Restrictions on free trade 4.
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Define free trade
When people can trade without any barriers or restrictions
What are the 4 trade barriers/restrictions on free trade
Tariffs
Quotas
Subsidies to domestic producers
Non tarrif barriers
Define a tariff
A tax on imported goods
Who are tariffs imposed by
Governments
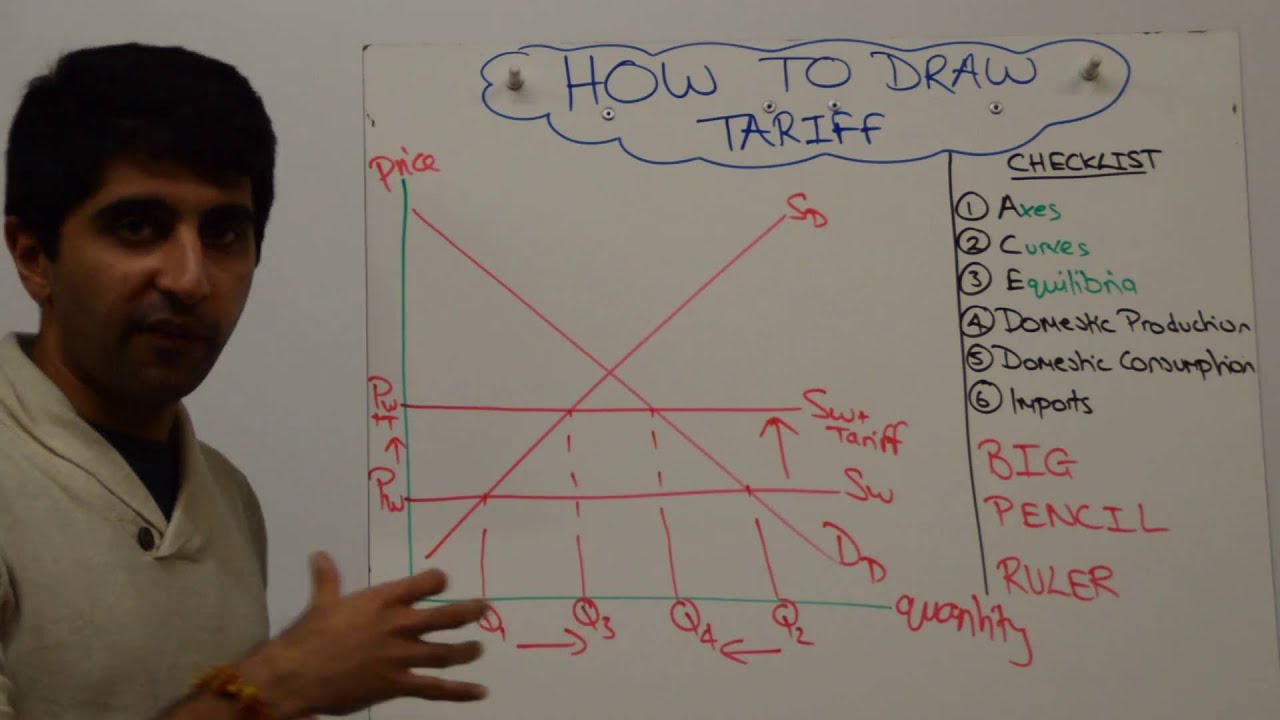
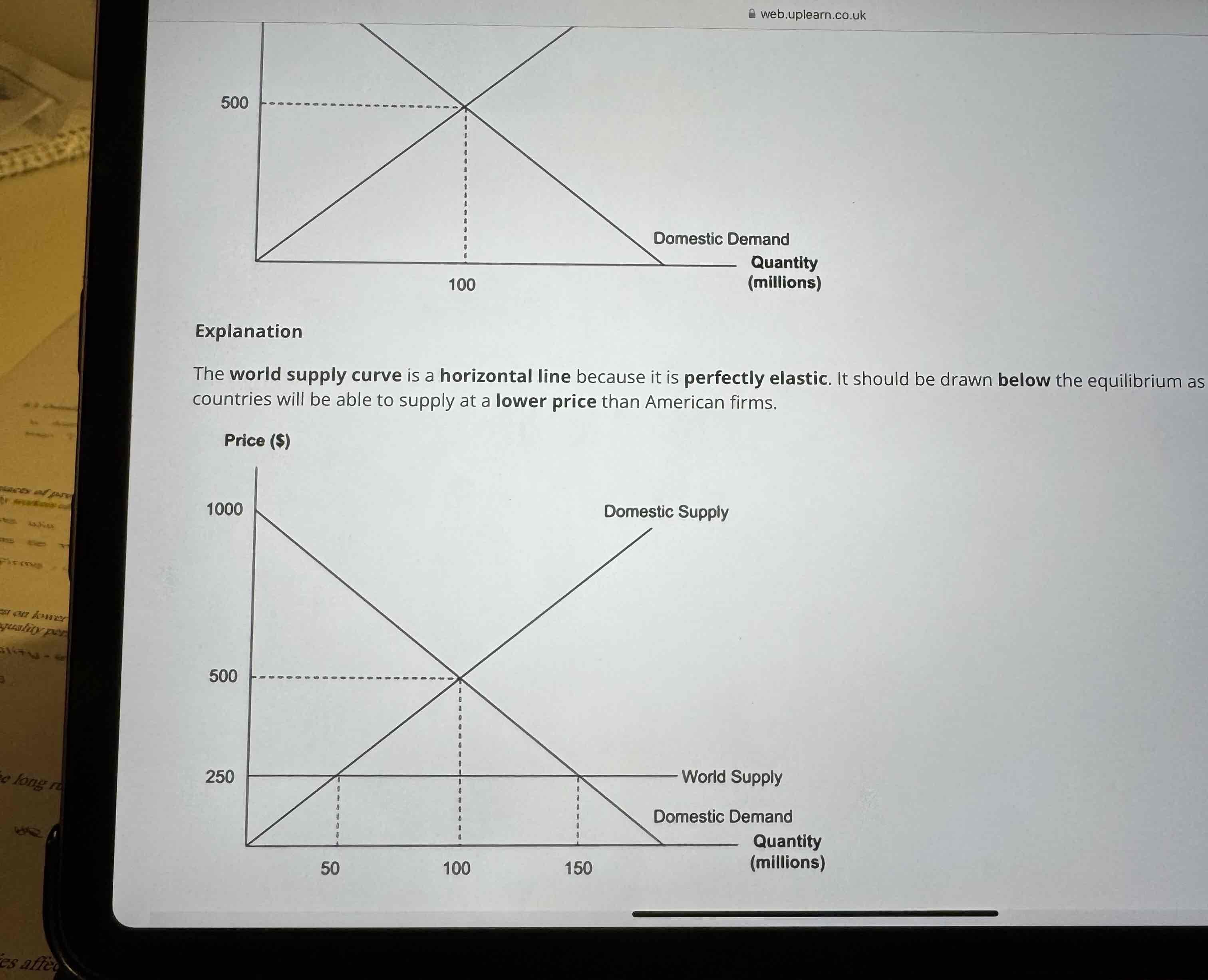
