Microbio Exam 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/239
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 12:02 AM on 5/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
240 Terms
1
New cards
Aerobic Respiration
Catabolic reaction that collects the most energy (38 ATP per Glucose)
\
1. Glycolysis (8 ATP)
1. Glucose + 2 NAD+ → 2 Pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH
2. 2 NADH + Oxidative Phosphorylation → 6 ATP
2. CAC (15 ATP x2)
1. Pyruvate + 4 NAD+ + GDP + FAD → 3 CO2 + 4 NADH + FADH2 + GTP
2. 4 NADH + Oxidative Phosphorylation → 12 ATP
3. 1 FADH2 + Oxidative Phosphorylation → 2 ATP
\
Involves:
* Glycolysis
* The Krebs Cycle
* The ETS
\
1. Glycolysis (8 ATP)
1. Glucose + 2 NAD+ → 2 Pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH
2. 2 NADH + Oxidative Phosphorylation → 6 ATP
2. CAC (15 ATP x2)
1. Pyruvate + 4 NAD+ + GDP + FAD → 3 CO2 + 4 NADH + FADH2 + GTP
2. 4 NADH + Oxidative Phosphorylation → 12 ATP
3. 1 FADH2 + Oxidative Phosphorylation → 2 ATP
\
Involves:
* Glycolysis
* The Krebs Cycle
* The ETS
2
New cards
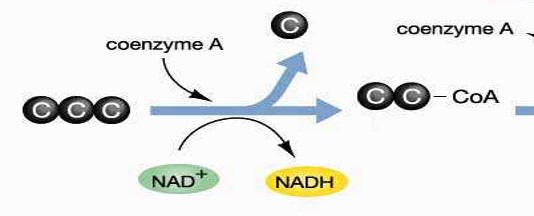
Glycolysis of Pyruvic Acid
Preparation for the Krebs Cycle in Aerobic Respiration
\
Pyruvic acid (3C) → acetyl CoA (2C) + CO2
1 NADH formed per pyruvate conversion
\
Pyruvic acid (3C) → acetyl CoA (2C) + CO2
1 NADH formed per pyruvate conversion
3
New cards
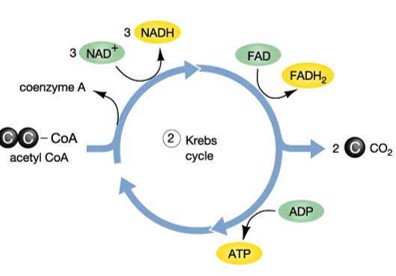
Krebs Cycle
An oxidative metabolic pathway that starts with Acetyl Co A and produces CO2 and NADH
\
Repetitive cycle involving 9 carbon compounds used in Aerobic Respiration
\
Primed w/ Glycolysis of Pyruvic Acid to create Acetyl CoA (2C)
\
1. Acetyl group (2C) + Oxaloacetic acid (4C) → Citric acid (6C)
2. Citric acid (6C) → 7 steps → Oxaloacetic acid (4C)
\
Generates many compounds available for Biosynthetic purposes:
1. Alpha Ketoglutarate
2. Oxaloacetate
3. Succinyl-CoA
4. Acetyl-CoA
NADH + 1 FADH2 formed per acetyl group
1 GTP formed per acetyl group
\
Releases CO2
\
Fumarate → Succinate w/in this cycle, which is important to some bacteria:
* Escherichia coli
* Proteus sp.
* Enterococcus sp.
\
Repetitive cycle involving 9 carbon compounds used in Aerobic Respiration
\
Primed w/ Glycolysis of Pyruvic Acid to create Acetyl CoA (2C)
\
1. Acetyl group (2C) + Oxaloacetic acid (4C) → Citric acid (6C)
2. Citric acid (6C) → 7 steps → Oxaloacetic acid (4C)
\
Generates many compounds available for Biosynthetic purposes:
1. Alpha Ketoglutarate
2. Oxaloacetate
3. Succinyl-CoA
4. Acetyl-CoA
NADH + 1 FADH2 formed per acetyl group
1 GTP formed per acetyl group
\
Releases CO2
\
Fumarate → Succinate w/in this cycle, which is important to some bacteria:
