Grade 12 Kinesiology - 2.1 The Human Skeleton Theory
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
5 Types of Bones
Long Bones
Short Bones
Flat Bones
Irregular Bones
Sesamoid Bones
Long Bones + example(s)
any bone whose length greatly exceeds its diameter
provide wide range of motion (act as levers)
example: femur
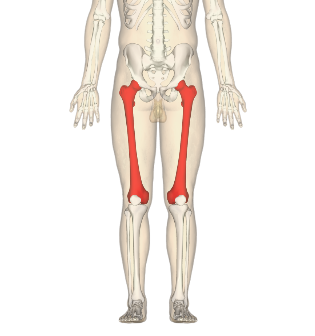
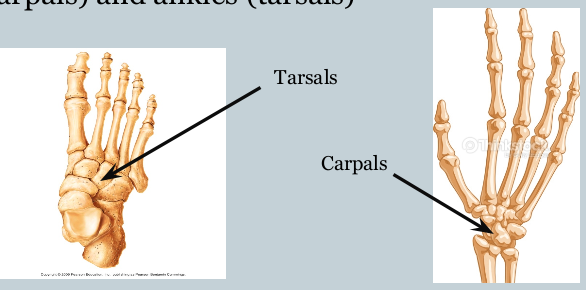
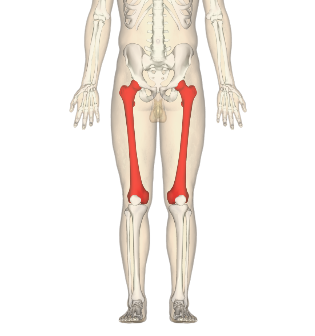
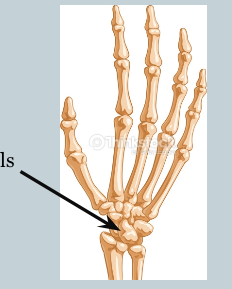
Short Bones + example(s)
serve as shock absorbers + fine motor control
examples: carpals, tarsals
Femur
thigh bone
Carpals
bones of the wrist
Tarsals
bones of the ankle
Flat Bones + example(s)
are flat and thin
protect underlying organs
examples: skull, scapula, sternum, clavicle
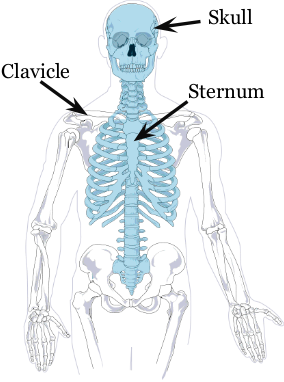
Scapula
shoulder blade
Sternum
breastbone
Clavicle
collarbone

Irregular Bones + example(s)
bones that cannot be placed into any other category
fulfill a specific function
example: vertebrae
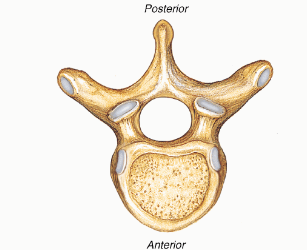
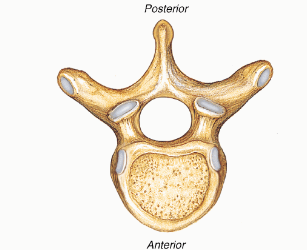
Vertebrae
bones that make up the spine
protect the spinal cord
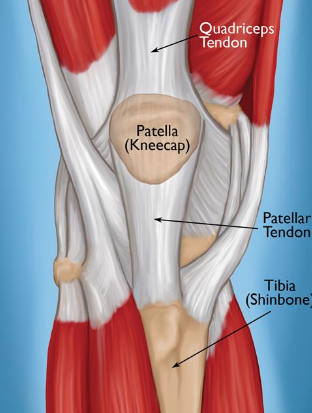
Sesamoid Bones + example(s)
unusual, small bones
wrapped within tendons that move over bony surfaces
example: patella
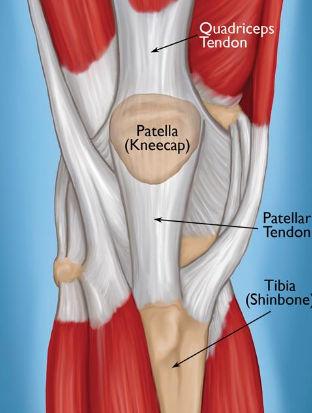
Patella
kneecap
How many bones are in the adult body?
