Chapter 3- Interlude A
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Atoms
Building blocks of minerals
Elements form chemical bonds with other elements to form chemical compounds
Neutron and Protons (+) in the nucleus
Electrons (-)
Types of Atomic Bonds
Ionic Bond
Between positively and negatively charged atoms (ions)
Coulomb’s Law: opposite charges attract
Covalent Bond
Between atoms sharing valence electrons
Metallic Bond
Each atom contributes to a pool of valence electrons
Gives metals their electrical conductivity
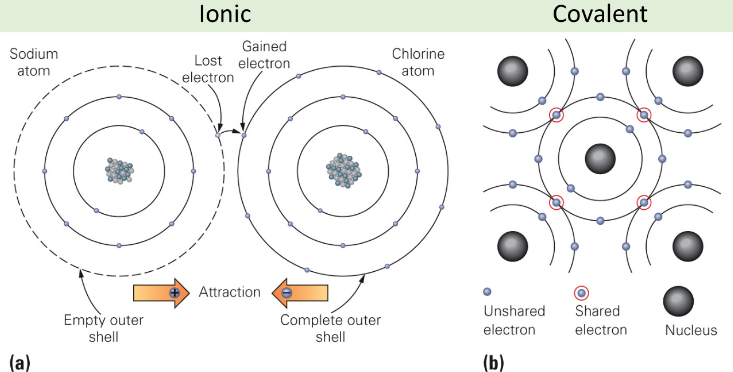
Ionic Bonding of Sodium Chloride
A- the transfer of an electron from a sodium (Na) atom to a chlorine (Cl) atom leads to the formation of a Na ion and a Cl ion
B- The arrangement of Na and Cl in the Solid ionic compound sodium chloride (NaCl) AKA halite, salt
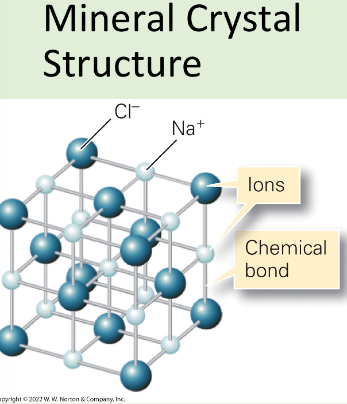
Lattice
3D array of regular spaced points
Crystalline material
Atoms situated in a repeating 3D array
Amorphous materials
Material with no such order
Unit cell
Basic building block unit (such as a flooring tile) that repeats in space to create the crystal structure.
Mineral
1- Naturally Occuring
2- Inorganic
3- Solid
4- Ordered crystal structure
5- Definite chemical composition
Rock
A solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter that occurs naturally
Crystalline Structures
Crystalline: most solid materials
Glasses: solids lacking internal atomic order (aka amorphous)
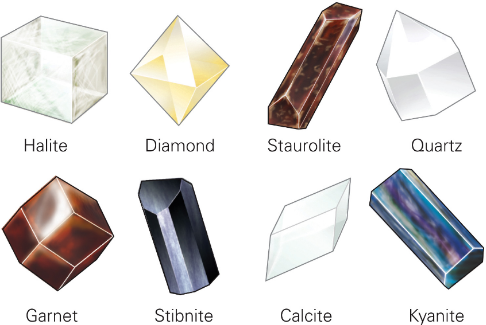
Crystal
A single, continuous piece of crystalline solid typiclly bounded by flat crystal faces.
Ordered atomic arrangement inside minerals imparts symmetry to crystals
Equivalent faces found on two samples of the same mineral always bear the same angular relationship.
Types of Mineral Crystals
Polymorphs
Minerals that share the same chemical composition but have different crystal structures.
Synthetic Minerals
“Man-made” lab-grown equivalents to minerals
Mineral Formation
Crystallization of a melt
Precipitation from aqueous solution
Precipitation by organisms (biomineralization)
Crystal Growth
Early crystals act as a seed for further growth of the mineral
As crystals grow, they often encounter other growing crystals
Mineral growth is often restricted by space, which prevents development of good crystal faces.
Mineral Identification
Based on:
Color: can be diagnostic of some minerals, but poor indicator for others.
Luster
Streak
Hardness
Specific gravity
Crystal habit
Cleavage
Reaction to acid
Fracture tendency
Luster
The way a mineral surface scatters light, can tell us if it is metallic or nonmetallic.
Streak
Color of a mineral in powdered form, rubbed against a streak plate. Mostly useful to identify metallic minerals.
Hardness
Measure of resistence to abrasion or scratching. Mohs Scale of Relative Hardness. Diamond is the hardest (10), Talc the softest (1)
Crystal habit
Common of characteristic shape of individual crystals or aggregates of crystals.
Cleavage
The tendency of mineral to break along plans of weak bonding.
Described as the number of cleavage directions/planes and the angles at which they meet. e.g. two planes at 90 degrees

Fracture
When a mineral has no weak bonds, it will fractire )it has no cleavage planes)

Density- Specific Gravity
Ratio of minerals weight to wieight of equal volume of water
Most common minerals: 2-3
Metallic minerals higher, more dense.
