CSAD 111 Exam 3 - Davis
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Source filter theory
Source = vocal folds
Filter = vocal tract
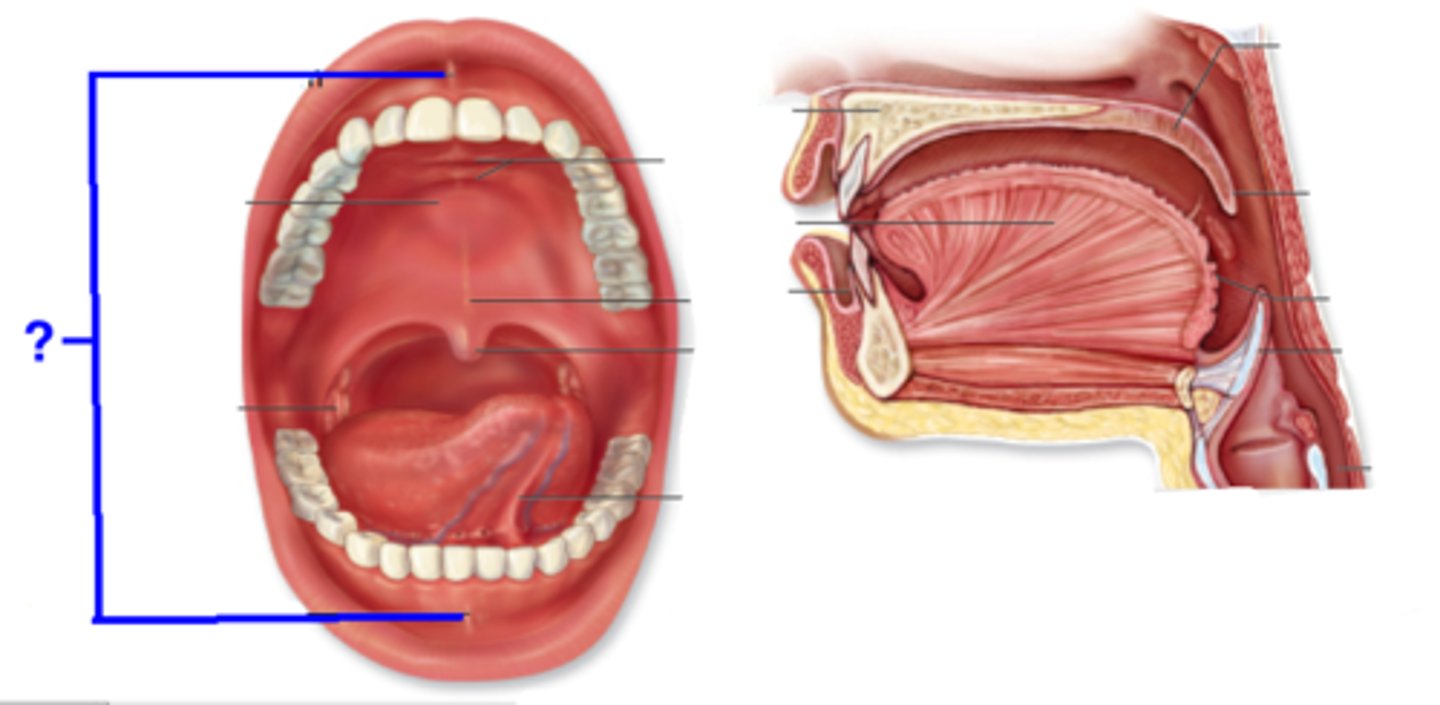
Lips
• make ____ and _____ consonants
• Used to remove _____ from spoon
• Drink from a ___
• make /p b m/ and /f v/ consonants
• Used to remove bolus from spoon
• Drink from a cup
Labial frenulum
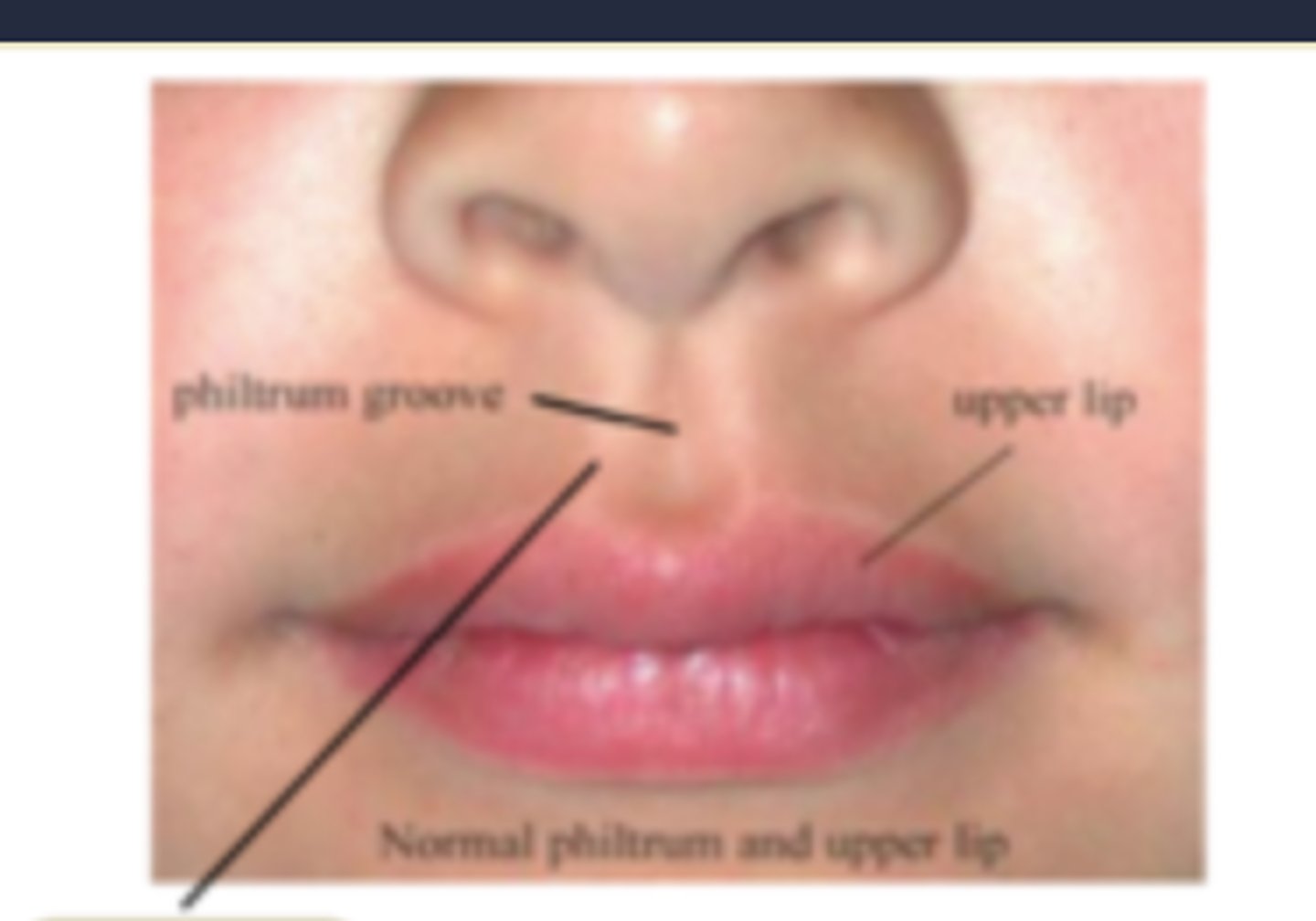
Philtral ridge
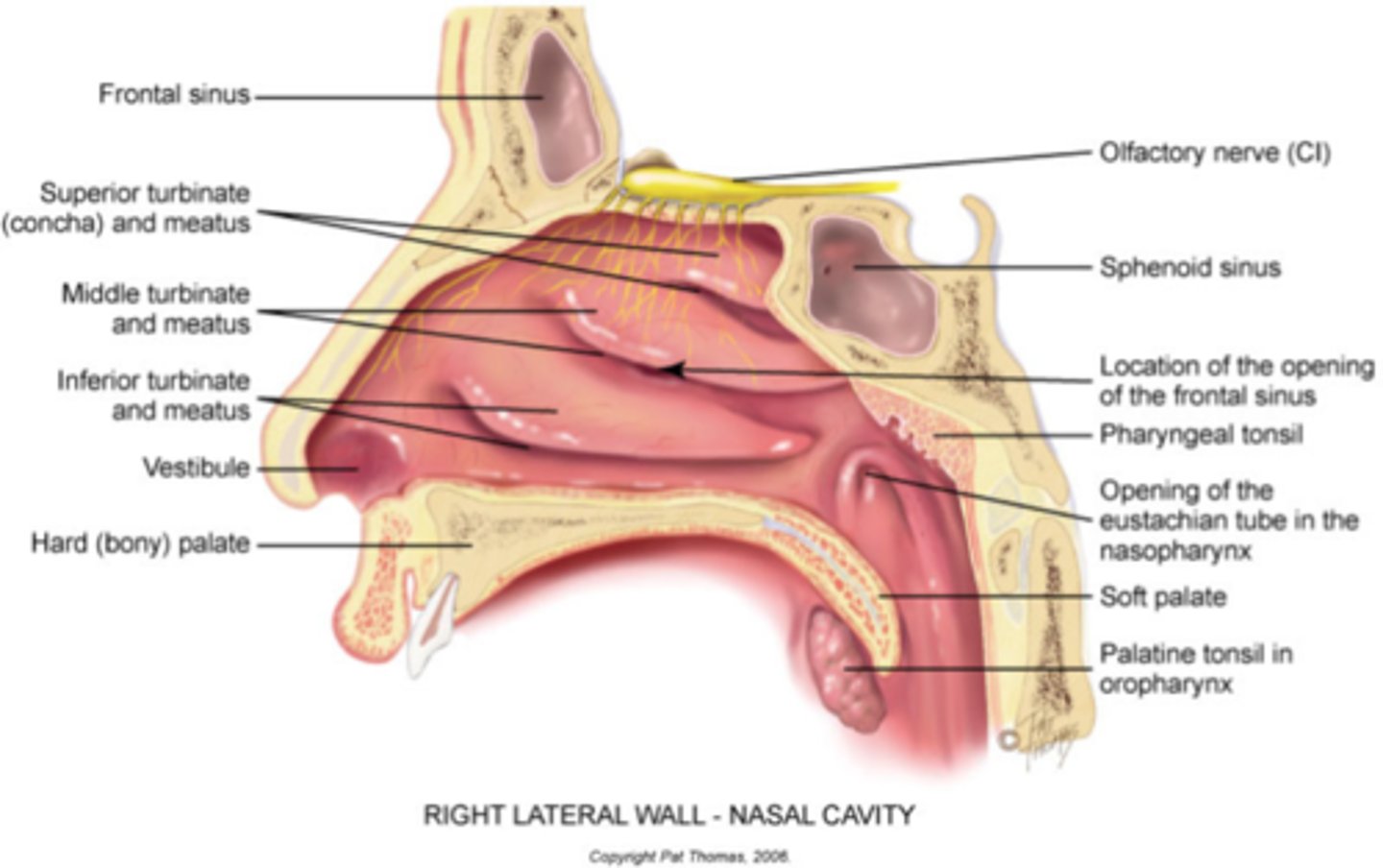
Nose'
Purpose: O___ (smelling), ______ regulation, H____y, _____ control
• Used for production of /m n/
• ____ at tip
• Divided in two by _____
• Purpose: Olfaction, Temperature regulation, Humidity, Particle control
• Used for production of /m n/
• Cartilage at tip
• Divided in two by septum
Nasal vestibule
Nasal turbinates provide _____ and ______
provide moisture, humidity
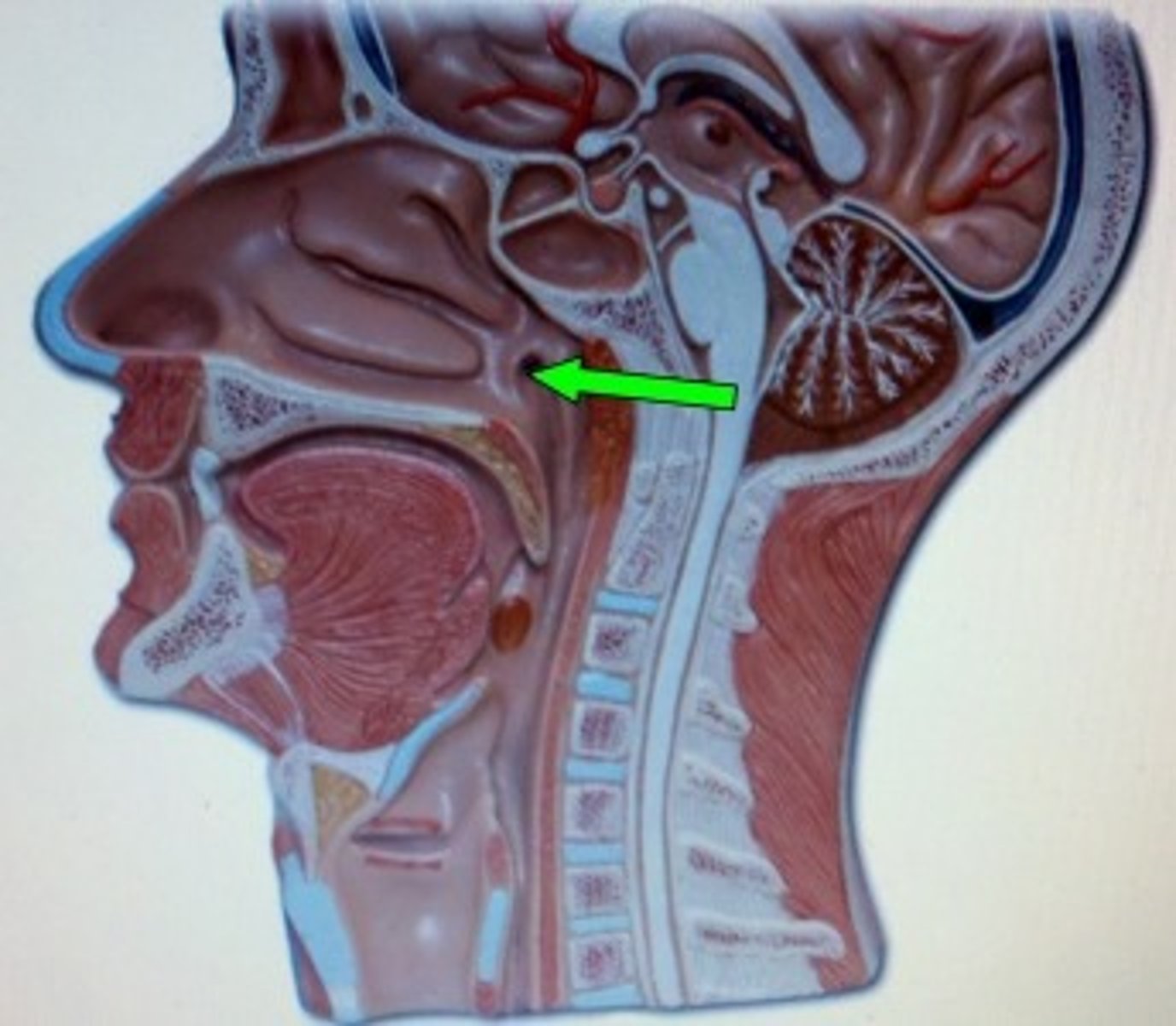
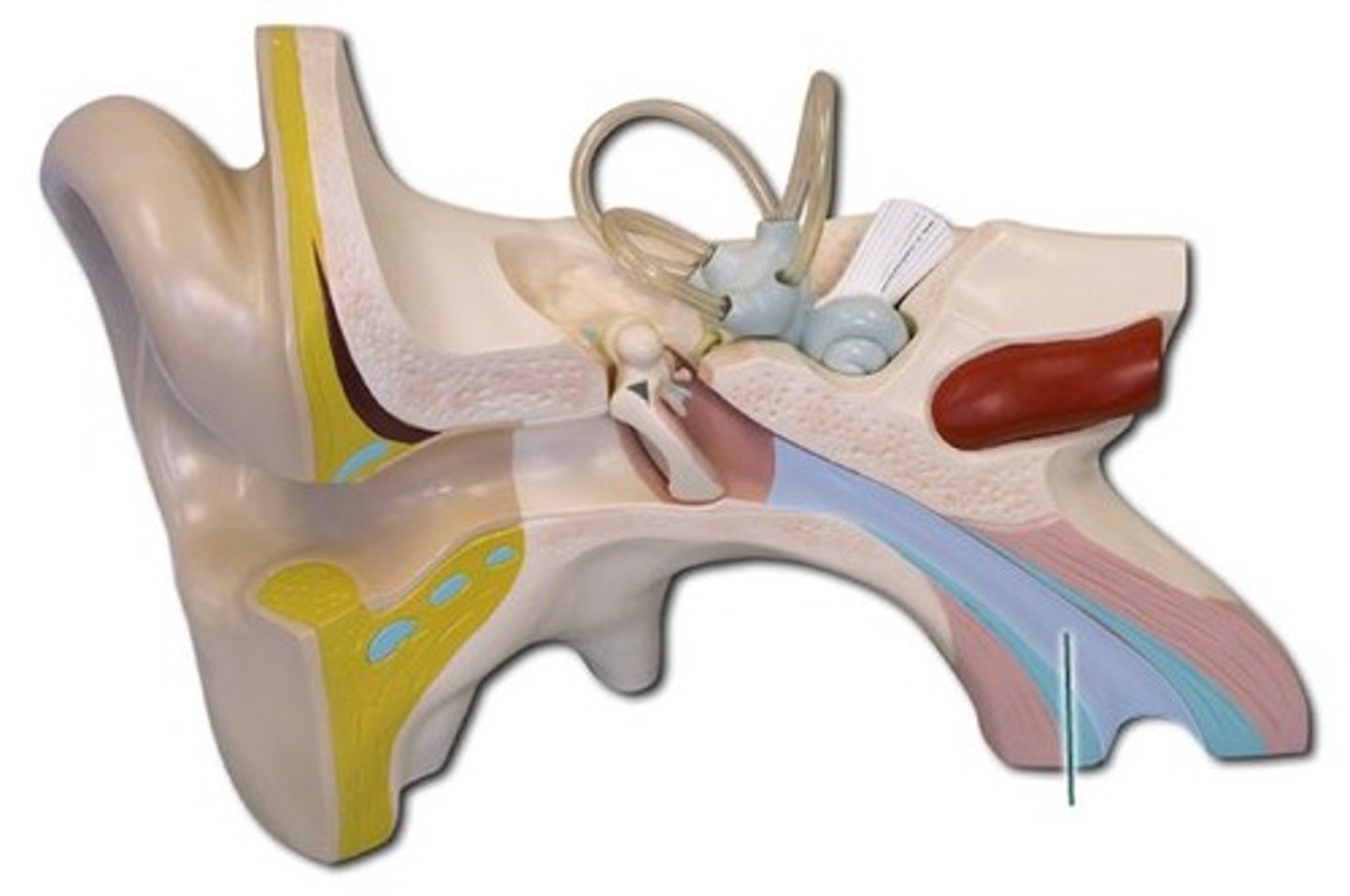
Eustachian tube in nasopharynx function
• Pressure changes, drainage

ET
Nasal cavity
Buccal Cavity aka your _____
muscles from ____ to ____
contain ______ salivary gland
creates ____ SPACE
puff up/ suck in your _____
• AKA your cheeks
• Muscles from jaw to skull
• Contain parotid salivary gland
• Creates oral SPACE
• Puff up your cheeks
• Suck in your cheeks
Tongue
• "Lingual"
• Movement (Protrude/retract, Lateralize, Tip up/down, Narrow/widen)
• #1 articulator
Tongue tip
____/____
part that touches ______ ridge
Apex/blade
- part that touches alveolar ridge
