Exam Lecture Number 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:25 PM on 4/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
165 Terms
1
New cards
2
New cards
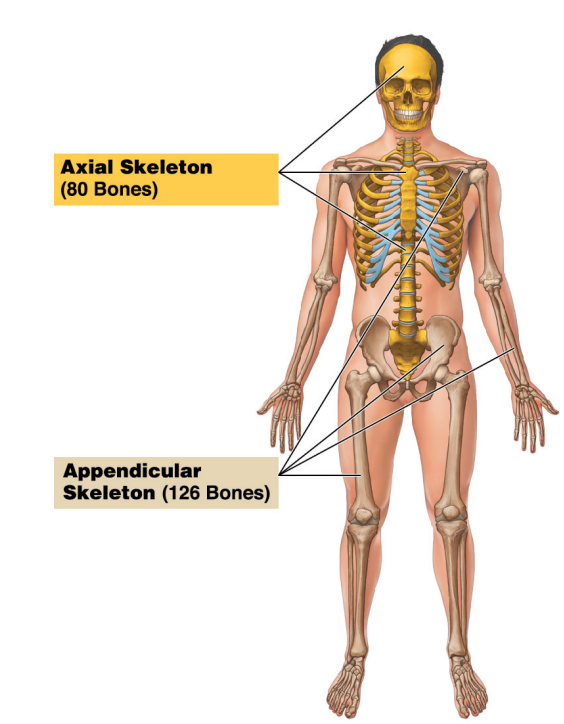
What bones are part of the Axial Skeleton?
It consists of bones of the skull, thorax, and vertebral column.
3
New cards
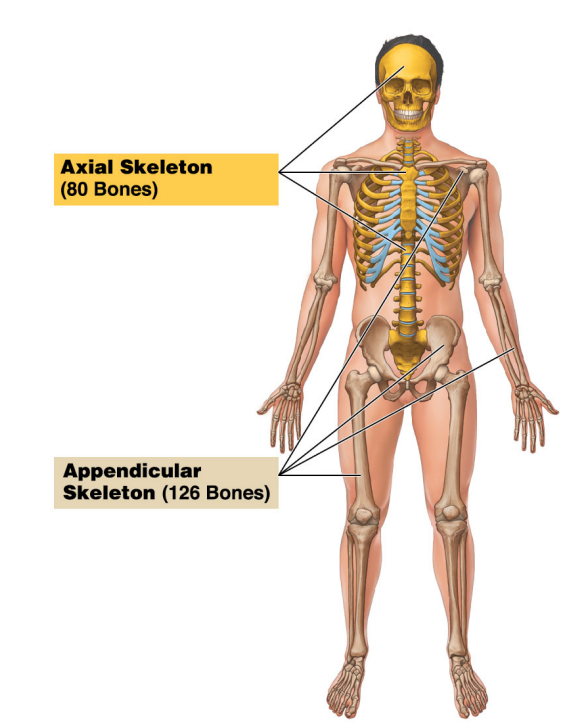
What bones are part of the Appendicular Skeleton?
It consist of bones of the limbs and gridles that attach them to the axial skeleton
4
New cards
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
* It provides support
* Keeps us upright
* It stores minerals and lipids
* Minerals
* Large amount of calcium
* Lipids
* Fats
* Bones have a hollow center and in that center it has marrow. The marrow is made out of fat cells/ adipose tissue.
* Our bones store energy molecules
* It produces blood cells
* Protection
* Protects our organs
* Leverage
* Allow movement
* Keeps us upright
* It stores minerals and lipids
* Minerals
* Large amount of calcium
* Lipids
* Fats
* Bones have a hollow center and in that center it has marrow. The marrow is made out of fat cells/ adipose tissue.
* Our bones store energy molecules
* It produces blood cells
* Protection
* Protects our organs
* Leverage
* Allow movement
5
New cards
What inorganic componnent make up the bone composition?
Calcium
* Main source of bones/ stores in bones
* Main source of bones/ stores in bones
6
New cards
What are the 2 most highly concentrated inorganic molecules found in our bones?
* Calcium
* Phosphate
* Phosphate
7
New cards
What organic compound is combined with calcium?
* collagen
* protein
* protein
8
New cards
What are the 3 activties that maintain calcium levels?
* Intestine (Digestive System)
* Absorbs calcium and phosphate under hormonal control
* Bones
* Osteoclasts erode the matrix and release calcium
* Osteoblasts use calcium to deposit new matrix/create more bones
* Kidneys
* Reabsorbs calcium depending on the levels of the body from the urine under hormonal control
* Varying levels of calcium and phosphate loss in urine under hormonal control
* Absorbs calcium and phosphate under hormonal control
* Bones
* Osteoclasts erode the matrix and release calcium
* Osteoblasts use calcium to deposit new matrix/create more bones
* Kidneys
* Reabsorbs calcium depending on the levels of the body from the urine under hormonal control
* Varying levels of calcium and phosphate loss in urine under hormonal control
9
New cards
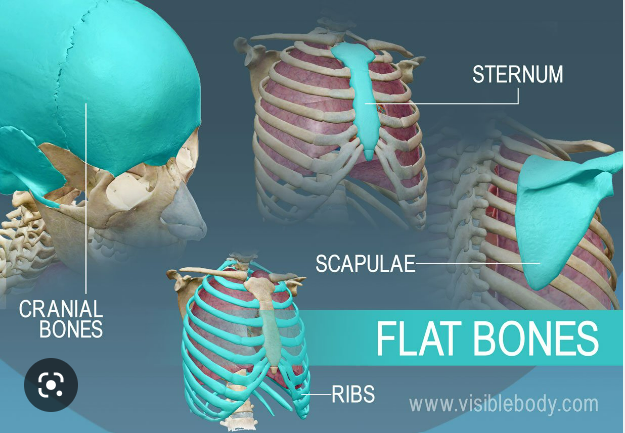
What are flat bones?
Thin, roughly parallel surfaces
* Flat plate
* Flat plate
10
New cards
What are examples of flat bones?
Cranial bones, sternum, ribs, scapulae
11
New cards
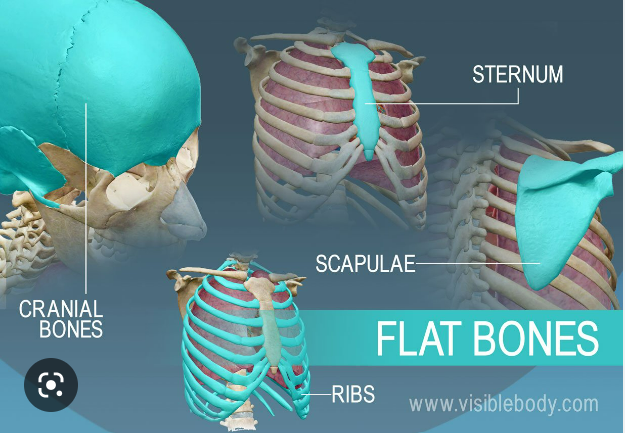
What does the flat bone provide?
* Protect underlying soft tissues (ex. Brain)
* Provide a surface area for skeletal muscle attachment
* Can’t move without the use of muscles provide locations for the muscle to attach
* Provide a surface area for skeletal muscle attachment
* Can’t move without the use of muscles provide locations for the muscle to attach
12
New cards
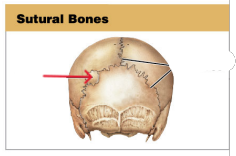
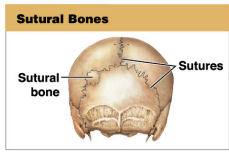
What are sutural bones?
Irregular bones formed between cranial bone
* only found on the cranial bone
* only found on the cranial bone
13
New cards
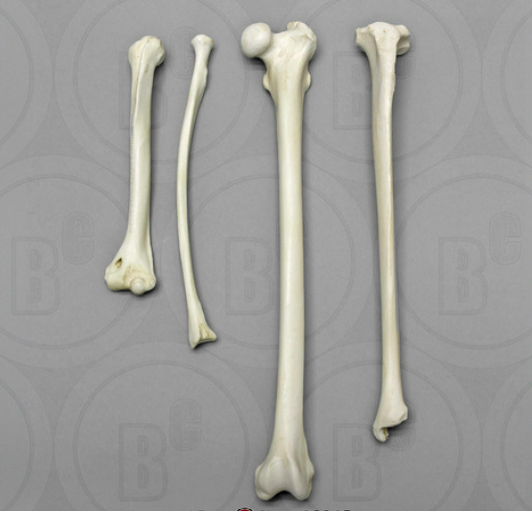
What are long bones?
They are long and slender
14
New cards
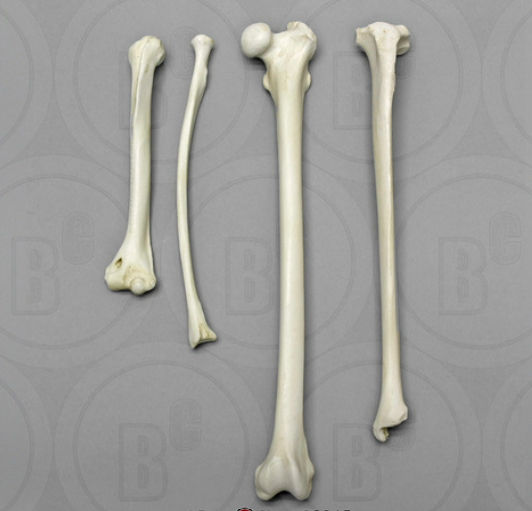
What are examples of long bones
* Femur and Humerus
* Various bones of the limbs
* Various bones of the limbs
15
New cards
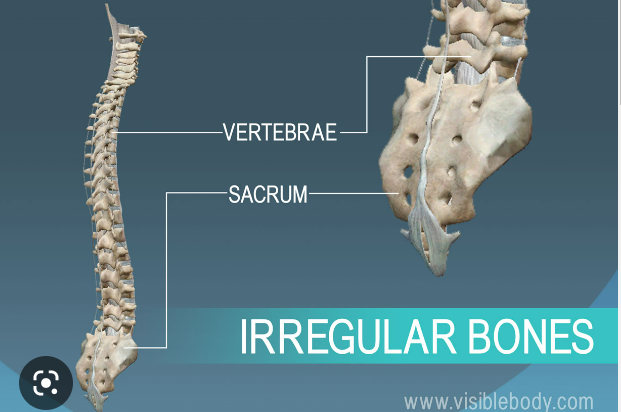
What are irregular bones?
They are complex shapes with short, flat, notched, or ridged surfaces
16
New cards
What are examples of irregular bones?
* Vertebrae
* Pelvis bones
* Facial Bones
* Pelvis bones
* Facial Bones
17
New cards
What are sesamoid bones?
Small flat, shaped like a sesame seed
18
New cards
What are examples of sesamoid bones?
* Patella
* Developed inside tendons of the knee, hands, and feet
* Developed inside tendons of the knee, hands, and feet
19
New cards
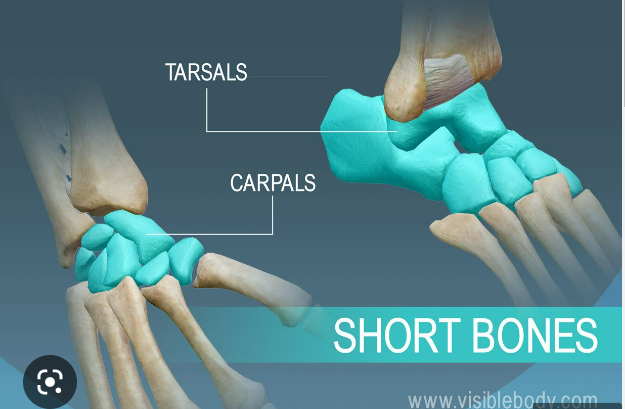
What are short bones?
Small and boxy
20
New cards
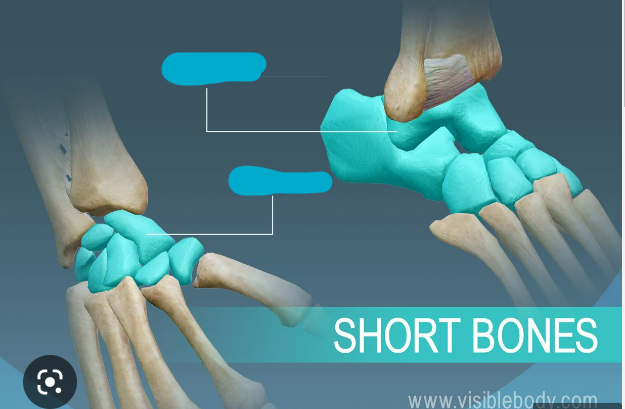
What are examples of short bones?