* Escherichia coli
* Proteus sp.
* Enterococcus sp.
4
New cards
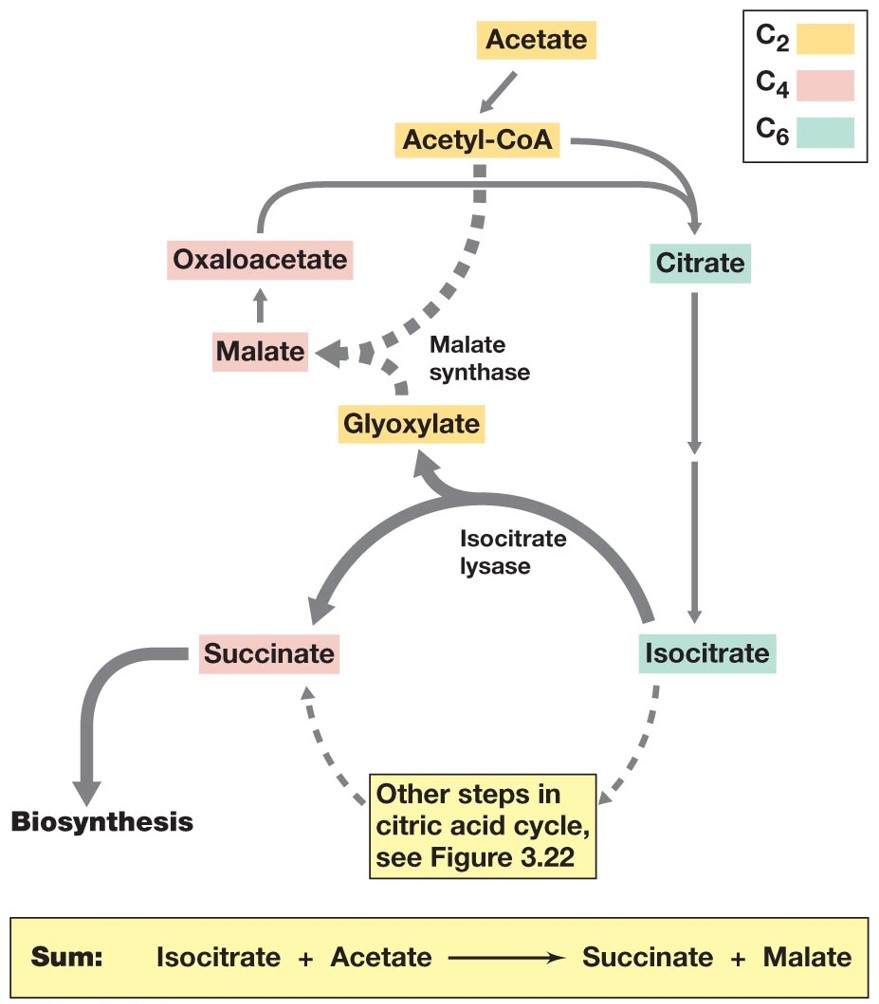
Glyoxylate Cycle
Involved in Aerobic Respiration
\
Catabolism of C2-C3 organic acids typically involves the Oxaloacetate produced through this cycle
\
Variation of the Krebs Cycle
\
Catabolism of C2-C3 organic acids typically involves the Oxaloacetate produced through this cycle
\
Variation of the Krebs Cycle
5
New cards
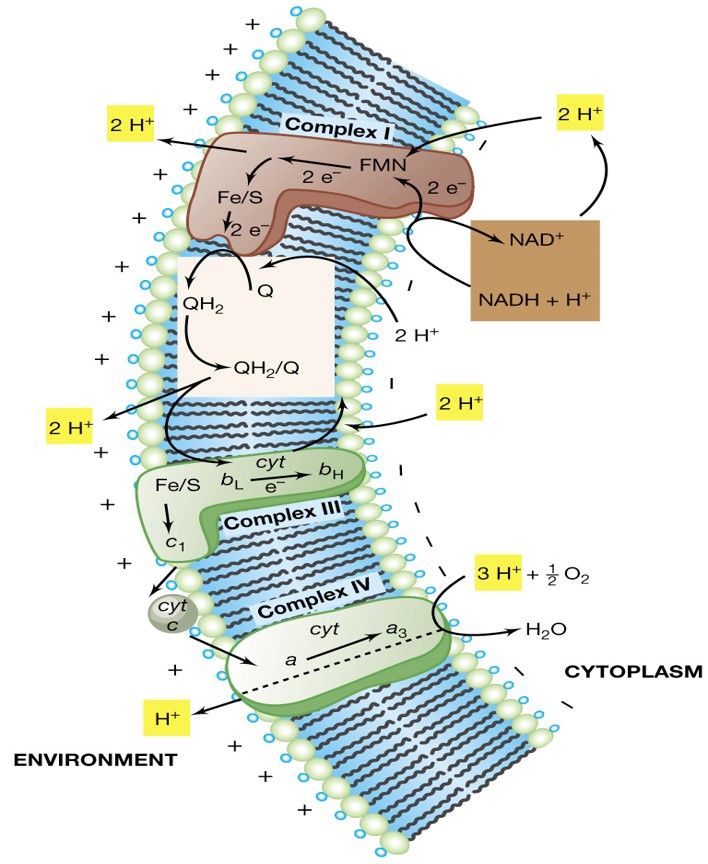
Electron Transport System (ETS)
Involved in Aerobic Respiration and located in Cell Membranes
\
Utilizes NADH and FADH2 formed in Glycolysis of Pyruvic Acid and Krebs Cycle
\
e- released to this system and provides energy for active transport of H+ from matrix to outside of membrane to form a membrane potential
\
The process by which NADH transfers electrons along a chain of acceptors to oxygen
\
Utilizes NADH and FADH2 formed in Glycolysis of Pyruvic Acid and Krebs Cycle
\
e- released to this system and provides energy for active transport of H+ from matrix to outside of membrane to form a membrane potential
\
The process by which NADH transfers electrons along a chain of acceptors to oxygen
6
New cards
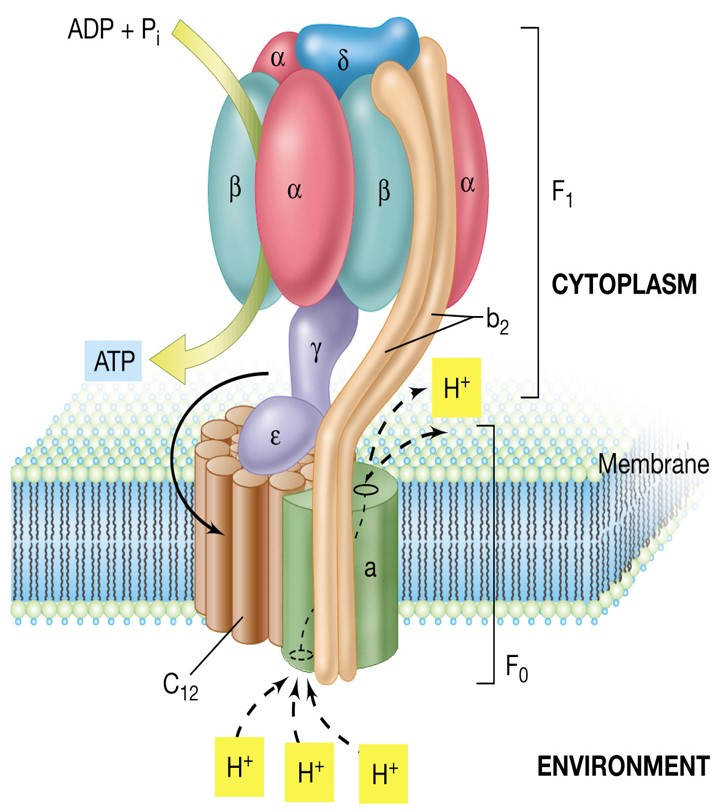
Chemiosmotic ATP Synthesis
Involved in Aerobic Respiration
\
e- released from ETS provides energy for active transport of H+ from matrix to outside of membrane to form a membrane potential
\
Movement of H+ down concentration gradient provides energy to make ATP from ADP and Pi
\
e- released from ETS provides energy for active transport of H+ from matrix to outside of membrane to form a membrane potential
\
Movement of H+ down concentration gradient provides energy to make ATP from ADP and Pi
7
New cards
Oxygen
The final acceptor for hydrogen ions in aerobic respiration
\
Terminal e- acceptor, important role in ETS and ATP synthesis in Aerobic Respiration
\
Superoxide dismutase and catalase work together to convert superoxide into this
\
Terminal e- acceptor, important role in ETS and ATP synthesis in Aerobic Respiration
\
Superoxide dismutase and catalase work together to convert superoxide into this
8
New cards
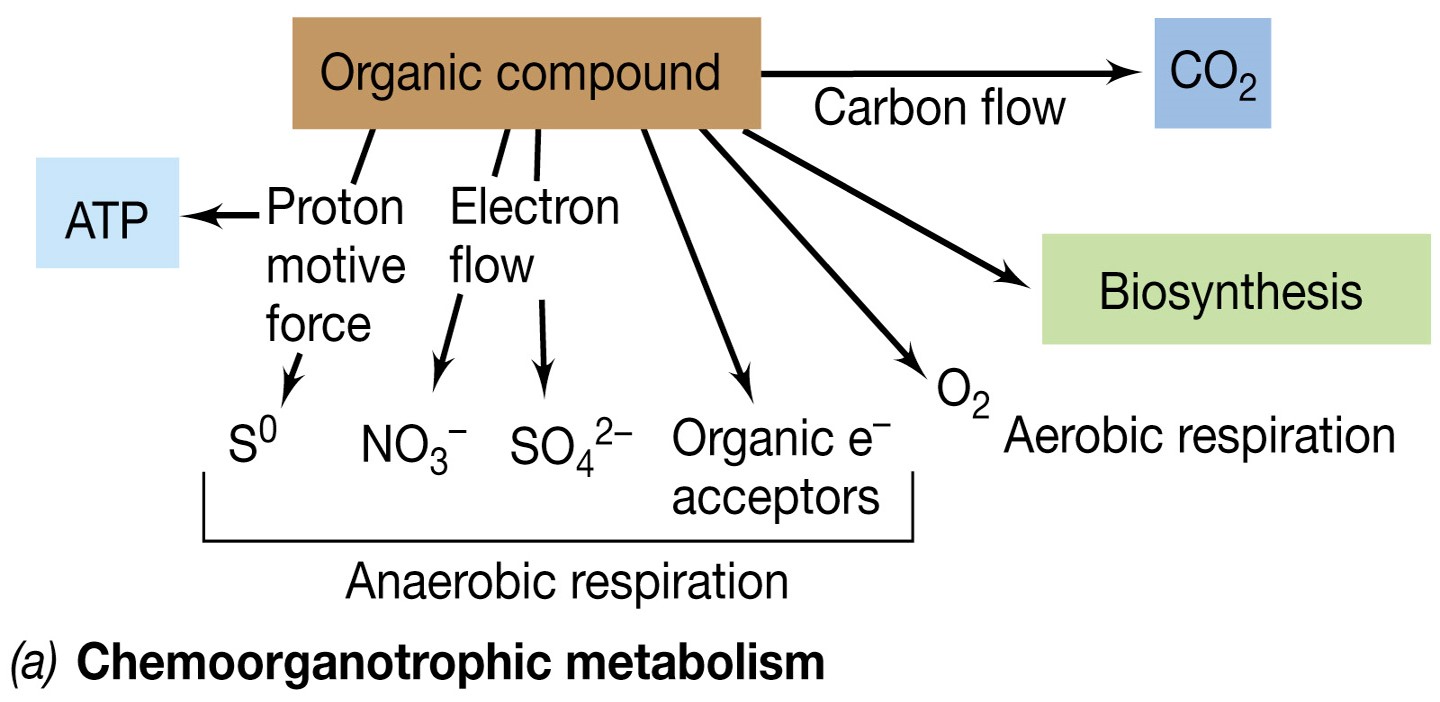
Anaerobic Respiration
The use of e- acceptors other than oxygen
\
Collects less energy compared to Aerobic Respiration
\
Completely dependent on ETS, generation of Proton Motive Force, and ATPase activity
\
Collects less energy compared to Aerobic Respiration
\
Completely dependent on ETS, generation of Proton Motive Force, and ATPase activity
9
New cards
Facultative Anaerobes
Microbes that use oxygen when available, but can continue to grow without oxygen
\
NO3- → N2O → N2
\
Ex.
