VEX Robotics Parts Identification
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
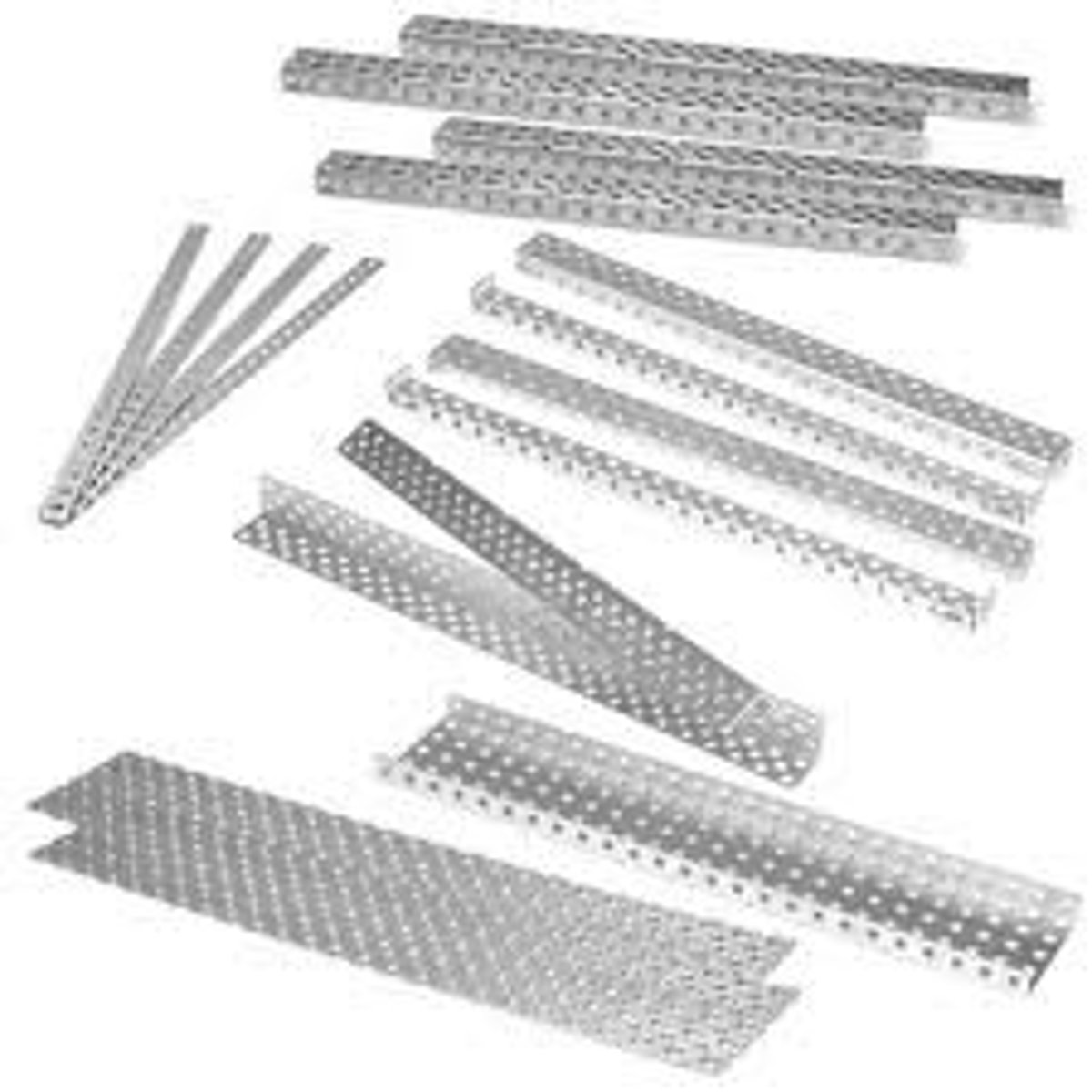
angle structure
An "L" shaped structure part used to form the "skeleton" of the robot.
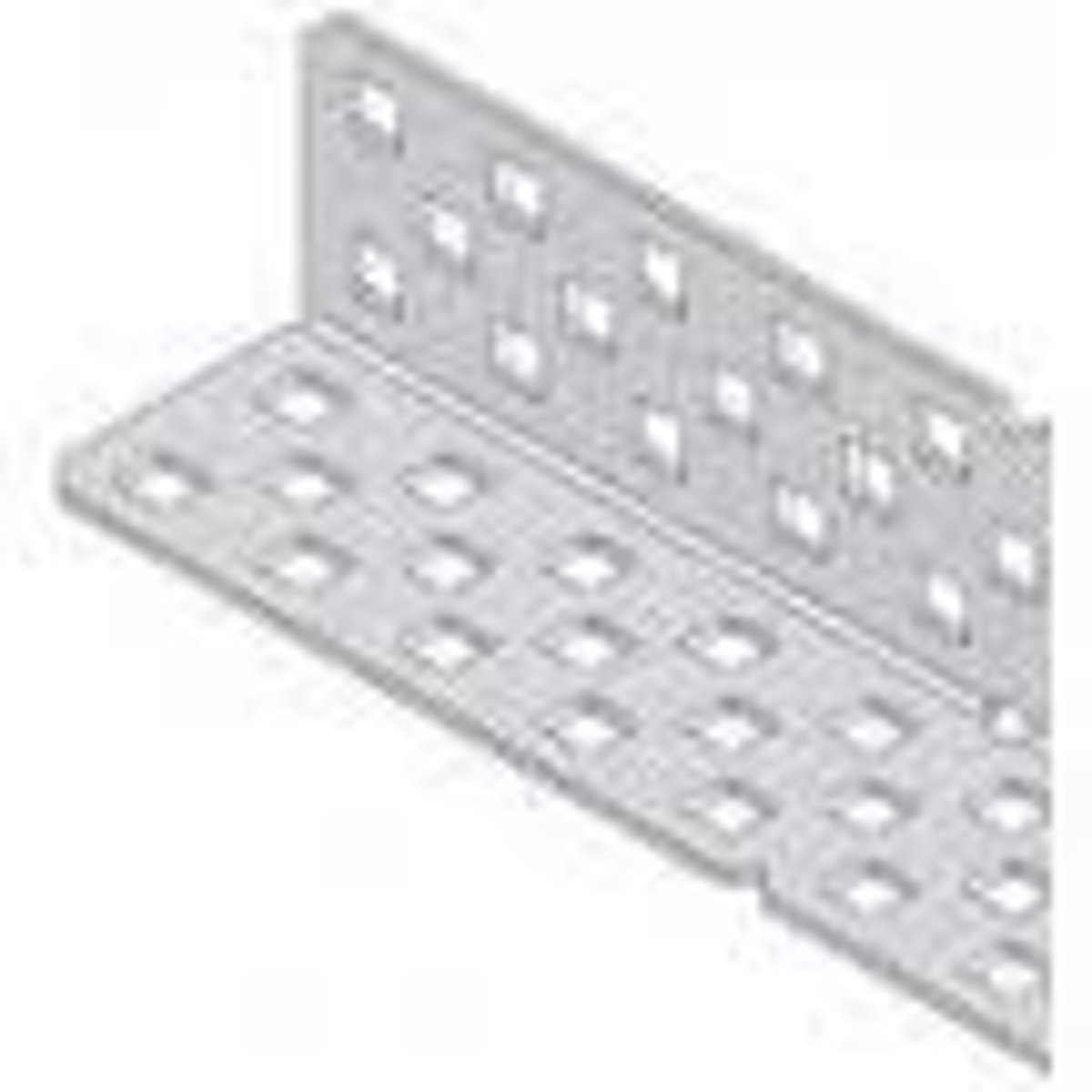

Shaft or axle
A long, rigid piece through the rotational center of an object (like a gear or wheel).

bearing
An axle is passed through the center hole which allows it to spin freely. It lowers friction and prevents metal to metal moving parts.

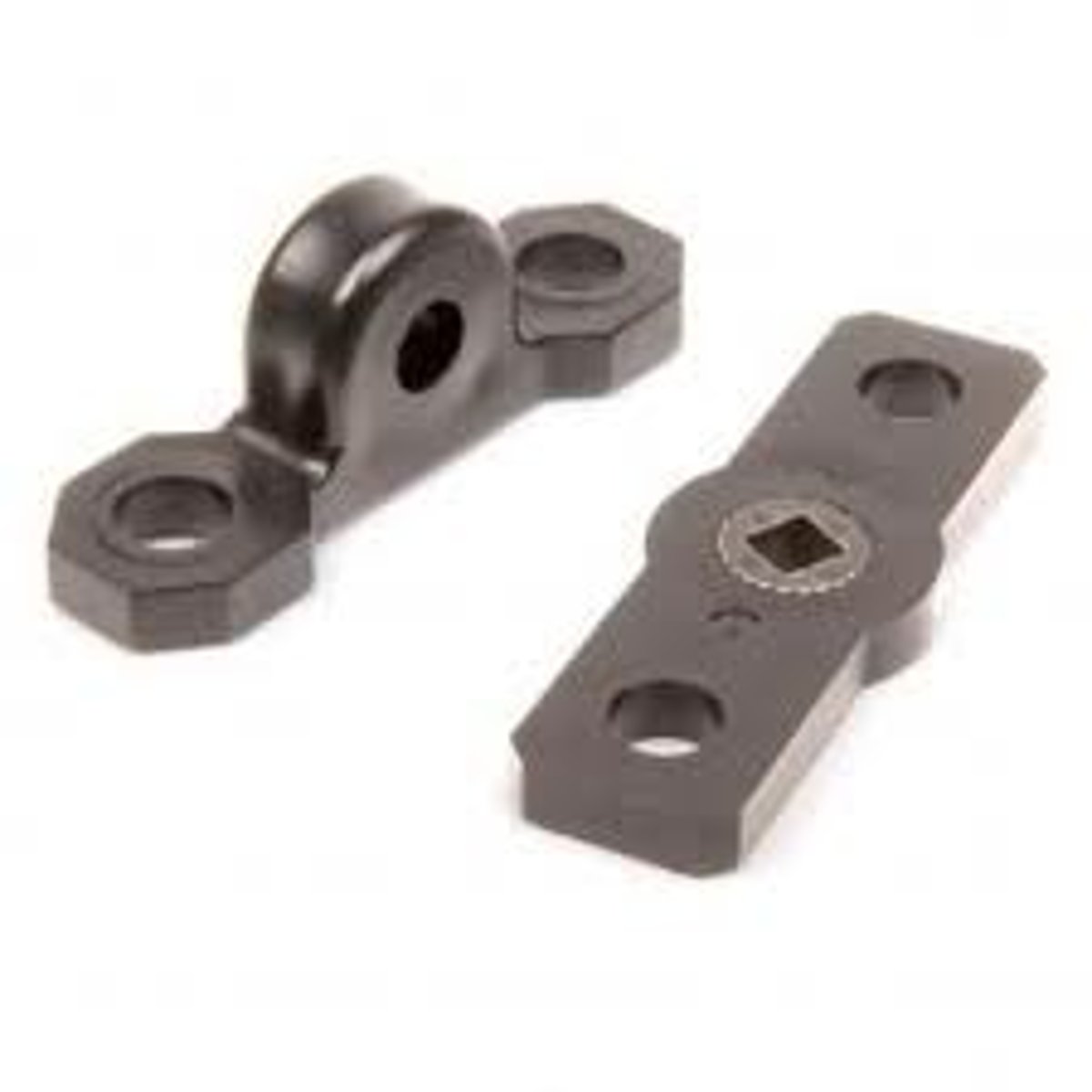
pillow block bearing
A piece that is used to hold a moving piece (such as an axle) in place relative to the rest of the system.

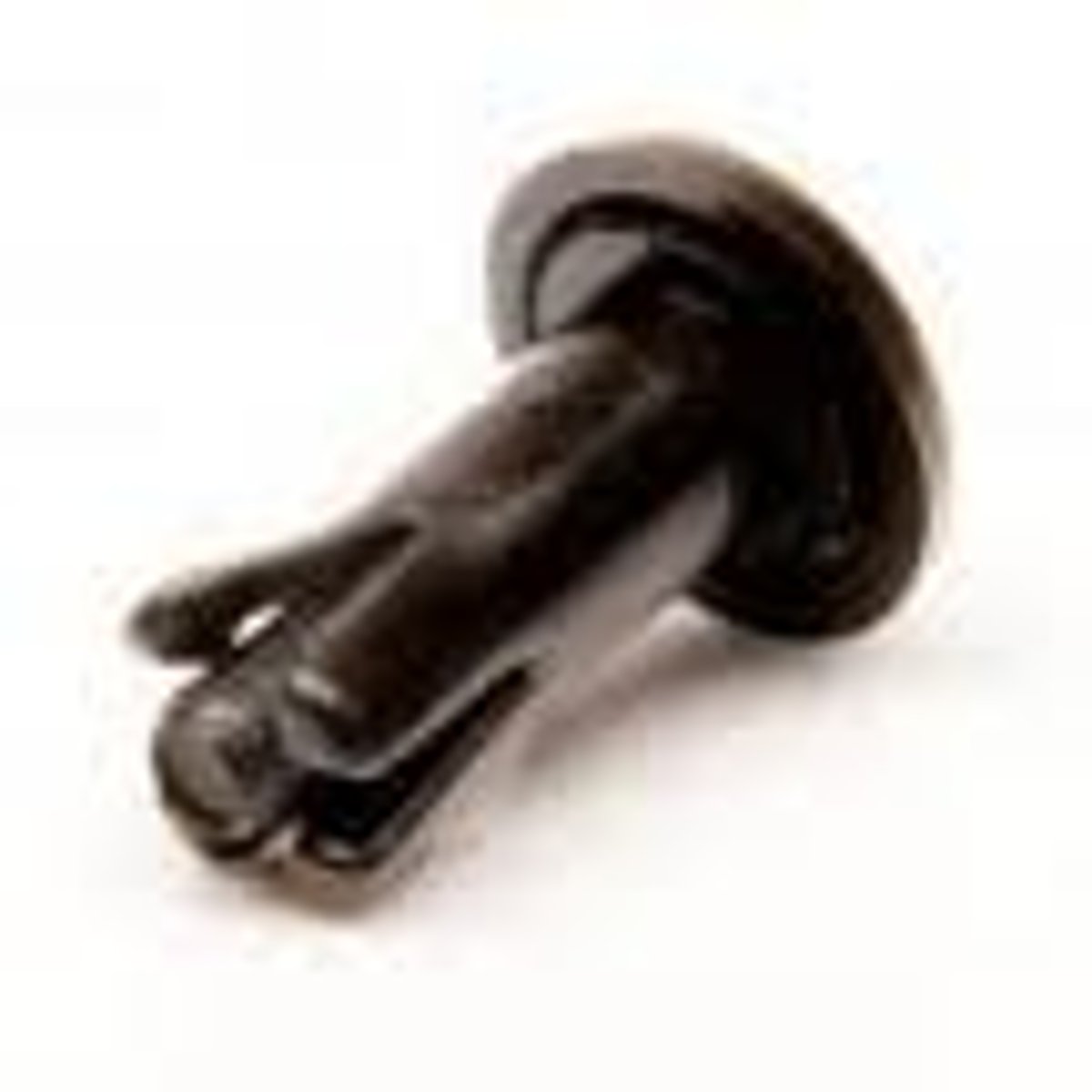
bearing pop rivet
A plastic fastener system consisting of two parts and used to hold the VEX bearing Flat part in place on the structure system.

caster wheel
A free-swiveling wheel mounted on a robot to provide stability while producing a minimum of friction.

