AP Macroeconomics Vocabulary
1/99
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
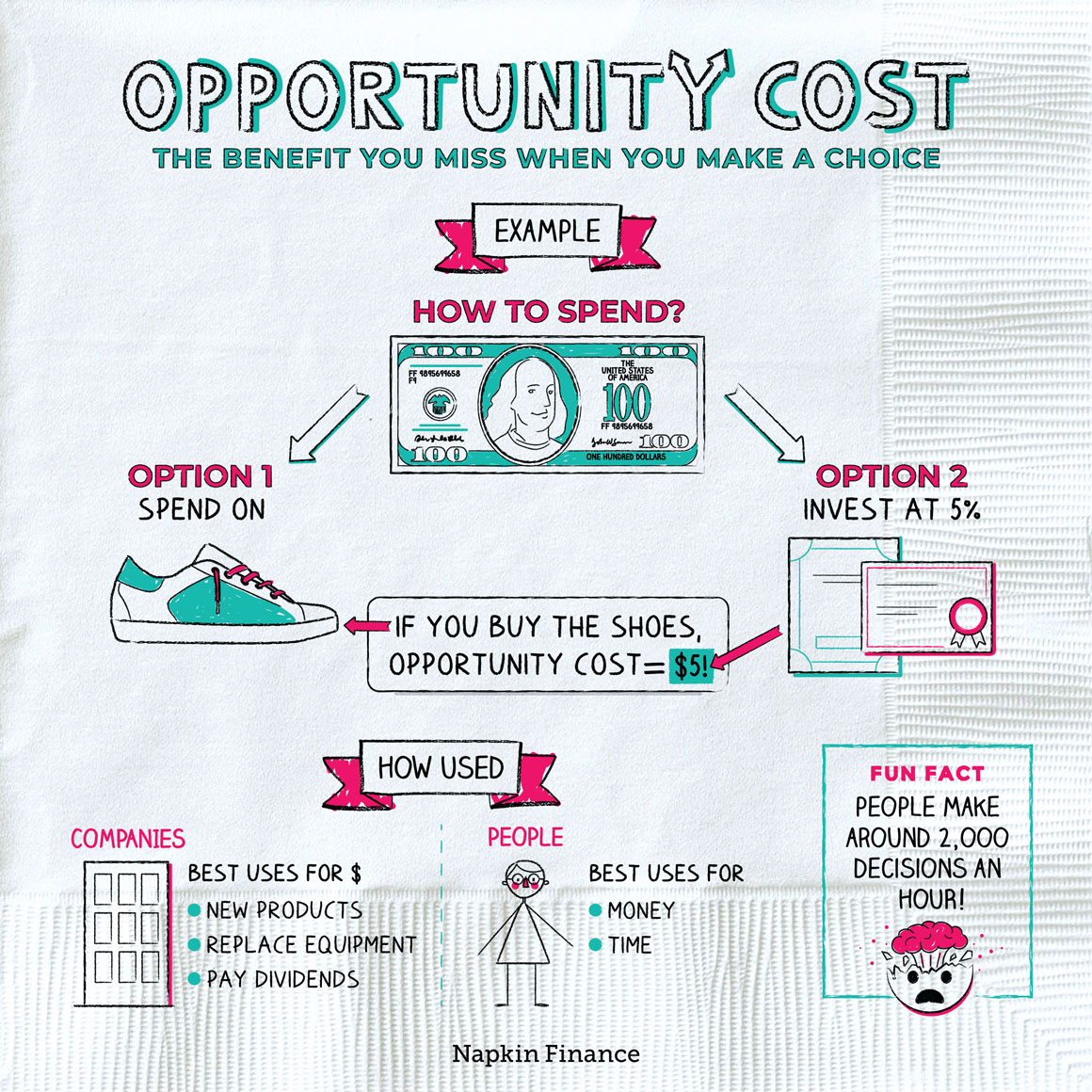
Opportunity Cost
The value of what you must give up when you make a particular choice.