Tongue body
the main mass of the tongue
Tongue root ____ or _____ extends to _____ bone
Root or base of tongue extends to hyoid bone

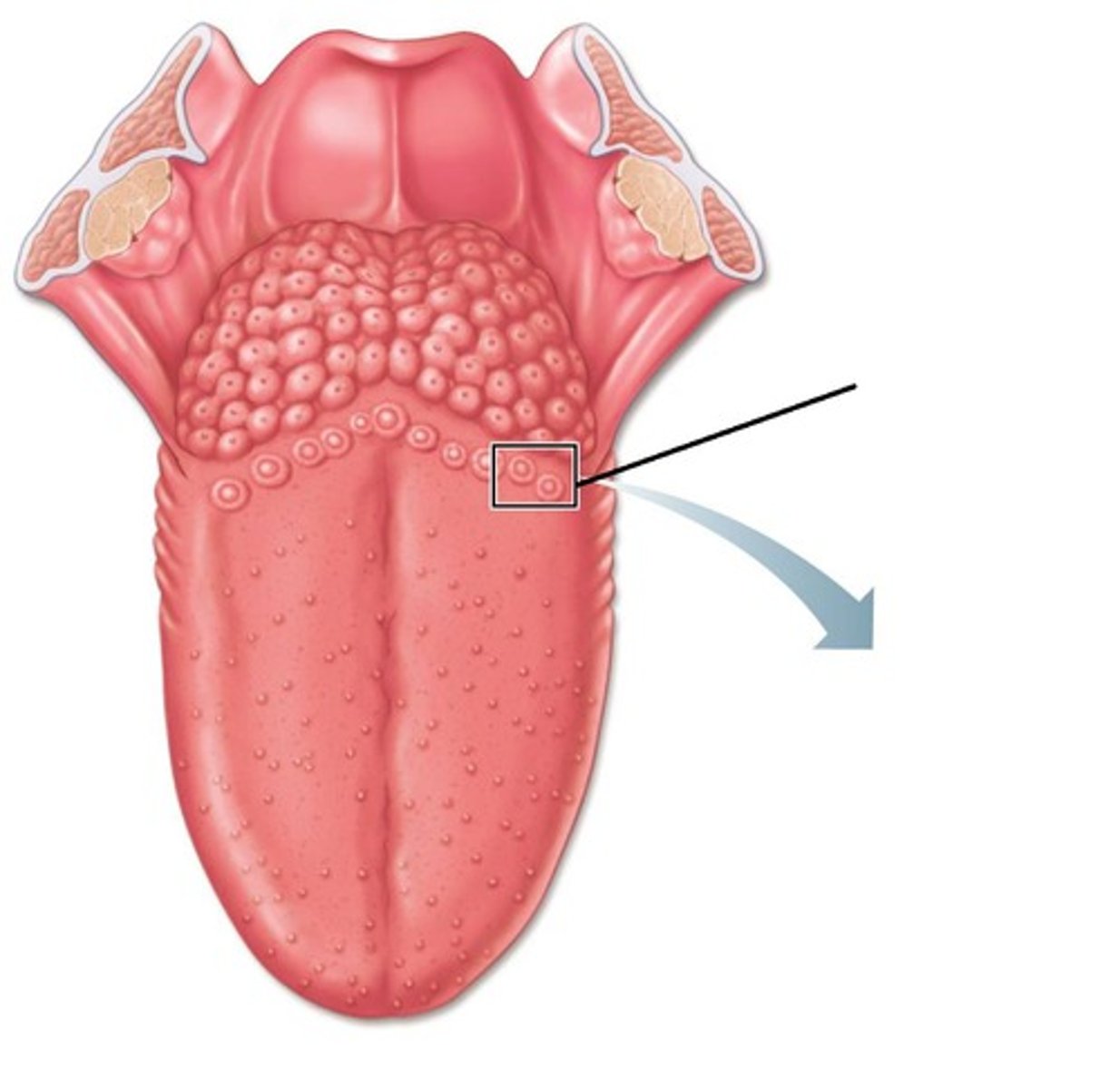
papillae
Lingual frenulum
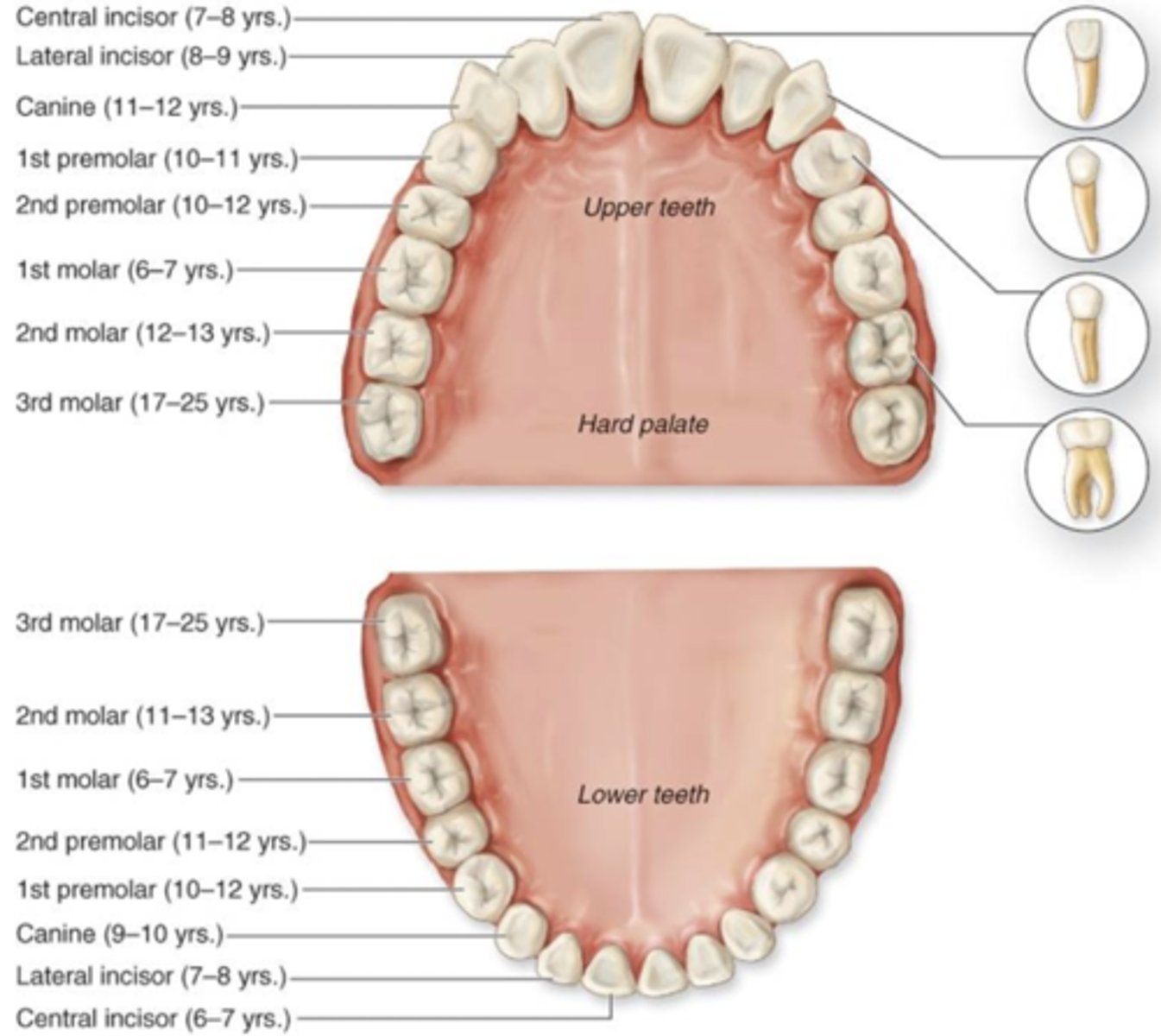
Types of teeth
____ incisors
______ incisor
c_____
1/2nd _____
1-3 _____
Central incisors, lateral incisor, canine, 1st premolar, 2nd premolar, 1st molar, 2nd molar, 3rd molar
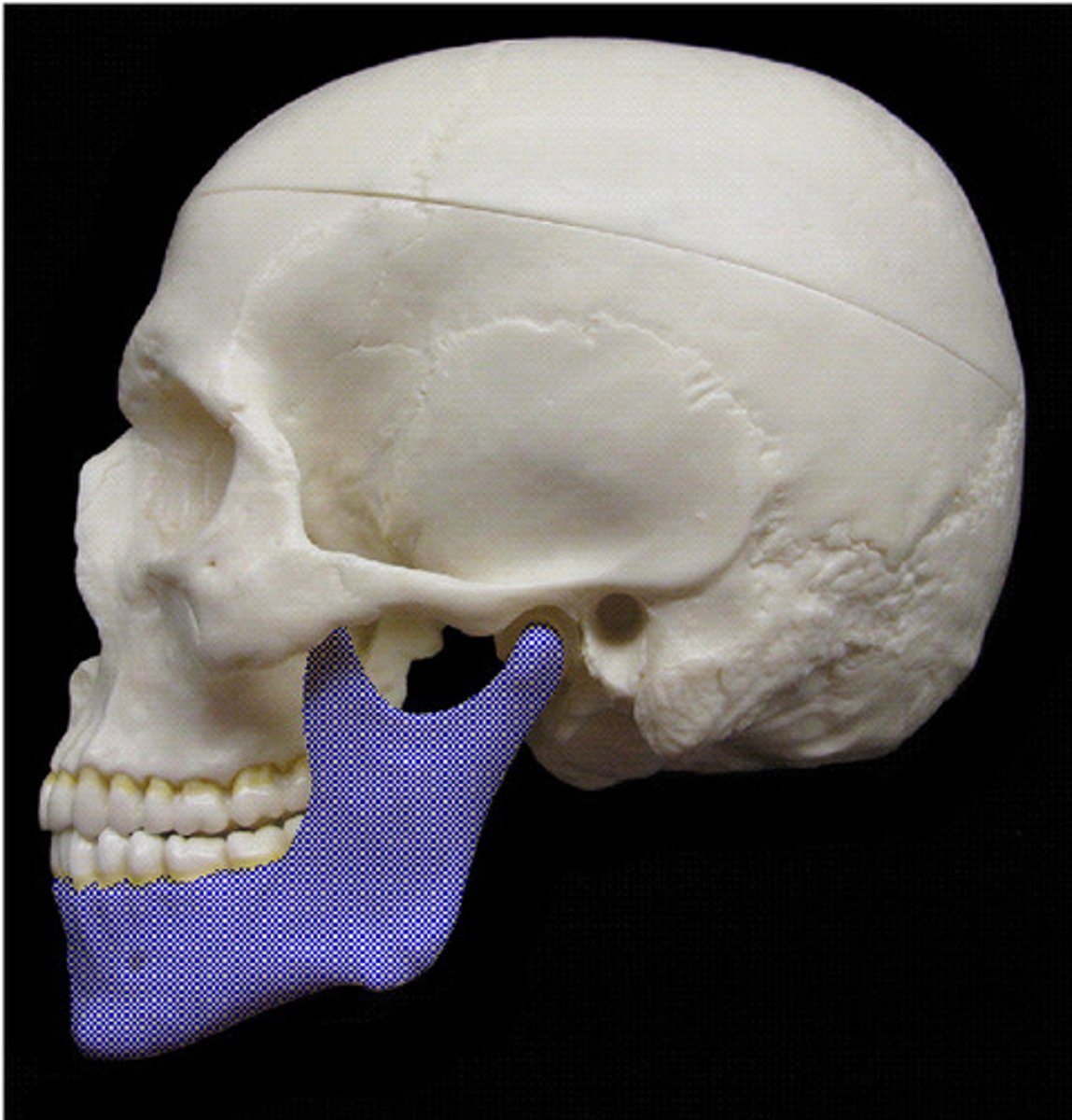
Mandible physiology
• _____ skull bone (detachable)
• _______ joint
• Movement (Raise/lower, Protrude/retract, Lateralize)
• Primary function is ______
• Secondary function is _____
• Unfused skull bone (detachable)
• Tempomandibular joint
• Movement (Raise/lower, Protrude/retract, Lateralize)
• Primary function is mastication (chewing)!
• Secondary function is talking
Hard and soft palate
functions to separate ____ and ____ cavities
open/close _____ port
• Velum (n) or velar (adj)
• Functions to separate nasal and oral cavities
• Hard (bony) vs. soft (muscle & mucosa)
- Soft palate can move
- Open/close velopharyngeal port
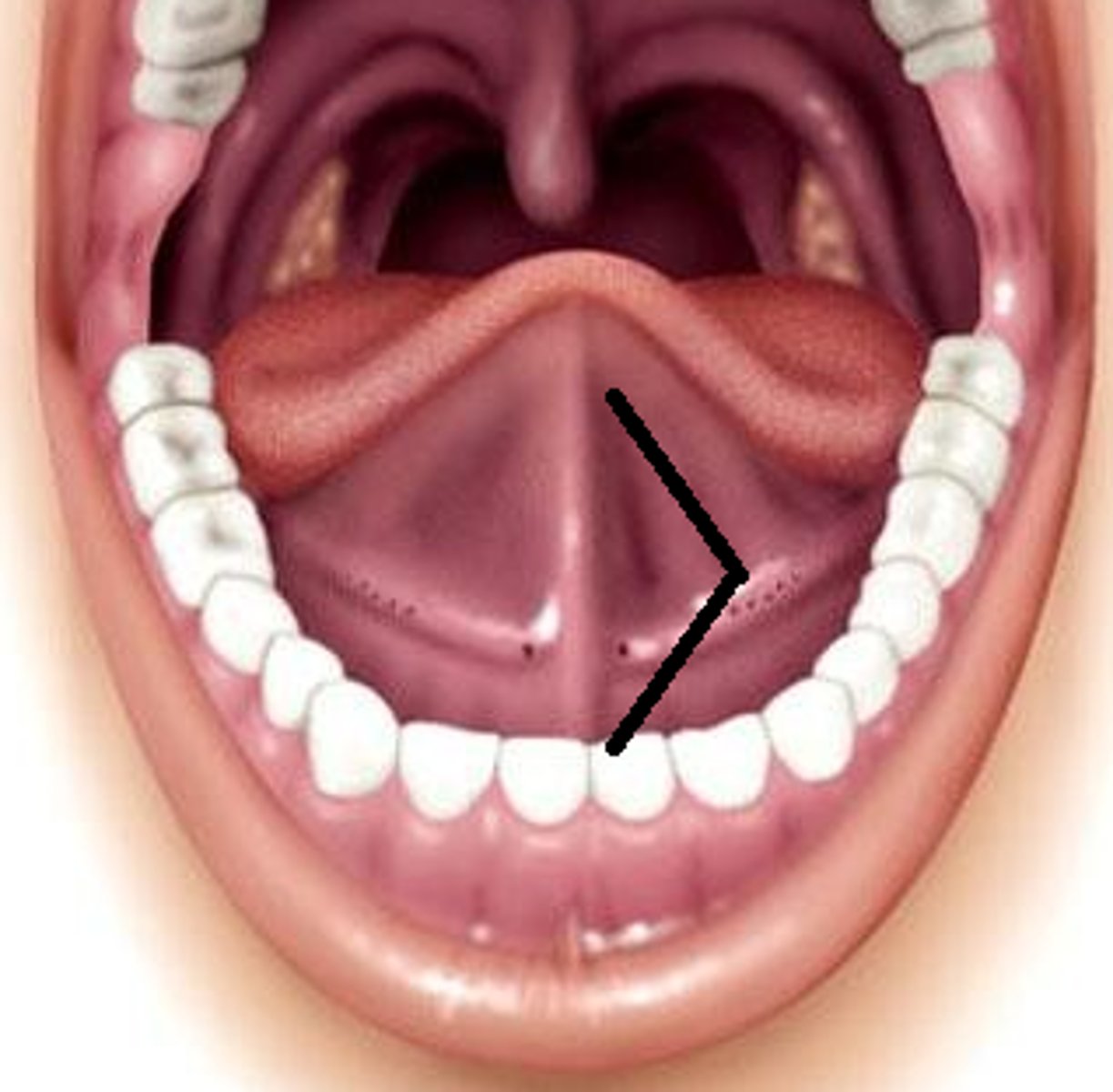
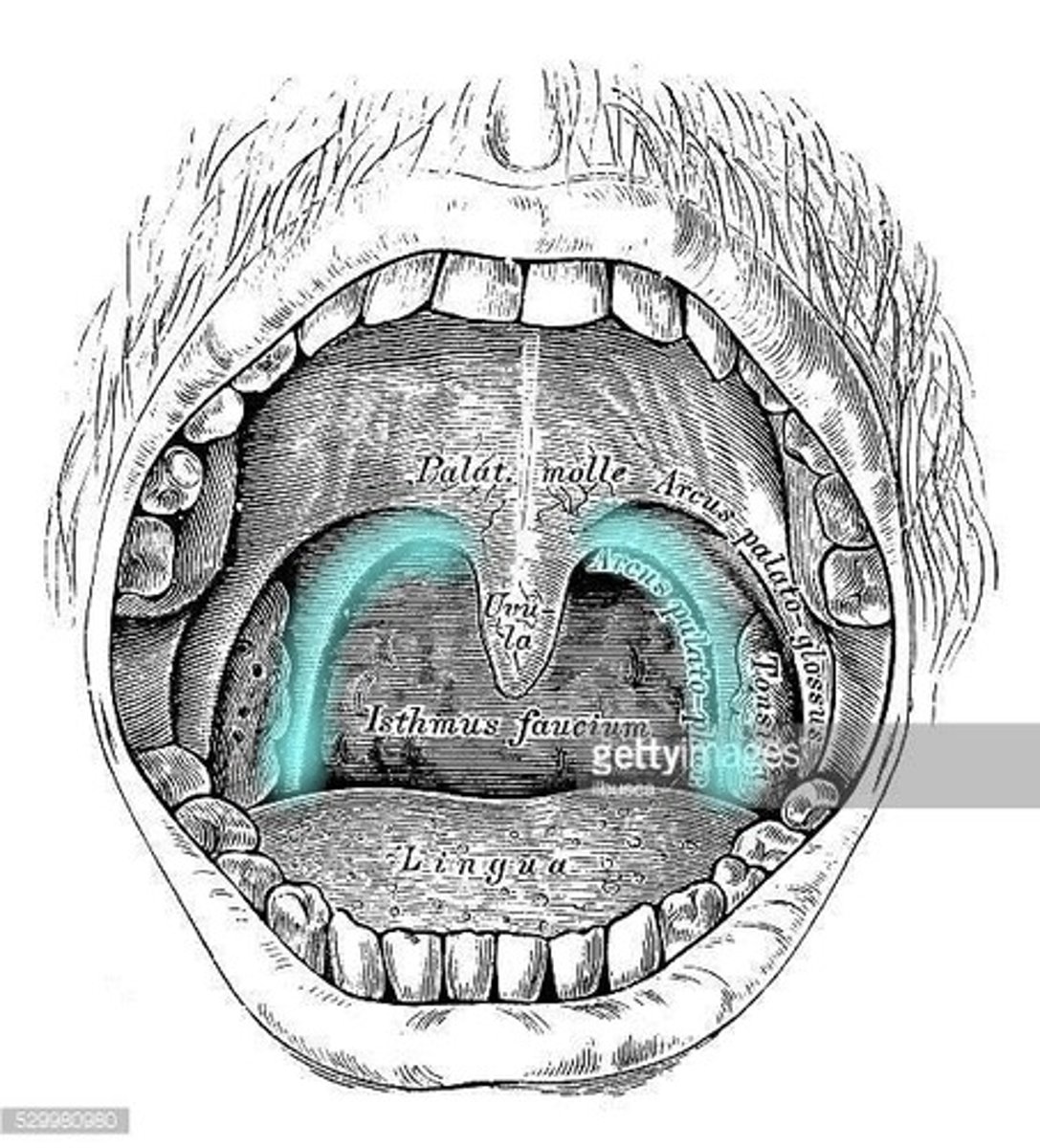
• Markers: Alveolar ridge (t, d, s, z, l, n), Postalvelor hard palate (SH, R) Palatine raphe (midline sagittal), Uvula, Faucial pillars (palatoglossal, palatopharyngeal arches)
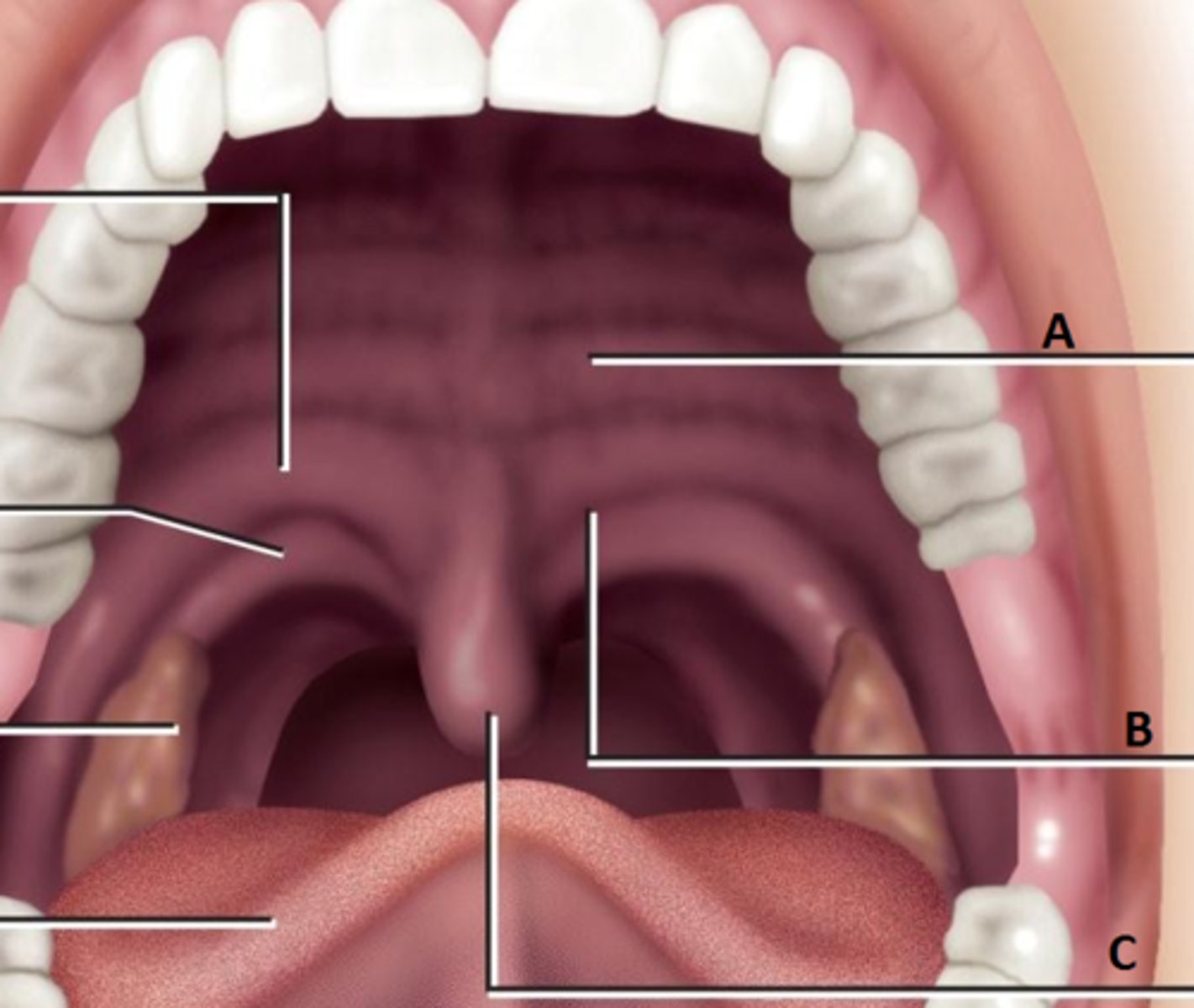
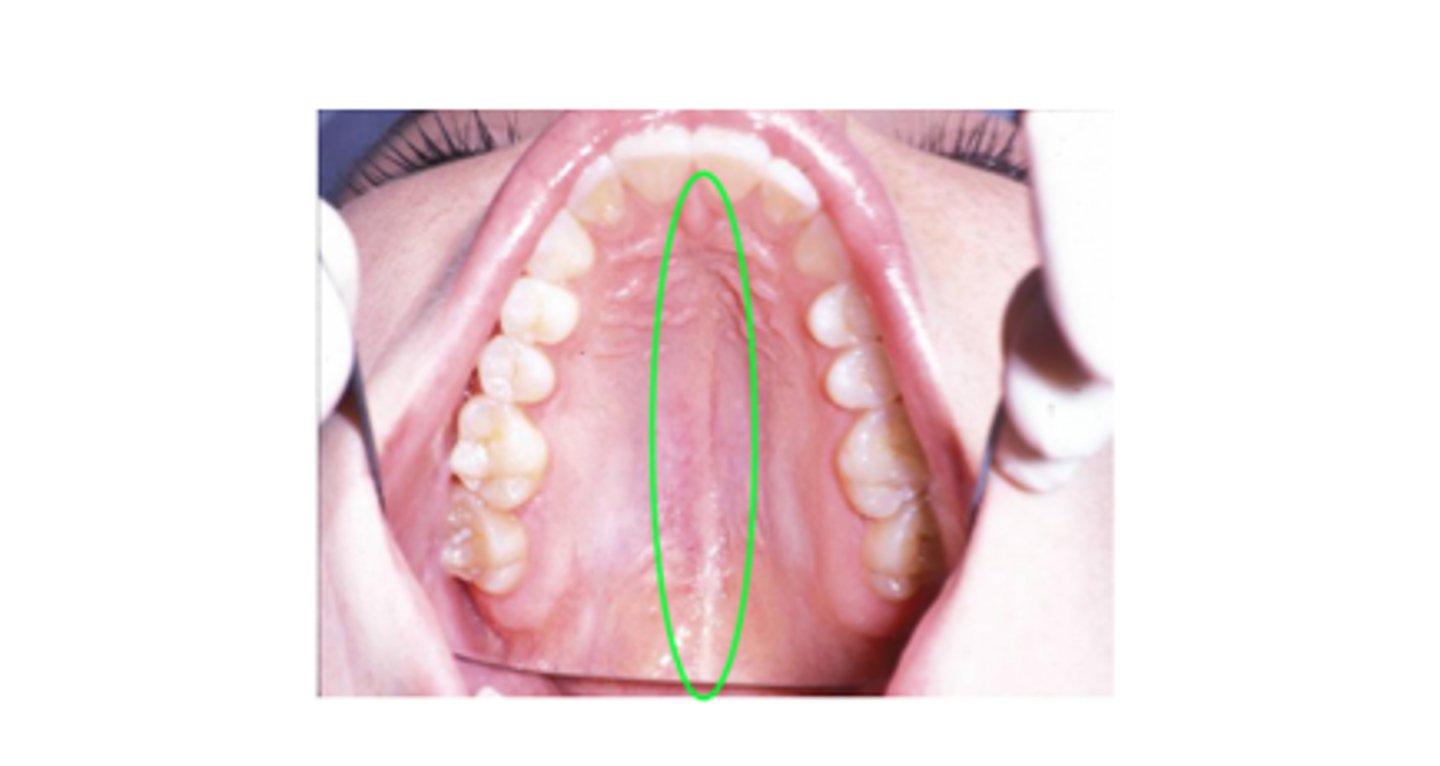
Palatine raphe
faucial pillars
Palatoglossal and Palatopharyngeal arches