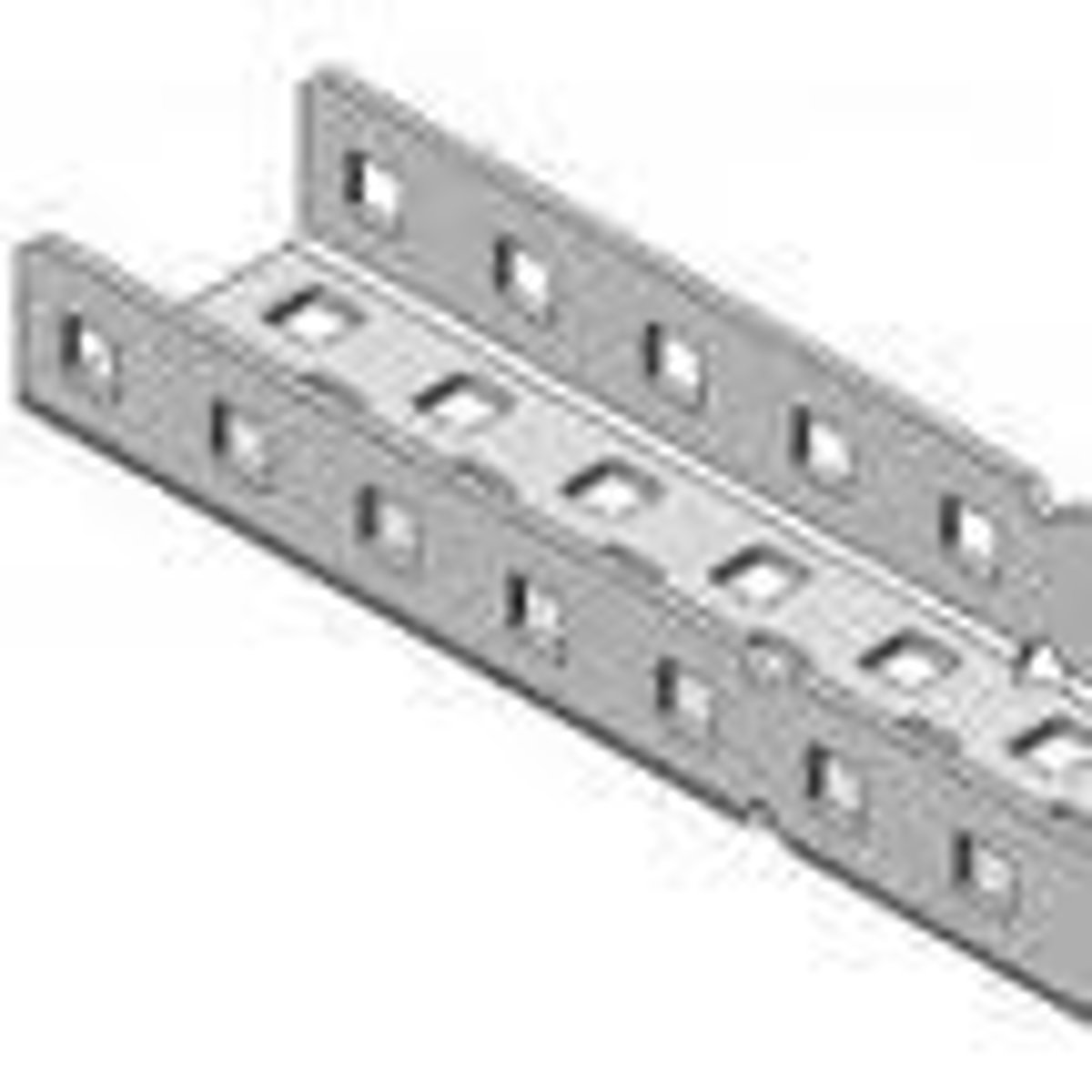
c-channel
A structure system beam used as a support to form the "skeleton" of the robot.

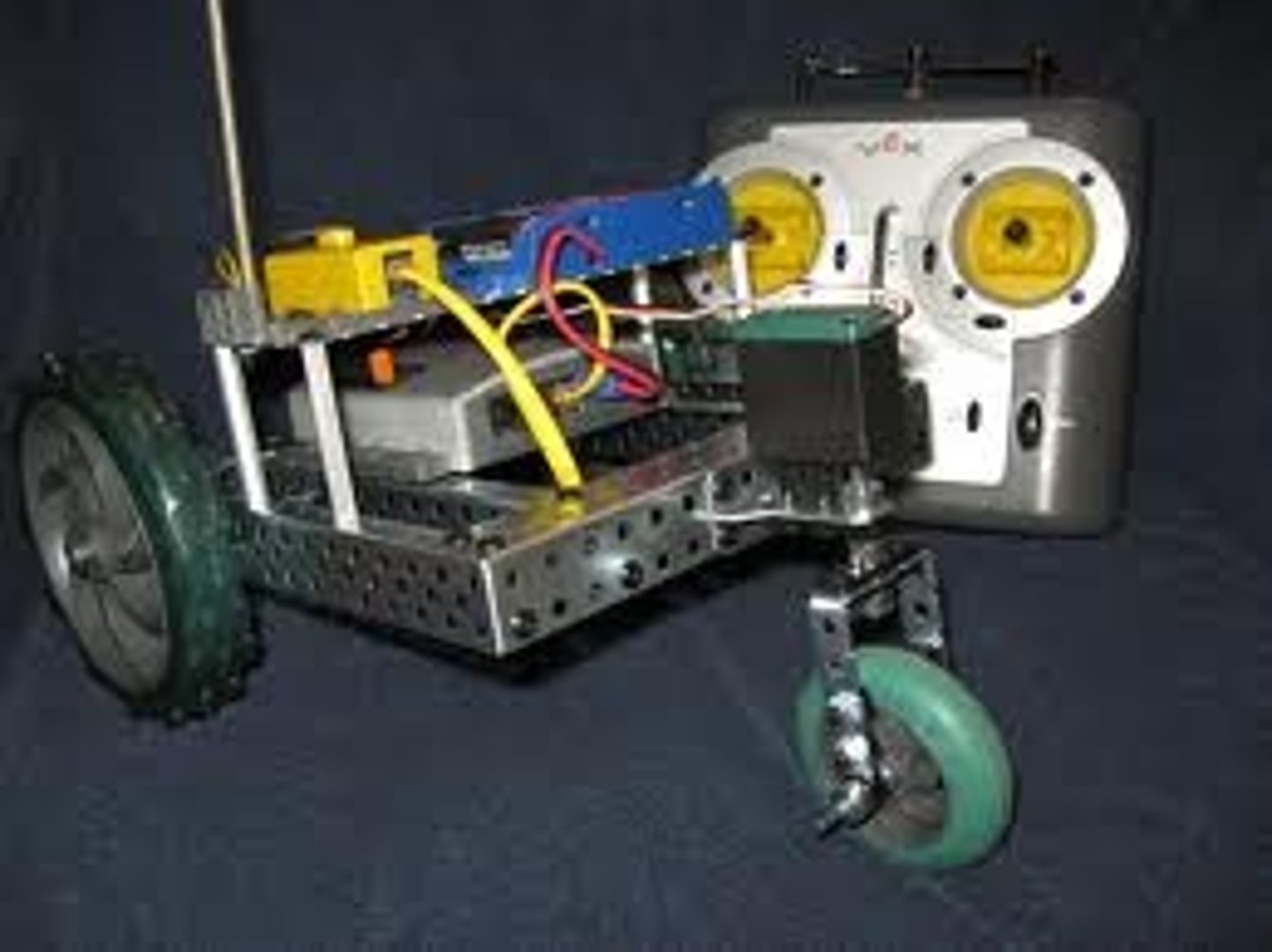
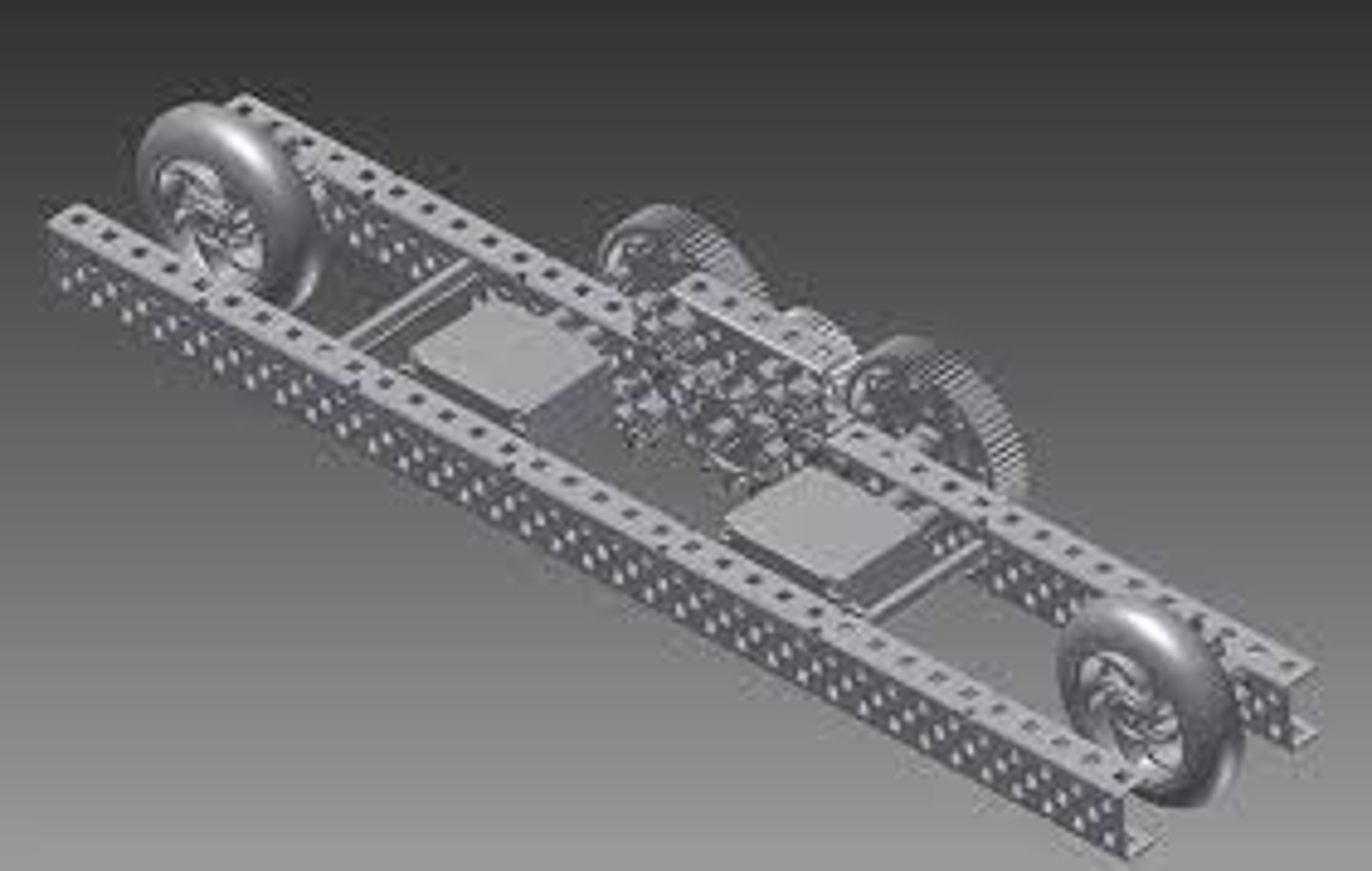
chassis
A vehicle's basic structural frame, plus its locomotion systems.
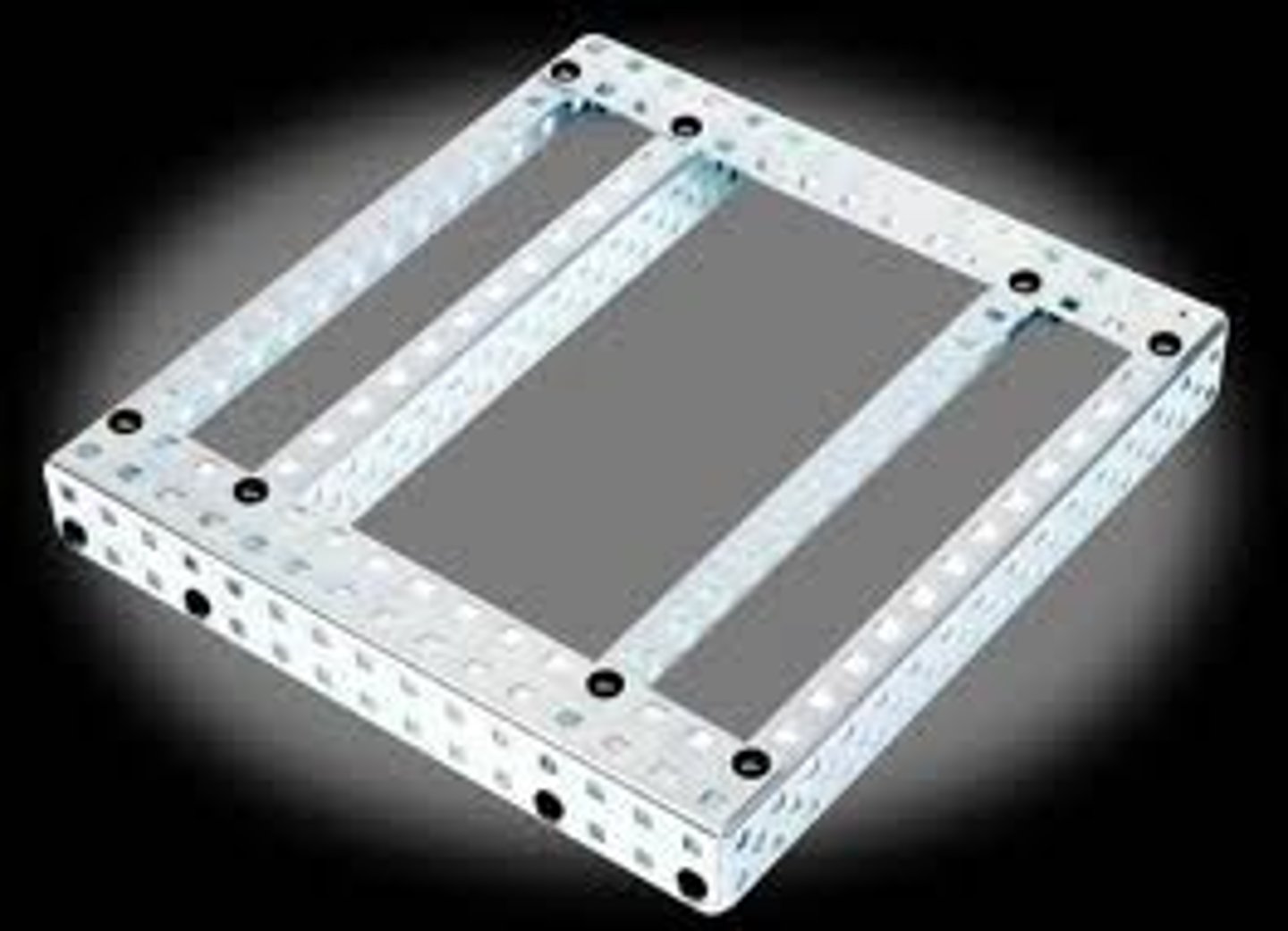
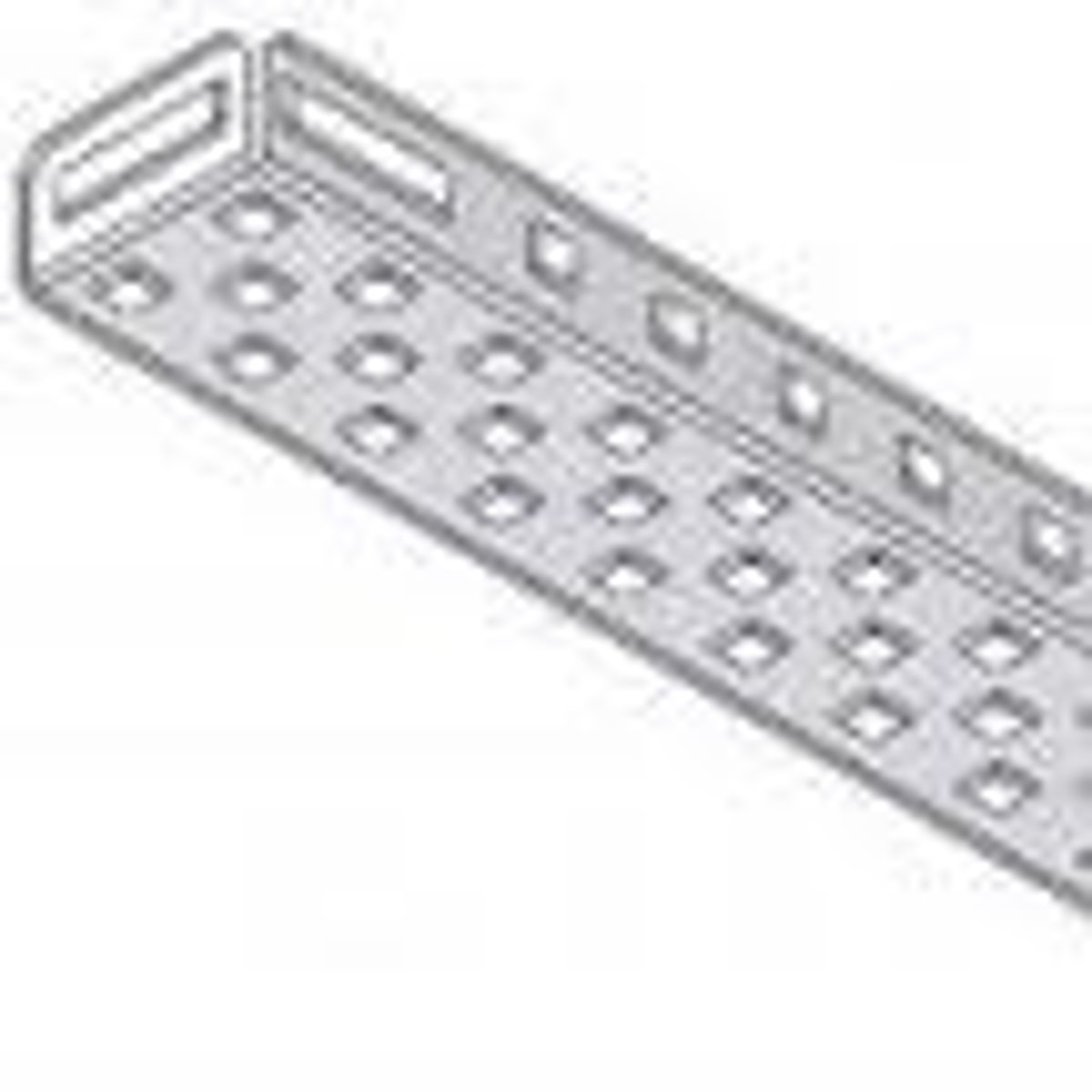
chassis rail
A part of a vehicle's basic structural frame or a structure system beam used to form the "skeleton" of a robot.

