Biopsychology Exam 1
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Toward the front (nose)
Anterior
Toward the back (tail) (not dorsal)
Posterior
Toward the top of the brain
Dorsal
Toward the bottom of the brain
Ventral
Toward the midline
Medial
Away from the midline
Lateral
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Motor and sensory neurons that connect to the CNS (everything else)
The brain and spinal cord are two structures in the blank nervous system
Centra l
Schwann Cells
Oligodendrocytes
Axodendritic
axon to dendrite synapse
Axosomatic
Axon to soma synapse
Axoaxonic
Axon to axon synapse
Ions
Electrically charged molecules
Neurons have a blank
Electrical charge
Membrane potential
the difference in electrical charge between the extracellular fluid and the intracellular fluid (difference = approx -70mV)
The inside of a neuron (intracellular) is …
More negative (-) than the outside (extracellular)
Cations are
Positively charged ions
Anions are
Negativity charged ions
Membrane potential of a neuron at rest
-70mV
Gated ion channels are
channels that can be open or closed depending on various environmental conditions (binding of a neurotransmitter or the voltage of the neuron)
Ions are able to move between
the extracellular and intracellular fluids via specialized membrane-spanning proteins called ion channels
Leak ion channels
Are channels that are always open! Doesn’t matter the circumstance
Voltage-Gated ion channels
Opens and closes dependent on the electrical charge of the neuron
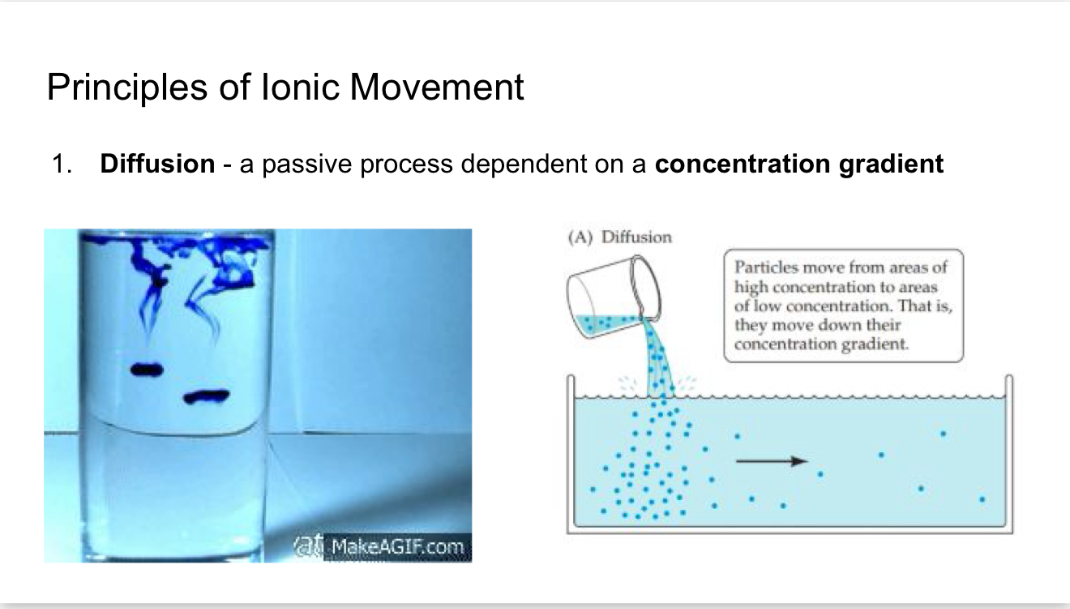
Diffusion 1
Is a passive process that’s dependent on a concentration gradient
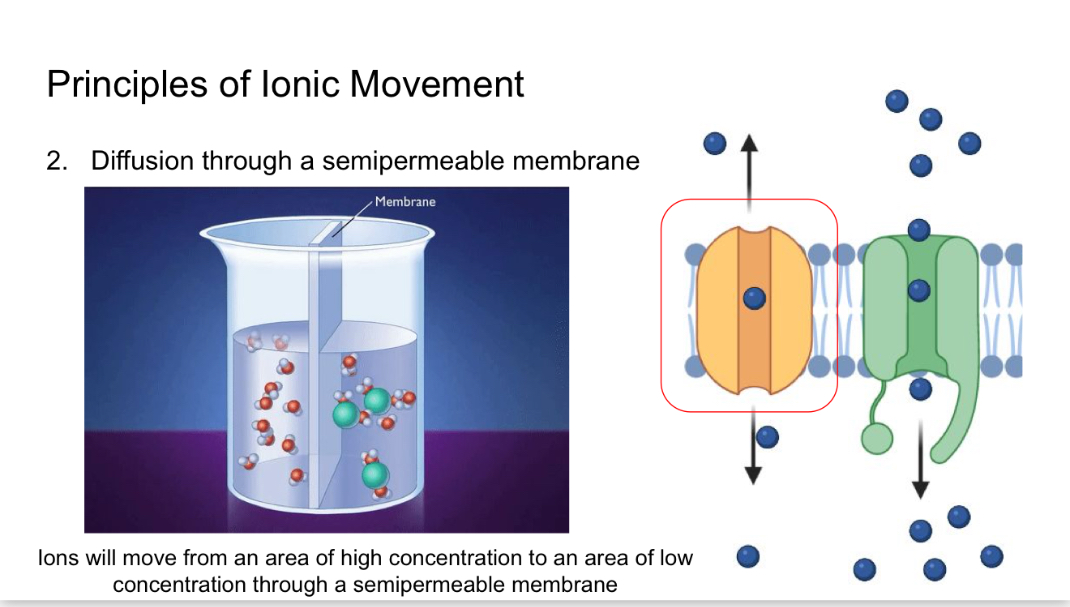
Diffusion 2
Diffusion through a semipermeable membrane
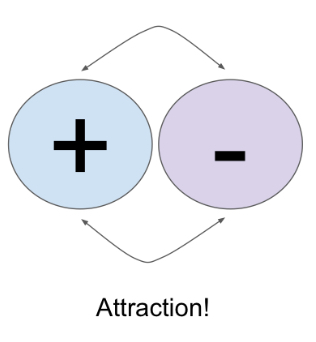
Electrostatic forces (diffusion 3, attraction)
Ions flow towards oppositely charged ares
Electrostatic forces (Repulsion)
Ions flow towards oppositely charged areas
Electrical Driving Force = …
Electrostatic potential
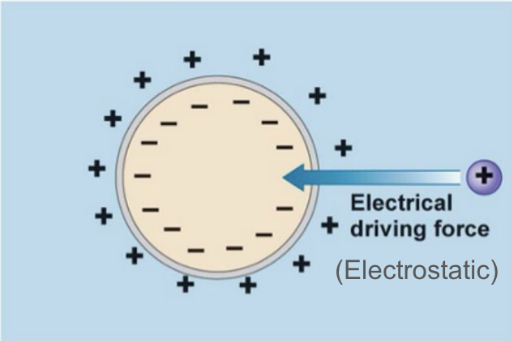
External positive charges are attracted to …
Negative inside
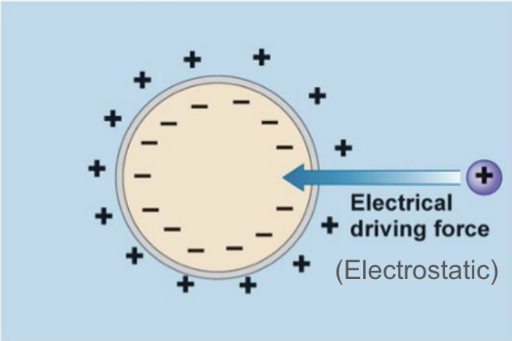
Internal negative charges are attracted to …
Positive outside
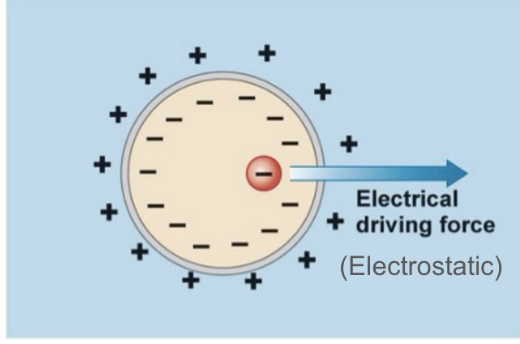
Actively (cell does this)
(Meaning using energy) to push sodium out of the neuron and potassium into the neuron
Passively (cell does this)
(Meaning without using energy) to allow potassium free movement between the inside and outside of a neuron
Potassium is most dense when?
