PAPER 1 all topics
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/174
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:10 PM on 5/7/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
175 Terms
1
New cards
what is the equation for efficiency
efficiency (0….) = useful energy transferred out (J) / total energy transferred in (J)
2
New cards
what are the circuit symbols
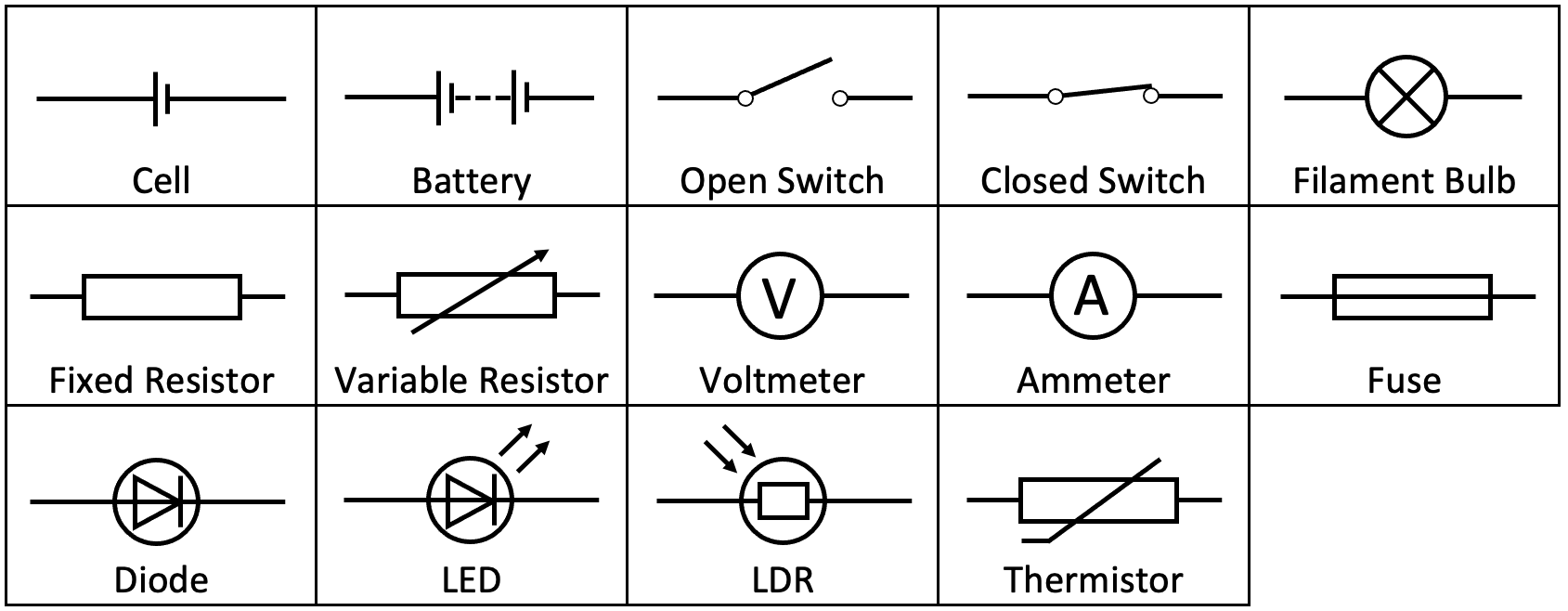
3
New cards
what is potential difference
work done / energy transferred measured in volts
4
New cards
what is current like in a series circuit
the same everywhere
5
New cards
what is needed for current to flow
voltage to push current through components
6
New cards
how to improve efficiency when there is friction between moving parts
oil parts so they move more easily
7
New cards
how to improve efficiency when hot objects transfer energy to surroundings, wasting it
use an insulator to stop heat escaping
8
New cards
how to improve efficiency when there is air resistance from an object which oppose motion
streamline the object
9
New cards
how to improve efficiency when there is sound created by machinery
fix machinery in place or cushion parts
10
New cards
what is electric current
rate of flow of charge
11
New cards
what does a sankey diagram look like
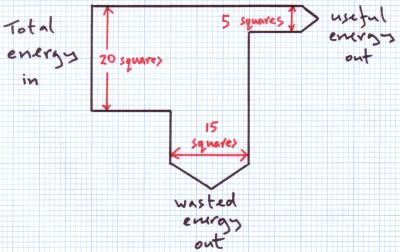
12
New cards
what does a sankey diagram show
efficiency
13
New cards
what does a risk assessment table look like
hazard risk safety precaution
14
New cards
what is current like in a parallel circuit
all current into a junction adds up to all the current leaving it and the total current supplied is split between the components on different loops
15
New cards
what are the different variables for a test of how good an insulator is
independent variable is type of insulator dependent variable is temperature change and control variable is starting temperature amount of water and thickness of insulator
16
New cards
what does an insulator do
reduce flow of heat
17
New cards
how can a polythene rod be used to pick up a small piece of paper using friction
the rod is positively charged from friction so attracts the negative electrons in paper causing the paper to attract to the rod
18
New cards
what is specific heat capacity
the amount of energy needed to raise 1kg of something by 1c
19
New cards
what is the symbol equation for specific heat capacity
ΔE = mcΔθ
20
New cards
what is the word equation for specific heat capacity
change in joules = mass x specific heat capacity x temperature change
21
New cards
what is specific heat capacity measured in
c = J/kgc
22
New cards
what creates a potential difference
transfer of electrons due to a frictional force
23
New cards
how does a battery work
a battery is full of chemicals so energy is shifted from the chemical store of the battery to the moving charge and the charge moves in all the circuit at once. energy is shifted from the moving charge to the component to make it work
24
New cards
what is beta radiation
a neutron becomes a proton and an electron is emitted from the nucleus
25
New cards
how does beta radiation change mass and atomic number
atomic number increases by 1 and mass number stays the same
26
New cards
what is the relative mass of beta radiation
very small
27
New cards
how far can beta radiation travel in air
1m
28
New cards
what is the charge of beta radiation
\-1
29
New cards
what absorbs beta radiation
thin about 2mm of aluminium
30
New cards
what is the penetrating power of beta radiation
medium or mid
31
New cards
what is the ionising power of beta radiation
medium or mid
32
New cards
what is alpha radiation
a helium nucleus or alpha particle of 2 protons and 2 neutrons is emitted from the nucleus
33
New cards
how does alpha radiation affect mass and atomic number
atomic number decreases by 2 and mass number decreases by 4
34
New cards
what is the relative mass of alpha radiation
4
35
New cards
what is the charge of alpha radiation
