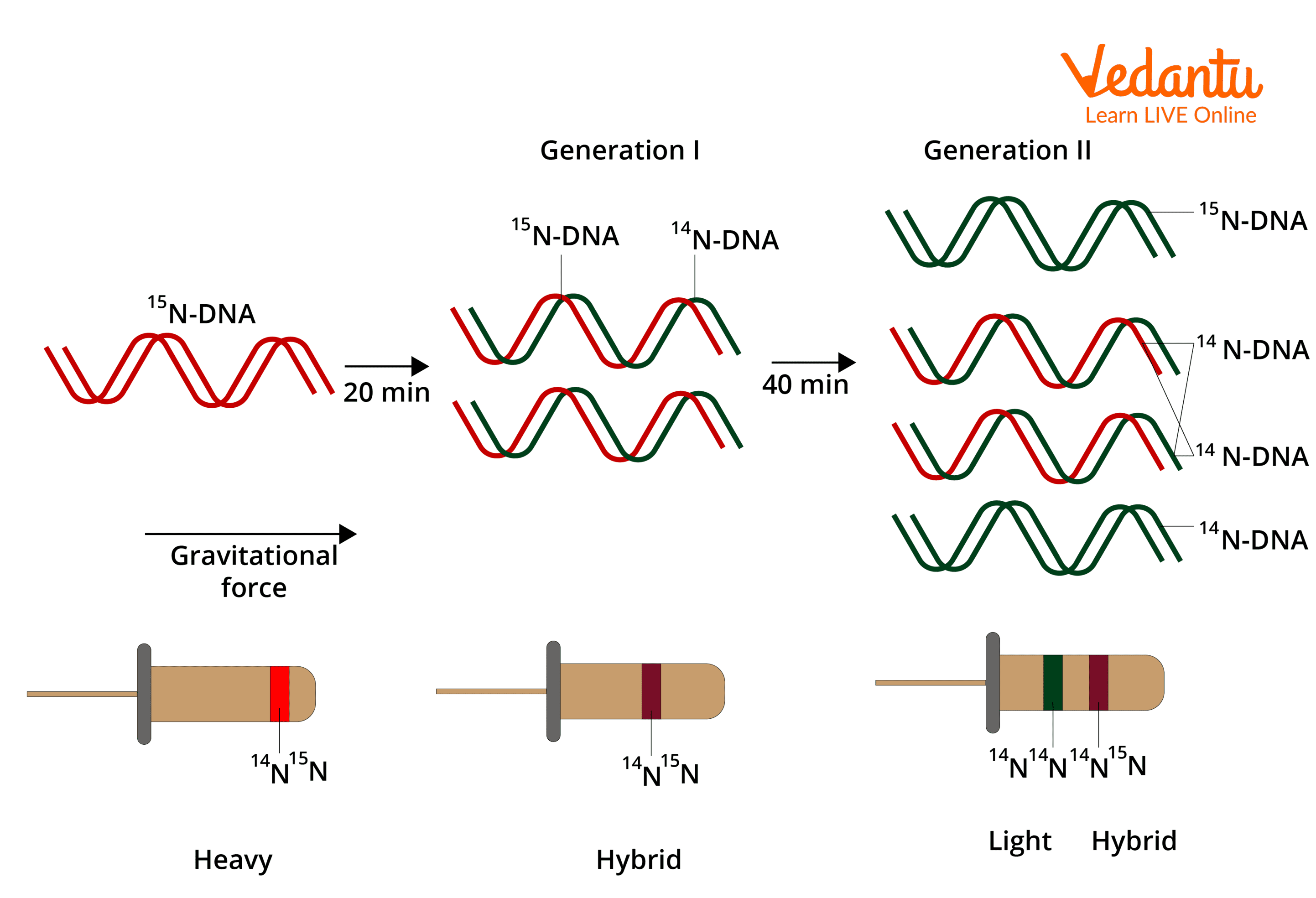
what would have happened if the conservative theory was correct?
the original heavy DNA would still be together and settle at the bottom and the new light DNA would settle at the top
what does ATP stand for?
adenosine triphosphate
what is the structure of this nucleotide derivative?
nucleotide base adenine, ribose sugar and 3 phosphate groups
where is ATP made and stored?
made from energy released from glucose and stored in high energy bonds between the phosphate groups
what is ATP broken down into?
ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and Pi (inorganic phosphate)
what reaction is the breakdown of ATP and what catalysed it?
hydrolysis reaction where phosphate bond is broken and energy is released catalysed by ATP hydrolase
what can ATP hydrolysis do?
couple to other energy required reactions meaning the energy released can be used directly to the coupled reaction rather than being lost as heat
what can the inorganic phosphate do?
phosphorylate other compounds often making them more reactive
how is ATP resynthesised?
by the condensation of ADP and Pi catalysed by ATP synthase during photosynthesis or respiration
what is the polarity of water?
water is a polar molecule with slight negative charge on one side and slight positive on the other
why are there hydrogen bonds between molecules of water?
sightly negative charged oxygen atoms of water attract the slightly positive hydrogen atoms
how does water help in metabolic reactions?
it is a metabolite which means its involved in many reactions like hydrolysis and condensation
how is being a solvent useful for water?
living organisms can take up useful substances dissolved in water and these can be transported around the organisms body
why is water having a high heat capacity good?
it can buffer changes to temperature meaning that water doesn’t experience rapid temperature change in habitats and in organisms helping to maintain a constant body temperature
why is having a high latent heat of vapourisation good?
there is a cooling effect with little loss of water through evaporation because it takes a lot of energy to break hydrogen bonds between water molecules so lots of energy is used up
what is cohesion and why is water cohesive?
the attraction between molecules of the same type which molecules have because they are polar
why is it god that water is very cohesive?
this supports columns of water in the tube-like transport cells of plants and produces surface tension where water meets air
where do inorganic ions occur?
in solution in the cytoplasm and body fluids of organisms, some in high concentrations and others in very low concentrations
what are inorganic ions?
ions that don’t contain carbon
where are iron ions found?
in haemoglobin and it is the molecule that binds to oxygen
what are hydrogen ions used in?
pH based on the concentrations of it and enzyme controlled reactions are all affected by this
what are sodium ions used in?
the co transport of glucose and amino acids
what are phosphate ions used in?
components of DNA and ATP