Tonsils
T/F they are vestigial
____ tissue
part of the body’s _____ system
can stop ____ entering the body through the ___ or ____
contain a lot of ___ blood cells
• Lymphatic tissue
• The tonsils are part of the body's immune system. Because of their location at the throat and palate, they can stop germs entering the body through the mouth or the nose. The tonsils also contain a lot of white blood cells, which are responsible for killing germs.
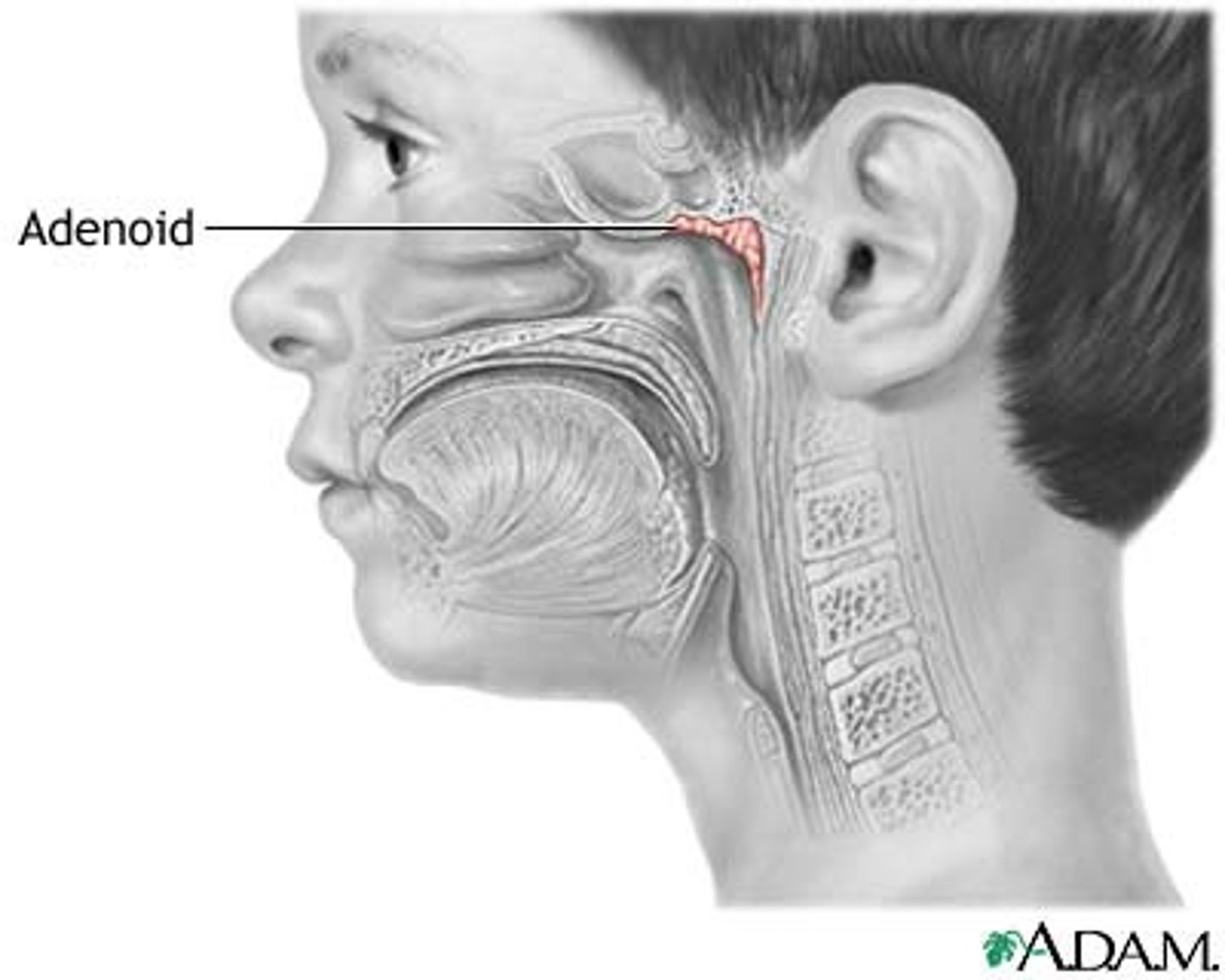
Adenoids
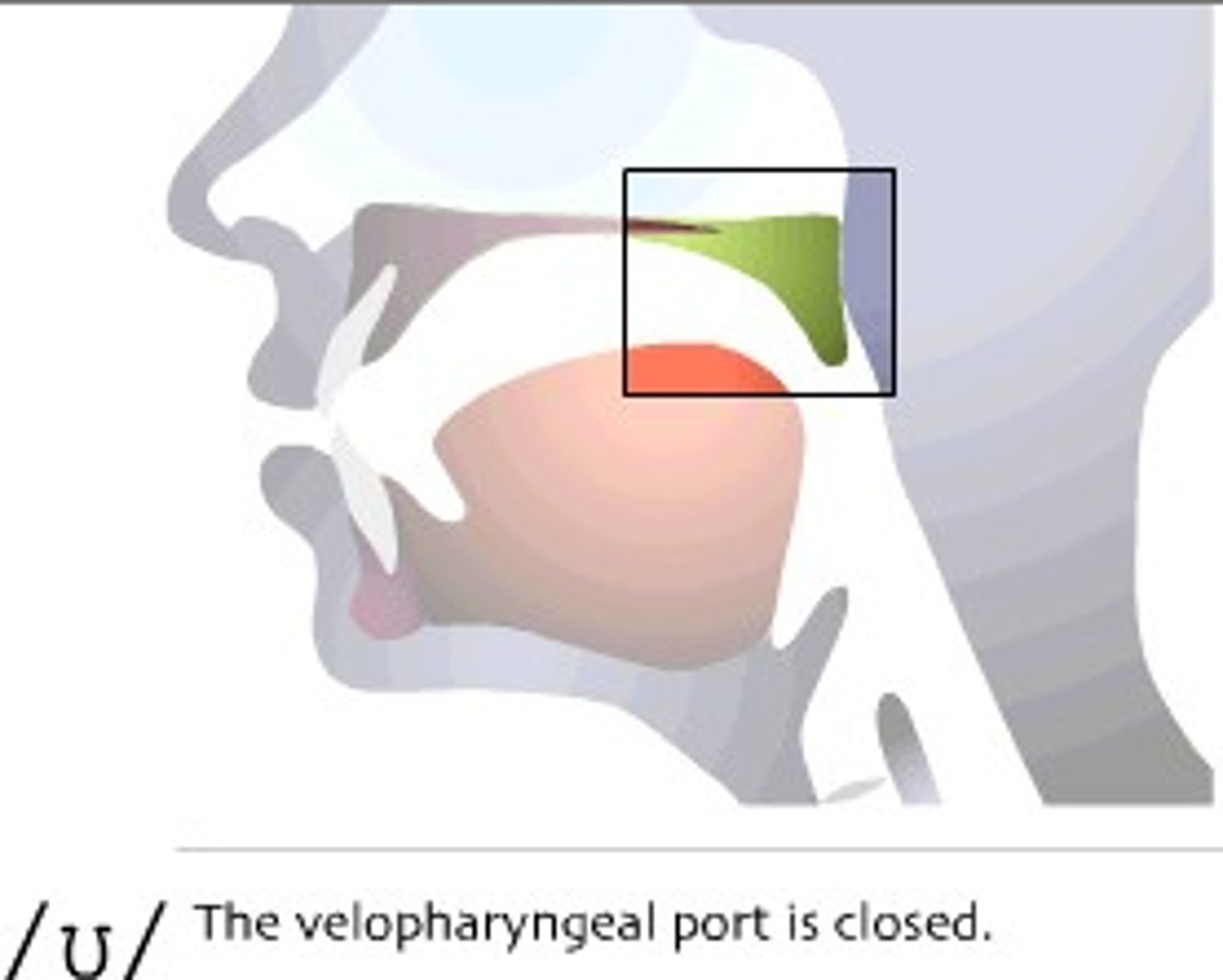
Velopharyngeal port
elevated and closed by the ____ palate when swallowing to protect the ____ cavity
remains open for ___ and ___
Elevated and closed by the soft palate when swallowing to protect the nasal cavity. Remains open for speech and breathing.
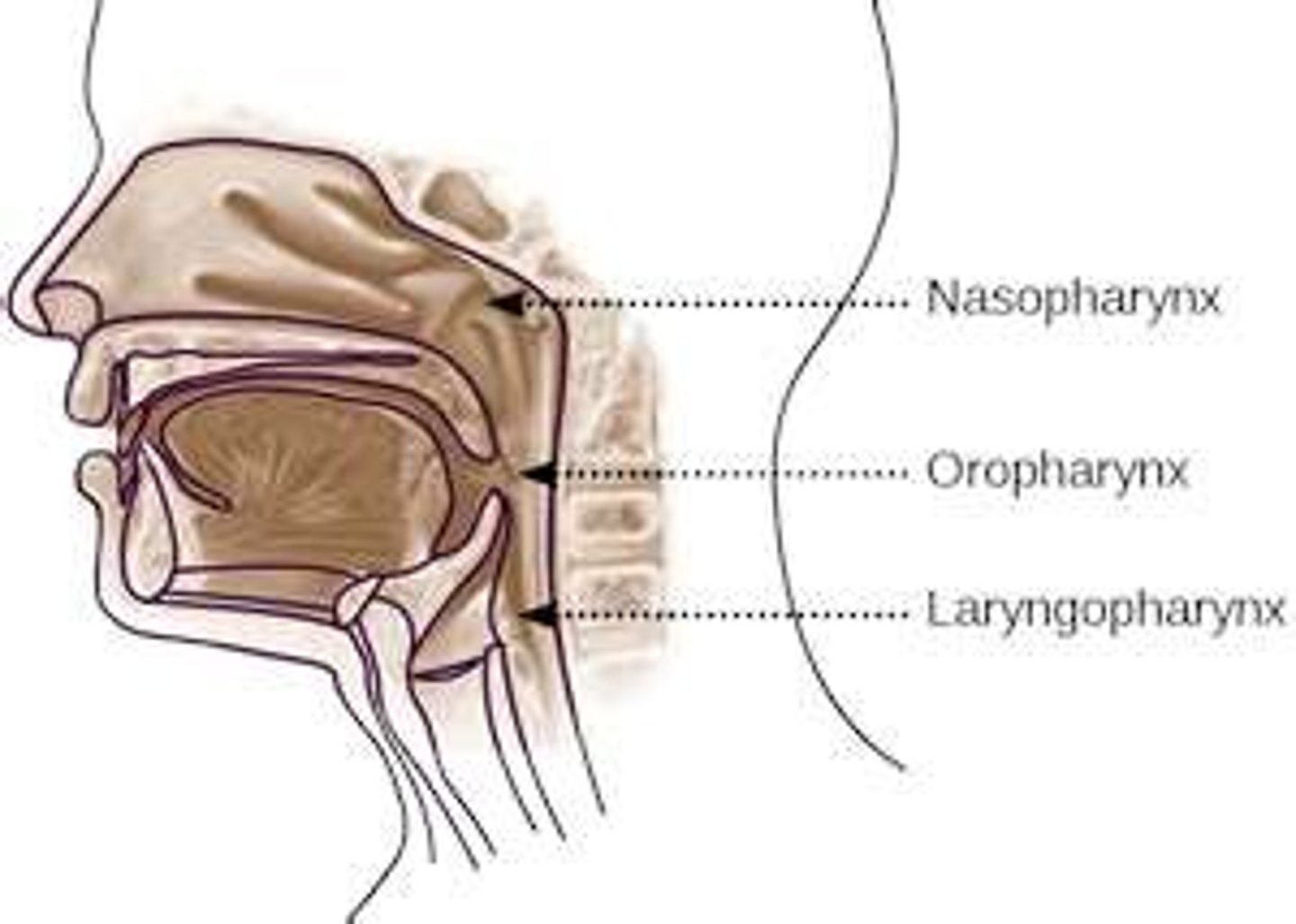
Pharynx
nasopharynx: ___ palate to _____ cavity
______ tube
a______
closes for non-_____ sounds and during _____
oropharynx: dynamic, ____ pillars to ____ level
laryngopharynx: ____ to entrance of _____ vestibule
• Nasopharynx: soft palate to nasal cavity
• Eustachian tube
• Adenoids
• Closes for non-nasal sounds and
during swallowing
• Oropharynx: dynamic, faucial pillars to hyoid level
• Laryngopharynx: hyoid to entrance of laryngeal
vestibule
Eustachian tube
• Equalizes pressure between middle ear and pharynx
• Allows drainage from middle ear
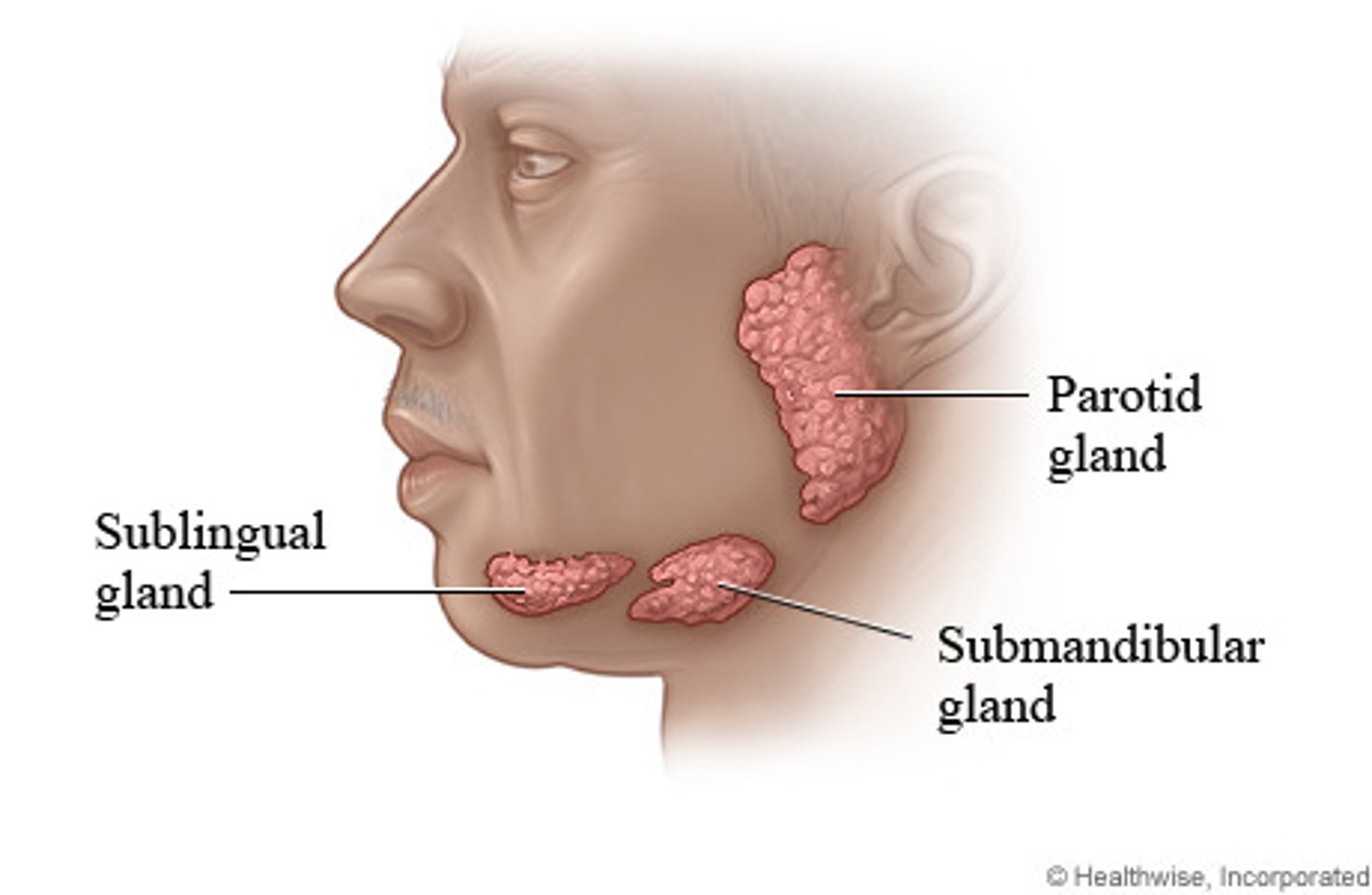
Salivary glands
what are the 3 major glands
function?