* Carpals
* Tarsals
* Tarsals
21
New cards
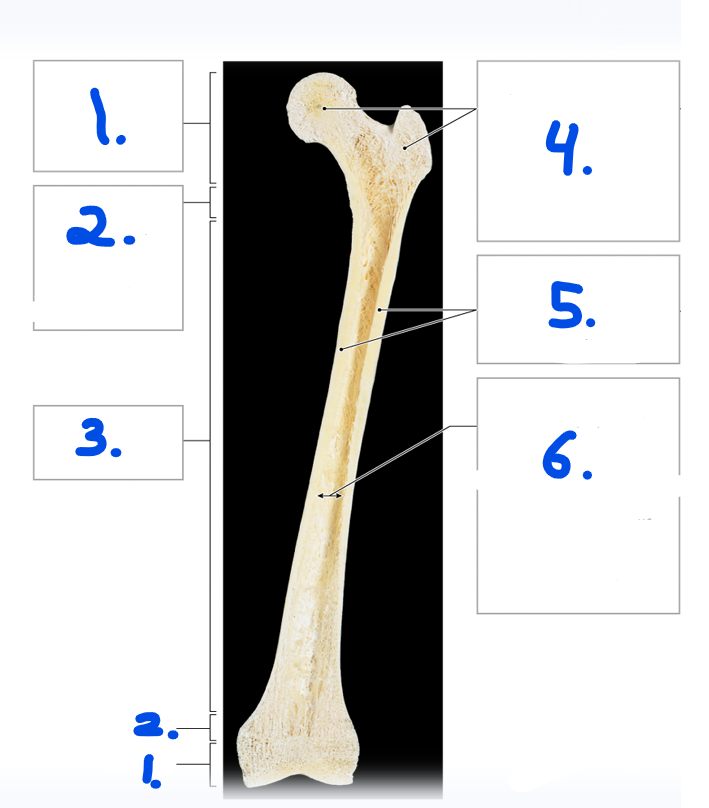
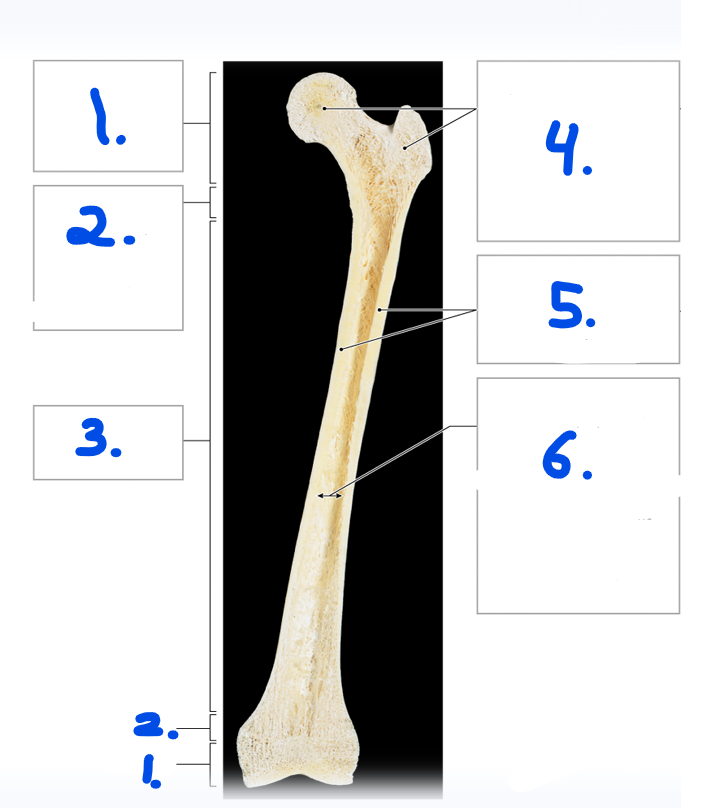
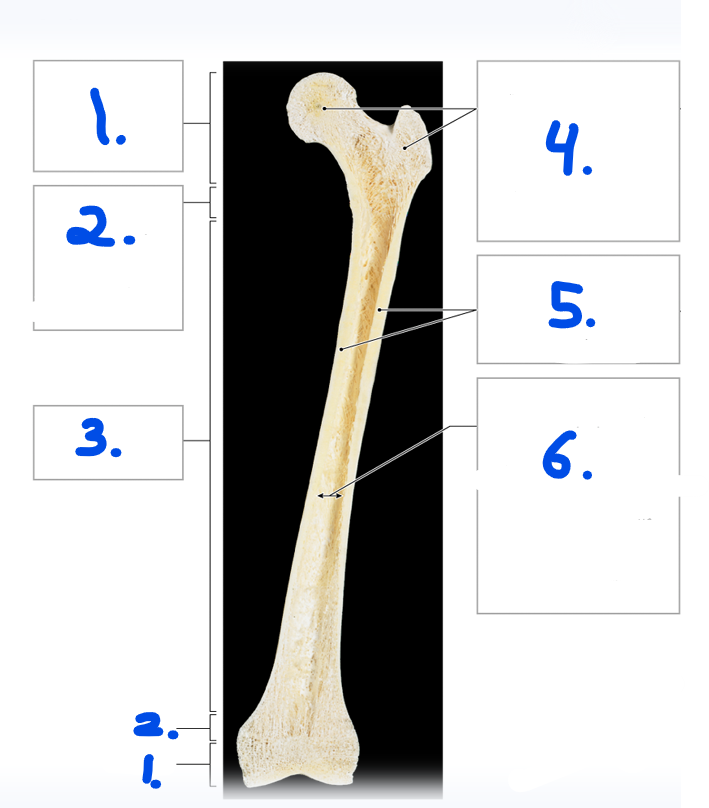
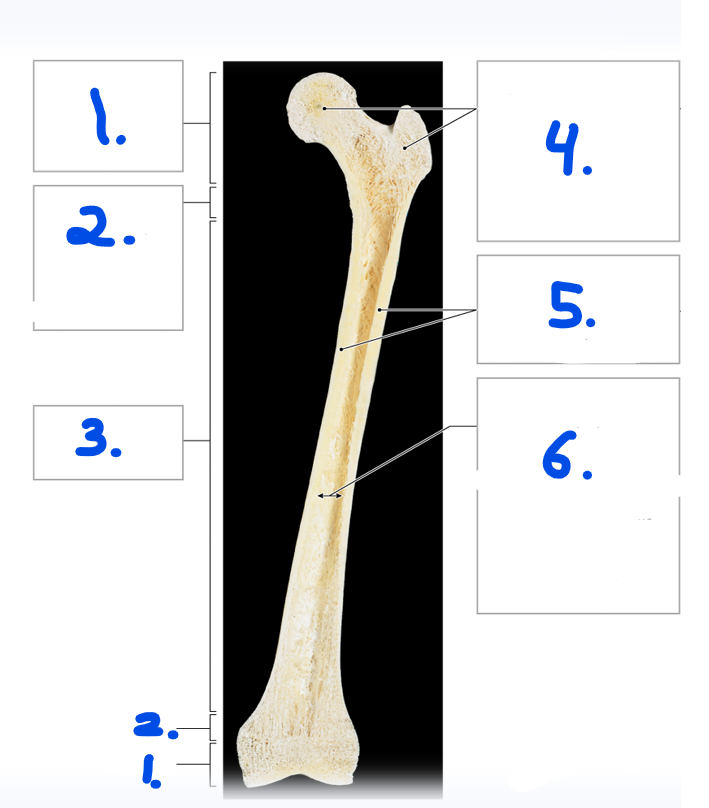
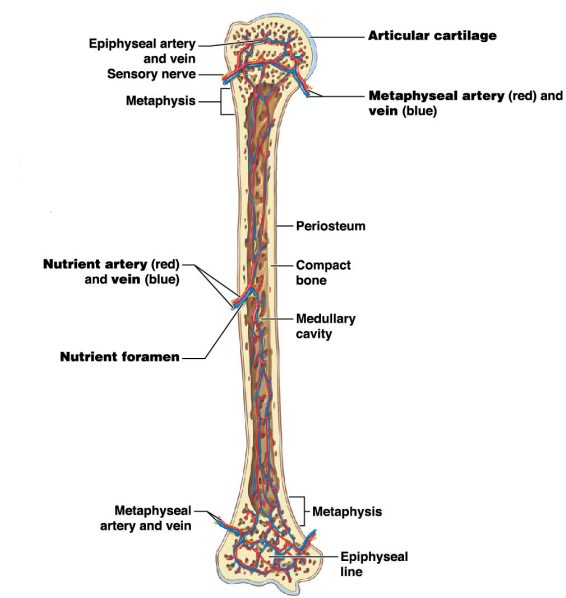
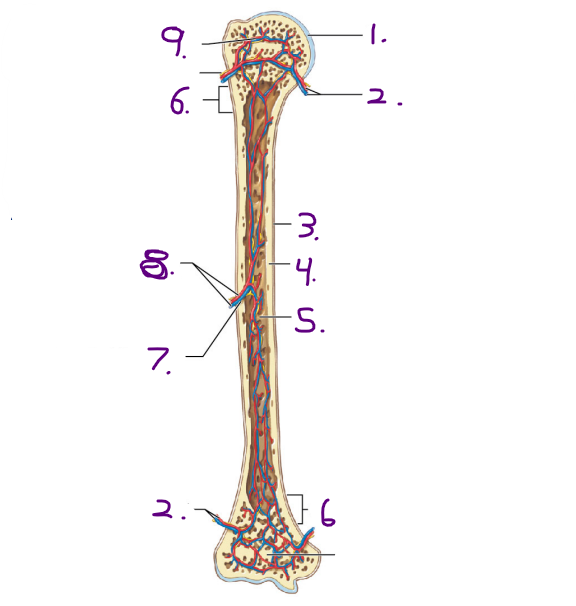
Name for #1
Epiphysis
22
New cards
What type of marrow is found in the epiphysis?
Red bone marrow
23
New cards
What type of bone is the epiphysis consist of?
Spongy bone/ trabecular bone
24
New cards
Name strucuture for #1
Articular cartilage
25
New cards
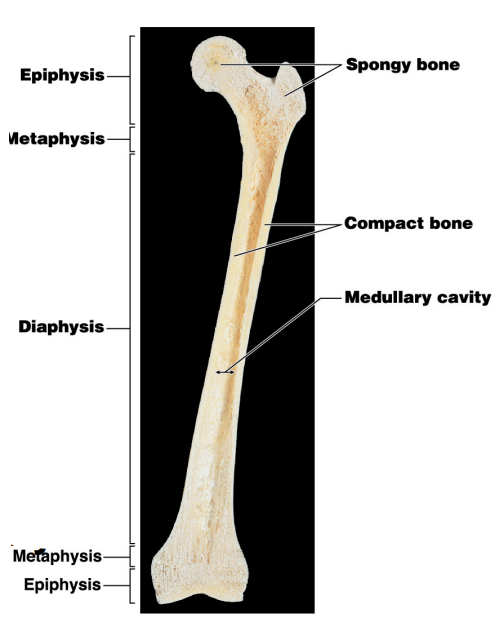
Epiphysis
* It consists largely of spongy bone/ trabecular bone
* Red bone marrow is found
* The articular cartilage covers the portions of the epiphysis that form articulations
* Articular means one bone meets another bone
* Red bone marrow is found
* The articular cartilage covers the portions of the epiphysis that form articulations
* Articular means one bone meets another bone
26
New cards
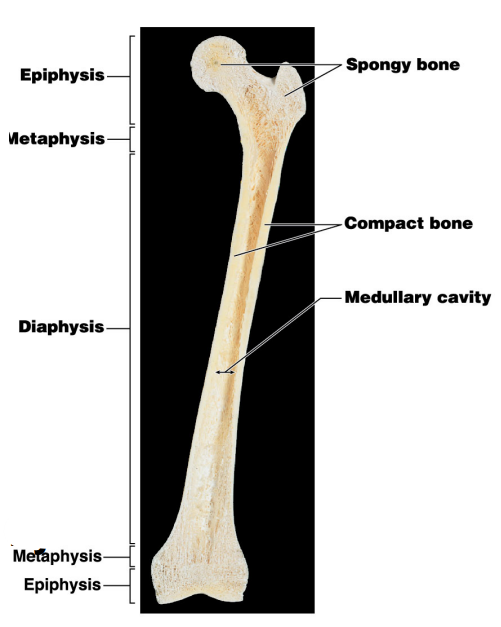
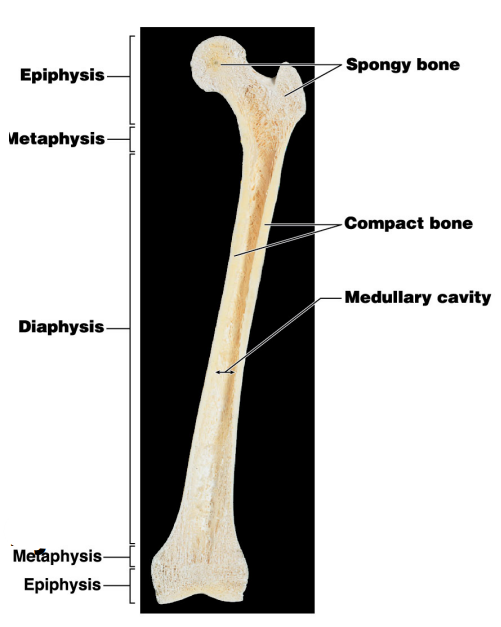
Where is red bone marrow usually found?
Epiphysis
27
New cards
Where is yellow bone marrow usually found?
Diaphysis / Medullary cavity
28
New cards
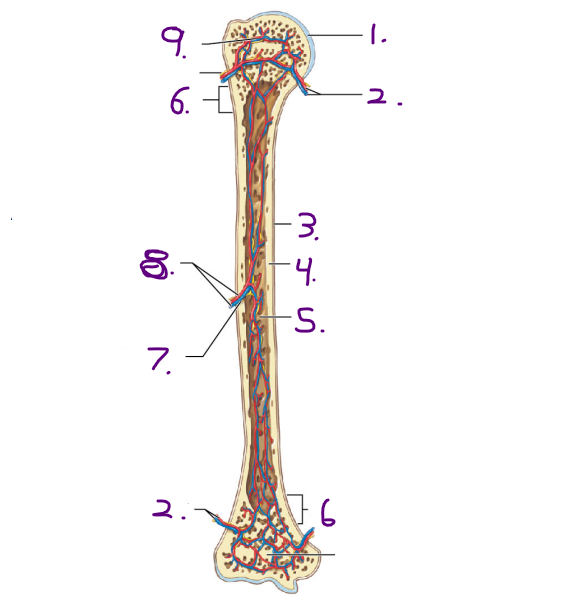
What covers the surface of the epiphysis when it meets other bones? #1
Articular cartilage
29
New cards
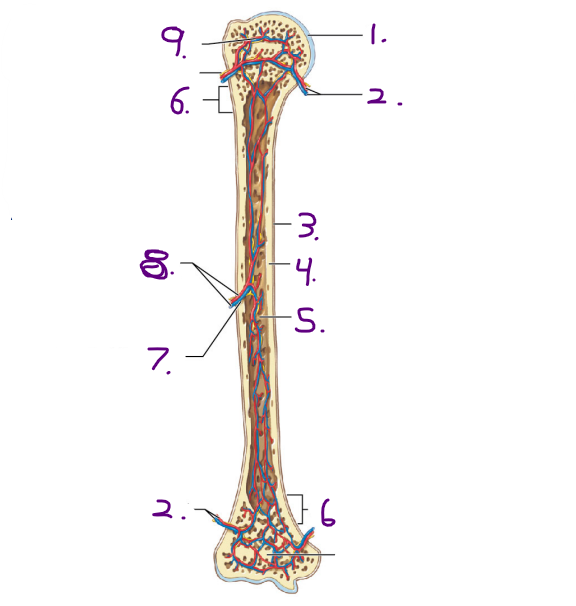
What is the purpose of the metaphysis? #2
It is the entry site where the metaphyseal artery and metaphyseal vein enter
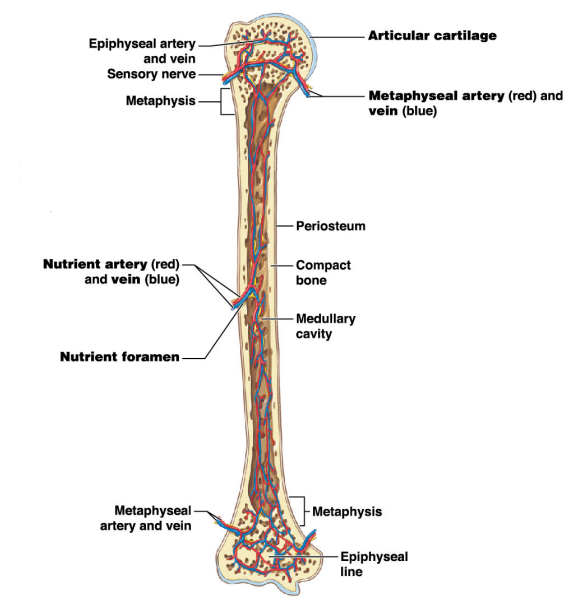
30
New cards
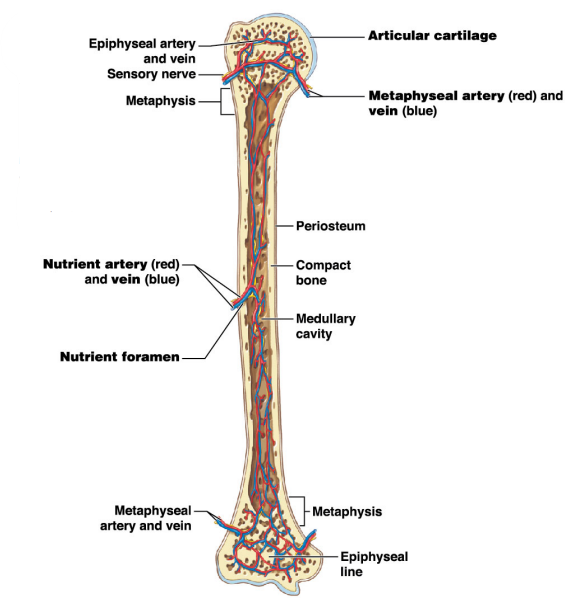
What do the metaphyseal artery and metaphyseal vein do?