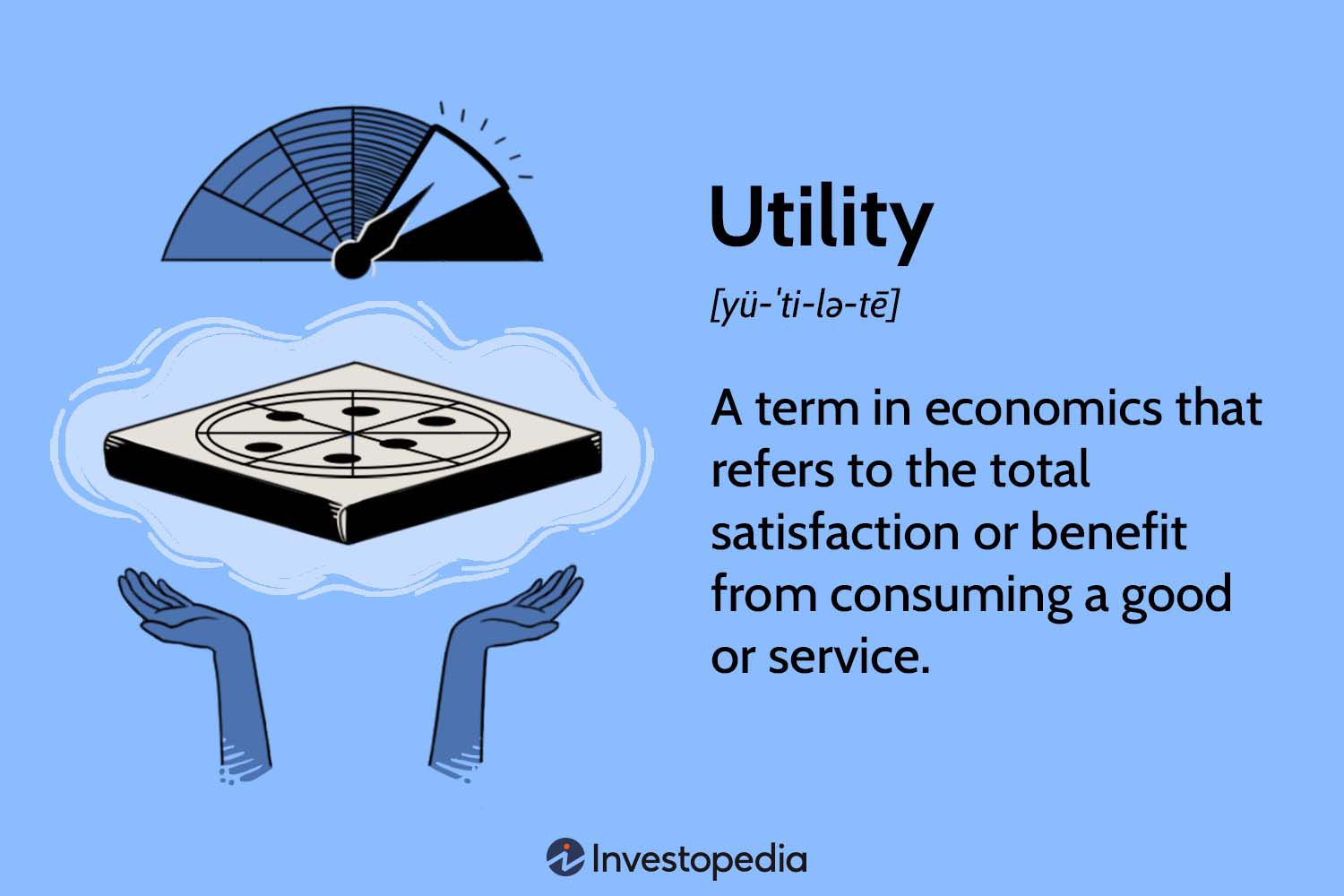
Utility
The satisfaction received from consuming a good or service.