* Pseudomonas sp.
* Bacillus sp.
* Moraxella sp.
\
NO3- → N2O → N2
\
Ex.
* Pseudomonas sp.
* Bacillus sp.
* Moraxella sp.
10
New cards
Pseudomonas sp.
Example of Facultative Anaerobe
11
New cards
Bacillus sp.
Example of Facultative Anaerobe
\
Subtilis species uses the enzyme Amylase to convert Starch to Glucose
\
Species Stearothermophilus is an example of a Thermophile that grows best at 60 degrees C
\
Controlled via Triphenyl Methane Dyes
\
Subtilis species uses the enzyme Amylase to convert Starch to Glucose
\
Species Stearothermophilus is an example of a Thermophile that grows best at 60 degrees C
\
Controlled via Triphenyl Methane Dyes
12
New cards
Moraxella sp.
Example of Facultative Anaerobe
13
New cards
Anaerobic
Microbes that grow without the presence of oxygen
Oxygen is toxic to them
\
Ex.
* Desulfovibrio sp.
Oxygen is toxic to them
\
Ex.
* Desulfovibrio sp.
14
New cards
Desulfovibrio sp.
Example of an Anaerobe
\
An organism that can convert H2SO4 to H2S
\
An organism that can convert H2SO4 to H2S
15
New cards
Escherichia coli
Bacteria that grows using the Fumarate → Succinate portion of the Krebs Cycle
\
Uses the Beta Galactosidase enzyme to convert Lactose into Glucose and Galactose
\
Example of a Mesophile, growing best at 39 degrees C
\
Facultative Anaerobe
\
Uses the Beta Galactosidase enzyme to convert Lactose into Glucose and Galactose
\
Example of a Mesophile, growing best at 39 degrees C
\
Facultative Anaerobe
16
New cards
Proteus sp.
Bacteria that grows using the Fumarate → Succinate portion of the Krebs Cycle
17
New cards
Enterococcus sp.
Bacteria that grows using the Fumarate → Succinate portion of the Krebs Cycle
18
New cards
Methanogenic bacteria
Anaerobic bacteria found in intestinal tracts, sewage plants, and ruminants
\
Grow by converting CO2 to CH4
\
Ex.
* Methanobacter sp.
* Methanococcus sp.
\
Grow by converting CO2 to CH4
\
Ex.
* Methanobacter sp.
* Methanococcus sp.
19
New cards
Methanobacter sp.
Example of Methanogenic Bacteria
20
New cards
Methanococcus sp.
Example of Methanogenic Bacteria
\
Obligate Anaerobe
\
Obligate Anaerobe
21
New cards
Acidophiles
Like low pH
\
Anaerobic bacteria of this group grow by converting Fe3+ to Fe 2+
\
Ex.
* Thiobacillus feroxidans
* Fungi
* Yeast
\
Anaerobic bacteria of this group grow by converting Fe3+ to Fe 2+
\
Ex.
* Thiobacillus feroxidans
* Fungi
* Yeast
22
New cards
Thiobacillus Feroxidans
Example of Acidophilic Bacteria
23
New cards
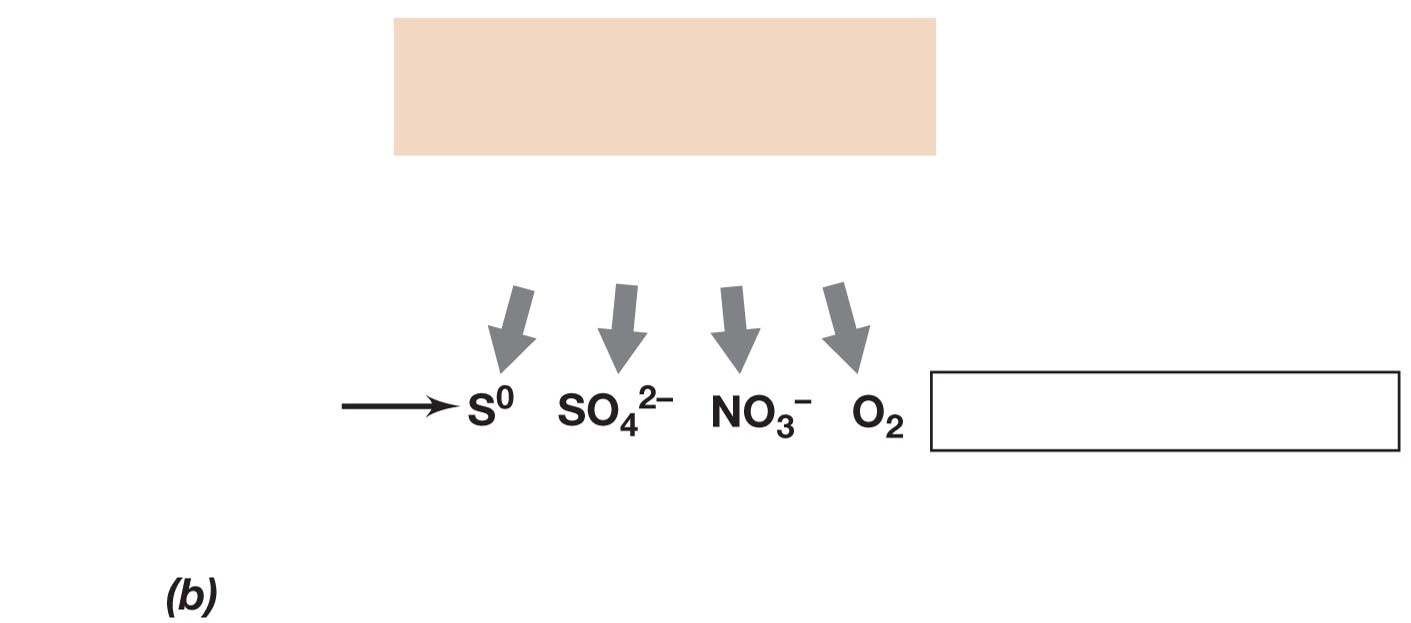
Chemolithotrophy
Catabolism type that uses inorganic chems as e- donors
\
Typically Aerobic
\
1. Oxidation of inorganic e- donor
2. ETS/Proton Motive Force
3. Autotrophy, using CO2 as C source
\
e- donors typically include:
1. H2S (Hydrogen Sulfide)
2. H2 (Hydrogen Gas)
3. Fe2+ (Ferrous Iron)
4. NH3 (Ammonia)
\
Typically Aerobic
\
1. Oxidation of inorganic e- donor
2. ETS/Proton Motive Force
3. Autotrophy, using CO2 as C source
\
e- donors typically include:
1. H2S (Hydrogen Sulfide)
2. H2 (Hydrogen Gas)
3. Fe2+ (Ferrous Iron)
4. NH3 (Ammonia)
24
New cards
Catabolism
Rxns that break down big chems into small chems to release energy
\
Ex.
