Y10S1 What is the Universe?
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Astronomy
The study of the moon, stars, and other objects in space

Universe
Space and all the matter and energy in it

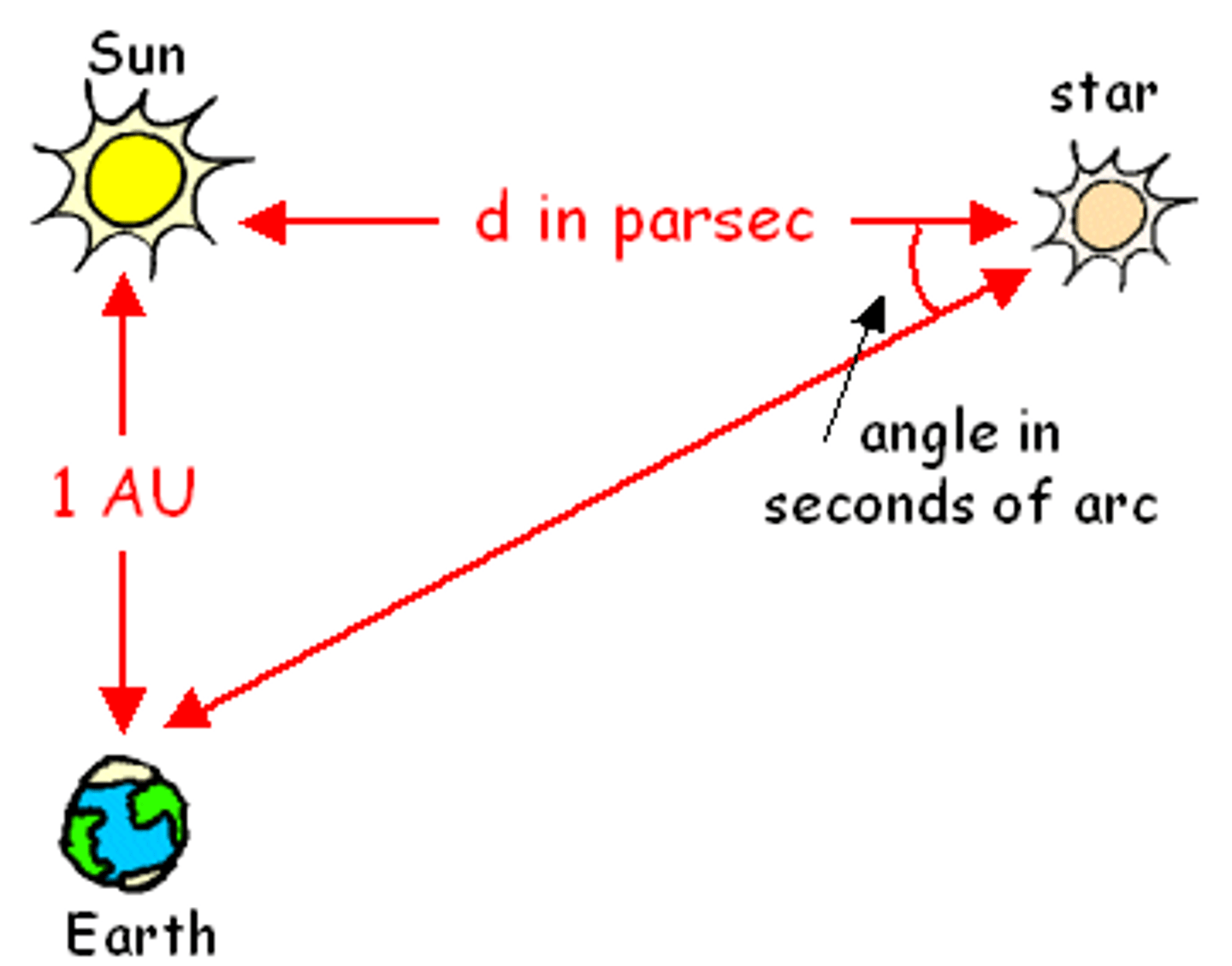
Parsec
A unit of distance that is equal to 3.26 light years (about 31 trillion km)
Light year
The distance that light travels in one year (about 9.5 trillion km)
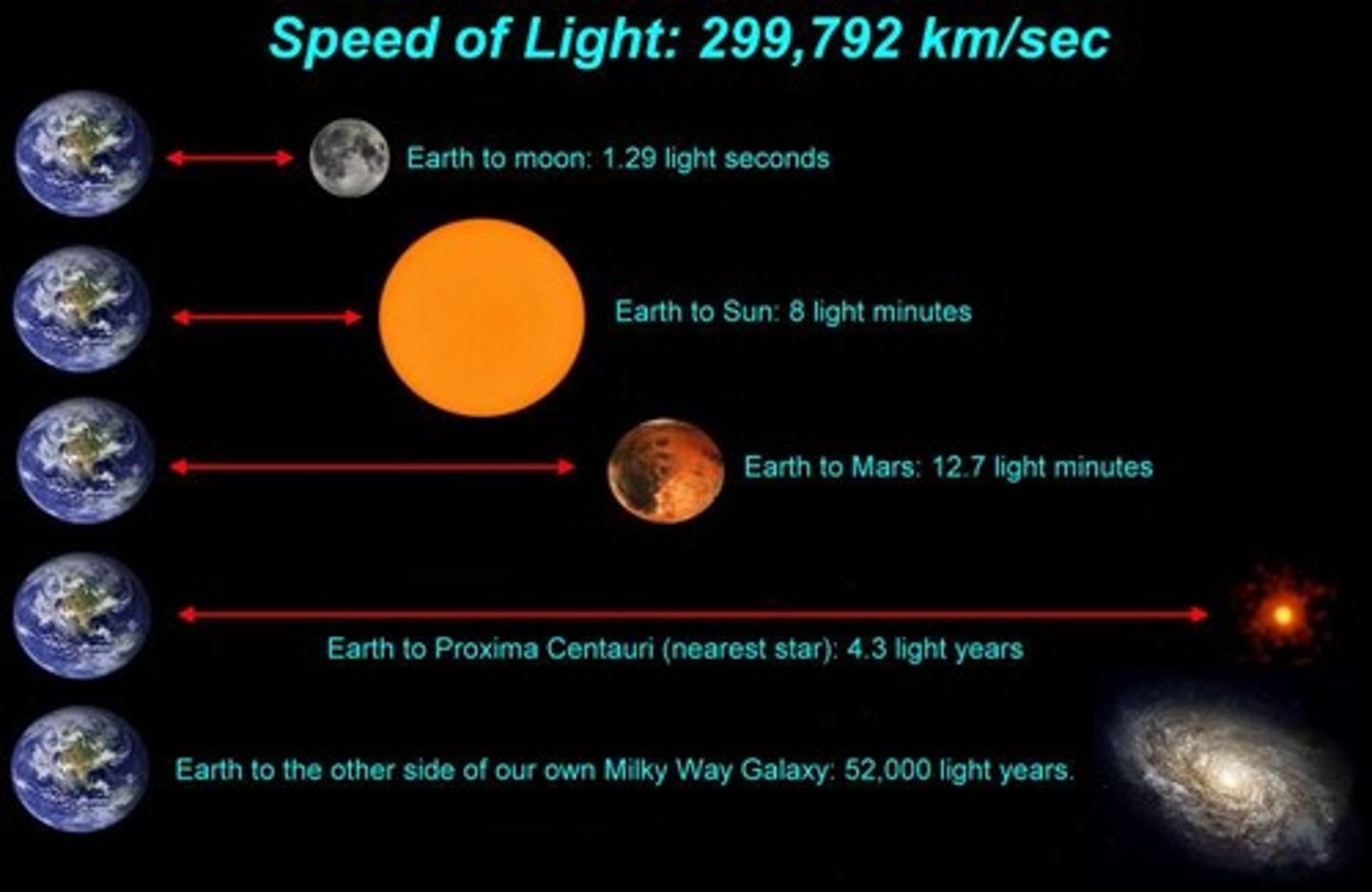
Astronomical Unit (AU)
The average distance between the earth and the sun (about 150 million km)