-They carry blood to/from the metaphysis
-They also conncet to the epiphyseal arteries and veins
-They also conncet to the epiphyseal arteries and veins
31
New cards
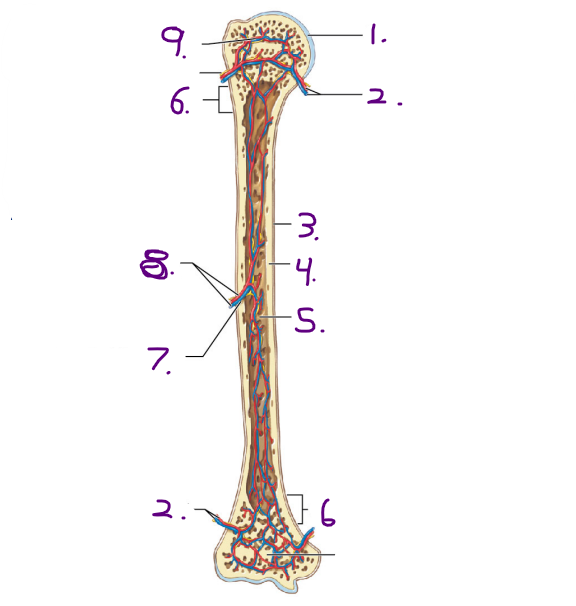
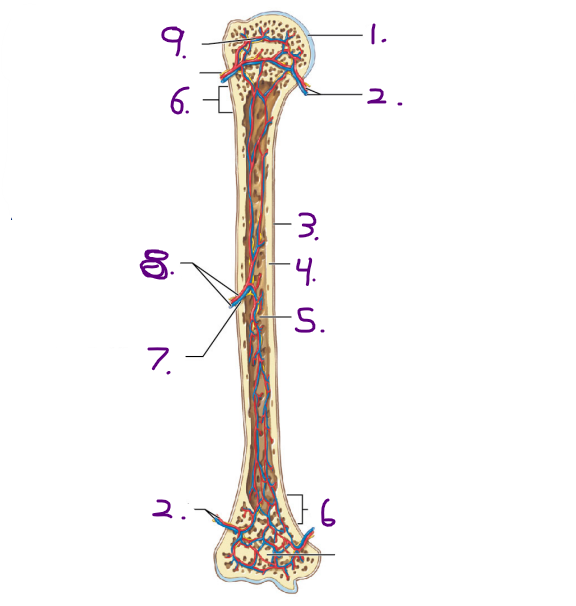
Name the strucuture for #8
Nutrient artery and vein
32
New cards
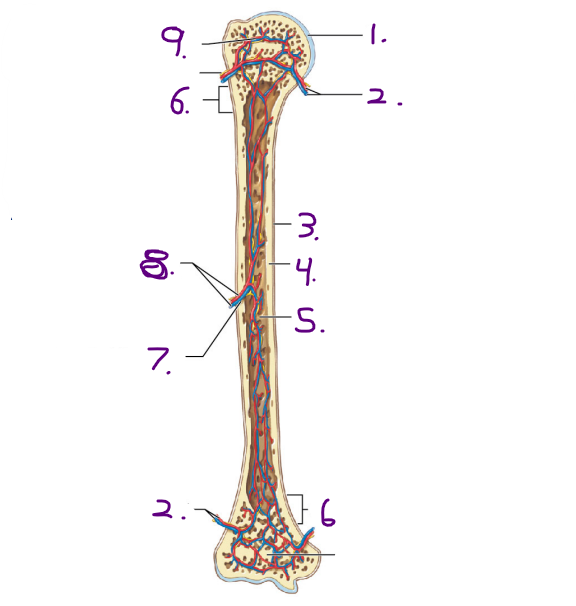
Name the opening/ hole for #7
Nutrient foramen
33
New cards
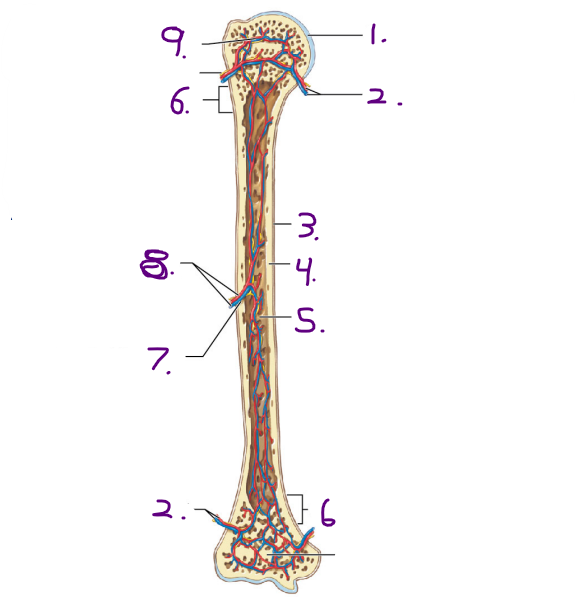
Where is the nutrient artey and nutrient vein located on the long bone?
Diaphysis
34
New cards
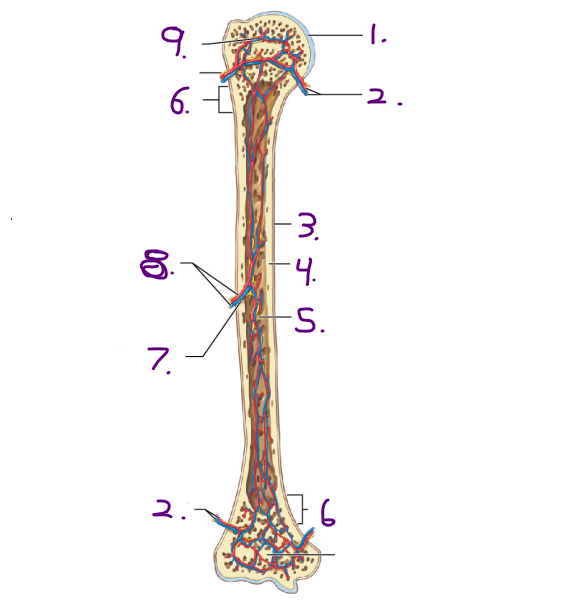
Name #3
Periosteum
35
New cards
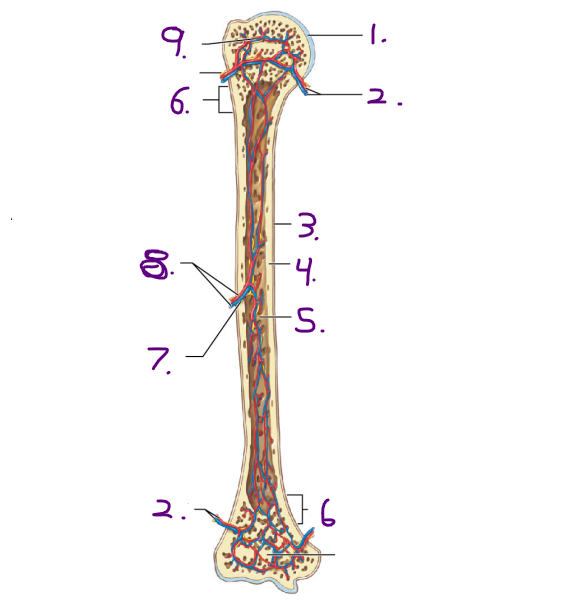
Name #4
Compact bone
36
New cards
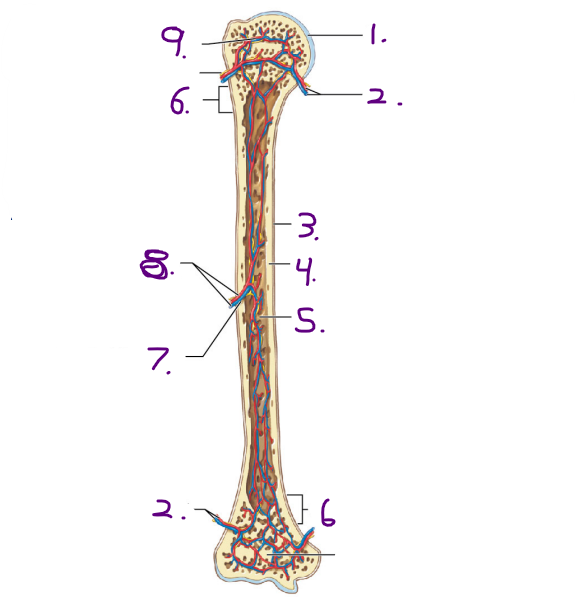
Name #5
Medullary cavity
37
New cards
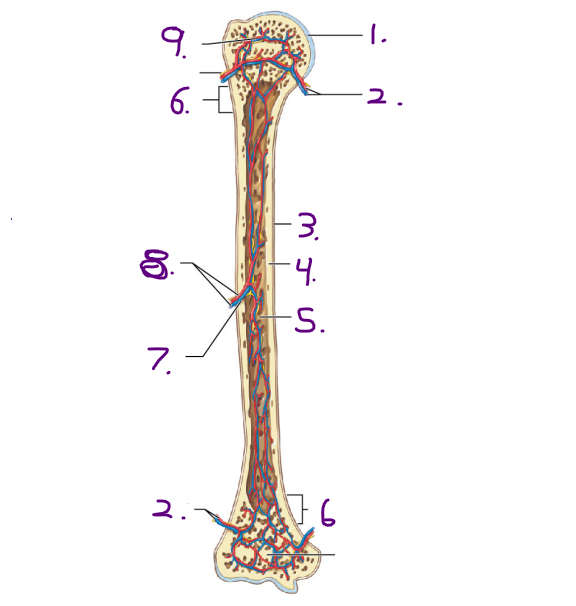
Name #6
Metaphysis
38
New cards
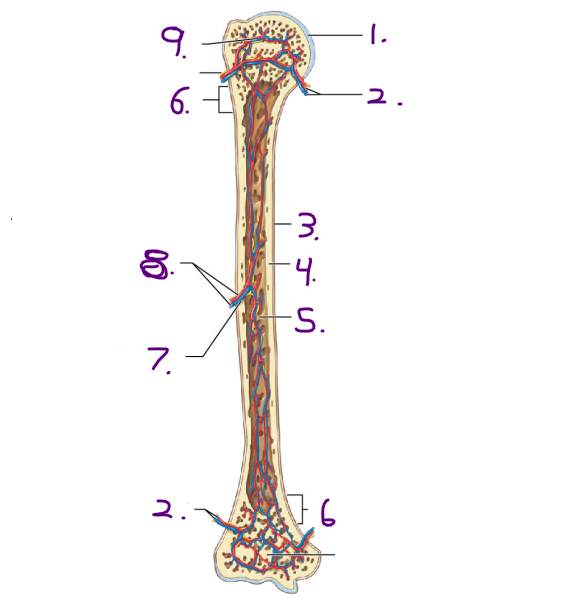
Name #9
Epiphyseal artery and vein
39
New cards
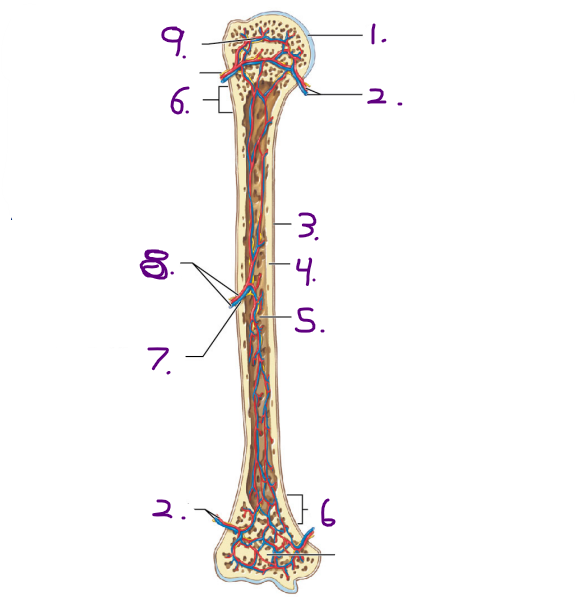
Name #2
Metaphyseal artery and vein
40
New cards
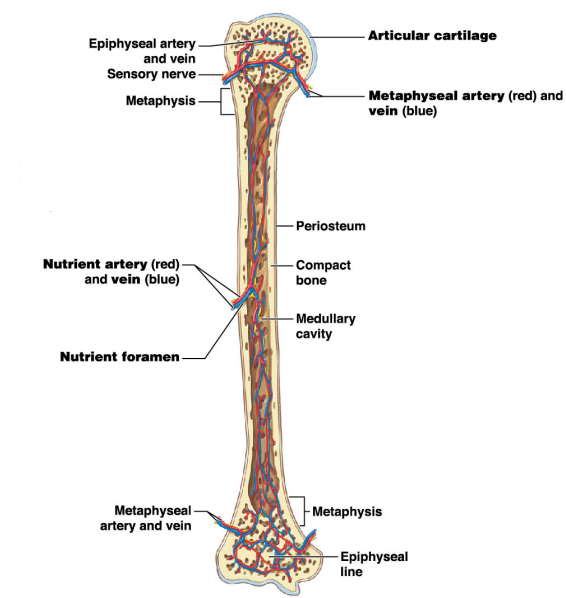
Metaphyseal artery and vein
* Carry blood to/from metaphyseal
* Connect to epiphyseal arteries/veins
* Connect to epiphyseal arteries/veins
41
New cards
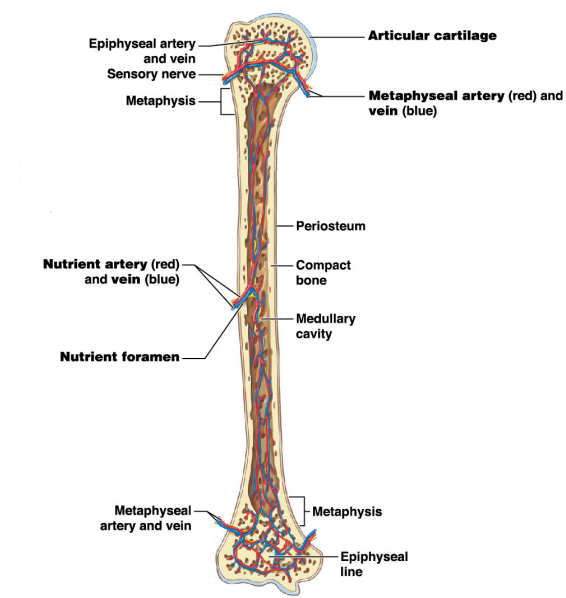
Periosteum
* Thin-layer
* Outer-layer
* Incasement
* Around the bone (outside)
* Made of dense regular tissue
* Outer-layer
* Incasement
* Around the bone (outside)
* Made of dense regular tissue
42
New cards
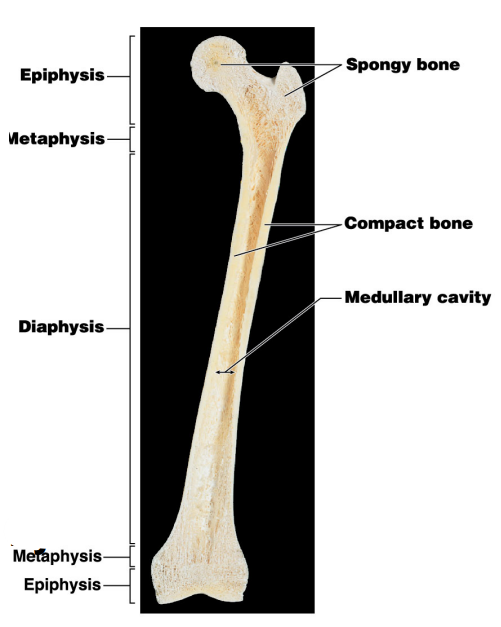
What does the diaphysis contain?