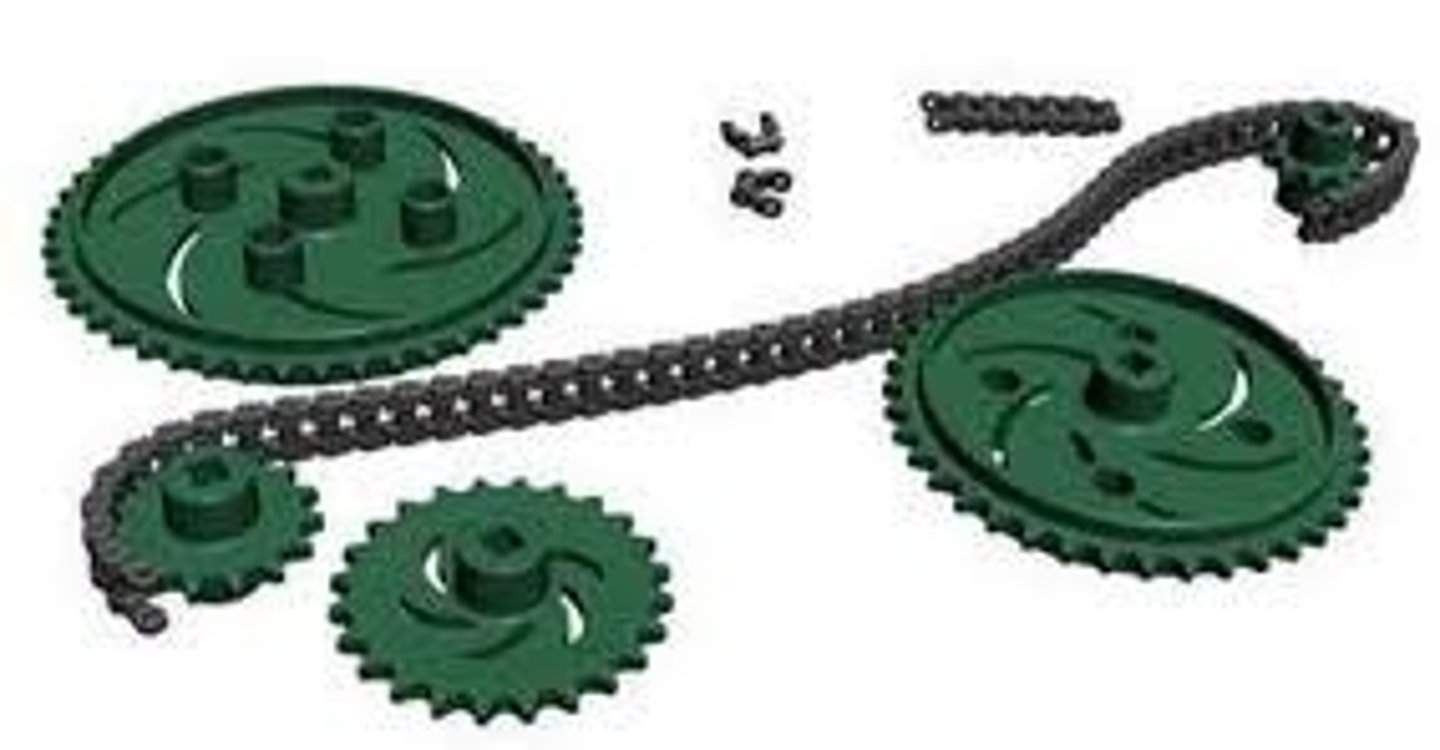
chain and sprocket
Parts to provide a chain drive in the motion system of the robot.

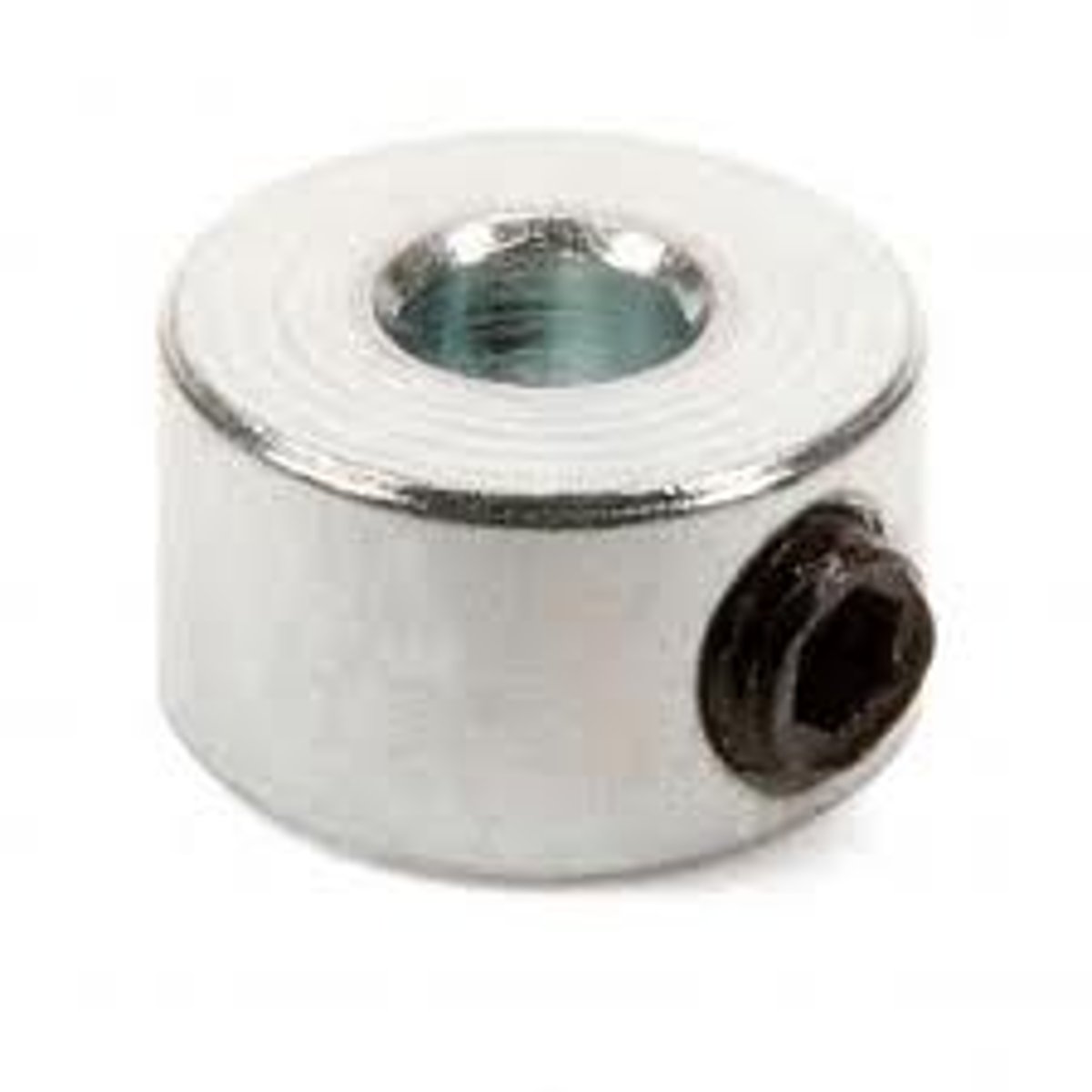
Shaft Collar
A type of spacer that can be set to remain stationary at any given point along an axle.

drive train
All the parts involved in the primary locomotion system of a robot, including the motors, gears, axles, and wheels.
flexible structure
An adjustable part used to form the "skeleton" of the robot or specialized applications.
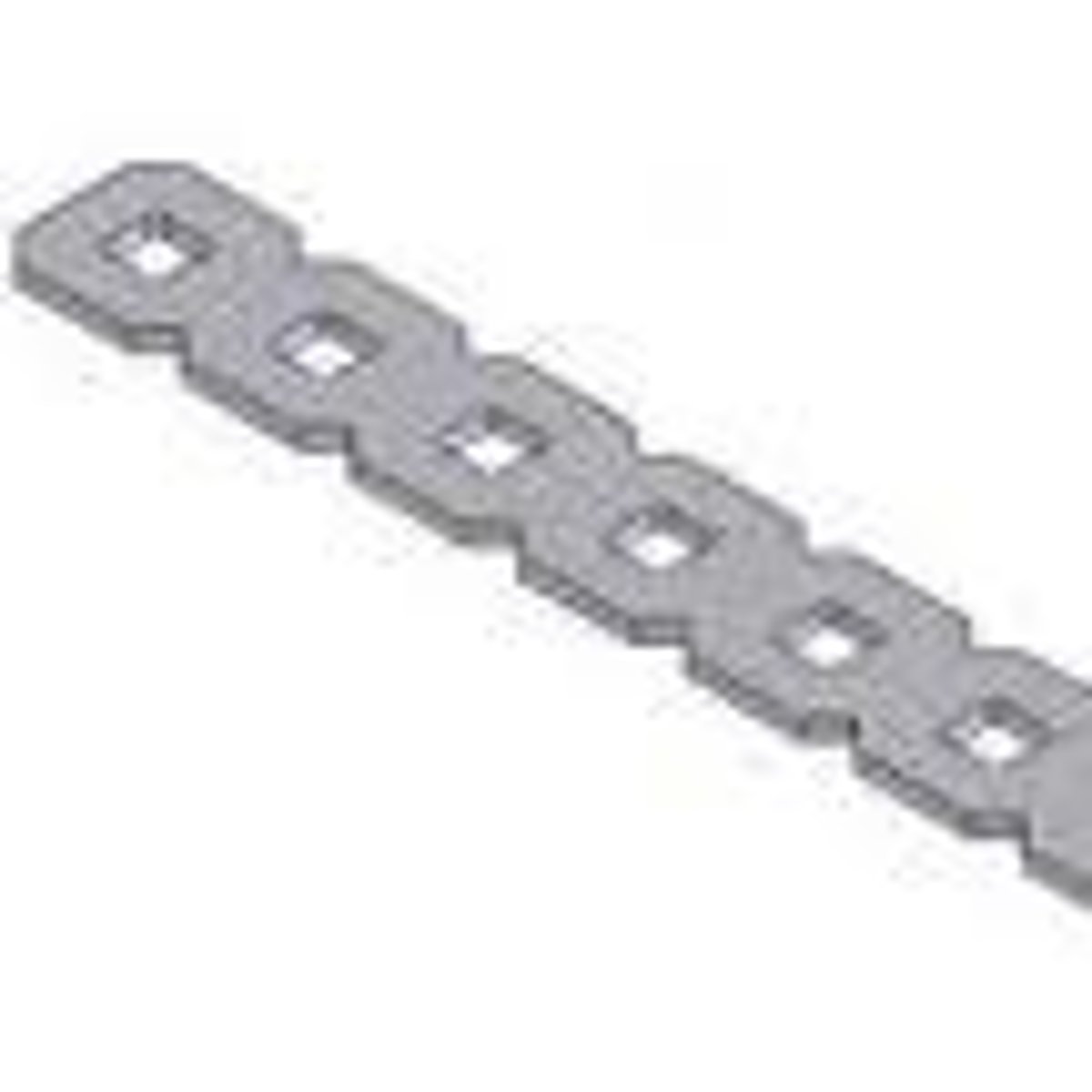