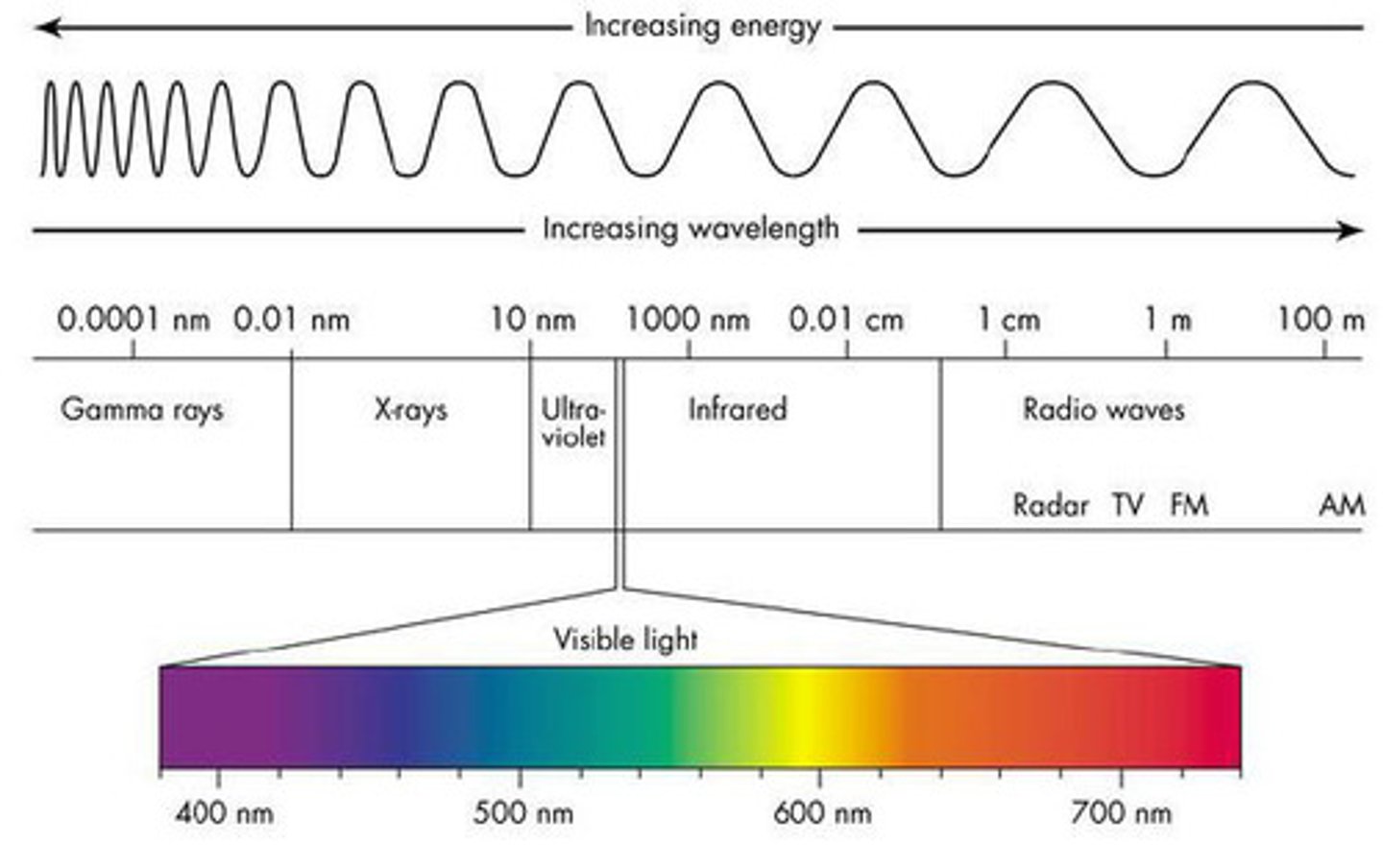
Electromagnetic radiation
The energy transferred through space by electromagnetic waves.
Telescope
An instrument that collects electromagnetic radiation from the sky and concentrates it for better observation

Star
A ball of extremely hot gas, mostly hydrogen and helium, that undergoes nuclear fusion.
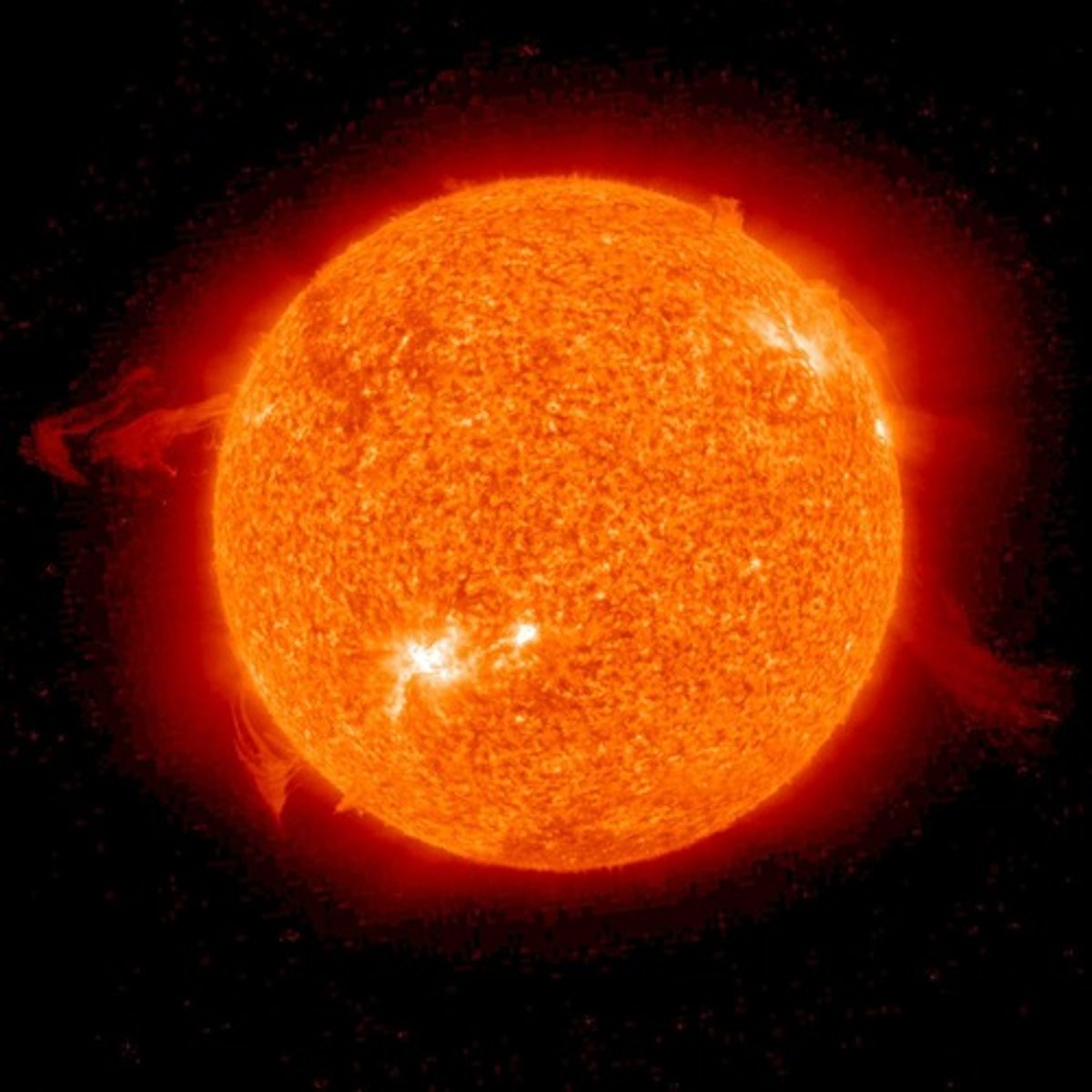
Main sequence star
A typical star that is undergoing nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium. Our sun is a main sequence star.
