f - Ionic bonding
1/19
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Ions form…
when atoms lose/gain electrons
Negative ions (anions) form when atoms gain electrons
Positive ions (cations) form when atoms lose electrons
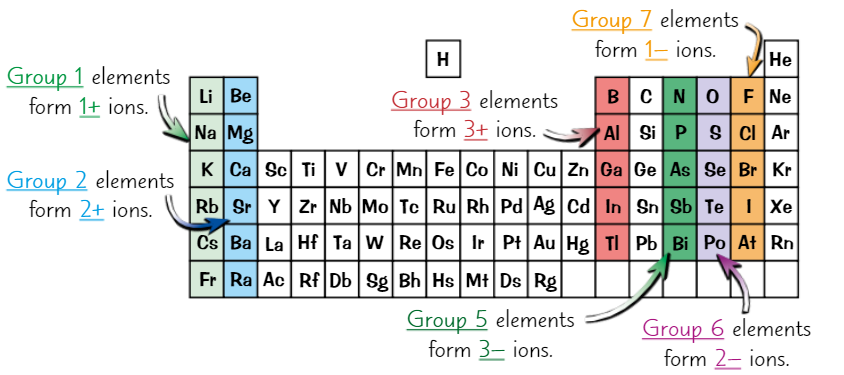
Using group number to predict ions formed
Groups 1, 2, 3 are metals. They lose electrons to form +ve ions.
Groups 5, 6, 7, are non-metals. They gain electrons to form -ve ions.
Elements in same group have same number of electrons in outer shell
So can lose/gain same number of outer electrons
So form ions with same charge
Silver
Ag⁺
Copper
Cu²⁺
Iron(II)
Fe²⁺
Iron(III)
Fe³⁺
Lead
Pb²⁺
Zinc
Zn²⁺
Hydrogen
H⁺
Hydroxide
OH⁻
Ammonium
NH₄⁺
Carbonate
CO₃²⁻
Nitrate
NO₃⁻
Sulfate
SO₄²⁻
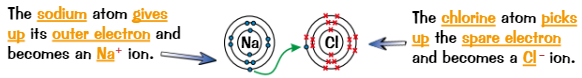
Ionic compounds are produced by…
transfer of electrons
When metal + non-metal react, metal atom loses electrons to form positive ion and non-metal gains these electrons to form negative ion
Formula of ionic compounds
Ionic compounds are made up of positively charged part + negatively charged part
Overall charge of ionic compound = 0
So negative charges must balance positive charges

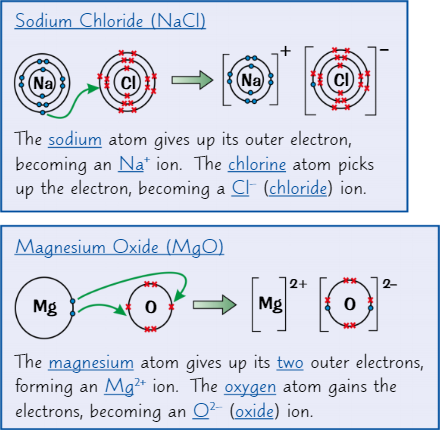
Ionic dot and cross diagrams
Dots represent electrons from one of the atoms
Crosses represent atoms from the other atom
Ionic bond
Electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions
Giant ionic lattice
Compounds with ionic bonding have giant ionic structures
Ions held together in closely packed 3D lattice
Electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions is very strong
→ a lot of energy needed to overcome strong attraction
→ high melting + boiling points
Ionic compound electrical conductivity
Solid - don’t conduct electricity
Molten/in aqueous solution - conduct electricity