1. Glycolysis
2. Fermentations
3. Aerobic Respiration
4. Anaerobic Respiration
5. Chemolithotrophy
6. Phototrophy
\
Ex.
1. Glycolysis
2. Fermentations
3. Aerobic Respiration
4. Anaerobic Respiration
5. Chemolithotrophy
6. Phototrophy
25
New cards
Phototrophy
Catabolism that uses light as energy source
\
3 types:
1. Photophosphorylation
2. Photoautotrophs
3. Photoheterotrophs
\
3 types:
1. Photophosphorylation
2. Photoautotrophs
3. Photoheterotrophs
26
New cards
Photophosphorylation
A type of Phototropic Catabolism
\
Light-mediated ATP synthesis
\
Light-mediated ATP synthesis
27
New cards
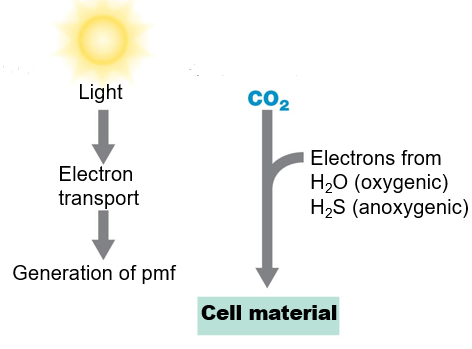
Photoautotrophy
A type of Phototrophic Catabolism
\
uses ATP for assimilation of CO2 for biosynthesis
\
uses ATP for assimilation of CO2 for biosynthesis
28
New cards
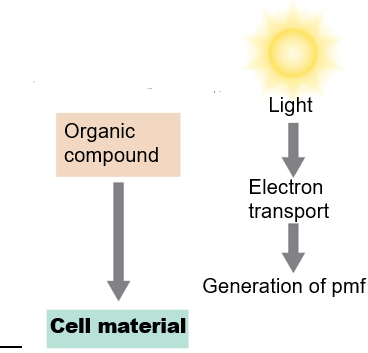
Photoheterotrophy
A type of Phototrophic Catabolism
\
uses ATP for assimilation of organic carbon for biosynthesis
\
uses ATP for assimilation of organic carbon for biosynthesis
29
New cards
Cellulase
Enzyme that converts the Carbohydrate Cellulose substrate into the Glucose monomer
\
Used by:
1. Clostridium sp.
2. Actinomyces sp.
\
Used by:
1. Clostridium sp.
2. Actinomyces sp.
30
New cards
Clostridium sp.
Bacteria that uses Cellulase to convert Cellulose to Glucose
\
Perfringens species is the etiolytic agent for Gas Gangrene due to the enzyme Phospholipase, converting Phospholipids into Phosphorylcholine and Fatty Acids
\
Sporogenes species is a Obligate Anaerobe
\
Perfringens species is the etiolytic agent for Gas Gangrene due to the enzyme Phospholipase, converting Phospholipids into Phosphorylcholine and Fatty Acids
\
Sporogenes species is a Obligate Anaerobe
31
New cards
Amylase
Enzyme that converts the Carbohydrate Starch substrate into the Glucose monomer
\
Used by:
1. Bacillus Subtilis
\
Used by:
1. Bacillus Subtilis

32
New cards
Bacillus Subtilis
Aerobe
\
1. Uses the Amylase enzyme to convert Starch into Glucose
2. Uses the Lipase enzyme to convert Triglycerides into Glycerol and Fatty Acids
\
Can be tested for using:
1. Starch Agar
2. Spirit Blue Agar
\
1. Uses the Amylase enzyme to convert Starch into Glucose
2. Uses the Lipase enzyme to convert Triglycerides into Glycerol and Fatty Acids
\
Can be tested for using:
1. Starch Agar
2. Spirit Blue Agar
33
New cards
Beta Galactosidase
Enzyme that converts the Carbohydrate Lactose substrate into the Glucose and Galactose monomers
\
Used by:
1. Escherichia Coli
\
Used by:
1. Escherichia Coli
34
New cards
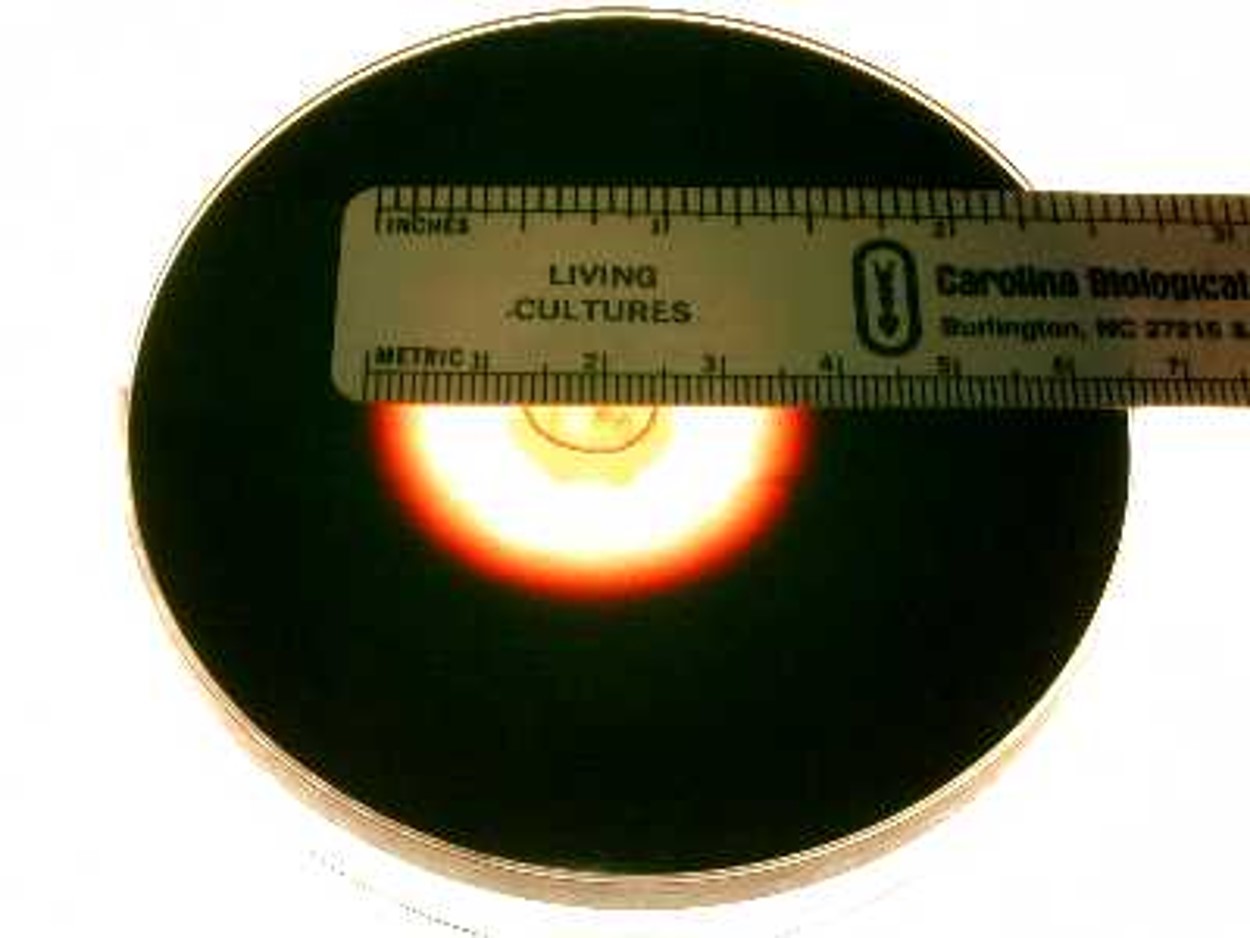
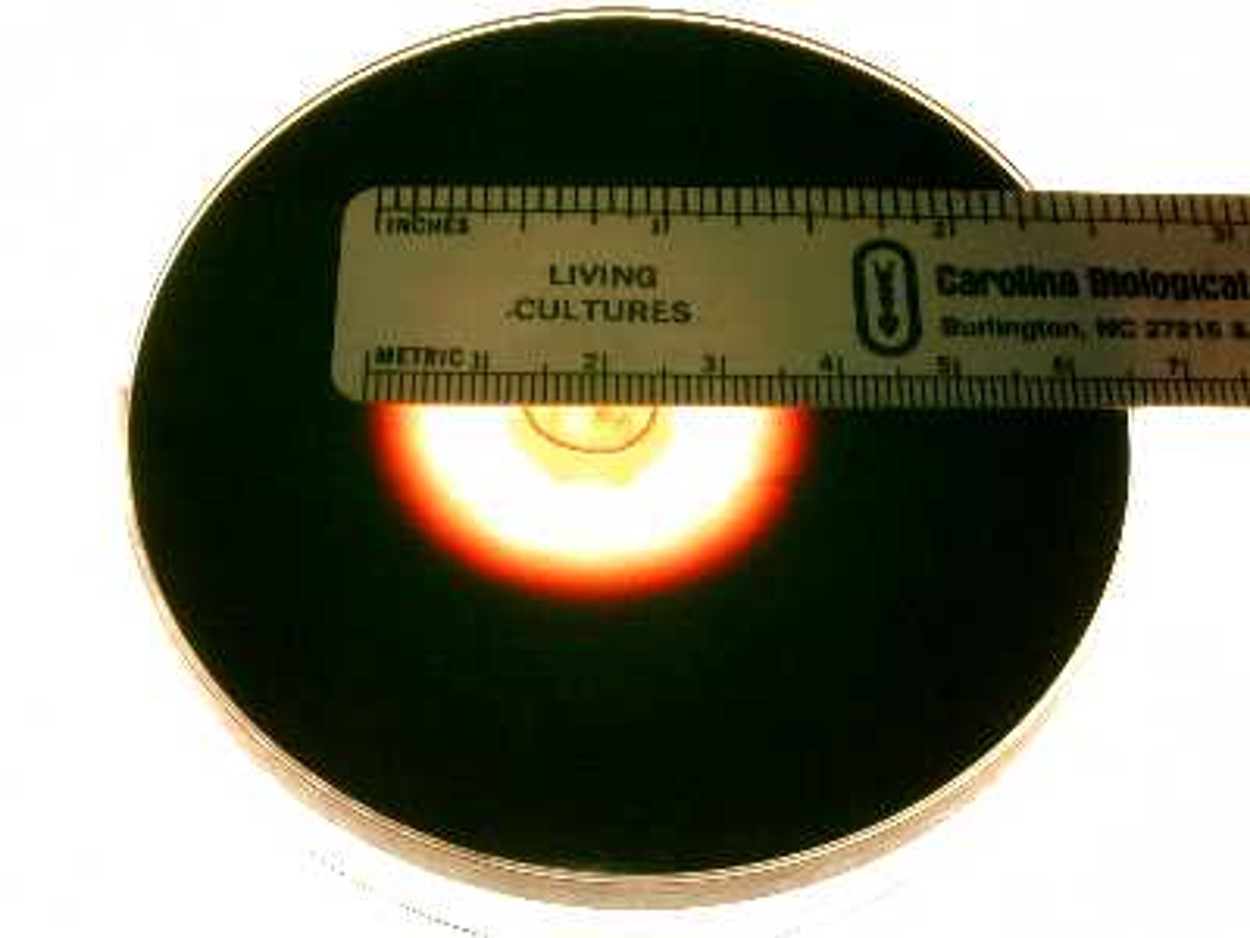
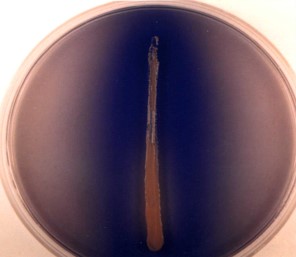
Starch Agar
Media that tests for the production of the Amylase enzyme
\
Picture shows a positive result, as seen by the degradation
\
Microbes that produce a positive effect:
1. Bacillus Subtilis
\
Picture shows a positive result, as seen by the degradation
\
Microbes that produce a positive effect:
1. Bacillus Subtilis

35
New cards
Lipase
Enzyme that converts the Lipid Triglyceride substrate into the Glycerol and Fatty Acid monomers
\
Used by:
1. Bacillus Subtilis
2. Staphylococcus Aureus
\
Tested for using the Spirit Blue Agar media
\
Used by:
1. Bacillus Subtilis
2. Staphylococcus Aureus
\
Tested for using the Spirit Blue Agar media
36
New cards
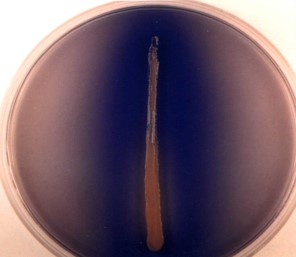
Spirit Blue Agar
Differential Media used to test for the production of the Lipase enzyme
\
Picture shows a positive result, as seen by the degradation of fat
\
Microbes that produce a positive effect:
1. Bacillus Subtilis
2. Staphylococcus Aureus
\