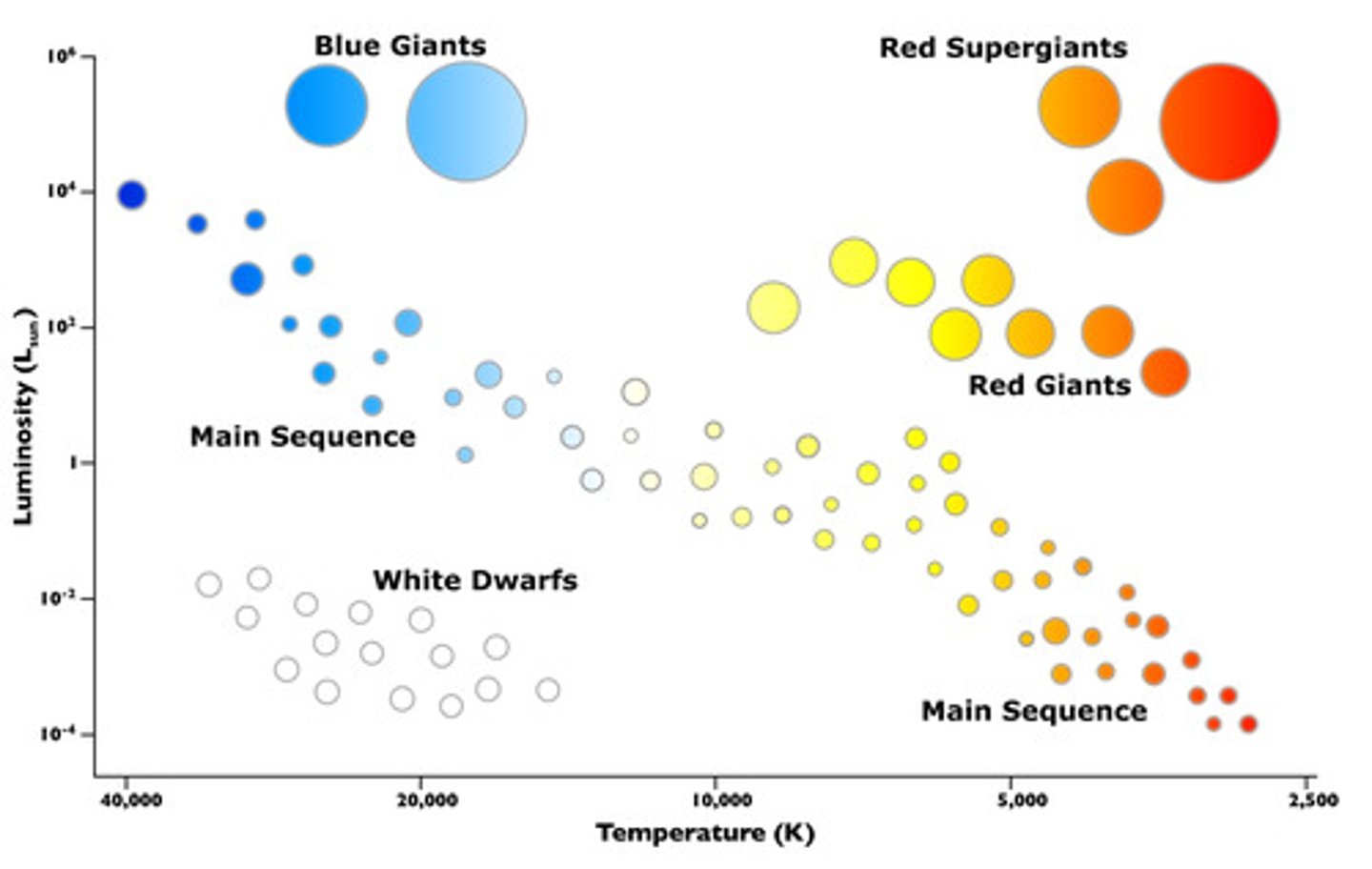
Red giant star
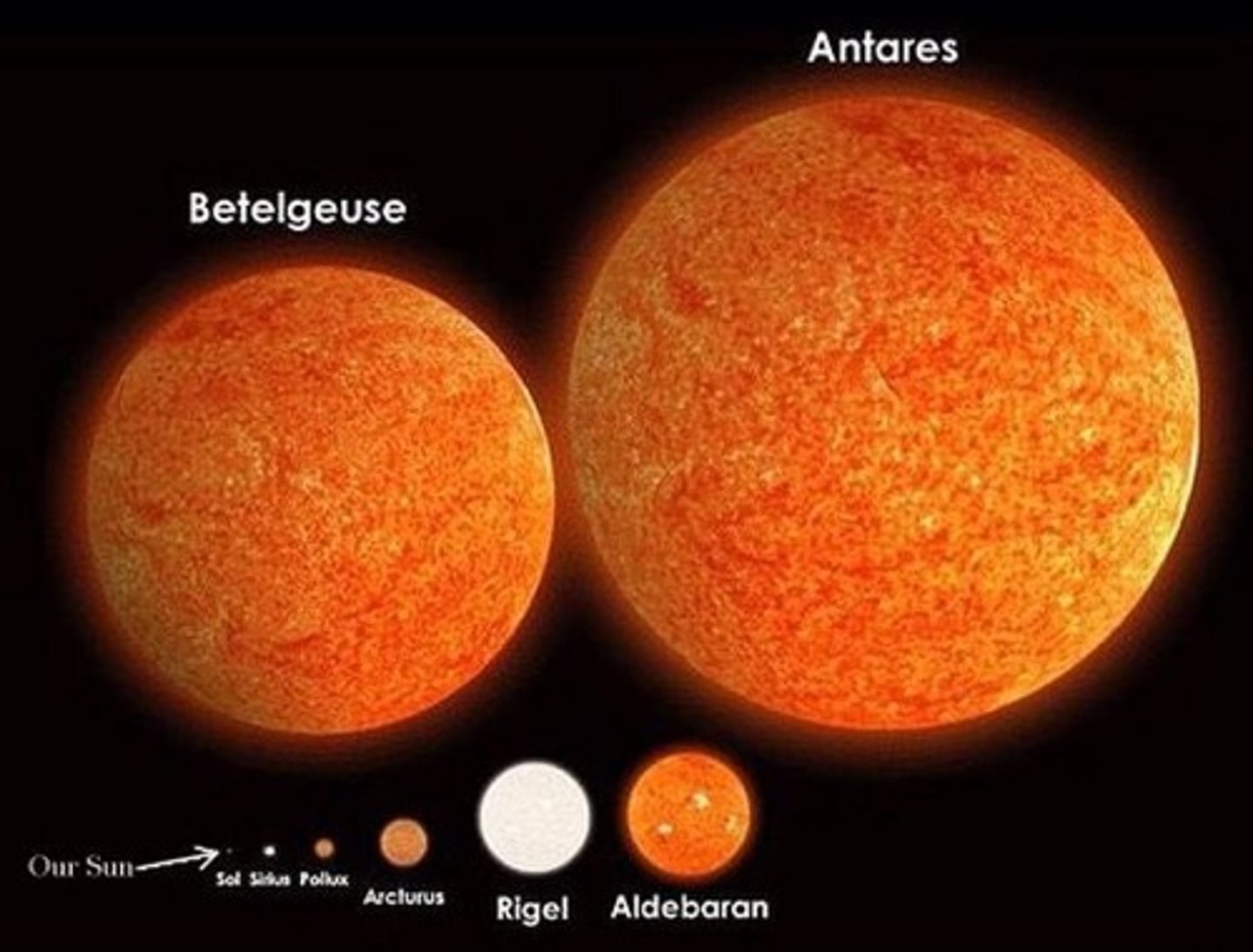
A large, old luminous star; has a relatively low surface temperature and a diameter large relative to the sun. Undergoing nuclear fusion of helium into other elements.