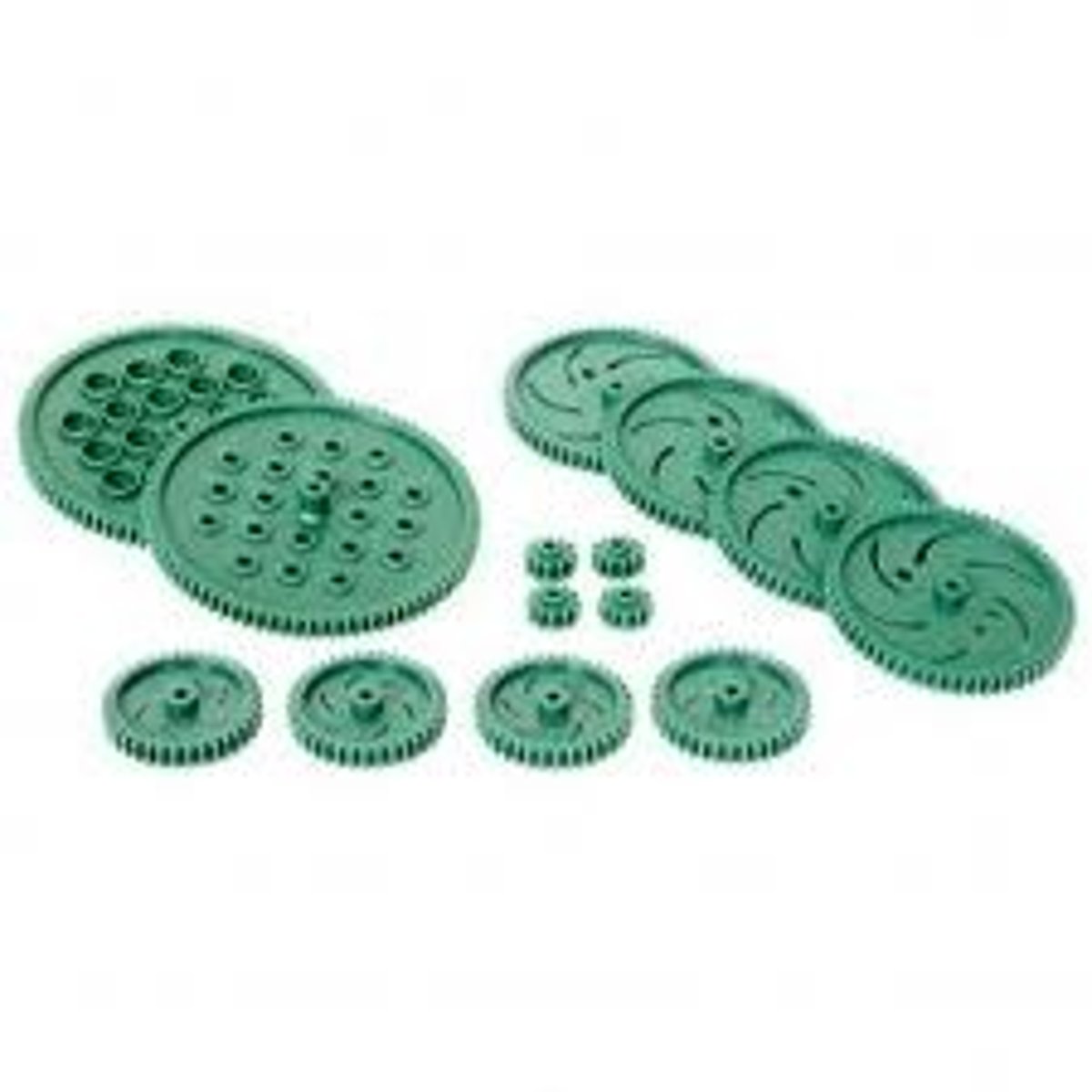
gears
Spinning discs with teeth that prevent them from slipping past each other. Gears are frequently used to transfer rotational motion from one piece to another, and to provide mechanical advantage while doing so.

gear train
A group of gears that turn together to transmit motion from one point to another on the robot, often providing mechanical advantage along the way.
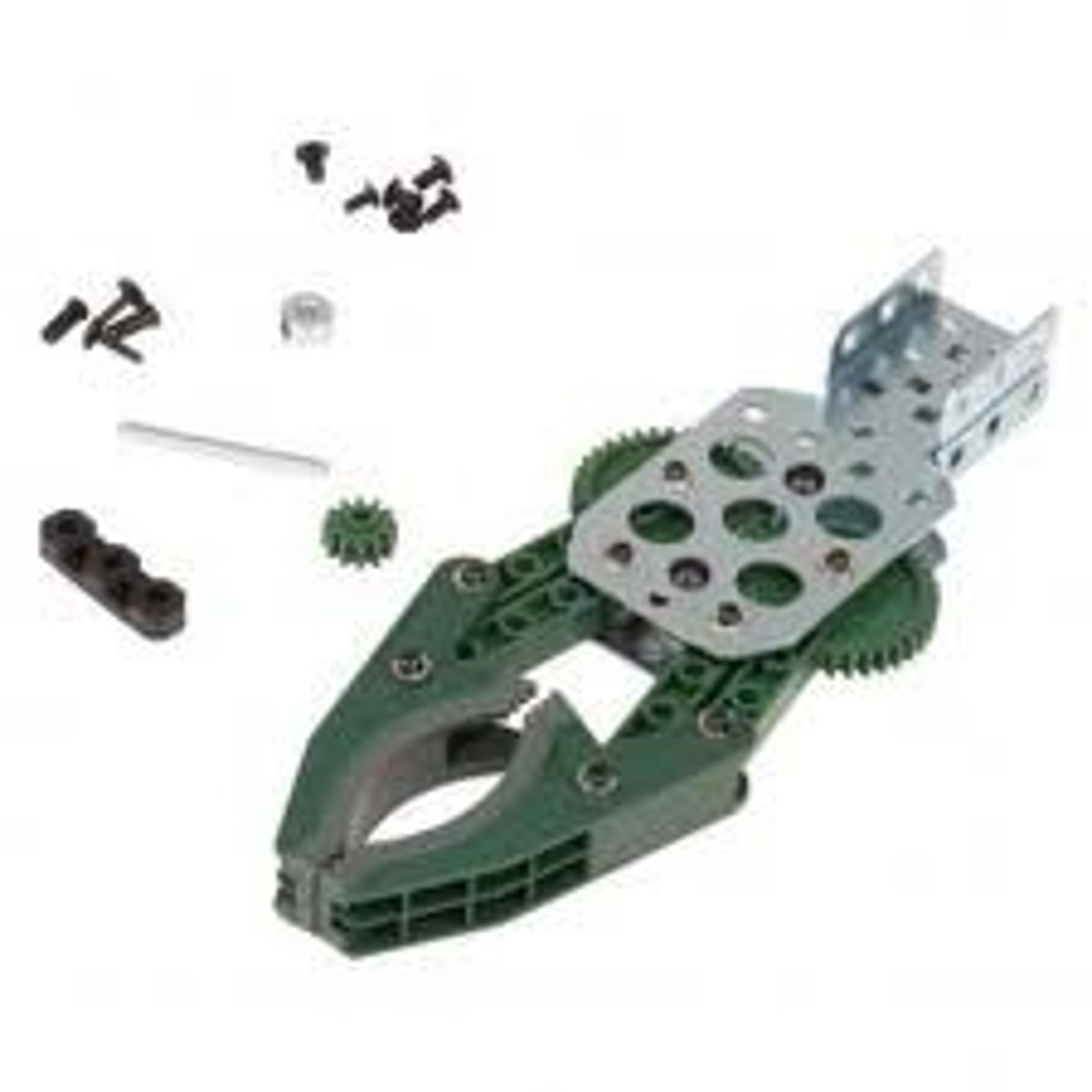
claw
An attachment designed to pick up or hold an object, often by "gripping" it with claw-like appendages.

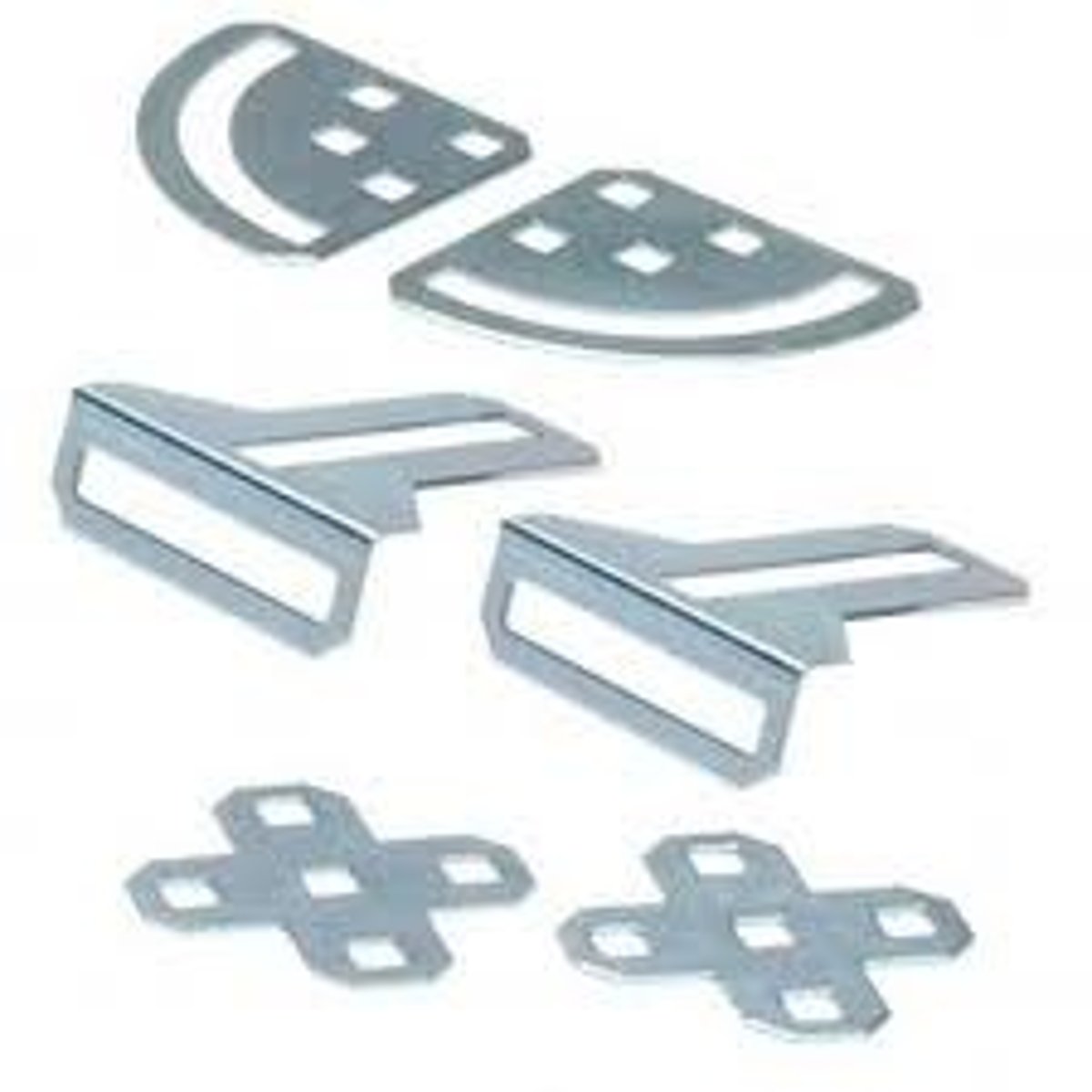
gusset
A piece used to strengthen an angled joint.

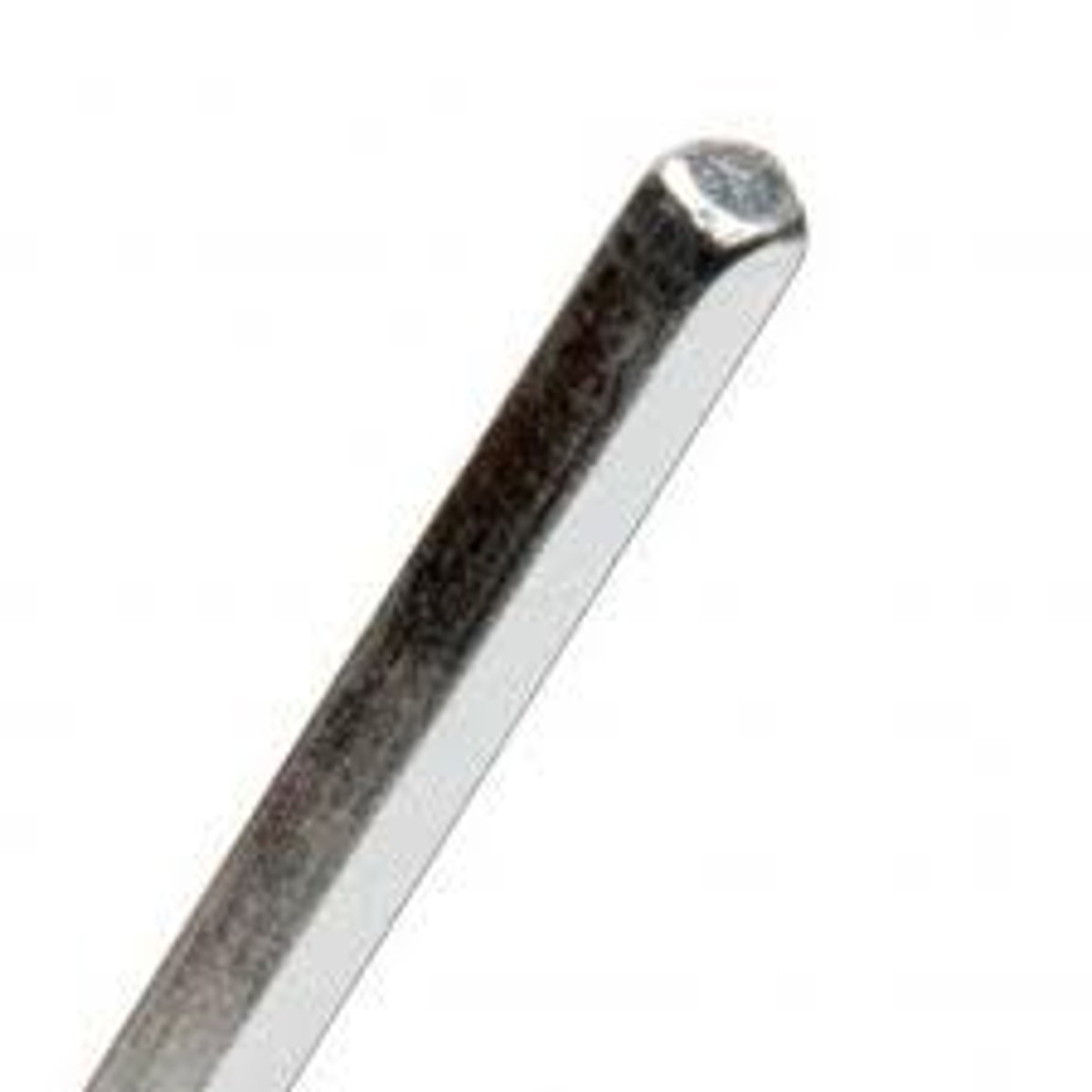
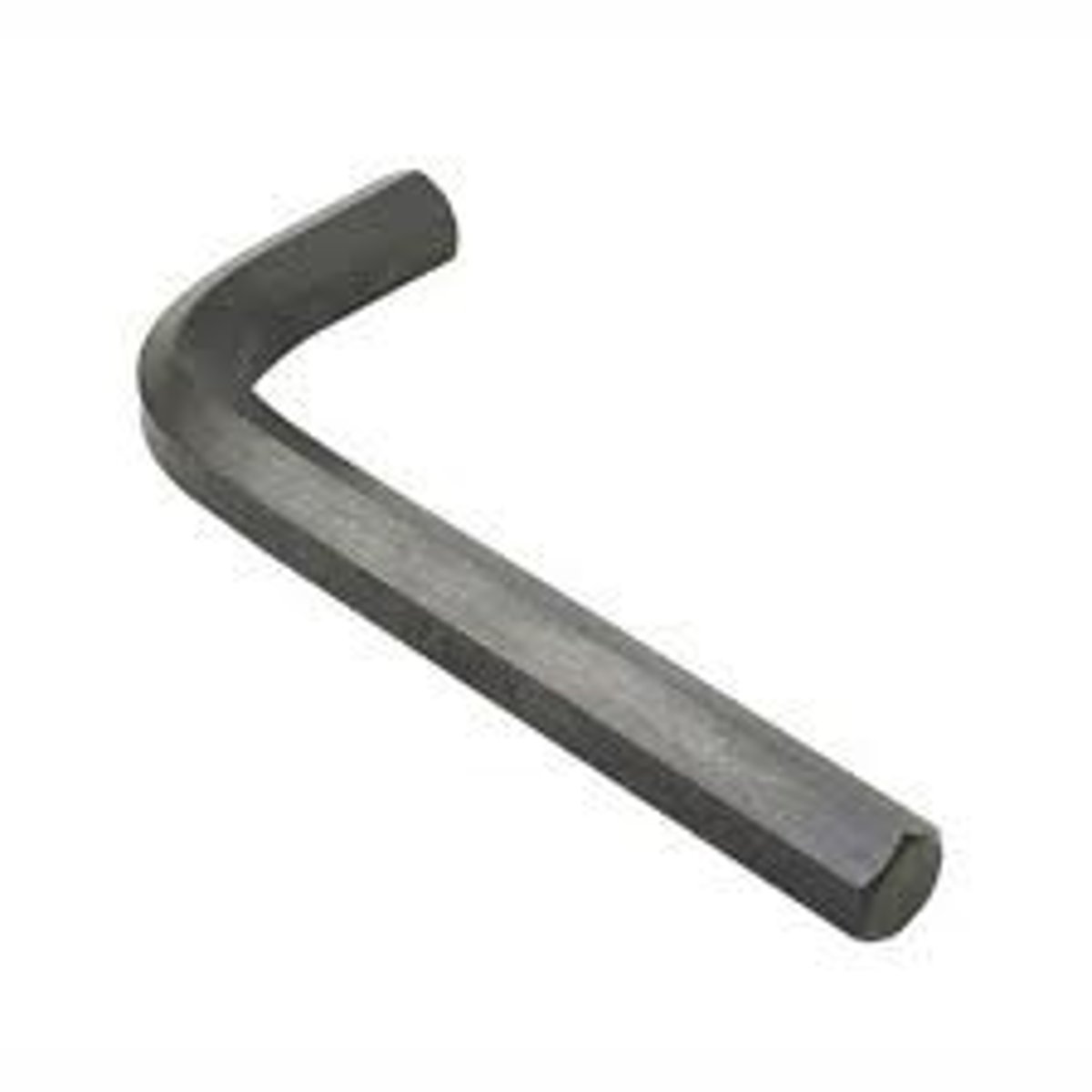
hex wrench
An L-shaped tool used to tighten screws.

