carbohydrates structure
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
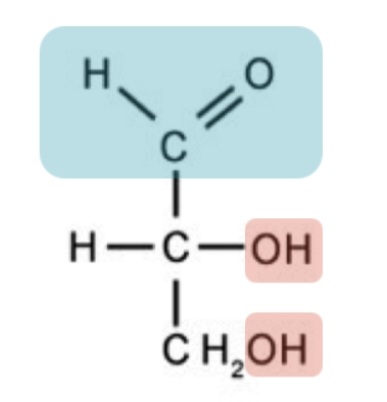
Glyceraldehyde structure
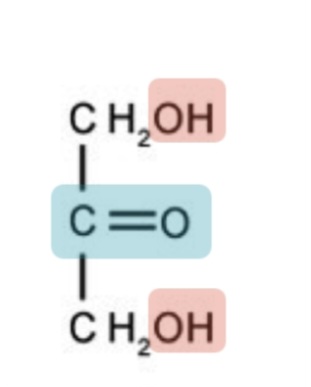
Dihydroxyacetone structure
polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones.
In biochemical perspective, a carbohydrate is defined as
hydrates of carbon
Initially carbohydrates are referred to as “____“ which follows stoichiometric formula (CH2O)n
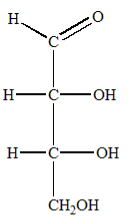
Four Carbons
D-Erythrose
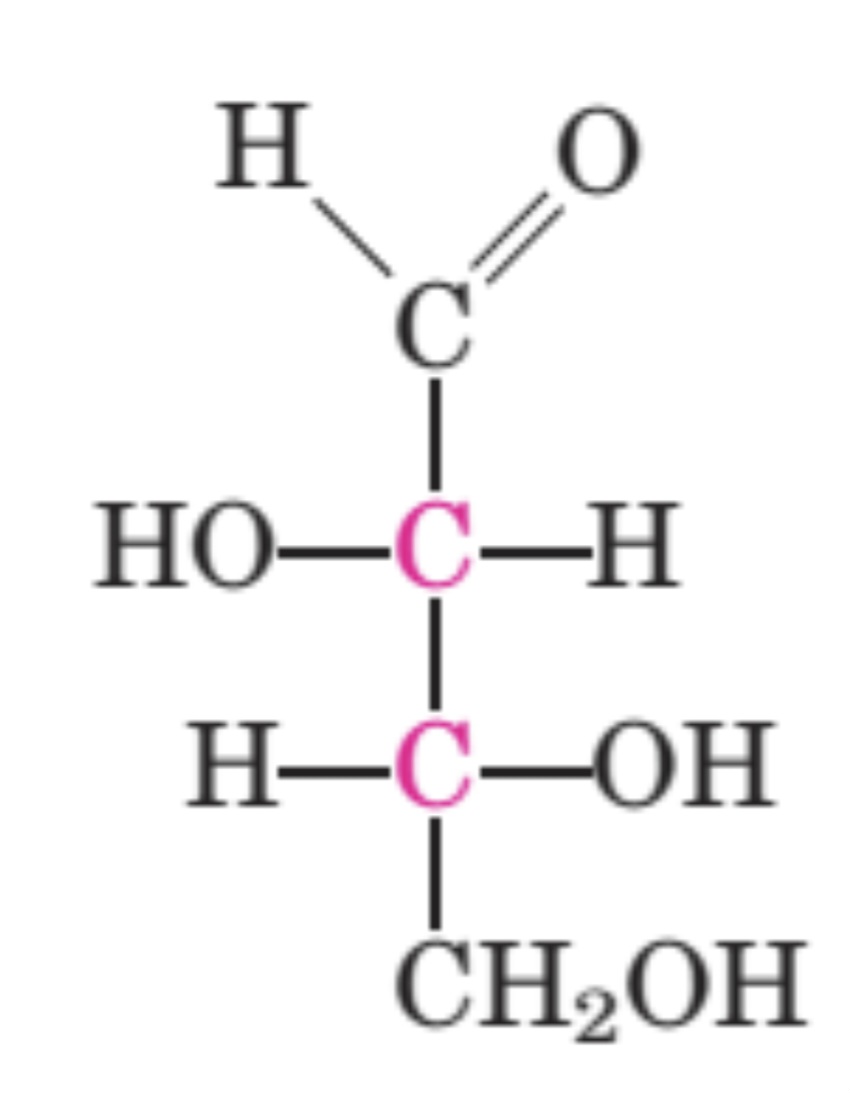
Four Carbons
D-Threose
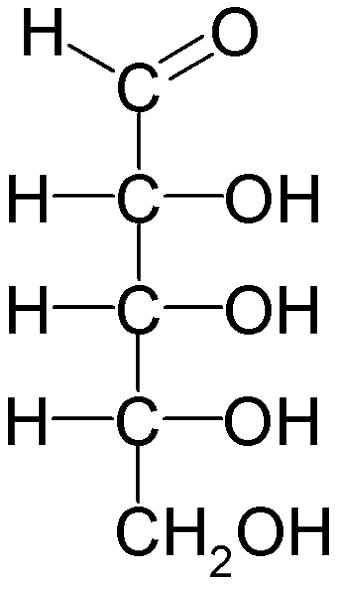
