[MDCU] Abortion and ectopic pregnancy
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What is the threshold of viability of a baby born in KCMH?
GA 22 weeks
Birth weight >500 g
Early pregnancy loss is defined as a nonviable intrauterine pregnancy with ___ occurring before GA ___
CRL >7 mm + no fetal heart beat
Gestational sac >25 mm
Occurs before GA 13 weeks
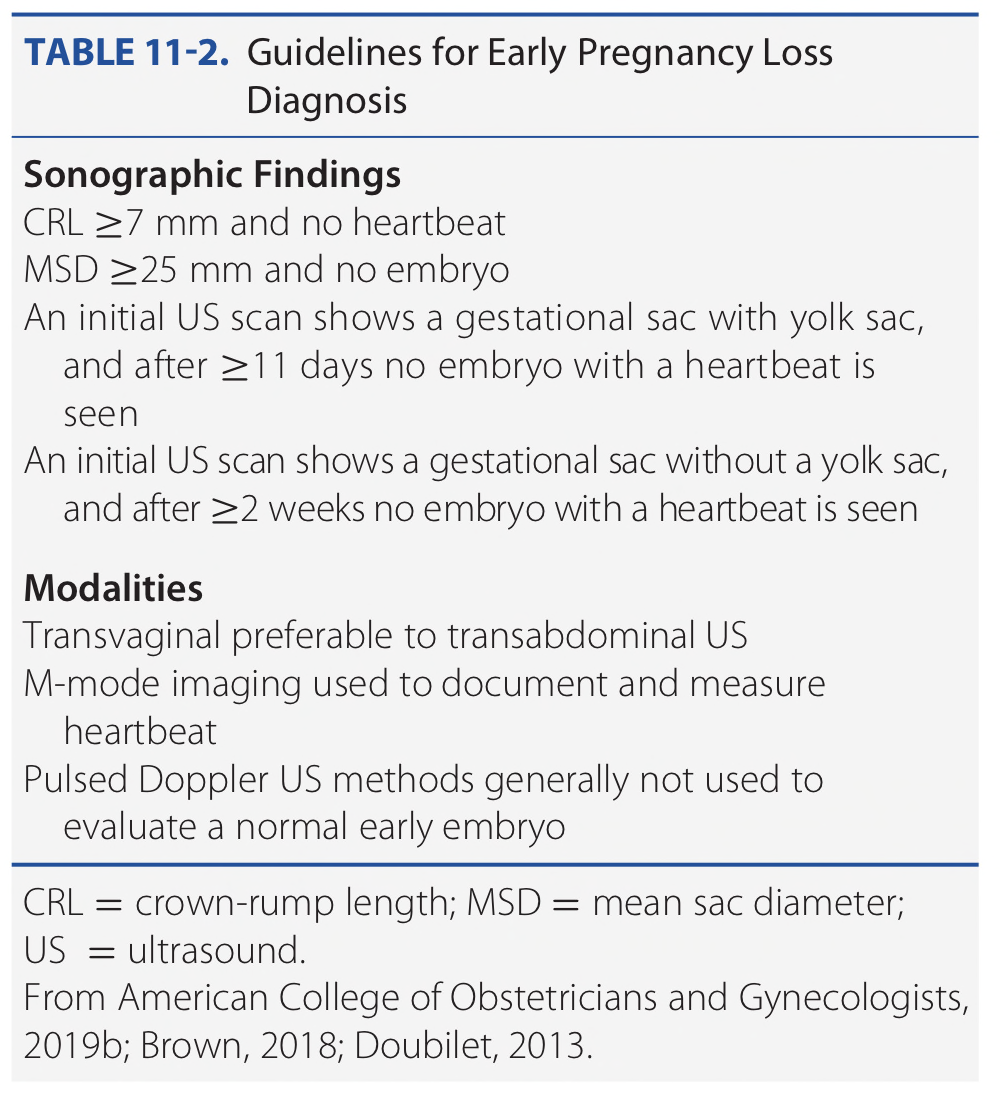
80% of spontaneous abortion occur before GA ___
GA 12 weeks

Chromosomal abnormality responsible for ___ % of abortions in the 1st trimester
55%
95% of autosomal trisomy resulting in spontaneous abortion is caused by ___?
Maternal gametogenesis error
Removal of corpus luteum before GA ___ most likely results in abortion
GA 10 weeks
What is the presentation of threatened abortion?