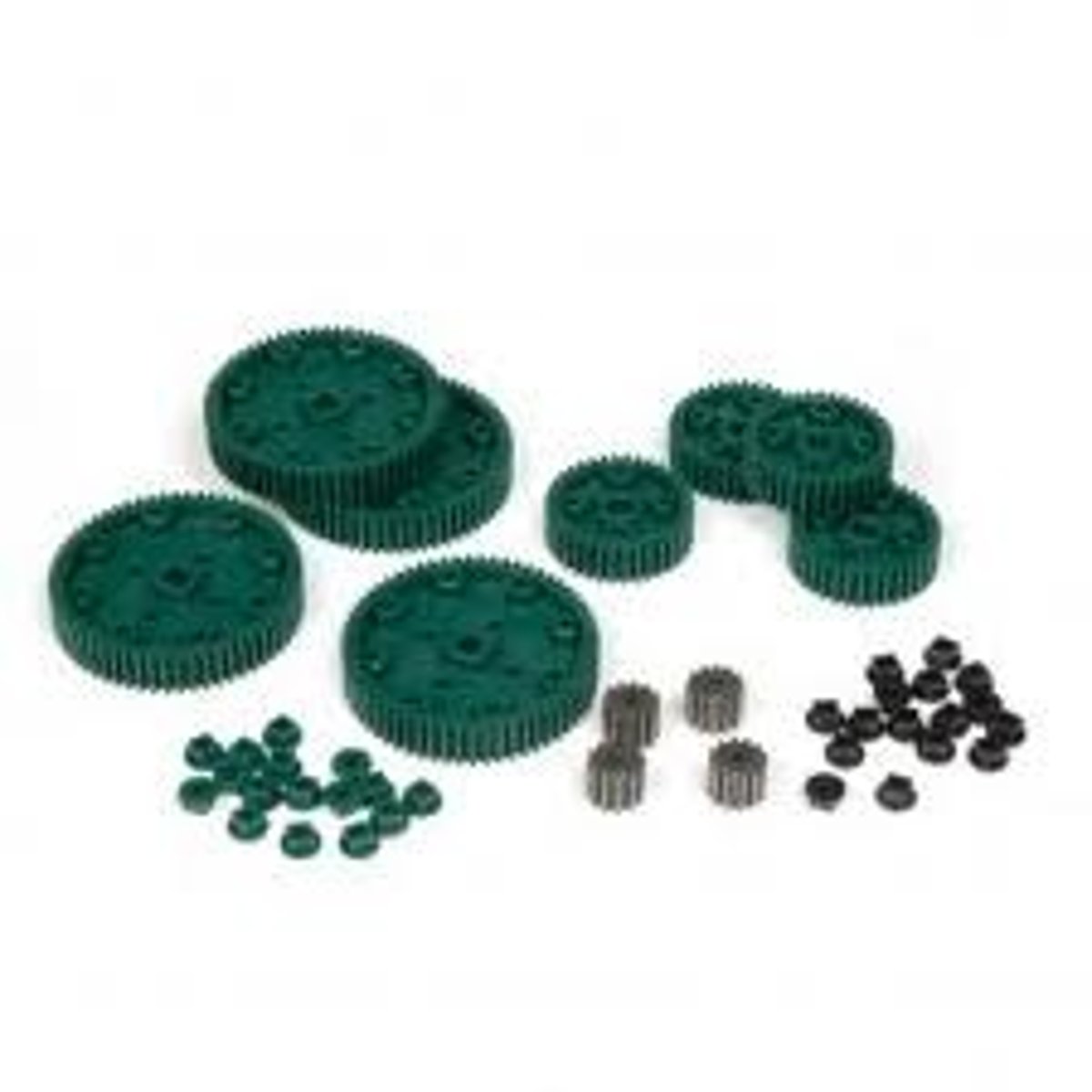
idler
A gear in the gear train that is neither the driven not the driving gear, and does not share an axle with another gear in the train.

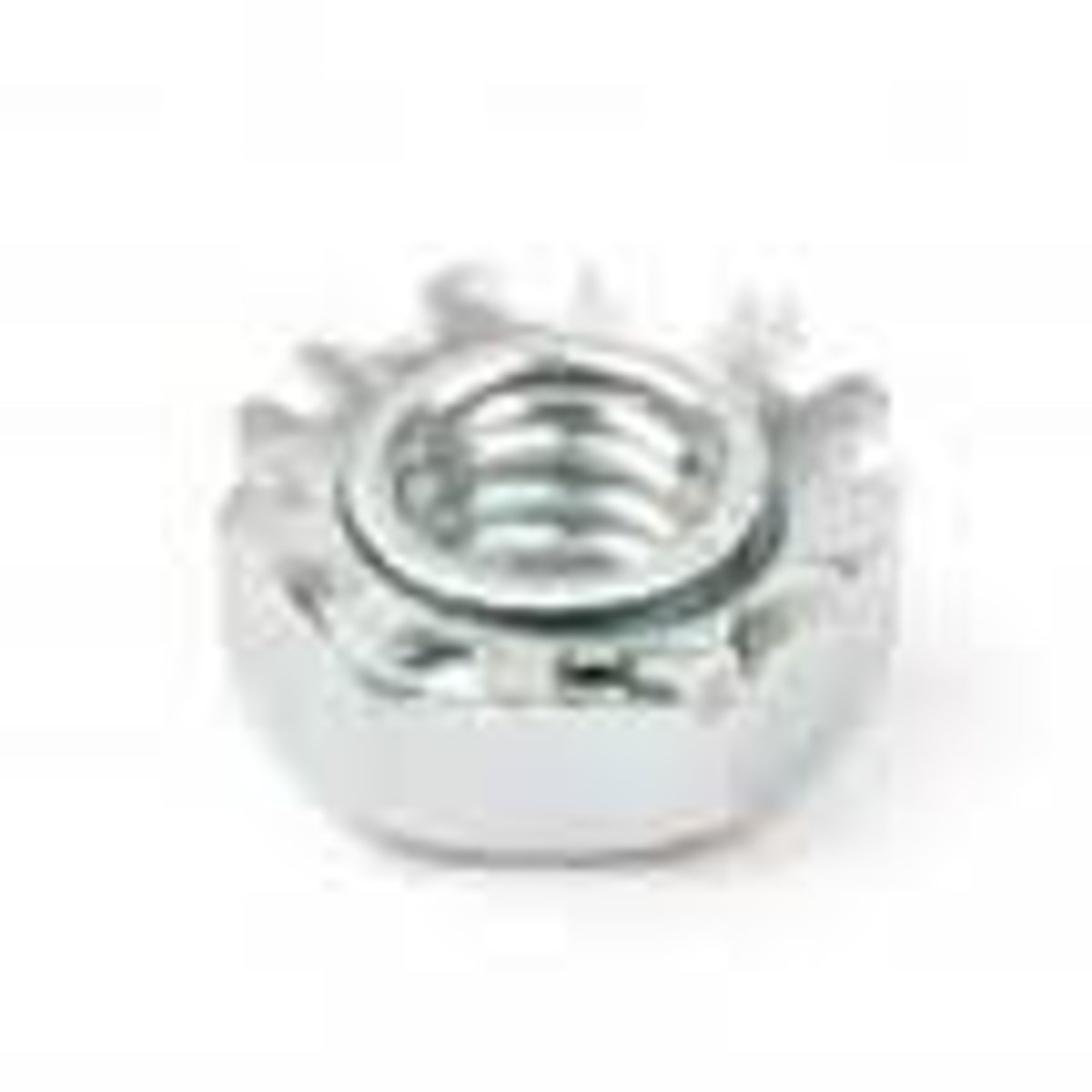
KEPS
A standard nut that includes a toothed "crown" designed to bite into a mounting surface and prevent the nut from slipping.

lever
One of six "simple machines" that provides a mechanical advantage. They are long pieces that rotate around any point on their length.

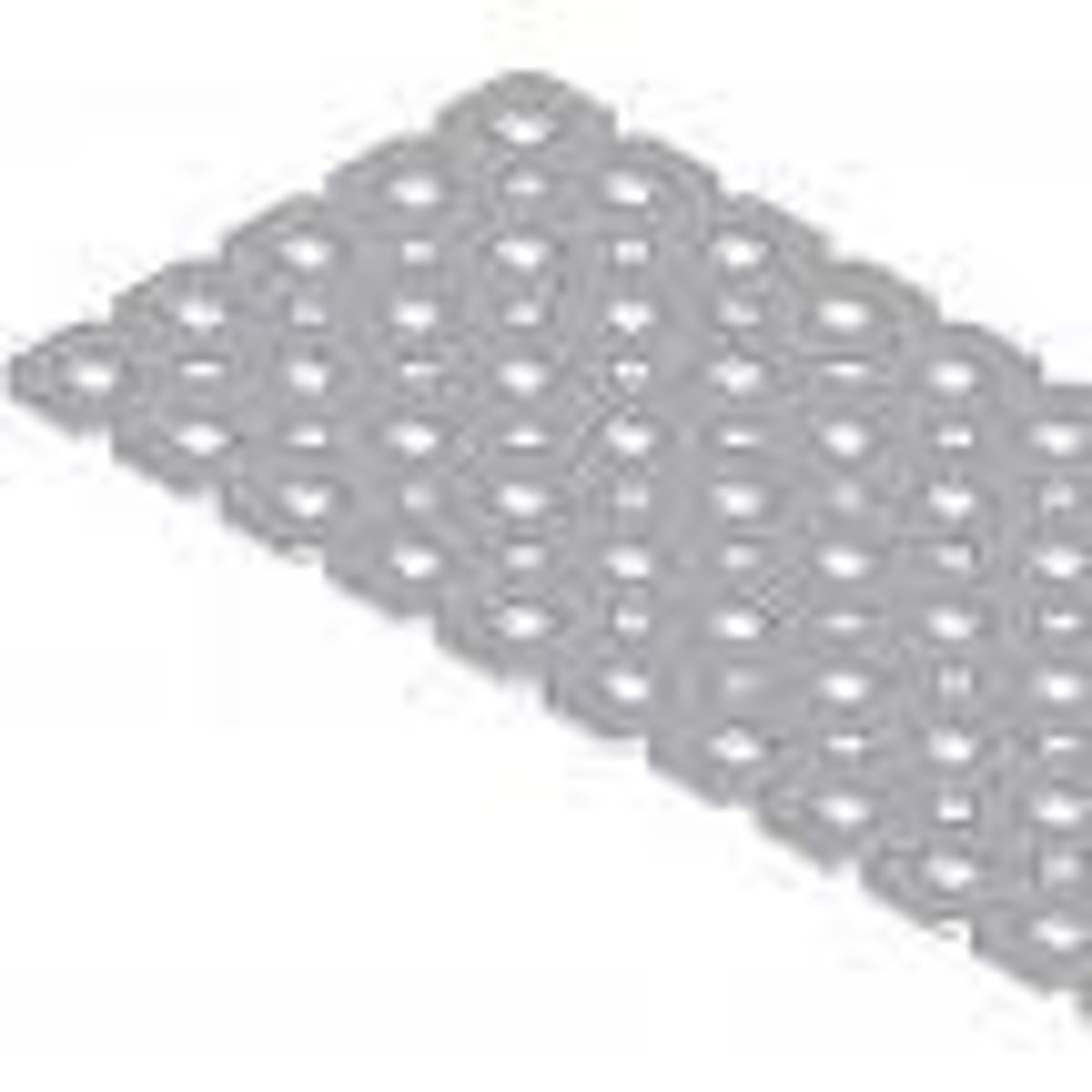
flat plate
A structural part used to provide a mounting surface for other robot parts.

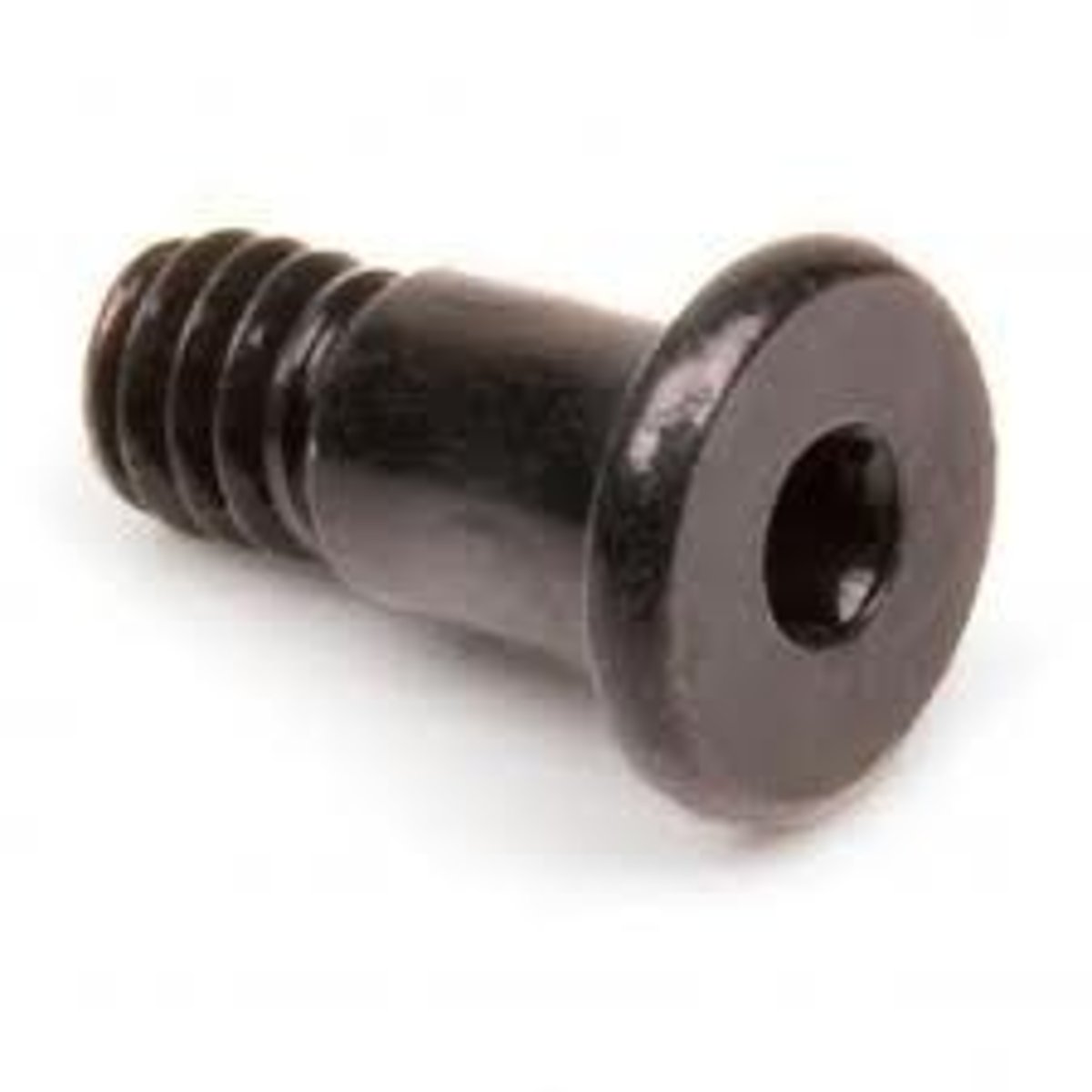
hex screw
A screw with a hexagon-shaped hole in the head, allowing the screw to be tightened or loosened with a hex L wrench.

