pulmonary neoplasms
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
4 major types of lung cancer
small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC)
non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC)
-adenocarcinoma
-squamous cell carcinoma
-large cell carcinoma
lung cancer epidemiology
-most common cause of cancer death
-40-80 yo
-cigarette smoke= 10x more risk
lung cancer metastasis
-mediastinum and hilar lymph nodes
-lung pleura
-heart
-breast
-liver
lung cancer screening
-early detection is key before metastasis
-low dose CT screening for lung cancer for: 50-80 yo, >20 pack-year smoke hx, either current or within the last 15 years
presentation of lung cancer
ABCDE
-A: bronchial airway disruption > pneumonia
-B: blood
-C: cough
-D: distribution (metastasis)
-E: wheezing
lung cancer sx
-cough
-weight loss >10lbs
-dyspnea
-chest pain
-hemoptysis
-bone pain
-clubbing, wheezing, weakness, fever, SVC obstruction, striodor
-neurologic sx
lung cancer dx
-confirmatory= tissue biopsy
-sputum cytology: less invasive, not diagnostic
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
-squamous cell carcinoma: central, smoking
-adenocarcinoma: peripherally, NO link to smoking
-large-cell carcinoma: throughout lungs, dx of exclusion if SCC and adenocarcinoma not it
-bronchial carcinoid tumor: low grade malignancy of neuroendocrine cells
NSCLC dx/tx
-dx: fine needle aspiration of the lung
-tx: surgical resection
-5 year survival 40%
small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
-strongly associated with smoking
-develops centrally in the lugn near bain bronchus
-fast and rapid
-secrete hormones
-paraneoplastic syndromes
SCLC- paraneoplastic syndromes
-cushing syndrome: excrete cortisol, elevated BP and glucose