Five Carbons
D-Ribose
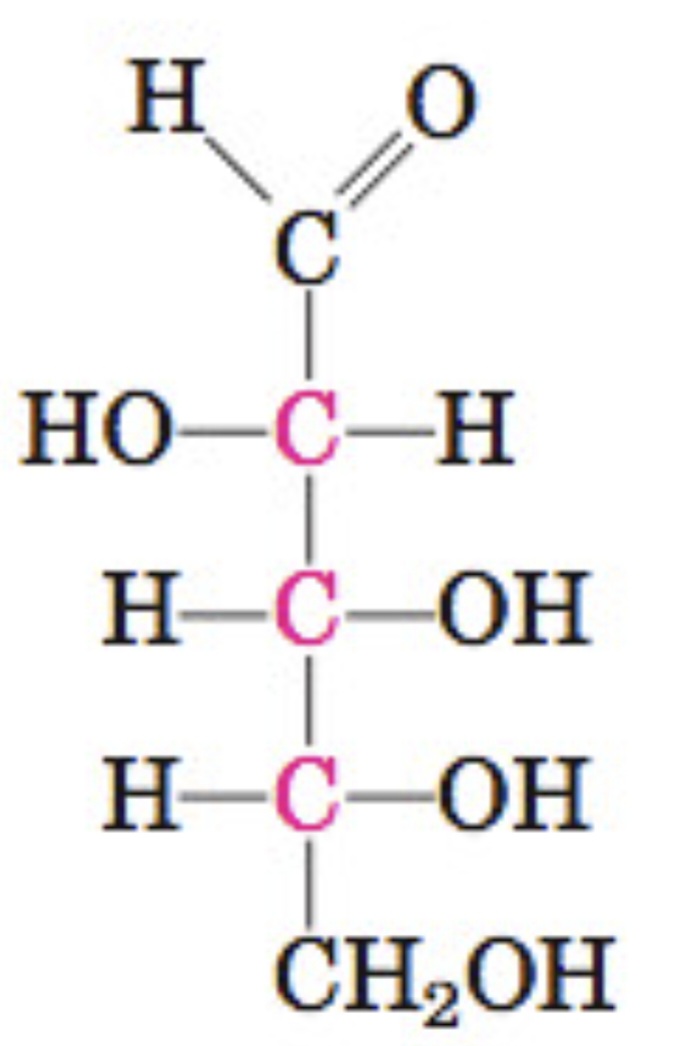
Five Carbons
D-Arabinose
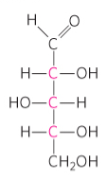
Five Carbons
D-Xylose
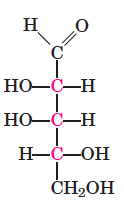
Five Carbons
D-Lyxose
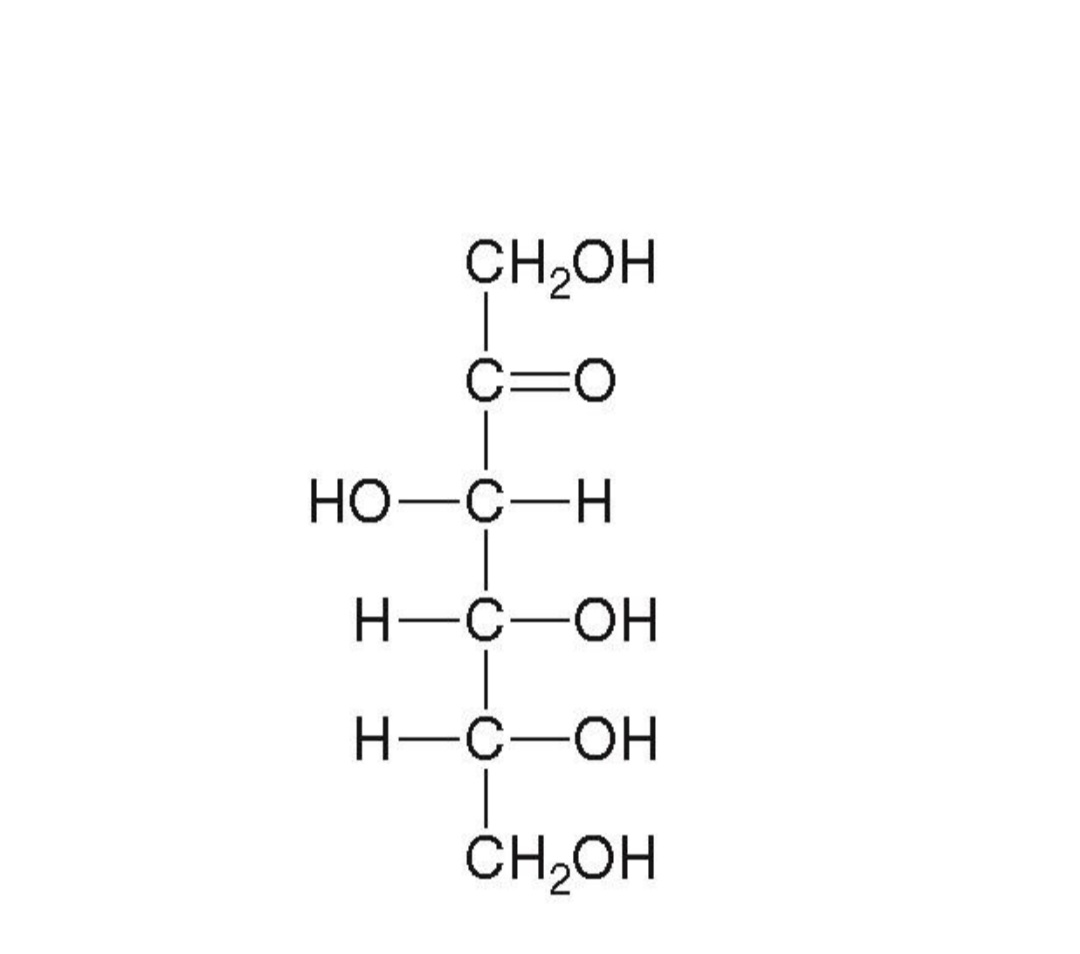
Fructose
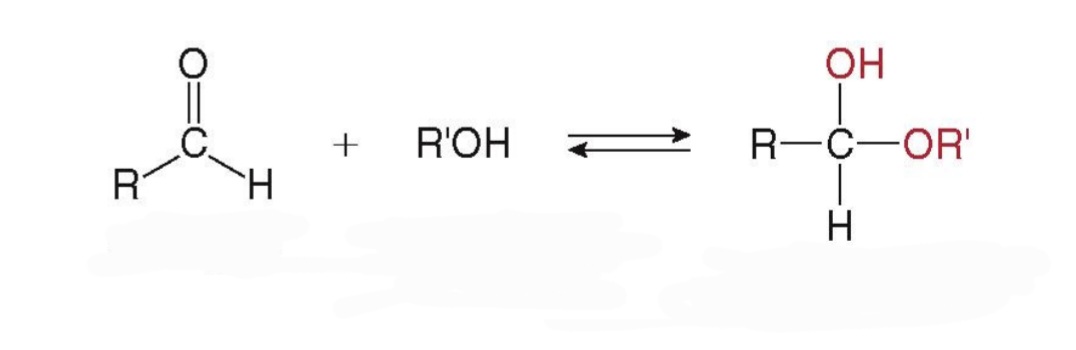