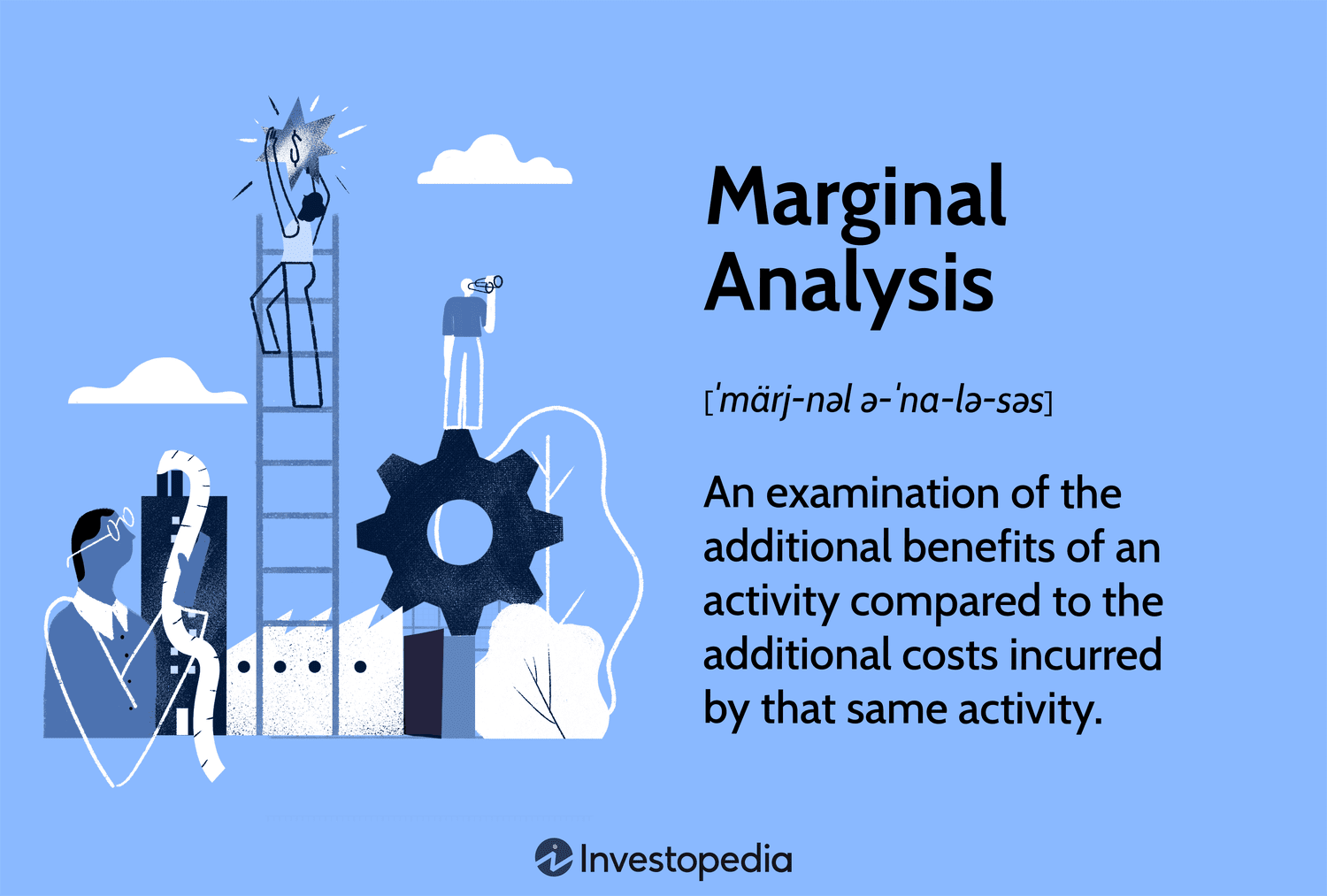
Marginal Analysis
When you focus on the additional cost or benefit associated with a decision.
Microeconomics
The study of the economy of a region or individual business.
Macroeconomics
The study of the economy of a nation.
The basic economic problem.
Having unlimited wants with limited resources.
