Week 13- Biological Transportation of Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide and Arterial Blood Gases
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
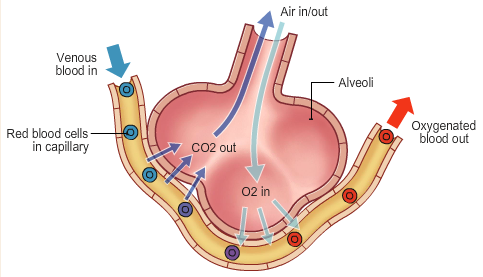
Gas Exchange
happens due to diffusion
gases move from a high concentration to low concentration region
oxygen diffuses from the air in the lungs to the bloodstream.
At the same time, carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood to the air in the lungs
from where it is blown out of the body the next time a person exhales as shown in the diagram to the right.
Oxygen Transport
the basis of the aerobic respiration
oxygen molecules attach to red blood cells
which travel from the alveoli to the blood capillaries
therefore oxygen from the blood reaches the tissues.
O2 binds to hemoglobin which is present in red blood cells, and the molecule known as Oxyhemoglobin (O2Hb)
oxygen is transported to the tissues for metabolic functions
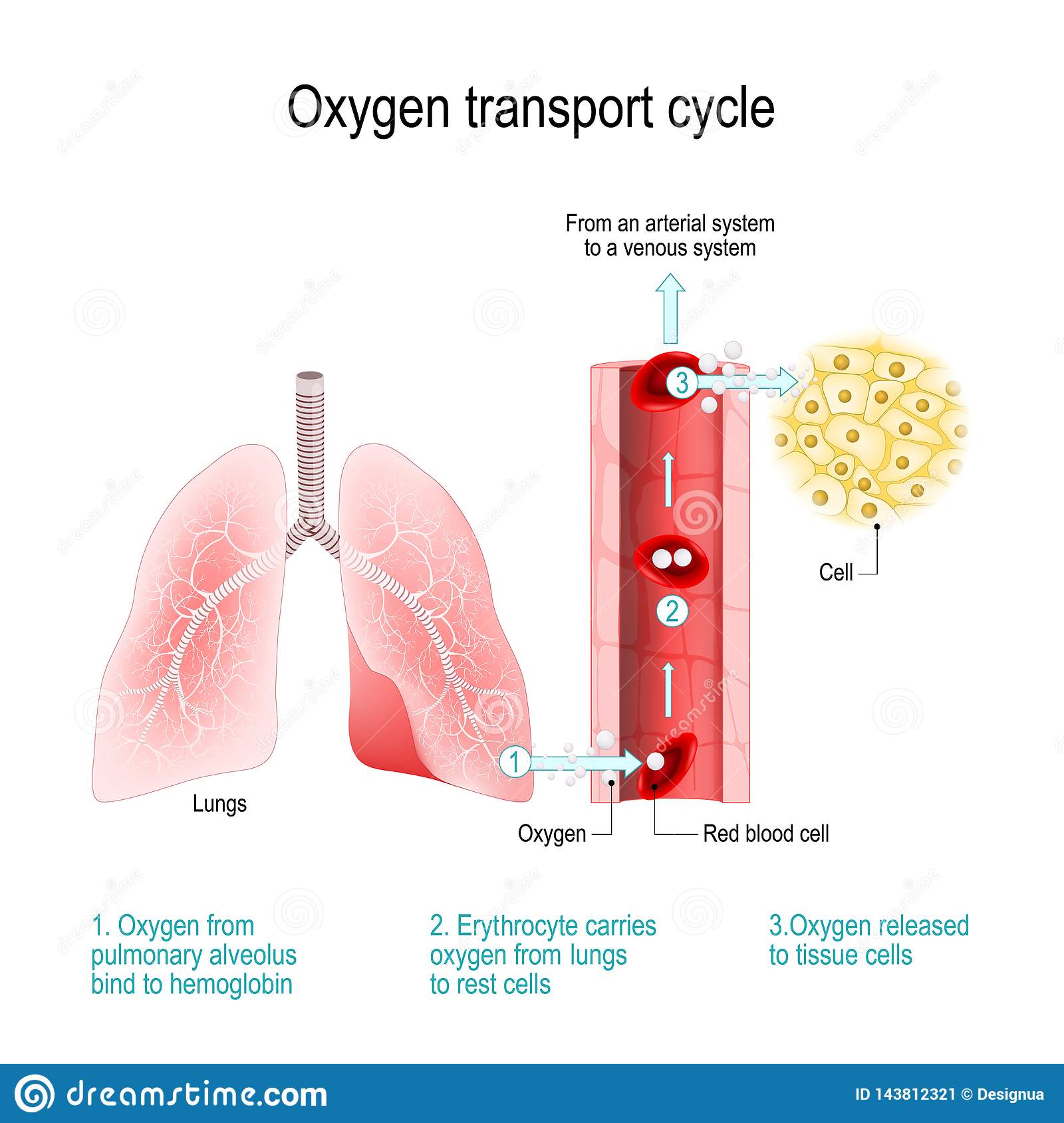
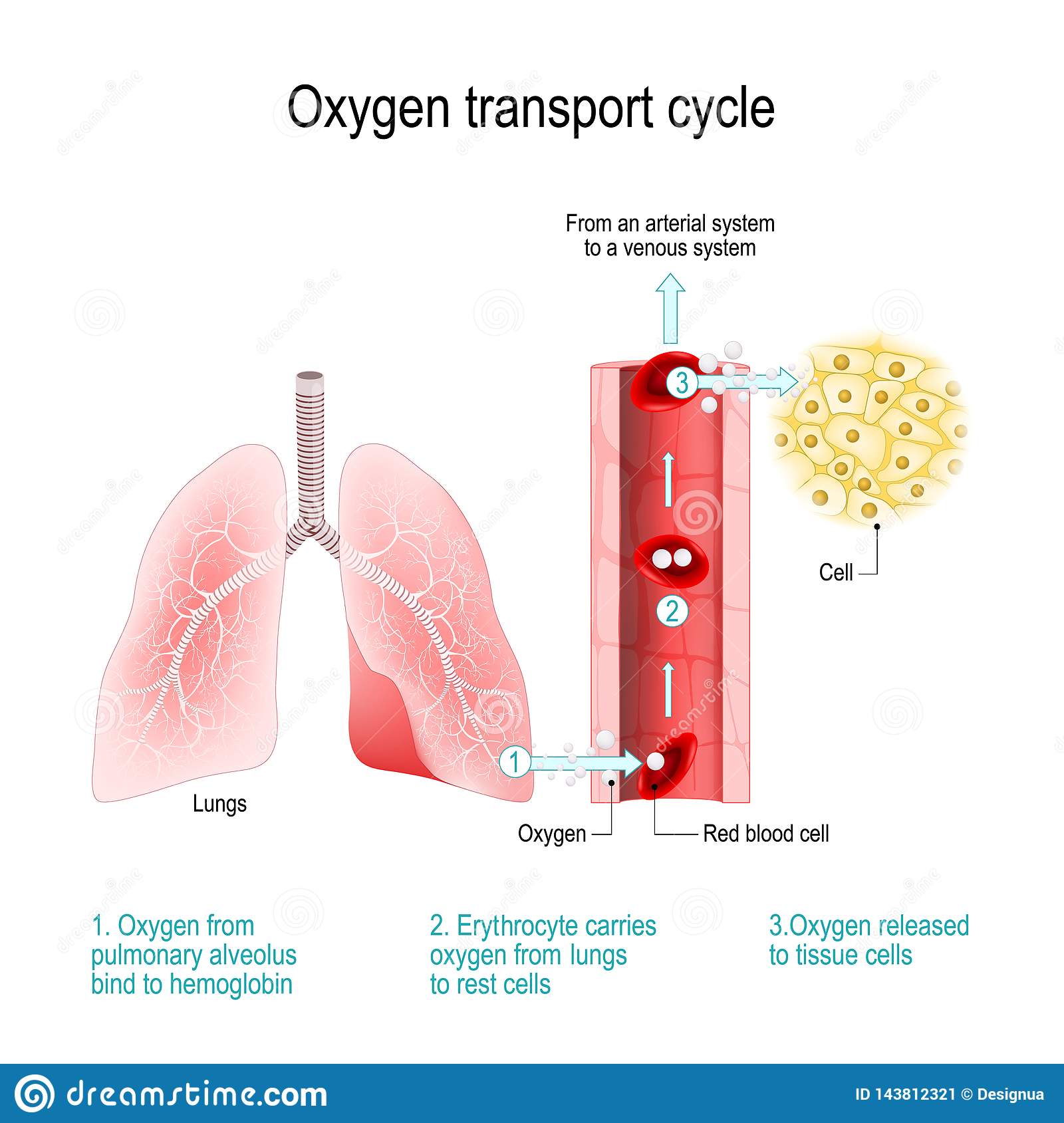
Oxygen transport cycle/steps
Oxygen from pulmonary alveolus bind to hemoglobin
Erythrocyte carries oxygen from lungs to rest cell.