Hemiacetal
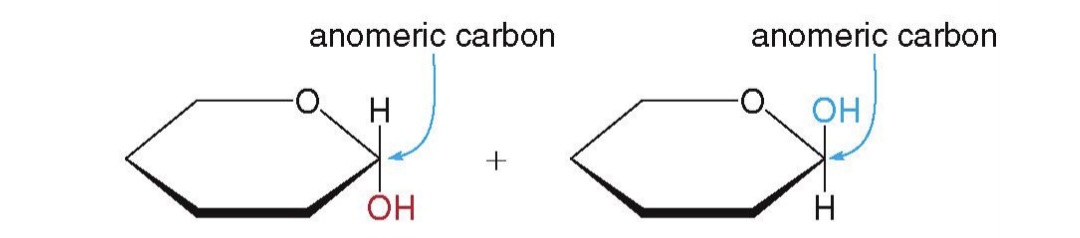
alpha anomer, beta anomer
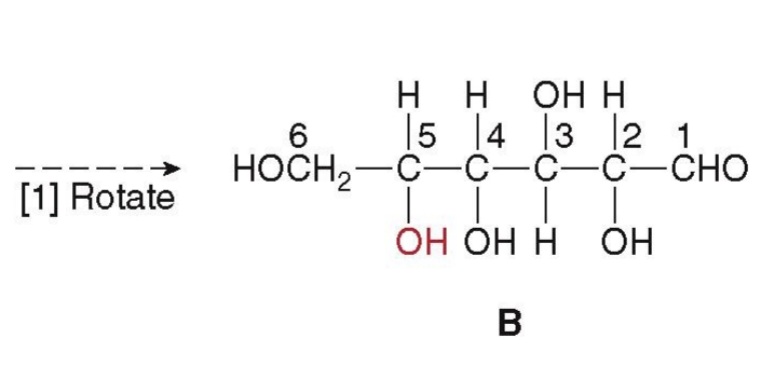
first step in cyclization - rotate glucose 90°
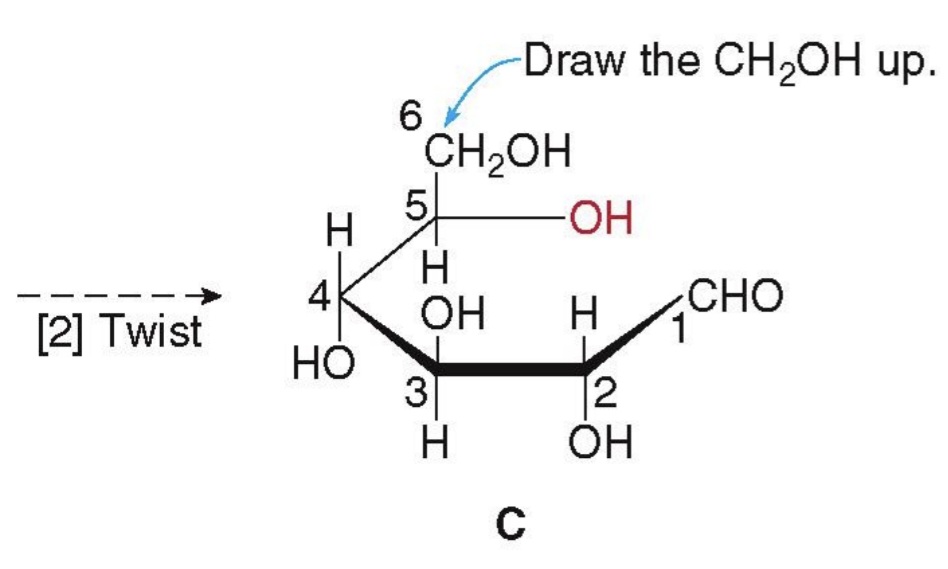
the chain must be twisted around, forming
a six-membered ring:
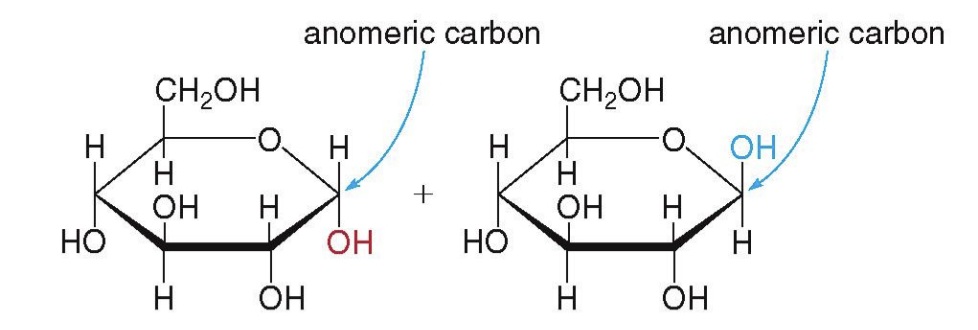
