7-8. antigens and antigen recognition by lymphocytes
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
immunogen
substance capable of stimulating a specific immune response and binding to immune component
examples of immunogens
bacterial
O antigens
flagellin
toxins
viral
capsid proteins
envelope glycoproteins
antigens
substance capable of binding specifically to the final products of the immune response
characteristics of haptens
low molecular weight
antibiotics, drugs
examples: penicillin, streptomycin, aspirin
not immunogenic on their own, unless conjugated to high molecular weight compounds (carriers)
what are factors that affect immunogenicity?
route of administration
host genetics
chemical stability
foreignness
dose
complexity
size of molecule
immunogenicity of chemical families
proteins: almost always
carbohydrates: potentially
glycoproteins (protein + carb): usually
lipids: poor
nucleic acids: poor
requirements for immunogenicity
high molecular weight
chemically complex
degradable — susceptible to enzymatic degradation
foreignness
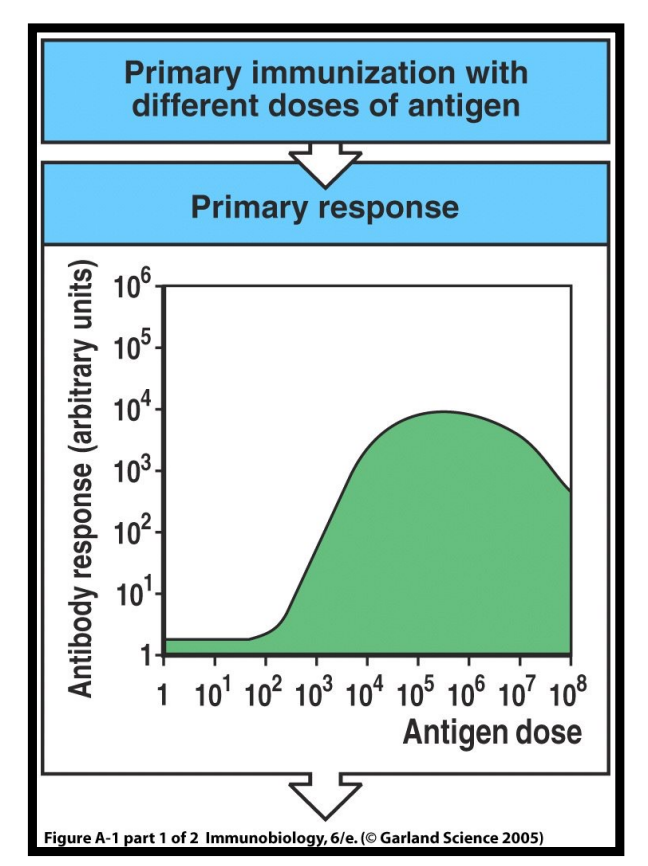
how does the dosage of antigen affect immunogenicity?
when the dosage is too low or too high, the immune response is decreased
what is the best route of antigen administration?
SQ > IM > IP > IV
depot adjuvants
delayed release of antigen
prolonged antigen persistence and stimulation
ex.
aluminum hydroxide
incomplete freund’s adjuvant (antigen in aqueous solution, mineral oil, and emulsifying agent)
immunostimulatory adjuvants
made of PAMPS (complex microbial products)
ex. LPS, CpG, mycobacterial extract
how do immunostimulatory adjuvants act on the immune system?
activate macrophages and dendritic cells
enhance antigen processing and presentation
enhance innate immunity → inflammation
stimulates lymphocytes nonspecifically
antigen recognition by B lymphocytes
use cell surface receptors = immunoglobulin (antibody)
do not need help from any other cells
antibodies can only bind extracellular antigens
functions of antigen receptors
antigen recognition
signal transduction
what form(s) of antigens do antibodies (B cells) recognize?
macromolecules (proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids)
small chemicals
conformation and linear epitopes
what type of receptors do T cells use to recognize antigens?
αβ receptors
what form(s) of antigens can T cells recognize?
MHC-restricted antigen recognition
only peptides that are presented by major histocompatiblity complex (MHC) molecules on an antigen-presenting cell
cannot recognize soluble native antigens or bind to free peptides
derived from intracellular antigens
what is dual specificity of the MHC-peptide complex?
T cell recognizes a specific peptide bound to a specific MHC → if either is different, T cell does not recognize
what is the physiological function of MHC molecules?
present peptides to T cells
present in all vertebrates
MHC class I molecules present antigens to which type of T cell?
CD8+ T cells
CD8 molecules on cytotoxic T cells bind to what domain on MHC class 1 molecules?
selectively binds α3 domain
only recognize peptides presented by the animal’s own MHC molecules → self MHC I-restricted antigen recognition
what cells express MHC class I molecules?
all nucleated cells of the body
MHC class I peptide-binding clefts can accommodate what size peptides?
8-11 amino acids
MHC class II molecules present antigens which type of T cell?
CD4+ T cells
CD4 molecules on helper T cells bind to which domain on MHC class II molecules?
selectively binds to β2 domain
self MHC II-restricted antigen recognition
what cells express MHC class II molecules?
dendritic cells, B cells, macrophages (professional AP cells)
these are the only cells that express BOTH MHC I and MHC II → can interact with both CD4+ & CD8+ T cells
MHC class II peptide-binding clefts can accommodate what size peptides?
10-30 amino acids