Review These Anatomy Topics
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:25 PM on 5/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
1
New cards
What transmits the sensation of contact with the teeth when they occlude?
PDL
Functions of the PDL include formation and maintenance to fibrous and calcified tissue, nutritional metabolites transport and sensory functions of pain and displacement sensitivity (sensation = occlusion)
Functions of the PDL include formation and maintenance to fibrous and calcified tissue, nutritional metabolites transport and sensory functions of pain and displacement sensitivity (sensation = occlusion)
2
New cards
1. Which vein of the head and neck is formed by the drainage of venous blood from the pterygoid plexus?
Maxillary Vein
3
New cards
Lingual Vein drains what?
Areas of the tongue
4
New cards
Facial Vein and Retromandibular drains what?
Into the interjugular
5
New cards
Which premolars often has a third cusp?
Mand 2nd premolar
6
New cards
Pits in the occlusal surfaces of molars and premolars are generally found at the junction of:
Developmental grooves
7
New cards
Which tooth has a non-functional lingual cusp?
Mand 1st premolar
8
New cards
The cusp of Carabelli of the permanent maxillary first molar is located on the:
Mesiolingual cusp
9
New cards
The Curve of Spee is from the buccal aspect with the cusp tips of posterior teeth curved anteroposteriorly
True
10
New cards
For mandibular teeth, the curve is convex, and for maxillary teeth, it is concave
False
11
New cards
The largest and longest cusp in posterior teeth is the:
Mesiolingual cusp of a maxillary first molar
12
New cards
Which of these structures is NOT located on the sphenoid bone?
Stylomastoid foramen
13
New cards
Which muscle pulls the lateral borders of the tongue downward?
Hyoglossus
14
New cards
Hyoglossus
Depresses tongue
15
New cards
Styloglossus
Retracts tongue
16
New cards
Genioglossus
Protrudes tongue
17
New cards
Extrinsic Muscles
Genioglossus
Styloglossus
Hyoglossus
Styloglossus
Hyoglossus
18
New cards
Innervation of Extrinsic Muscles
CN 12 (Motor) (hypoglossal nerve)
Sensory innervation = Anterior 2/3rd is the lingual nerve (V3) & chorda tympani
Posterior 3rd is CN 9 (glossopharyngeal)
Blood Supply: Lingual artery
Sensory innervation = Anterior 2/3rd is the lingual nerve (V3) & chorda tympani
Posterior 3rd is CN 9 (glossopharyngeal)
Blood Supply: Lingual artery
19
New cards