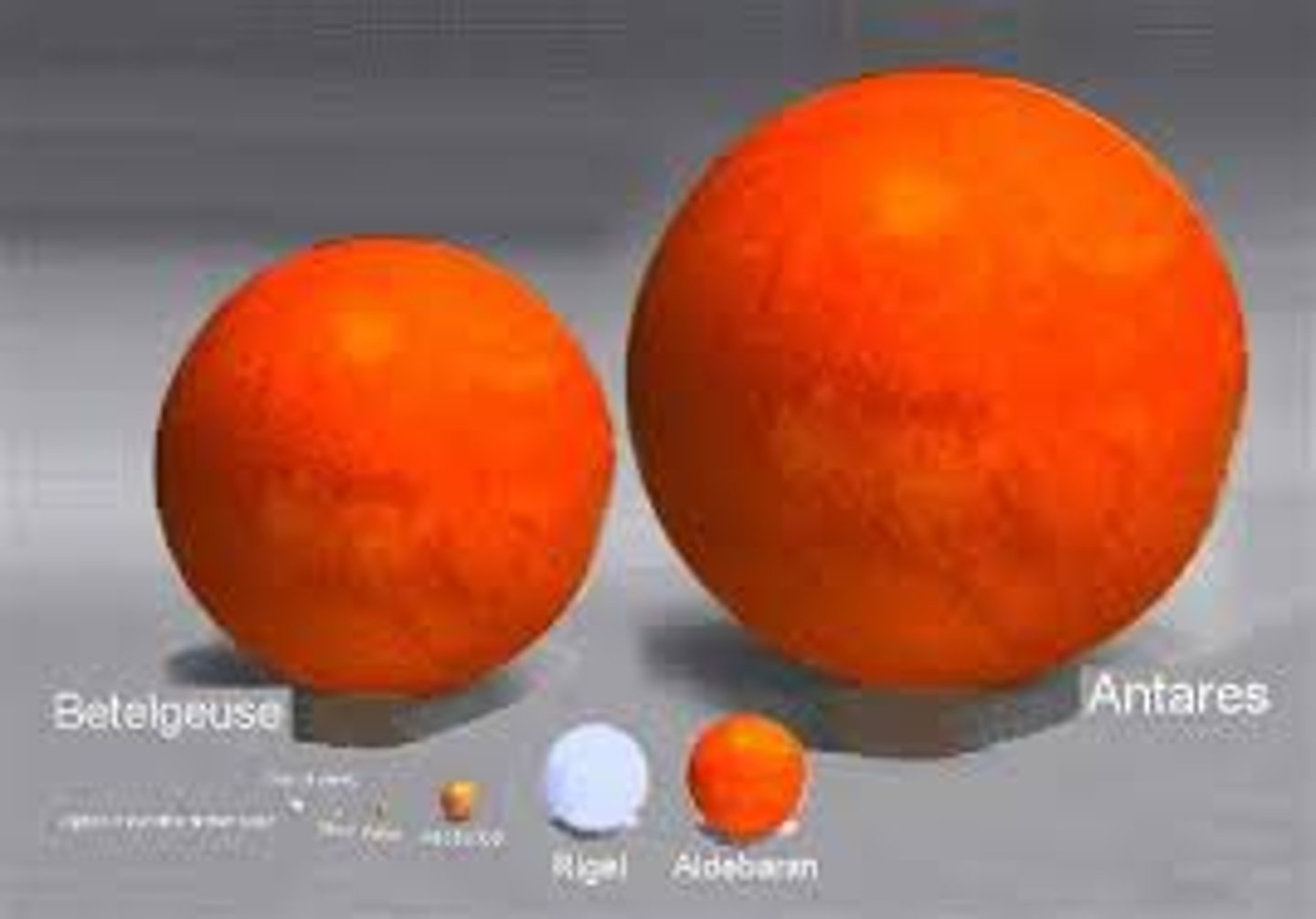

White dwarf star
A small, hot, dim star that is the leftover center of an old star

Supergiant star
A star with a diameter up to 1000 times the diameter of the sun; largest of all stars.
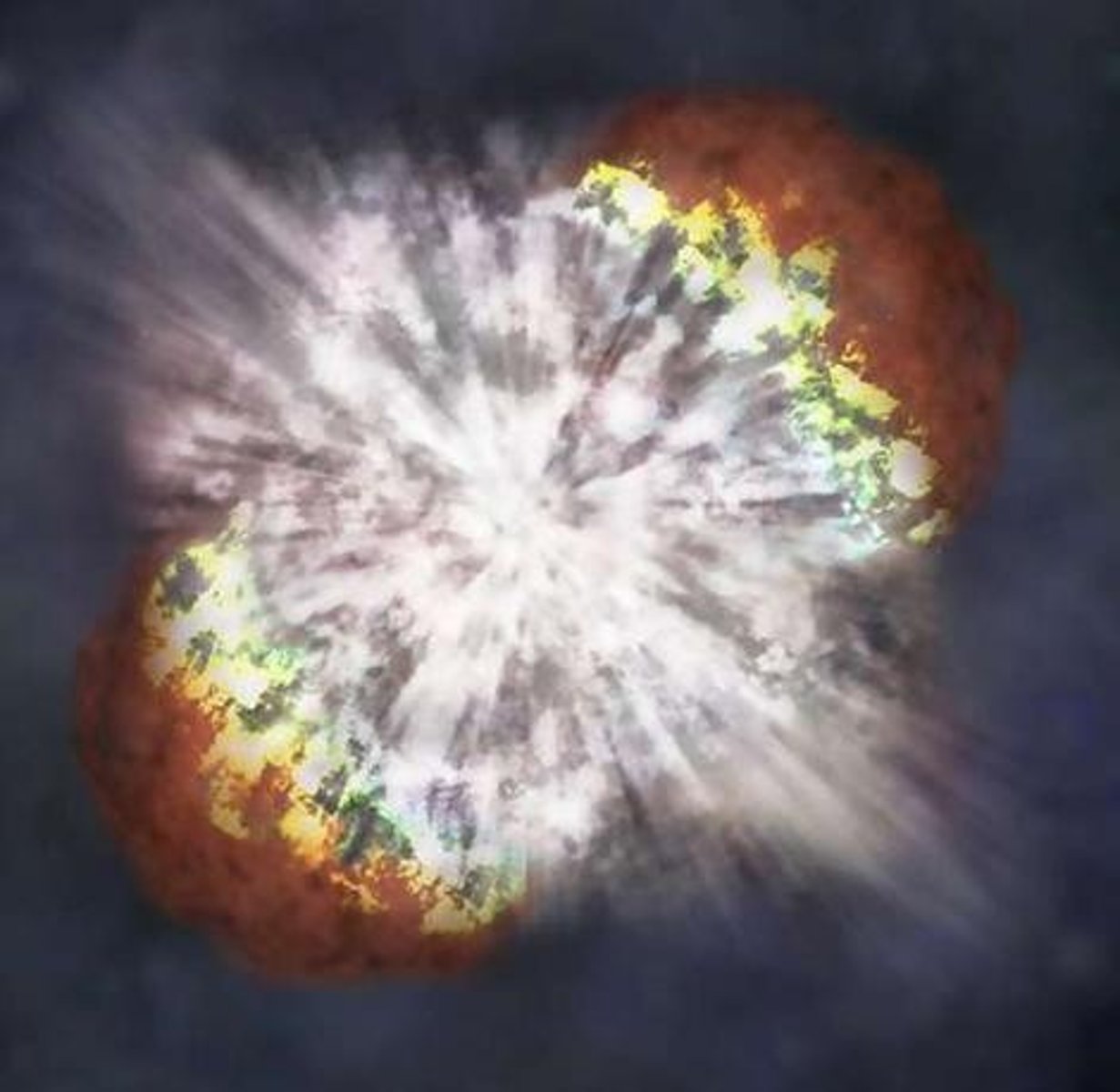
Supernova
A gigantic explosion in which a massive star collapses and throws its outer layers into space

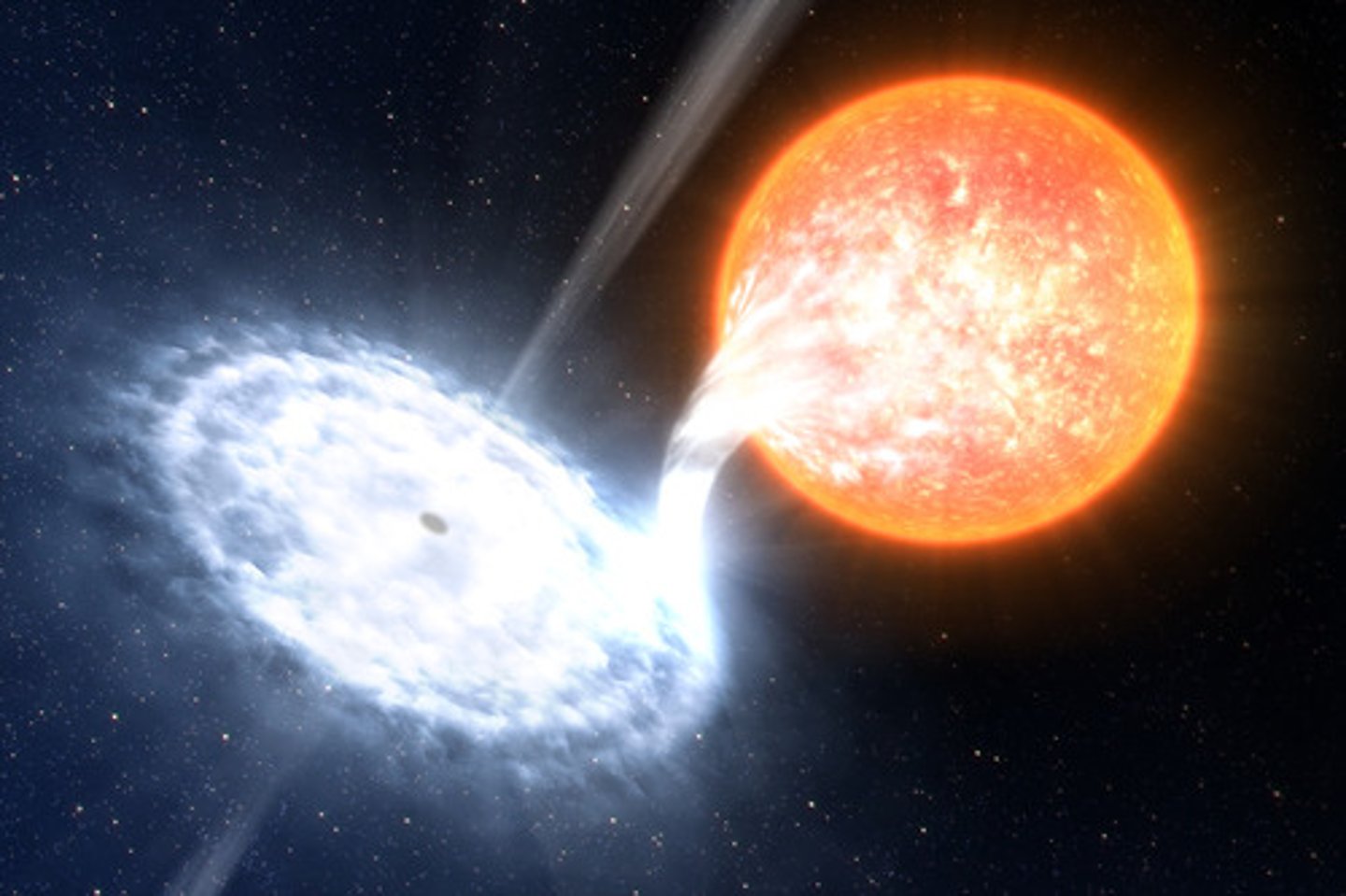
Black hole
A region of space having a gravitational field so intense that spacetime is curved to the point that light cannot escape. Formed when a massive stars collapses at the end of its lifecycle.