keep mouth ___, _____ cohesion, “____” swallow ability, begin to help in breaking down _____
• Three major glands:
1. Sublingual
2. Submandibular
3. Parotid
• Function: Keep mouth moist, Bolus cohesion, "Dry" swallow ability, Begin to help in breaking down food
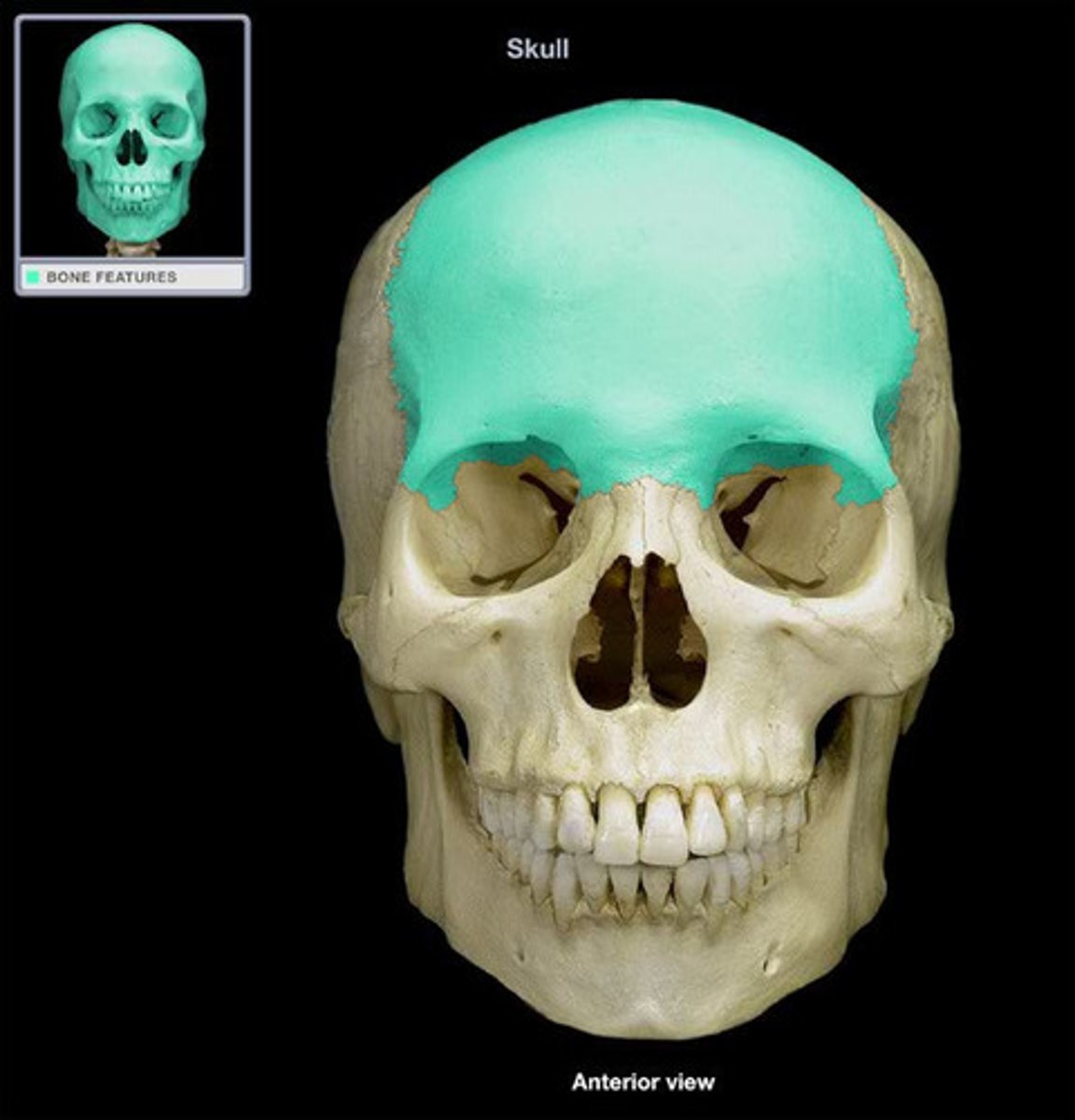
Frontal bone
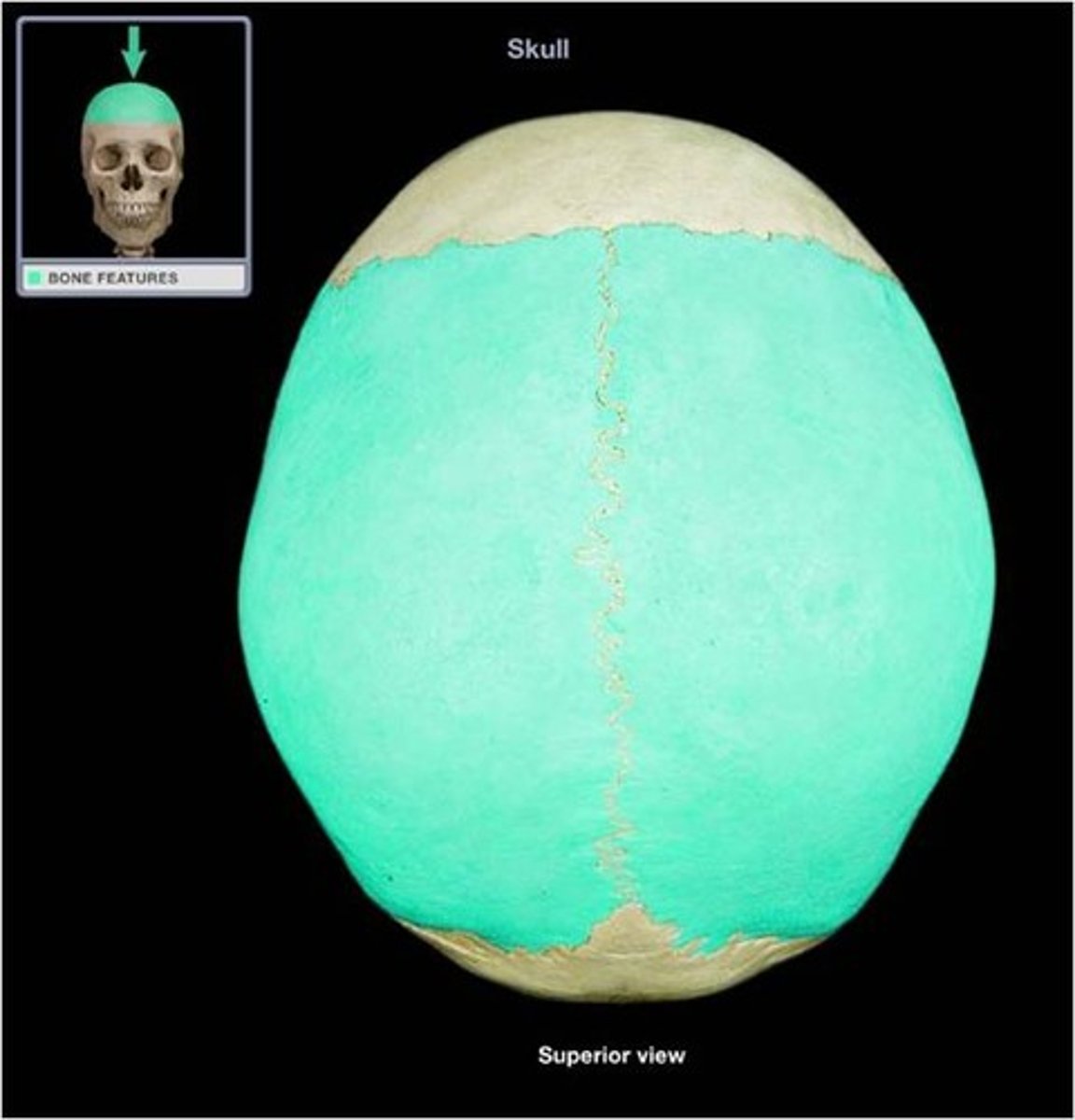
parietal bones
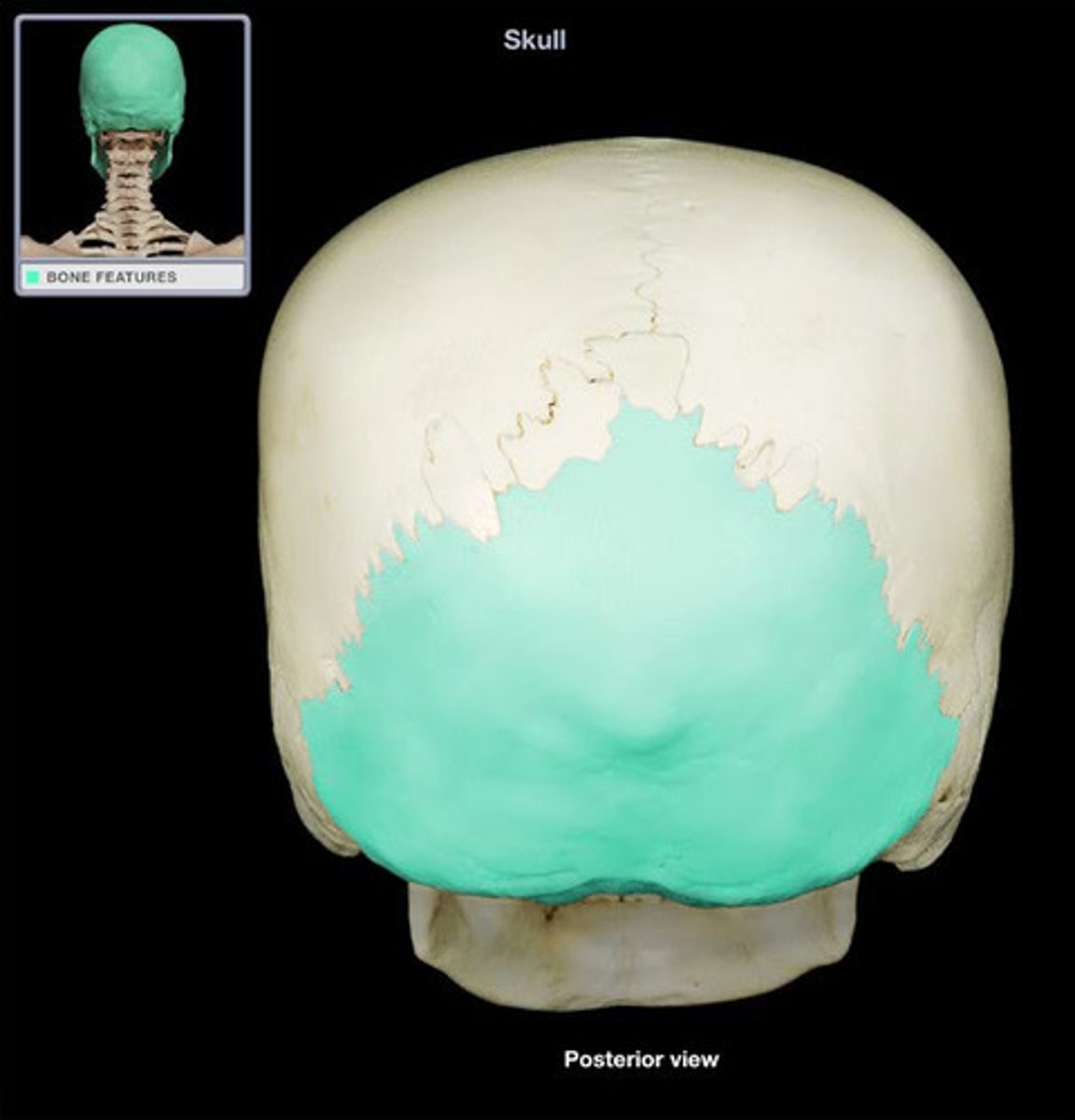
Occipital bone
includes which foramen
Includes foramen magnum
Foramen magnum → medulla oblongata (most caudal portion of brain), accessory nerve (XI), vertebral arteries
Jugular foramen (with temporal bone) → Glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves ( N IX, X, XI)
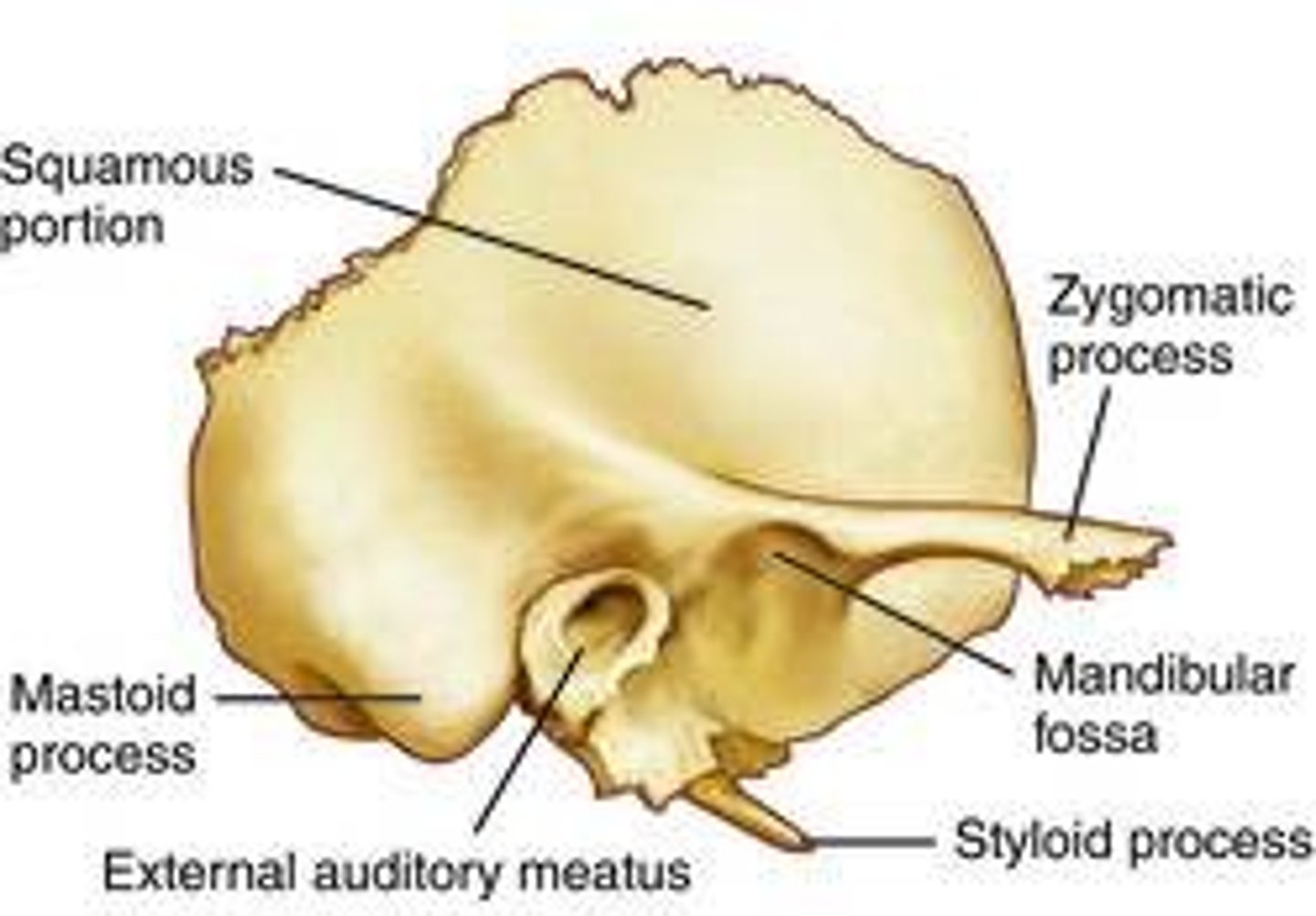
Temporal bones
• Squama
• External auditory meatus
• Processes:
• Zygomatic process
• Styloid process
• Mastoid process
External acoustic meatus → air in meatus conducts sound to the eardrum
Carotid canal → internal carotid artery
Stylomastoid foramen → Facial nerve (N V)
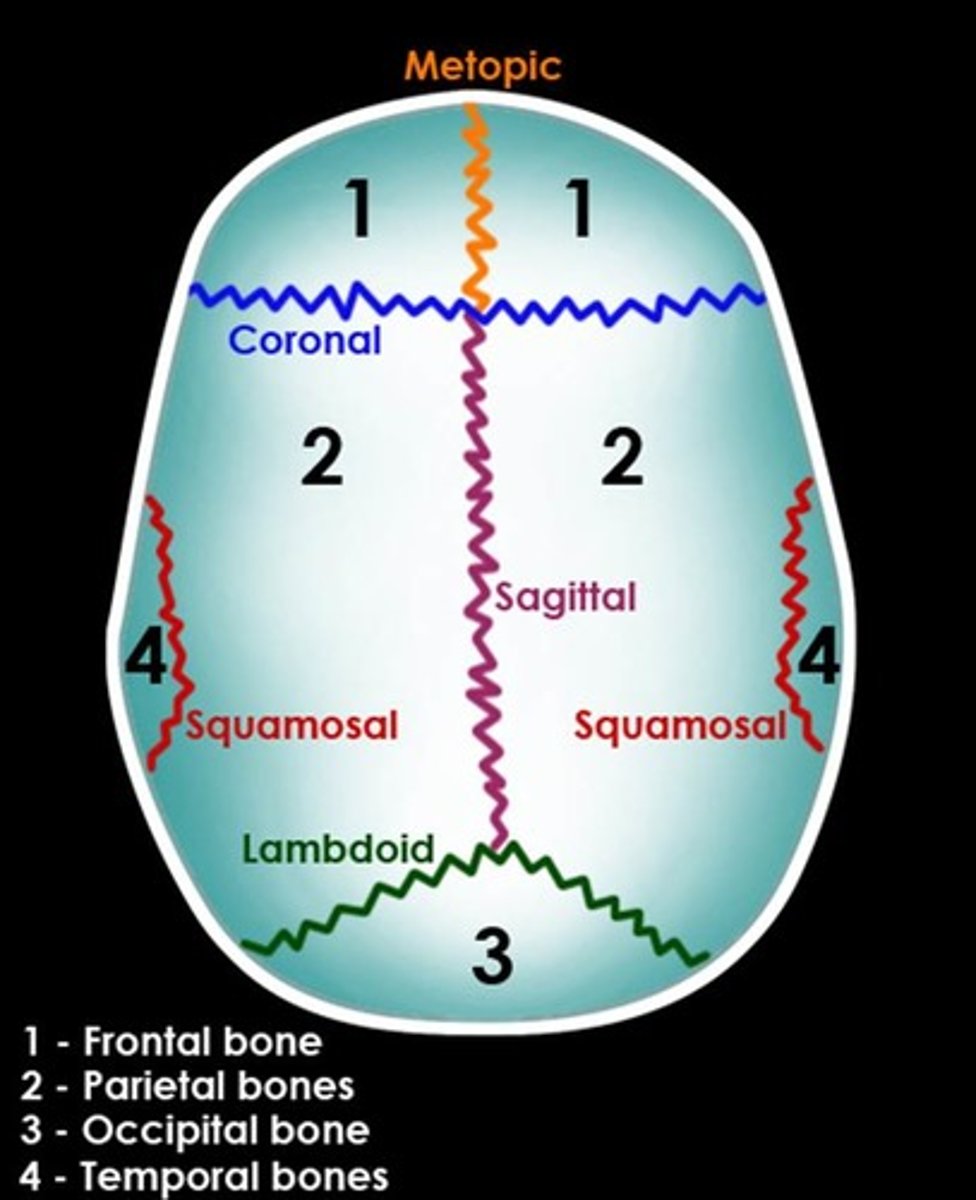
Sutures of the brain
• Sagittal
• Coronal
• Lambdoidal
