HMI104 - Neck
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Where is the internal jugular vein formed from?
Dural venous sinuses
What is the function of the internal jugular vein?
Return venous blood from the brain
Where does the internal jugular vein travel from?
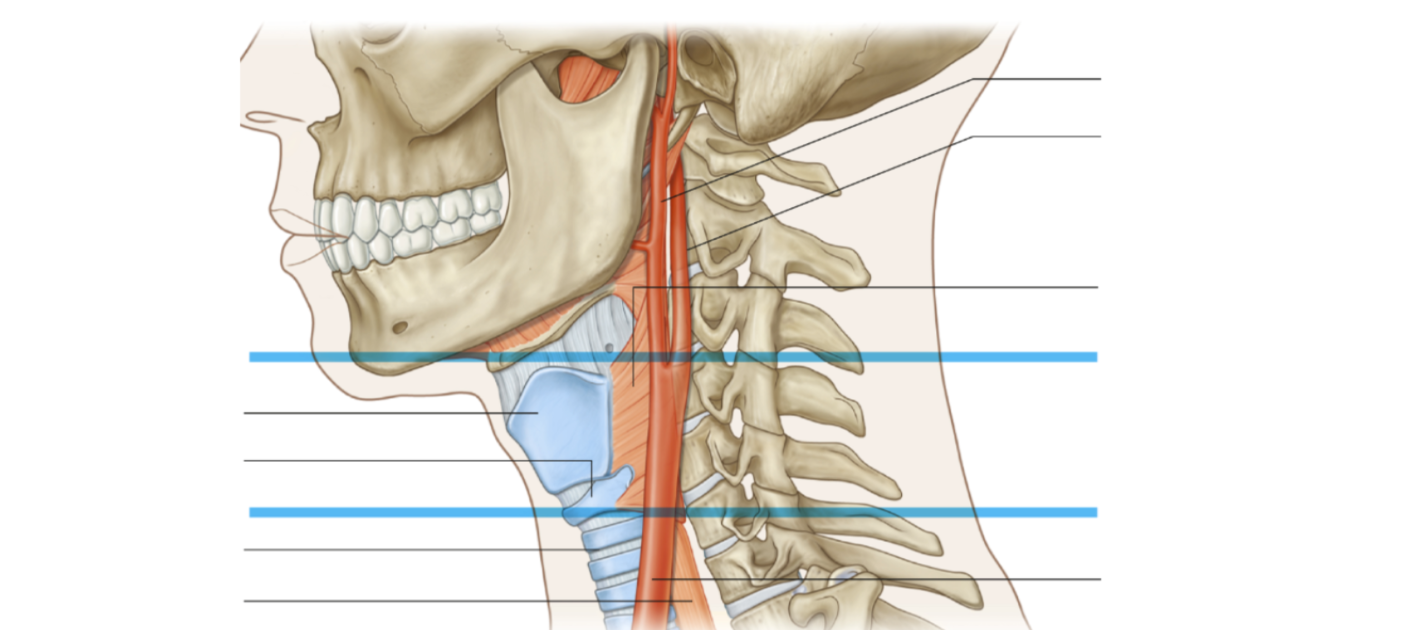
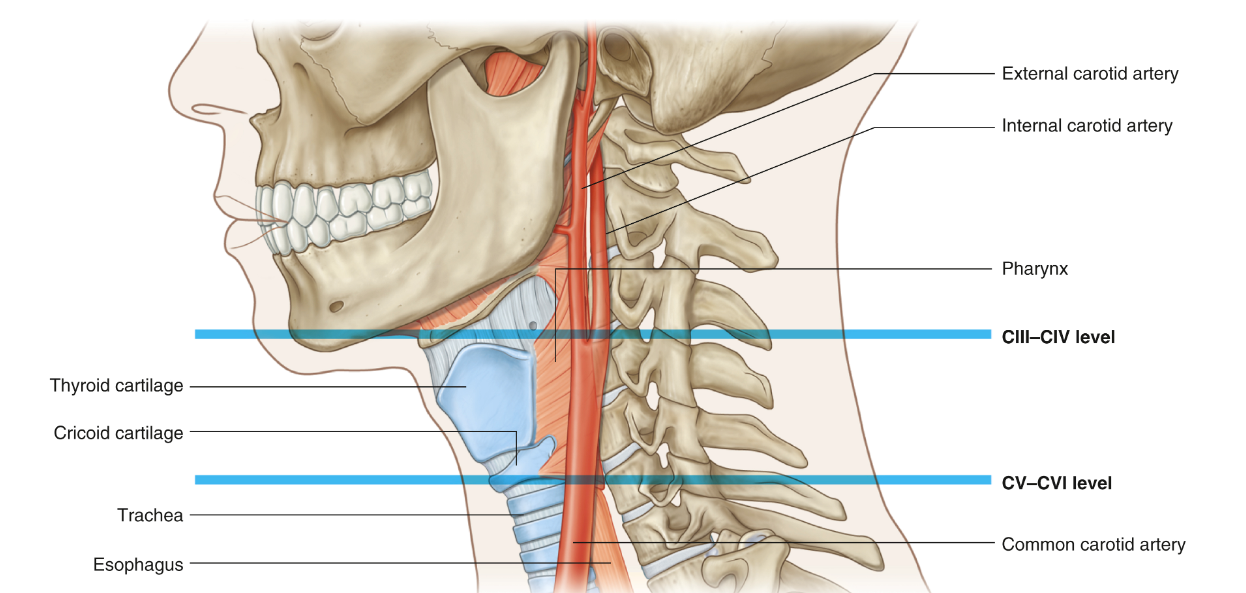
Travels within the carotid sheath laterally and posterior to the common carotid artery
Where does the common carotid artery ascend in and where does it bifurcate?