206 bones
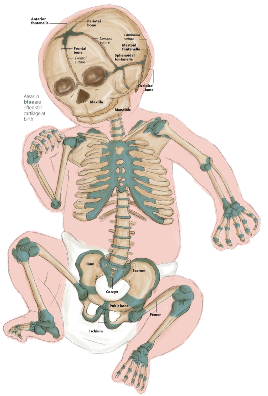
How many bones in a baby?
300 bones
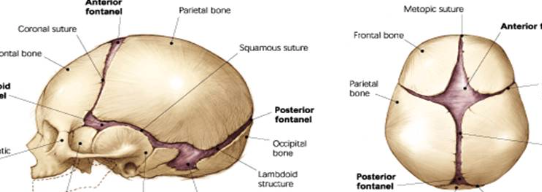
Fontanelle
soft spots on a newborn’s head where ossification has not been completed yet
Simple (closed) Fracture
fractures that stay within the body
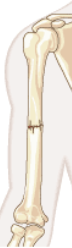
Compound (open) Fracture
fractures that break through the skin

Simple Fracture
no separation of the bone

Compound Fracture
bone breaks in two

Comminuted Fracture
ends of broken bone are shattered into many small pieces
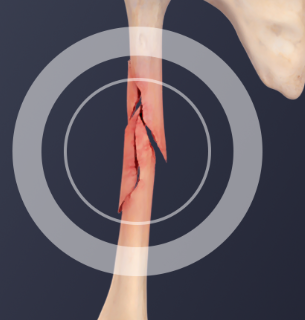
Stress Fracture
tiny cracks in bone caused by repeated activity
hardest to detect
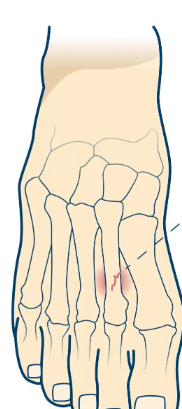
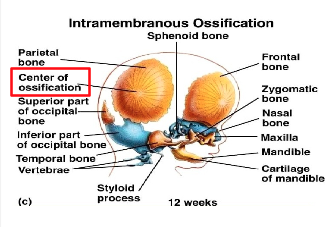
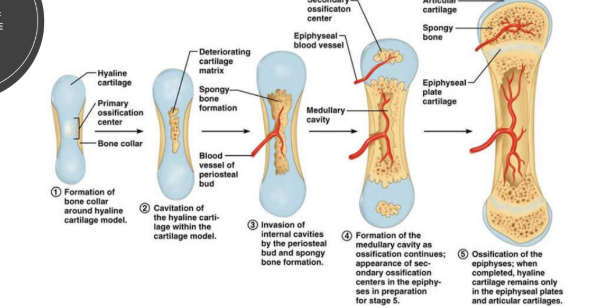
Ossification Center
area where bone tissue forms (same as epiphyseal plates)
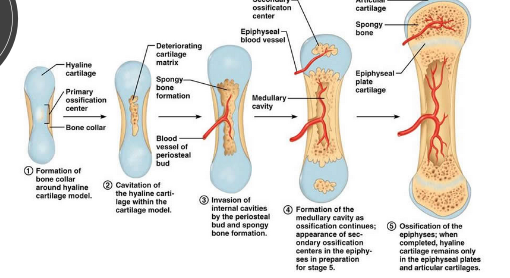
How many ossification centers are there in long bones vs short bones?
long bones: 3 ossification centers (one at each end and one in the center)
short bones: 1 ossification center
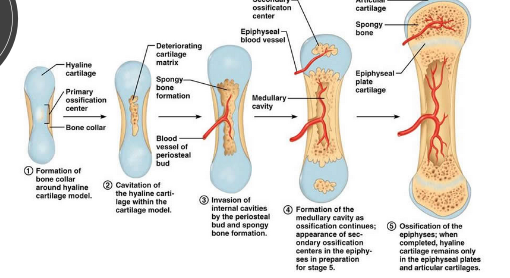
How is compact bone formed?