• Squamous
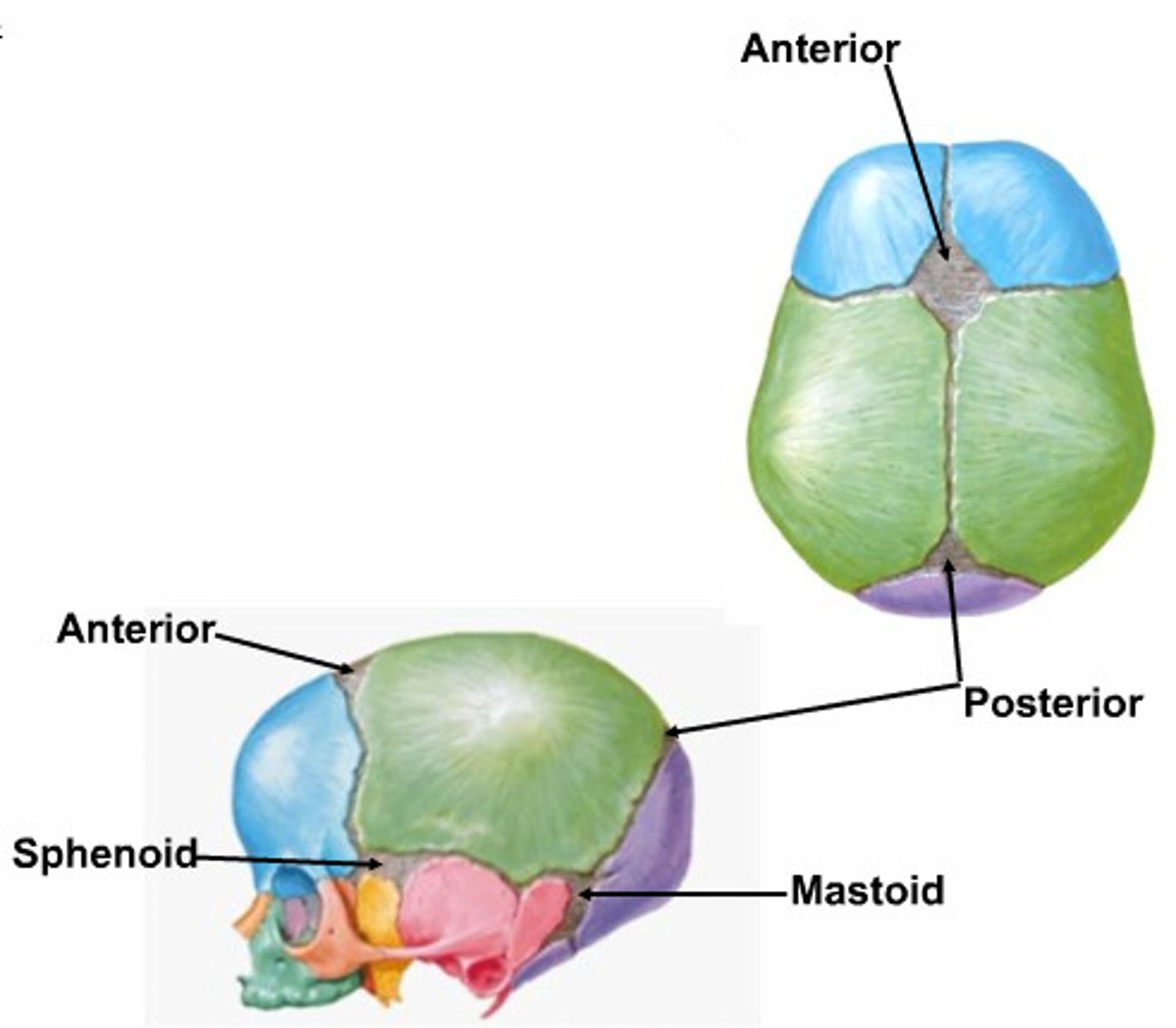
Fontanelles
• Anterior
• Posterior
• Mastoid
• Sphenoid
Ethmoid bone
seperates _____ cavity from ____
• Separates nasal cavity from brain
• Perpendicular plate = nasal septum
sphenoid bone
inner ____ of the eyes
seperates ____ from _____
• Inner orbit of the eyes (separates eyes from brain)
• Bat or butterfly
Foramen lacerum (with temporal and occipital bones) → internal carotid artery after leaving carotid canal, auditory tube
Foramen ovale → mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve ( N V)
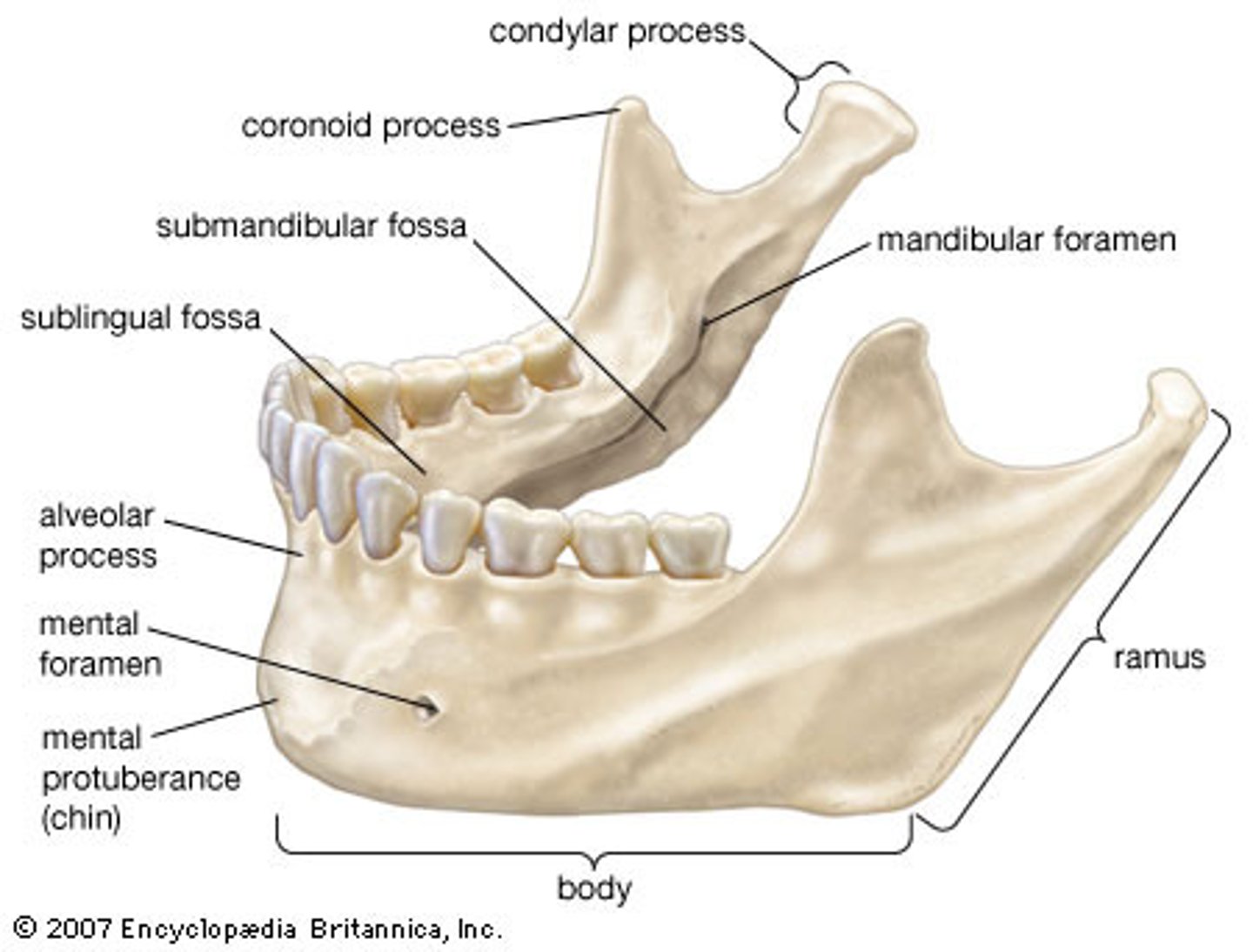
Mandible anatomy
• Ramus
• Coronoid process
• Condylar process
• Tempomandibular joint
• Body
• Mental protuberance
• Lower teeth
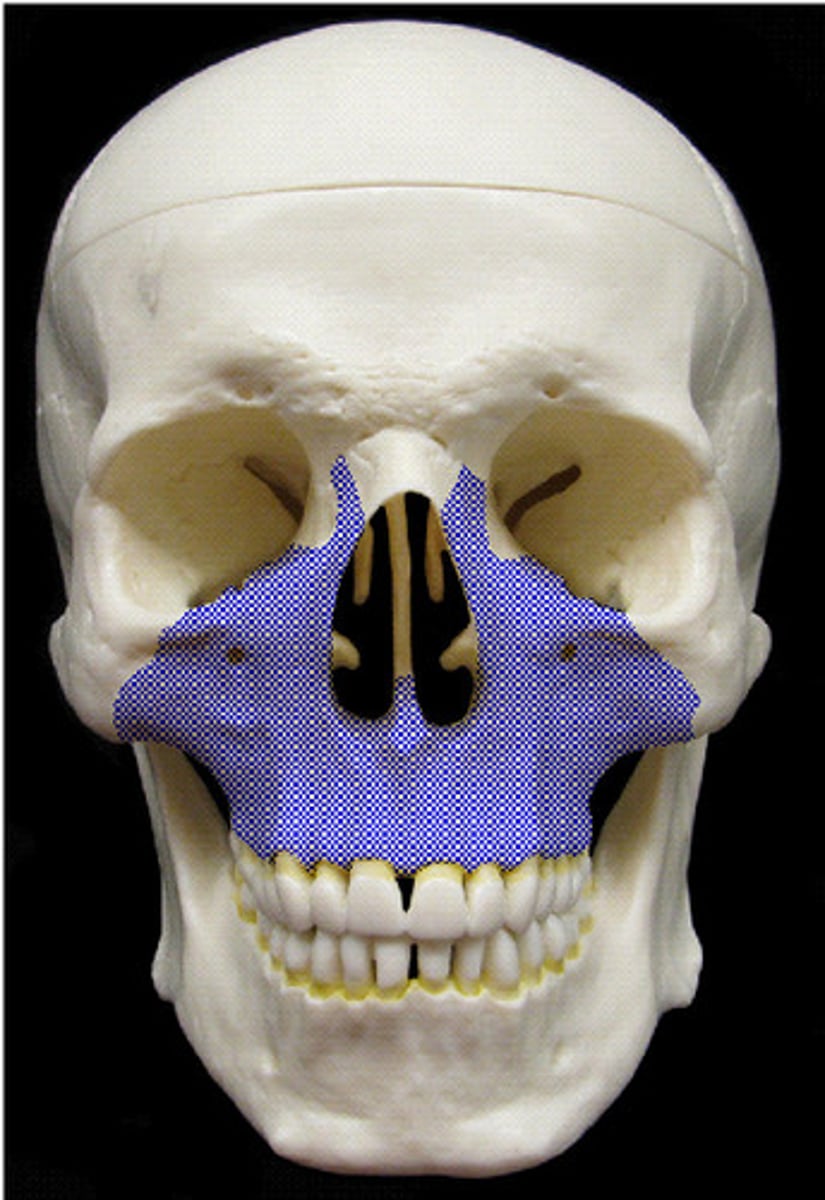
Maxillae
• Upper jaw & upper teeth
• Anterior ¾ of hard palate
• Lower edge of eye orbit
• Intermaxillary suture
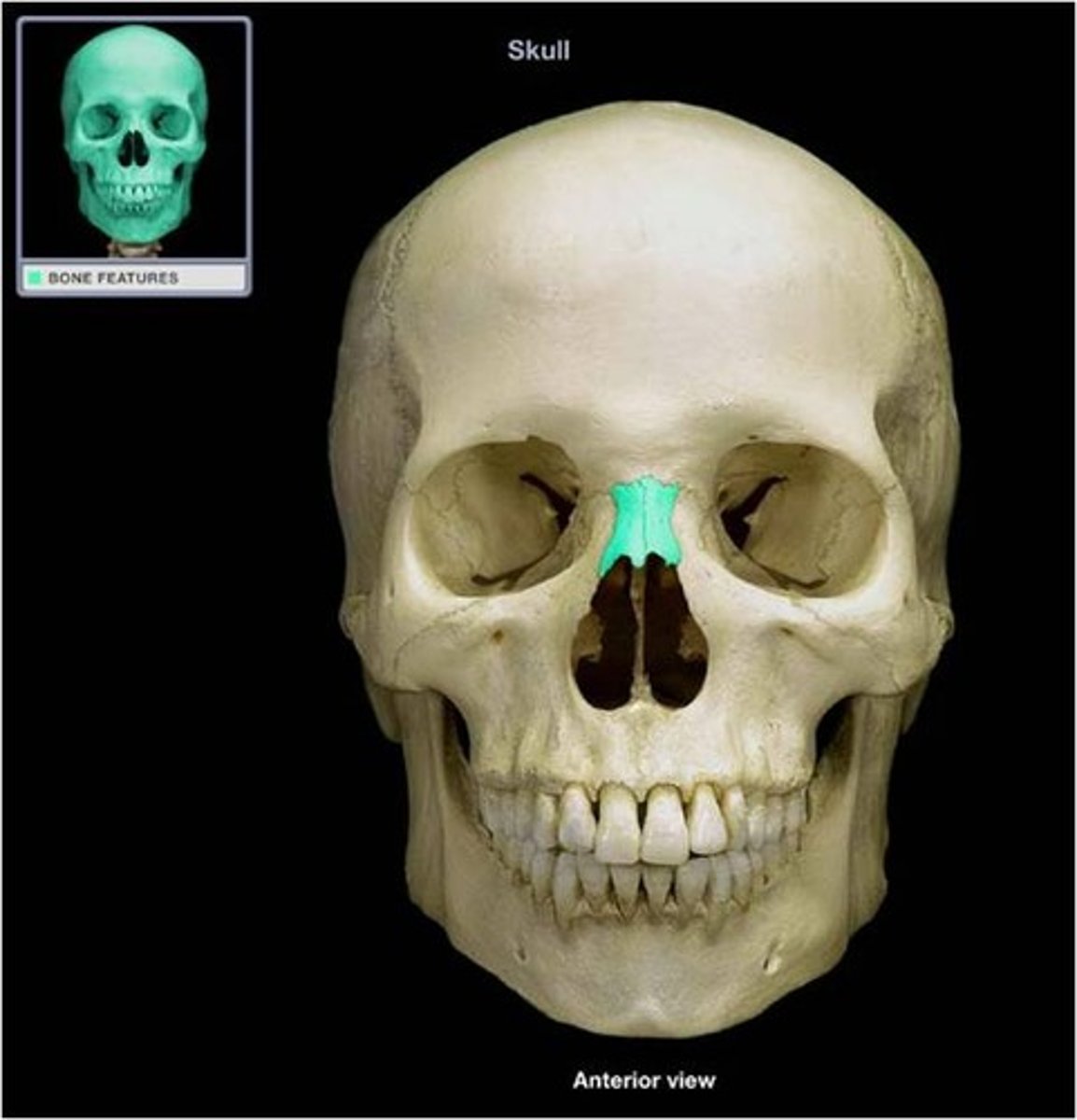
•nasal bones
Form bridge of nose

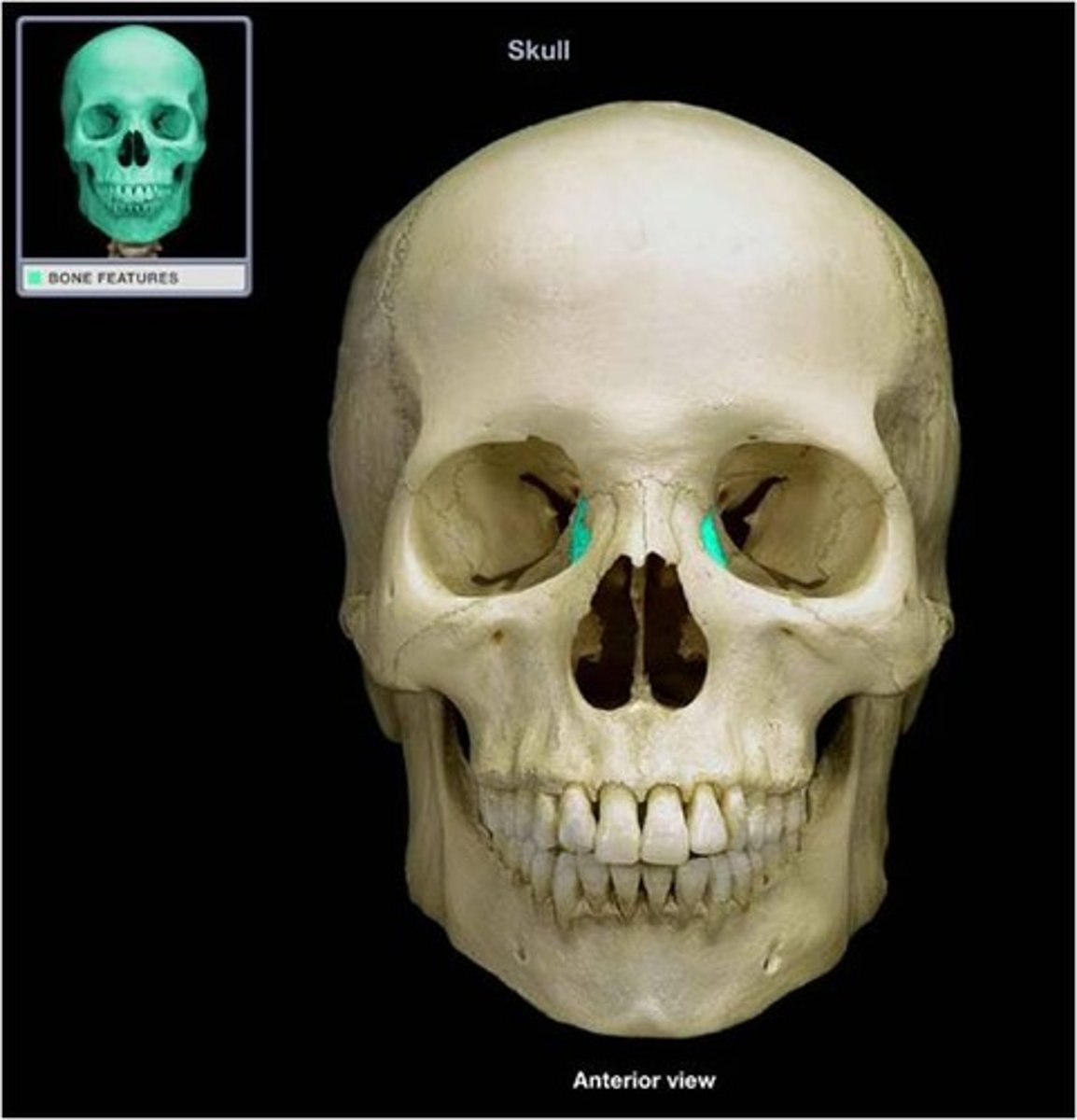
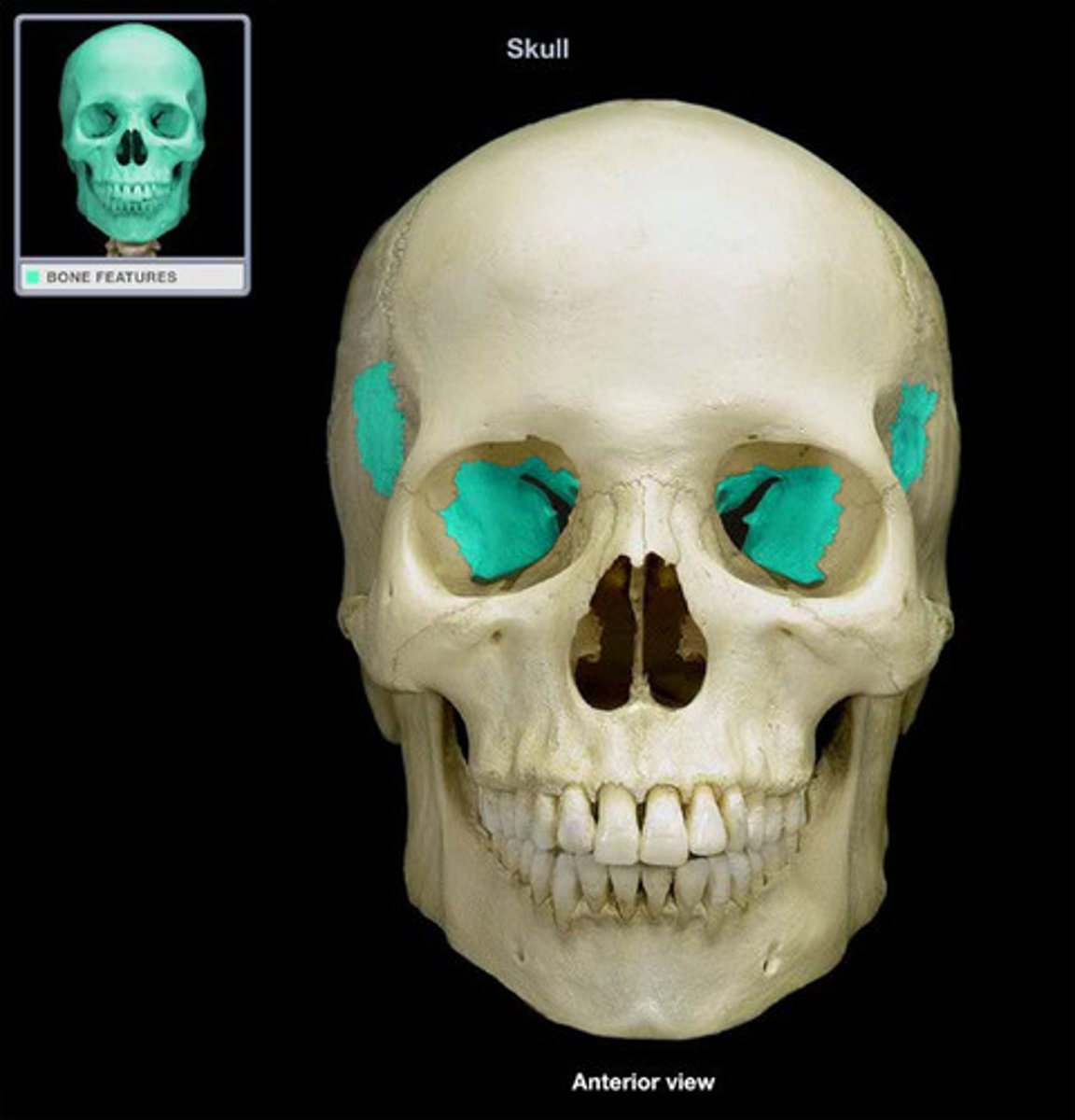
•lacrimal
Form medial wall of eye socket

