Module 11 - Order Cyclophyllidea (True Tapeworms) I
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
Members of this FAMILY occurs in mammals and birds which has only one set of reproductive organ and some species can reproduce asexually
Family Mesocestoidea
Members of this genus occasionally occur in humans. However, its normal DH are various types of birds and mammals and they are found in the small intestines.
Mesocestoides sp.
Its scolex has 4 elongate oval suckers and has no rostellum
Mesocestoides sp.
Its proglottids have 1 set of genitalia. Wherein its genital pore are found in the ventromedian and eggs are in par-uterine organ.
Mesocestoides sp.
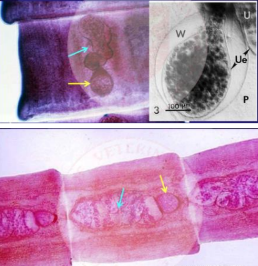
Identify
Mesocestoides sp.
IHs of Mesocestoides sp.
1st IH - oribatid mites and beetles
2nd IH - rodents and reptiles
In the 1st IH such as oribatid mites and beetles of Mesocestoides sp., this stage is formed.
cysticercoids
In the 2nd IH such as rodents and reptiles of Mesocestoides sp., this stage is formed.
tetrathyridia
This mesocestode is capable of asexual multiplication by longitudinal splitting of the parent scolex in the small intestine of the 2nd IH.
Tetrathyridia
This isolate of Mesocestoides sp. can undergo asexual multiplication in the DH if these are dogs and skunks; through longitudinal fission of the scolex.
Mesocestoides vogae
Give other species of Mesocestoides aside from M. vogae
M. variabilis
M. lineatus
M. corti
Normally, the adults of Mesocestoides sp. are harmless in its host such as dog. The tetrathyridia on the other hand may cause this disease in cats and dogs.
severe peritonitis
In humans, Mesocestoides sp. infestation may result in what clinical symptoms?
severe diarrhea
Treatment and prevention of Mesocestoides sp. (2)
Praziquantel
Hygienic food preparation
Under Mesocestoides sp., this species is found in the smaller bile ducts or blood vessels of the liver of kitfox (Vulpis microtis) in California
Mesogyna hepatica
This family usually occur in mammals, usually ruminants and equine. It is either single or double-pored tapeworm. IH is usually oribatid mites.
Family Anoplocephalididae
IH - oribatid mites
DH - hoofed animals
Has unarmed scolex
Genus Moniezia
T/F. Genus Moniezia has eggs which are roughly triangular or square with pyriform apparatus
TRUE
Interproglottidal glands are present and it open along the junctions between proglottids are present
Genus Moniezia
Genus Moniezia has this type of metacestode that develops in its IH, oribatid mites
cysticercoids
Genus Moniezia are collectively known as?
Double pored tapeworm
The first anoplocephalid which life cycle was discovered. It mainly occurs in sheep and goats.
Moniezia expansa
Eggs of Moniezia expansa are more ________ in shape.
triangular
The interproglottidal glands of this species are linearly arranged and in roseate formation.
Moniezia expansa
Its eggs are more square in shape and its interproglottidal glands are more concetrated in the middle of the junctions.
Moniezia benedini
IH of Moniezia sp. (give one)
Galumna
Oribatula
Peloribates
Protoscheloribates
Scheloribates
Scutorvex
Zygoribatula
Infective cysticercoids of Moniezia sp. are produce in about how many months?
4 months
Prepatent period of Moniezia sp.
37-40 days (5-6 weeks)
Infection caused by Moniezia sp. are more prevalent in young animals ages _____?
under 6 months
T/F. The PPP of Moniezia sp. are 37-40 days but infected lambs may pass out proglottids as early as 6 weeks old.
True
Heavy infection of Moniezia sp. are:
diarrhea
unthriftiness
intestinal obstruction
high incidence of enterotoxemia
Treatment and control of Moniezia sp. (3)
benzimidazole compounds, bunamidine, bithionol, niclosamide
plowing and reseeding pasture
pasture rotation
Cestodes of horses and donkeys usually don’t have hooks in its sucker and has 1 set of genital organs.