* Medullary cavity
* Red bone marrow
* Involved in red blood cell production
* Yellow bone marrow
* Adipose tissue
* Important as energy reserve
* Red bone marrow
* Involved in red blood cell production
* Yellow bone marrow
* Adipose tissue
* Important as energy reserve
43
New cards
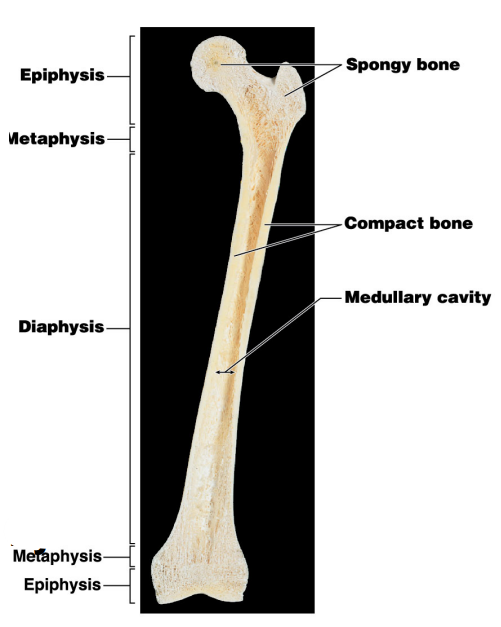
What type of marrow is found in the diaphysis?
Yellow bone marrow
44
New cards
What is the name of the cavity for #6?
What type of marrow is found here?
What type of marrow is found here?
* Medullary cavity
* Yellow bone marrow
* Yellow bone marrow
45
New cards
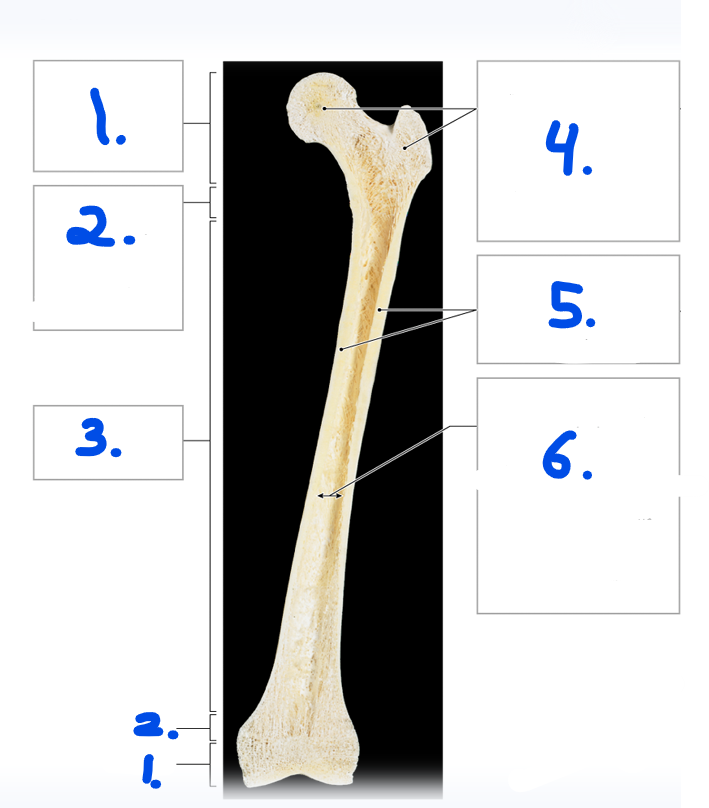
Name #4
Spongy bone/ trabecular bone
46
New cards
Name #5
Compact bone
47
New cards
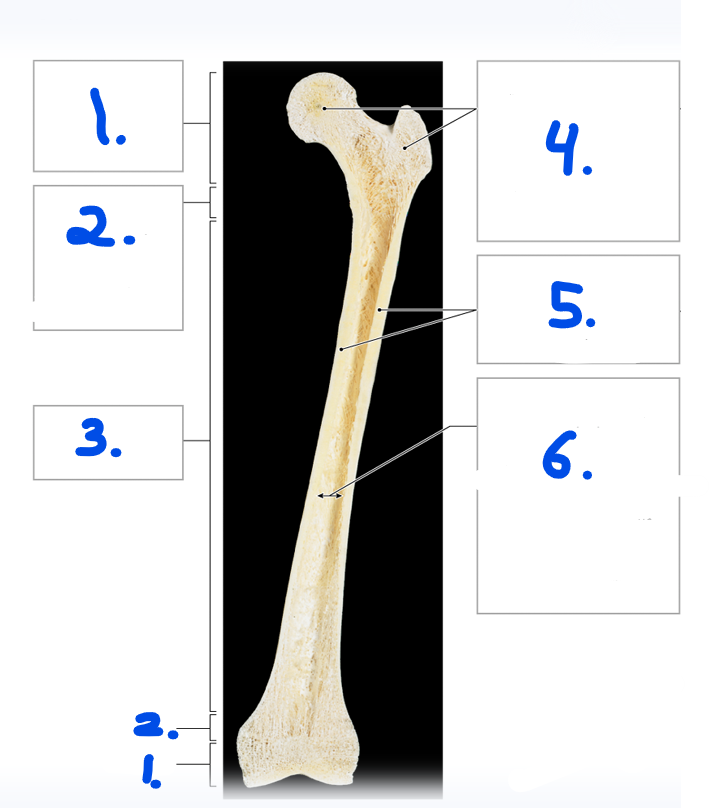
Name #3
Diaphysis / shaft
48
New cards
Name #2
Metaphysis
49
New cards
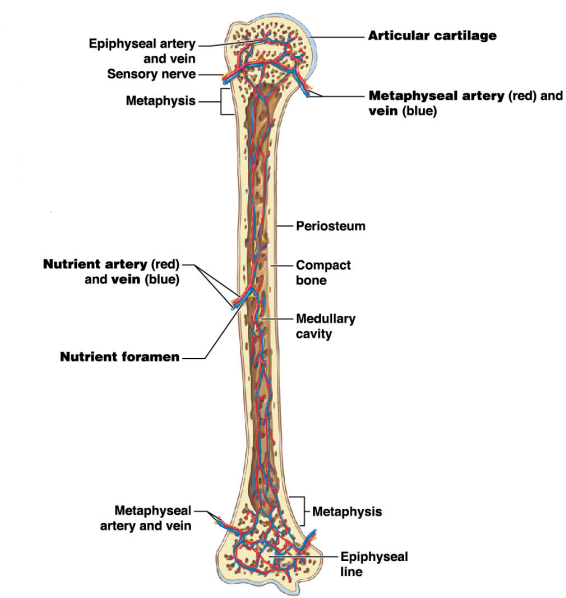
What does red bone marrow do?
It involves red blood cell production
50
New cards
What does yellow bone marrow do?
What does it contain?
What does it contain?
* It reserves energy
* It contains adipose tissue
* It contains adipose tissue
51
New cards
What does the nutrient foramen contain?
Nutrient artey and vein
52
New cards
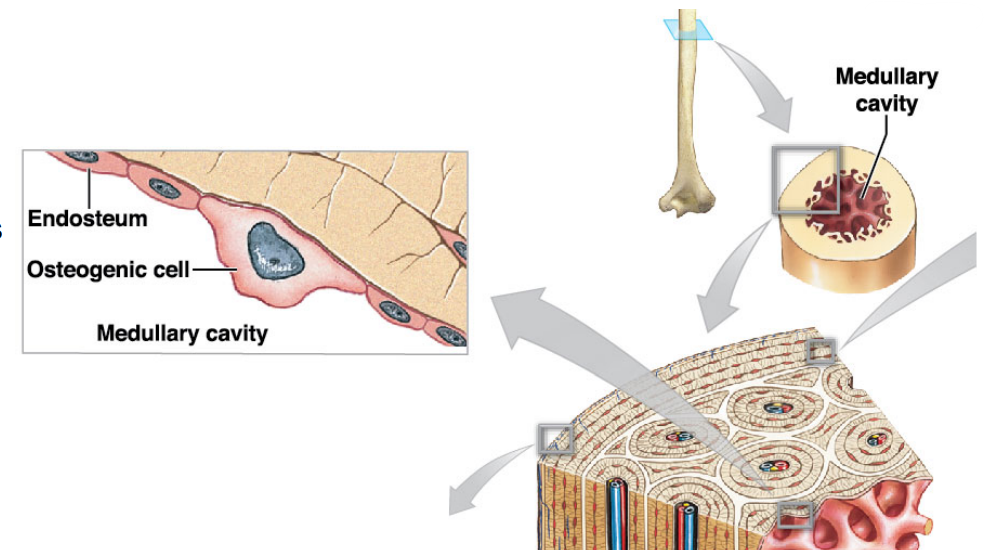
Osteogenic cells (osteoprogenitor cells)
* Stem cells that produce more cells that will differentiate (change into) osteoblasts (mature cells) or osteoclasts
* They are important for fracture repair
* Locations
* Inner lining of periosteum
* Lining endosteum in medullar cavity
* Lining passageways containing blood vessels
* Ex. Central canal
* They are important for fracture repair
* Locations
* Inner lining of periosteum
* Lining endosteum in medullar cavity
* Lining passageways containing blood vessels
* Ex. Central canal
53
New cards
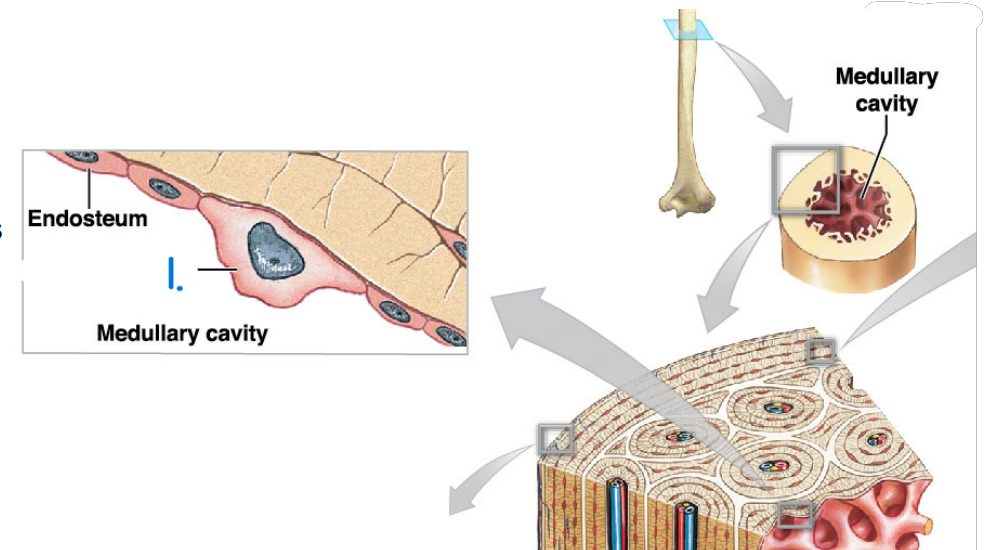
What is the name of this cell #1?