Oxygen is released to tissue cells.
hemoglobin
can carry 4 oxygen molecules
can be reused and they pick up more O2 molecules.
Oxyhemoglobin
Hemoglobin bound to Oxygen
deoxygenated hemoglobin (HHb)
The hemoglobin molecule without any oxygen molecule
oxygenated blood
blood with oxygen
it is found in arteries, through which it reaches the tissues
Carbon Dioxide Transport
carbon dioxide in the tissues
which is produced as a waste product of cellular respiration,
is carried through the blood capillaries and brought to the lungs.
This process is done in different ways.
CO2 diffuses in the red blood cells (RBC) and binds to the hemoglobin
bicarbonate buffer system
majority of the CO2 molecules are carried this way
CO2 diffuses in the red blood cells (RBC) and binds to the hemoglobin
carbon dioxide binds to the hemoglobin,
the molecule is referred to as carbinohemoglobin.
The blood with carbon dioxide is referred to as the venous blood and is found in the veins.
This blood is carried to the lungs, where, the carbon dioxide gets dissociated from the hemoglobin and is expelled from the body.
carbinohemoglobin
carbon dioxide binds to the hemoglobin,
venous blood
The blood with carbon dioxide
carried to the lungs
where, the carbon dioxide gets dissociated from the hemoglobin and is expelled from the body.
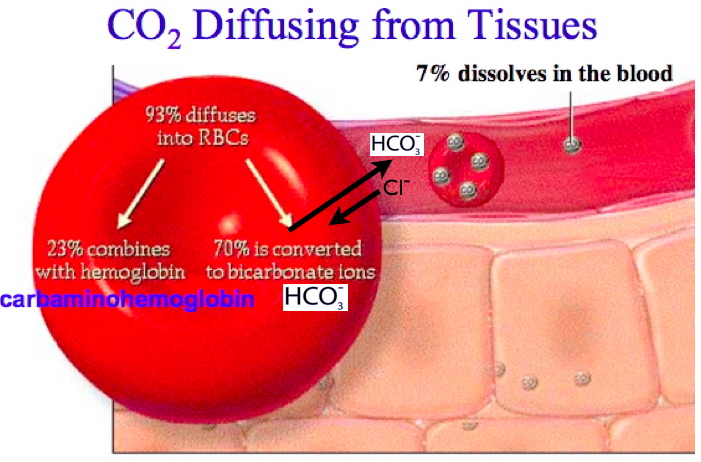
bicarbonate buffer system for CO2 transport
CO2 reacts with water in the RBC to produce carbonic acid (H2CO3).
Carbonic acid is very instable so it quickly dissociates into
bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) and Hydrogen (H+).
The hemoglobin binds to the free H+ and limits the pH change of blood.
The HCO3- is then transported out of the RBCs and released in the plasma, in exchange for a chloride ion, as seen in the following image.
In this process, a chloride Cl- ion comes into the RBC from the blood to balance the charge (known as chloride shift), and HCO3- is transported to the lungs. There, the HCO3- dissociates into H20 and CO2 from where CO2 is expelled out during exhalation.
chloride shift
a chloride Cl- ion comes into the RBC from the blood to balance the charge in exchange for a HCO3-
which is transported out of the RBCs and released in the plasma
Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) Test
measures the pH of blood from an artery
the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood from an artery.
used to check how well the lungs are able to
move oxygen into the blood
remove carbon dioxide from the blood.
The ABG test is performed in the following cases:
Check for severe breathing problems and lung diseases, such as
asthma
cystic fibrosis
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
See how well treatment for lung diseases is working.
Find out if extra oxygen or help with breathing (mechanical ventilation) is needed.
Find out if the patient is receiving the right amount of oxygen when using oxygen in the hospital.
Measure the acid-base level in the blood of people who have
heart failure
kidney failure
uncontrolled diabetes
sleep disorders
severe infections
after a drug overdose.
Partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) (measurment of ABG)
the pressure of oxygen dissolved in the blood
how well oxygen is able to move from the airspace of the lungs into the blood.
Partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO2) (measurment of ABG)
the pressure of carbon dioxide dissolved in the blood
how well carbon dioxide is able to move out of the body.
pH (measurment of ABG)
hydrogen ions (H+) in blood.
The pH of blood is usually between 7.35 and 7.45.
Bicarbonate (HCO3) (measurment of ABG)
a chemical (buffer) that keeps the pH of blood from becoming too acidic or too basic.