Neutron star
The small, dense remains of a high-mass star after a supernova

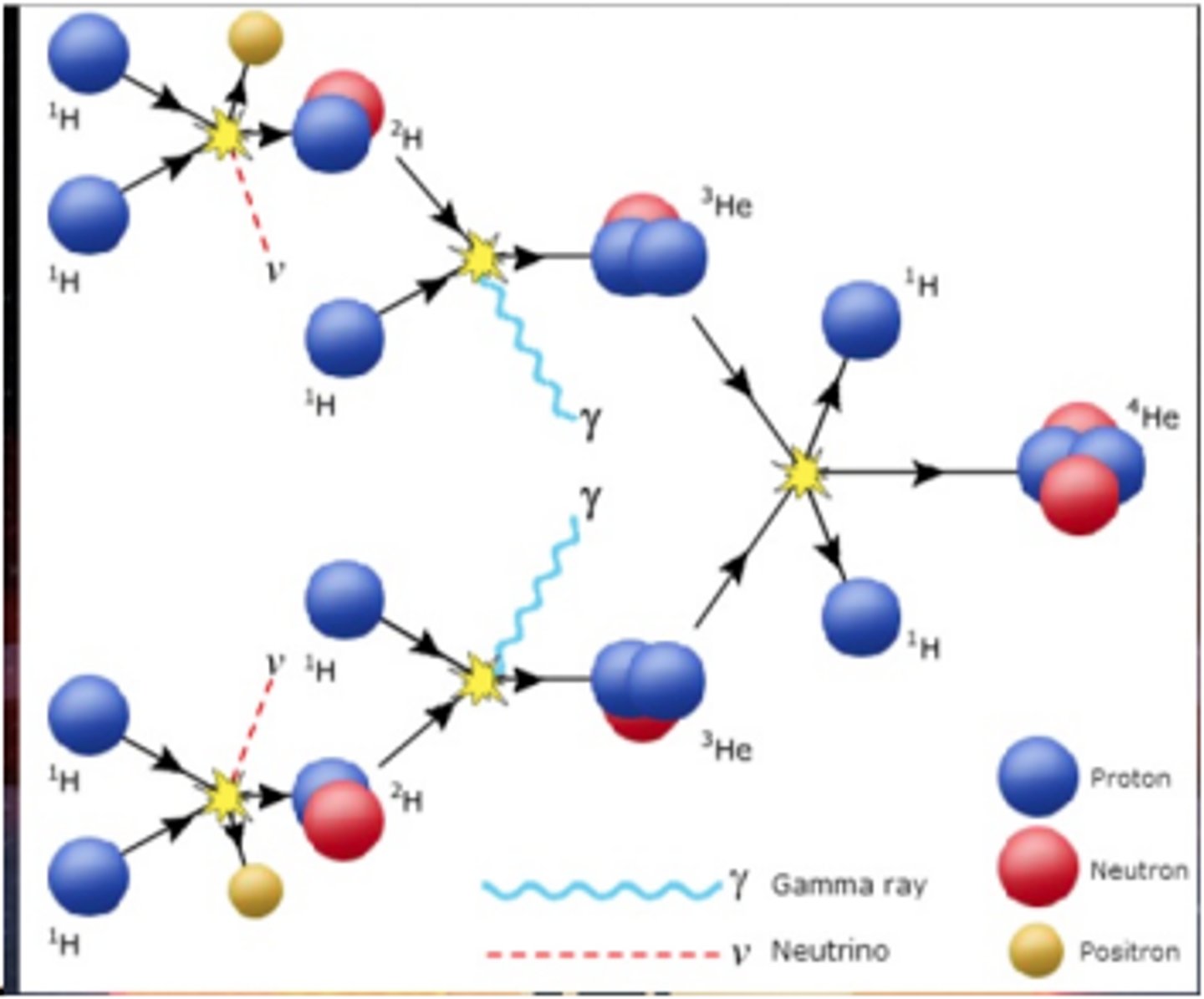
Stellar nucleosynthesis
The production of new elements by nuclear reactions in the core of a star
Galaxy
A collection of stars, dust, and gas bound together by gravity

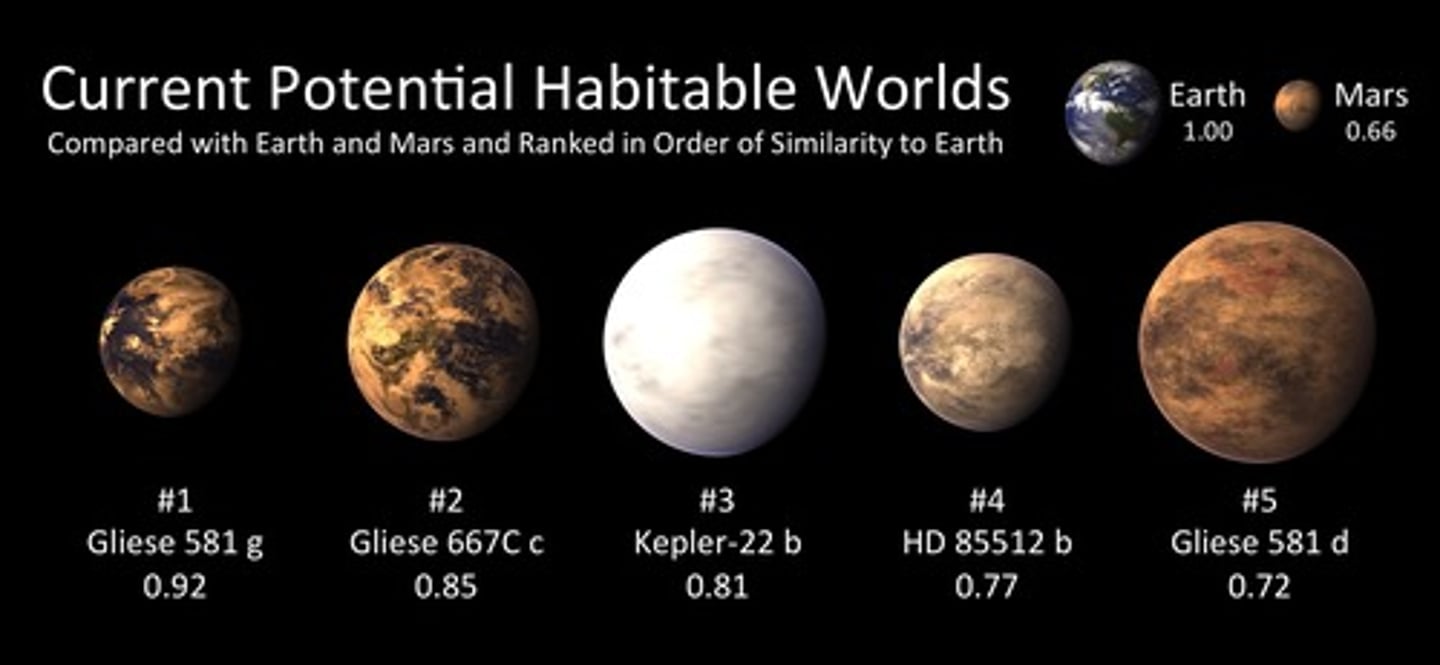
Exoplanet
A planet that orbits a star outside the solar system
Scientific Theory
A well-tested explanation for a wide range of observations or experimental results.