Osteogenic cells
54
New cards
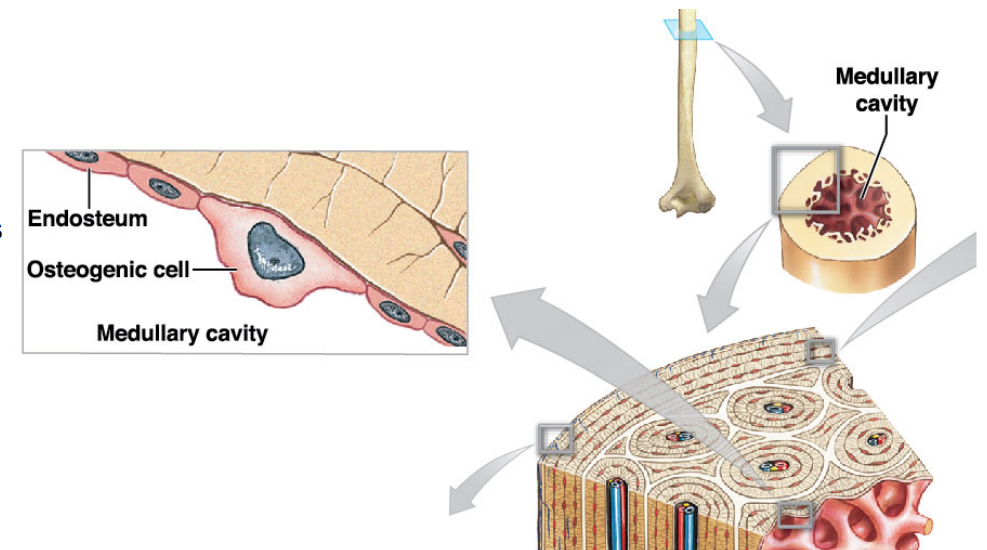
What are osteogenic important for?
* In fracture repair
55
New cards
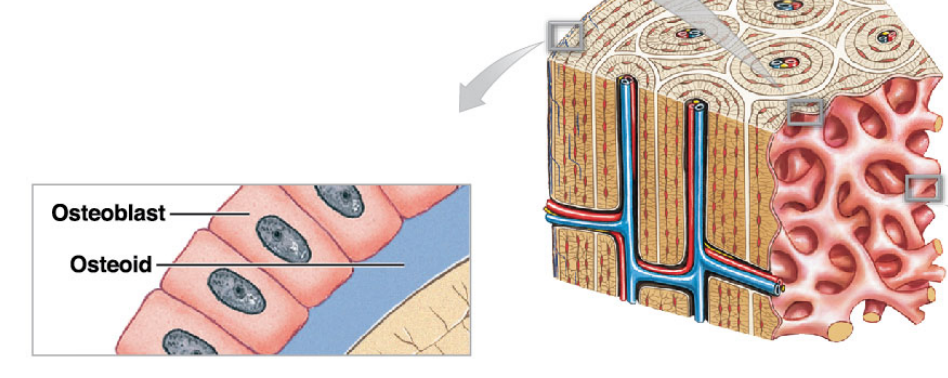
Osteoblasts
* They produce new bony matrix
* First matrix is called Osteoid
* Its an unmineralized matrix
* Its a immature bone that hasn’t fully developed into bone
* It hasn’t been solidified
* It’s just collagen (type of protein) in the matrix
* Second matrix is called bone
* Calcium salts is added to solidify bone
* The matrix becomes bone
* Mature bone
* First matrix is called Osteoid
* Its an unmineralized matrix
* Its a immature bone that hasn’t fully developed into bone
* It hasn’t been solidified
* It’s just collagen (type of protein) in the matrix
* Second matrix is called bone
* Calcium salts is added to solidify bone
* The matrix becomes bone
* Mature bone
56
New cards
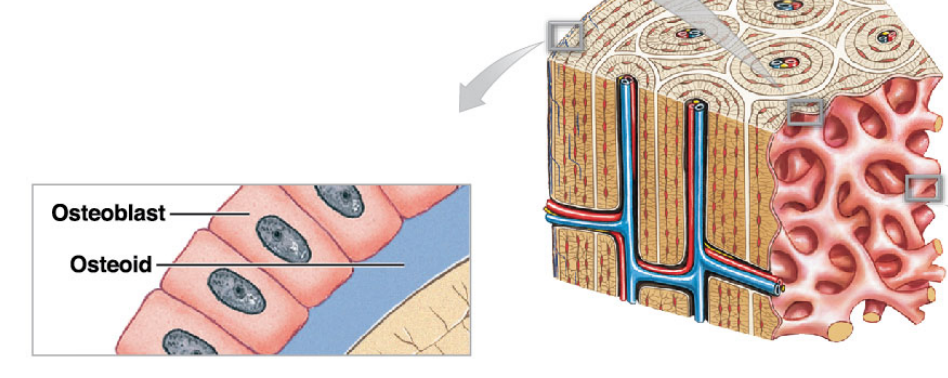
Osteoblasts (Continuation)
* Osteoblast become osteocytes once they surrounded/ trapped themselves by the bone matrix
* They get stuck in a lacuna
* They get stuck in a lacuna
57
New cards
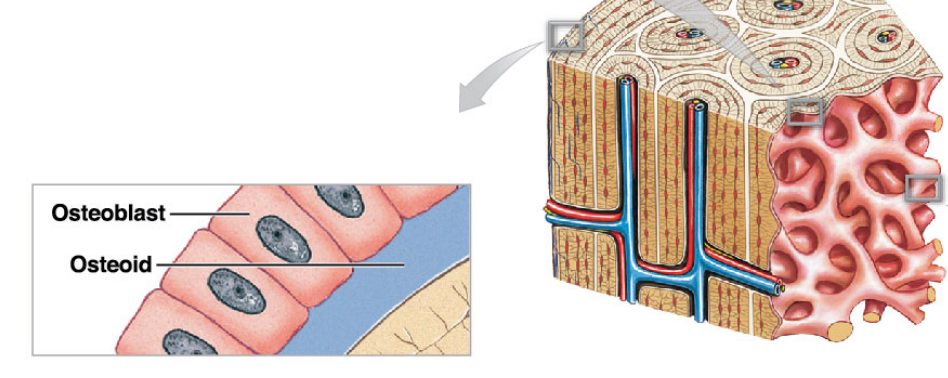
Osteogenesis / Ossification
Is the name of the processes that makes osteoid
58
New cards
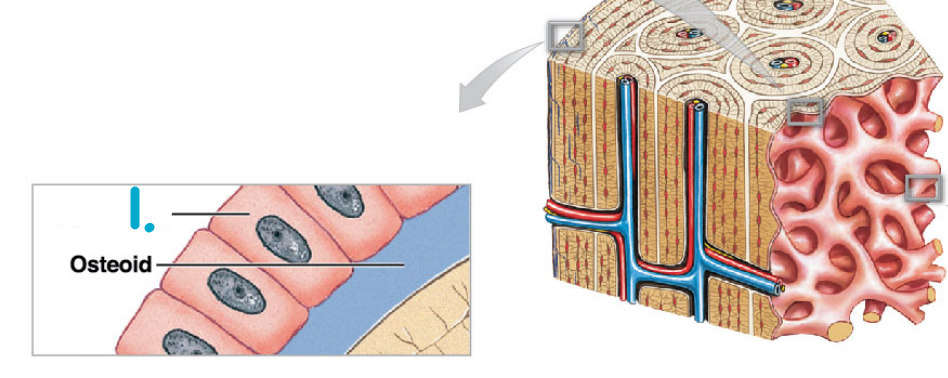
What is the name of this type of cell #1?
Osteoblasts
59
New cards
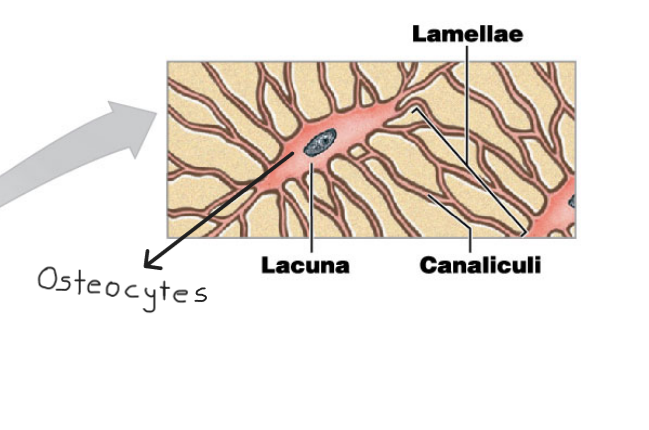
Osteocytes
* They are mature bone cells that cannot divide
* They occupy lacuna/e
* They are seperated by layers of matrix called lamellae
* They are interconnected by canaliculi
* Small little canals
* They maintain protein and mineral content of surrounding matrix
* They occupy lacuna/e
* They are seperated by layers of matrix called lamellae
* They are interconnected by canaliculi
* Small little canals
* They maintain protein and mineral content of surrounding matrix
60
New cards
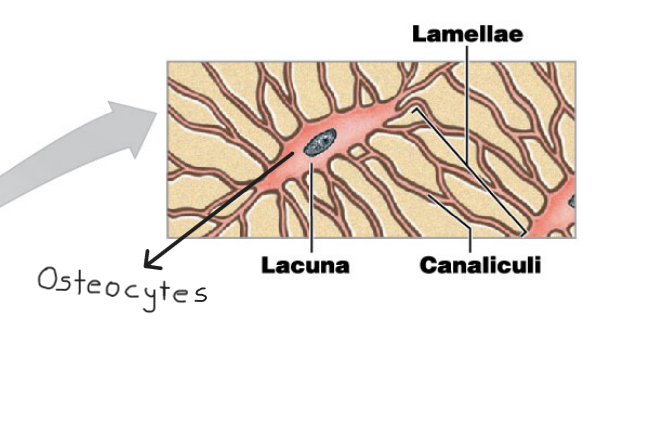
What do osteocytes maintain?
Protein and mineral content of the surrounding matrix
61
New cards
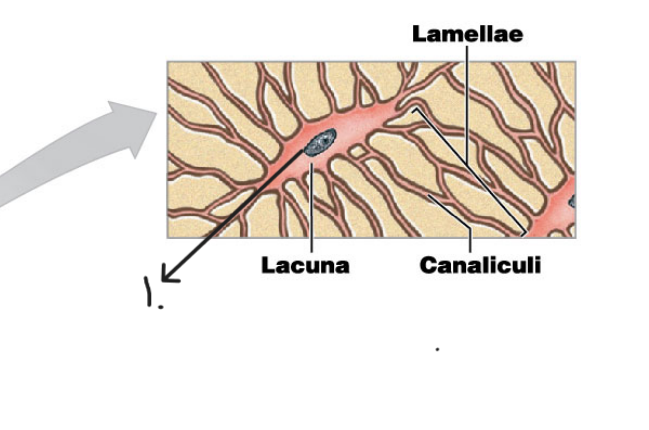
What is the name of this cell? #1
Osteocytes
62
New cards
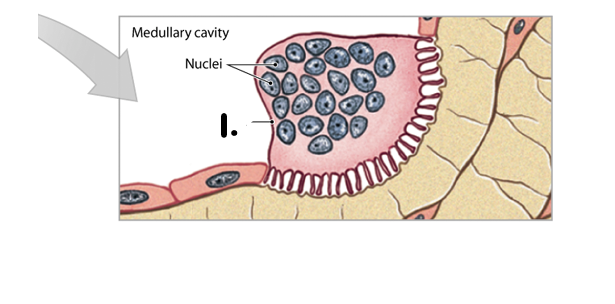
What is the name of this cell?
Osteoclasts
63
New cards
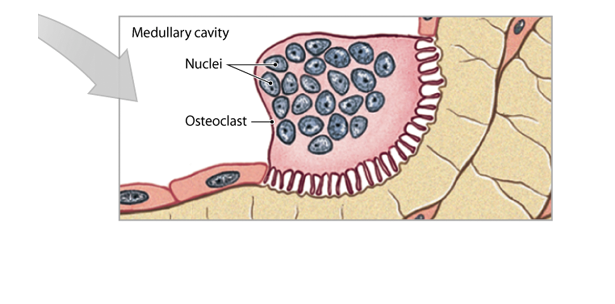
Osteoclasts
* They remove and remodel bone matrix
* It releases acids and proteolytic enzymes to dissolve matrix and release stored minerals / calcium
* This processes is called osteolysis
* Digest
* It releases acids and proteolytic enzymes to dissolve matrix and release stored minerals / calcium
* This processes is called osteolysis
* Digest
64
New cards
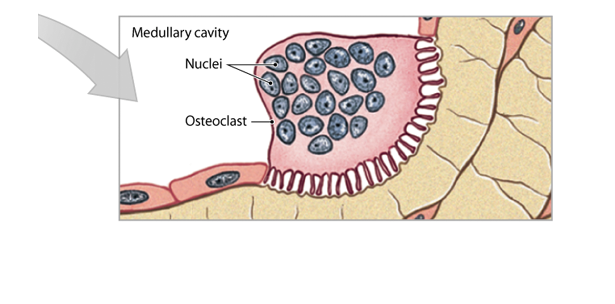
What do osteoclasts do?