Show a tarrif diagram which has world supply and domestic supply
World supply curve is drawn below the equilibrium as we assume other countries will be able to supply at a lower price than American firms
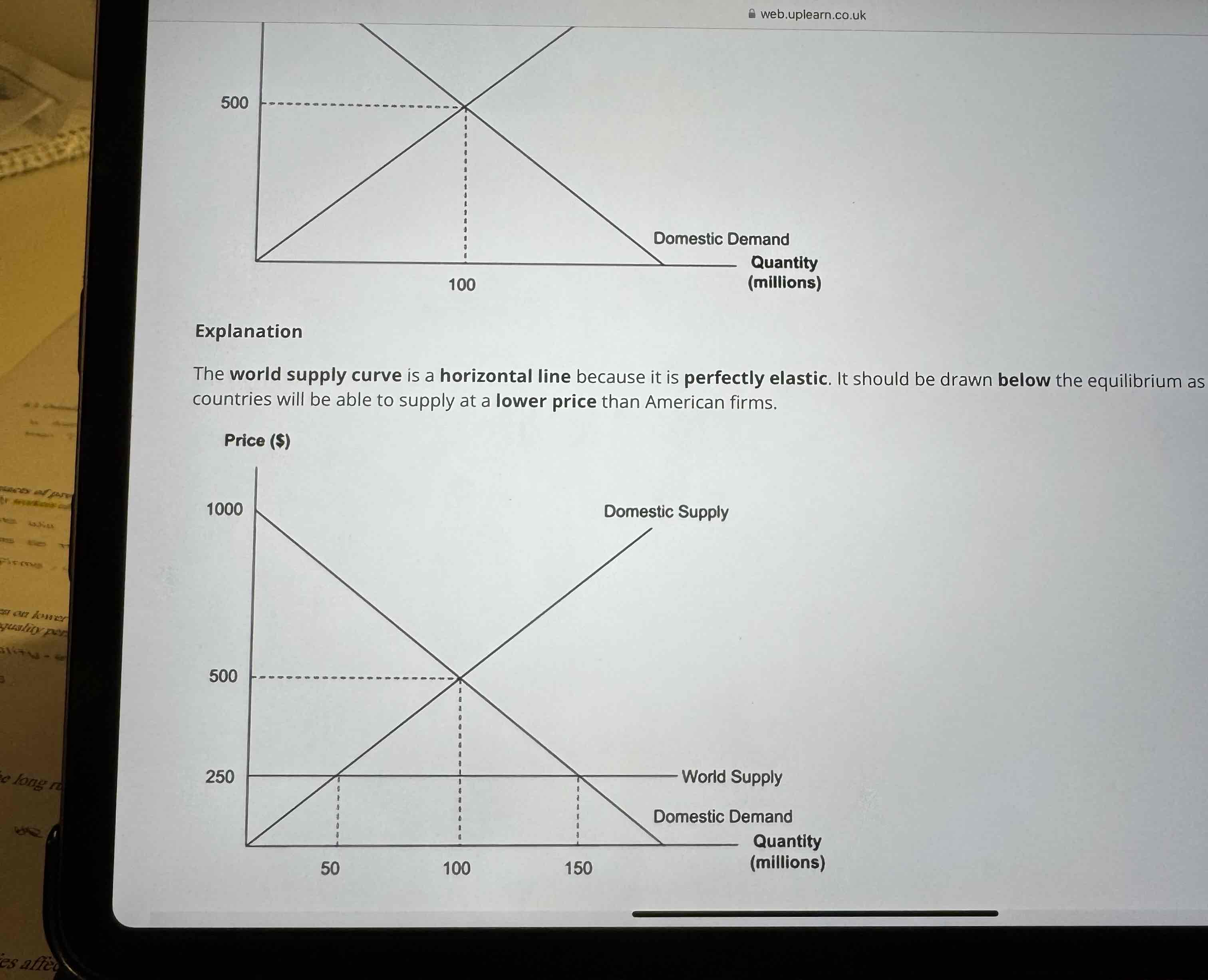
Show a tariff diagram
How do you find out the quantity of imports
the difference between domestic demand and domestic supply, it’s what they get from foreign firms