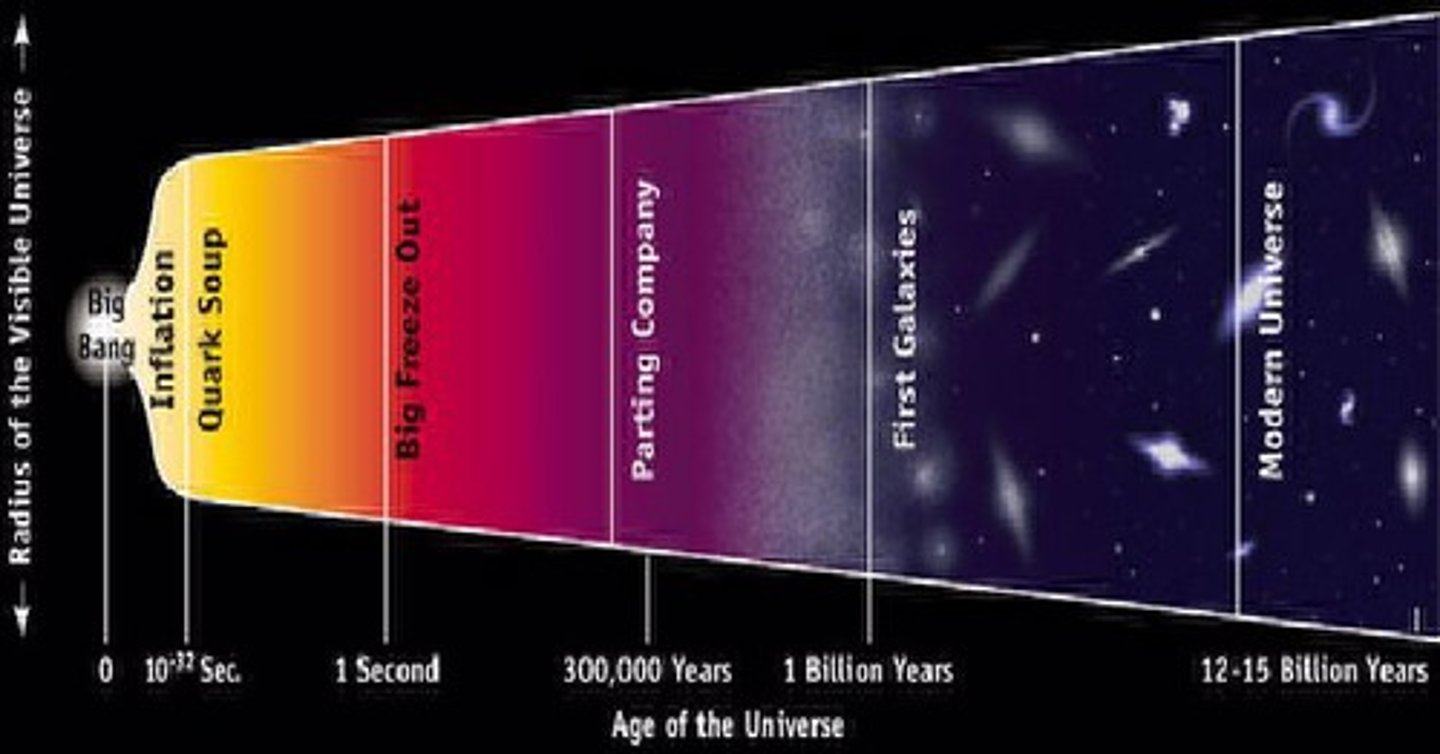
Big Bang Theory
A theory that explains the sudden development of the universe through the continued expansion from a hot, dense state.
Steady State theory
a theory which states that there was no beginning to the universe and that the universe does not change in appearance.

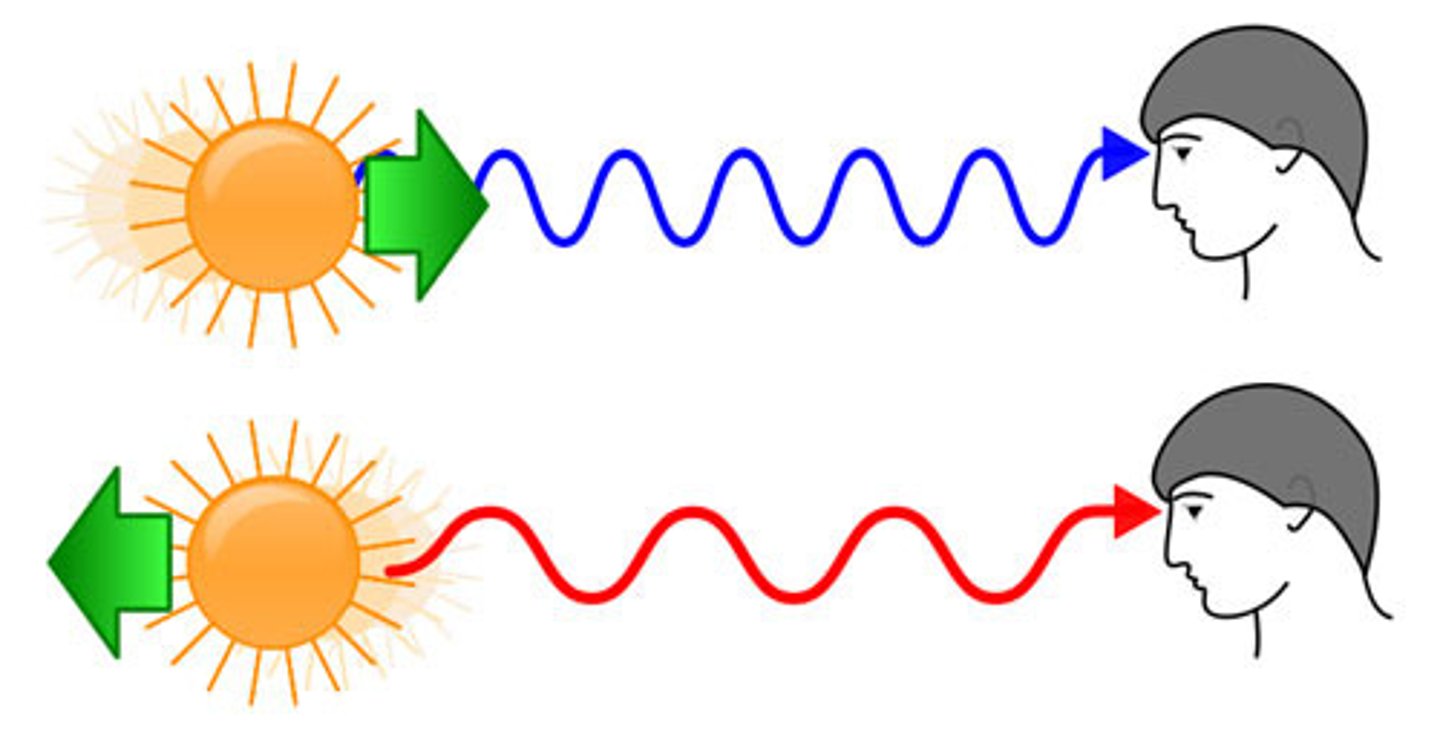
Red shift
The change in the wavelength of light due to an object moving away from the observer.
