MLT 111 Exam 2 (Ch. 5 & 6 )
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
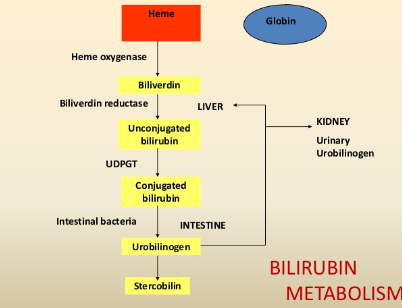
What is the order of bilirubin metabolism?
Heme—blank—Stercobilin
Biliverdin - unconjugated bilirubin (liver), conjugated bilirubin - urobilinogen (intestines)
What is the value of renal threshold?
160-180 mg/dL
Which of the three ketones bodies is not detected with reagent strips?
beta hydroxybutyric acid
For leukocyte esterase the reagent strip tests for…?
enzymes from WBC
A random urine specimen and plasma glucose test that are to be drawn and collected at the same time can be used to confirm:
Glomerulonephritis
Fanconi's syndrome
Nonpathogenic glycosuria
Urinary tract infection
Nonpathogenic glycosuria
A spotted reaction on the reagent strip reaction for blood can indicate:
Myoglobinuria
Hematuria
Porphyrinuria
Hemoglobinuria
Hematuria
Failure to blot the edge of the reagent strip may result in errors in color interpretation caused by:
Run over
Excess dilution
Chemical concentration
Reagent leaching
Run over
Microalbumin tests are frequently used to screen patients with:
Diabetes insipidus
Fanconi's syndrome
Diabetes mellitus
Porphyrinuria
Diabetes mellitus
Quality control on reagent strips must be performed whenever a/an:
New bottle of strips is opened
Different person performs the test
Abnormal result is obtained
Student is training in the laboratory
New bottle of strips is opened
Reagent strip reactions for blood are based on the:
Oxidation of hemoglobin peroxidase
Reduction of a chromogen by hemoglobin
Reaction of hemoglobin with bromothymol blue
Peroxidase activity of hemoglobin
Peroxidase activity of hemoglobin
Tests for nitrite tend to be positive:
When gram-positive bacteria are present
When a renal transplant rejection occurs
When gram-negative bacteria are present
When the urine sits in the bladder for less than 2 hours
When gram-negative bacteria are present
The chemical principle of the reagent strip test for bilirubin is that bilirubin:
Is oxidized to biliverdin
Combines with a diazonium salt to form a colored complex
Causes a pH change detected by the reagent pad indicator
Causes a color change when it binds to a buffered pH indicator
Combines with a diazonium salt to form a colored complex
The normal range of urine pH is:
4.5 to 6.0
4.5 to 9.0
4.5 to 8.0
5.0 to 7.0
4.5 to 8.0
The principle of the reagent strip test for protein is the:
pH effect on bromothymol blue
Acid precipitation of protein
Protein "error of indicators"
Salting out of proteins
Protein "error of indicators"
The pseudoperoxidase reaction is the principle for the reagent strip test(s) for:
Nitrite
Urobilinogen
Specific gravity
Blood
Blood
The reagent strip test for ketones may detect the urinary presence of:
Acetoacetic acid and acetone
Acetone and beta-hydroxybutyric acid
Beta-hydroxybutyric acid and diacetic acid
Acetoacetic acid and beta-hydroxybutyric acid
Acetoacetic acid and acetone
The substance that produces the brown color associated with normal feces is:
Conjugated bilirubin
Urobilinogen
Unconjugated bilirubin
Stercobilin
Stercobilin
What can cause a test on a yellow-green urine specimen from a jaundiced patient to be negative for bilirubin?