Uterine size = ___
Vaginal bleeding
Closed cervical os
Uterine size = gestational age
___% of threatened abortion will result in actual abortion
50%
Except present cardiac activity (<5%)
The risk for the threatened abortion to actually abort will be significantly lower if ___
Fetal cardiac activity is present
50% → <5%
What is the management of threatened abortion?
Speculum examination → ensure os close
Ultrasound → viability & locate pregnancy
Bed rest, abstinence, follow-up
What is the definition of blighted ovum?
Mean gestational sac diameter >25 mm with no embryo
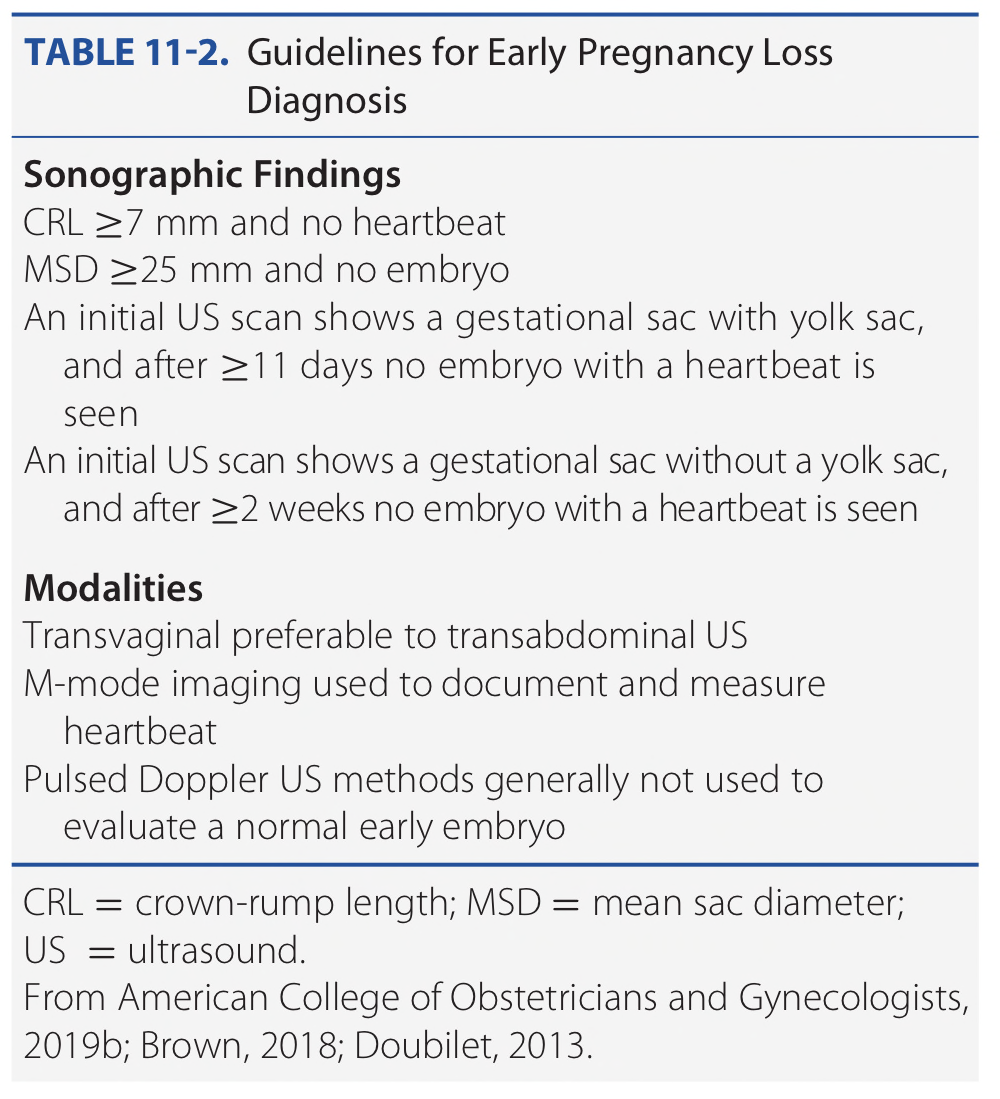
What is the definition of embryonic death?