Ascends in carotid sheath and bifurcates at around C3 to C4
What does the internal carotid artery supply?
Brain
What does the external carotid artery supply?
Neck, head and face
What are the symphysis joints between vertebral bodies
Intervertebral discs: Annuluses fibrosis and nucleus pulposis
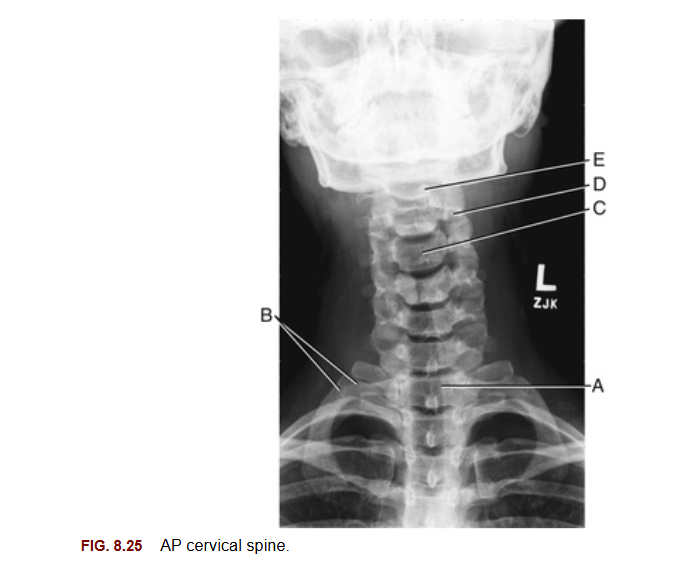

Why are the in vertebral discs of the cervical region smaller than other regions of the vertebral column?
Support less weight, allowing increased mobility and flexibility
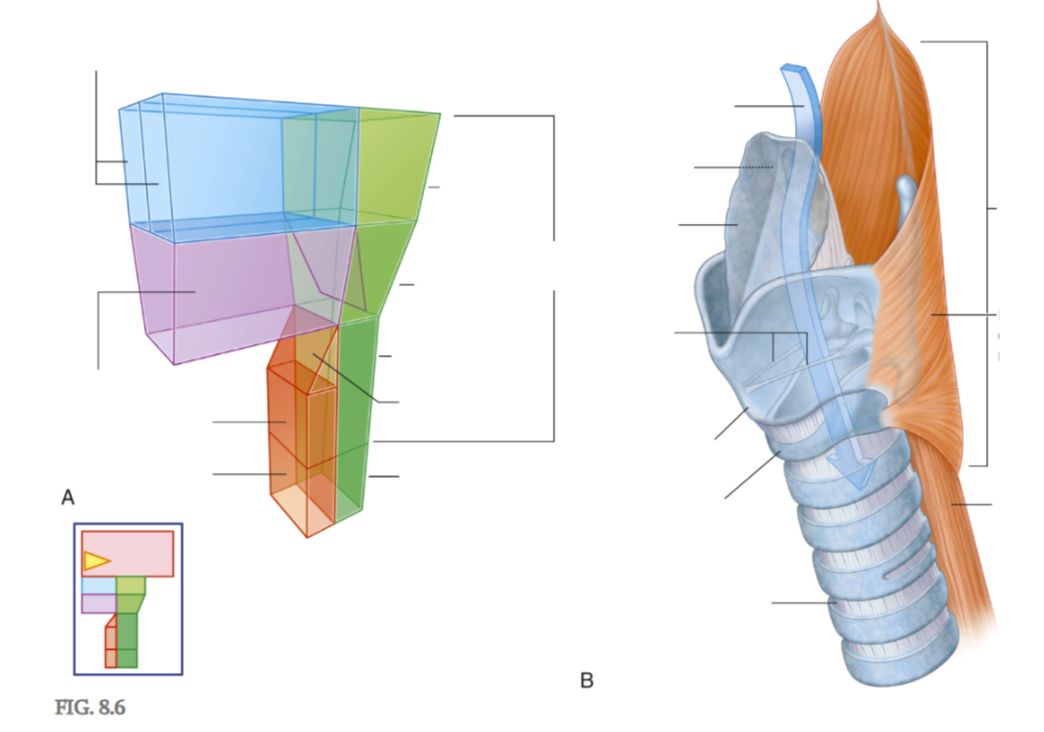
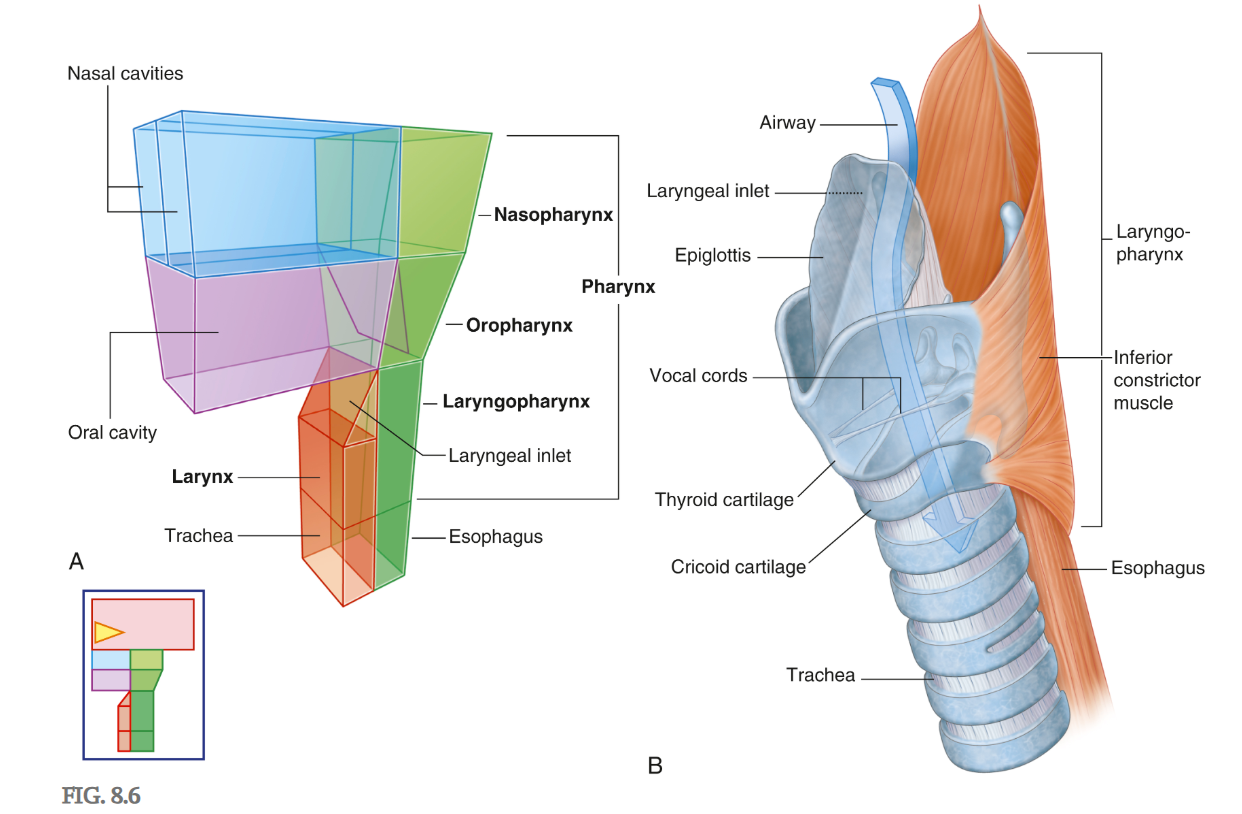
Which of the divisions of the laryngopharynx facilitates the passage of air?
Anterior
Which of the divisions of the laryngopharynx facilitates the passage of food?
Posterior
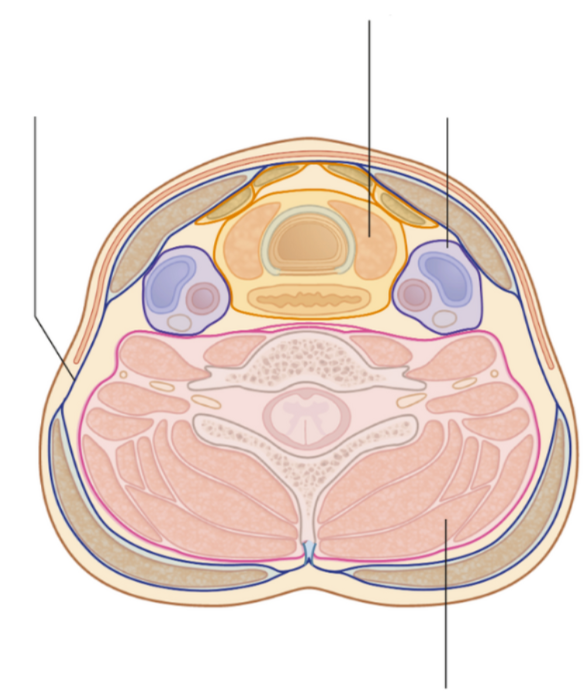
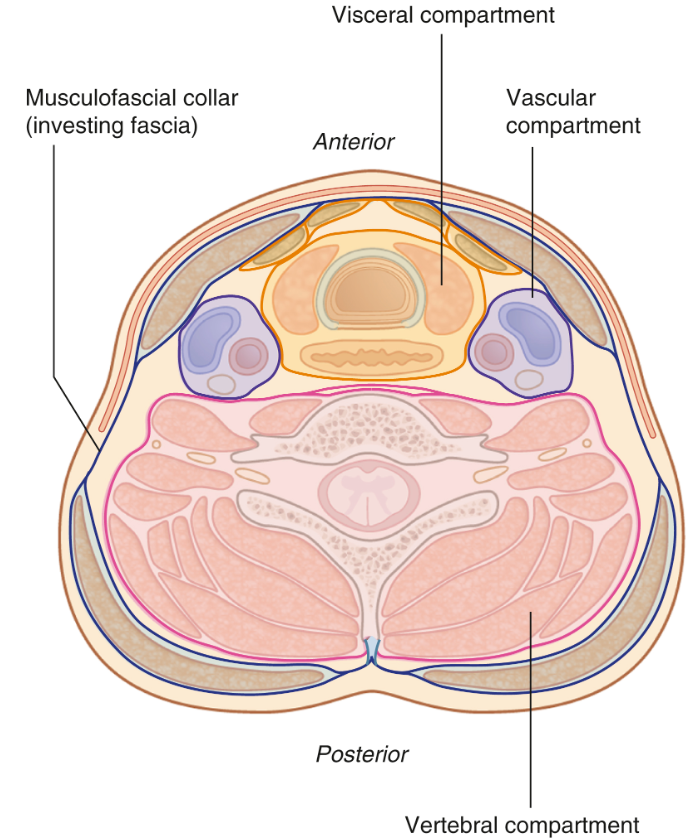
Lists the contents of the carotid sheath, and list which superficial neck muscle this sheath is located beneath
Common carotid artery - medially