It’s intercellular. Its particularly accomplished through sodium potassium pumps
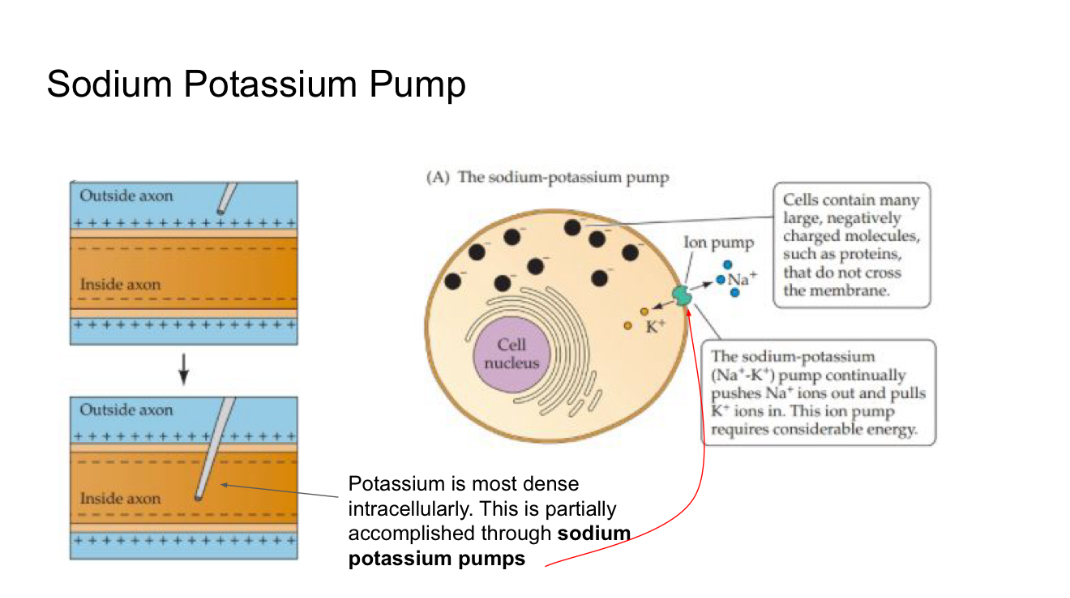
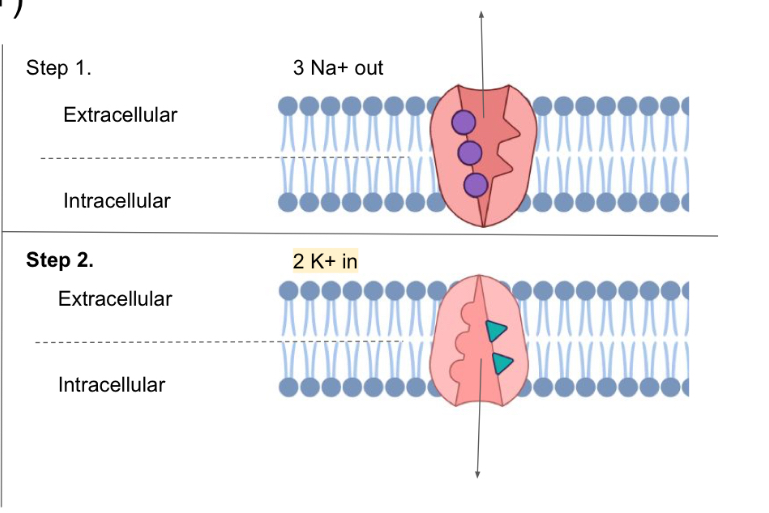
The sodium potassium pumps push …
3 Na+ out of the neuron for every 2 K+ they pump into the cell
Why do sodium potassium pumps use a lot of energy?
Because it is against the concentration gradient
Potassium wants to move from…
an area of high potassium concentration to a lower concentration area (intracellular -> extracellular).