CRL >7 mm with no fetal heartbeat
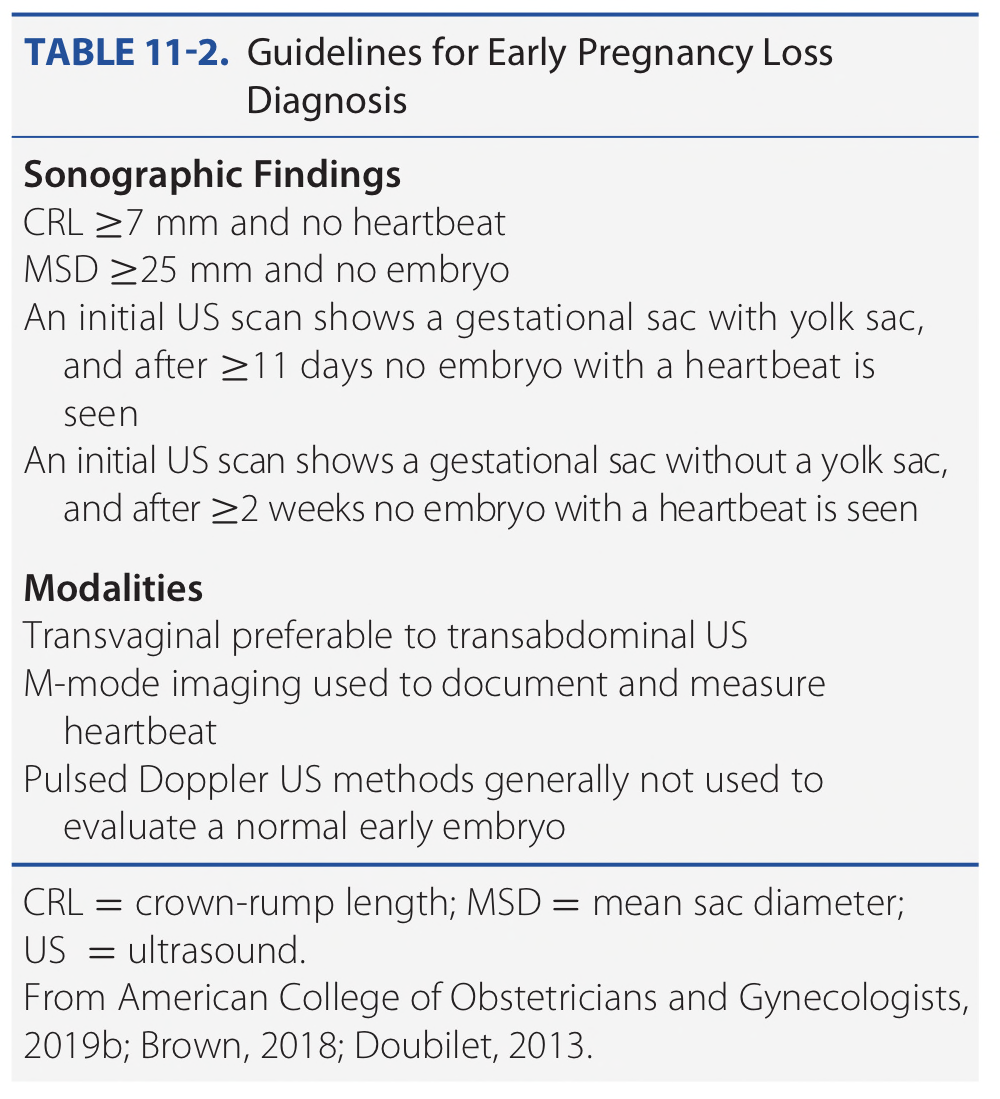
What is the presentation of inevitable abortion?
Vaginal bleeding
Uterine contraction
Cervical dilatation
Gross rupture of membranes
What is the presentation of imminent abortion?
Vaginal bleeding
Uterine contraction
Cervical dilatation
Gross rupture of membranes
What is the management of inevitable abortion?
Termination of pregnancy based on uterine size
<12 week : curettage
>12 week : oxytocin 10-20 u drip in NSS 1,000
Incomplete abortion
Os
Uterine size
Partial expulsion of conceptive product
Os open
Uterine size < gestational age
What is the complication and management of incomplete abortion?
Severe bleeding
Conservative + blood transfusion
Uterine evacuation (D&C)
Oxytocin
Missed abortion is defined as a dead products of conception that were retained for ___ with a closed cervical os.
>8 weeks
What are 4 signs & symptoms of missed abortion?
Disappearing signs and symptoms of pregnancy
Uterine size gradually becomes smaller
Threatened abortion
Persistent amenorrhea
Whais is the management of missed abortion
Termination of pregnancy
Medabon
D&C, MVA
Complication: perforation, coagulopathy from tissue thromboplastin
What is the presentation of septic abortion?