Internal jugular vein - laterally
Vagus nerve - posteriorly
What ligament resist extension?
Anterior longitudinal ligament
What ligament resist flexion?
Posterior longitudinal ligament, ligamentum flavum, interspinous ligament, supraspinous ligament
Location of the anterior longitudinal ligament
Anterior to vertebral bodies
Location of the posterior longitudinal ligament
Posterior to vertebral bodies
Location of ligamentum flavum
Connects laminae of adjacent vertebrae
Location of interspinous ligament
Between spinous process
Location of supraspinous ligament
Between spinous processes
Nucleus polposus
Internal gelatinous mass
Function of nucleus polposus
Deals with compression load and directs weight bearing force to outer portion of disc
Annulus fibrosus
A ring of collagen and ring of fibrocartilage
Function of annulus fibrosus
Buffers shear force when moving neck
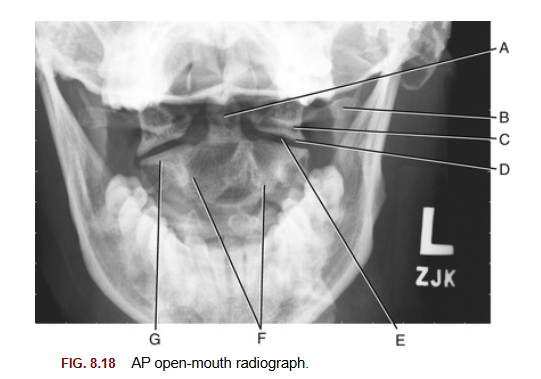
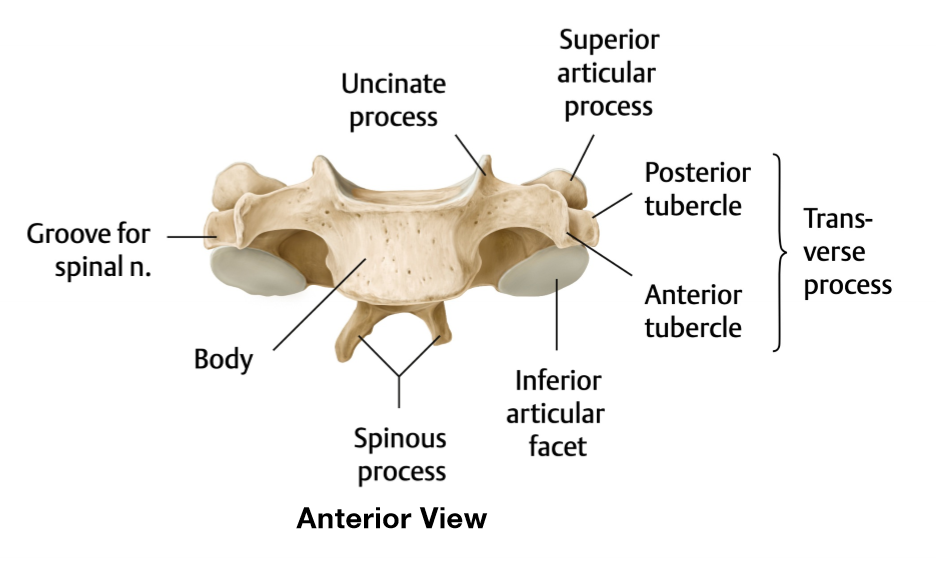
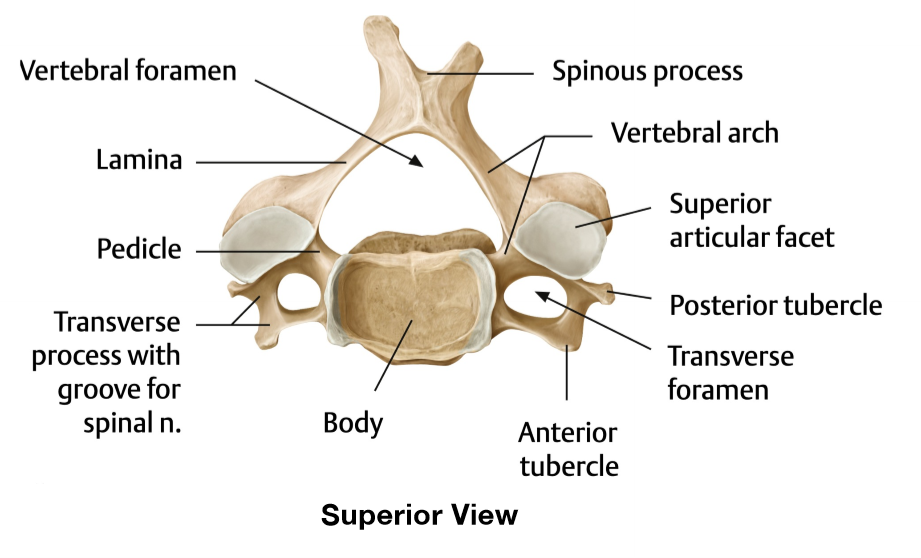
Atypical features of C1