Genus Anoplocephala
Families with only one set of reproductive organs
Mesocestoides
Anoplocephalididae
Members of this families have eggs that are roughly triangular or square, with pyriform apparatus
Moniezia
Anoplocephala
Members of Genus Anoplocephala
Anoplocephala perfoliata
Anoplocephala magna
Paranoplocephala mamillana
Genus Anoplocephala: Found in the posterior SI
Anoplocephala magna
Genus Anoplocephala: It attaches to the ileocecal valve, hence the name ileocecal tapeworm
Anoplocephala perfoliata
Genus Anoplocephala: has lappets
Anoplocephala perfoliata
Genus Anoplocephala: Longest in size among the three
Anoplocephala magna
Genus Anoplocephala: Occurs in the anteriot SI, ocassionally stomach. has narrow proglottids.
Paranoplocephala mamillana
Genus Anoplocephala: lappets are absent (2)
Anoplocephala magna
Paranoplocephala mamillana
In the large and small intestine of horses and donkeys. It is the most frequent tapeworm of horses.
Anoplocephala perfoliata
proglottids are wider than long with single set of reproductive organs
Anoplocephala perfoliata
IH of Anoplocephalididae
oribatid mites
Scheloribates laevigatus
S. latipes
Galumna nervosus
Achiperia spp.
Ceratozetes spp.
It occcurs in the SI (jejunum), rarely in the stomach of horses and donkeys. It may reach up to 80 cm long and 2.5 cm wide.
Anoplocephala magna
It has narrow scolex, suckers are slit-like and are situated dorsally and ventrally. Usually found in the SI of horses
Paranoplocephala mamillana
Cysticercoids of this species are produced in the IH 2-4 months after infection.
Genus Anoplocephala
T/F. Genus Anoplocephala usually has no clinical signs. However, in heavy infection, it may lead to ill health, unthriftiness, and death.
TRUE
It can cause small, dark, depressed, ulcerative lesions in the ileocecal orifice may be seen, edema and excessive granulation tissue may also occur, rarely partial occlusion of the orifice.
Anoplocephala perfoliata
It causes catarrhal or hemorrhagic enteritis in large numbers; perforations of the intestine have been reported.
Anoplocephala magna
member of Anoplocephala that is not pathogenic
Paranoplocephala mamillana
Treatment and Control of Anoplocephala
Mebendazole, bithionol, niclosamide
Pyrantel pamoate or tartrate has activity vs. A. perforliata
Control measures as for Moniezia spp.
Cestodes of rabbits and hares
Genus Cittotaenia
Found in the SI of rabbit in Europe, up to 80 cm long and 1 cm wide.
Eggs with pyriform apparatus
Proglottids – broader than long, have 2 sets of posteriorly placed genital organs
Cittotaenia ctenoides
Cittotaenia sp. that has no neck
Cittotaenia denticulata
Cittotaenia sp. that has neck
Cittotaenia pectinata
IH of Cittotaenia sp.
oribatid mites
Achipteria
Allopelops
Cepheus
Galumna
Scheloribates
Scutovertex
Trichoribates
Xenillus
Genus with oribatid mites as IH (6)
Mesocestoididae
Moniezia
Anoplocephala
Cittotaenia
Bertiella
Stilesia
Heavy infection of Cittotaenia spp. (esp C. ctenoides) may cause what implications in rabbits?
digestive disturbances
emaciation
death
Anoplocephalids of monkeys
Genus Bertiella
Parasite of Old World monkeys; has been reported in humans in southern Asia, the East Indies, and the Philippines; has unarmed scolex
Bertiella studeri
Its egg has a bicornuate pyriform apparatus on the inner shell
Bertiella studeri
Ripe segments are shed in chains of about a dozen at a time
Bertiella studeri
IH of Bertiella studeri
oribatid mites
Bertiella sp. in New World monkeys, also man
Bertiella mucronata
good to eat Bertiella sp.