Picture shows a positive result, as seen by the degradation of fat
\
Microbes that produce a positive effect:
1. Bacillus Subtilis
2. Staphylococcus Aureus
37
New cards
Staphylococcus Aureus
Bacteria that produces the enzyme Lipase to convert Triglycerides into Glycerol and Fatty Acids
\
Can be tested for using:
1. Spirit Blue Agar
\
Example of a Halotolerant
\
Facultative Anaerobe
\
Controlled via Triphenyl Methane Dyes and Acridine Dyes
\
Can be tested for using:
1. Spirit Blue Agar
\
Example of a Halotolerant
\
Facultative Anaerobe
\
Controlled via Triphenyl Methane Dyes and Acridine Dyes
38
New cards
Phospholipase
Enzyme that converts the Lipid Phospholipid substrates into Phosphorylcholine and Fatty Acids
\
Responsible for the development of Gas Gangrene due to its Hemolytic nature
\
Used by:
1. Clostridium Perfringens
\
Tested for using the Egg Yolk Agar media
\
Responsible for the development of Gas Gangrene due to its Hemolytic nature
\
Used by:
1. Clostridium Perfringens
\
Tested for using the Egg Yolk Agar media
39
New cards
Clostridium Perfringens
Microbe that uses the enzyme Phospholipase to convert Phospholipids into Phosphorylcholine and Fatty Acids
\
Etiologic agent for Gas Gangrene due to Phospholipase
\
Also uses the Cellulase enzyme to convert Cellulose into Glucose
\
Etiologic agent for Gas Gangrene due to Phospholipase
\
Also uses the Cellulase enzyme to convert Cellulose into Glucose
40
New cards
Egg Yolk Agar
Media used to test for the production of the enzyme Phospholipase
\
Microbes that produce a positive effect:
1. Egg Yolk Agar
\
Microbes that produce a positive effect:
1. Egg Yolk Agar
41
New cards
Beta Oxidation
Metabolizes fatty acids released by lipases and phospholipases
\
Converts:
1. Co A into Acetyl Co A
2. FAD into FADH
3. NAD into NADH
\
Converts:
1. Co A into Acetyl Co A
2. FAD into FADH
3. NAD into NADH
42
New cards
Protease
Enzyme that converts Protein substrates into Amino Acid monomers
\
Used by:
1. Serratia Marcescens
\
Tested for using Skim Milk Agar
\
Used by:
1. Serratia Marcescens
\
Tested for using Skim Milk Agar
43
New cards
Serratia Marcescens
Microbe that uses the Protease enzyme to convert Proteins into Amino Acids
\
Can be tested for using:
1. Skim Milk Agar
\
Can be tested for using:
1. Skim Milk Agar
44
New cards
Skim Milk Agar
Media used to test for the production of Protease, converting Protein into Amino Acids
\
Microbes that produce a positive effect:
1. Serratia Marcescens
\
Microbes that produce a positive effect:
1. Serratia Marcescens
45
New cards
Glutamate Dehydrogenase
Enzyme that removes or adds ammonia during Amino Acid Metabolism and Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
\
Using this enzyme:
Alpha Ketoglutarate + NH3 + NADH → Glutamate (NH2)
\
Using this enzyme:
Alpha Ketoglutarate + NH3 + NADH → Glutamate (NH2)
46
New cards
Glutamine Synthetase
Enzyme that adds ammonia during Amino Acid Metabolism and Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
\
Using this enzyme:
Glutamate (NH2) + NH3 + ATP → Glutamine (2 NH2)
\
Using this enzyme:
Glutamate (NH2) + NH3 + ATP → Glutamine (2 NH2)
47
New cards
Trasaminase
Enzyme that transfers ammonia during Amino Acid Metabolism and Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
\
Using this enzyme:
Glutamate (NH2) + Oxaloacetate → Alpha Ketoglutarate + Aspartate (NH2)
\
Using this enzyme:
Glutamate (NH2) + Oxaloacetate → Alpha Ketoglutarate + Aspartate (NH2)
48
New cards
Glutamate Synthase
Enzyme that transfers ammonia during Amino Acid Metabolism and Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
\
Using this enzyme:
Glutamine (2 NH2) + Alpha Ketoglutarate + NADH → 2 Glutamate (NH2)
\
Using this enzyme:
Glutamine (2 NH2) + Alpha Ketoglutarate + NADH → 2 Glutamate (NH2)
49
New cards
Oxaloacetate
A product of the Krebs Cycle and Glyoxylate Cycle
\
Precursor of several amino acids
\
Becomes Aspartate (NH2) during Amino Acid Metabolism due to the enzyme Transaminase
\
Also converted to phsophoenolpyruvate, a precursor for glucose
\
Produces the following for Biosynthesis of Amino Acids:
1. Aspartate
1. Asparagine
2. Lysine
3. Methionine
4. Threonine
5. Isoleucine
\
Precursor of several amino acids
\
Becomes Aspartate (NH2) during Amino Acid Metabolism due to the enzyme Transaminase
\
Also converted to phsophoenolpyruvate, a precursor for glucose
\
Produces the following for Biosynthesis of Amino Acids:
1. Aspartate
1. Asparagine
2. Lysine
3. Methionine
4. Threonine
5. Isoleucine
50
New cards
Anabolic Reactions
Includes:
1. Carbohydrate Metabolism
2. Lipid Metabolism
3. Amino Acid Metabolism
4. Nucleotide Metabolism
1. Carbohydrate Metabolism
2. Lipid Metabolism
3. Amino Acid Metabolism
4. Nucleotide Metabolism
51
New cards
Alpha Ketoglutarate
A product of the Krebs Cycle
\
A precursor for several amino acids
\
Produces the following for Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
1. Glutamate
1. Proline
2. Glutamine
3. Arginine
\
A precursor for several amino acids
\
Produces the following for Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
1. Glutamate
1. Proline
2. Glutamine
3. Arginine
52
New cards
Succinyl CoA
A product of the Krebs Cycle
\
Required for synthesis of:
1. Cytochromes
2. Chlorophyll
3. Other Tetrapyrrole compounds
\
Required for synthesis of:
1. Cytochromes
2. Chlorophyll
3. Other Tetrapyrrole compounds
53
New cards
Acetyl CoA
A product of Krebs Cycle Preparation and Glyoxylate Cycle
\
Pyruvic acid (3C) → acetyl CoA (2C) + CO2
\
Necessary for fatty acid Biosynthesis
\
Pyruvic acid (3C) → acetyl CoA (2C) + CO2
\
Necessary for fatty acid Biosynthesis
54
New cards
Succinate
A product of the Glyoxylate Cycle
\
A key precursor in biosynthesis
\
A key precursor in biosynthesis
55
New cards
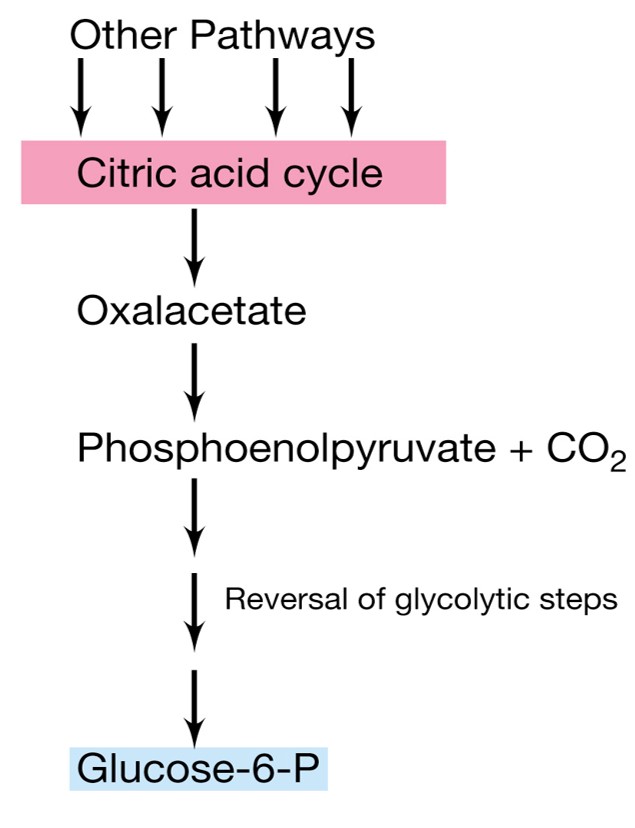
Gluconeogenesis
Synthesis of glucose from phsophoenolpyruvate
56
New cards
Adenosine Diphosphoglucose (ADPG)
Precursor for Glycogen biosynthesis
\
This + Glycogen → ADP + Glycogen-Glucose
\
This + Glycogen → ADP + Glycogen-Glucose
57
New cards
Uridine Diphosphoglucose (UDPG)
Precursor of some glucose derivatives needed for biosynthesis of important polysaccharides
1. N-acetylglucosamine
2. N-acetylmuramic Acid
1. N-acetylglucosamine
2. N-acetylmuramic Acid
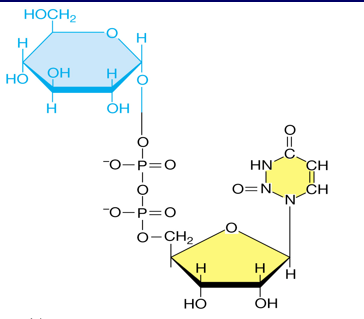
58
New cards
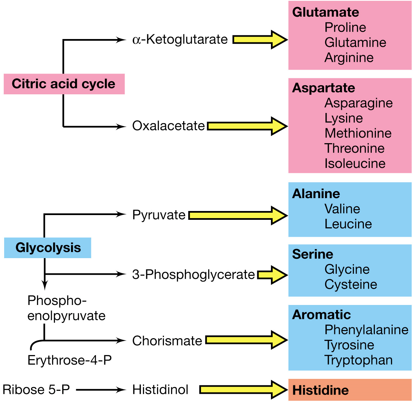
Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
Carbon skeletons come from Krebs Cycle or Glycolysis
\
Ammonia comes from:
1. Dehydrogenase
2. Synthetase
3. Transaminase
4. Synthase
\
Ammonia comes from:
1. Dehydrogenase
2. Synthetase
3. Transaminase
4. Synthase
59
New cards
Pyruvate
A product of Glycolysis
\
Produces the following for Biosynthesis of Amino Acids:
1. Alanine
1. Valine
2. Leucine
\
Produces the following for Biosynthesis of Amino Acids:
1. Alanine
1. Valine
2. Leucine
60
New cards
3-Phosphoglycerate
A product of Glycolysis
\
Produces the following for Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
1. Serine
1. Glycine
2. Cysteine
\
Produces the following for Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
1. Serine
1. Glycine
2. Cysteine
61
New cards
Chorismate
A product of Glycolysis post-phosphoenolpyruvate
\