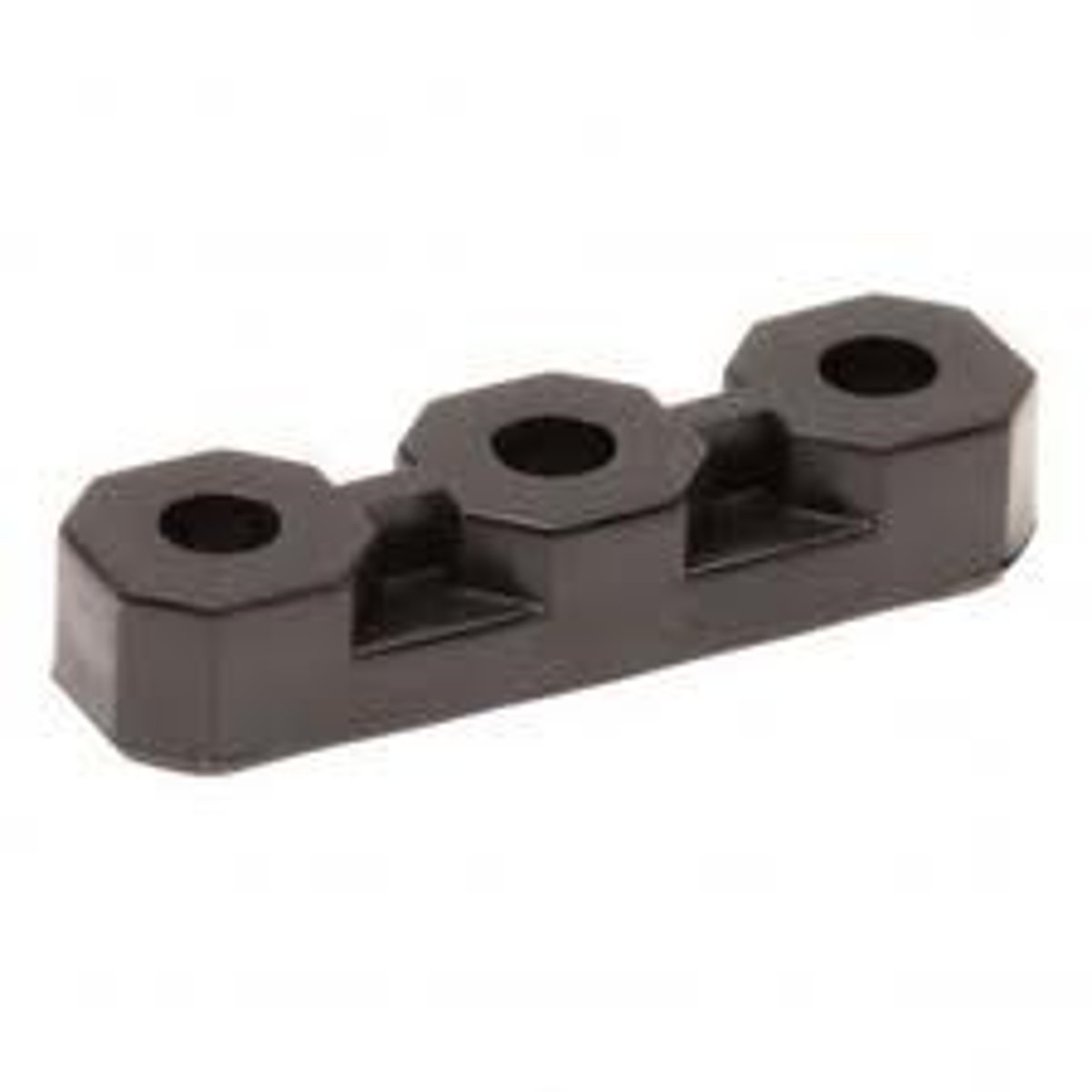
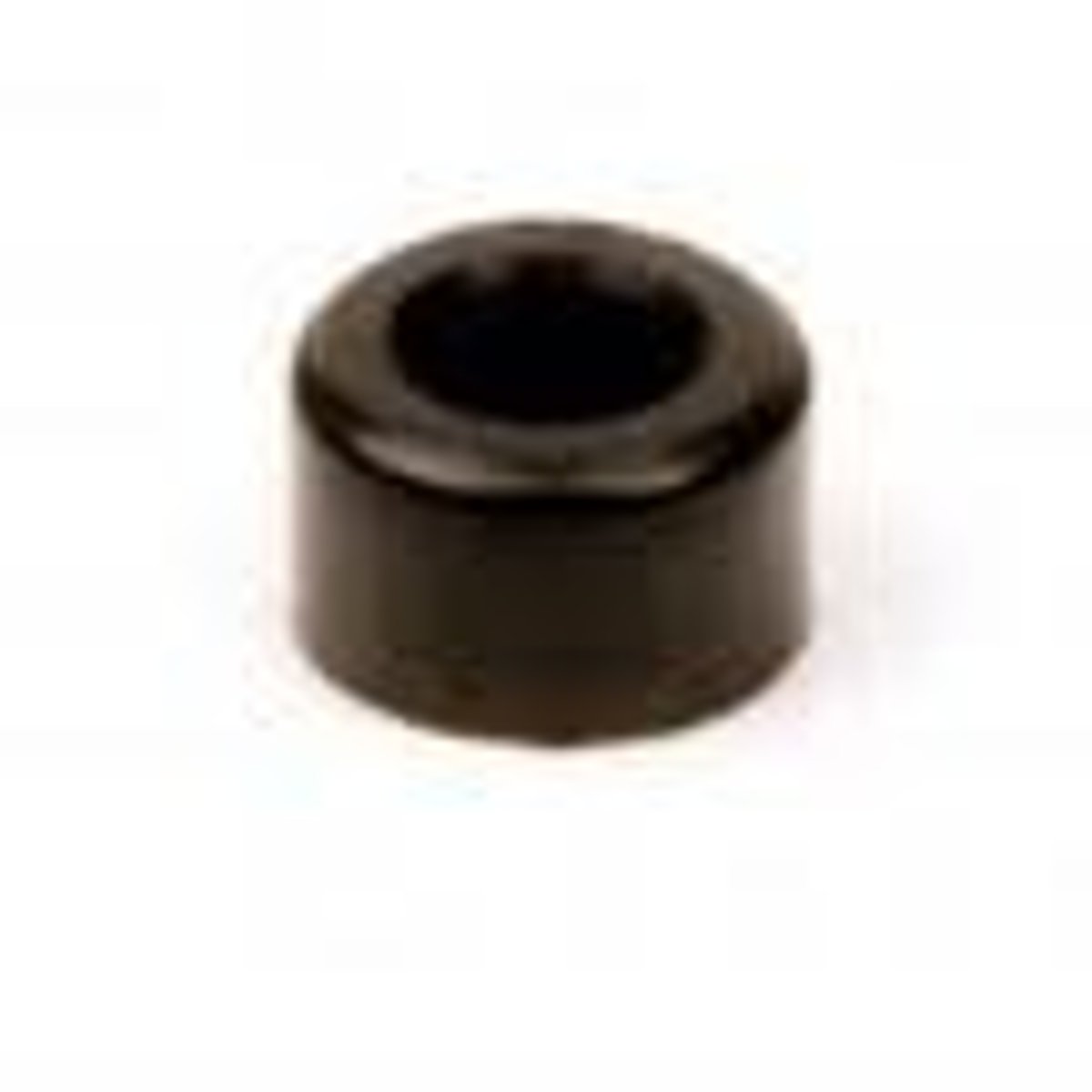
spacer
Plastic pieces which are designed to slide onto axles between other parts (or between parts and rails) to keep them from moving too close together.

structure parts
Parts used to construct the chassis, levers, and sub systems.

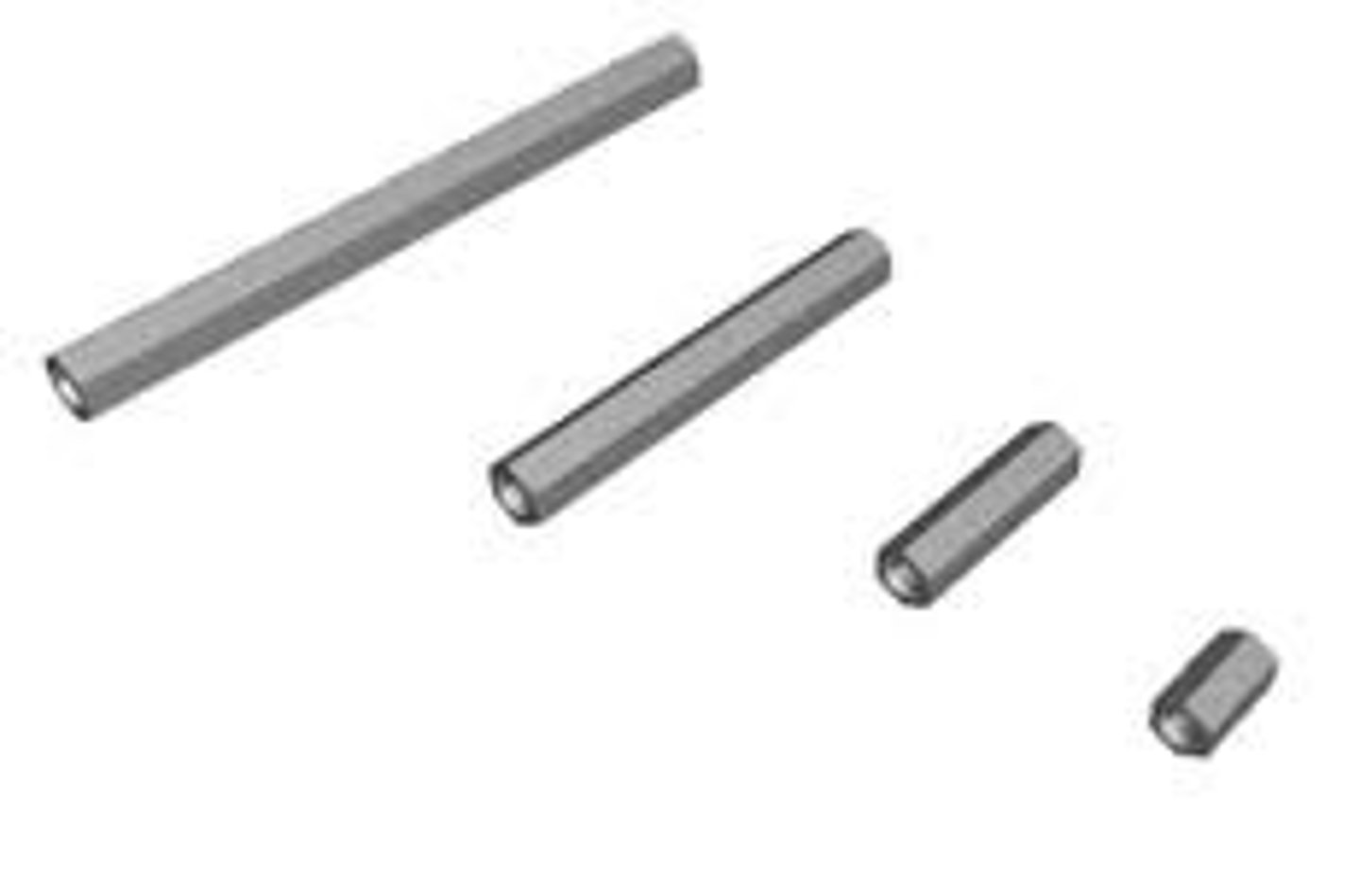
stand-off
A threaded piece that has threading on it or in it, which allows a screw to be fastened into it. Helps create a structure subsystem.

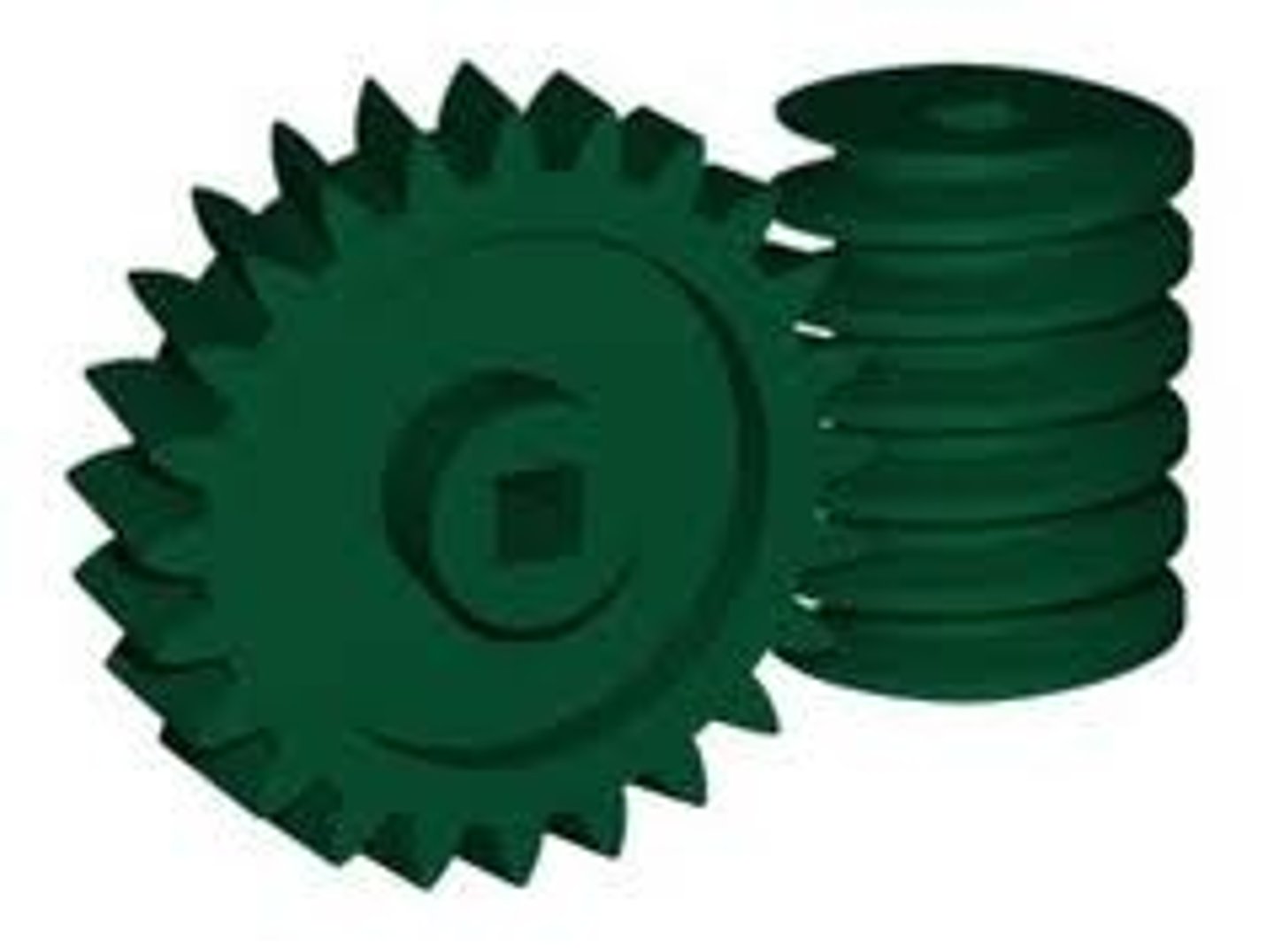
Worm Gear
An gear part used to reduce rotational speed or increase torque.

