Opisthokonta (pt 1)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Choanoflagellates — closest relative to animals
Extant group that is model for last unicellular ancestor of animals
Both free-living and colonial species
Ovoid or spherical cell body
Single flagellum
Collar of microvilli engulfs food particles
Animals (Metazoa) are
Multicellular eukaryotes that lack cell walls
Heterotrophic
Most have nerve and muscle cells (Porifera**, Cnidaria*)
Mostly reproduce sexually
Animals ingest their food
suspension feeding
bulk feeding
fluid feeding
Intracellular Digestion
Ex. Porifera
Food particles flow through ostia (s. ostium) and flows out osculum
Intracellular digestion (via flagellated choanocyte cells)
choanocytes: collar of microvilli and single flagellum- create water flow and trap food particles
Extracellular digestion
Ex. Cnidaria
Tentacles encircle mouth and aid in food capture (incomplete gut)
Extracellular digestion (via enzymes in gut)
Intracellular digestion (via nutritive-muscular cells)
Lepidoptera (Insecta, Hexapoda, Arthropoda)
bulk feeding
Porifera
filter feeding
Most animal groups have cell types organized into tissues, which are organized into systems
Sensory system
Detect prey
Capture prey
Movement system
Approach prey
Subdue prey
Ingest prey
Circulatory/ Respiratory system
Move oxygen, nutrients, and waste
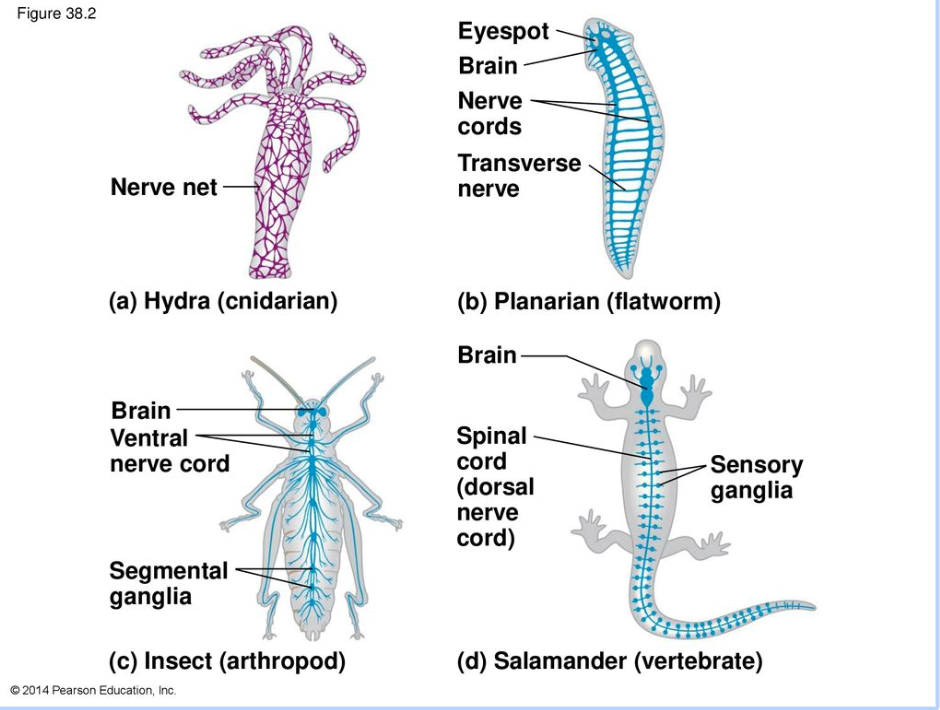
Sensing system = nervous system
Nerve cells rapidly convey messages from one cell to another
alert the animal to environmental stimuli
enable the animal to respond with coordinated movements
Animal Reproduction
Internal fertilization :
Sperm unites with the egg inside of the adult
External fertilization :
Egg and sperm unite outside of the adult
Monoecious :
One individual produces both M and F gametes
Dioecious :
One individual produce either M or F gametes
Neuron
nerve cells stimulated by electrical/ chemical signals to transmit information between different areas of brain and rest of nervous system
Sensory neurons
carry information from sense organs to brain
Motor neurons
transmit information from brain to muscles
Almost all animals reproduce sexually*
*Some can switch sexes or reproduce asexually
Zygote:
Fusion of two haploid gametes
Large maternal gamete (egg or ovum)
Small paternal gamete (sperm)
Results in a diploid (2n) zygote
Contains 2 alleles of each gene