Using the picture, what’s the quantity of imports
100mill units which is 150-50
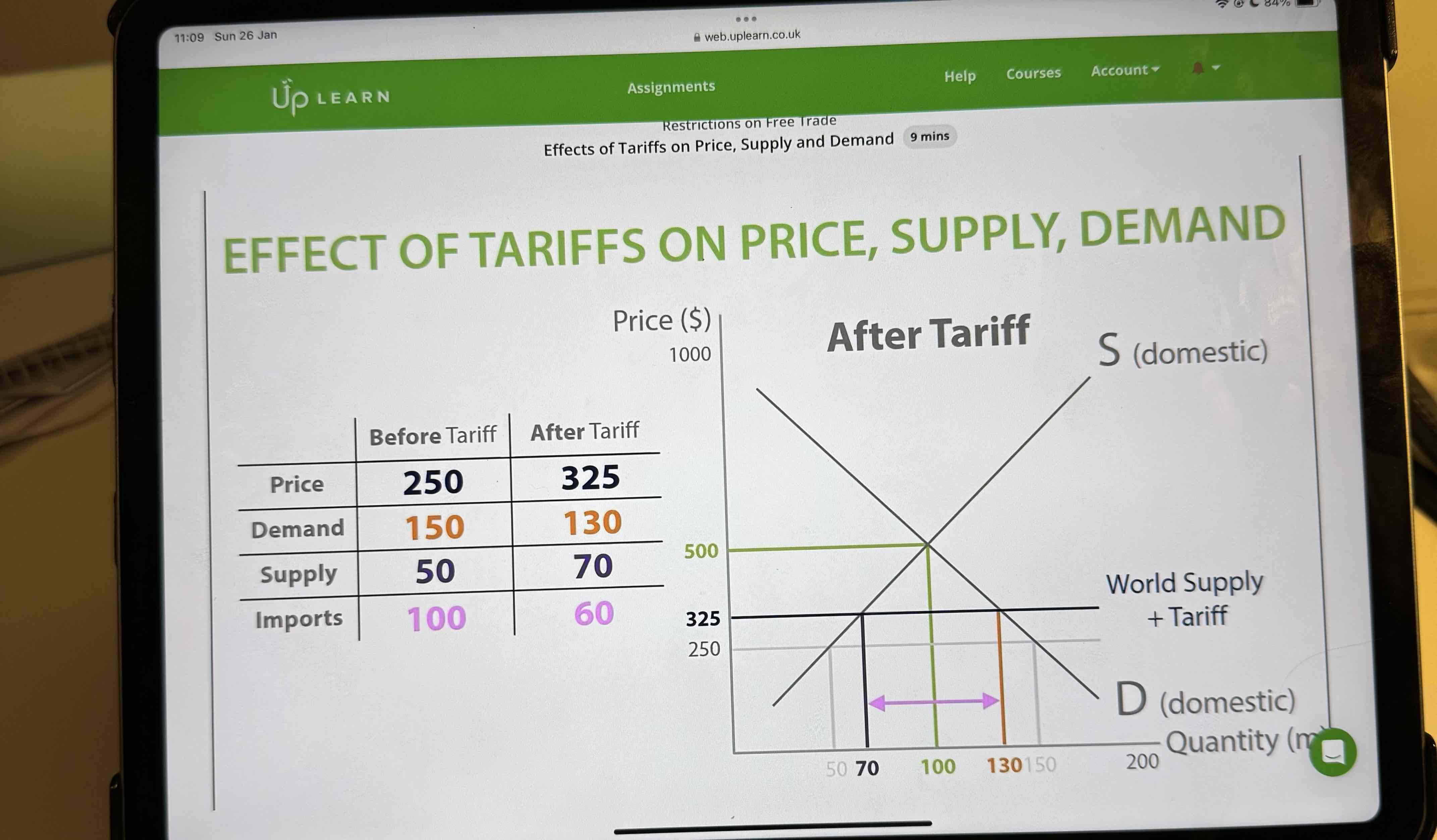
What’s the effect of a tarrif on price
Increase
What’s the effect of tarrifs on supply and demand
demand decreased after tariff was introduced and supply increased after tariff and the quantity of imports decreased
Show this effect on a table
A tariff is a tax and so it will increase the price of the imported good and shift the world supply curve up. This will lead to an extension (increase) in domestic supply as domestic producers are willing to sell more at a higher price - remember they don't have to pay the tariff. There will be a contraction (decrease) in domestic demand as consumers don't want to pay a higher price.
If domestic consumers are demanding less and domestic producers are supplying more, there will be a reduction in imports.
