Chapter 7 Honors Bio Vocab
1/17
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Prokaryotic Cells
The smallest and simplest cell which evolved first and doesn’t contain DNA in its nucleus.
Eukaryotic Cells
The larger and more complex cells that contain DNA in the nucleus.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
These two cells contain a cell membrane, Ribosomes, cytoplasm, and DNA and RNA but in different locations.
Vacuoles
Sac-like structures responsible for storing water and other materials in plant cells, but in animal cells help hide waste products and are generally smaller.
Nucleus
Stores and contains a cell’s DNA in the form of chromatin
Mitochondria
Produces energy, converting chemical energy found in food into a form in which a cell can use. The mitochondria also contains its own DNA.
Ribosomes
Produce Proteins
Golgi Aperartus
Sorts and transports proteins for transport outside of a cell.
Cytoplasm
A gel-like substance responsible for holding the organelles in place.
Endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth ER contains enzymes responsible for producing lipids and the Rough ER (studded with ribosomes) produces and transports lipids and proteins.
Lysosomes
Sacs that are membrane bound containing digestive enzymes, digesting food and getting rid of unwanted cell parts.
Chloroplasts
responsible for capturing solar energy and converting it into chemical energy known as glucose during a process known as photosynthesis. (Found in plant cells and contains its own DNA).
Cell Wall
Made of cellulose, cell walls exist outside of the cell membrane in prokaryotic cells responsible for supporting the shape of a cell (only found in plant cells).
Cell Membrane
Consists of a double layer of fat - phospholipid bilayer used to separate a cell from the outside, maintaining homeostasis, controls what enters & leaves a cell, and allows for communication between cells via signals.
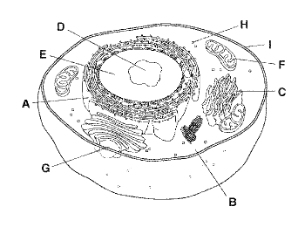
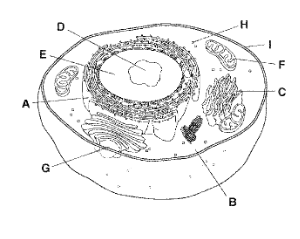
A
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
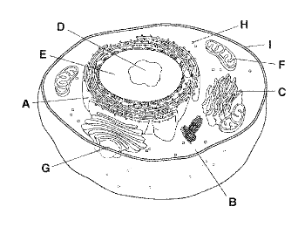
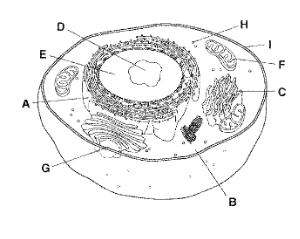
B
Cytoplasm
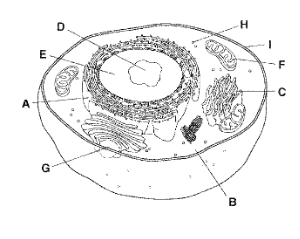
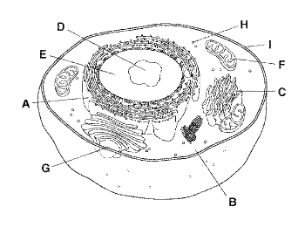
C
Golgi Apparatus
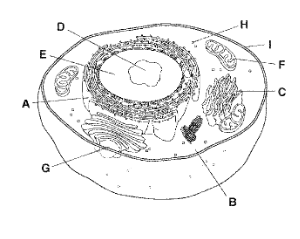
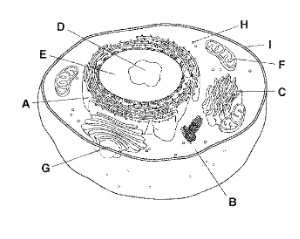
D
Nucleolus