Alpha-D-Carbon and Beta-D-Glucose
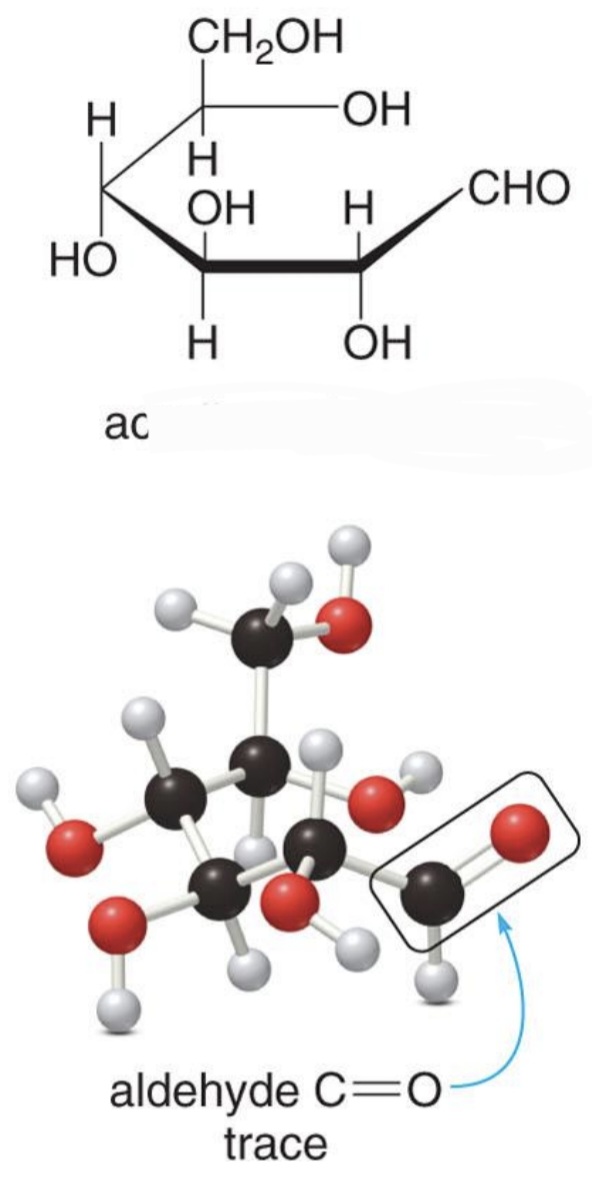
Acylic-D-Glucose
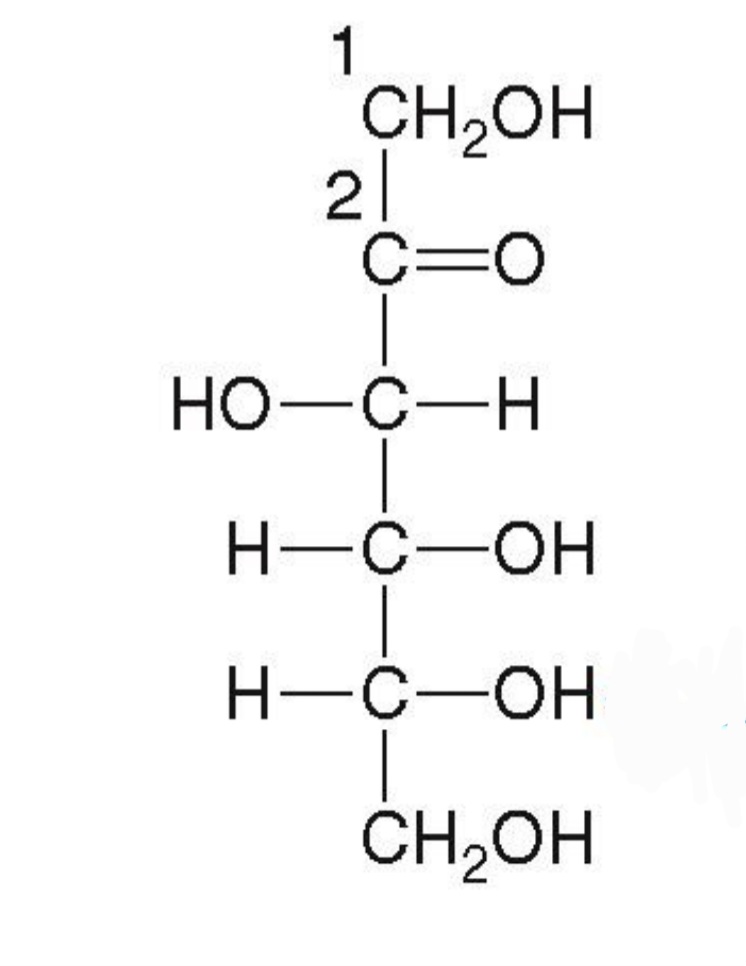
Acylic-D-Fructose
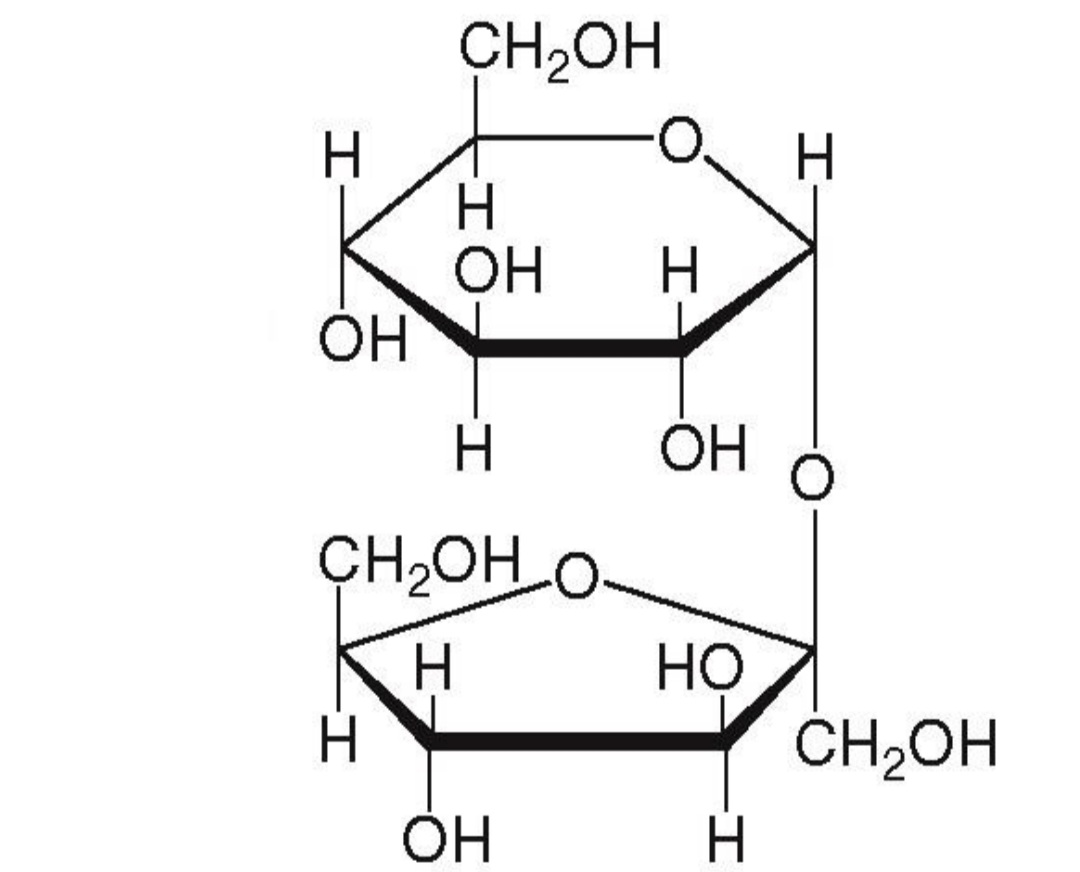
Sucrose
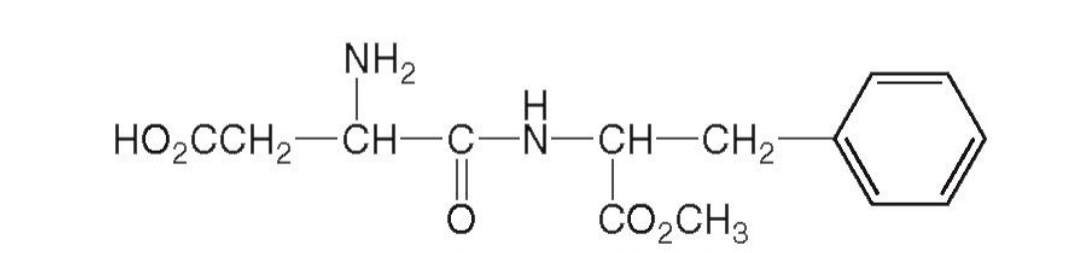
Aspartame(Trade name:Equal)