Bilirubin oxidized to biliverdin
Presence of iodine
Bilirubin reduced to urobilinogen
Glucose interference
Bilirubin oxidized to biliverdin
The urinalysis result most closely associated with renal disease is a positive:
Protein
Bilirubin
Glucose
Nitrite
Protein
diazo-
leukocyte
Greiss-
nitrate
Ehrich-
urobilinogen
Tetra-
Protein
bromo meth-
pH
pseudo pero-
blood
bromo-
SG (specific gravity)
Prussied-
ketones
enzyme
WBC
Ico-
bilirubin
Ace-
ketones
Protein-
SSA (sulfosalicylic acid)
Port wine color
porphyrins
myoglobin (uria)
brownish red
Infection
Green
A clinically significant cause of turbidity is:
a. mucus
b. lipids
c. amorphous urates
d. Squamous epithelial cells
Lipids
A patient who has been diagnosed with diabetes mellitus (excessive glucose in urine) will produce urine with:
a. Increased volume and increased specific gravity
b. Increased volume and decreased specific gravity
c. Decreased volume and increased specific gravity
d. Decreased volume and decreased specific gravity
Increased volume and increased specific gravity
A specific gravity was performed by the refractometer and the reagent strip method. The refractometer reading was 1.033 and the reagent strip was 1.010. The difference in the two readings is caused by:
a. Refractometer error
b. Clinical laboratory scientist error
c. Refractometer measures only nonionizing substances
d. Reagent strip measures any substance in urine
Refractometer measures only nonionizing substances
A urine specimen that turns black after standing may contain:
a. Myoglobin
b. Carboxyhemoglobin
c. Porphobilinogen (port wine color)
d. Homogentisic acid
Homogentisic acid
An antidiuretic deficiency (ADH issues, diabetes insipidus SG?) is associated with a:
a. Specific gravity close to 1.025
b. Low specific gravity
c. Variable specific gravity
d. High specific gravity
Low specific gravity
If a refractometer reads 1.003 with distilled water, the medical laboratory scientist should:
Use a reagent strip to measure the specific gravity
Calibrate the refractometer by adjusting the set screw
Add 0.003 to the specimen results
Subtract 0.003 from the specimen results
Calibrate the refractometer by adjusting the set screw
Slightly warming a turbid urine specimen may dissolve:
Amorphous urates
Radiographic contrast media
Talcum powder
Amorphous phosphate
Amorphous urates
Specimens that contains intact RBC’s can be visually distinguished from specimens that contain hemoglobin because:
Intact red blood cells produce a cloudy specimen
Intact red blood cells are rapidly converted to hemoglobin
Hemoglobin produces a cloudy pink specimen
Hemoglobin produces a brighter red color
Intact red blood cells produce a cloudy specimen
The color of a urine specimen containing blood can be attributed to all of the following EXCEPT the:
Amount of blood
Length of contact
pH of the urine
Blood type of patient
Blood type of the patient
The presence of a white precipitate in freshly voided urine can be caused by:
acid 1-4 ; alkaline 9-14pH
Amorphous urates in alkaline urine
Amorphous phosphates in acid urine
Amorphous phosphates in alkaline urine
Amorphous urates in acid urine
Amorphous phosphates in alkaline urine
The refractive index compares:
Light scattering by particles in solutions
Light scattering by air with light scattering by solutions
Light velocity in solutions with light velocity in solids
Light velocity in air with light velocity in solutions
Light velocity in air with light velocity in solutions
Quality control must be…
Ran once every 24 hours.
Run once a week
Run only when a new bottle is opened
Run using distilled water
Ran once every 24 hours.
A urine specimen that turns black after standing may contain:
Myoglobin
Porphobilinogen
Carboxyhemoglobin
Homogentisic acid
Homogentisic acid
Urine from a patient diagnosed with hepatitis will appear:
a. red
b. amber
c. pale yellow
amber
The urinalysis result most closely associated with renal disease is a positive:
Protein
Glucose
Bilirubin
Nitrite
Protein
Specimens that contain intact red blood cells can be visually distinguished from specimens that contain hemoglobin because:
Intact red blood cells are rapidly converted to hemoglobin
Intact red blood cells produce a cloudy specimen
Hemoglobin produces a brighter red color
Hemoglobin produces a cloudy pink specimen
Intact red blood cells produce a cloudy specimen
What test removes all substances withing the urine sample except glucose to test for metabolism errors? It can only be run for patients 2 years old & under.
Clinitests
The confirmatory test for protein?