-SIADH: release ADH, water retention, high BP and edema
-eaton-lambert: tumor producing autoantibodies, destroy neurons
SCLC sx
-limited (one lung) or extensive (spread)
-dyspnea, wheezing, cough, hemoptysis
SCLC sx
-biopsy= large cells with limited cytoplasm and nuclear moulding
Staging:
-CT + contrast scan chest and PET scan
-neuro or adenocarcinoma >3cm: MRI of the head w/o and w contrast
-CT abdomen
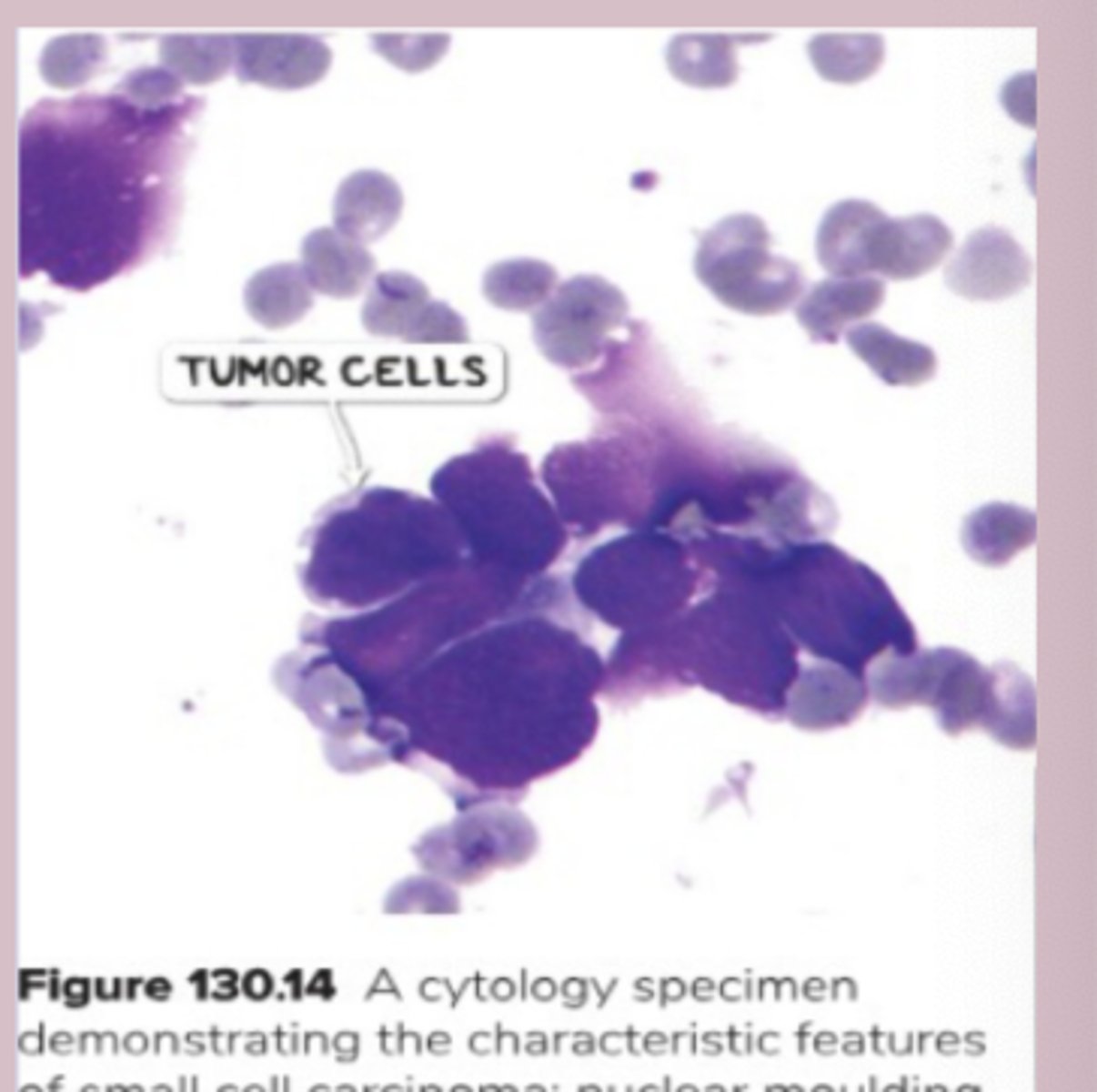
SCLC tx
-supportive care: palliative care, smoking cessation,
-NSCLC give chemotherapy before resection
-EGFR mutation + in NSCLC: erlotinib, gefitinib, afatinib
-tyrosine kinase inhibitors: erlotinib, gefitinib
-monoclonal antibody: cetuximab, necitumumab
-surgery and radiation
SPHERE
-SVC syndrome
-Pancoast tumor
-Horners syndrome
-Endocrine: flushing, diarrhea, telangiectasias
-Recurrent laryngeal nerve: hoarseness
-Effusions: exudative
pancoast tumor
-pulmonary neoplasms located in lung apices
-most NSCLC
-cervical sympathetic nerves, brachial plexus, laryngeal nerves, SVC
pancoast tumor sx
-cough, angia, dyspnea, hemoptysis, wheezing, pnuemonias, weight loss, loss of appetite, weakness
-local inflammation , pain in upper extremities and weakness due to brachial plexus
-compression of cervical sympathetic nerves
-voice hoarsenss
-flushing, edema, dyspnea
pancoast tumor dx
-CT of chest: tumor in lung apex
-biopsy= confirm
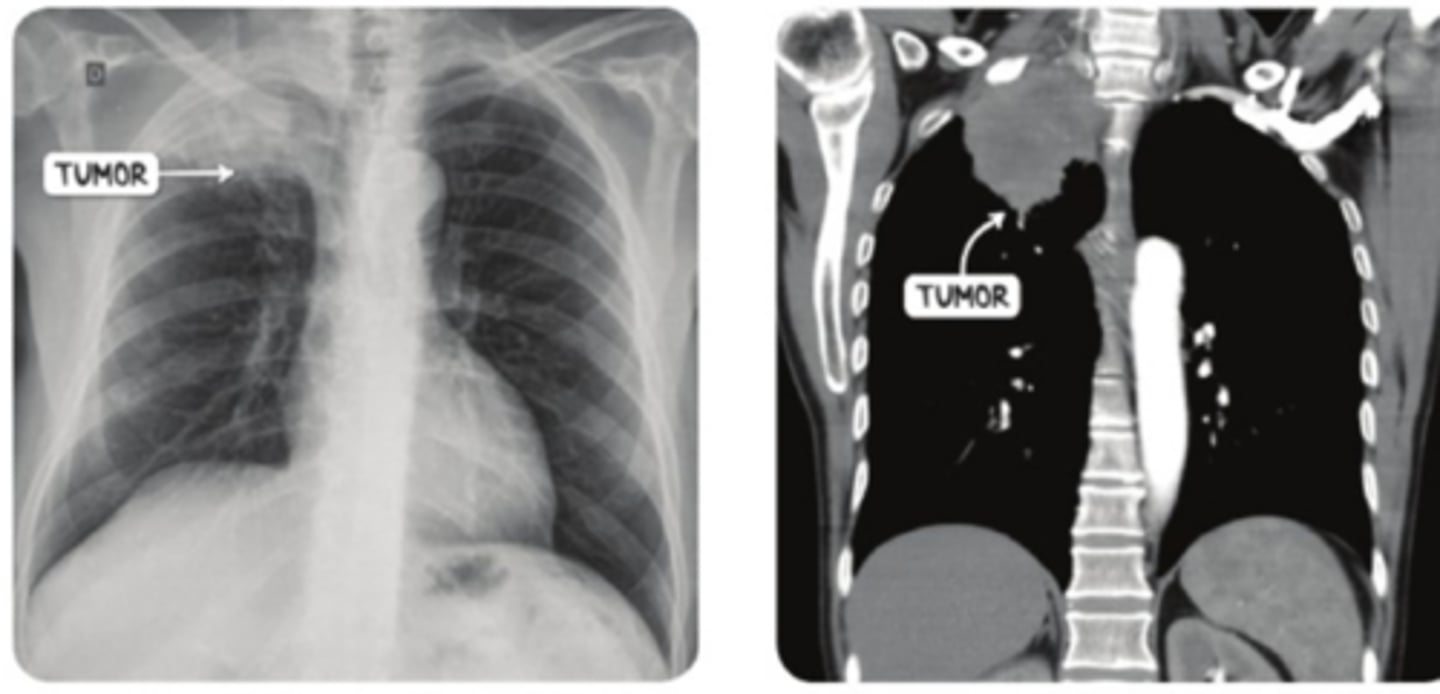
pancoast tumor tx
-manage impingement first before resection
-chemotherapy
-surgical resection
-radiation
Superior vena cava syndrome
-obstruction of SVC
-increased venous pressure and dilation
-caused by: lung cancers, blood clots, tumor invasion
Superior vena cava syndrome sx
-edema of face and neck
-inspiratory stridor
-voice change
-flushed appearance
Superior vena cava syndrome dx