Oxygen content (O2 CT) (measurment of ABG)
measures the amount of oxygen in the blood.
Oxygen saturation (O2 Sat) values.(measurment of ABG)
measures how much of the hemoglobin in the red blood cells is carrying oxygen (O2).
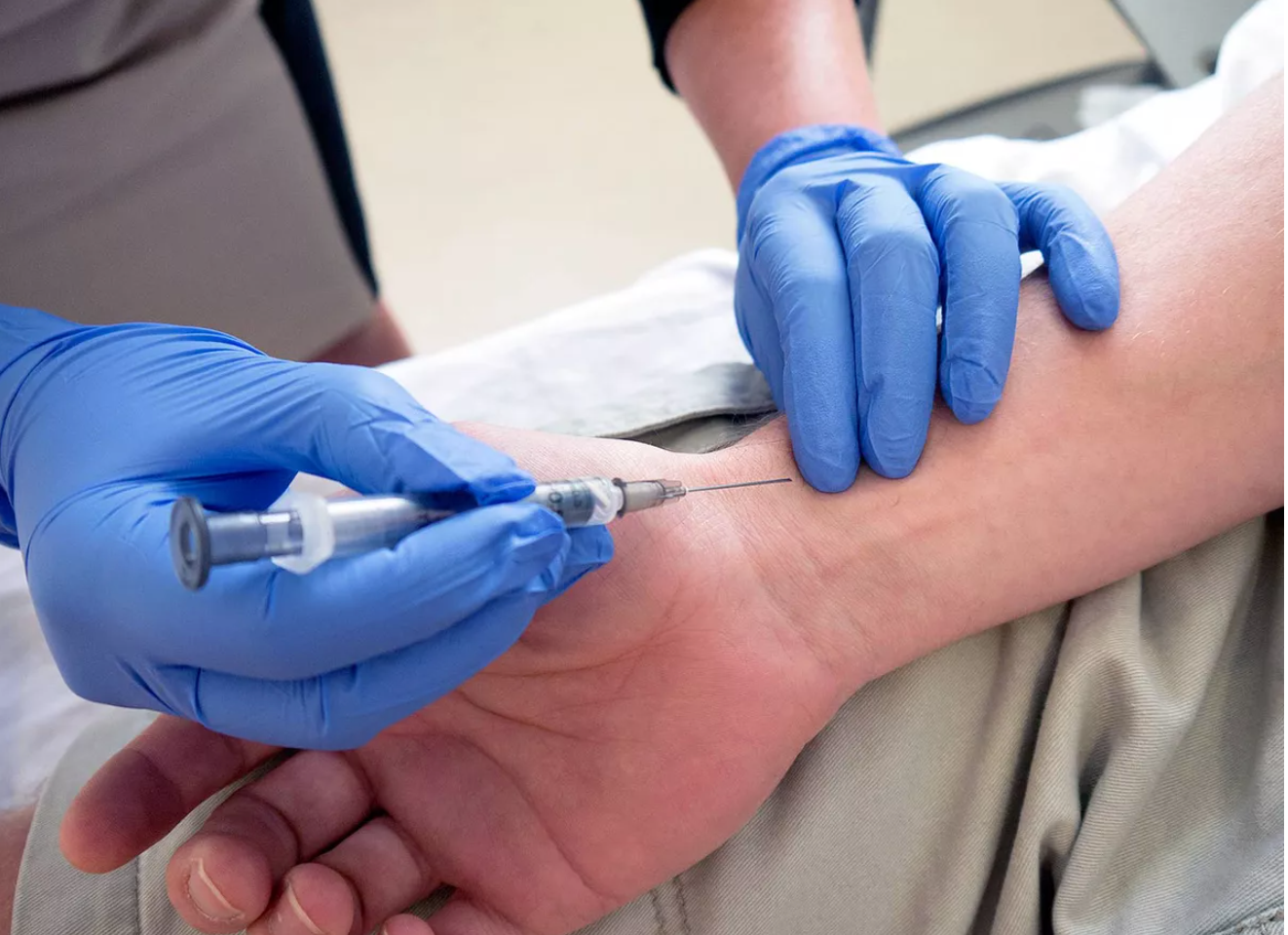
Specimens that can be used for ABG
arterial blood specimen
The preferred specimen
is usually taken from an artery from the inside of the wrist (radial artery)
see image
venous blood specimen
collected from the veins.
capillary blood specimen
collected by dermal puncture to
heel (always heel for babies)
finger
toe
a lancet is used to make an incision of smaller than 2.0 mm
ABG sorting
is always a STAT test
is ideally to be analyzed within 15 minutes of collection.