SSA (Sulfosalicylic Acid)
The confirmatory test for bilirubin?
Icotest

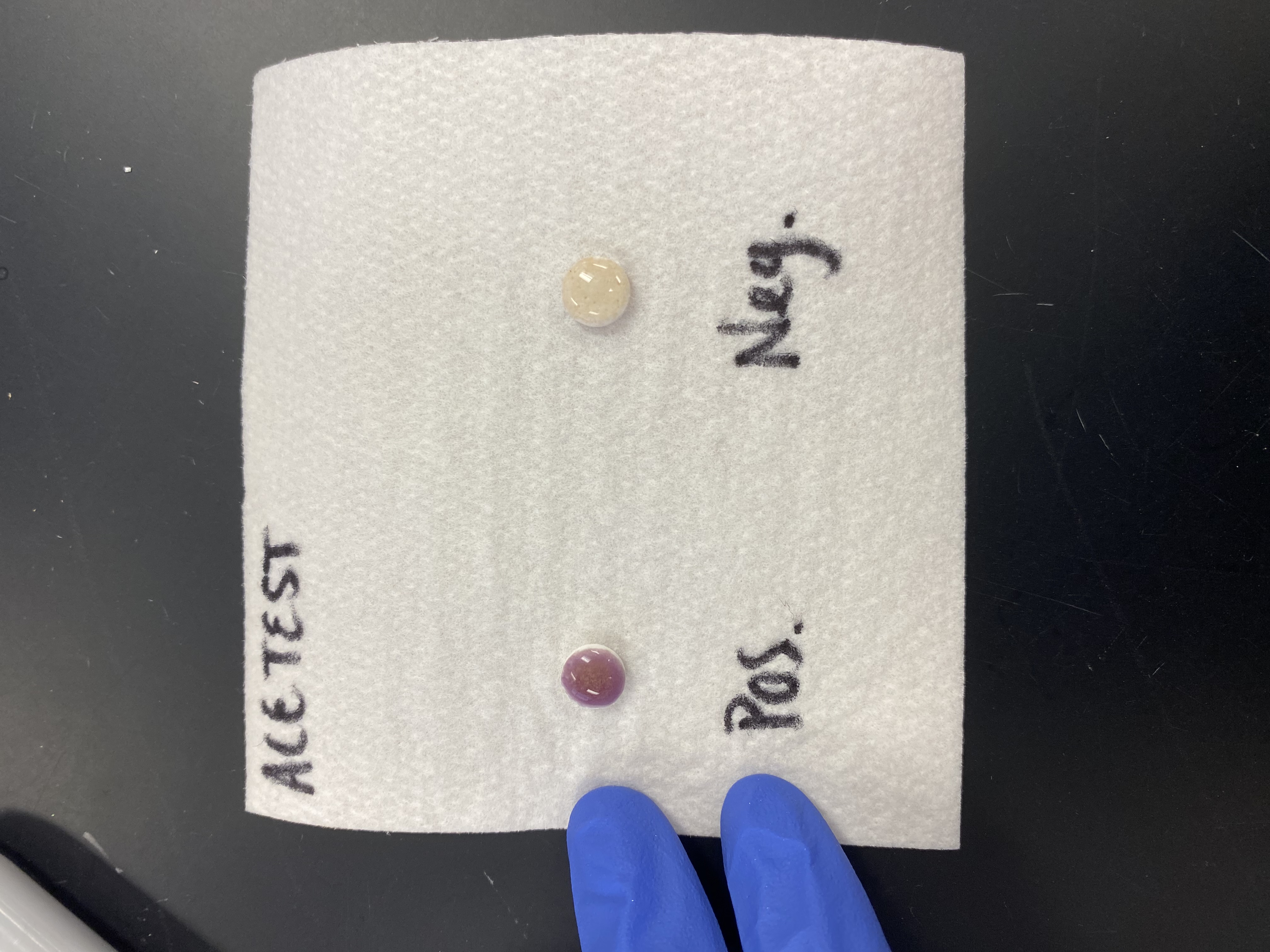
The confirmatory test for ketones?
Acetest