Indirect Taxes and Subsidies
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Government Intervention
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is an indirect tax?
A tax paid on the consumption of goods/services, which the tax burden is passed from producers to consumers
Why may the government impose a indirect tax?
Discourage consumption of demerit goods
Raise government revenue
How is the indirect taxes transferred?
Governments put the tax on producers → why the supply curve shifts
Producers put it on their products which then is paid by the consumers
What are the two types of indirect taxes?
Ad valorem
Specific
What is a specific tax?
A fixed tax per unit of output (specific amount)

What is tax incidence?
The share/burden of the total tax to be paid
In this diagram, what is the consumer incidence (share) and producer incidence (share) of the tax?

Consumer incidence: AREA A = P2-P2 x Q2
Producer incidence: AREA B = P1-P3 x Q2
What is a ad valorem tax?
A tax that is a percentage of the purchase price
The more goods/services consumed, the larger the tax bill
Causes supply curve to diverge from original supply curve
Raises significant government revenue

In this diagram, what is consumer and producer incidence?
Consumer incidence: Area A = P2-P1 x Q2
Producer incidence = Area B = P1-P3 x Q2
What are the advantages of indirect taxes?
Raise the price and reduces the QD of demerit goods
Reduces external costs of consumption and production
Raises revenue for government programs
What are the disadvantages of indirect taxes?
The effectiveness of the tax in reducing the use of demerit foods depends on the PED
Many consumers who purchase products that are price inelastic will continue to do so
It may help create illegal markets as consumers seek to avoid paying the taxes
Producers may be forced to lay off some workers as output falls due to the higher prices
How does PED influence the effectiveness of indirect taxes?
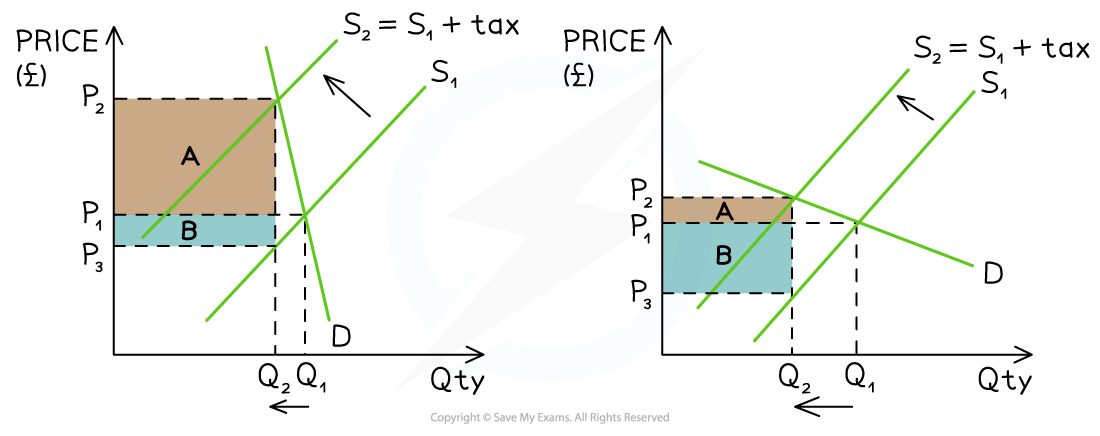
Inelastic goods:
Curve is steep
Producers pass on much higher proportion of the tax to consumers and pay the rest themselves
QD decreases but in a much smaller proportion compared to the increase in price
Elastic goods:
Curve is flatter
Producers pass on a much smaller proportion of the tax to consumers and pay the rest themselves
QD decreases but by a much larger proportion in comparison to the increase in price
Both goods:
Increase in price and decrease in QD
Tax revenue is collected
What are subsidies?
The per unit amount of money given to a firm by the government to increase production or increase the provision of a merit good
How is a subsidy shared between producers and consumers?
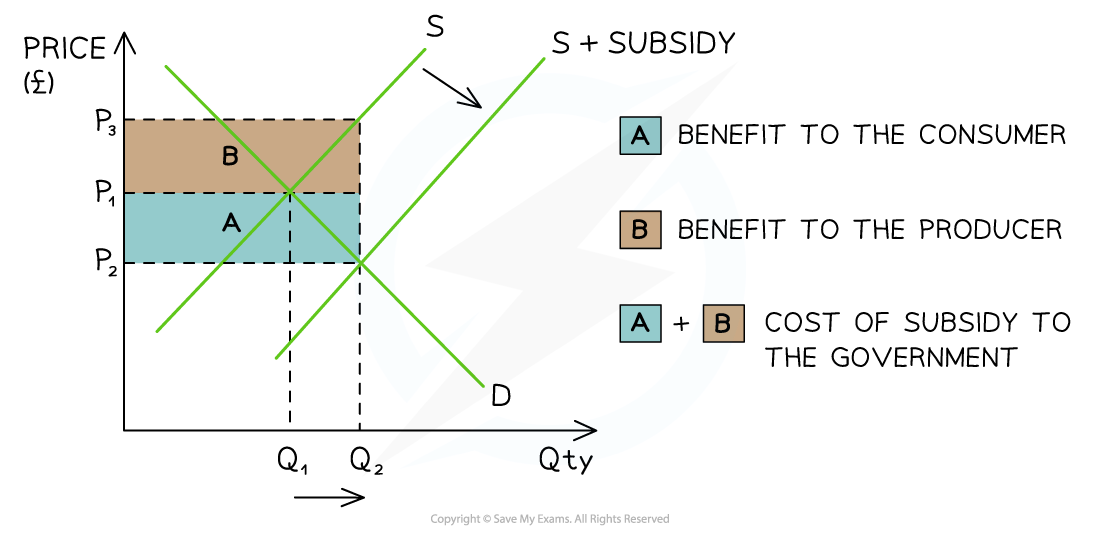
Producers keep some of the subsidy
Pass the rest to consumers in the form of lower prices
Determined by the PED of the product
What are the advantages of producer subsidies?
Can be targeted to helping specific domestic industries
Lower prices and increases demand for merit goods
Helps to change destructive consumer behaviour over a longer period of time
Can be used to help domestic firms compete internationally
What are the disadvantages of producer subsidies?
Distorts the allocation of resources in markets
There is an opportunity cost associated with the government expenditure
Subsidies are prone to political pressure and lobbying by powerful business interests
Subsidies can disincentives firms from becoming more efficient or competitive as they provide extra funds which reduce the need to be more competitive