Economic Resources
Land, Labor, Capital, and Entrepreneurial Ability
Absolute Advantage
When a country can produce more of an item than its trading partner
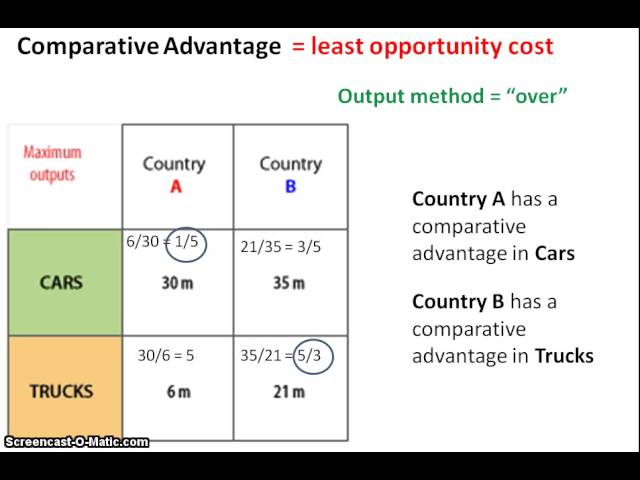
Comparative Advantage
When a country loses less when producing an item compared to its trading partner
Market System
Consumers hold the power to direct the course of the economy
Command Economy
Government coordinates economic activities
Physical Capital
Factories, tools, and equipment used to produce items
Land
Natural resources used to produce goods and services
Labor
People’s physical and mental efforts used to help make goods
Entrepreneur
Risk taker and owner that uses other resources to produce goods or services
Economic Investment
Spending to accumulate capital equipment to increase production
Production Possibilities Curve (PPC)
Model of the economy that shows consequences of tradeoffs in the economy
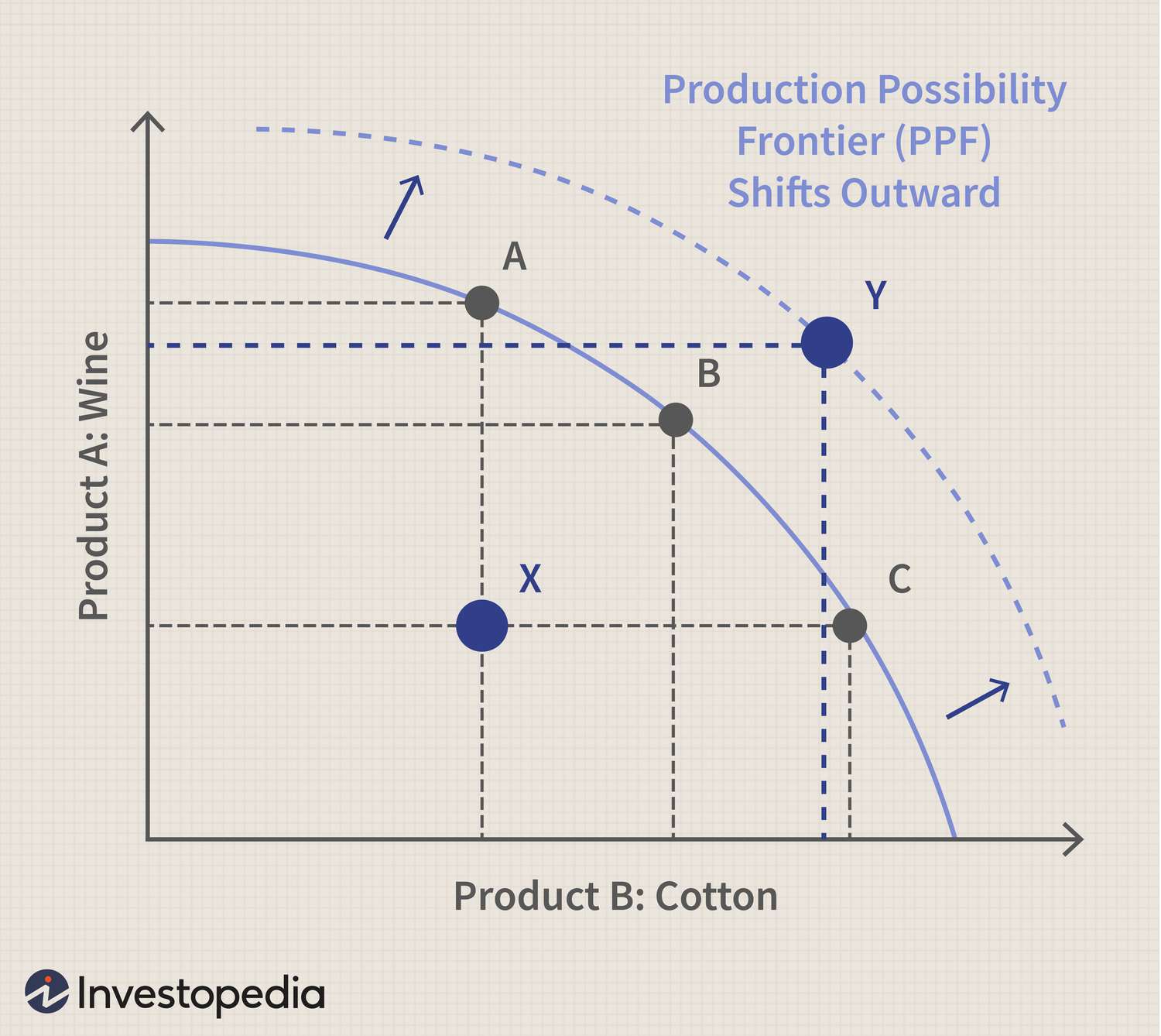
Law of increasing opportunity cost
When productions of one good result in more and more sacrifices of another good
Economic Growth