Spur Gear
A gearwheel with teeth projecting parallel to the wheel's axis.

Sprocket Gear
A gear that has a row of teeth around its edge which fit into the holes of something (such as a bicycle chain or a piece of film) and cause it to turn when the wheel turns
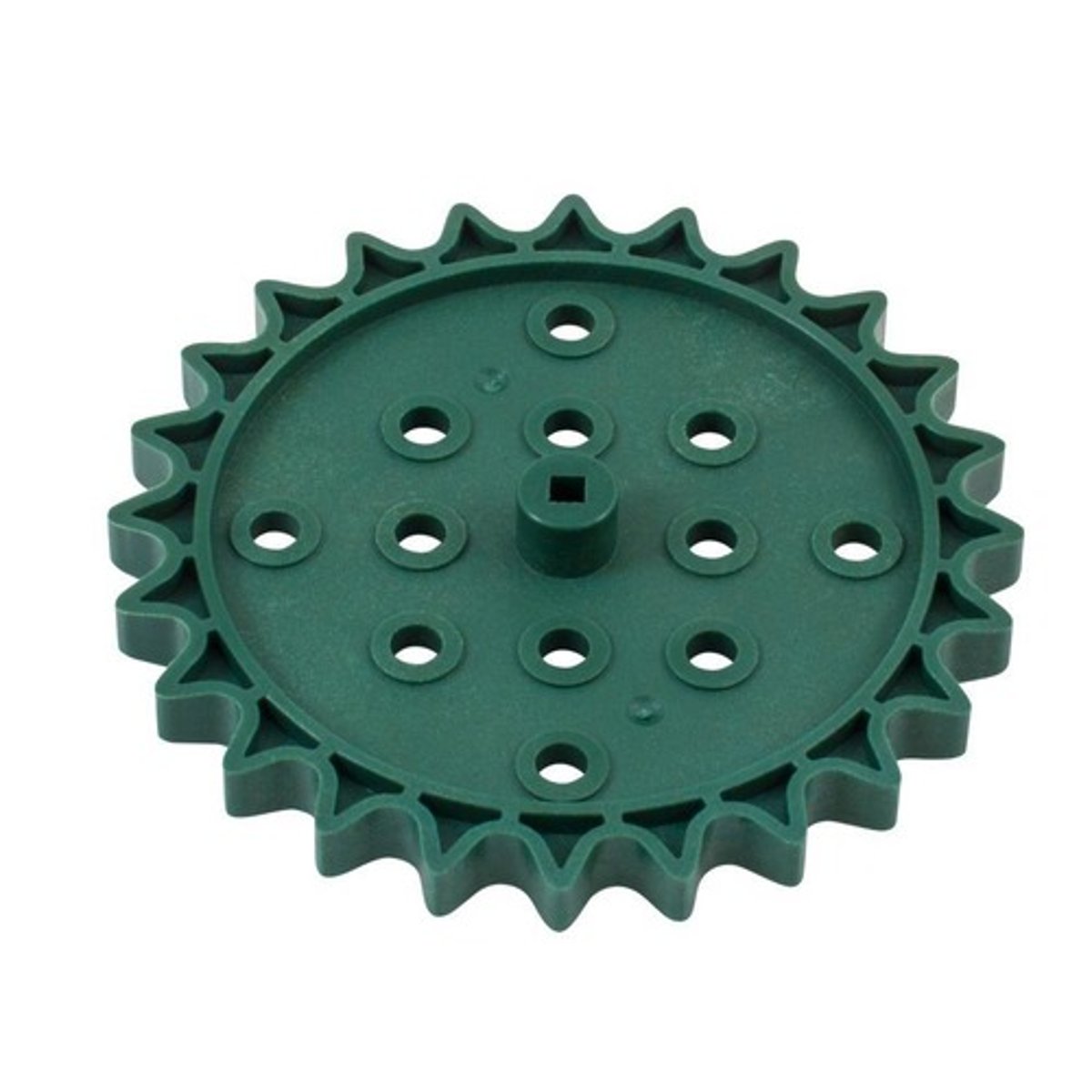

Base plate
A 30x15 plate used as the basic structural component for building in VEX.
Bracket
a right-angled support vex part used mainly for gear support.
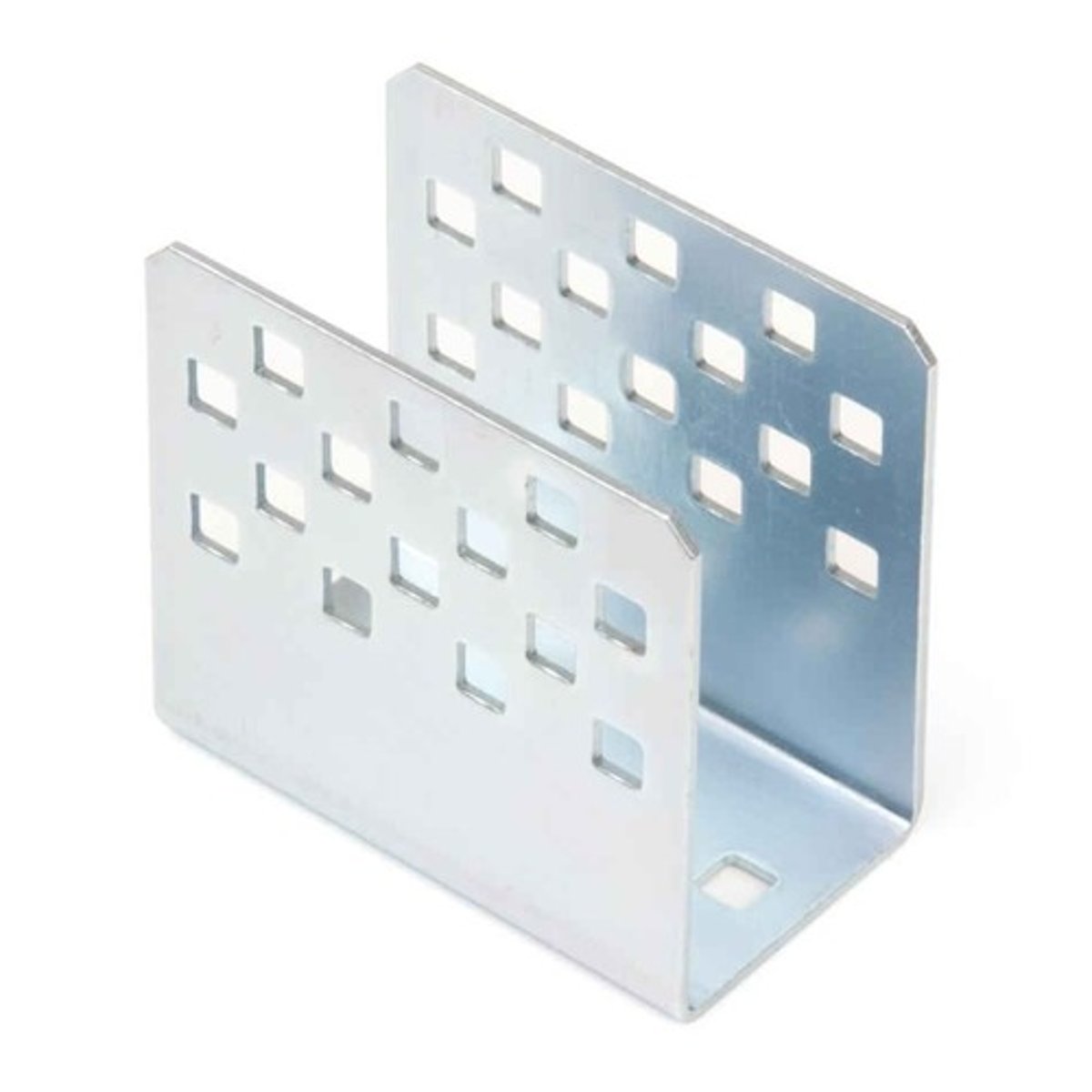

Pulley
A wheel with a grooved rim around which a cord passes. It acts to change the direction of a force applied to the cord and is chiefly used (typically in combination) to raise heavy weights.

Slide Truck
Parts of a linear motion mechanism kit that attach to a linear slide.
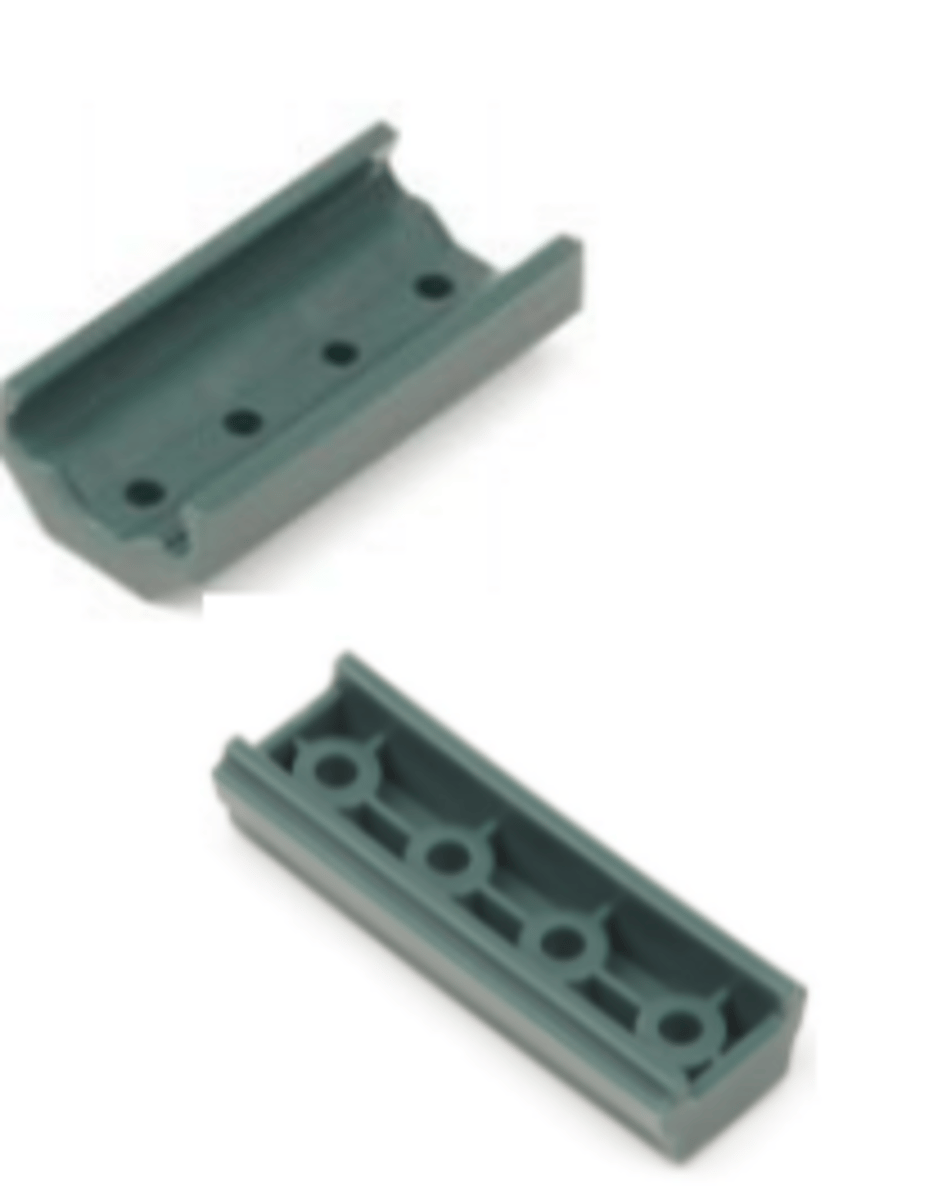

Linear Slide
Part of a motion mechanism. It is a bearing which provides free motion in one direction.
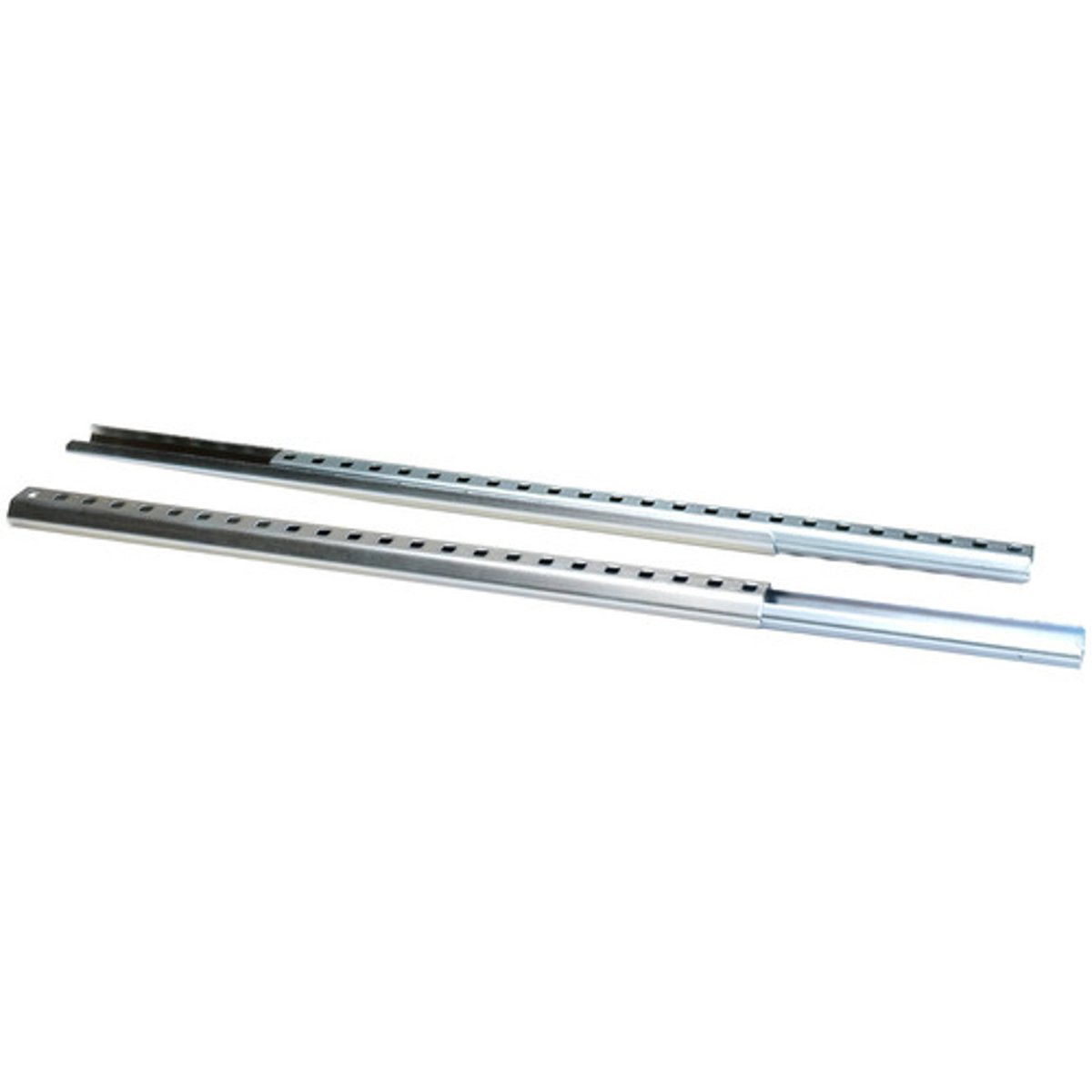