Intrinsic Muscles
Superior longitudinal
Transverse
Vertical
Inferior longitudinal
Shapes the tongue
Innervation: CN: 12 - Hypoglossal
Blood supply artery: Lingual Artery
Transverse
Vertical
Inferior longitudinal
Shapes the tongue
Innervation: CN: 12 - Hypoglossal
Blood supply artery: Lingual Artery
20
New cards
Palatoglossus muscle
Elevates base of tongue
Depresses soft palate
Innervated by pharyngeal plexus; separates oral cavity and pharynx
Initiates swallowing
Innervation: CN 10 and CN 11
Depresses soft palate
Innervated by pharyngeal plexus; separates oral cavity and pharynx
Initiates swallowing
Innervation: CN 10 and CN 11
21
New cards
Pterygomandibular fold
Tissue that extends from the junction of the hard and soft palates down to the mandible (distal to the last tooth) and stretches upon opening
Referred to as raphe
Referred to as raphe
22
New cards
Sublingual Caruncle
A small papilla on the lingual frenum which are duct openings from submandibular and sublingual salivary glands
23
New cards
Plica sublinguals
V shaped ridges on each side of the frenum which empty the sublingual salivary glands
24
New cards
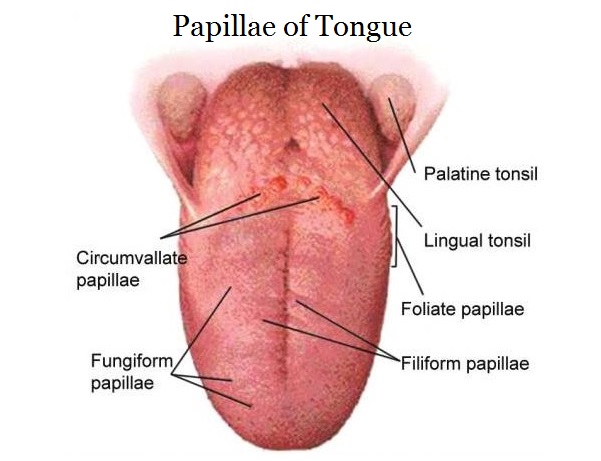
Foliate
Contain taste buds (red in color)
25
New cards
Circumvallate
10-14
Contain taste buds
associated with ducts of Von Ebner’s glands
Large
Contain taste buds
associated with ducts of Von Ebner’s glands
Large
26
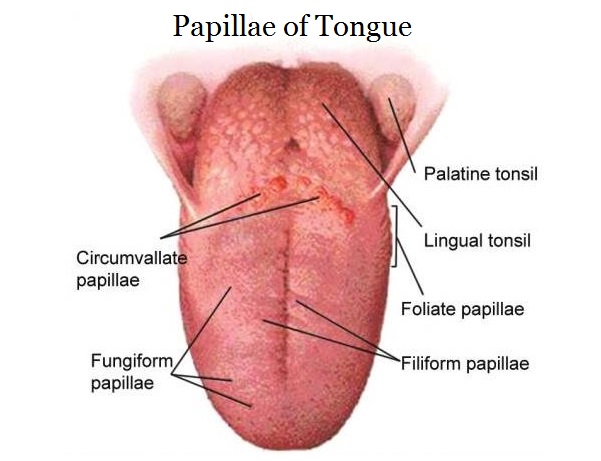
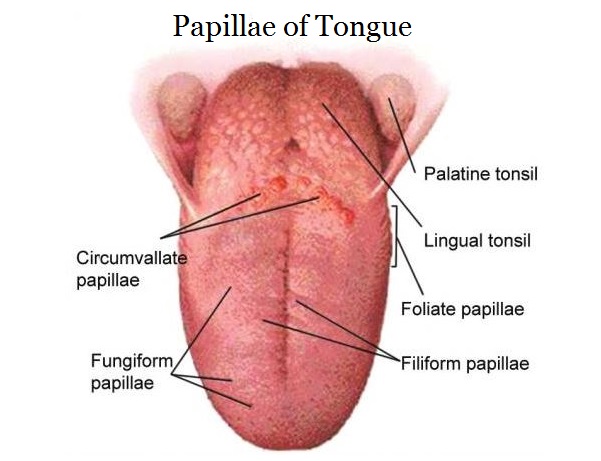
New cards
Filiform
The most numerous but do not contain taste buds
Keratinized tissue give tongue a velvety texture
Associated with geographic tongue and hairy tongue (whitish tint in color)
Keratinized tissue give tongue a velvety texture
Associated with geographic tongue and hairy tongue (whitish tint in color)
27
New cards
Foliate Lingual
Located on the lateral surface (side) of the tongue
Some contain taste buds
Some contain taste buds
28
New cards
Sulcus Terminalis
Separation of 1/3 posterior and 2/3 anterior portions of the tongue with the foramen cecum at the point (which is remnant of median thyroid diverticulum in early embryonic development/origin of the thyroid gland)
29
New cards
Which of the following papilla does NOT have taste buds?
Filiform
30
New cards
Where is the insertion of the lateral pterygoid muscle?
TMJ disc and neck of the mandibular condyle
31
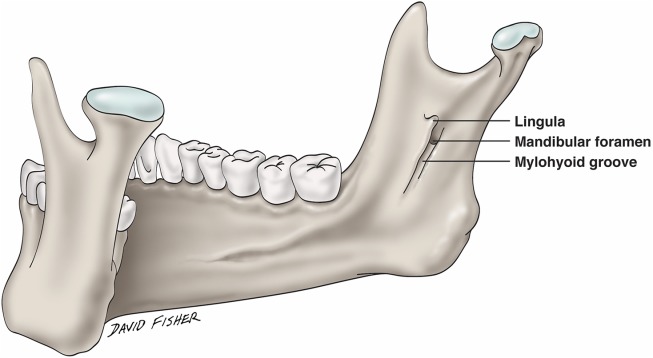
New cards
What best describes a lingula?