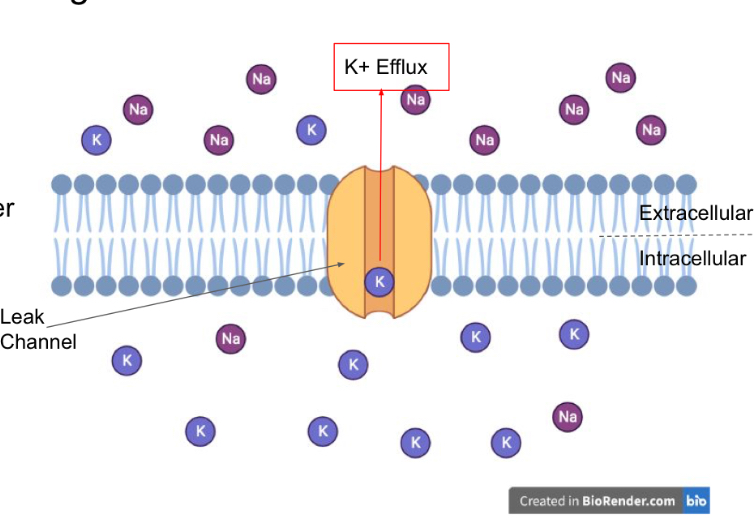
Potassium can what…
Efflux through leak channels
Electrostatic force maintains…
K+ intracellularly
Potassium is also attracted to the…
Anions and negative ions intracellularly
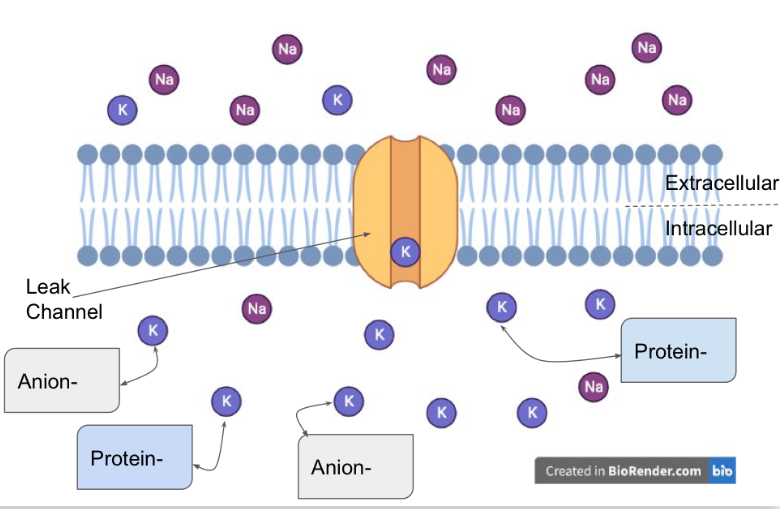
An equilibrium is obtained when the ….
Opposite forces of the concentration gradient (K+ efflux) is matched with electrostatic force (K+ influx)
Ions move through the neural membrane via ….
Ion channels
Electrical forces drive…
Oppositely charged ions together
Concentration gradient forces…
Identical ions to diffuse away from each other
Why are neurons negatively charged at rest?
They are negatively charged at rest because the sodium potassium pumps maintain more K+ inside the cell and Na+ outside the cell
What do potassium leak channels help maintain?
The resting membrane potential
Ion channels are
Proteins in the membrane that can form pores to allow the passage of ions through them
Voltage gated ion channels are
ion channels that open or close depending on the voltage/electrical charge of the inside of the neuron relative to the outside
Leak channels are
Ion channels that are always open
Anion
Negatively charged ion (chloride)
Cation
Positively charged ion (sodium, potassium, calcium)
Equilibrium Potential
The point in which there is no net flow of ions
Influx
Moving into the cell
Efflux
Moving out of the cell
Inhibitory signals
“Don’t Fire.” Results in hyperpolarization (the neuron gets MORE negative)
Excitatory signals
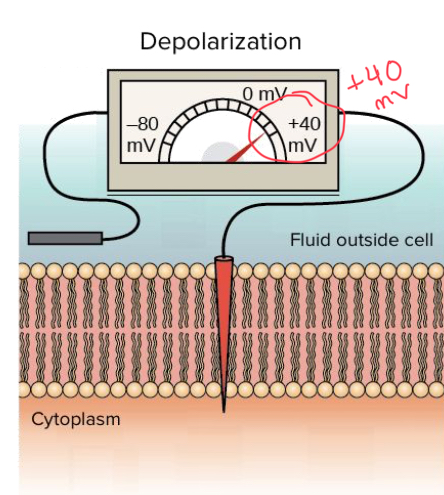
“Fire Away.” Results in depolarization (the neuron gets LESS negative, and brings it closer to 0mV)
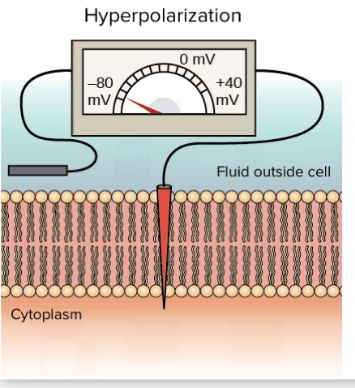
Inhibition (Hyperpolarized)
More negative than at rest
Excitation
More positive than at rest