They remove and remodel bone matrix by releasing acids and proteolytic enzymes
65
New cards
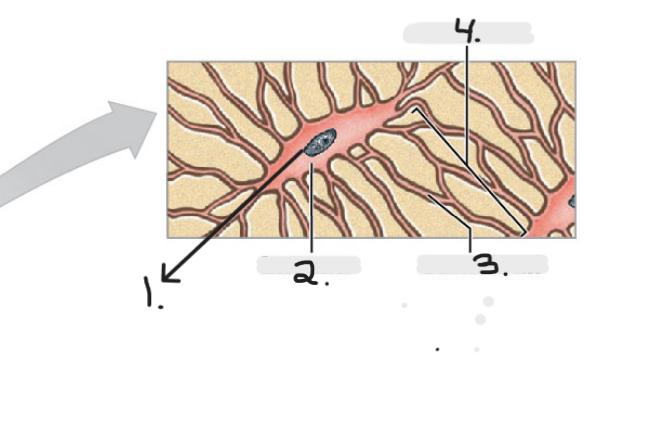
Name the structure for #2
Lacuna
66
New cards
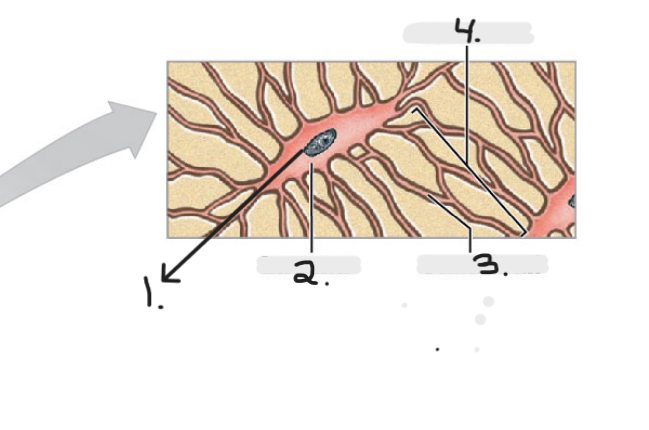
Name the structure for #3
Canaliculi
67
New cards
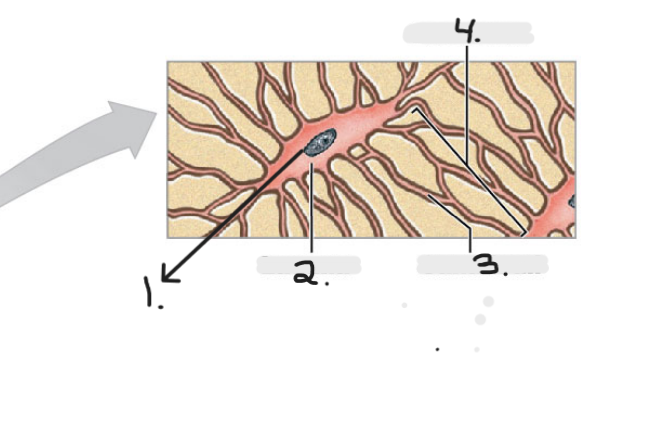
Name the structure for #4
Lamellae
68
New cards
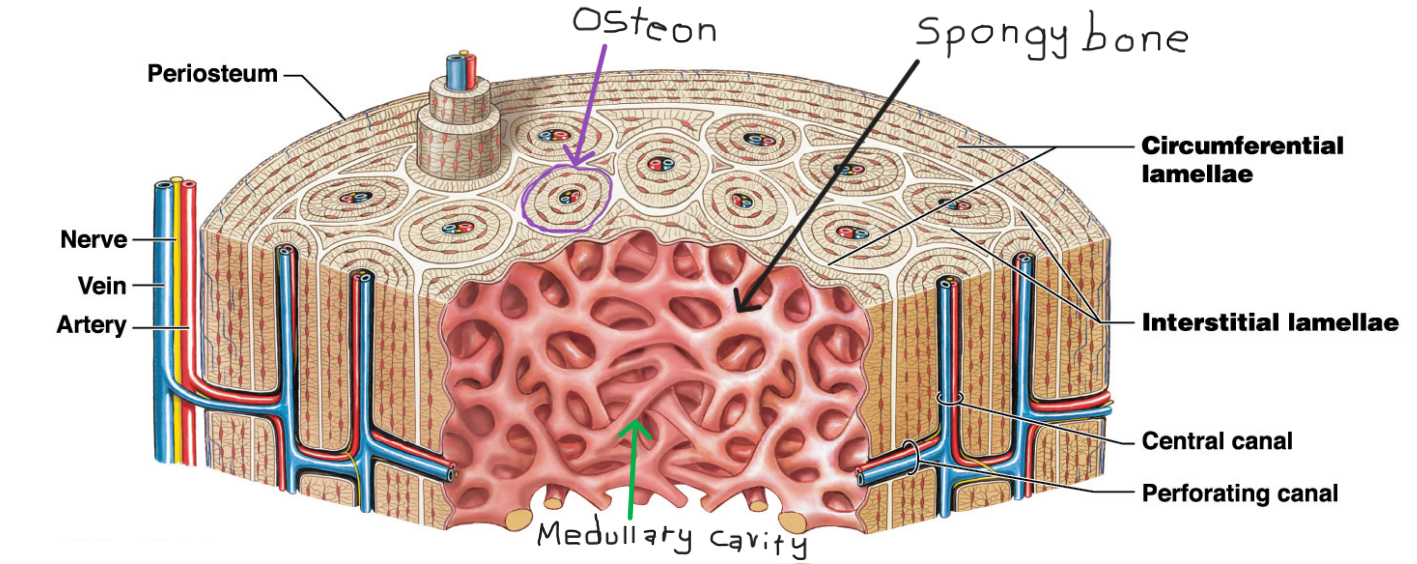
What is the functional unit for compact bone?
Osteon
69
New cards
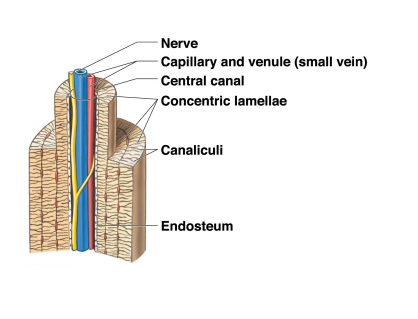
Osteon
* It is organized in concentric lamellae around a central cannal
* Osteocytes lie between lamellae
* Central canal contains small blood vessels
* Osteocytes lie between lamellae
* Central canal contains small blood vessels
70
New cards
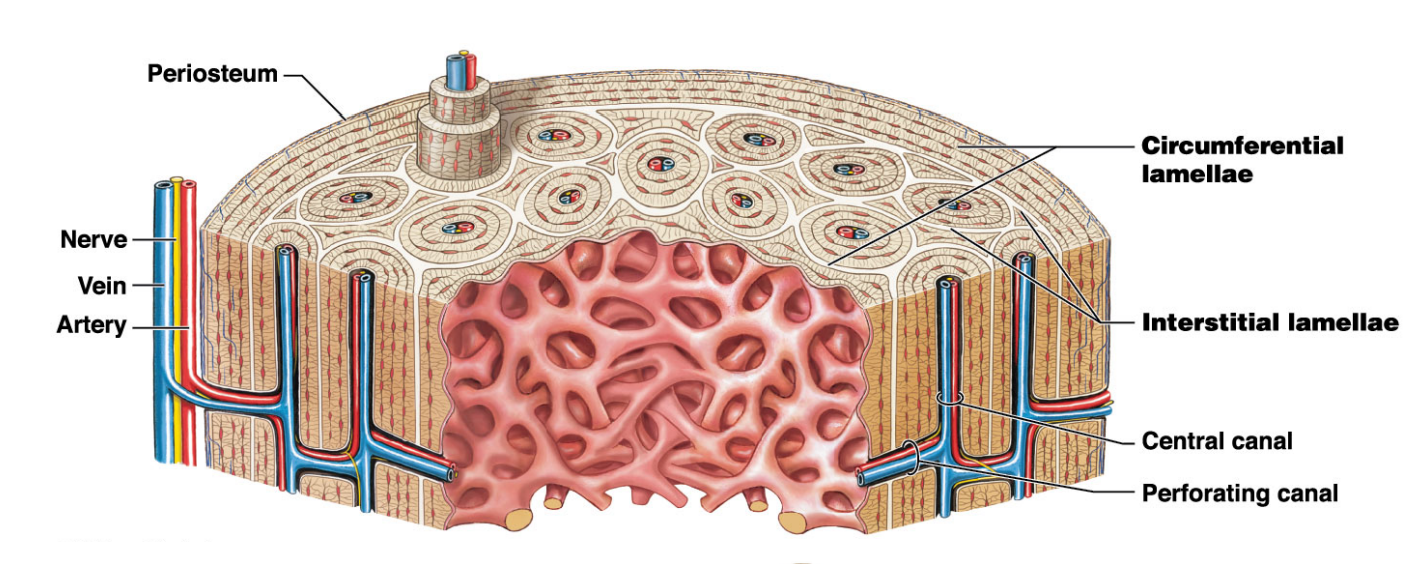
Periosteum
Outermost layer of the long bone
71
New cards
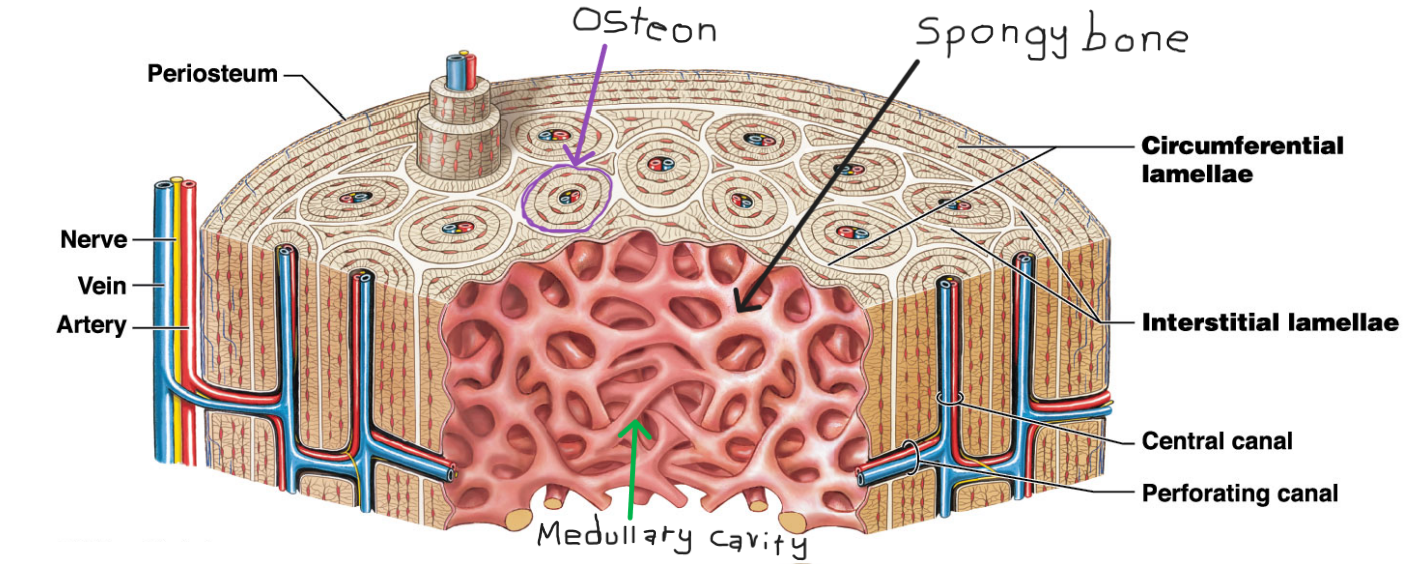
Compact bone
* Outer bone tissue layer
* Consists of
* Circumferential lamellae
* Outer and inner surfaces
* Interstitial lamellae
* Fill spaces between osteons
* Osteons
* Connected by performing canals (perpendicular to surface)
* Consists of
* Circumferential lamellae
* Outer and inner surfaces
* Interstitial lamellae
* Fill spaces between osteons
* Osteons
* Connected by performing canals (perpendicular to surface)
72
New cards
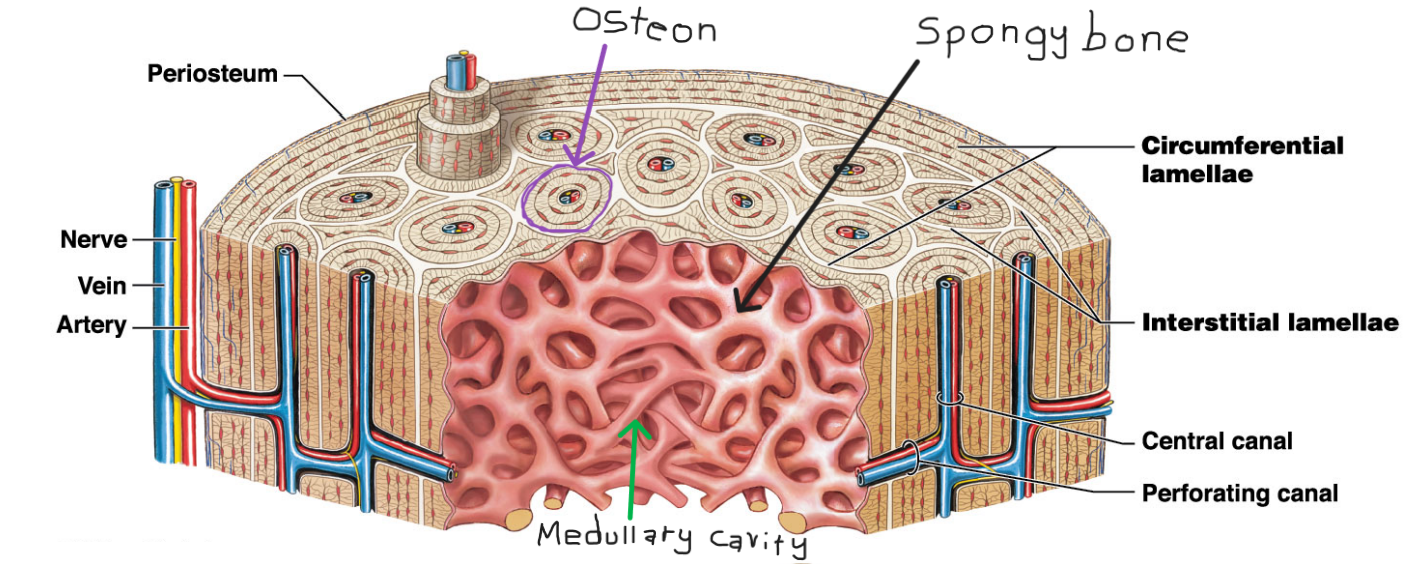
Spongy bone/ trabecular bone
* Inner most later
* Found in the medullary cavity
* Lamellae form struts and plates (trabeculae) creating an open network
* Theres no blood vessels in matrix
* Nutrients reach osteons through canaliculi open to trabeculae surfaces
* Found in the medullary cavity
* Lamellae form struts and plates (trabeculae) creating an open network
* Theres no blood vessels in matrix
* Nutrients reach osteons through canaliculi open to trabeculae surfaces
73
New cards
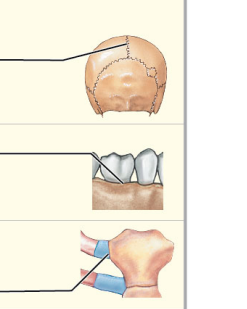
What type of movement is synarthrosis?
No movement In
* Extremely strong
* Extremely strong
74
New cards
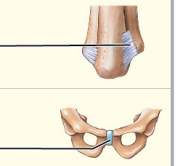
What type of movement is amphiarthrosis?
Little movement
* Much stronger than diarthrosis
* Articulating bones connected by collagen fibers or cartilage
* Collagen fibers - fibrocytes
* Cartilage - chondrocytes
* Much stronger than diarthrosis
* Articulating bones connected by collagen fibers or cartilage
* Collagen fibers - fibrocytes
* Cartilage - chondrocytes
75
New cards
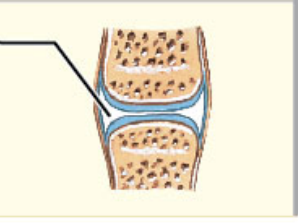
What type of movement is diarthrosis?