Produces the following for Biosynthesis of Amino Acids:
1. Aromatic
1. Phenylalanine
2. Tyrosine
3. Tryptophan
\
Produces the following for Biosynthesis of Amino Acids:
1. Aromatic
1. Phenylalanine
2. Tyrosine
3. Tryptophan
62
New cards
Histidine
A product of Ribose 5-P used for Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
63
New cards
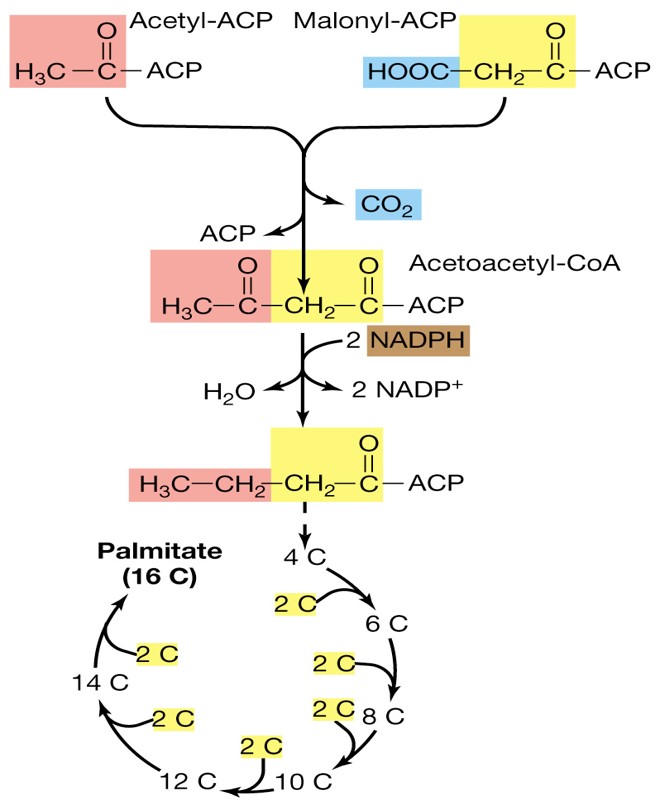
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids
Made up of 2 carbon atoms at a time
\
Requires:
1. Acyl Carrier Protein
2. NADPH
\
Requires:
1. Acyl Carrier Protein
2. NADPH
64
New cards
Acyl Carrier Protein
A protein required for the Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids
65
New cards
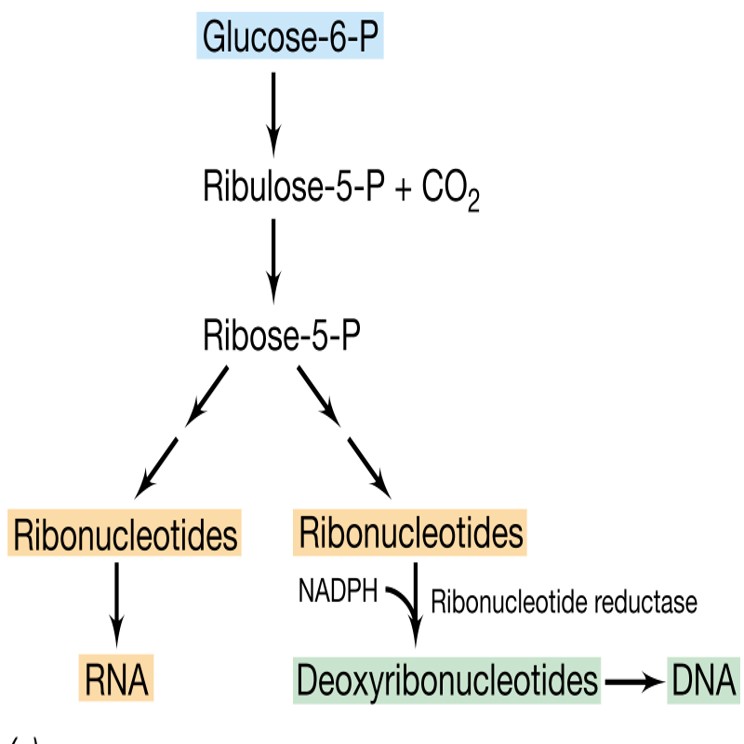
Synthesis of Pentose Sugar
Nucleotide anabolism
\
Phosphogluconate pathway
\
Pentose phosphate pathway
\
Hexose monophosphate shunt
\
Phosphogluconate pathway
\
Pentose phosphate pathway
\
Hexose monophosphate shunt
66
New cards
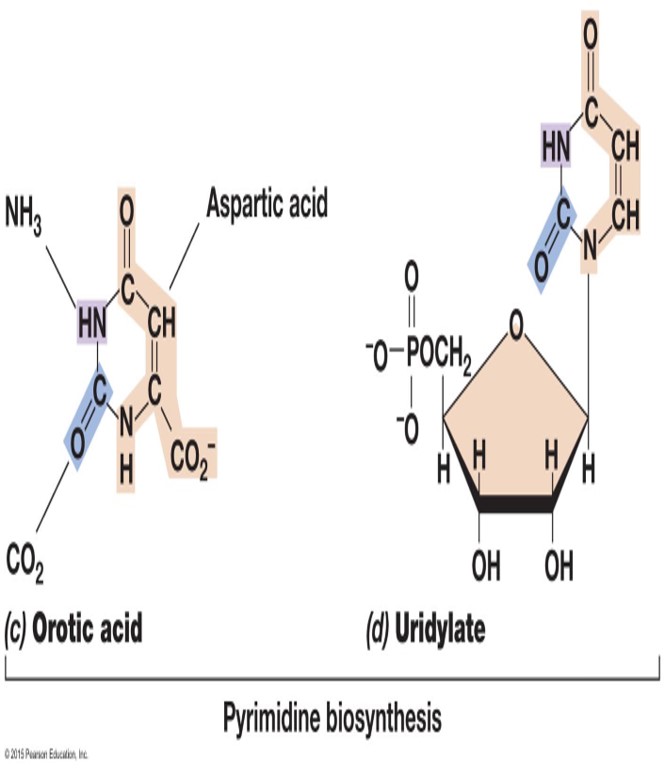
Biosynthesis of Pyrimidine
Nucleotide anabolism
\
Orotic acid precursor
\
Activated ribose is added
\
UMP intermediate
\
Products CTPT and TMP
\
A Growth Factor
\
Orotic acid precursor
\
Activated ribose is added
\
UMP intermediate
\
Products CTPT and TMP
\
A Growth Factor
67
New cards
Biosynthesis of Purine
Nucleotide anabolism
\
Starts from amino acids, CO2, and formyl groups
\
Formyl Groups added w/ folic acid
\
IMP intermediate forms AMP and GMP
\
A Growth Factor
\
Starts from amino acids, CO2, and formyl groups
\
Formyl Groups added w/ folic acid
\
IMP intermediate forms AMP and GMP
\
A Growth Factor
68
New cards
Methotrexate
Inhibitor of Nucleotide Synthesis
\
Inhibits tetrahydrofolate to TMP
\
Inhibits tetrahydrofolate to TMP
69
New cards
Aminopterin
Inhibitor of Nucleotide Synthesis
\
Inhibits tetrahydrofolate to TMP
\
Inhibits tetrahydrofolate to TMP
70
New cards
6-Mercaptopurine
Inhibitor of Nucleotide Synthesis
\
Inhibits conversion of IMP to AMP
\
Inhibits conversion of IMP to AMP
71
New cards
5 Fluoropyrimidine
Inhibitor of Nucleotide Synthesis
\
Blocks conversion on UMP to TMP
\
Blocks conversion on UMP to TMP
72
New cards
Sulfonamides
Inhibitor of Nucleotide Synthesis
\
Block folic acid synthesis
\
Block folic acid synthesis
73
New cards
Nutrients
Supply of monomers (or precursors of) required by cells for growth
\
2 types:
1. Macro
2. Micro
\
2 types:
1. Macro
2. Micro
74
New cards
Macronutrients
Nutrients required in large amounts
\
1. Carbon
2. Nitrogen
3. Phosphorus
4. Sulfur
5. Potassium
6. Magnesium
7. Calcium
8. Sodium
\
1. Carbon
2. Nitrogen
3. Phosphorus
4. Sulfur
5. Potassium
6. Magnesium
7. Calcium
8. Sodium
75
New cards
Carbon
Macronutrient
\
Required by all cells and major in all classes of macromolecules
\
Heterotrophs obtain this via organic means
Autotrophs obtain this via CO2
\
Required by all cells and major in all classes of macromolecules
\
Heterotrophs obtain this via organic means
Autotrophs obtain this via CO2
76
New cards
Nitrogen
Macronutrient
\
Key element in:
1. Proteins
2. Nucleic Acids
3. Many more cell constituents
\
Key element in:
1. Proteins
2. Nucleic Acids
3. Many more cell constituents
77
New cards
Phosphorus
Macronutrient
\
Used in synthesis of:
1. Nucleic Acids
2. Phospholipids
\
Used in synthesis of:
1. Nucleic Acids
2. Phospholipids
78
New cards
Sulfur
Macronutrient
\
Used in:
1. This-containing Amino Acids like Cysteine and Methionine
2. Vitamins like Thiamine, Biotin, Lipoic Acid
3. Coenzyme A
4. Proteins
\
Used in:
1. This-containing Amino Acids like Cysteine and Methionine
2. Vitamins like Thiamine, Biotin, Lipoic Acid