form prominence of _____ and inferior/lateral walls of ___ ____
attaches _____ process
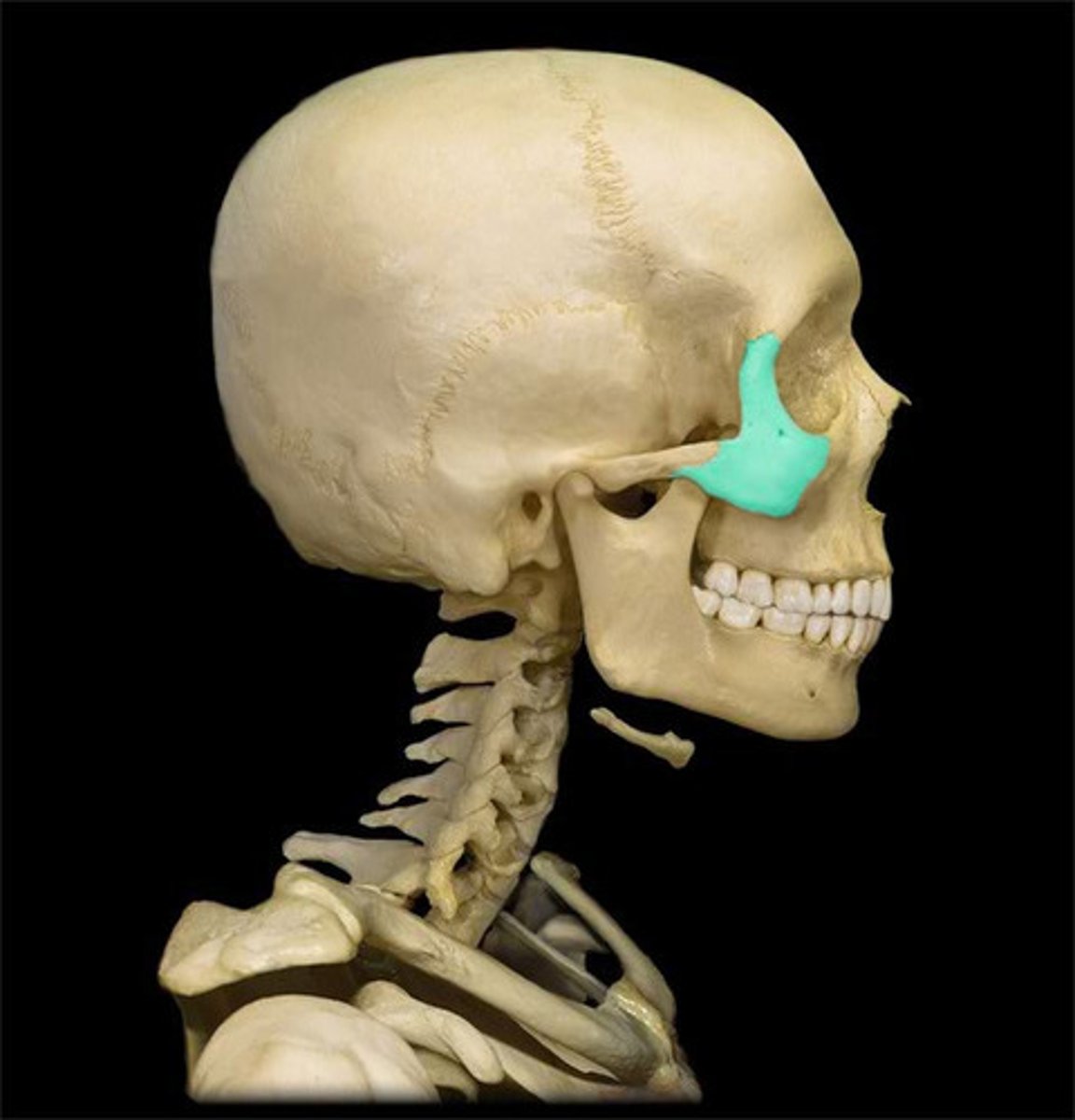
• Zygomatic bones
Form prominence of cheek & inferior/lateral walls of
eye socket
• Attaches to zygomatic process of temporal bone

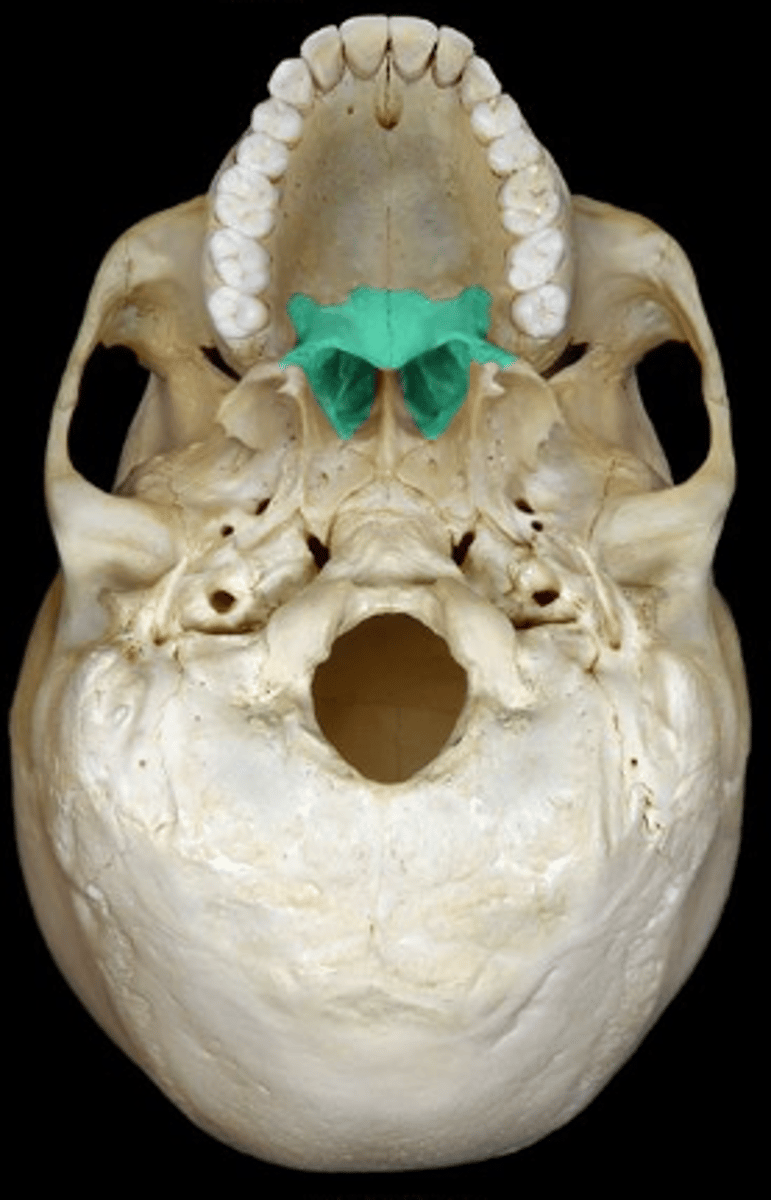
•palatine bones
Posterior to maxilla & inferior to sphenoid
• Form the letter "L" where the bottom of the "L" is the posterior ¼ of the hard palate = floor of the nose
• Sides of the "L" form the lateral walls of nasal cavity

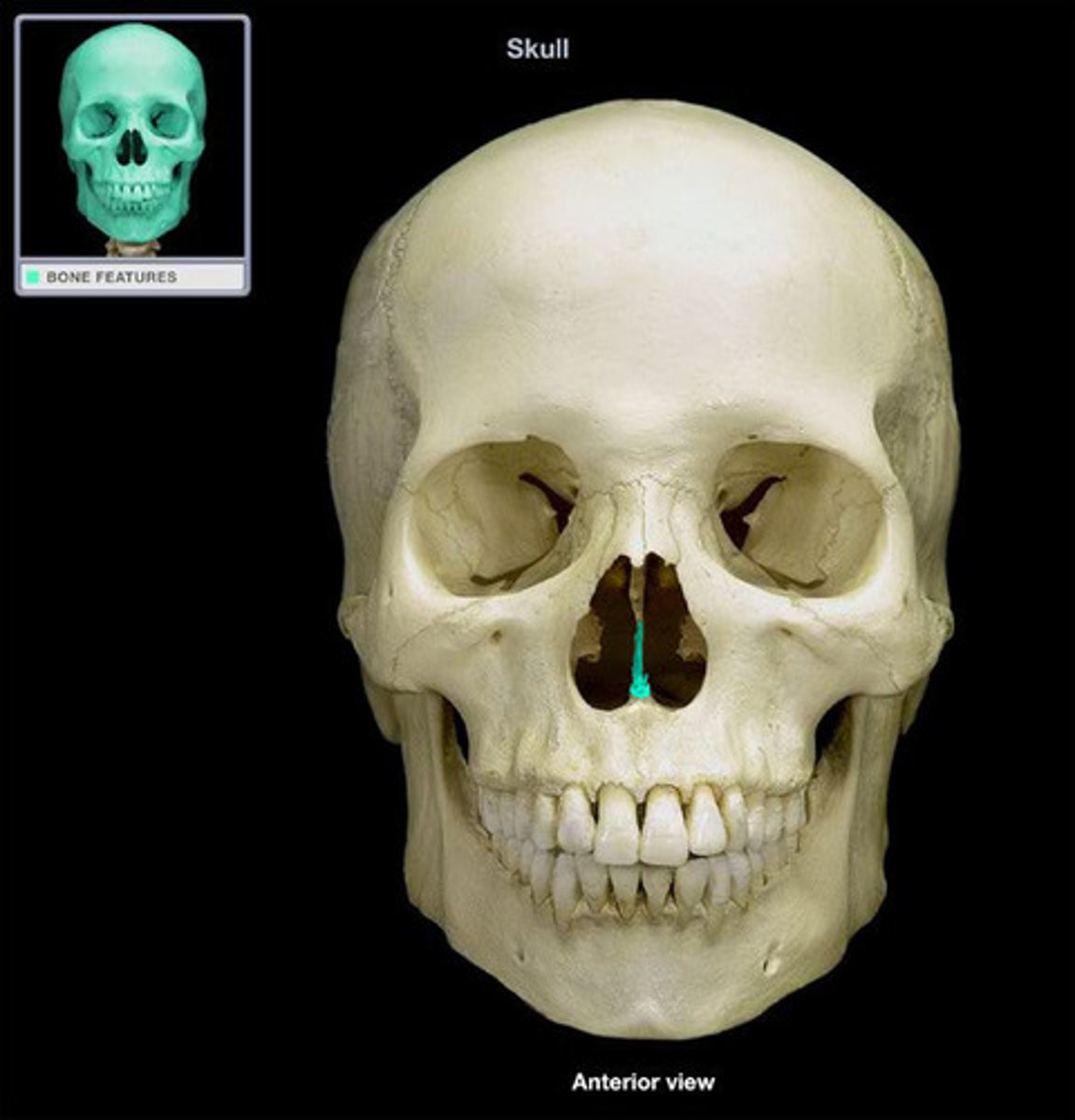
divides the nasal _____
•vomer
Divides the nasal septum (the ethmoid perpendicular
plate is posterior)

inferior nasal conchae
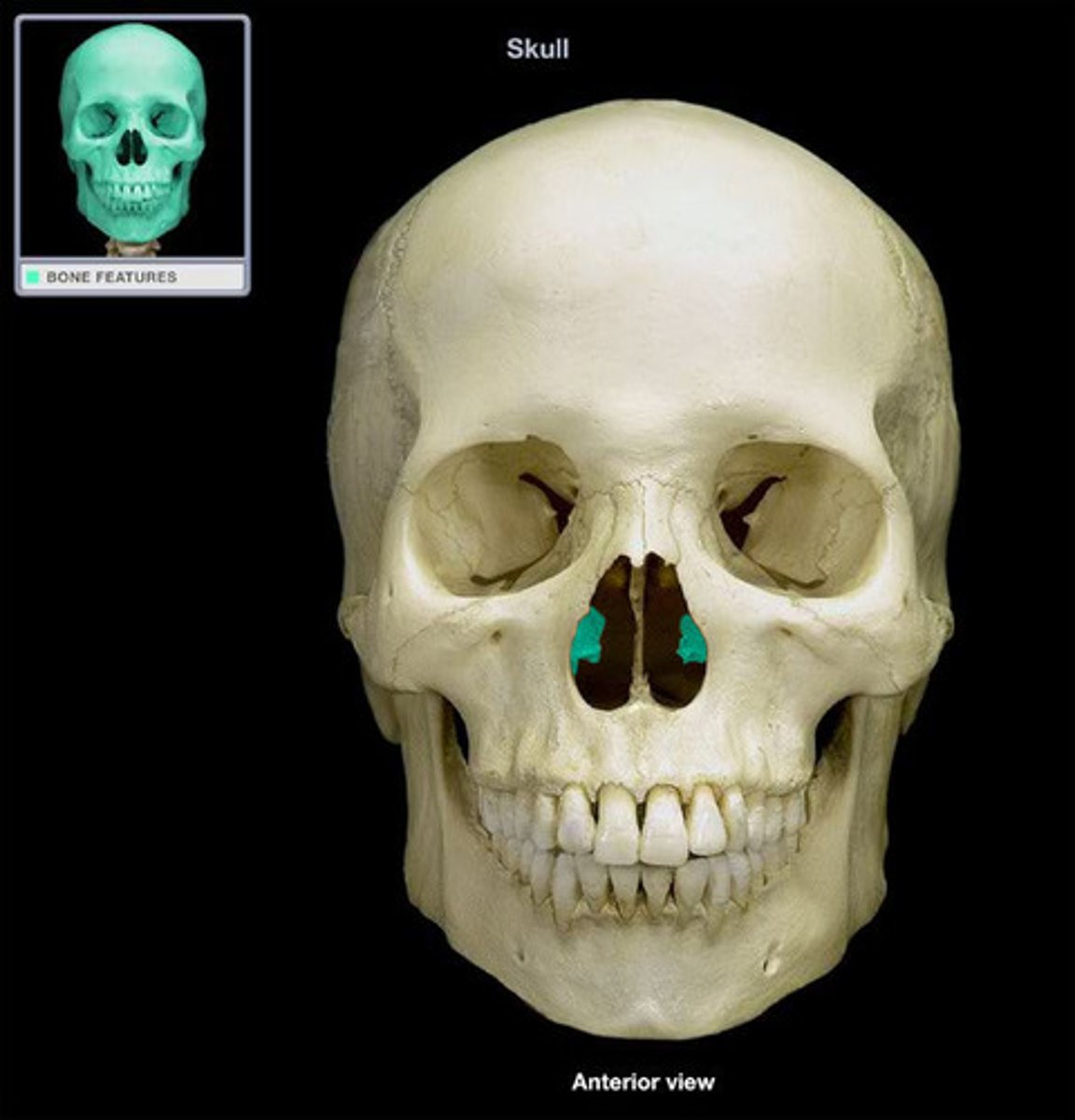
•inferior nasal conchae
AKA inferior nasal turbinates

Four sets of air-filled cavities in the skull all have openings that drain to the inside of the nose
10% of the population lack a _____sinus on side and around 4% of the pop. do not have any at all
The ______ are the first to form during human development. They are very small at birth and continue to grow throughout childhood.