\+2
36
New cards
how far can alpha radiation travel in air
up to 5cm
37
New cards
what absorbs alpha radiation
paper
38
New cards
what is the penetrating power of alpha radiation
weak or low
39
New cards
what is the ionising power of alpha radiation
high
40
New cards
what is gamma radiation
electromagnetic radiation is emitted from the nucleus
41
New cards
how does gamma radiation affect mass and atomic number
it doesn’t
42
New cards
what is the relative mass of gamma radiation
0
43
New cards
what is the charge of gamma radiation
0
44
New cards
how far can gamma radiation travel in air
over 1km
45
New cards
what absorbs gamma radiation
thick 10cm of lead or thick 50cm of concrete
46
New cards
what is the penetrating power of gamma radiation
strong or high
47
New cards
what is the ionising power of gamma radiation
low
48
New cards
what is ionisation
when electrons are removed from an atom by nuclear radiation
49
New cards
what is neutron emission
a neutron is emitted from the nucleus
50
New cards
how does neutron emission affect atomic and mass number
atomic number stays the same and mass number decreases by 1
51
New cards
what is the potential difference and current of batteries and cells
they have constant or direct potential difference so current always flows in the same direction which is called direct current DC
52
New cards
how does temperature affect pressure
more kinetic energy means faster moving particles and more collisions with each other and the edge. as they collide the force increases and more force in the same volume means higher pressure
53
New cards
what is count rate
number of decays per second recorded by a detector in one area
54
New cards
what is temperature
measure of average kinetic energy of particles
55
New cards
what happens to volume when pressure increases
volume decreases because the gas particles are forced closer together
56
New cards
what happens to volume when pressure decreases
volume increases because the gas particles can now move farther apart
57
New cards
how does increasing temperature affect brownian motion
when temperature increases brownian motion because particles have more kinetic energy so move faster and there are more collisions
58
New cards
what is boyle’s law
boyle's law states that for a gas at a constant temperature pressure × volume is also constant
59
New cards
what is resolution
the smallest change a device can detect
60
New cards
what is the symbol equation for density
p = m/v
61
New cards
what is the word equation for density
density kg/m3 = mass / volume
62
New cards
what is elastic potential
something stretching or contracting or changing shape
63
New cards
what is thermal or internal energy
something heating or cooling or changing state
64
New cards
what is chemical energy
a chemical reaction taking place
65
New cards
what is gravitational potential
something changing height or 2 masses getting closer
66
New cards
what is kinetic energy
something getting faster or slower
67
New cards
what is the potential difference across components in a parallel circuit like
the total potential difference across all the components in one loop sums to the potential difference of the cells
68
New cards
how would you find out the peake potential difference on an oscilloscope
the highest the line goes is the peak potential difference
69
New cards
what is a closed system
a system where energy cannot enter or leave
70
New cards
what is the resistance of a circuit
how difficult it is for current to flow through a circuit
71
New cards
what is resistance measured in
ohms Ω
72
New cards
what is the potential difference across the components in a series circuit like
the total potential difference across all the components sums to the potential difference of the cells
73
New cards
what does directly proportional look like on a graph
line of best fit will go through the origin
74
New cards
describe current through an ohmic resistor