A tongue shaped, sharp bony spine overlapping the mandibular foramen, giving attachment to the sphenomandibular ligament.
32
New cards
The TMJ structure consists of:
Two synovial compartments
33
New cards
Which of the following signs is not expected to be seen in a temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorder?
Swelling and erythema over the joint
34
New cards
Temporal Bone
Includes:
Articular eminence
Articular fossa
Postglenoid process
Articular eminence
Articular fossa
Postglenoid process
35
New cards
Mandible
Includes:
Condyle
Coronoid process
Mandibular notch
Condyle
Coronoid process
Mandibular notch
36
New cards
Joint Capsule
Completely encloses the TMJ
Wraps around the margin of the articular eminence, articular fossa, and around the circumference of the condyle including the condyle neck
Wraps around the margin of the articular eminence, articular fossa, and around the circumference of the condyle including the condyle neck
37
New cards
Articular Discs
Also called meniscus of the joint which divides the TMJ into two compartments called synovial cavities where synovial fluid is produced to lubricate the joint
Fibrous, dense, CT
The disk can thin over time and/or dislocate
Fibrous, dense, CT
The disk can thin over time and/or dislocate
38
New cards
Ligaments
TMJ ligament
Sphenomandibular ligament
Stylomandibular ligament
Sphenomandibular ligament
Stylomandibular ligament
39
New cards
Movement
Allows movement of the mandible for speech and mastication
Two types of movement including gliding and rotational
Includes protrusion (jaw forward) for gliding/speech/mastication Retraction (jaw backwards), depression (jaw lowered), and elevation (jaw raised) for rotation
Two types of movement including gliding and rotational
Includes protrusion (jaw forward) for gliding/speech/mastication Retraction (jaw backwards), depression (jaw lowered), and elevation (jaw raised) for rotation
40
New cards
Trismus
Limited ability to open the mouth (hypomobility) due to the contraction of the MOM (lockjaw)
41
New cards
Subluxation
Dislocation of both joints caused by opening the mouth too wide
42
New cards
Arteiries
Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart
O2 is bound to hemoglobin
O2 is bound to hemoglobin
43
New cards
Veins
Carry deoxygenated blood to the heart
44
New cards
The exception:
The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs
The pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from lungs to the left side of the heart
The pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from lungs to the left side of the heart
45
New cards
Right Side
Aorta --- Brachiocephalic ---- Common Carotid ---- internal and external carotids
46
New cards
Left Side
Aorta --- Common Carotid --- internal and external carotids
47
New cards
Common Carotid Branches
Internal Carotid (supplies the brain and associated structures)
External Carotid (supplies extra-cranial tissues including the oral cavity)
\
External Carotid (supplies extra-cranial tissues including the oral cavity)
\
48
New cards
Common Carotid Branches: Key Branches
Facial artery: supplies muscles of facial expression, nose, soft palate, pharynx
Lingual artery: supplies superahyoid, tongue, and floor of the mouth
Superior thyroid: supplies thyroid and adjacent muscles
Maxillary artery (terminal branch) supplies teeth, muscles of mastication, hard/soft palate, and nasal (blood supply for BOTH maxilla and mandible)
Lingual artery: supplies superahyoid, tongue, and floor of the mouth
Superior thyroid: supplies thyroid and adjacent muscles
Maxillary artery (terminal branch) supplies teeth, muscles of mastication, hard/soft palate, and nasal (blood supply for BOTH maxilla and mandible)
49
New cards
Glandular tissues
Include:
Lacrimal
Salivary
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Thymus
Pituitary gland
\
Glands produce chemical secretions and include exocrine and endocrine glands
Lacrimal
Salivary
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Thymus
Pituitary gland
\
Glands produce chemical secretions and include exocrine and endocrine glands
50
New cards
Endocrine glands
No ducts
Secretes directly into the blood
Secretes directly into the blood
51
New cards
Exocrine
Associated with a duct
52
New cards
Thyroid Gland
Endocrine gland that secretes thyroxine hormone which stimulates metabolic rate and protein synthesis
53
New cards
Parathyroid Gland
Endocrine gland that secretes parathyroid hormone to regulate calcium and phosphate levels
54
New cards
Thymus Gland
Endocrine gland that developes T-cell lymphocytes
55
New cards
Pituitary Gland
Endocrine
Protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the cranium which helps control: growth, blood pressure, certain functions of sex organs, thyroid glands, and metabolism as well as some aspects of pregnancy, childbirth, nursing, water/salt concentration at the kidneys, temperature regulation and pain relief
Protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the cranium which helps control: growth, blood pressure, certain functions of sex organs, thyroid glands, and metabolism as well as some aspects of pregnancy, childbirth, nursing, water/salt concentration at the kidneys, temperature regulation and pain relief
56
New cards
Which anatomical structure converts glucose to glycogen?