-CT of chest
-venous angiography= vessel dilation
-biopsy
Superior vena cava syndrome tx
-steroids to reduce inflammation
-surgery
-chemotherapy
-head above heart
tumor staging
TMN staging
-T: tumor size and extent
-N: regional lymph nodes: N0= none, N1= ipsilateral peribronchial, N2= ipsilateral mediastinal or subcarinal, N3= contralateral
-M: metastases: M0= none, M1= distant
solitary pulmonary nodule
-coin lesion
-asymptomatic
-adenocarcinoma- most common cause
-Infectious granulomas= 80% of benign lung nodules by histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, tuberculous, or nontuberculous mycobacteria
solitary pulmonary nodule dx
-evaluation of old imaging
-rapid progression, larger= higher risk of malignancy
-high resolution CT: any suspicious solitary pulmonary nodule
solitary pulmonary nodule tx
-watchingful waiting: low probability of malignancy, <30yo, stable for >2yo
-surgery: high probability of malignancy
bronchial carcinoid
-malignant tumors from neuroendocrine cells
-favorable prognosis
-pedunculated or sessile growth in central bronchi
bronchial carcinoid sx
-hemopytsis, cough, focal wheezing, recurrent post obstructive pneumonia
bronchial carcinoid dx
-fiberoptic bronchoscopy: pink or purple tumor in central airway
-CT scan
-grow slowly
bronchial carcinoid tx
-surgical excision lymph node dissection and resection
mediastinal masses
-nonspecific depends on surrounding structures
-sx: insidious onset of retrosternal chest pain, dysphagia, dyspnea
-dx: CT scan, tissue biopsy=diagnostic
-tx: depends on underlying cause
mesothelioma
-cancer of the mediastinum
-found in lungs and chest wall pleural lining
-associated with asbestosis exposure
-dx: CXR or CT scan
-biopsy: calretinin helps distinguish, fried egg appearance
-tx: chemotherapy, radiation