Who pays the tarrif
The importer is responsible to pay this which goes to the government. This can raise prices which the consumer pays
Show the area of producer surplus, welfare loss and tax rev
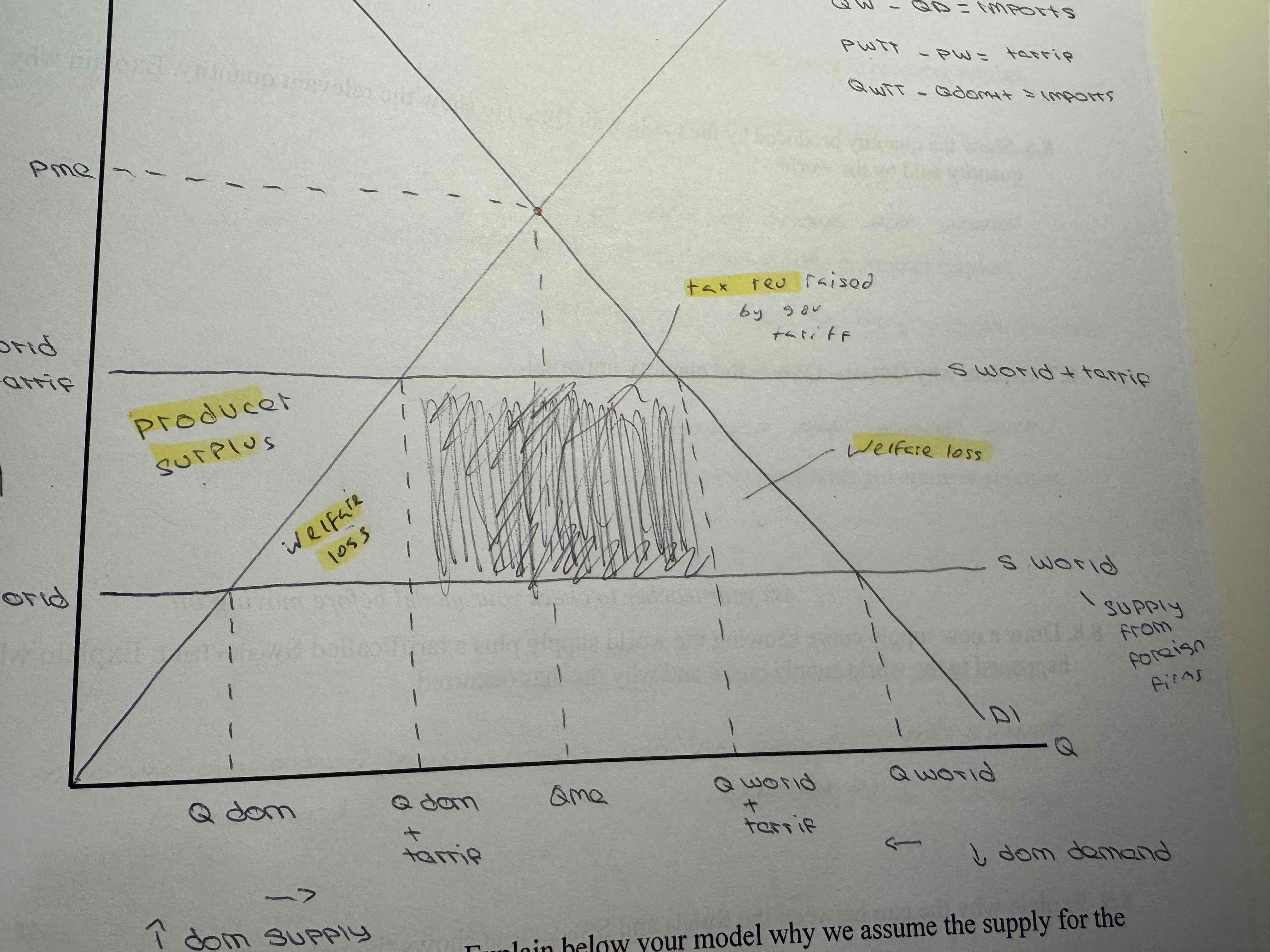
What’s the effect of a tariff on producer and consumer surplus
Producer surplus has increased as they’ll be supplying more at higher prices
Consumer surplus decreased as there paying higher prices
What’s the effect of tariff on gov tax rev
It increased tax rev
Overall what’s the effect of a tariff
Protect domestic industry, domestic producers and gov have benefited
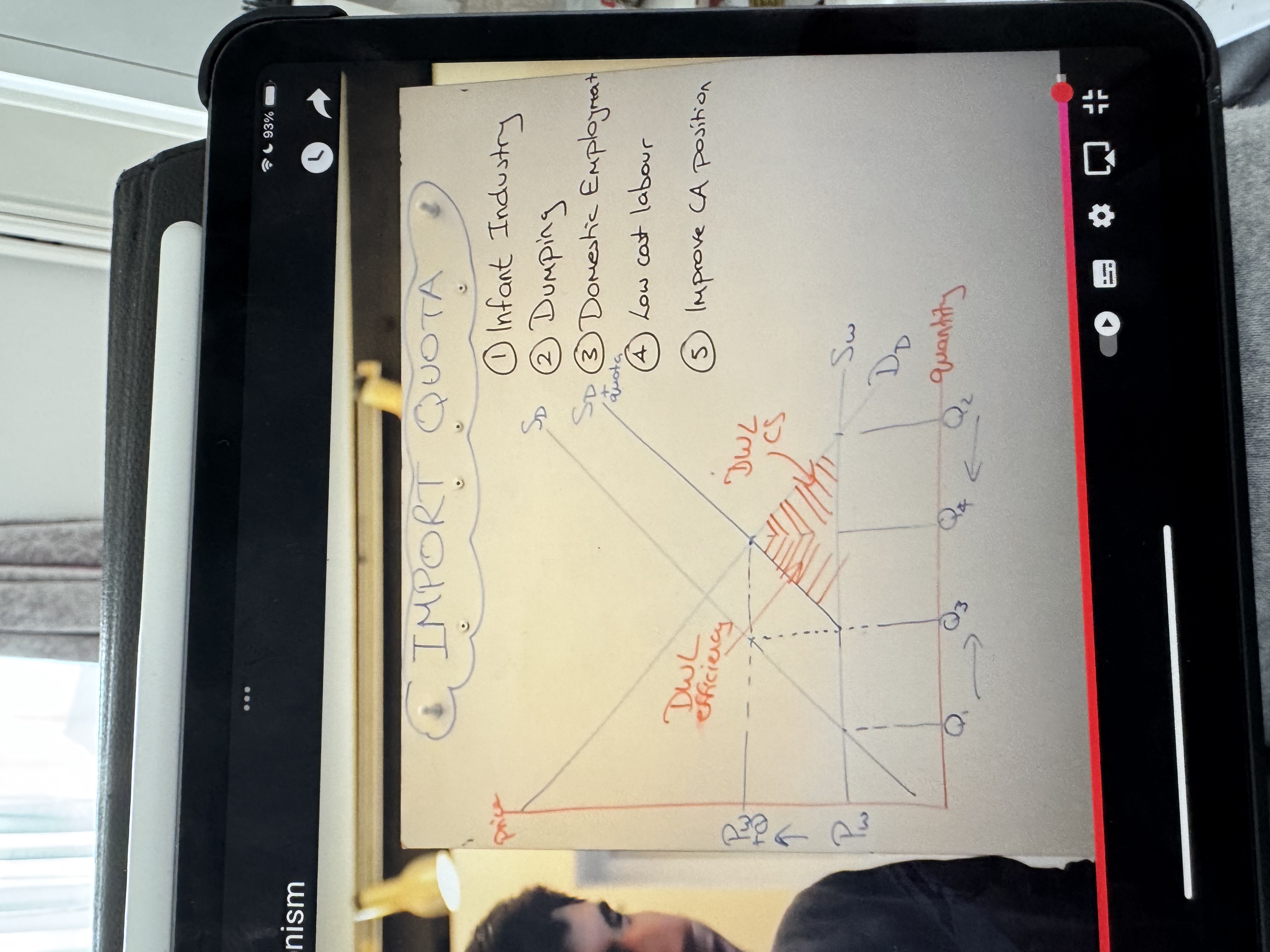
What’s a quota
Is a physical limit on the quantity of imported goods
What are the two main drawbacks of quotas
They don’t raise any tax revenue because there’s no tax placed on imports only a limit
They create shortages - Quotas completely restrict imported goods once the limit of imports are met
Give an example of a quota
Us limiting the number of Japanese car imports to 2 million a year
What’s the effect of quotas on domestic firms
Quotas will reduce imports and help domestic suppliers they also gain more revenue due to higher prices supplying more
What’s the effect on producer
Producer surplus increases as they benefit from higher prices and reduced competition which leads to more profits/investments
What’s the effect of quotas on world supply
World exporters will make less revenue – unless demand is very inelastic, meaning increase in price is greater than fall in quantity.