Liver
57
New cards
Where does the exchange of materials between blood and tissues occur?
Capillaries
58
New cards
Where does the kidney filter blood through?
Glomerulus
59
New cards
Which of the following is the only artery to carry deoxygenated blood?
Pulmonary artery
60
New cards
Which vein of the head and neck is formed by the drainage of venous blood from the pterygoid plexus?
Maxillary vein
61
New cards
Which artery provides blood flow to the floor of the mouth?
Lingual artery
62
New cards
What is the correct direction of the blood flow through the heart?
Right atrium - tricuspid valve - right ventricle - pulmonary artery (deoxygenated blood) - lungs -pulmonary vein (oxygenated blood) - left atrium - mitral valve - left ventricle - aorta
63
New cards
The volume of blood pumped per minute by each ventricle is the:
Cardiac output (CO)
64
New cards
Exocrine Glands
Salivary Glands
Parasympathetic stimulation: evokes a copious flow of saliva
Sympathetic stimulation: produces either a small flow which is rich in protein or no flow at all
\
Both are exocrine glands and have associated ducts which drain saliva into the oral cavity
Parasympathetic stimulation: evokes a copious flow of saliva
Sympathetic stimulation: produces either a small flow which is rich in protein or no flow at all
\
Both are exocrine glands and have associated ducts which drain saliva into the oral cavity
65
New cards
Parodid
Largest salivary gland
25% of saliva produced
Facial nerve passes through parotid DOES NOT innervate
Stenson’s duct or parotid duct (empties opposite maxillary molars)
25% of saliva produced
Facial nerve passes through parotid DOES NOT innervate
Stenson’s duct or parotid duct (empties opposite maxillary molars)
66
New cards
Submandibular
2nd largest salivary gland
Produces 60-65% of total volume
Wharton’s duct or submandibular duct (anterior of the floor of the mouth, empties into caruncle)
Most common gland to be associated with a salivary stone or Sialoliths
Produces 60-65% of total volume
Wharton’s duct or submandibular duct (anterior of the floor of the mouth, empties into caruncle)
Most common gland to be associated with a salivary stone or Sialoliths
67
New cards
Sublingual
Smallest
Produces 10% of total volume
Bartholin’s duct or sublingual duct, near the midline of the the floor of the mouth on each side of the lingual frenum
Also empties along the sublingual fold known as the Rivinus ducts
Both ducts empty at caruncle
Produces 10% of total volume
Bartholin’s duct or sublingual duct, near the midline of the the floor of the mouth on each side of the lingual frenum
Also empties along the sublingual fold known as the Rivinus ducts
Both ducts empty at caruncle
68
New cards
Von Ebner’s glands
Minor salivary glands
Found at circumvallate papillae
Secrete serous fluid
Facilitate perception of taste through secretion of digestive enzymes and proteins
Found at circumvallate papillae
Secrete serous fluid
Facilitate perception of taste through secretion of digestive enzymes and proteins
69
New cards
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Cerebrum, brainstem, cerebellum, and spinal cord
70
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Nerve ganglion, nerve, afferent (sensory) nerve from skin and efferent (motor) nerve tp muscle that stretch from the CNS
71
New cards
Cervical nerves
Composed of 8 nerve pairs arising from the spinal cord distributed in other parts of the body such as the skin, skeletal muscles, and blood vessels (C1-C8)