no vertebral body, instead of spinous process they have tubercles, no lamina
Atypical features of C2
vertebral body is large, has a dens, huge spinous process and body
Atypical features of C7
transverse foramen can be absent, transverse processes are non-byford (single), and spinous process is non-byford but huge
Why is the spinous process huge in C7?
For ligamentous attachment of the nuchal ligament
What are the bony borders of the anterior triangle
inferior border of mandible (superiorly), anterior border of sternocleidomastoid muscle (laterally) and midline of neck (medially)
What are the bony borders of the posterior triangle
posterior border of sternocleidomastoid muscle (anteriorly), anterior border of trapezium muscle (posteriorly), and middle of clavicle (inferiorly)
Describe the pathway of drainage of the internal jugular vein to the right atrium of the heart
Internal jugular vein → brachiocephalic vein → superior vena cava → right atrium
A trauma patient’s open‑mouth X‑ray shows a ring‑shaped vertebra lacking a body, with prominent lateral masses and both anterior and posterior arches. Which of these features is characteristic and unique to the C1 vertebrae?
Groove for vertebral artery
On a lateral cervical X‑ray, you observe the C2 vertebrae. Presence of which feature is most indicative of the C2 vertebrae?
Odontoid process
A CT cervical scan shows arterial blood flow in the transverse foramina of C1–C6 but not in C7’s. What explains this finding?
Vertebral artery enters transverse foramen at C7, meaning the vertebral artery is occluded. | |
 | Vertebral artery ascends from C6, and based on this the scan is normal |
 | Common carotid ascends in the transverse foramen from C6, and based on this the scan is normal |
 | Common carotid artery enters transverse foramen at C7, meaning the Common carotid artery is occluded. |
Vertebral artery ascends from C6, and based on this the scan is normal
The vertebral foramen is relatively largest in the cervical region to accommodate which structure?