Fever, pelvic pain, abortion
Endomyometritis → peritonitis, septicemia
DIC
Management of septic abortion
__
__
__
__
__
Resuscitation, blood transfusion
Septic workup
IV Gentamicin + Clindamycin
Uterine evacuation after 4-6 hours
TT + TAT
What is the presentation of cervical incompetence?
Painless cervical dilatation in 2nd trimester
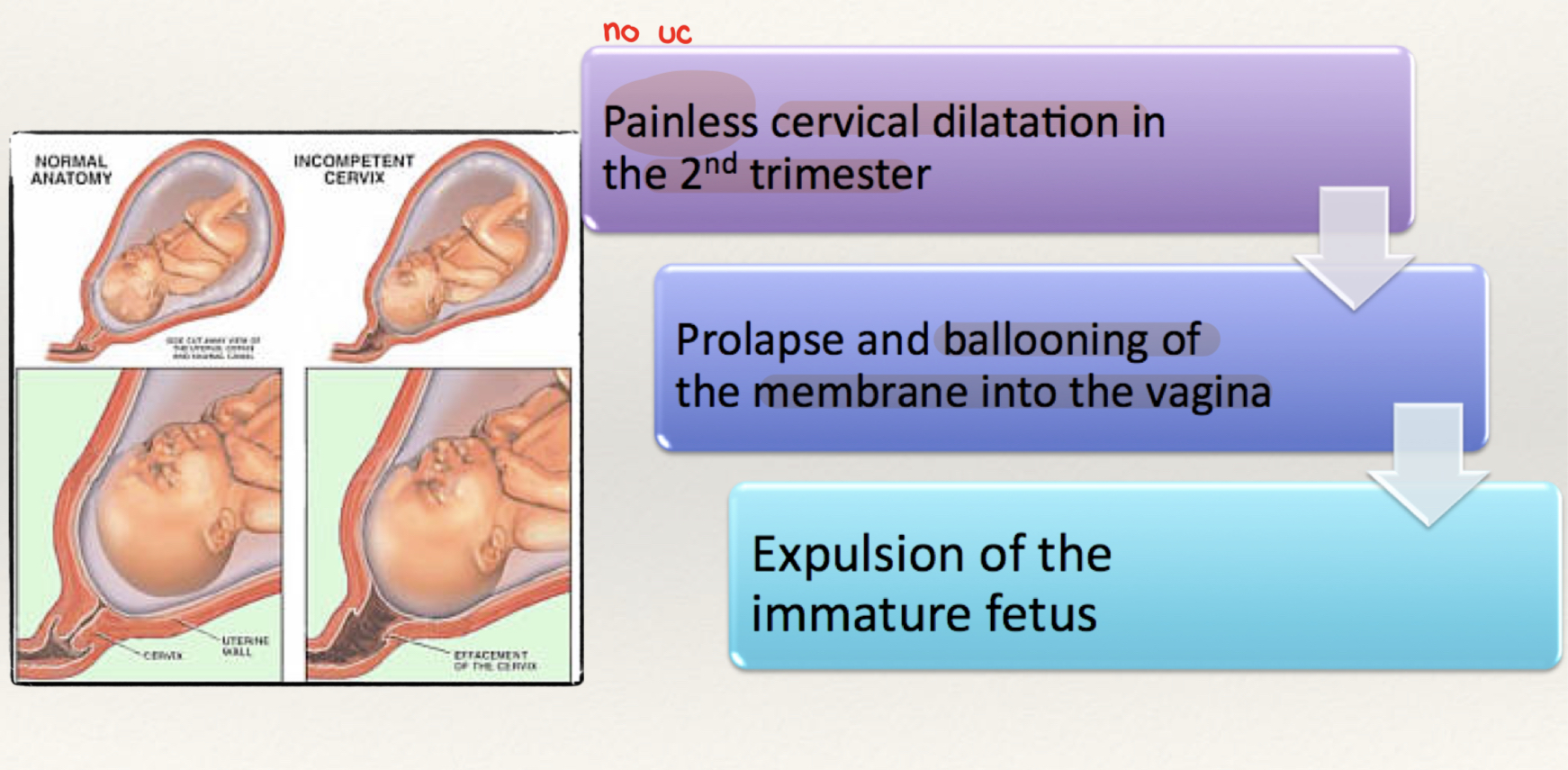
What are risk factors of incompetent cervix?
D&C
Conization
Exposure to DES in utero
Timing for elective and emergency cervical cerclage
Elective GA 12-14
Emergency GA <23
What is the most common cause of recurrent miscarriage?