Lead Screw
A screw designed to translate turning motion into linear motion.
Cam Gear
A rotating or sliding piece (such as an eccentric wheel or a cylinder with an irregular shape) in a mechanical linkage used especially in transforming rotary motion into linear motion or vice versa using a bracket and follower.
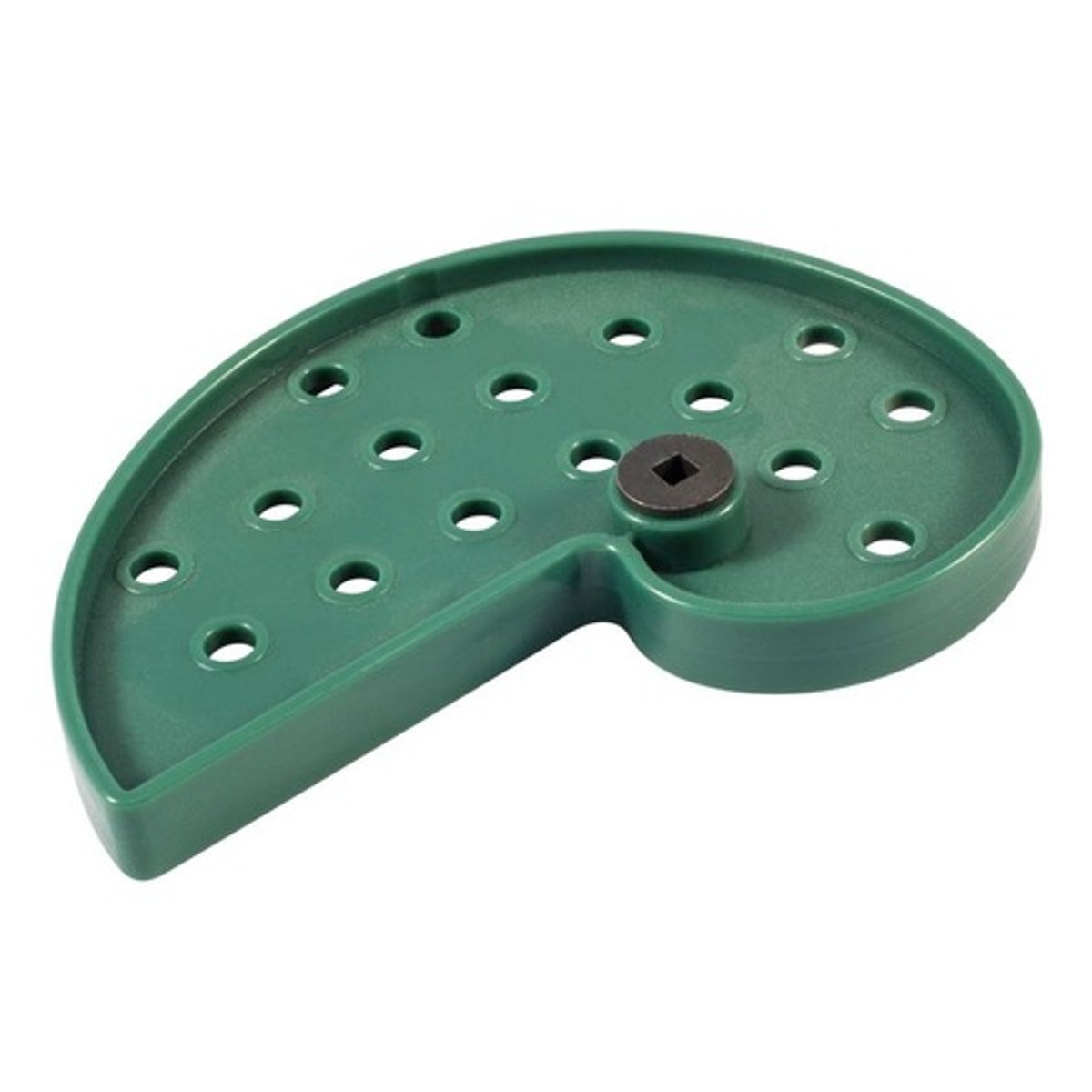

Follower with Bracket

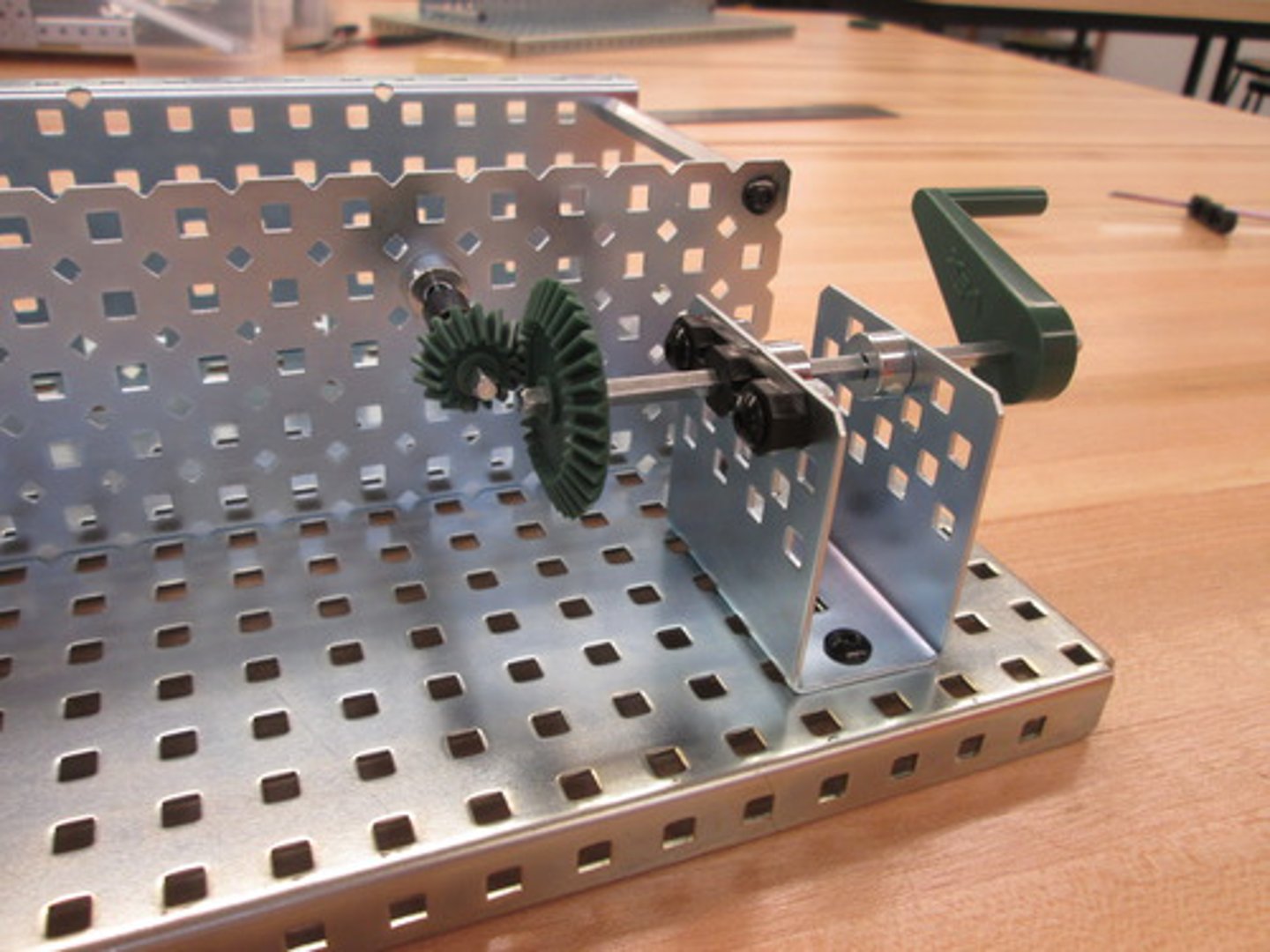
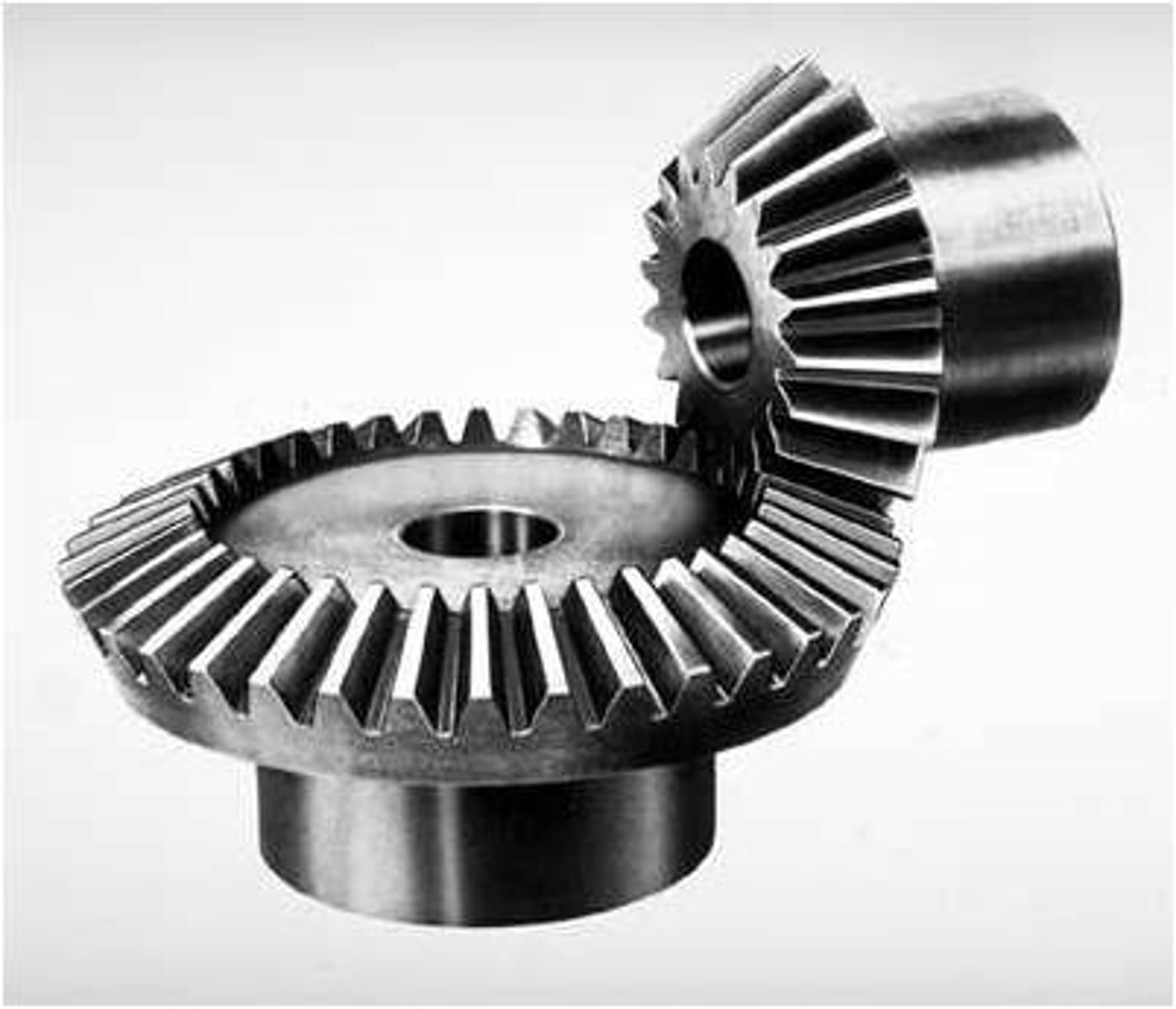
Beveled Gears
Meshed gears that have angled spurs to change the direction of the ouput.

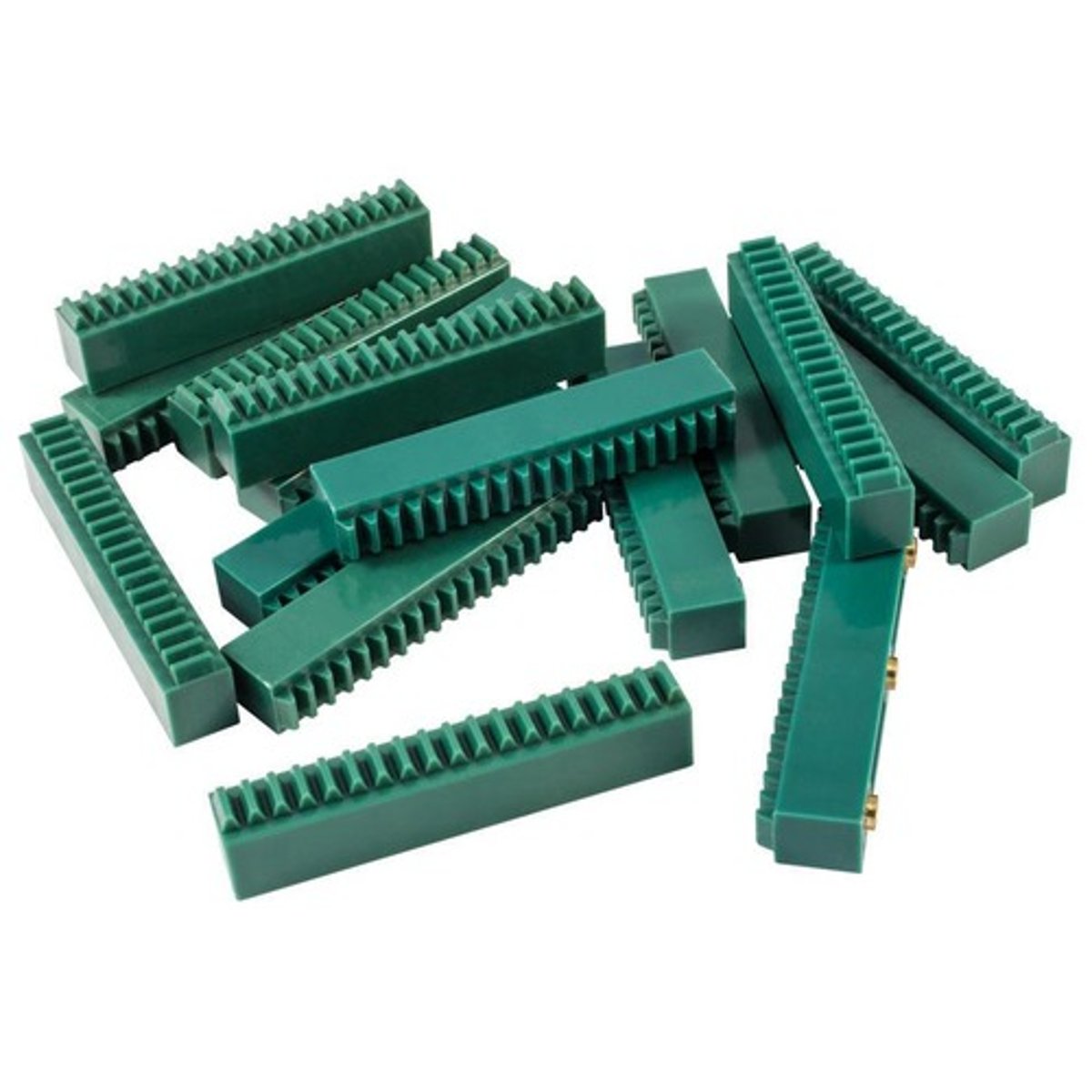
Rack gear
this is a flat gear with teeth along its length; used to create linear motion from rotary.

Structural Subsystem
These parts are the "skeleton" of the robot to which all other parts are attached.