it is directly proportional to the potential difference across it
75
New cards
how can you change the resistance of a wire
change its cross sectional area or its material or its length or its temperature
76
New cards
what is conservation of energy
energy cannot be created or destroyed but it can be stored or transferred between stores or dissipated
77
New cards
how many millivolts in a volt
1000 mV in 1V
78
New cards
how many cm3 in 1m3
1000000cm3 or 1 x 106 in 1m3
79
New cards
what is parallax error
when an object looks a different size or position when viewed from different angles
80
New cards
what is inversely proportional
when you double one you half the other and you can prove this by multiplying them together to get a constant. y = 1/x
81
New cards
what is brownian motion
smoke particles moving around in a random zig zag dance
82
New cards
how do you find the density of irregular shaped objects
1. measure the mass of the object and record
2. fill displacement can with water and put empty beaker under spout so water should drip from the spout into the beaker
3. when water stops dripping from the spout put a measuring cylinder underneath the spout
4. tie the object to a string and use the string to gently lower it into the water until it is just submerged
5. collect the water which comes out and measure it and record this volume as the amount of ml of water which came out is the volume of the object in cm3
6. divide the mass by the volume to get the density in g/cm3
83
New cards
explain electron energy level stuff
when an electron absorbs an electromagnetic wave it gives it energy which causes it to move to a higher energy level further away from the nucleus. when it has an energy crash it jumps back down to a lower energy level releasing energy and electromagnetic radiation
84
New cards
what is electrostatic potential
charges moving closer together or further apart
85
New cards
what is the equation for resistance
resistance = voltage / current (VIR)
86
New cards
what does the earth wire do
safety feature to stop the case of the appliance going live
87
New cards
what is the potential difference of the earth wire
0V
88
New cards
what is activity
the rate at which a source of unstable nuclei decay - the number of decays per second measured in becquerel Bq
89
New cards
what does the live wire do
carries alternating potential difference
90
New cards
what is the potential difference of the live wire
230V
91
New cards
describe mains electricity
it has an alternating potential difference and an alternating current AC meaning the current keeps changing from positive to negative and it keeps changing direction
92
New cards
why should an electrician not replace a shower until it is disconnected from the mains supply
because there is a big potential difference between the electrician 0v and the live wire in the shower of 230v so the current would flow through the electricians body to the earth if they touched it and they would get an electric shock
93
New cards
what does a fuse do
when current gets too large when there is a fault in an appliance the metal strip in the fuse melts and the circuit cannot flow so the appliance is turned off
94
New cards
what does the neutral wire do
completes the circuit
95
New cards
what is the potential difference of the neutral wire
about 0V
96
New cards
what is nuclear potential
nuclear decay or fission or fusion
97
New cards
what is magnetic potential
magnets moving closer together or further apart
98
New cards
what are cables made up of
earth neutral and live wires surrounded by different colours of plastic or rubber insulation to stop electric shocks and make them easily identifiable. copper is used for the wires because it is a good conductor of electricity
99
New cards
what is the equation for pressure
pressure Pa = force N / area m2
100
New cards
what are the different colours of insulation for each of the wires
earth is yellow and green striped neutral is blue and live is brown