OCR A Level Chemistry 6.1.2.1 Carbonyl Groups - Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is the aldehyde functional group?
CHO
What is the ketone functional group?
CO
What are the conditions required for the oxidation of aldehydes and ketones?
Heat under reflux, Cr₂O₇²⁻ ions, dilute H₂SO₄
What is the equation for the oxidation of aldehydes?
RCHO + [O] → RCOOH
What is formed during the oxidation of aldehydes?
Carboxylic acids
What is the equation for the oxidation of ketones?
Ketones do not undergo oxidation
How does a C=O bond form?
•Sigma bond formed from direct overlap of atomic orbitals
•Pi bond formed from sideways overlap of p orbitals above and below the plane of the bonding C and O atoms
Why do carbonyl groups tend to undergo nucleophilic addition instead of electrophilic addition?
•C=O bond is polar
•Greater electron density is found closer to the O atom due to higher electronegativity
•Carbon has a slight positive charge, atracting nucleophiles
•Nucleophiles attack slightly positive carbon, resulting in addition across the C=O bond
What is used as a reducing agent for the reduction of aldehydes and ketones?
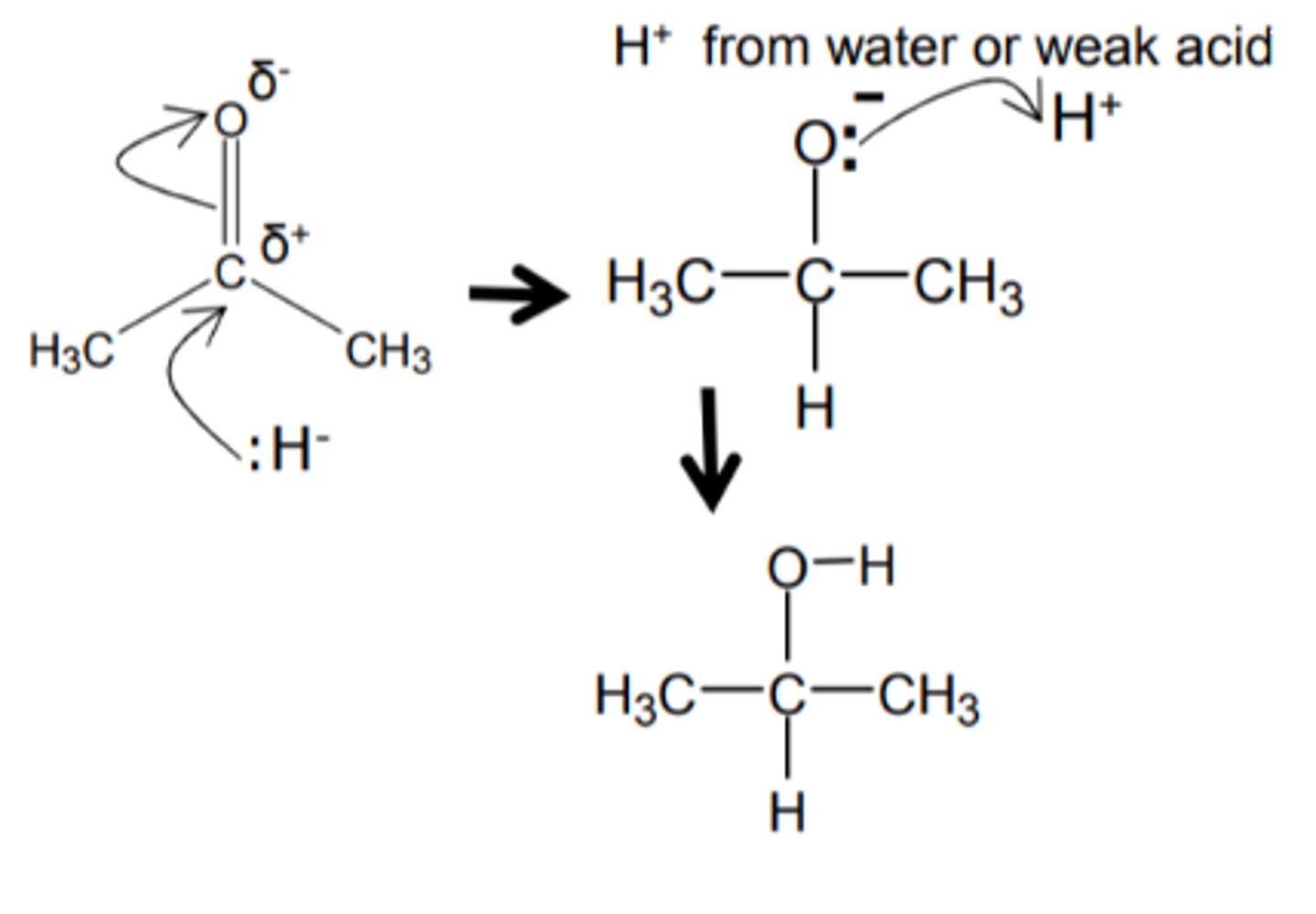
Sodium tetrahydridoborate (III), NaBH₄
What does NaBH₄ act as a source of?