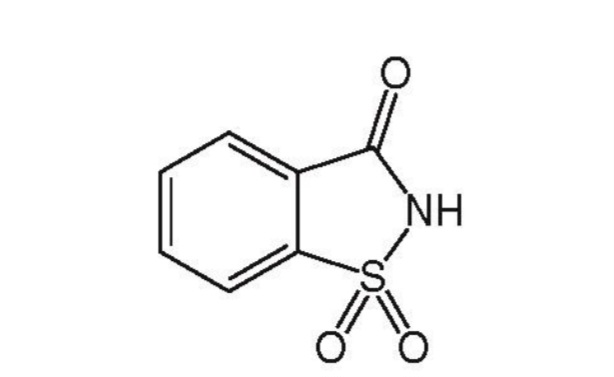
Saccharin(Trade name: Sweet’n Low)
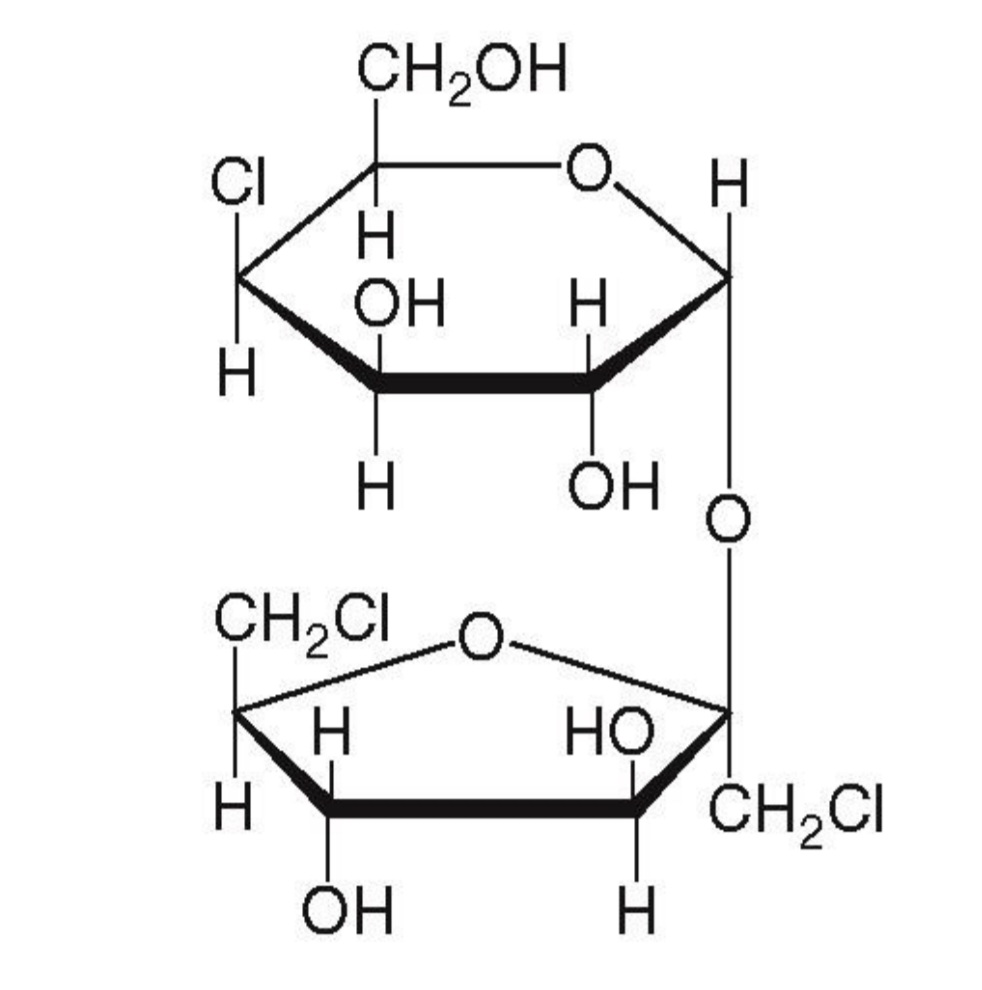
Sucralose(Trade name: Splenda)
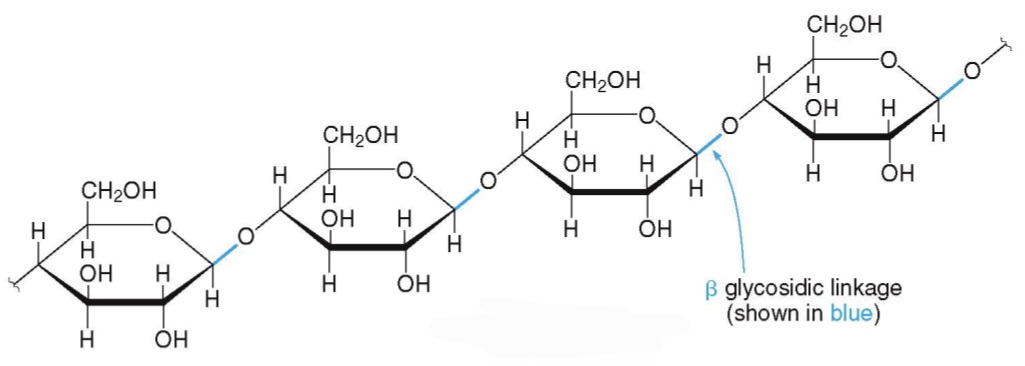
Cellulose
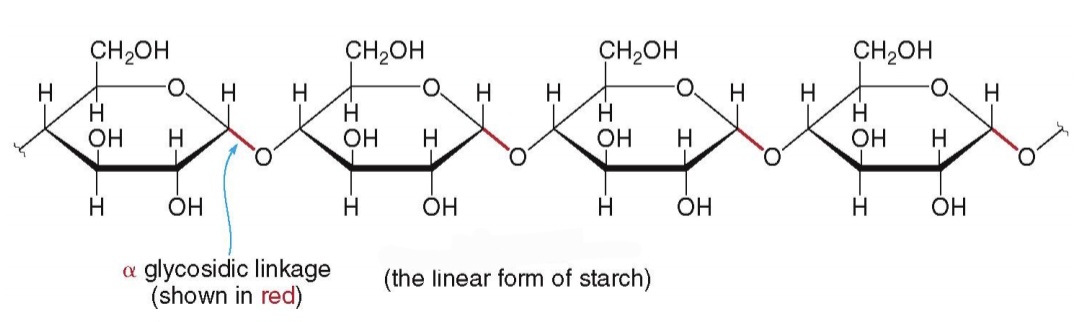
The first main type of starch is: Amylose
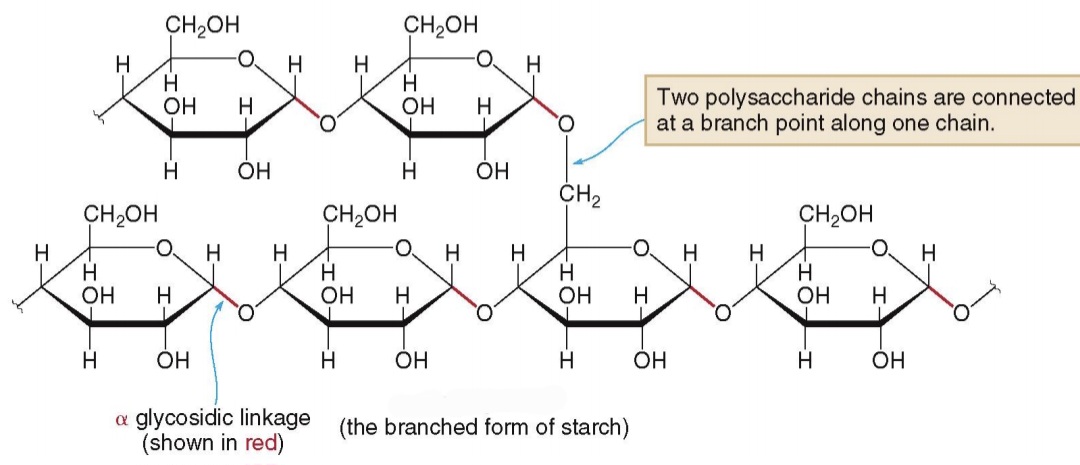