Uterine anatomical defect, incompetent cervix
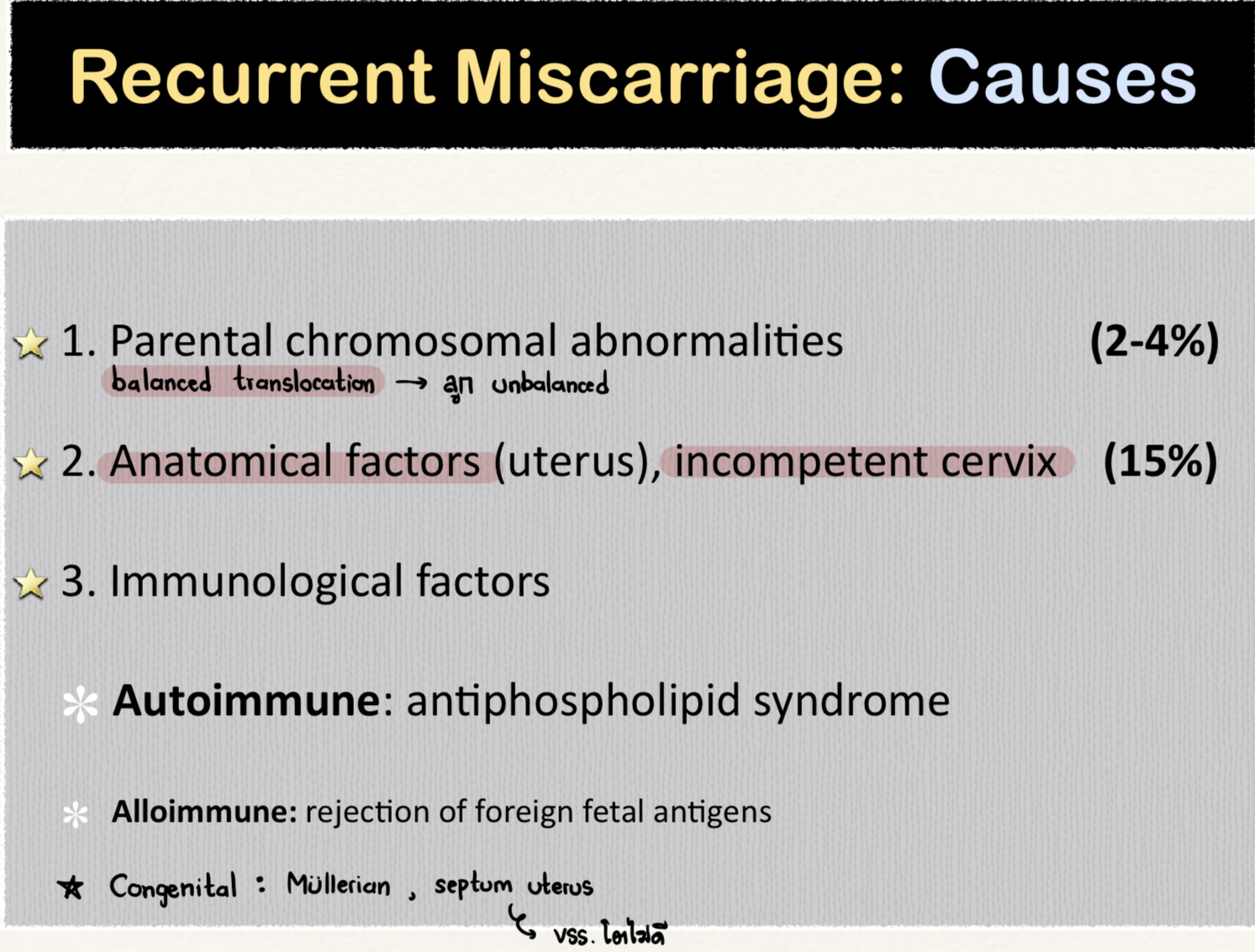
Which test should be done to investigate recurrent abortion?
Hysteroscopy
Thyroid function test (TSH, anti-TPO)
Anti-phospholipid Ab

Which surgical technique should be used for TOP in the 1st trimester?
D&C
MVA
Menstrual aspiration
Which surgical technique should be used for TOP in the 2nd trimester?
Hysterotomy
Hysterectomy
Dilatation and extraction / evacuation
What are complications of dilatation & curettage?
Uterine perforation
Visceral organ injury
Infection
Incompetent cervix
Uterine synechiae
What are drugs used for medical abortion?