Four sets of air-filled cavities in the skull all have openings that drain to the inside of the nose
10% of the population lack a frontal sinus on side and around 4% of the pop. do not have any at all
The maxillary are the first to form during human development. They are very small at birth and continue to grow throughout childhood.
Sinuses
The four sinuses are...
frontal, maxillary, ethmoid, sphenoid
Front sinus percentages
About 10% of the population lack a frontal sinus on one side
and around 4% of the population do not have frontal sinuses at all.
Sinus purpose
T/F remain largely unkown but theories:
Functioning as _____ chambers for ____
• Supplying _____ air to _____ with ___air in the
nose
• To assist with the sense of ____
• To protect the _____
• To lighten the ____
The function of the sinuses remains largely unknown. Many
theories exist on the reason we have sinuses. They include:
• Functioning as resonance chambers for speech
• Supplying conditioned air to diffuse with inhaled air in the
nose
• To assist with the sense of smell
• To protect the brain (by acting as a "crumple zone" during
blunt trauma to the face and forehead)
• To lighten the skull (hollow spaces in the skull instead of
solid bone)
4 Phases of deglutition
• Oral preparatory phase = mastication + bolus management
• Oral transit phase
• Pharyngeal phase
• (Esophageal phase)
Oral transit pt 1
Form _____ with tongue
• Vallecula = “ _____ ___”
• Tongue base _____
• Laryngeal ____ begins
• Form "bowl" with tongue
• Vallecula = "spit trap"
• Tongue base retraction
• Laryngeal elevation begins
Pharyngeal Phase of Swallowing pt 2
• ____ port closes
• Epiglottis ____ as base of tongue moves _____
• Vocal folds ____(extra protection)
• Larynx ___-
• Laryngeal vestibule ___-
• ____ constricts
• Velopharyngeal port closes
• Epiglottis inverts as base of tongue moves posteriorly
• Vocal folds adduct (extra protection)
• Larynx elevates
• Laryngeal vestibule compresses
• Pharynx constricts
Esophageal Phase of Swallowing pt 3
• Upper ____ sphincter opens
• _____ (rhythmic contractions)
• ____ esophageal sphincter ___
• Bolus reaches ____
• Upper esophageal sphincter opens
• Peristalsis (rhythmic contractions)
• Lower esophageal sphincter opens
• Bolus reaches stomach
If you exclusively breastfeed until 12 months
the kiddo will not develop a munching pattern because kiddos should not be munching on mom! This is totally fine
and appropriate.
decreased ability to chew or pain during chewing; reference for soft foods or hard candies
Decay of Feeding & Chewing Skills In Adults: Dentition
losing control of the bolus, difficulty clearing residue ("stuck in my throat")
Decay of Feeding & Chewing Skills In Adults: Motor control during the swallow
(e.g., tremor): preference for foods that don't need to be cut; difficulty with soups; spilling (consider the social impact of this!)
Decay of Feeding & Chewing Skills In Adults: Motor control during self-feeding
Decay of Feeding & Chewing Skills In Adults: Alertness
T/ F - It is normal to stop eating as a natural part of the dying process. Dying adults are not hungry. Their bodies are shutting down