Free movement Info
* Freely moveable
* Freely moveable
76
New cards
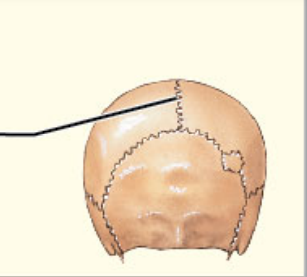
What structural category is this?
What functional category is this?
What functional category is this?
1. Suture
2. Synarthrosis

77
New cards
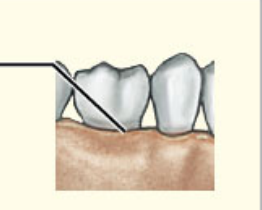
What structural category is this?
What functional category is this?
What functional category is this?
1. Gomphosis
2. Synarthrosis

78
New cards
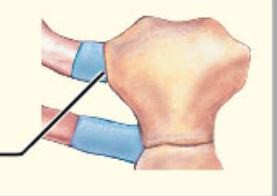
What structural category is this?
What functional category is this?
What functional category is this?
1. Synchondrosis
2. Synarthrosis

79
New cards
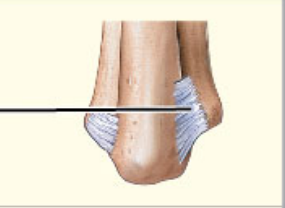
What structural category is this?
What functional category is this?
What functional category is this?
1. Syndesmosis
2. Amphiarthrosis

80
New cards
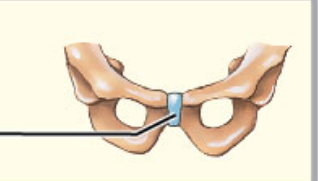
What structural category is this?
What functional category is this?
What functional category is this?
1. Symphysis
2. Amphiarthrosis

81
New cards
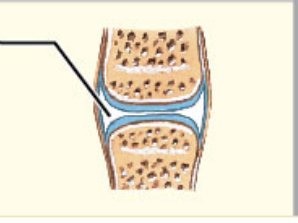
What structural category is this?
What functional category is this?
What functional category is this?
1. Synovial
2. Diathrosis

82
New cards
Joints or articulation
* Means locations where two or more bones meet
* Only points at which movements of bones can occur
* Joints allow mobility while perserving bone strength
* Amount of movement allowed is determined by anatomical structure
* Categorized
* Functionally by amount of motion allowed, or range of motion (ROM)
* Structurally by anatomical organization
* Only points at which movements of bones can occur
* Joints allow mobility while perserving bone strength
* Amount of movement allowed is determined by anatomical structure
* Categorized
* Functionally by amount of motion allowed, or range of motion (ROM)
* Structurally by anatomical organization
83
New cards

Suture
* Synarthrotic joint connected by dense fibrous connective tissue
* Location between bones of the skull
* Location between bones of the skull
84
New cards

Gomphosis
* Synarthrotic joint binding teeth to bony sockets in maxillae and mandible
85
New cards

Syndesmosis
* Amphiarthrotic joint with bones connected by a ligament
* Ex
* Distal joint between tibia and fibula
* Ex
* Distal joint between tibia and fibula
86
New cards

Symphysis
* Amphiarthrotic joint where articulating bones separated by a pad of fibrocartilage
* Ex
* Joint between the two pubic bones
* Ex
* Joint between the two pubic bones
87
New cards

Synchondrosis
* Synarthrotic joint formed by a rigid, cartilaginous bridge between two articulating bones
* Ex
* Between ends of the first pair of ribs and the sternum
* Ex
* Between ends of the first pair of ribs and the sternum
88
New cards

Synovial
* Diarthrotic joints
* Permit wider range of motion than any other joint type
* Located at the ends of long bones
* Permit wider range of motion than any other joint type
* Located at the ends of long bones
89
New cards
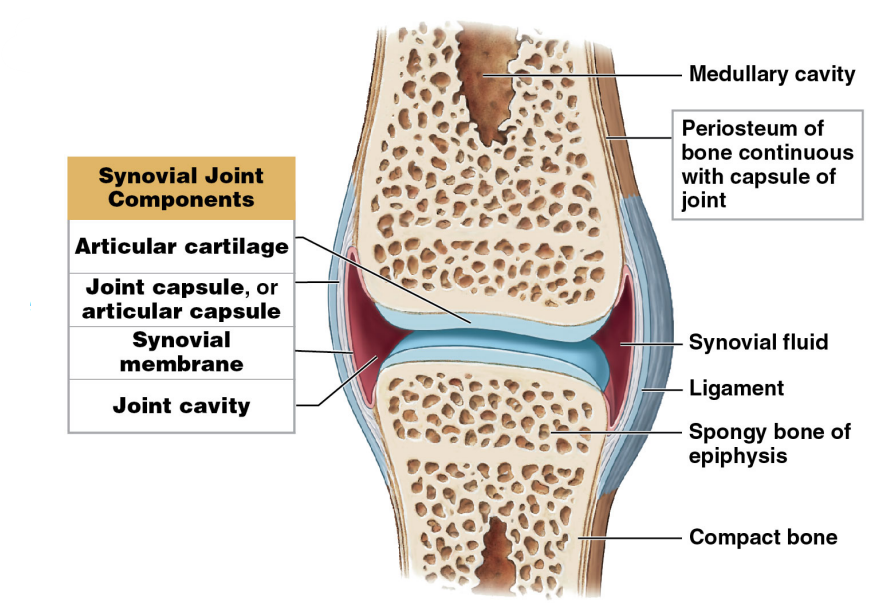
Components of a synovial joint
* Articular cartilage
* Joint capsule or articular capsule
* Synovial membrane
* Synovial fluid
* Joint capsule or articular capsule
* Synovial membrane
* Synovial fluid
90
New cards
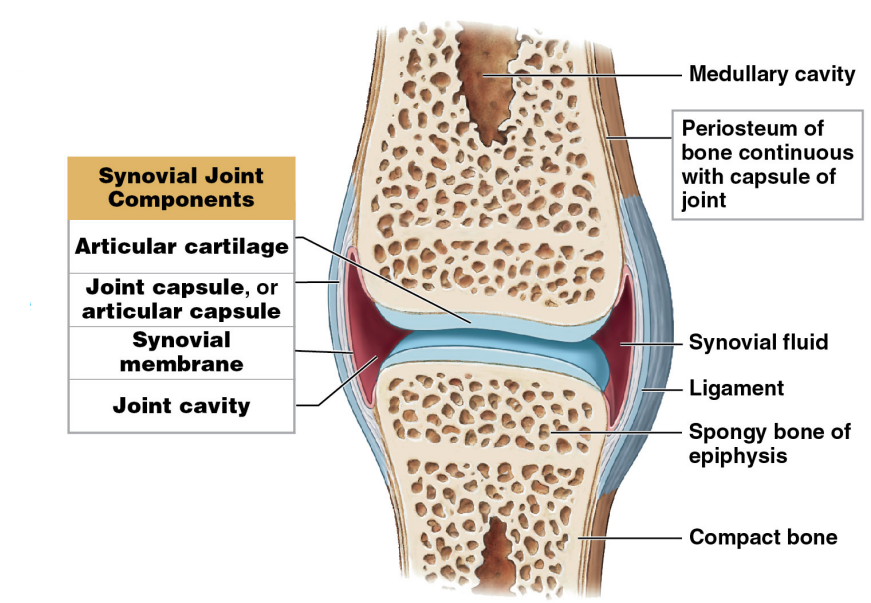
Articular cartilage
* ==Covers bones at joint to prevent degradation==
* Structure resembles hyaline cartilage but with no perichondrium\\
* Matrix contains more water than other cartilages
* Structure resembles hyaline cartilage but with no perichondrium\\
* Matrix contains more water than other cartilages
91
New cards
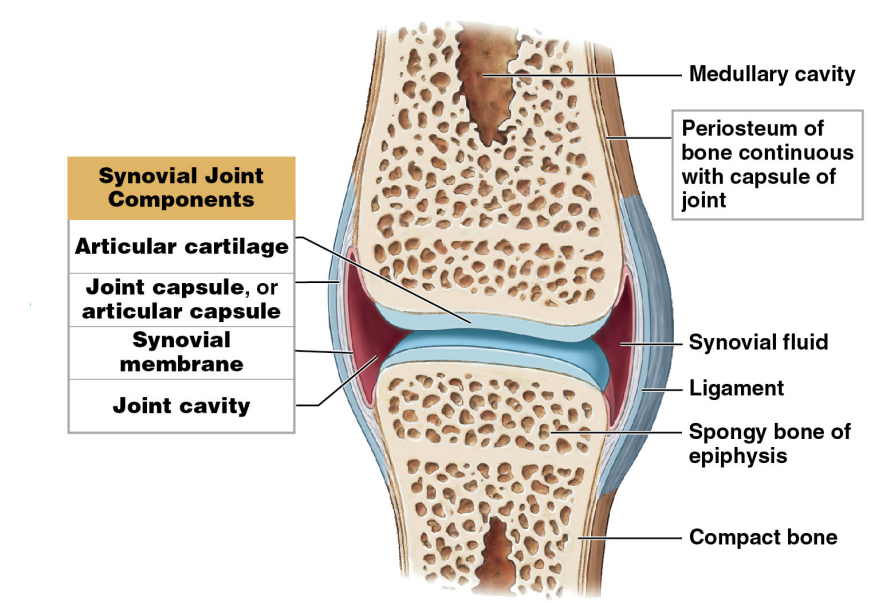
Joint capsule or Articular Capsule
* ==Sac enclosing the articular ends of the bones in a joint ; like an encasement between the bones==
* Reinforced with accessory structure (tendons, ligaments)
* Continuous with the periosteum of each bone
* ==Adds strength and mobility to the joint==
* Reinforced with accessory structure (tendons, ligaments)
* Continuous with the periosteum of each bone
* ==Adds strength and mobility to the joint==
92
New cards
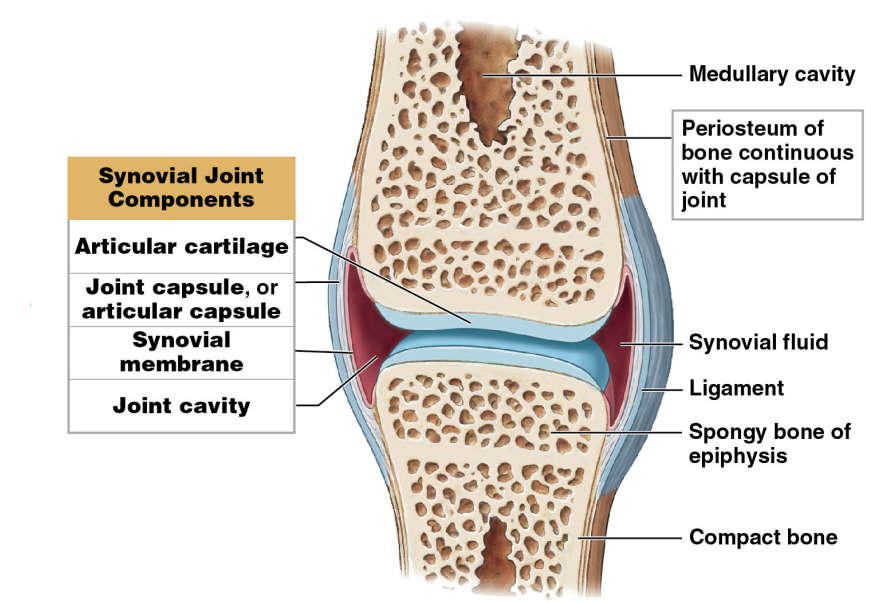
Synovial membrane
* Lines the interior of the joint capsule
* Secretes synovial fluid into the joint cavity
* Fluid lubricates, cushions, prevents abrasion, and supports chondrocytes
* Secretes synovial fluid into the joint cavity
* Fluid lubricates, cushions, prevents abrasion, and supports chondrocytes
93
New cards
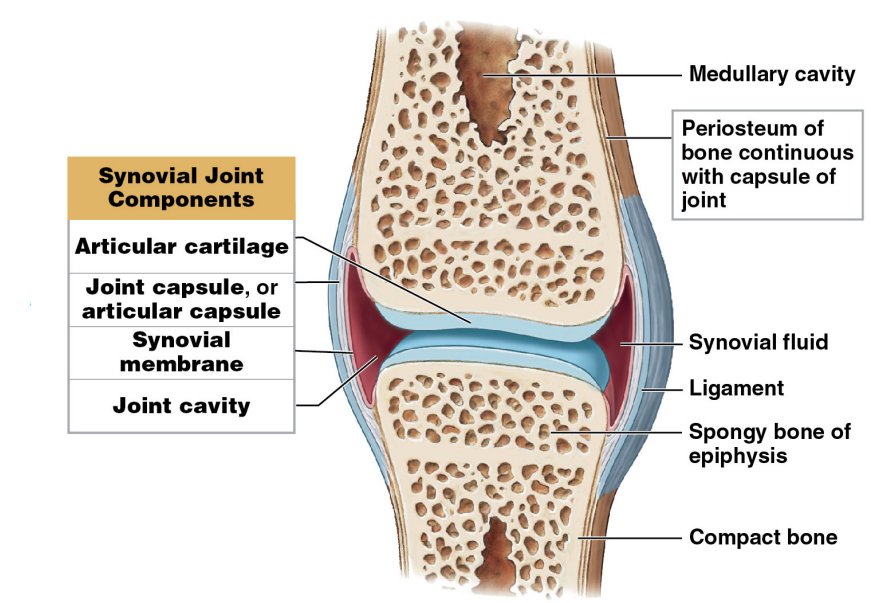
Synovial fluid
* Clear, strawed-colored, viscous fluid
* Consistency of raw egg white
* %%Viscosity due to high concentration%%
* Consistency of raw egg white
* %%Viscosity due to high concentration%%
94
New cards
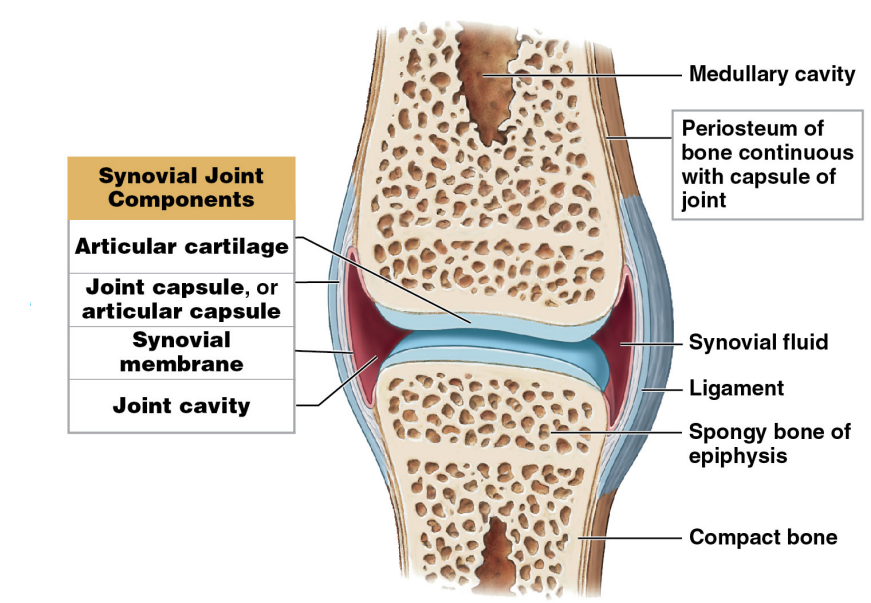
Functions of Synovial Fluid
* %%Lubrication%%
* Under compression, fluid squeezes out of the cartilage and into the space between bones
* Layer of fluid reduces friction
* %%Nutrient distribution%%
* Circulates continuously, providing nutrients and carrying away wastes
* Compression and expansion of articular cartilage assist in circulation
* %%Shock absorption%%
* Viscosity increases with increasing pressure
* Under compression, fluid squeezes out of the cartilage and into the space between bones
* Layer of fluid reduces friction
* %%Nutrient distribution%%
* Circulates continuously, providing nutrients and carrying away wastes
* Compression and expansion of articular cartilage assist in circulation
* %%Shock absorption%%
* Viscosity increases with increasing pressure
95
New cards
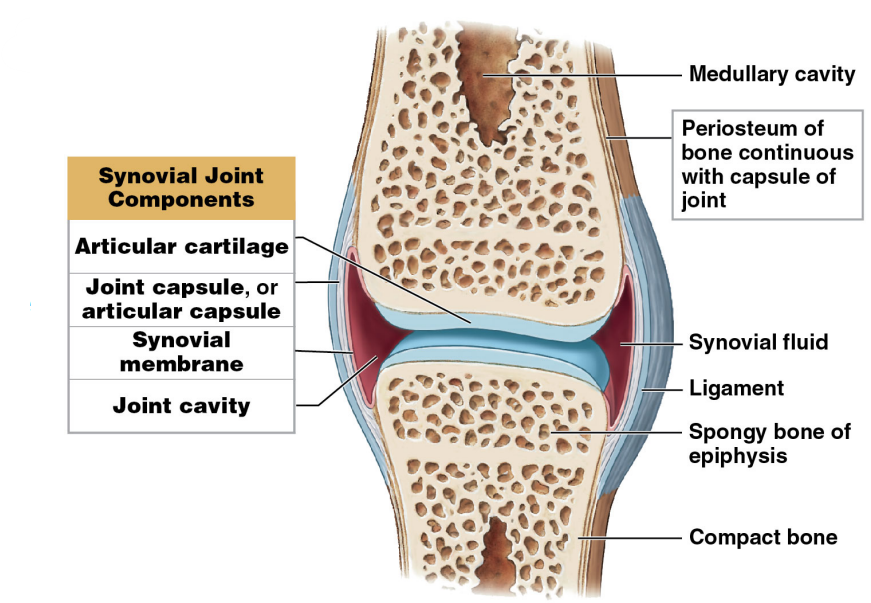
What are the 3 functions of the synovial fluid?