Prostaglandin E1 / E2 / F2a (Misoprostol)
Anti-progesterone (Mifepristone)
Oxytocin IV drip
What is the mechanism of action of misoprostol in abortion?
Cervical collagen degradation
Uterine contraction
What is the mechanism of action of mifepristone in abortion?
Anti-progestin → uterine contraction
What is the drug component of Medabon?
Misoprostol 200 mcg
Mifepristone 200 mg
What is the most common site of ectopic pregnancy?
Ampullary pregnancy
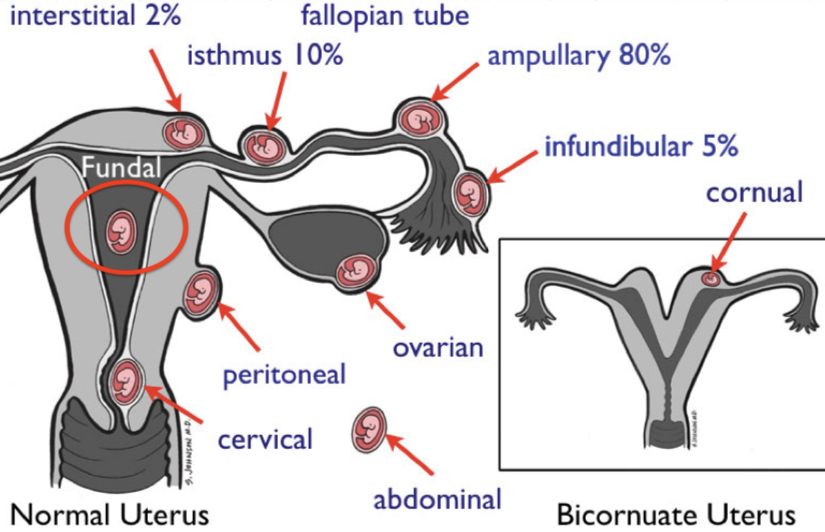
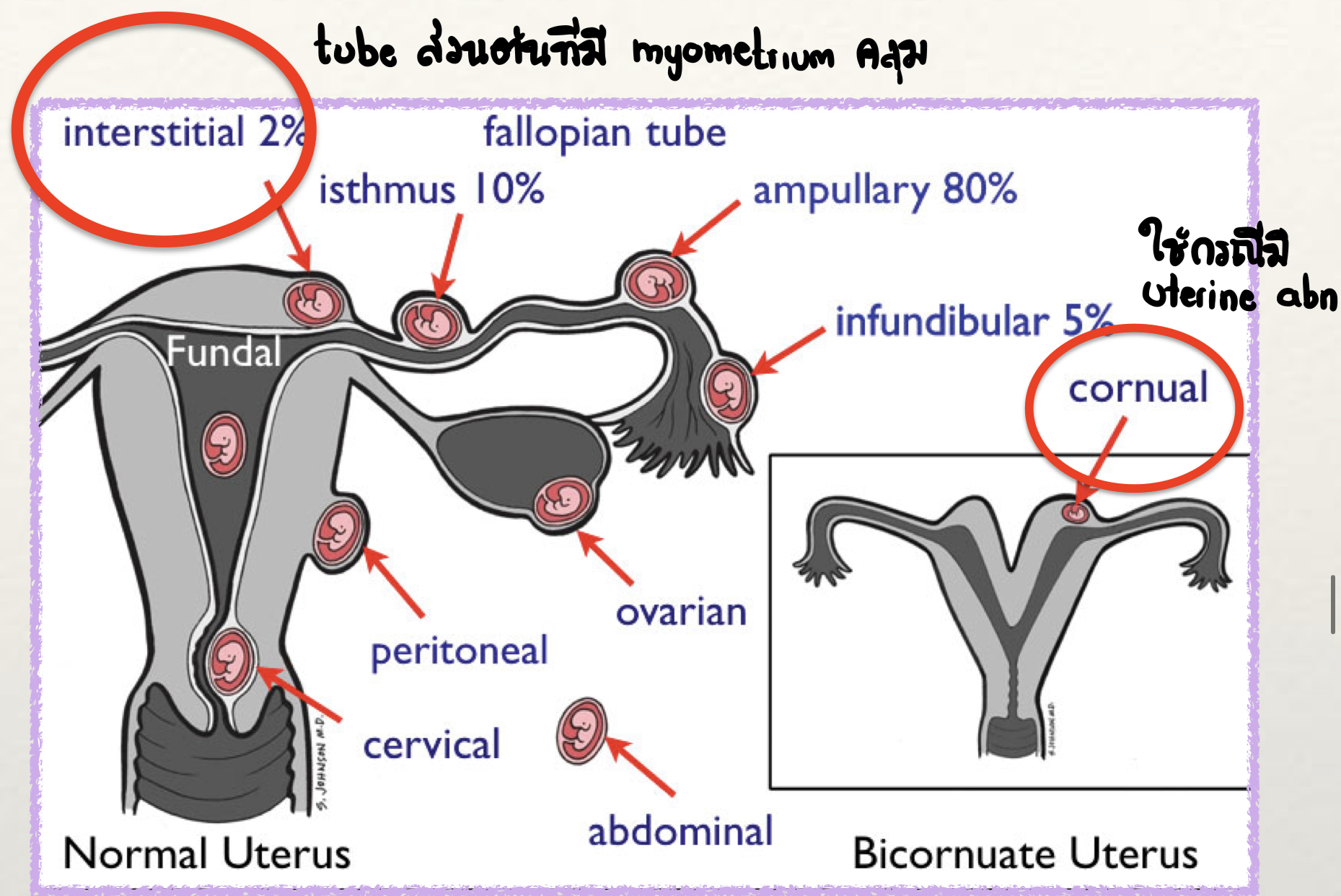
Interstitial pregnancy is defined as an implantation at ___