Other distinctive properties
Reaction with acid (effervescence) e.g. Calcite reacts with acid
Magnetism, e.g. Magnetite
Taste, e.g. Halite (salt)
Smell, e.g. Sulfur
Feel, e.g. Talc (feels greasy)
Double refraction, e.g. (calcite or quartz)
What elements make up the majority of earth’s rock-forming minerals?
Silicon (Si)
Oxygen (O)
Aluminum (Al)
Iron (Fe)
Calcium (Ca)
Potassium (K)
Magnesium (Mg)
Minerals that make up most of the Earth
Silicates
Feldspars
Quartz
Amphiboles
Micaas
Olivine
Garnet
Pyroxene
Calcite (not a silicate)
Common Mineral Groups
Minerals that share the same basic “building block”
Silicates (SiO4)
Sulfides (S2)
Oxides (O2)
Halides (Cl1,F1,Br1)
Carbonates (CO3)
Sulfates (SO4)
Native elements
Silicates
Most abundant class of minerals in Earth’s crust
Oxygen and Silican in combination
Classified into:
Mafic (less % silica)
Felsic (more % silica)
Quartz
Olivine
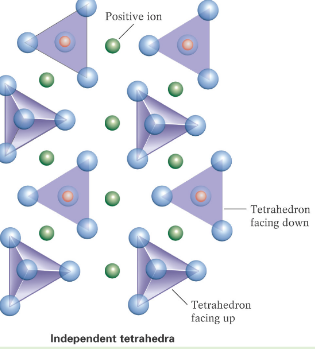
Isolated Tetrahedra Silicates
Do not share any oxygens, they are bonded together by cations.
Garnet and Olivine
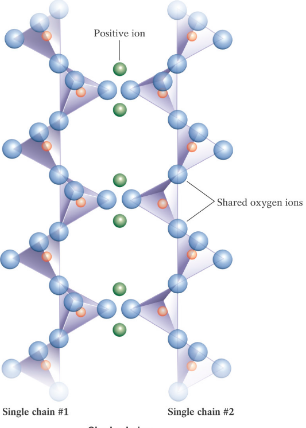
Single-Chain Silicates
Form chains by sharing two oxygen atoms.
Pyroxene
Double-chain silicates
Share two or three oxygen atoms
Amphibole
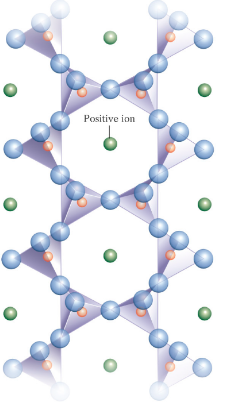
Sheet Silicates
All tetrahedra share two or three oxygens to form 2D sheets
Have cleavage in one direction
Muscovite Mica and Biotite Mica
Framework Silicates
Share all four oxygens
Form 3D structure
Feldspars
What holds a rock together?
Clastic rocks: Natural cement bonds together the grans of some rocks (sndstone)
Crystalline rocks: others are held together with interlocking minerals crystals (granite)
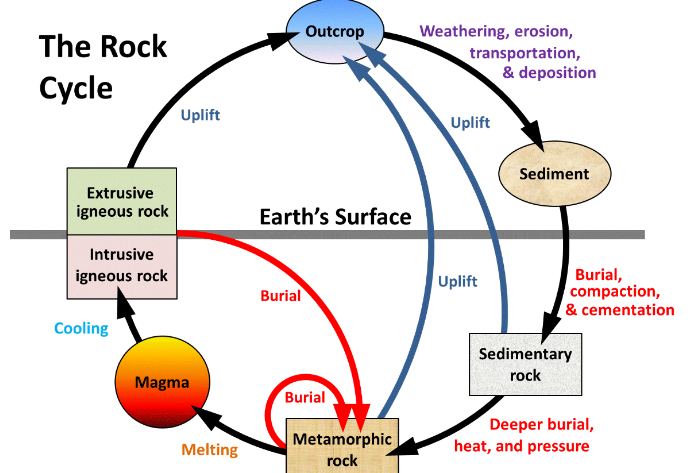
Bedrock
Rock that remains attached to the Earth’s crust
An exposure of berock is called an outcrop
Bedrock exposures can be either natural or man-made
Rock cycle
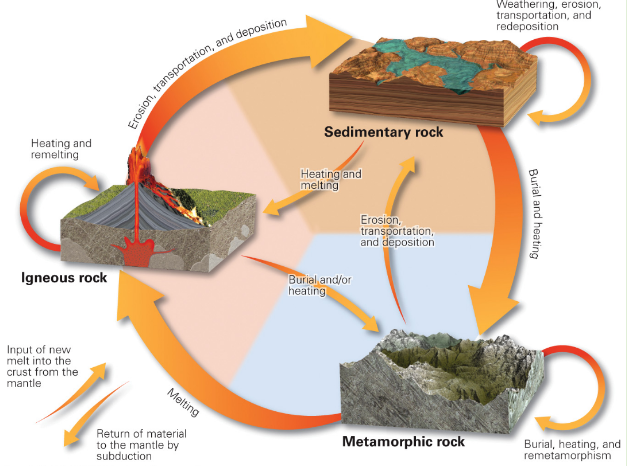
Other Rock Cycle diagram