Producing more with finite resources. Shown by outward shift on PPC.
Law of Demand
an increased price results in a decrease of demand (inverse relationship)
Law of supply
an increase in price increases the amount supplied (direct correlation)
Law of diminishing marginal utility
as a consumer increases consumption of a good, the resulting satisfaction decreases
Income Effect
The change in a quantity demanded resulting from a change in real income or purchasing power
Substitution
The change in quantity demanded resulting from a price change in a related product
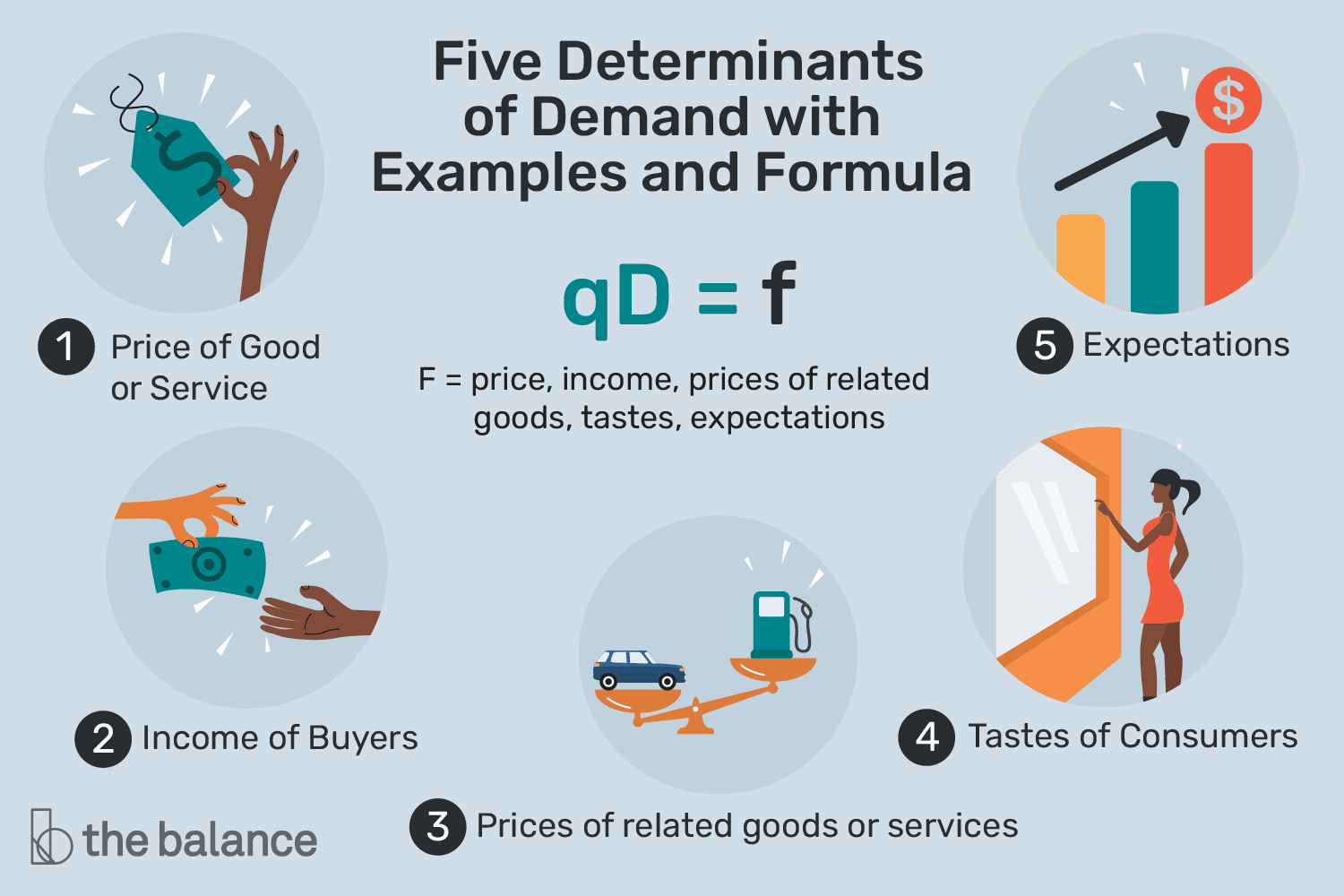
Determinants of Demand
factors that determine demand
Inferior Good
A good whose demand will go up following a decrease in income
Normal Good
A good whose demand will go down following a decrease in income
Complimentary goods
Products often used together
Substitute Goods
Goods that can be used in place of each other
Productive Efficiency
Production of goods in the least costly way
Allocative efficiency
Distribution of resources to produce goods in high demand
Surplus
Supply exceeds demand
Shortage
Demand exceeds supply