* Lubrication
* Nutrient distribution
* Shock absorption
* Nutrient distribution
* Shock absorption
96
New cards
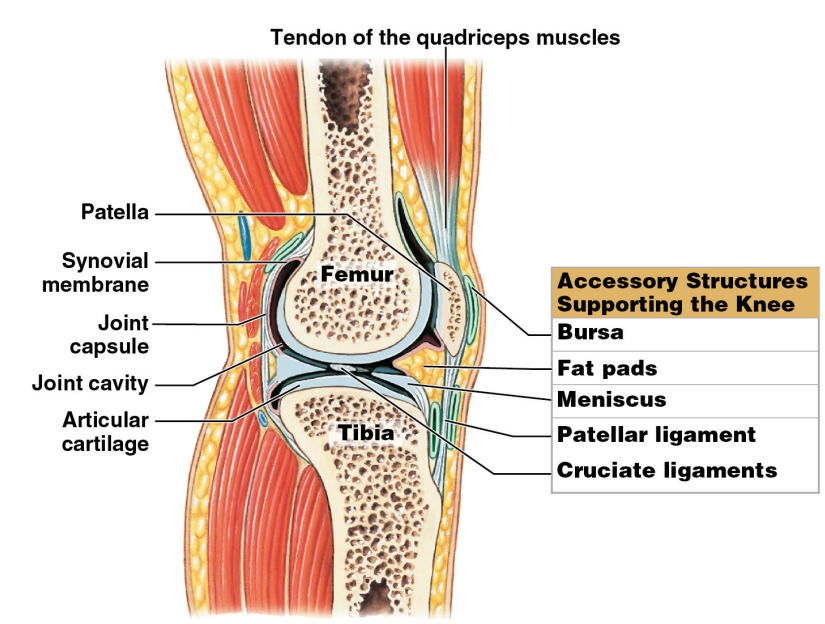
Accessory Structures Supporting the Knee
* It provides support and additional stability
* ^^Tendon of the quadriceps muscle^^
* ^^It is not part of the knee joint itself^^
* ^^It limits the range of motion and provides mechanical support^^
* Bursa
* Fat pads
* Meniscus
* Patellar ligament
* Cruciate ligaments
* ^^Tendon of the quadriceps muscle^^
* ^^It is not part of the knee joint itself^^
* ^^It limits the range of motion and provides mechanical support^^
* Bursa
* Fat pads
* Meniscus
* Patellar ligament
* Cruciate ligaments
97
New cards
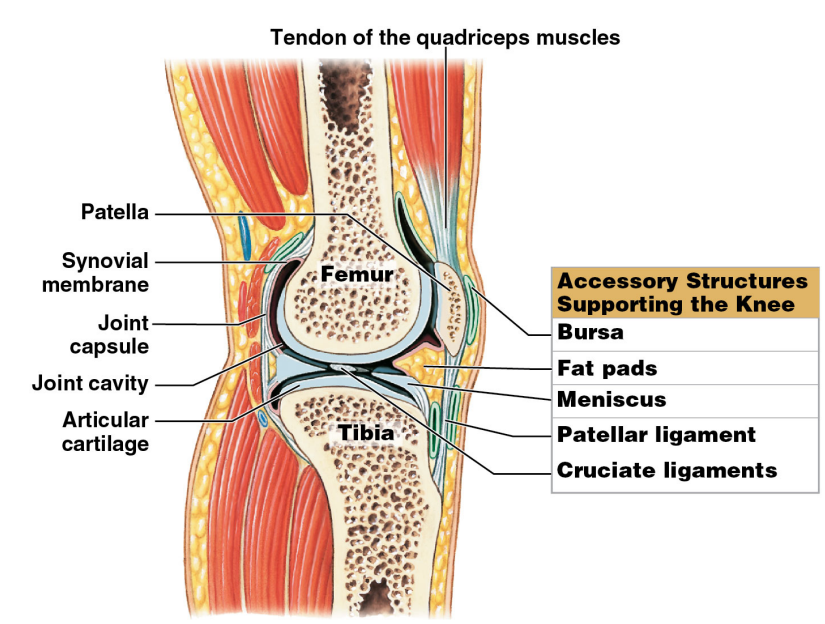
Bursa
* Small, thin fluid-filled pocket filled with synovial fluid and lined by synovial membrane
* Mini sacs / bags
* Forms in connective tissue outside a joint capsule
* Reduces friction
* Acts as shock absorber
* Mini sacs / bags
* Forms in connective tissue outside a joint capsule
* Reduces friction
* Acts as shock absorber
98
New cards
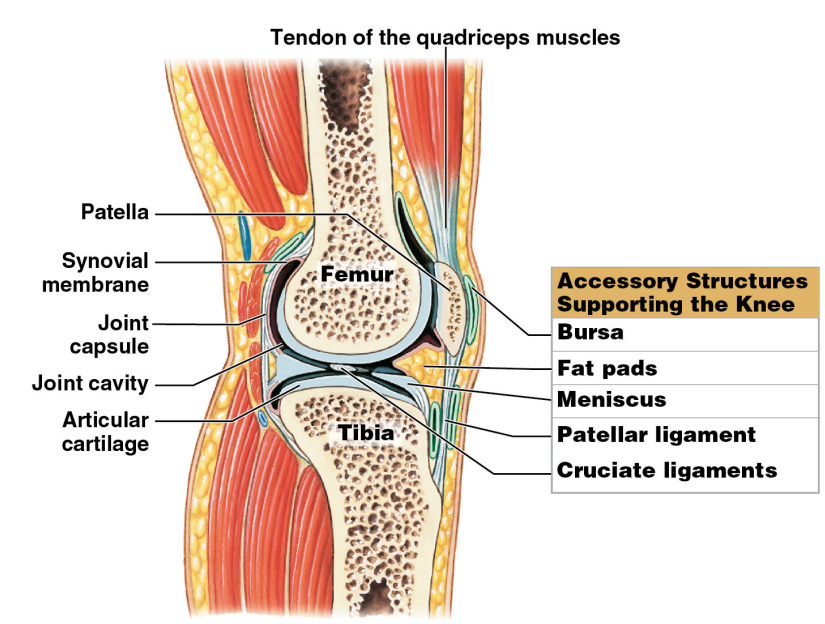
Fat pads
* Localized masses of adipose tissue covered by a layer of synovial membrane
* Usually superficial to joint capsule
* Protect articular cartilage
* Fill in spaces created as joint moves and joint cavity changes shape
* Storage of nutrient molecules
* Absorbs more shock/compression shock
* Usually superficial to joint capsule
* Protect articular cartilage
* Fill in spaces created as joint moves and joint cavity changes shape
* Storage of nutrient molecules
* Absorbs more shock/compression shock
99
New cards
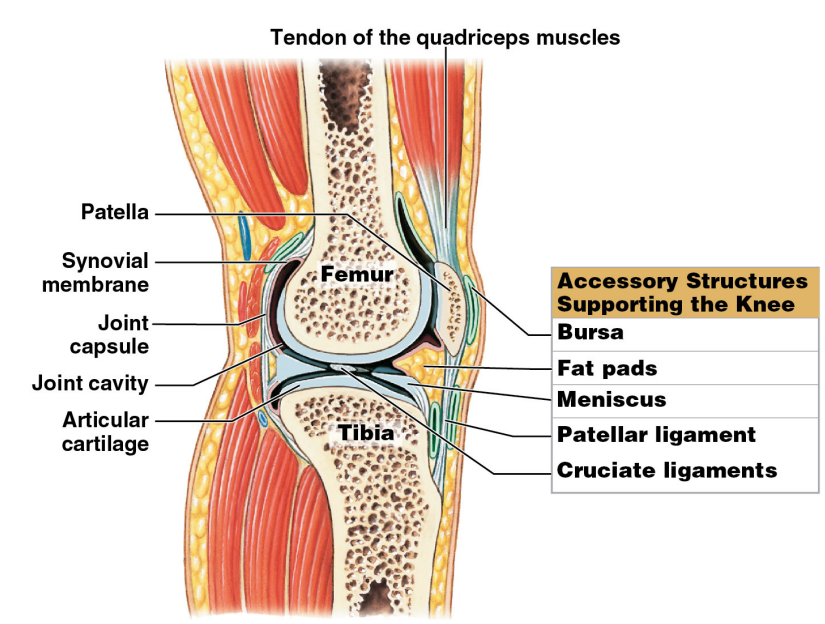
Meniscus
* Pad of fibrocartilage between opposing bones in a synovial joint
* May subdivide a synovial cavity
* May channel synovial fluid flow
* Allows variations in the shapes of the articular surfaces
* Made of chondrocytes; its cartilage
* May subdivide a synovial cavity
* May channel synovial fluid flow
* Allows variations in the shapes of the articular surfaces
* Made of chondrocytes; its cartilage
100
New cards
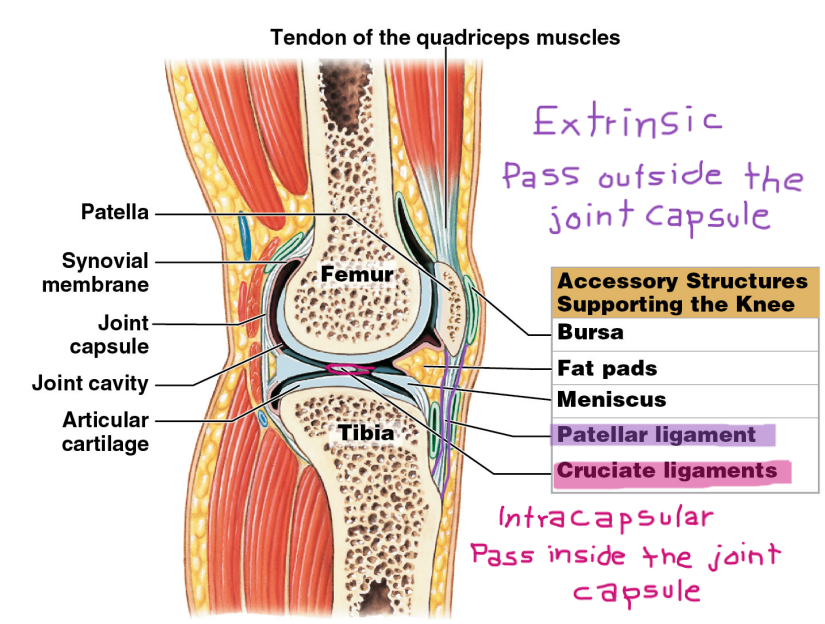
2 Type of Accessory Ligaments
* %%Extrinsic liagments%%
* Separate from the joint capsule
* Extracapsular ligaments (pass outside the joint capsule)
* Ex. Patellar ligament
* %%Intracapsular ligaments%%
* passes inside the joint capsule
* Ex. cruciate ligaments
* Separate from the joint capsule
* Extracapsular ligaments (pass outside the joint capsule)
* Ex. Patellar ligament
* %%Intracapsular ligaments%%
* passes inside the joint capsule
* Ex. cruciate ligaments