The sample of should be mixed well to avoid any air bubbles.
The specimen must be tested immediately upon arrival in the lab.
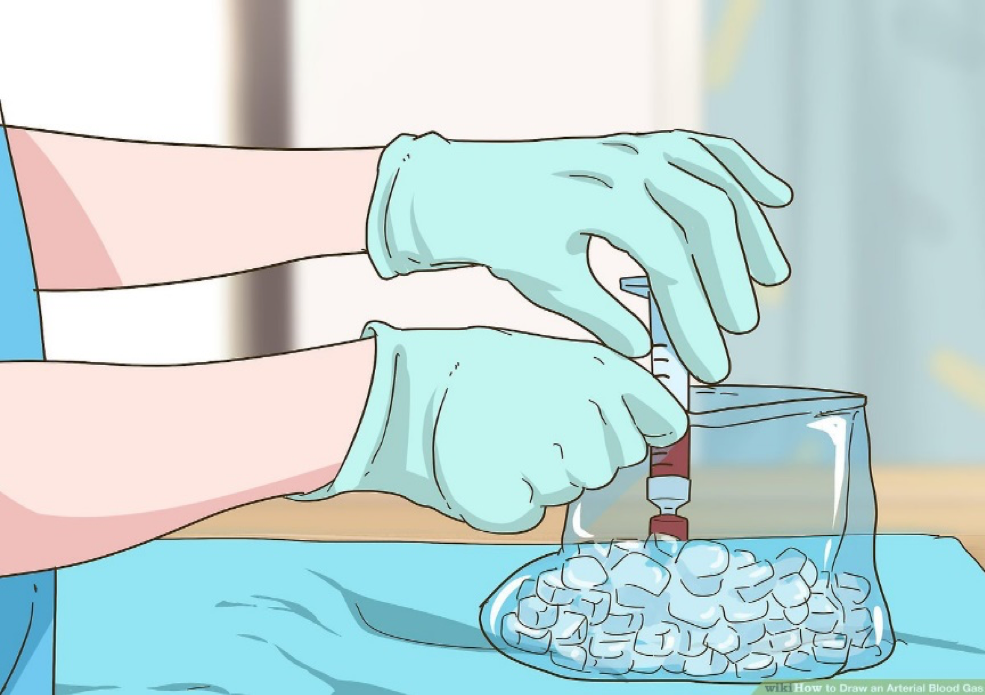
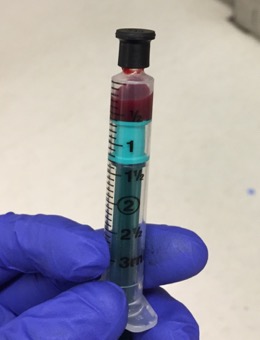
Arteril blood for ABG test storaging/transporting to lab
Specimen should arrive to the lab in a sealed heparinized syringe as shown in the image below.
Traditionally specimen must be placed in ice slurry immediately (not frozen)
If the test is performed within 15 minutes, ice may not be required.
It is important to follow the lab’s SOP (standard operating procedure).
As per recent guidelines
if a plastic syringe is used, it should be kept at room temperature and not on ice slurry.
If glass syringe is used, it can be kept on ice slurry.

if a plastic syringe used for ABG collection
is used, it should be kept at room temperature and not on ice slurry.
only arterial blood in a syringe
If glass syringe is used for ABG
it can be kept on ice slurry.
only arterial blood in a syringe
limits of venous blood for ABG
it cannot be used to test for PO2 and O2 saturation
as it does not allow for accurate measurement.
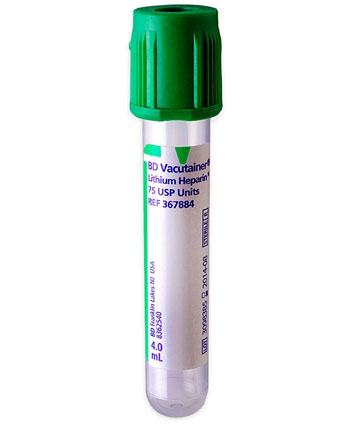
What ABG can be done on venous blood
Blood gas tests for samples taken from venous blood include
pH
pCO2,
bicarbonate (HCO3).
ABG container for venous blood
dark green top lithium heparin vacutainer or blood tube
Venous blood is not placed on ice slurry.
Capillary sample container
heparinized capillary tubes with caps
a lancet is used to make an incision of smaller than 2.0 mm