The second type of starch is: Amylopectin
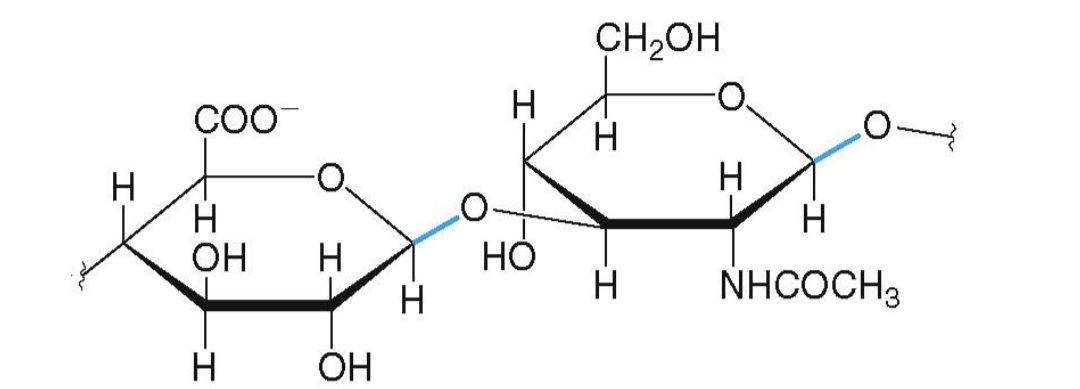
hyaluronate
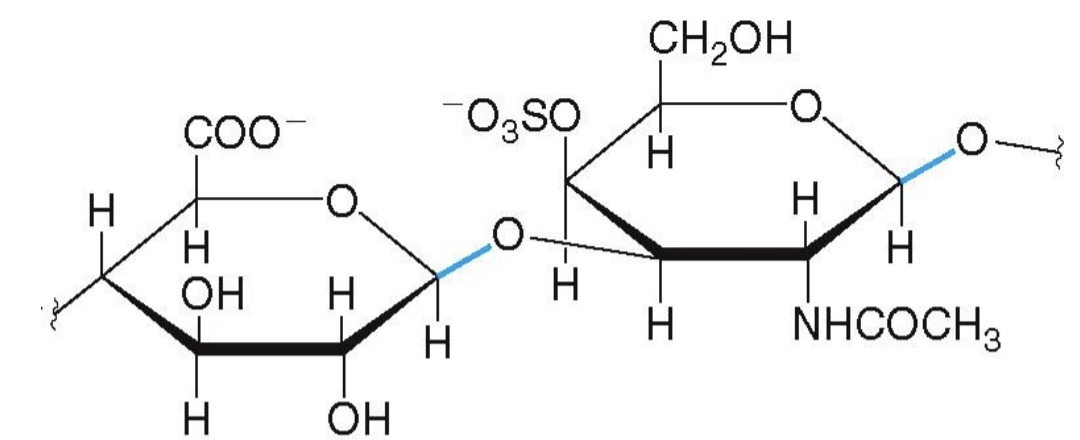
a component of cartilage and tendons: Chondroitin
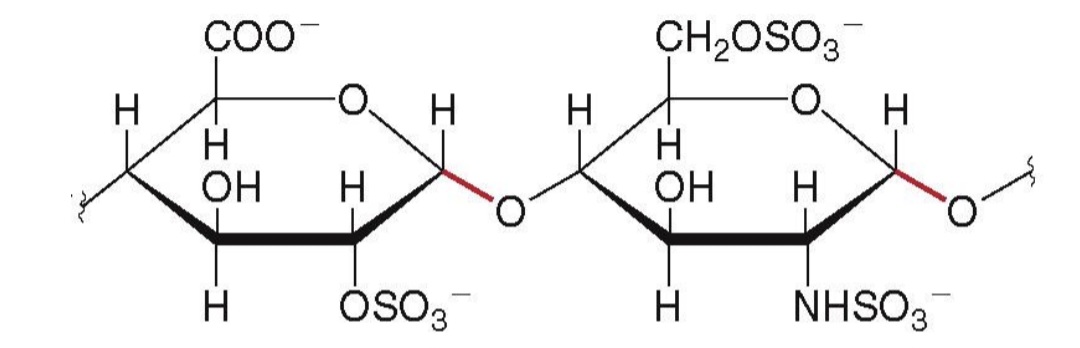
Heparin - stored in the mast cells of the liver, helps prevent blood clotting.