Proximal intramural portion of the tube
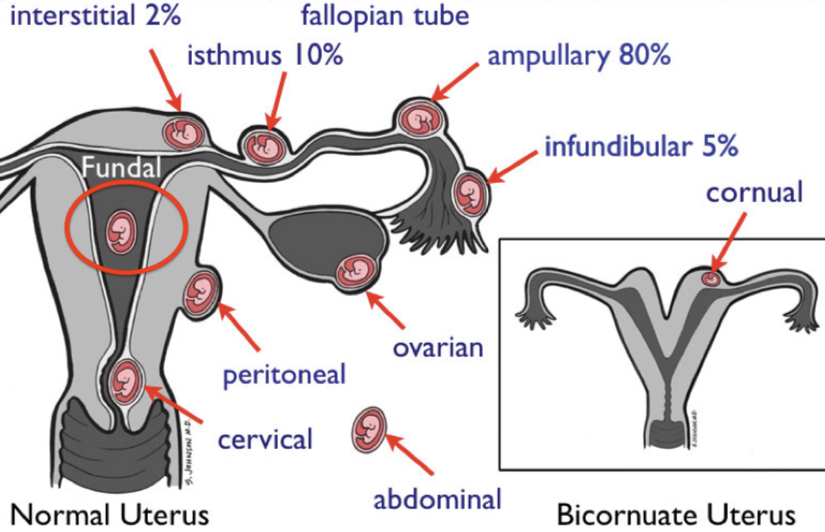
Cornual pregnancy is defined as an implantation at ___
Rudimentary horn of a uterus with a Müllerian anomaly
What are risk factors for heterotopic pregnancy?
Previous ectopic pregnancy
Tubal sterilization, IUD
Tubal corrective surgery
Documented tubal pathology
ARTs
Peritubal adhesion
What is the most common type of abortion in ampullary pregnancy?
Tubal abortion
What is the classic triad of tubal pregnancy?
Missed period
Pain (pelvic / abdominal)
Vaginal bleeding
What are the signs of tubal pregnancy?