Spinal cord
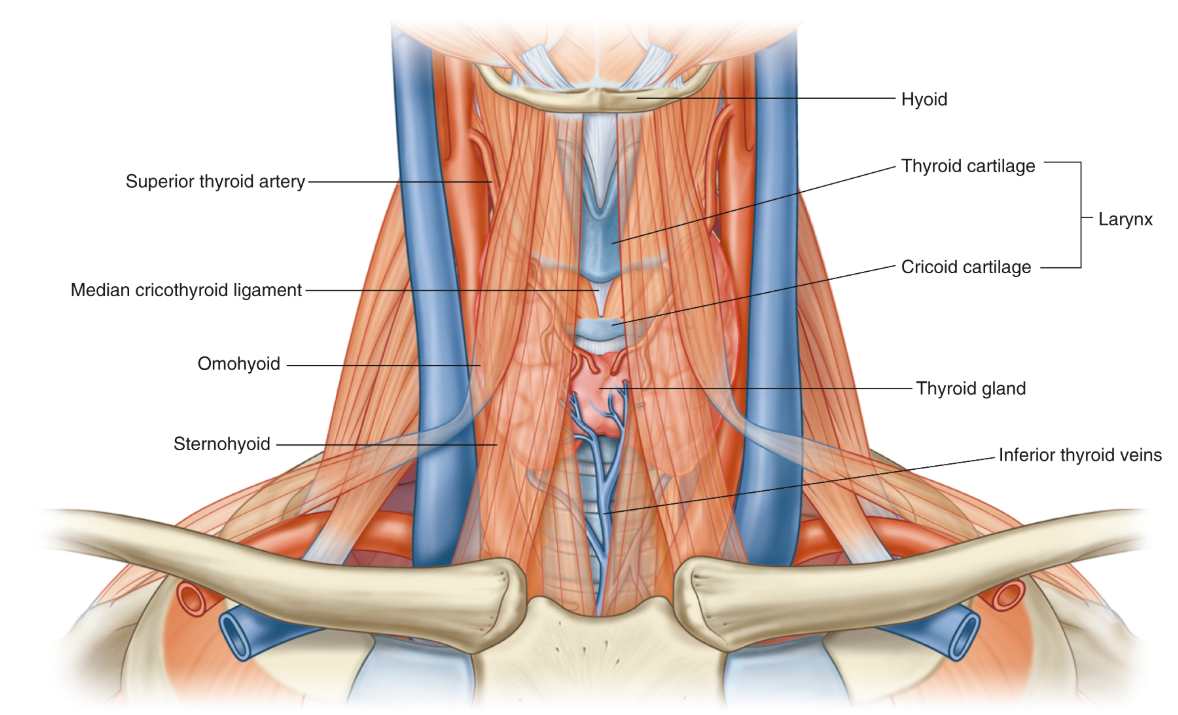
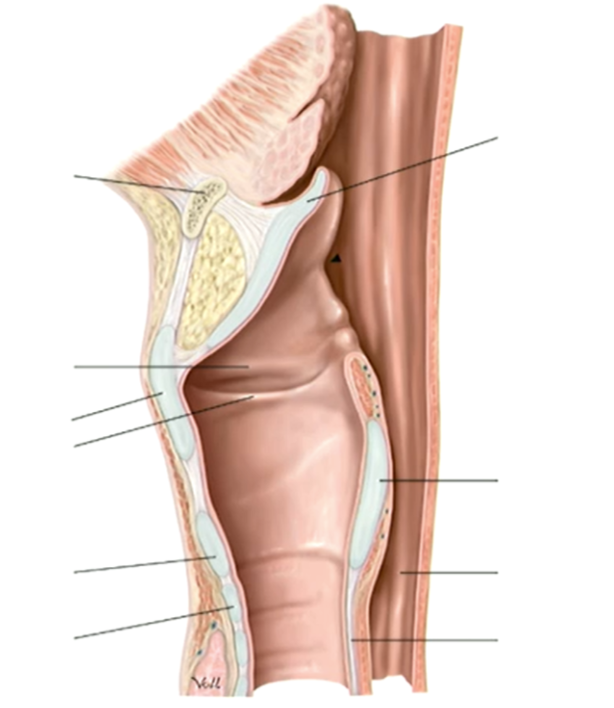
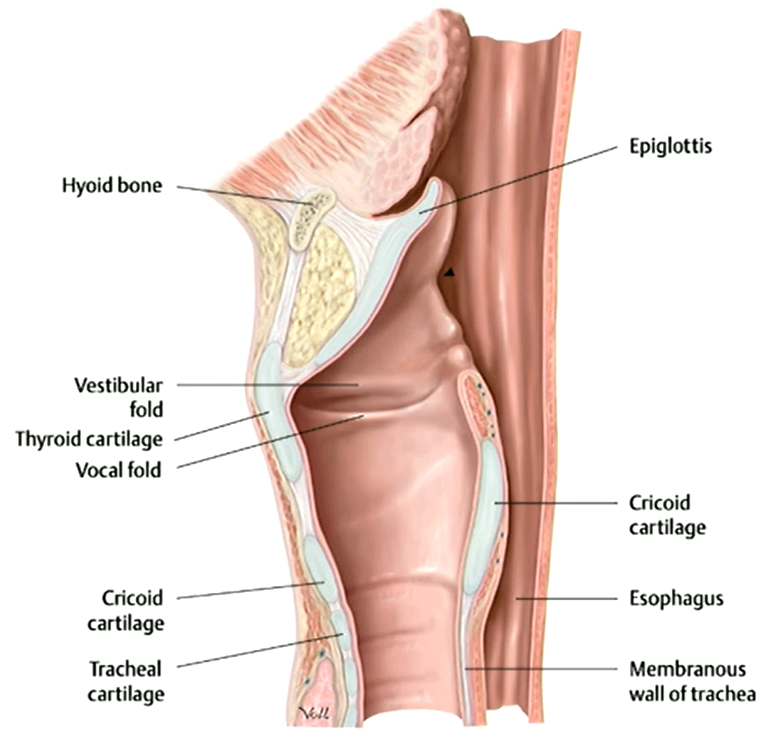
A student palpating the neck feels a firm prominence at the level of C4, described in laymans terms as the 'Adam’s apple'. They are palpating a landmark on which aspect of the larynx?
Thyroid Cartilage
The vascular compartment of the neck is enclosed in a layer of fascia, known as the 'carotid sheath'. Which three structures are best described as contents of this sheath?
Common carotid artery, internal jugular vein, vagus nerve
Which important ligament has the important function of limiting anterior translation of the C1 vertebrae from the dens, stabilizing the AA joint?
Cruciform ligament of the atlas
Which structure forms the posterior border of a cervical intervertebral foramen?
Zygapophyseal (facet) joint
Which of the following ligaments of the vertebral column is most likely involved in limiting extension between vertebral segments?