What’s the effect on employment
dom firms will be able to supply more this may increase the level of employment for domestic firms
Whats the effect on consumer surplus
Reduced consumer surplus as they’ll have to pay higher prices
What’s the effect on welfare loss in society
There will be a net welfare loss to society because the increase in producer surplus is outweighs the decline in consumer welfare
Show a quota graph
Dom demand decreases, domestic supply increases
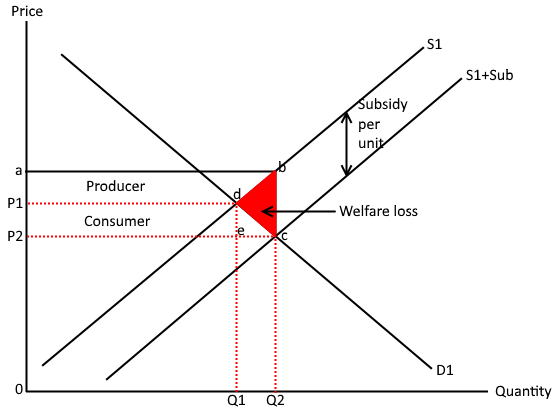
What are subsidies to domestic producers
When a government gives a grant to producers to increase supply
What’s the effect of a subsidy on price and quantity
A decrease in the cost of production will shift supply to the right this decreases price and increases quantity
Why are subsidies given to domestic producers
To make domestic goods relatively cheap compared to imports, it encourages domestic production to increase making it more competitive
What’s the effect on consumers
As domestic goods will be cheaper they should switch to their domestic goods reducing the demand for imports from abroad
What’s downside of using a subsidy
expensive for government
In the long run firms may become inefficient as they will rely on the subsidy
if supply is inelastic producers benefit more as they can maintain production levels whilst benefiting from lower costs, increasing rev
If it’s elastic
Consumers will only benefit slightly as there’s lower prices
How can a subsidy make a firm more internationally competitive
If firms are able to meet all of the domestic demand than the excess supply may be exported and dom employment can increase
What type of goods are subsidised
Merit goods usually such as agriculture, transport, housing, healthcare exc
What’s an example in the Uk that’s subsidies
Uk steel industry
Show a subsidy model
What’s a non tariff barrier
Any measure other than a customs tariff that acts as a barrier to free trade
What do non tariff barriers include
Non tariff barrier include regulations regarding health and safety, eviromental regulations and correct labelling of products which restrict free trade.
What’s customs duty
Another word for tariffs
What are the reasons to restrict free trade
Preventing dumping, protecting domestic employment, protecting infant industry, health and safety
What are trade barriers also known as
Protectionist barriers
What’s dumping
selling goods in a foreign market at a very low price, usually lower than the cost of production. This aims to increase market share and drive out competitors
How can a trade barrier be used to prevent dumping
A tariff will increase the price of an imported goods so that foreign firms won’t be able to undercut domestic firms by charging lower prices
How can trade barriers be used to protect domestic jobs
A restriction on imports will increase demand for domestic goods, this will increase the derived demand for labour and increase employment
What’s an infant industry
A newly established or developing industry which need protection from foreign markets as there unable to compete
What can be done to protect infant industry
restrictions on free trade so reduced production costs and decreased prices eg subsidy
How can health and safety be protected
The use of non tariff barriers such as health and safety regulations which doesn’t allow unsafe products to be imported
Analysis/ disadvantages of tariffs/ protectism
A tariff, causes market distortion. the price increases with an imposition of a tariff causes a decrease in consumer surplus not only with price but choice in the market so satisfaction loss.
Production inefficiency, allocation of resources can worsen.Dead weight welfare loss.
Cause Retaliation, The cost of the retaliation may be a lot higher than the benefits incurred from the tariff.
Size of tariff ? Impact, elasticity of demand and supply, aims to reduce imports so if there both inelastic the Q may increase but not by very much and contraction in demand not very much.