biology midterm
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
independent variable
variable being intentionally changed in an experiment
dependent variable
variable being measured, depends on the independent
control group
the group being used as a baseline for comparison
constants
factors kept the same across all groups
carbon
the primary skeleton for biomolecules
lipids
fats and oils that store energy and make up cell membranes
proteins
there are proteins build and repair body structures, proteins called enzymes that speed up chemical reactions in the body, proteins that provide immune defense, and proteins that transport substances in and out of cells
carbohydrates
sugars and starches that provide energy
nucleic acids
molecules that store genetic information
water polarity
water is polar because oxygen is slightly negative and hydrogen is slightly positive
cohesion
water molecules stick to each other, giving high surface tension
adhesion
water molecules stick to other substances, like when water clings to glass or plant walls
monomers
building blocks that link together to form polymers
proteins
there are enzymes that speed up reactions in the body, proteins that structurally support cells, proteins that provide immune defense, and proteins that transport substances around the body
lysosome
breaks down and recycles cellular waste
mitochondria
produces ATP
nucleus
stores genetic material
cell membrane
fluid mosaic model, selectively permeable (some substances can pass through, other s can’t)
passive transport
the movement of molecules with no energy required
active transport
molecules moving against the normal flow of diffusion, therefore using more energy
hypotonic
higher water concentration outside, cell gains mass
hypertonic,
higher solute concentration outside, cell loses mass
isotonic
equal concentration
light dependent reactions
captures energy from sunlight, occurs in the thylakoid membrane, produces oxygen and ATP from water
light independent reactions
occur in the stroma and produces glucose from carbon dioxide
chlorophyll
a molecule that absorbs light energy, found in chloroplasts, essential for photosynthesis
glycolysis
glucose (six carbons) is broken in half, (each half 3 carbons called pyruvate)
krebs cycle
produces a small amount of atp and other molecules to carry energy to the next part of respiration, and makes CO2 as waste
electron transport chain
final step in cellular respiration for ATP production, energy is moved through a chain of proteins, producing ATP.
fermentation
anaerobic process when oxygen is unavailable
ATP
primary energy currency of the cell
mitosis
the division of the cell nucleus and the DNA inside it
mitosis stages
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis
prophase
chromosomes condense, nuclear envelope diappears
metaphase
chomosomes align at the center
anaphase
chromosomes separate to opposite poles
telophase
chromosomes at poles, nuclear envelope reforms
cytokinesis
cytoplasm divides, forming two cells
cell cycle stages
G1, synthesis, G2
gap 1
cell growth
synthesis (S phase)
DNA replication
gap 2
preparation for division
ratio
smaller cells have more surface area compared to their volume, making it easier to quickly take in nutrients and get rid of waste.
why does carbon make up the skeleton of all biomolecules?
it has 4 positions to bind with other elements
order of the path followed for the production of proteins
nucleus, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi body, vesicle
how are cellular respiration and photosynthesis related?
its goal is to use the products of photosynthesis to create ATP
final receptor of electrons in the ETC
oxygen
why is DNA replicated before mitosis?
so that each daughter cell has the same number of chromosomes as the original cell
pH scale
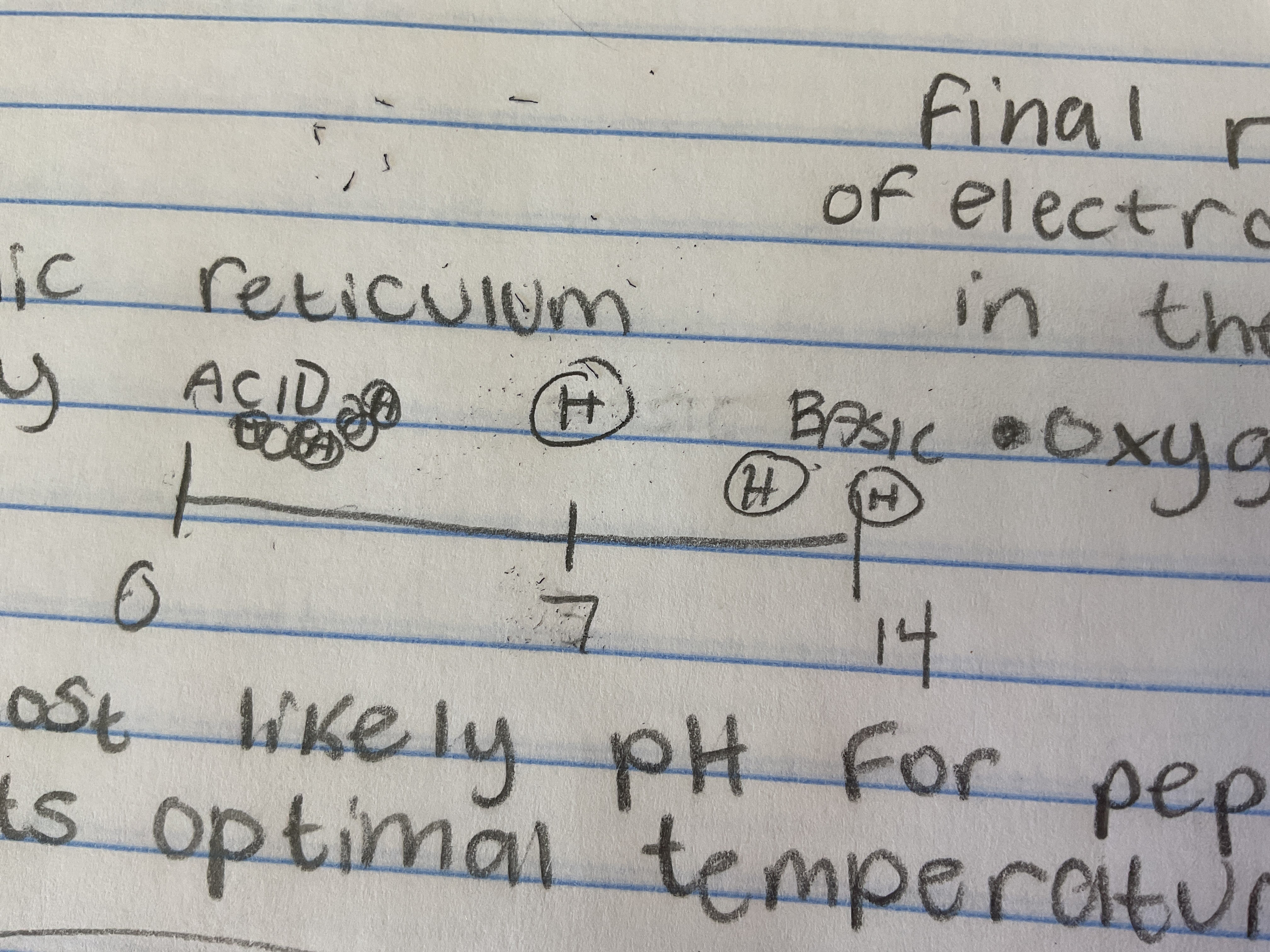
when are chromosomes surrounded by the nucleus
during prophase