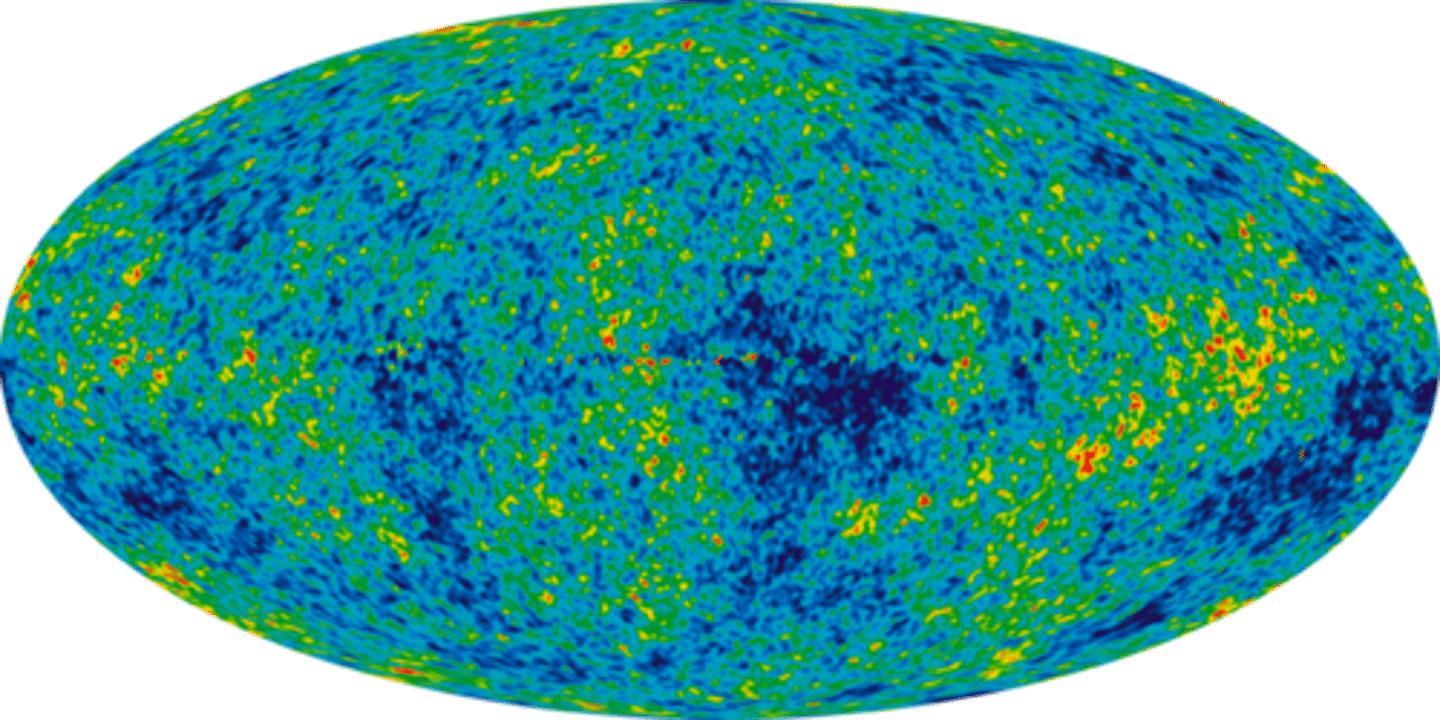
Cosmic microwave background
Radiation left over from the Big Bang

Cosmological inflation
The very very very rapid expansion at the very early stages after the Big Bang.
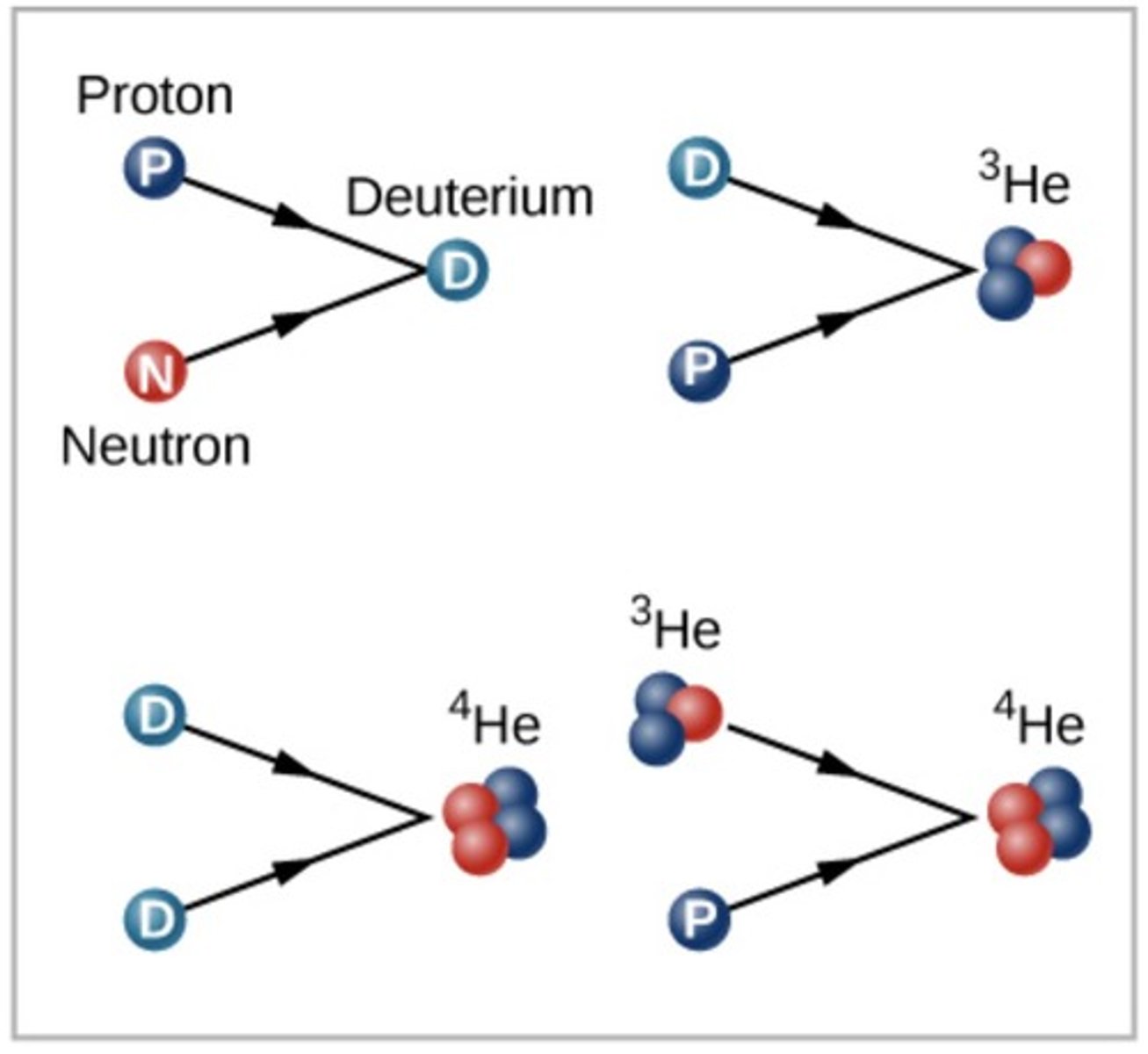
Big Bang nucleosynthesis
Formations of new elements in the first few minutes after the Big Bang before any stars existed.