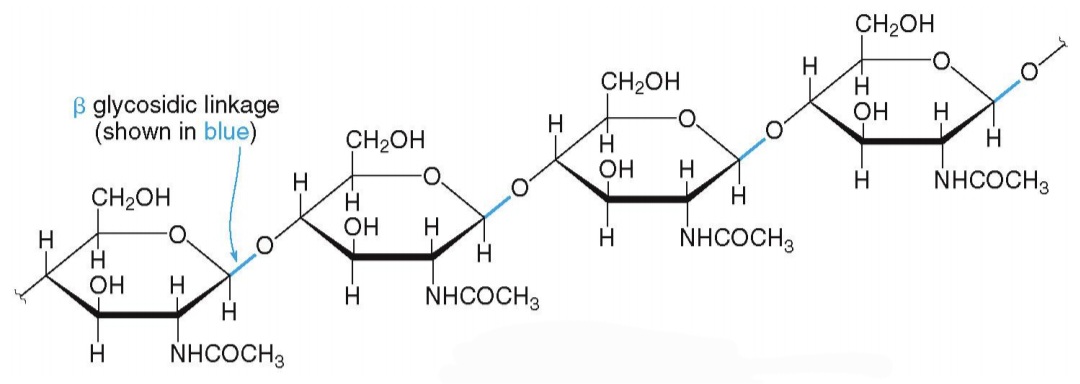
Chitin - is a polysaccharide formed from N-acetyl-D-glucosamine units joined together by 1→4-b-glycosidic linkages.
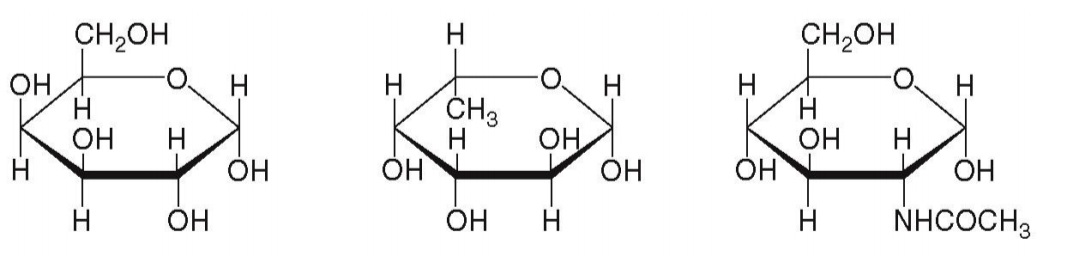
D - Galactose
L - Fucose
N - acetyl-D-Glucosamine
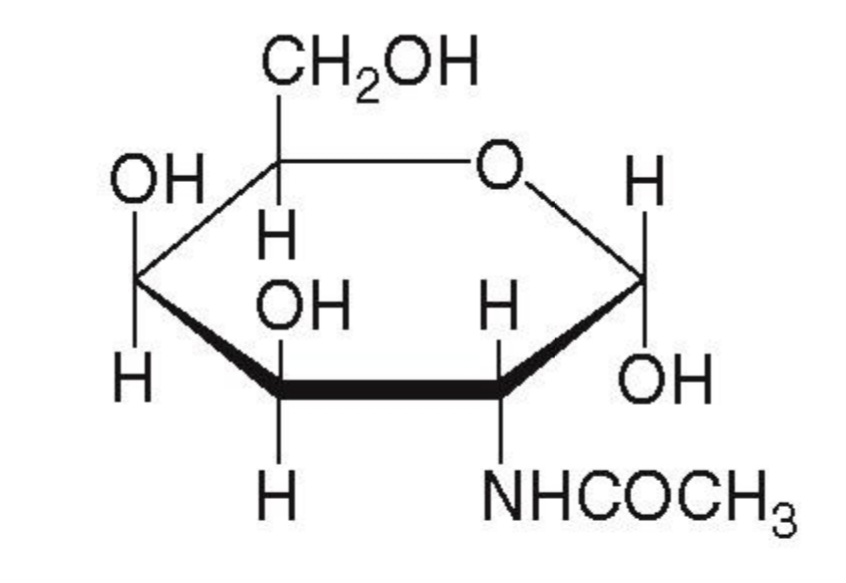
Type A blood contains a fourth monosaccharide:
N-acetyl-D-Galactosamine
Type B
contains an additional D-galactose unit