AT BUS
Abdominal distension
Tenderness (cervical motion, adnexal)
Bulging of posterior fornix
Uterine pushed to one side
S&S of abdominal hemorrhage
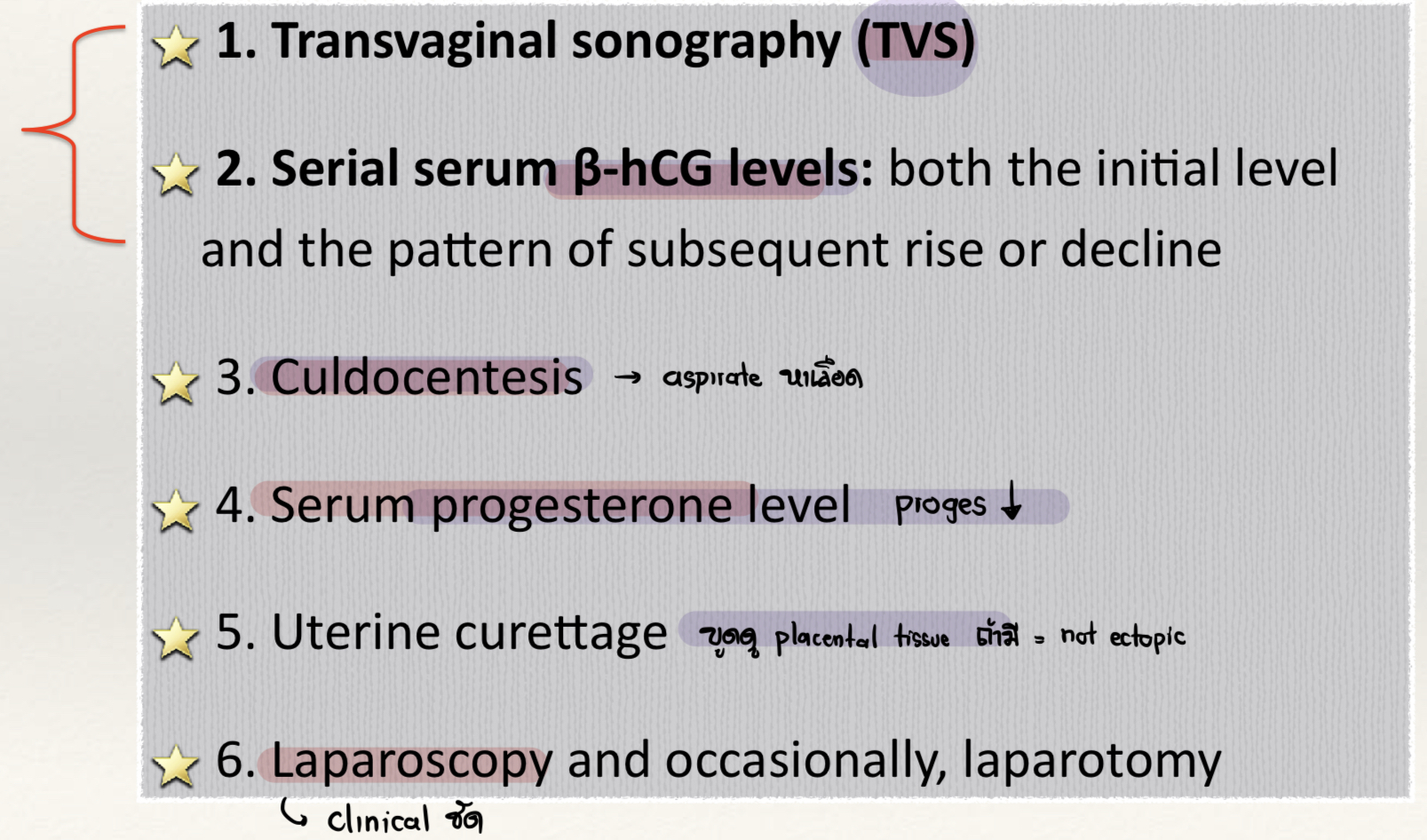
Which test is used to diagnose ectopic pregnancy?
Serial hCG
TVS
Discriminatory level = 1,500-2,000 MIU/ml
Serum progesterone in ectopic pregnancy is ___ (↑ / ↓)
Progesterone ↓
Discriminatory level of β hCG
1,500 - 2,000 mIU/ml
ควรเห็น gestational sac แล้ว
Which sonographic finding, if present, implies an ectopic pregnancy?
Positive β hCG assay
Absent intrauterine pregnancy
Free fluid in cul-de-sac
Abnormal tubal mass (ring of fire)
What is the lowest increase of β hCG in intrauterine pregnancy after 48 hours of sampling?
53-66%
Normal = doubling time
What is the gold standard of diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy?
Laparoscopic diagnosis
What is the indication of salpingectomy?
Ruptured ectopic pregnancy
Combined pregnancy
What are contraindications for methotrexate in treatment of ectopic pregnancy?
“ABCD”
Active intra-abdominal bleeding
Breastfeeding
Chronic liver / kidney / lung disease
Disorder of blood
Pregnancy
Patients eligible for methotrexate treatment of ectopic pregnancy
β hCG <5,000 mIU/ml
Size <3.5 cm
No fetal cardiac activity
Asymptomatic / mild symptom
Patients eligible for expectant treatment of ectopic pregnancy
Tubal pregnancy only
Declining hCG (initial <1,000)
Size <3 cm
No rupture / bleeding
Counseling for potential tubal rupture ***