3. Coenzyme A
4. Proteins
79
New cards
Potassium
Macronutrient
\
Required by enzymes for activity
\
Required by enzymes for activity
80
New cards
Magnesium
Macronutrient
\
Stabilizes:
1. Ribosomes
2. Membranes
3. Nucleic Acids
\
Required for many enzymes
\
Stabilizes:
1. Ribosomes
2. Membranes
3. Nucleic Acids
\
Required for many enzymes
81
New cards
Calcium
Macronutrient
\
Helps stabilize cell walls in microbes
\
Plays key role in heat stability of endospores
\
Helps stabilize cell walls in microbes
\
Plays key role in heat stability of endospores
82
New cards
Sodium
Macronutrient
\
Required by certain microbes (marine) to retain water and collect water in sodium-rich environments
\
Required by certain microbes (marine) to retain water and collect water in sodium-rich environments
83
New cards
Micronutrients
Nutrients needed in small amounts
\
1. Iron
2. Other trace elements
3. Growth Factors
\
1. Iron
2. Other trace elements
3. Growth Factors
84
New cards
Iron
Micronutrient
\
Key component of cytochromes and FeS proteins involved in ETS
\
Key component of cytochromes and FeS proteins involved in ETS
85
New cards
Growth Factors
Micronutrients
\
Organic compounds required in small amounts by certain organism
\
1. Vitamins
2. Amino Acids
3. Purines
4. Pyrimidines
\
Organic compounds required in small amounts by certain organism
\
1. Vitamins
2. Amino Acids
3. Purines
4. Pyrimidines
86
New cards
Vitamins
Most commonly required Growth Factor Micronutrient
\
Most function as coenzymes
\
Most function as coenzymes
87
New cards
Culture Media
Nutrient solutions used to grow microbes in the lab
\
Liquid or semi solid or solid
\
2 broad classes:
1. Defined
2. Complex
\
Types:
1. Enriched
2. Differential
3. Selective
\
Liquid or semi solid or solid
\
2 broad classes:
1. Defined
2. Complex
\
Types:
1. Enriched
2. Differential
3. Selective
88
New cards
Defined Media
Type of Culture Media
\
Precise chem composition is known
\
Precise chem composition is known
89
New cards
Complex Media
Type of Culture Media
\
Composed of digests of chemically undefined substances
\
Ex.
yeast
meat extracts
\
Composed of digests of chemically undefined substances
\
Ex.
yeast
meat extracts
90
New cards
Enriched Media
Type of Culture Media
\
Contains complex media plus addition nutrients
\
Contains complex media plus addition nutrients
91
New cards
Differential Media
Type of Culture Media
\
Allows multiple types of bacteria to grow but displays visible differences in how they grow
\
Ex.
Spirit Blue Agar
Starch Agar
Skim Milk Agar
\
Allows multiple types of bacteria to grow but displays visible differences in how they grow
\
Ex.
Spirit Blue Agar
Starch Agar
Skim Milk Agar
92
New cards
Starch Agar
An example of Differential Media
93
New cards
Skim Milk Agar
An example of Differential Media
94
New cards
Selective Media
A type of Culture Media
\
Inhibits the growth of certain bacteria
\
Ex.
Asparagine Agar
Phenyl Ethyl Alcohol Agar
\
Inhibits the growth of certain bacteria
\
Ex.
Asparagine Agar
Phenyl Ethyl Alcohol Agar
95
New cards
Asparagine Agar
Example of Selective Media
96
New cards
Phenyl Ethyl Alcohol Agar
Example of Selective Media
97
New cards
Salmonella Shigella Agar
Example of Selective and Differential Media
98
New cards
MacConkey Agar
Example of Selective and Differential Agar
99
New cards
Mannitol Salts Agar
Example of Selective and Differential Agar
100
New cards
Pure Culture
Contains only one type of microbe
\
Obtained via:
1. Growing on solid media
2. Using aseptic technique
3. Isolation
\
Obtained via:
1. Growing on solid media
2. Using aseptic technique
3. Isolation