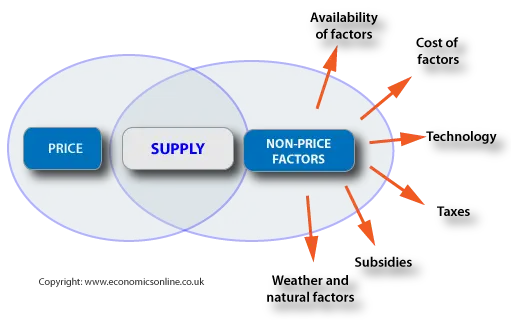
Determinants of Supply
Factors that determine the supply of a good
GDP
The total market values of the final goods and services produced annually in the U.S.
Expenditure Approach
Measuring GDP by all the spending in a year
(C+I+G+(x-M)
Income Approach
Measuring GDP by all the income earned from spending in a year (W+P+i+R)
Real GDP
The measure of GDP accounting for change in the price level.
Nominal GDP
A measure of GDP not adjusted for inflation. (Measures in current year’s $)
Consumption of fixed capital - Depreciation
The amount of capital equipment that is worn out in producing a level of GDP.
Net Private Domestic Investment
Business spending minus depreciation
Gross Private Domestic Investment
Business Spending
(CPI) Consumer Price Index
Measure of a market basket of goods and services indicating inflation/deflation
Business Cycle
The general ups and downs of an economy. Increases and decreases in economic activities.
Unemployment Rate
Percent of unemployed labor force
Frictional Unemployment
Unemployment from workers being fired, quitting, or those looking for work.