Anterior longitudinal ligament
A 48-year-old office worker presents with chronic neck pain and stiffness, worse on neck flexion. MRI reveals degeneration at the C5–C6 level, with hypertrophy of a ligament contributing to mild spinal canal narrowing. Based on the location and function, which ligament is most likely involved?
Ligamentum flavum
An ultrasound locates a carotid bifurcation behind the thyroid cartilage at the level of C4. This finding is described as:
Typical (expected)
Function of epiglottis
Closes laryngeal inlet
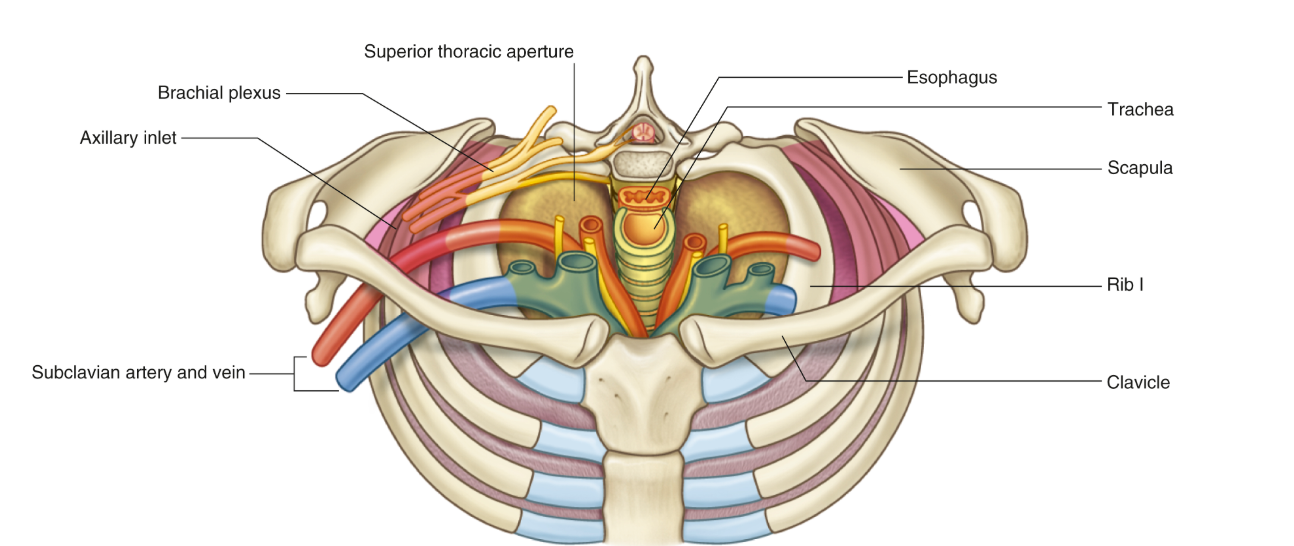
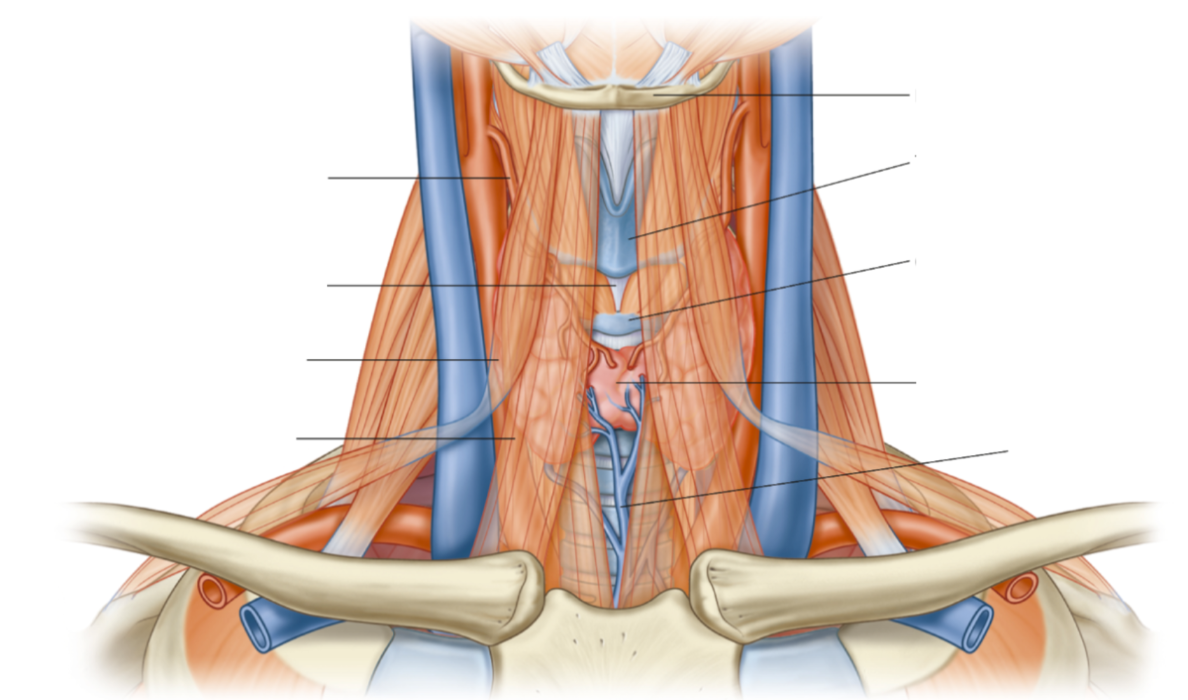
Structures in the anterior triangle
Thyroid gland, common carotid artery, jugular notch, vagus nerve, hyoid bone, laryngeal cartilage, infrahyoid muscles
Structures in the posterior triangle
Scalene muscles, subclavian artery, subclavian vein, external jugular vein, cervical plexus, brachial plexus, phrenic nerve