starts as cartilage
osteoblasts within the cartilage discharge osteoid
inorganic salts are deposited into the osteoid
osteoid hardens forming the compact bone
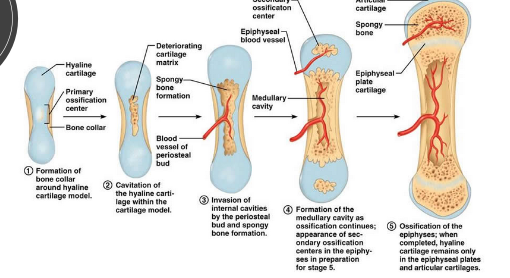
How is cancellous bone formed?
starts as fibrous membranes
osteoblasts release osteoid into the membrane
forms a sponge-like bundle of fibers
cancellous bone formation develops outwards from these centers in the membrane
Axial Skeleton
where most of the core muscles of the body originate from
protects major organs
consists of skull, ribs, sternum, vertebrae
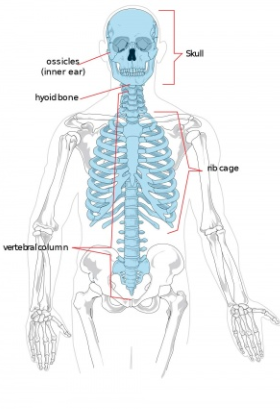
How many bones make up the axial skeleton?
80 bones
Appendicular Skeleton
moveable bones
bones of the limbs
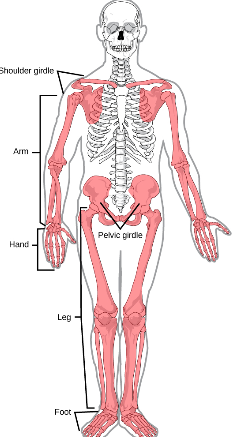
How many bones are in the appendicular skeleton?
126 bones
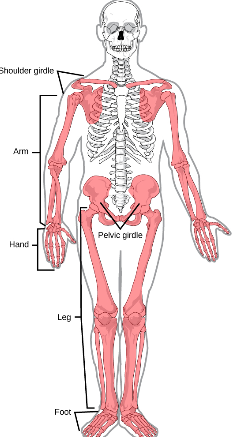
The upper limbs are connected to the ________ (shoulder) girdle, and the lower limbs are connected to the ______ (hip) girdle.
pectoral, pelvic
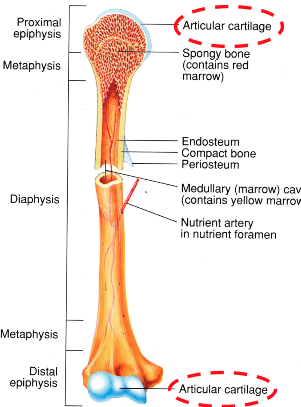
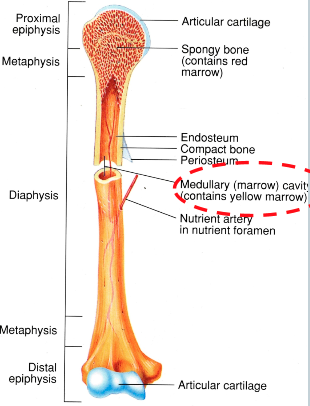
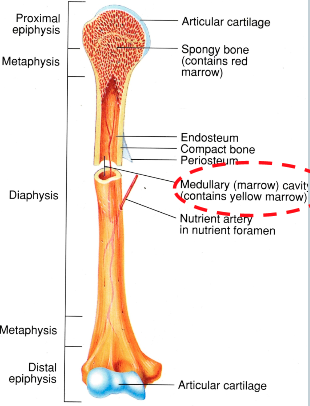
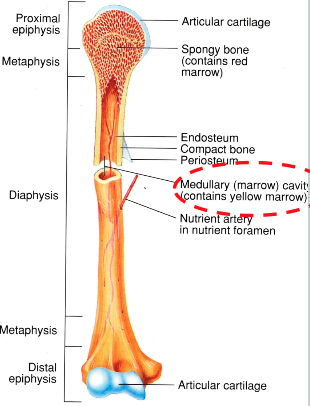
Articular Cartilage (AOLB)
at both ends of bone
allows for smooth movement while protecting the ends of the bones
True or False: Cartilage does have blood supply
False: Cartilage does not have blood supply
True or False: Blood supply is crucial to heal properly
True
Compact Bone (AOLB)
thick part of the bone
responsible for structural integrity
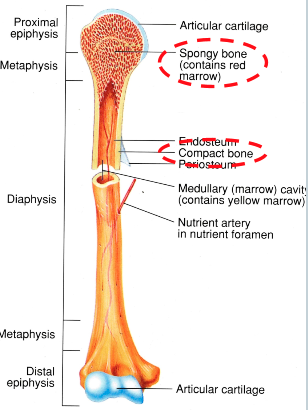
Cancellous (spongy) Bone (AOLB)
at ends of bone
filled with marrow
meant for shock absorption
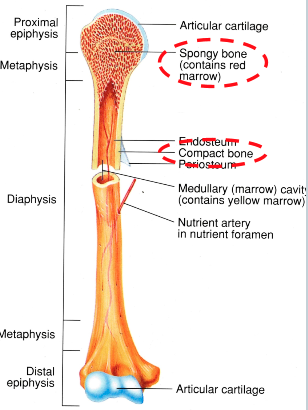
Epiphysis (AOLB)
ends of bones
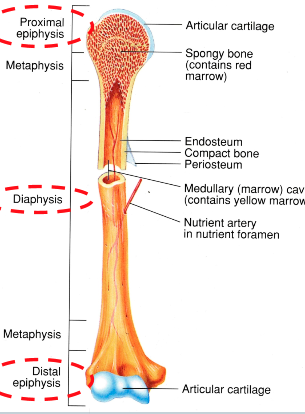
Diaphysis (AOLB)
shaft of bone
where the bone is thickest
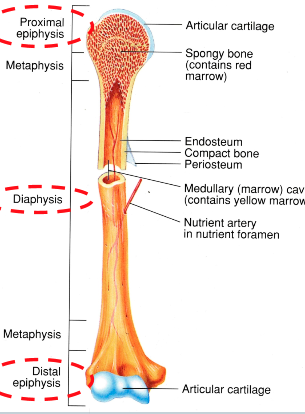