Specific tapeworms of the Papua New Guinean coppery ringtail possum, relished as food by natives here
Bertiella esculenta
Named after Tim Flannery who first came across this practice
Bertiella flanneryi
Normally parasitic in African rodents; has been reported in humans (South America and Cuba, (reported as I. cubensis) in which it is concluded that humans are the only DH outside of Africa
Inermicapsifer madagascariensis
Species that has unarmed scolex (6)
Moniezia
Anoplocephala
Bertiella studeri
Inermicapsifer madagascariensis
Raillietina cesticillus
Cotugnia digonophora
Its egg capsules contain 6-10 eggs each has no pyriform apparatus
Inermicapsifer madagascariensis
IH of Inermicapsifer madagascariensis
arthropods
Family of tapeworms that mainly affects the ruminant and the gravid uterus is replaced by par-uterine organs or capsules.
Family Thysanosomidae
Members of Family Thysanosomidae
Avitellina
Stilesia
Thysanosoma
Long and narrow tapeworms of ruminants with the short, indistinct segments and alternating genital pores
May be up to 3 m long and 3 mm wide, being almost cylindrical at the posterior end
Proglottids – short, not distinctly segmented, single genitalia,
Eggs – no pyriform apparatus
not as pathogenic as Moniezia
Avitellina sp.
Species of Avetillina
A. centripunctata
A. chalmersi
A. goughi
IH of Avitellina spp.
psocids (bark lice, book lice, dust lice)
It occurs in the bile ducts of sheep, goats, cattle and wild ruminants in Africa (90-100% prevalent in some areas) and Asia
Stilesia hepatica
It has prominant scolex, broad neck, and has single genital pore which appears alternate but irregular
Stilesia hepatica
IH of Stilesia hepatica
oribatid mites
T/F. Stilesia hepatica appear to not be pathogenic even in heavy infections but it causes dilatation, slight cirrhosis and thickening even appear in the duct because of the worms.
TRUE
In the SI of sheep, goat, cattle and other ruminants in Europe, Africa, and Asia
Stilesia globipunctata
IH of Stilesia globipunctata
oribatid mites
psocid mites
Stilesia globipunctata attaches primarily in the junction of the duodenum and jejunum; scolex of immature forms penetrate the mucous membrane leading to?
nodule formation
proliferative inflammation
cell infiltration
epithelial desquamation
death
Treatment of Stilesia globipunctata
Praziquantel
also known as fringed tapeworm
Thysanosoma actinioides
A double-pored tapeworm occurring in the bile ducts, pancreatic ducts and SI of sheep, cattle and deer in America
Thysanosoma actinioides
Thysanosoma actinioides has how many eggs in its par-uterine organs and how many set of reproductive organs.
6-12 eggs
2 sets
IH of Thysanosoma actinioides
psocids
Effects of Thysanosoma actinioides
partial obstruction of bile flow and pancreatic juice
digestive disorder
condemnation of liver
predisposing factor to black disease caused by Clostridium novyi
Treatment of Thysanosoma actinioides (3)
bithionol
praziquantel
niclosamide
In SI of domestic ruminants (sheep, goat, and cattle); in the Republic of South Africa, it is the most frequent tapeworm
Thysaniezia giardi
species with irregular alternates of genital pore (2)
Thysaniezia giardi
Stilesia hepatica
IH of Thysaniezia giardi; condition?
psocids but cannot produce infection in sheep
oribatid mites
T/F. All ages can be infected by Thysaniezia giardi but it does not occur in numbers sufficient to cause clinical signs
TRUE.
Treatment of Thysaniezia giardi
bithionol and other anthelmintics effective against Moniezia
Family in which eggs are in capsules, it occurs in mammals or birds
Family Davaineidae
In the duodenum of the fowl, pigeon and other gallinaceous birds, small, has armed rostellum and suckers.
Davainea proglotinna
Davainea proglotinna is also known as the?
most pathogenic tapeworm of poultry
IH of Davainea proglotinna where cysticercoids develop
gastropod (terrestrial)
molluscs (Limax, Arion, Cepoea, Agriolimax)