Hydride ions. H:⁻
What are the conditions for the reduction of aldehydes and ketones?
Warmed with NaBH₄ in aqueous solution
What is produced in the reduction of aldehydes?
Primary alcohols
What is the equation for the reduction of an aldehyde?
RCHO + 2[H]→ RCH₂OH
What is produced in the reduction of ketones?
Secondary alcohols
What is the equation for the reduction of a ketone?
RCOR + 2[H] → RC(OH)HR
What are the two main steps in nucleophilic substitution of ketones?
•Nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl group to form a negatively charged intermediate
•Protonation of the intermediate to form an alcohol
What is the nucleophile in the reduction of aldehydes/ketones?
Hydride ions, H:⁻
What is the mechanism for the reduction of aldehydes/ketones?
Why isn't hydrogen cyanide, HCN, used directly in the reaction between aldehydes/ketones and hydrogen cyanide?
It is a colourless, extremely poisonous liquid that boils slightly above room temperature
How is hydrogen cyanide supplied in the laboratory?
Sodium cyanide, NaCN, and sulphuric acid H₂SO₄
How does hydrogen cyanide act as a weak acid?
HCN dissociates into H+ and CN⁻
What is produced in the reaction between aldehyde/ketones and hydrogen cyanide?
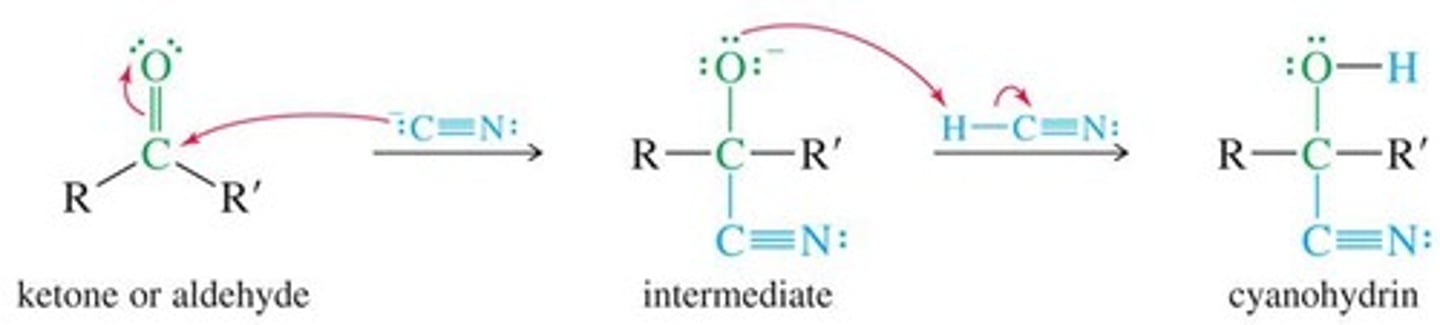
Hydroxynitriles/cyanohydrins
Why is the reaction between aldehydes/ketones and hydrogen cyanide useful?
Increases the length of the carbon chain
What is the equation for the reaction between aldehydes/ketones
RCHO + HCN → RC(OH)CN
What is the nucleophile in the reaction between aldehydes/ketones and hydrogen cyanide?
Cyanide ion, :CN⁻
What is the mechanism for the reaction between aldehydes/ketones and hydrogen cyanide?
Uses H⁺ to protonate oxygen