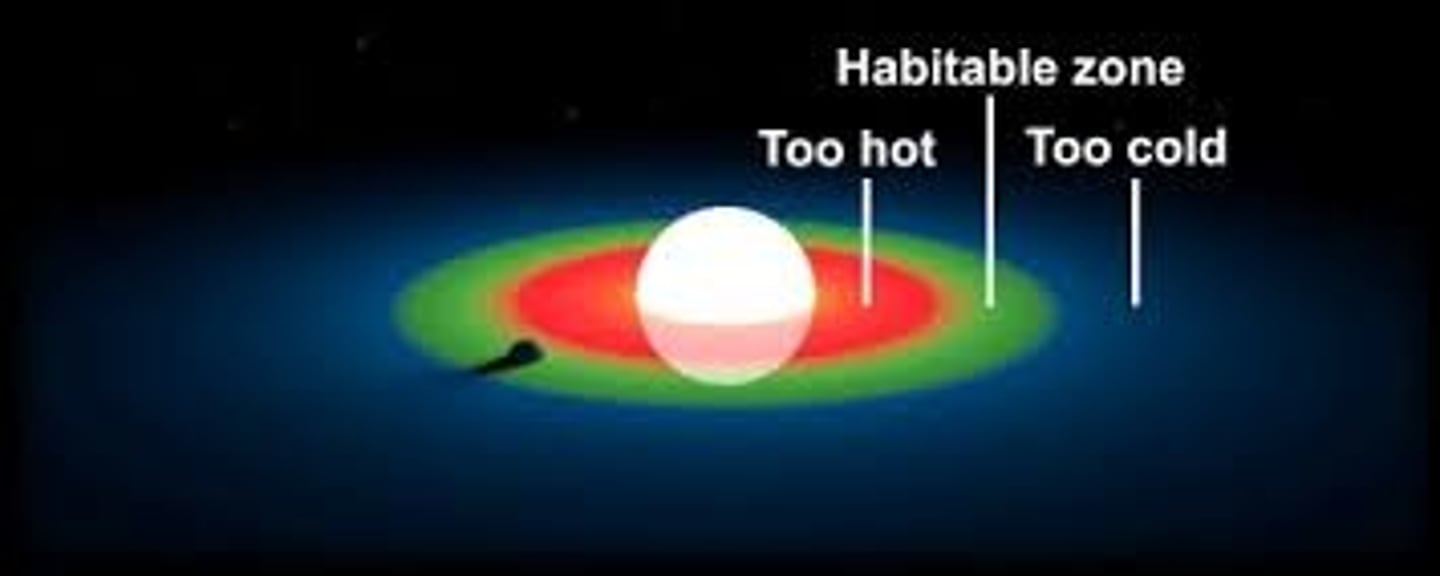
Habitable zone
A region around a star where liquid water could be present on a planet's surface and potentially have life
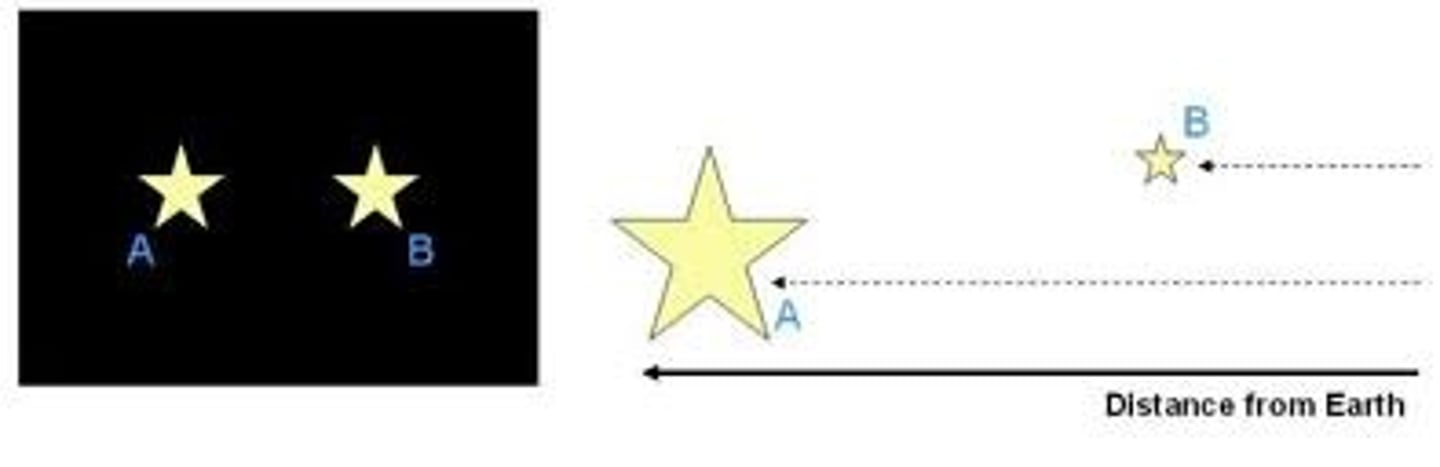
Apparent magnitude
The brightness of an astronomical object as seen from Earth.
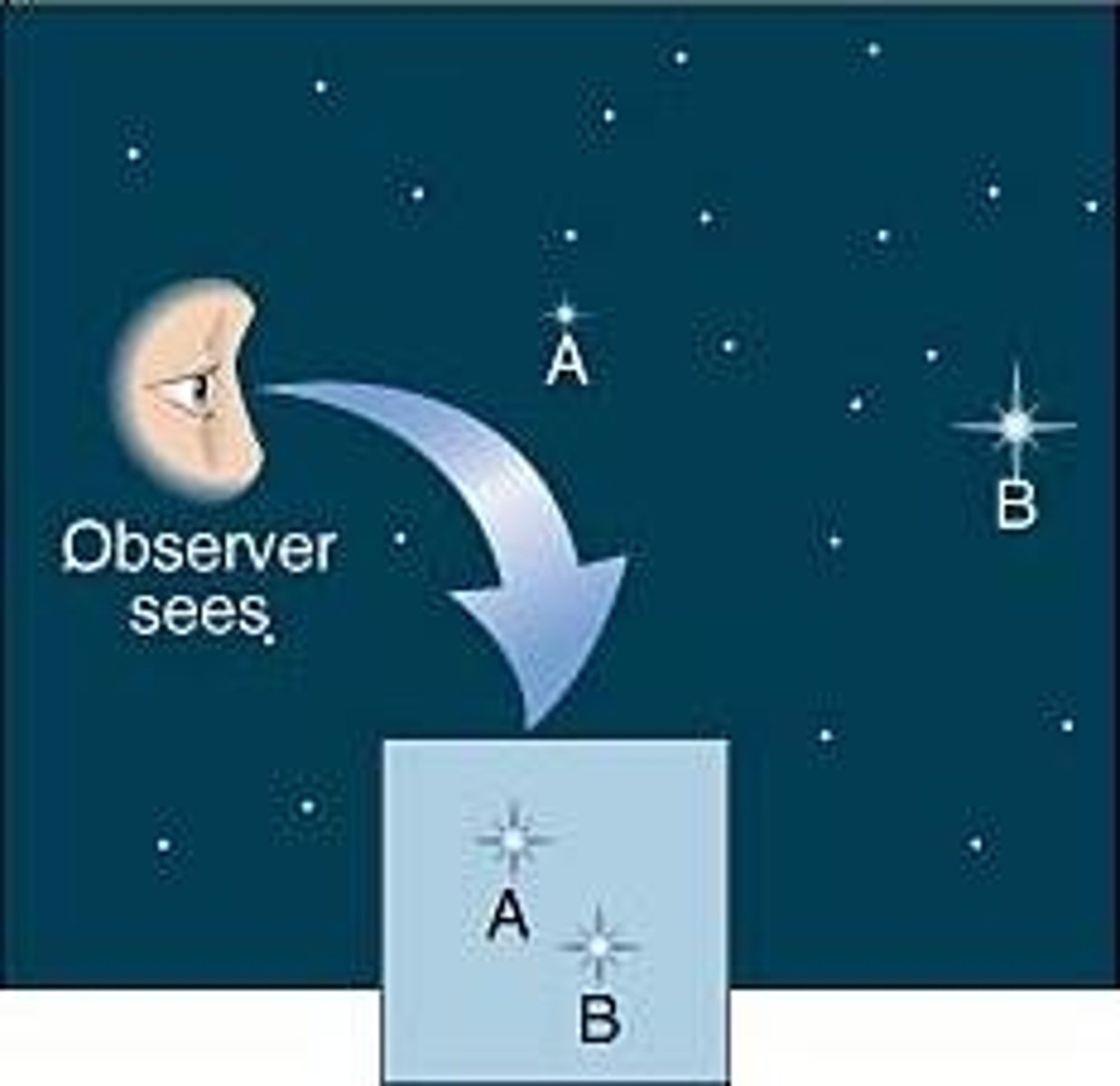
absolute magnitude
The brightness an astronomical object would have at a distance of 10 parsecs from Earth.
Electron
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge
Proton
A subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
Neutron
A subatomic particle that has no charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
Atom
Basic unit of matter
electron orbitals
areas within each energy level where electrons move around the nucleus of an atom
Energy Levels/Electron Shells
The region(s) surrounding the nucleus where electrons orbit the nucleus.
electron configuration
the arrangement of electrons in an atom
valence electrons
Electrons on the outermost energy level of an atom
valence shell
outermost electron shell
Period (periodic table)
Horizontal rows on the periodic table
Group (periodic table)
a vertical column of elements having the same valence electron configuration and showing similar properties
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
alkali metals
Group 1, 1 electron in outer level, very reactive, soft, silver, shiny, low density
alkaline earth metals
metallic elements in group 2 of the periodic table which are harder than the alkali metals and are also less reactive
transition metals
Groups 3-12, 1-2 electrons in the outer energy level, less reactive than alkali-earth metals, shiny, good conductor of thermal energy and electrical current, high density
Metalloids
Elements that have properties of both metals and nonmetals.
Non-metals
elements that are usually dull in appearance, poor conductors of heat and electricity, mostly gases at room temperature
Halogens
Contains nonmetals, 7 valence electrons in it's outermost energy level. Very reactive
noble gases
Group 18 - stable and non-reactive
Ion
A charged atom
Anion
A negatively charged ion
Cation
A positively charged ion
ionic bond
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
lattice network
A 3D network of atoms chemically bonded in a lattice
Delocalised electrons are
Electrons that aren't associated with a particular ion/atom. e.g in a metal the outer electrons can be free to move through a solid.
metallic bond
a bond formed by the attraction between positively charged metal ions and the electrons around them
Molecule
A group of atoms bonded together
covalent bond
A chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule
covalent network
atoms covalently bonded into a large structure that does not contain a specific number of atoms
amino acids
a simple organic compound containing both a carboxyl (—COOH) and an amino (—NH2) group.
nucleic acids
macromolecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus
emission spectra
the spectrum of light released from excited atoms of an element
emission lines
lines that are made when certain wavelengths of light, or colors, are given off by hot gases