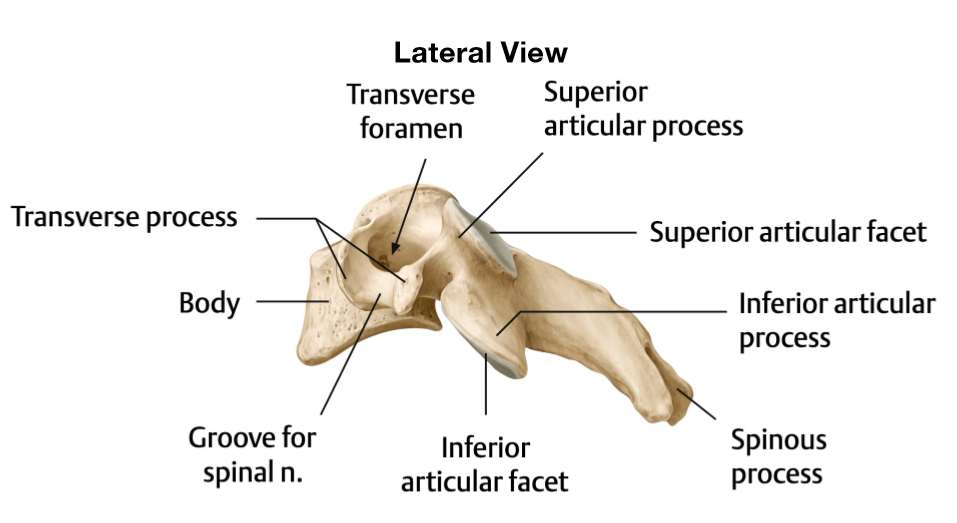
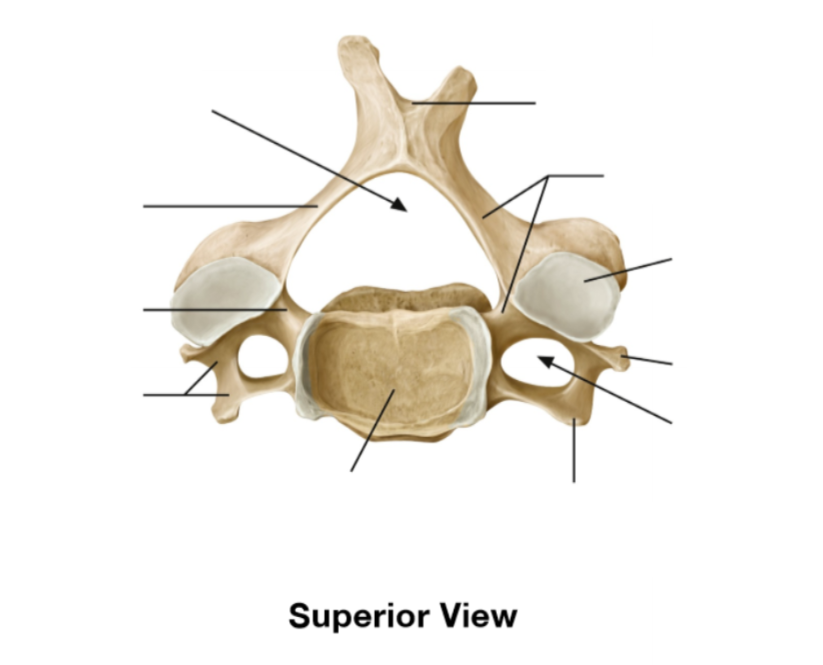
Where does the vertebral arteries ascend and where do they travel afterwards
Ascend in transverse foramen of C6 - C1 before entering the foramen magnum
What does the transverse foramen allow
Permits the passage of the vertebral arteries and veins
What type of joint is the atlantoaxial joint
Synovial pivot joint, which allows for rotation
What type of joint is the uncovertebral joint
Plane synovial joint
Articular surface of uncovertebral joint
Between uncinate process of inferior vertebrae and vertebral body above
What are secondary curvatures?
Cervical and lumbar
What are primary curvatures?
Thoracic and sacrum
Difference between secondary and primary curvatures?
Secondary - develops after birth, when infants pick up their head
Primary - persists from foetal life
Function of epiglottis
Closes laryngeal inlet during swallowing so food doesn’t enter the lungs