2.3 Flows of energy and matter
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Solar constant
The amount of solar energy reaching the top of the atmosphere of Earth being 1400 watts per second.
Productivity
The conversion of energy into biomass over a given period of time.
Rate of growth of biomass in plants and animals
measured in unit area per unit time
Primary
Dealing with plants
Gross primary productivity (GPP)
The total gain in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time by green plants.
Energy converted from light to chemical energy
Doesn’t consider anything loss
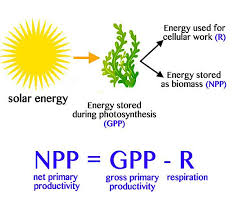
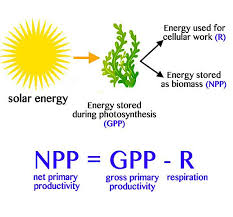
Net primary productivity (NPP)
Total gain in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time by green plants after allowing for losses to respiration
Increase in biomass of plant
Calculated with NPP = GPP-R
R = respiration
Secondary
Dealing with animals
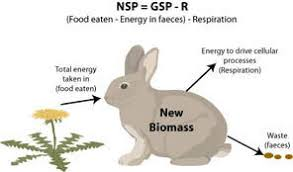
Net secondary productivity (NSP)
The total gain in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time by consumers after allowing for losses to respiration.
NSP = Energy in the food ingested - Energy lost in egestion (feces) - energy used in respiration
Carnivores assimilate 80% of energy in diet and egest less than 20%
Herbivores 40% of energy in diet and egest 60%
Biogeochemical cycle
The pathway through which a chemical substance moves through biotic and abiotic components of Earth. It includes processes like photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and nutrient cycling.
Carbon cycle
THe presence of organic and inorganic carbon molecules in both human-made and natural processes such as combustion, fossil fuels, soil microorganisms, photosynthesis, respiration, all part of the carbon cycle.
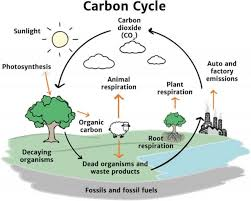
Carbon fixation
Carbon Fixation
When carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is converted into organic compounds by plants during photosynthesis. T
Nitrogen cycle
When nitrogen is converted between its various chemical forms in the environment, including nitrogen fixation, nitrification, assimilation, ammonification, and denitrification.
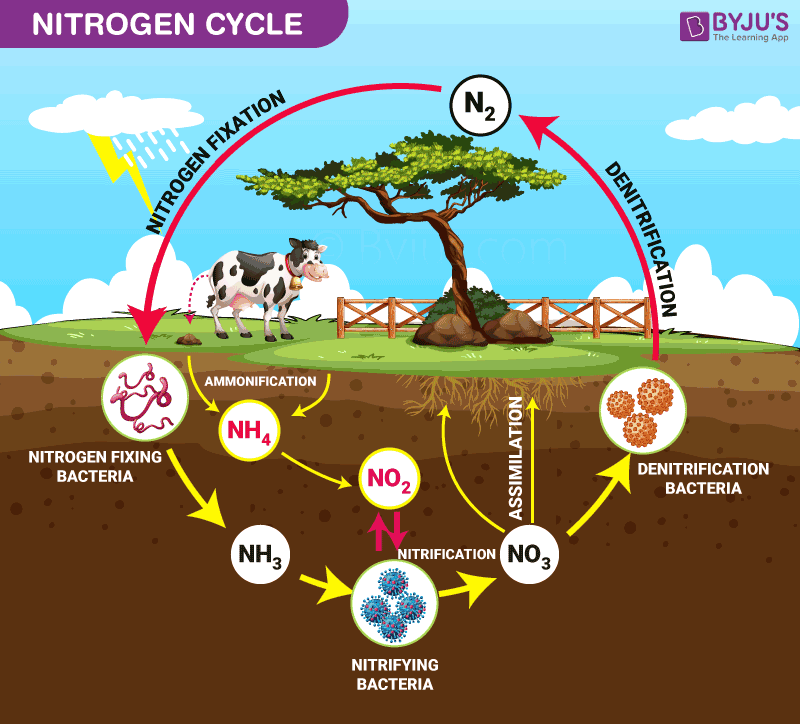
Nitrogen fixation
When atmospheric nitrogen is made available to plants through the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen.
Done by nitrogen fixing bacteria, cyanobacteria, lightning and the industrial Haber process.
Nitrification
The process of nitrifying bacteria in the soil converting ammonium into nitrites and then nitrites into nitrates which can be absorbed into plants
Denitrification
The opposite of nitrification where denitrificating bacteria convert nitrates, nitrites and ammonium into nitrogen gas that escapes into the atmosphere.
Decomposition
The breakdown of dead organisms by detrivores and saphotrophs into proteins and nitrogen ions.
These are then absorbed into plants
Assimilation
When living organisms take in nitrogen and build it into complex molecules.
Trophic efficiency
The efficiency of transfer from one trophic level to the next.
Anthropogenic
A process, effect or activity derived from humans
Maximum sustainable yield
The largest crop or catch that can be taken from the stock of a species (forest, shoal of fish), without depleting the stock.
Energy subsidy
The additional energy that has to be put into the system other than the natural energy there
Energy other than the sun for farming
Human and animal labor
system without energy subsidy will die
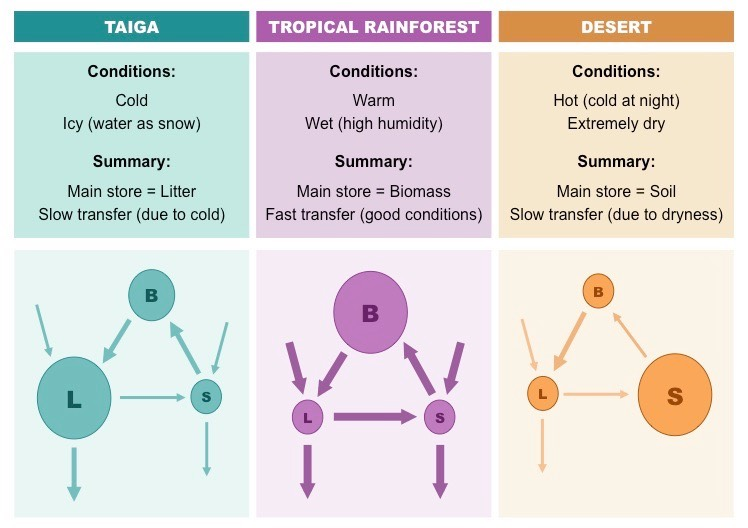
Gersmehl’s nutrient flow model
A model that shows the relationship between biomass, litter and soil
Biomass is nutrients in vegetation and animals
Litter is nutrients in dead organisms and leaves
Soil is nutrients in decomposing matter and soil humus