Epiphyseal Plate (AOLB)
growth plates
where growth of the bone occurs (same as ossification centers)
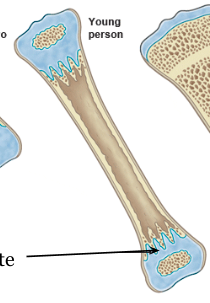
Epiphyseal Line
occurs when epiphyseal plates have fused together after growth has stopped
How do (long) bones grow? How do we know they have stopped growing?
the epiphyseal plates at each end and in the center of the bones expand outwards until they meet each other, which forms the epiphyseal lines
we can know they’ve stopped growing if an x-ray is taken and you can see the epiphyseal lines
Periosteum
outer connective tissue that covers the entire length of the bone
connects to tendons/ligaments to connect muscle to bone or bone to bone respectively
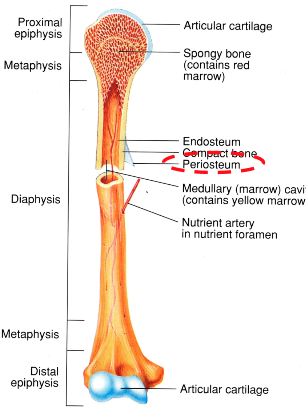
Medullary Cavity
inside the diaphysis of the bone
filled with red marrow and yellow marrow
Red Marrow
found inside the medullary cavity
is where RBCs are produced
Yellow Marrow
found inside the medullary cavity
made up of adipose cells and connective tissue
Hematopoiesis
production of RBCs
Osteocytes
bone cells
Osteoblasts
bone forming cells (lay down osteoid)
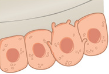
Osteoclasts
bone-destroying cells
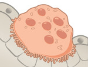
Ossfication
production of new bone
What % of total body weight comes from the skeletal system?
14%
4 Major Components of Bone
Calcium carbonate
Calcium phosphate
Collagen
Water

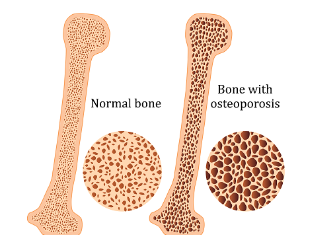
Osteoporosis
degenerative disease in which the holes in the cancellous part of the bone become too wide - the bone becomes brittle and easy to break
typically caused by low calcium intake and old age
4 Prevention Strategies for Osteoporosis
Eat a balanced diet (enough calcium and vitamin D)
Do weight training
Live a healthy lifestyle (no smoking or excessive alcohol)
Get regular bone density testing when necessary