Cyclical Unemployment
Unemployment due to insufficient spending or business activity in the economy (Due to recessions)
Structural Unemployment
Unemployed because of skills not being in demand/being replaced by machinery
Demand Pull Inflation
Increase in price level due to excess spending
Trough/Recession
Temporary minimum in business cycle, declining RGDP
GDP Gap
The amount RGDP falls short of potential GDP
Cost Push inflation
increase in price level from increased cost of doing business
Natural Unemployment Rate
5%; unemployment rate without Cyclical unemployment
Recovery
RGDP increase after decline in business cycle
Peak
Economy at temporary maximum; inflation will occur
Real Interest Rate
Interest rate adjusted for inflation
Nominal Interest rate
Advertised interest rate not adjusted for inflation
Disinflation
CPI/Price levels increase, just at a slower rate
Aggregate Demand
The amount that domestic consumers, businesses, the government, and the rest of the world is willing to purchase at a given price level.
Real Balance/Wealth Effect
When the price level increases thus reducing purchasing power
Interest Rate Effects
When the price level increases thus increasing the demand for money and interest rates
Foreign Purchase/Net export effect
When the price level rises thus making our exports less desirable
Leakages
Money withdrawn from the economy
Injections
Money put into the economy
tax multiplier
Used to figure out the larger impact of an increase/decrease in taxes
Simplified Spending Multiplier
Used to figure out the larger impact of an increase/decrease in government spending
Balanced Budget Multiplier
Used to figure out the larger impact of increasing/decreasing taxes and government spending respectively
Sticky Wages
Prevents Economy from self correcting
Short Run Aggregate Supply
The amount producers are willing/able to produce at a given price
Fiscal Policy
When government increases/decreases spending and raises/lowers taxes to influence the economy
National Debt
The accumulation of all deficits
Budget Deficit
When government spends more than it takes in
Structural Deficit
A planned deficit to pay for government program obligations
Cyclical deficit
unplanned deficit due to recession
Expansionary fiscal policy
Used for recession, gov spending up, taxes down
Contractionary Fiscal Policy
Used during inflation, gov spending down, taxes up
Built in/automatic stabilizer
Automatic fiscal adjustments to fix the economy without need for deliberate government action
Budget Surplus
When the government brings in more tax revenue than it spends
Crowding Out Effect
When the government deficit spending causes raised interest rates during recessions
M0 (Monetary Base)
Includes currency in circulation, checkable deposits, and savings accounts
M1
M0+Bank Reserves
M2
M0+M1+Money Market accounts, deposits under 100k
Unit of Account/Measure of Value
function of money that is used to compare the value of goods to each other
Demand Deposit
A deposit you can withdraw anytime
Medium of Exchange
the function of money that provides a way to exchange goods and services
Store of value
the function of money that serves as a way to set aside money for future use
Asset Demand
The amount of money people want to hold onto as a store of value
Transaction Demand
The amount of money people hold onto to exchange
Monetary Policy
A central bank’s changing of the money supply to influence interest rates
Contractionary Monetary Policy
Decreases money supply by selling bonds (omo down), increasing RRR, and increasing DR
Expansionary Monetary Policy
increasing money supply by buying bonds (omo up), decreasing RRR, and decreasing DR
Required Reserve Ratio
The fraction of checkable deposits a bank must hold in reserve. Set by the FED
Loanable Funds Market
Graph of borrowed money, borrowers, and savers
Required Reserves
the amount banks must hold onto to meet the RRR
Equation of exchange - Quantity Theory of Money
Formula used to argue that the value of money is determined by the quantity of money
Total/Actual Reserves
The amount that banks are currently holding onto (excess + required)
Federal Funds Rate
The interest rate banks charge each other on overnight loans
Discount Rate
The interest rate the FED charges banks for loans
Excess reserves
The amount a bank’s total reserve exceeds the required reserves (loanable money)
Money Multiplier
The multiple that 1 bank can increase the money supply with excess reserves (1/RRR)