Feeding tubes prolong life and prevent aspiration
(either from medication or overall status)
• It is normal to stop eating as a natural part of the dying process. Dying adults are not hungry. Their bodies are shutting down.
• Feeding tubes do not prolong life or prevent aspiration. They are major, unnecessary abdominal surgery in these cases.
The TWO main factors in preventing aspiration pneumonia are:
1. Feeding yourself (vs. having a feeder)
2. Good oral hygiene
Fist baby teeth
Lower central incisors: ____ months,
upper central incisors: ___ months
Lower central incisors: 8 months,
upper central incisors: 10 months
First permanent teeth
Lower central incisors: ___-___ years
First molars, upper and lower: ___-___years
Upper central incisors: -_ years
Lower central incisors: 6-7 years
First molars, upper and lower: 6-7 years
Upper central incisors: 7-8 years
Most common congenital craniofacial anomaly*
Oral clefts are present in 1/____ births or ___% (ASHA, 2020)
Can be associated with a variety of syndromes
Can also be _____ (1/1600 births)
Cleft lip/palate percentages
Oral clefts are present in 1/700 births or .15% (ASHA, 2020)
Can be associated with a variety of syndromes
Can also be idiopathic (1/1600 births)
Cleft lip/palate timeline in utero
Lips form around ___weeks, palate fuses by ___weeks
Lips form around 8 weeks, palate fuses by 12 weeks
Where does cleft lip occur?
At the philtral ridge
Where does cleft palate occur?
The roof of the mouth, at the intermaxillary suture
Skull function
_____ for the _____ tissues of the ___ and ___
encloses the ____, forms ___ that hold the ____, ____ ear, and vocal ____
Foundation/framework for the soft tissues of the face and head, encloses the brain, forms cavities that hold the eyes, internal ear, and vocal tract.
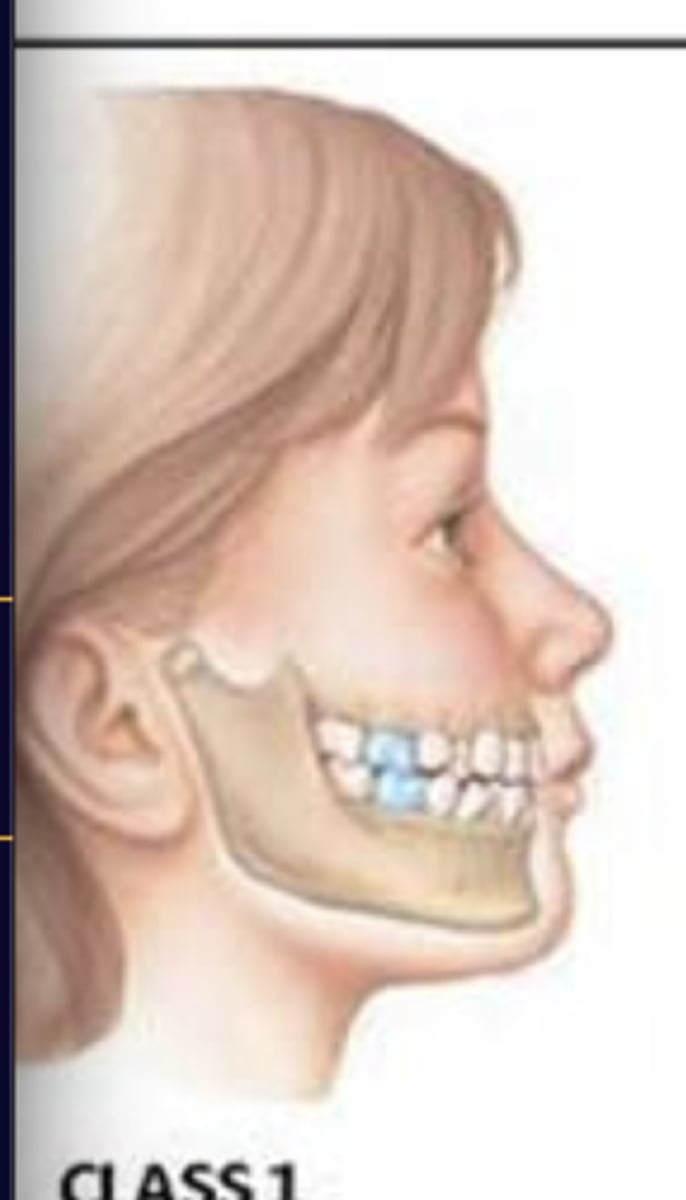
Normal occlusal relation, first permanent molar of the upper jaw is positioned one-half tooth behind the first permanent molar of the lower jaw.
Class I occlusion (neutroclosuion)
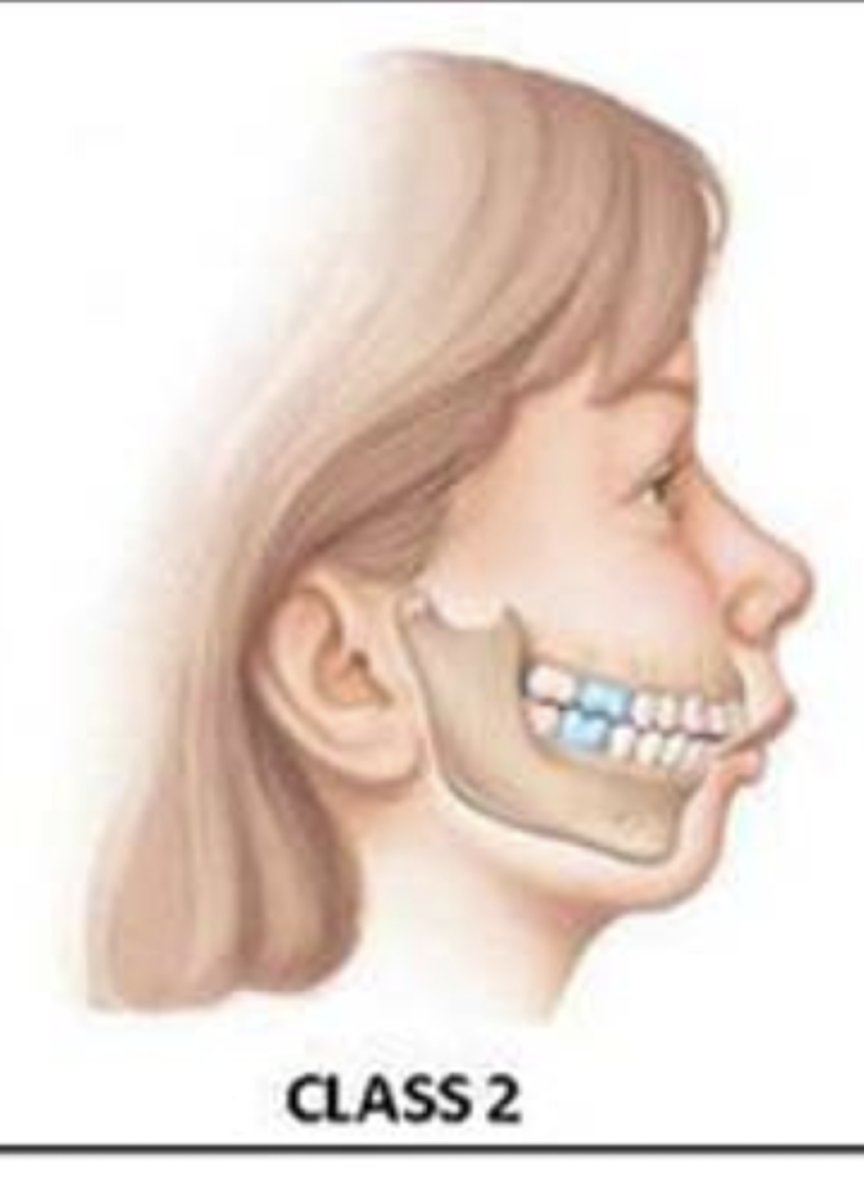
The first molar of the lower jaw is posterior to the normal position
Class II occlusion (distoclusion)
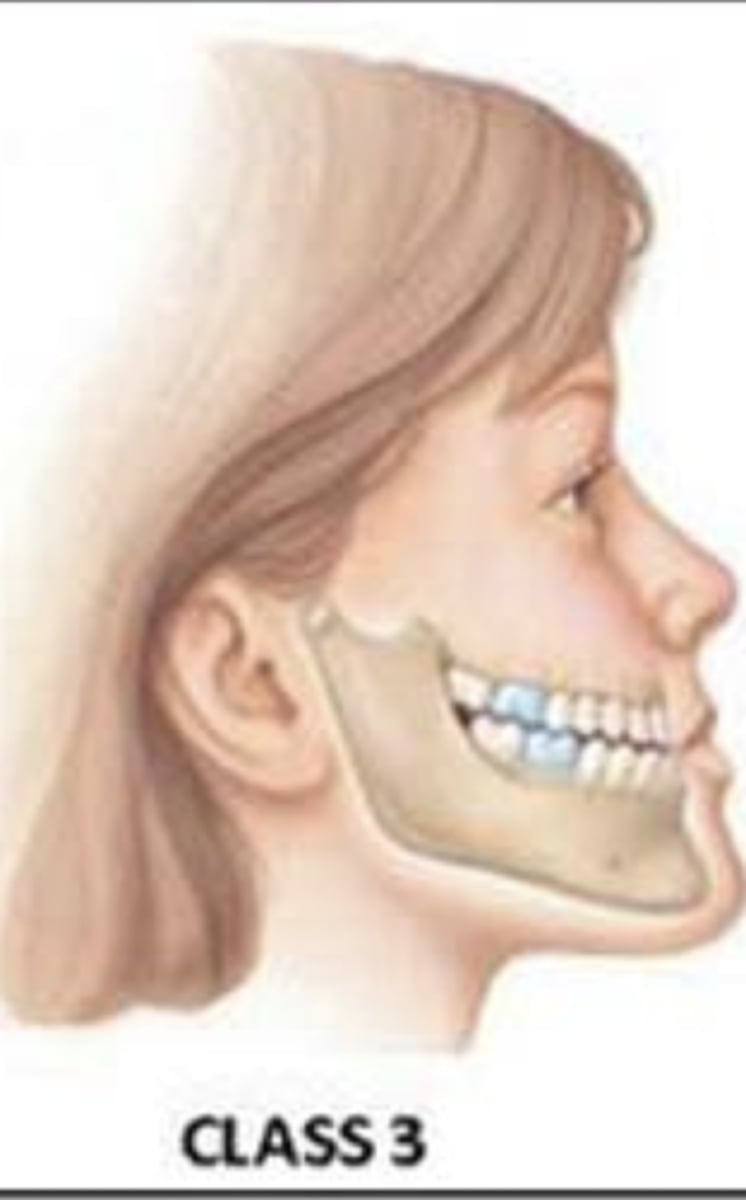
The first molar of the lower jaw is anterior to the normal position
Class III occlusion (mesioclusion)
- Can be opened or closed by velum movement
- When the velum is raised, it forms a barrier between the oral and nasal cavities to prevent sound waves and food from entering the nasal cavities
- When it's open, air can enter and exit the respiratory system through the nasal cavities
Velopharyngeal port
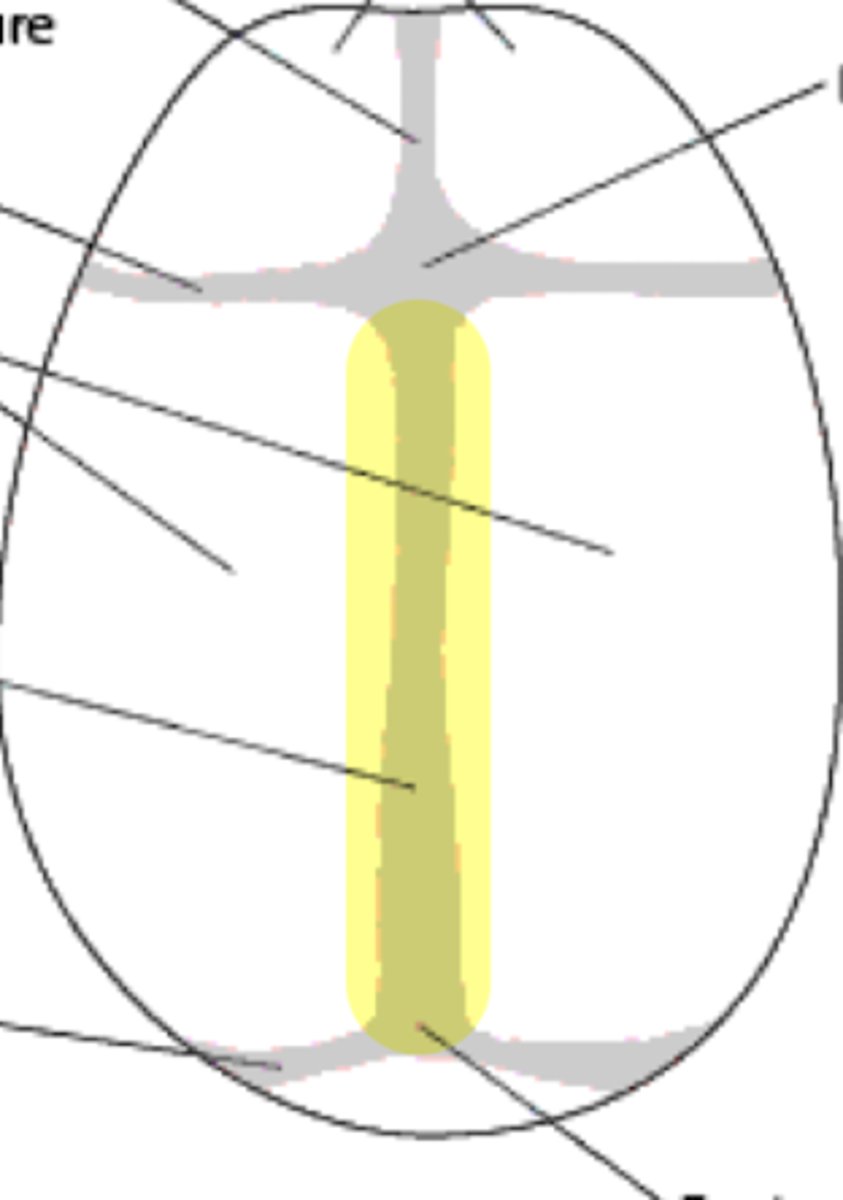
Sagittal suture
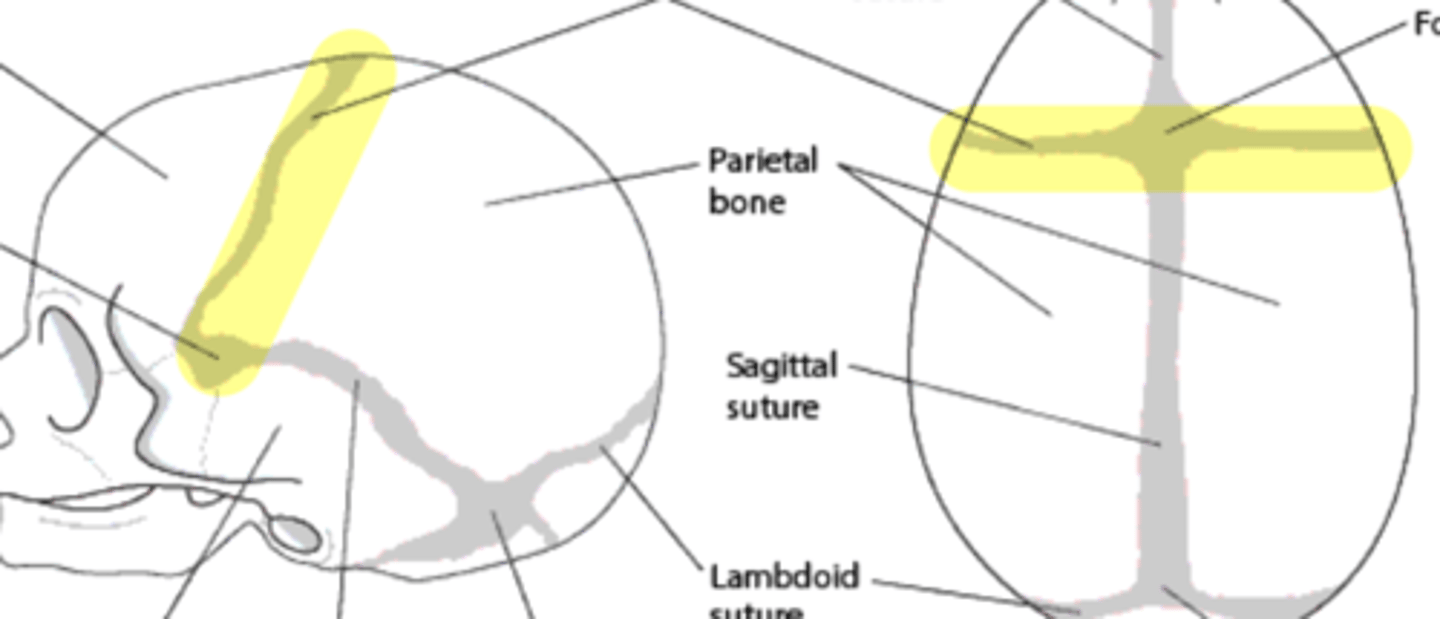
Coronal suture
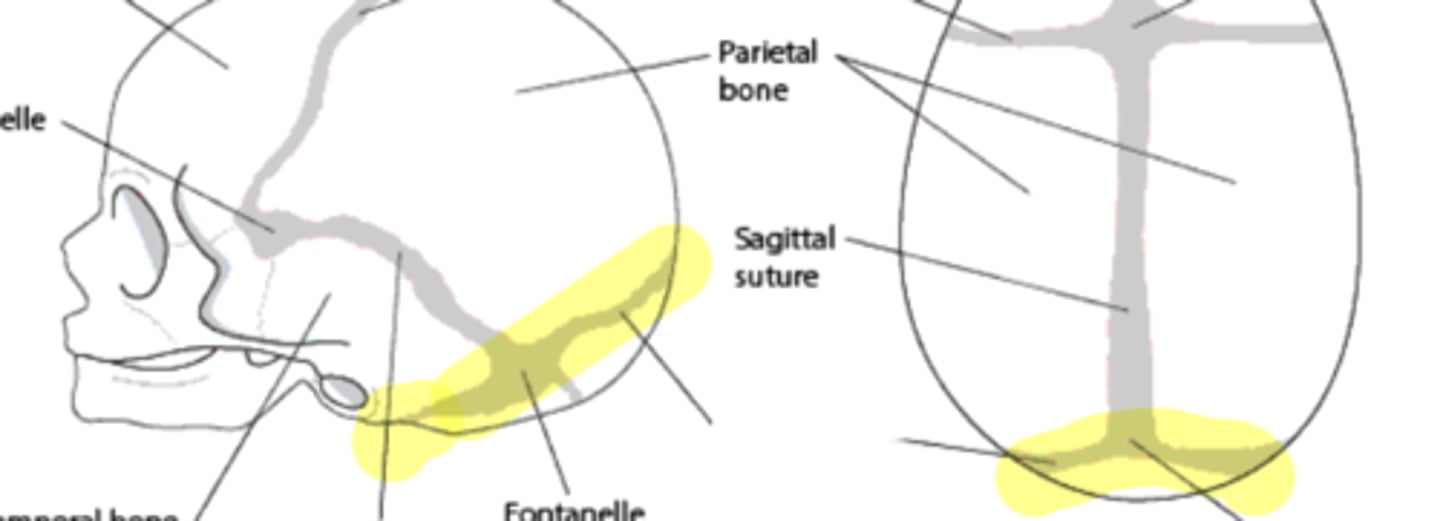
Lamboidal suture
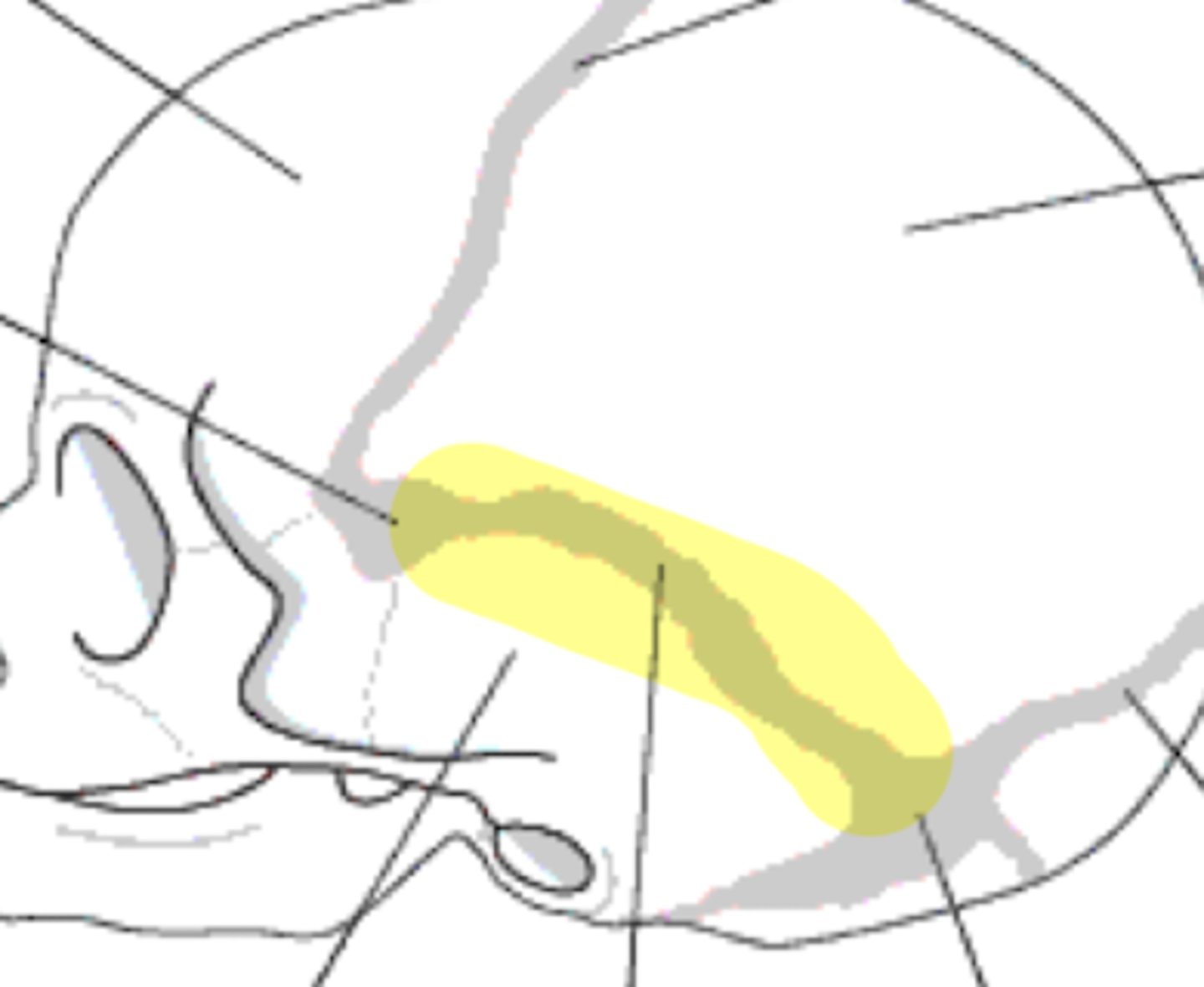
Squamos suture
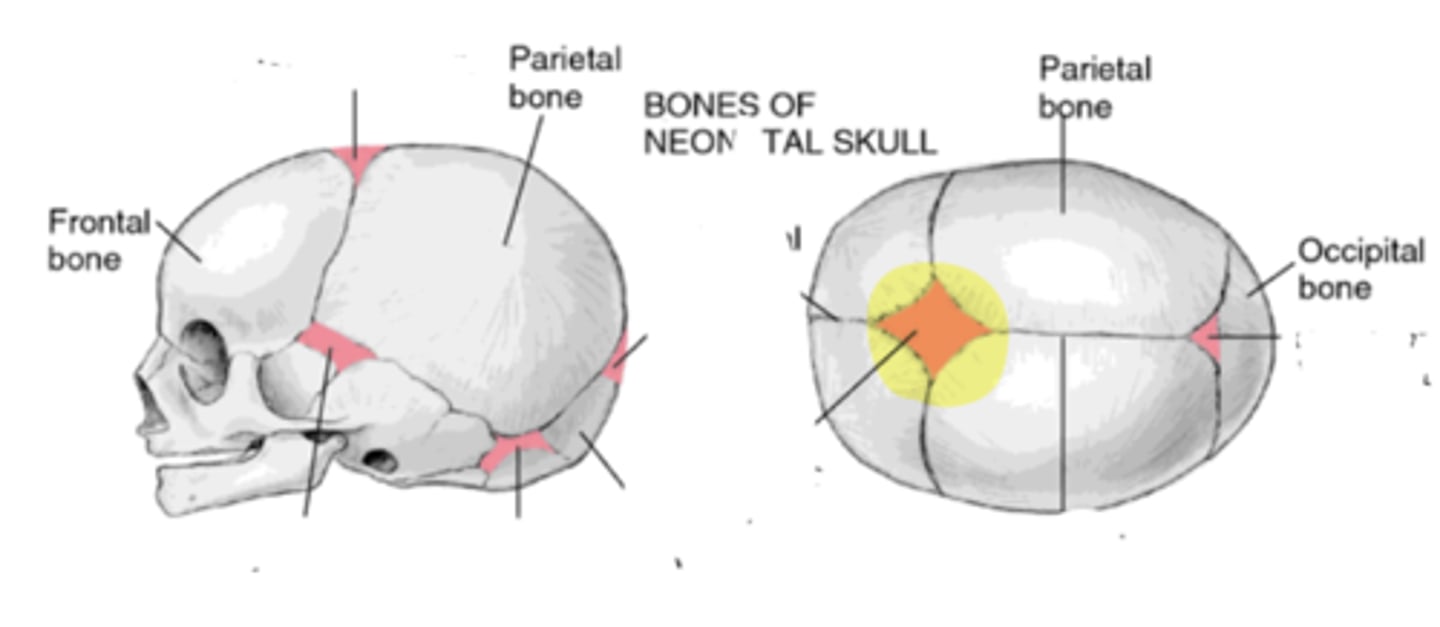
Anterior fontanelle
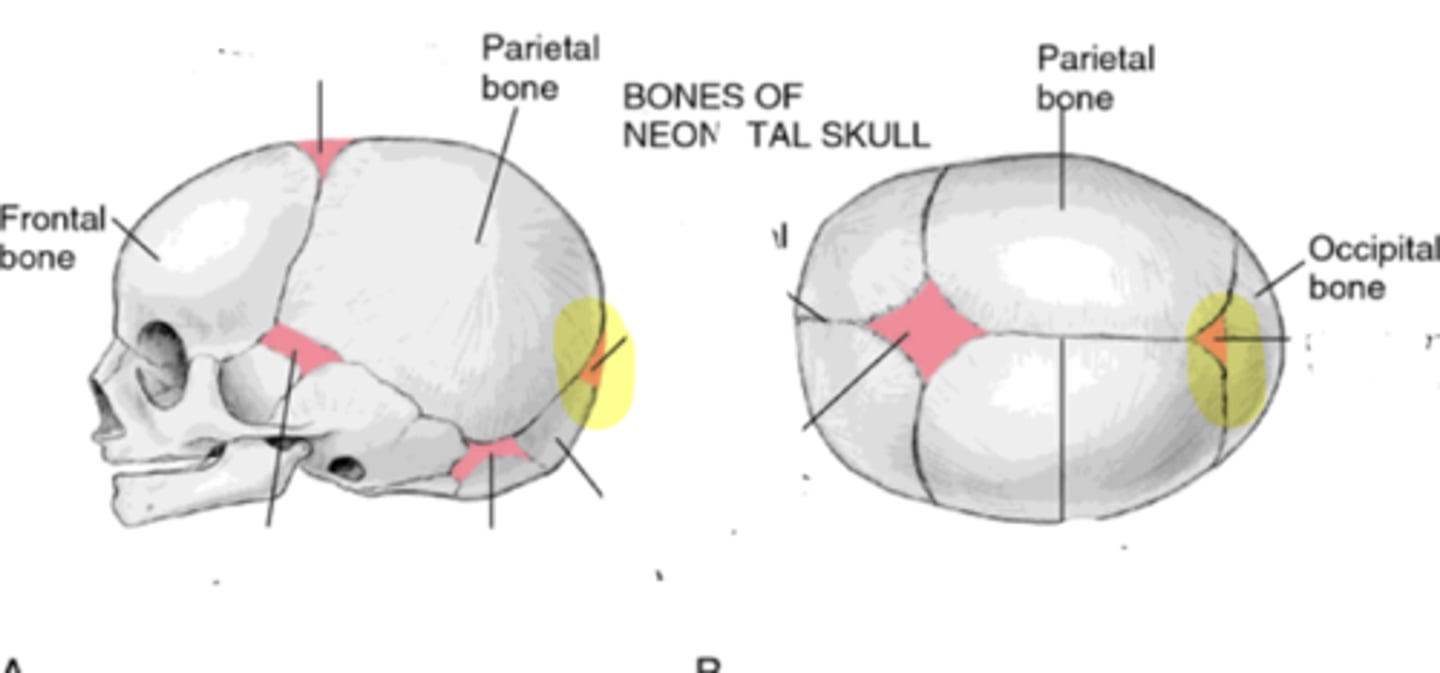
Posterior fontanelle
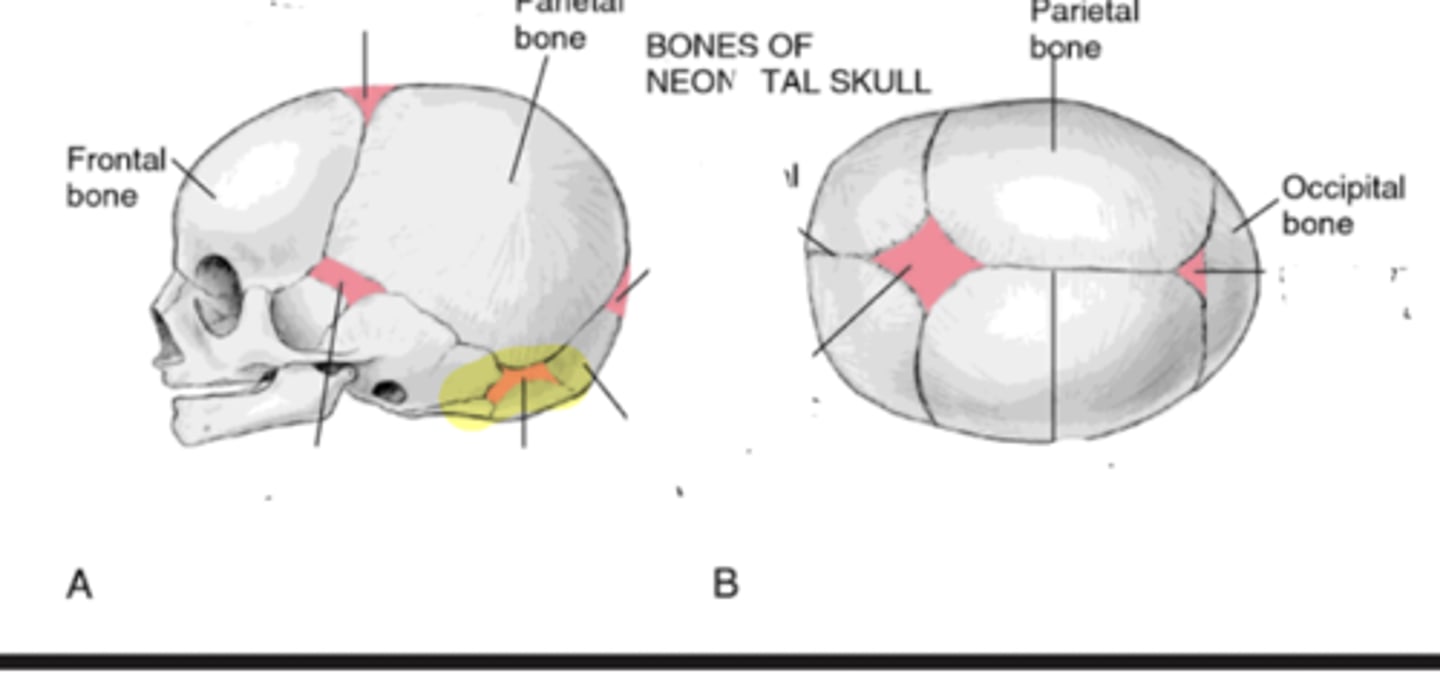
Mastoid fontanelle
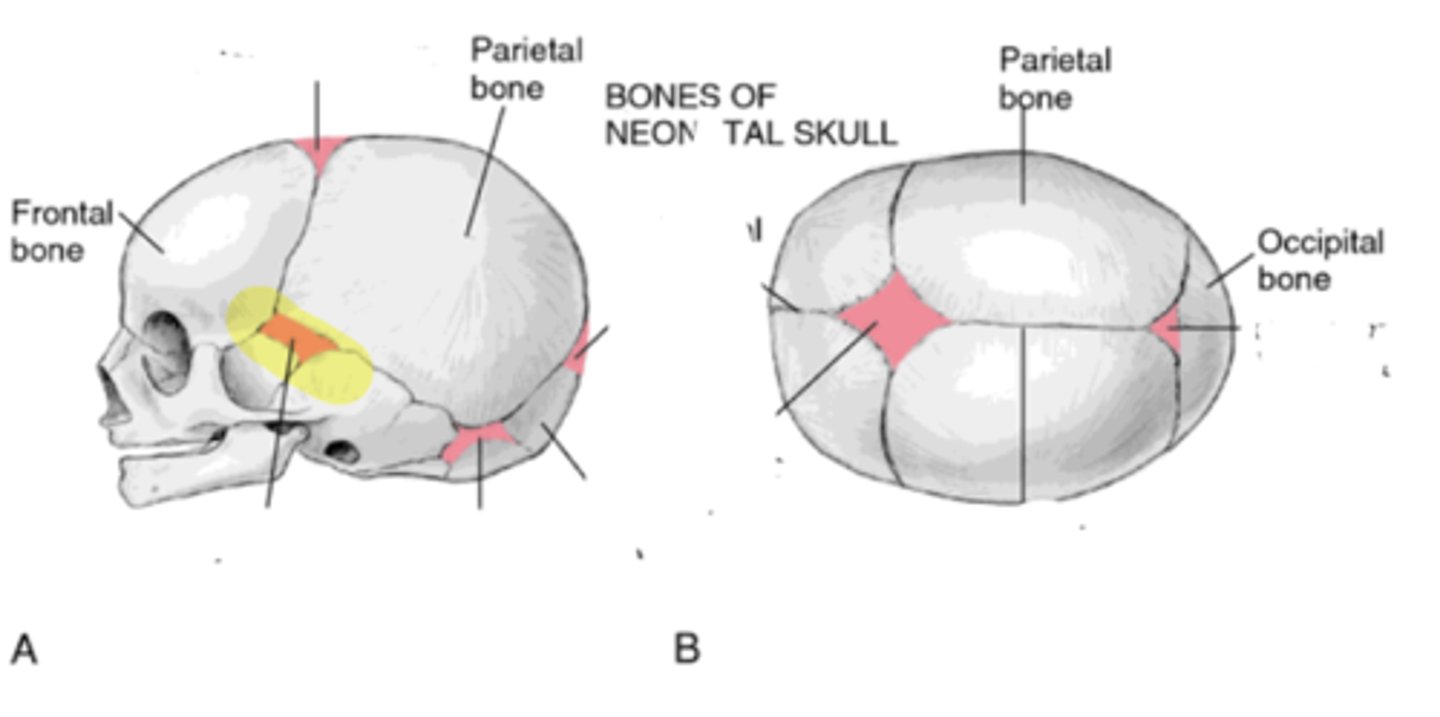
Sphenoid fontanelle