72
New cards
Cranial nerves
Composed of 12 pairs that arise from the brain and are distributed in the head, neck, and facial regions (I-XII)
73
New cards
Action potential
Rapid depolarization of the cell membrane that results in propagation of the nerve impulse along the membrane
74
New cards
Afferent nerve (arrive)
Sensory nerve that carries information from the periphery of the body to the brain or spinal cord
75
New cards
Efferent (exit)
Motor nerve that carries info away from the brain and spinal cord to the periphery of the body
76
New cards
Innervation
Supply of nerves to tissue or organs
77
New cards
Nerve
Bundle of neural processes outside of CNS
Part of the PNS
Part of the PNS
78
New cards
Synapse
Junction between two neurons or between a neuron and effector organ, where neural impulses are transmitted by electrical or chemical means
79
New cards
Cranial Nerves
1 Olfactory
2 Optic
3 Oculomotor
4 Trochlear
5 Trigeminal
6 Abducens
7 Facial
8 Vestibulocochlear
9 Glossopharyngeal
10 Vagus
11 Accessory
12 Hypoglossal
2 Optic
3 Oculomotor
4 Trochlear
5 Trigeminal
6 Abducens
7 Facial
8 Vestibulocochlear
9 Glossopharyngeal
10 Vagus
11 Accessory
12 Hypoglossal
80
New cards
1 Olfactory
Smell
81
New cards
2 Optic
Vison
82
New cards
3 Oculomotor
Eye muscles of the eye
83
New cards
4 Trochlear
superior oblique eye muscles
84
New cards
5 Trigeminal
Sensory from face and mouth
Motor to muscles of mastication (chewing)
Motor to muscles of mastication (chewing)
85
New cards
6 Abducens
Lateral rectus of eye muscles
86
New cards
7 Facial
Serves the muscles of facial expression, lacrimal glands, and salivary glands
87
New cards
8 Vestibulocochlear
Equilibrium and hearing
88
New cards
9 Glossopharyngeal
Serves the pharynx (throat) for swallowing, posterior third of the tongue and parotid salivary gland
89
New cards
10 Vagus
Sensations from visceral (internal) organs and parasympathetic motor regulation of visceral organs
90
New cards
11 Accessory
Serves muscles that move head, neck, and shoulders
91
New cards
12 Hypoglossal
Serves muscles of the tongue
92
New cards
Sensory or Motor CN Mnemonic
Some Say Marry Money, But My Brother Says Big Boobs Marry Money
93
New cards
V1
Ophthalmic
Sensory Only
Through the super orbital fissure
Sensory Only
Through the super orbital fissure
94
New cards
V2
Maxillary
Sensory Only
Through foramen rotundum to pterygopalatine fossa
Sensory Only
Through foramen rotundum to pterygopalatine fossa
95
New cards
V3
Through foramen ovale to infratemporal fossa
Sensory and Motor
Sensory and Motor
96
New cards
CN VII Facial Nerve
Serves the:
Muscles of facial expression
Posterior suprahyoid muscles
Lacrimal gland
Sublingual gland
Submandibular gland
Tongue part
Part of skin through its greater petrosal
Chorda tympani
Posterior auricular nerves
Muscular branches
Motor and Sensory
Muscles of facial expression
Posterior suprahyoid muscles
Lacrimal gland
Sublingual gland
Submandibular gland
Tongue part
Part of skin through its greater petrosal
Chorda tympani
Posterior auricular nerves
Muscular branches
Motor and Sensory
97
New cards
PSA Block
Maxillary molars bucccal / pulpul (except for MB root of 1st molar)
98
New cards
MSA Block
Max premolars buccal/pulpul and MB root of 1st molar
99
New cards
IO Block and ASA
Maxillary incisors, canine facial/pulpul and premolars buccal/pulpul
100
New cards
NP Block
Maxillary incisors and canine lingual