affect regulation & decision making
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
key structures in emotional processing
hippocampus
amygdala
emotion
a rapid and transient response to a stimulus with value to a person
consist of physiological changes, a behavioural response, and a subjective experience, intrinsically pleasant or unpleasant
mood
a more persistent state which shares some of the same subjective features of emotion
affect
a broader term encompassing emotion + mood
classifying emotions
positive vs negative
basic vs complex
arousal level vs valence
ekman theory of classifying emotion
core emotions biologically pre programmed
= happiness, sadness, disgust anger, fear, surprise
complex emotions draw on the same feelings, but combine them with social and cultural factors
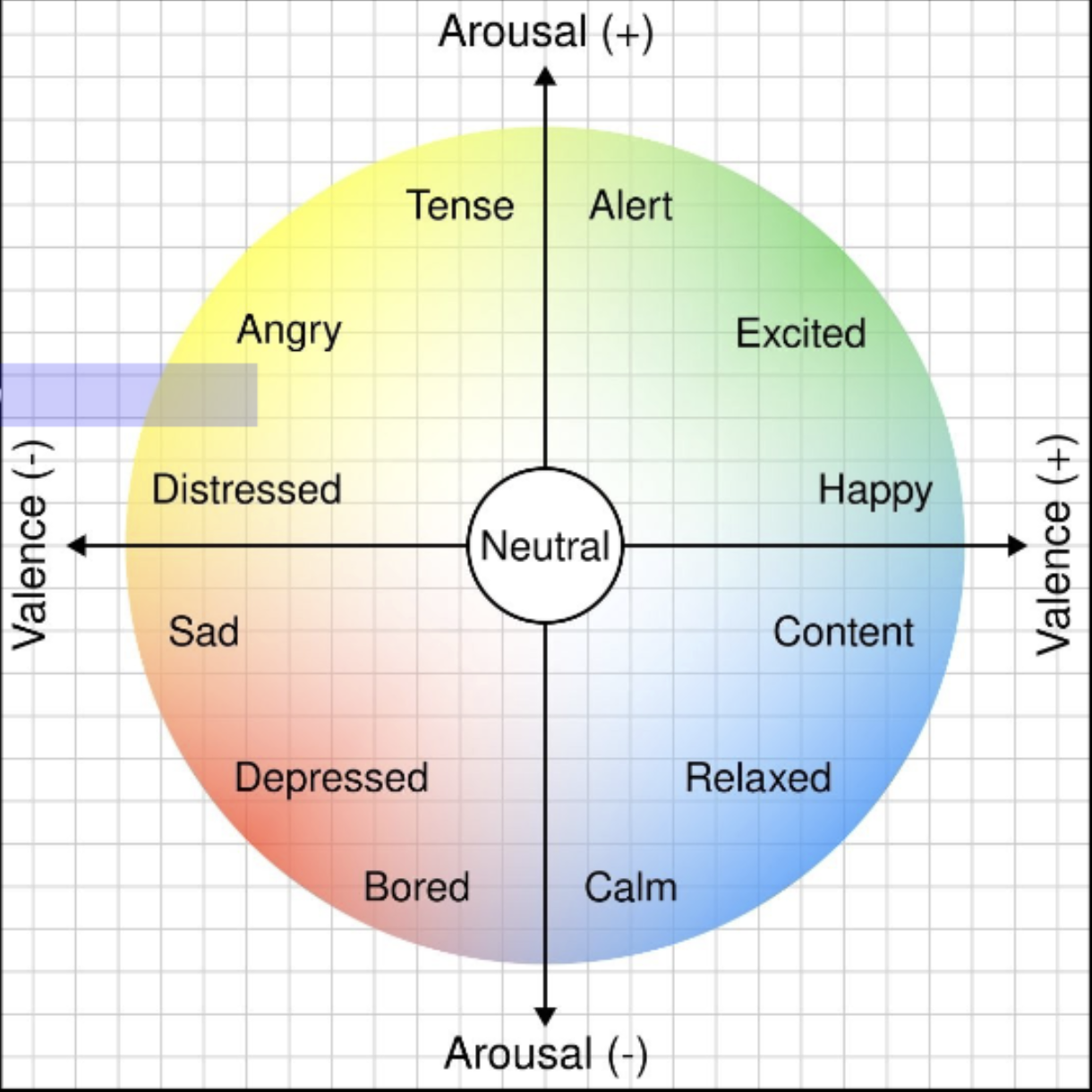
feldman-barrett theory of classifying emotion
you can put emotion on a continuum based on arousal and positivity / valence
high arousal = anger, excitement, nercousness
low arousal = sadness, contentment
physiological component of emotion
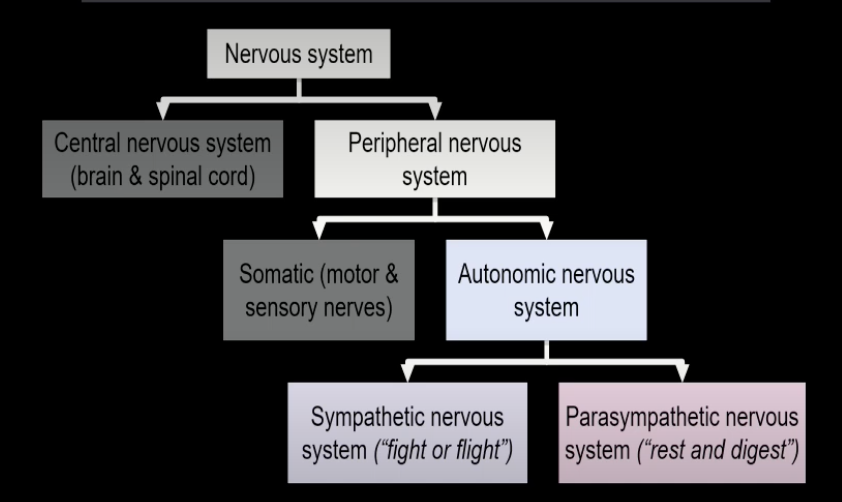
autonomic nervous system → sympathetic and parasympathetic systems
sympathetic nervous system
‘fight or flight’
up regulates respiration
dilates lungs, pupils, blood vessels
increases heart rate & perspiration
suppresses digestion
parasympathetic nervous system
‘rest and digest’
sleep rest & digestion
conservation of energy
measuring emotional responses
skin conductance response (SCR): measures change in perspiration
heart rate / heart rate variability
self report tools e.g PANAS
→ best to use the tools together so you can get a fuller picture of everything
PANAS
positive and negative affect schedule
looking at a person across a small period of time, usually a week
the amygdala: fMRI evidence
spohrs 2018
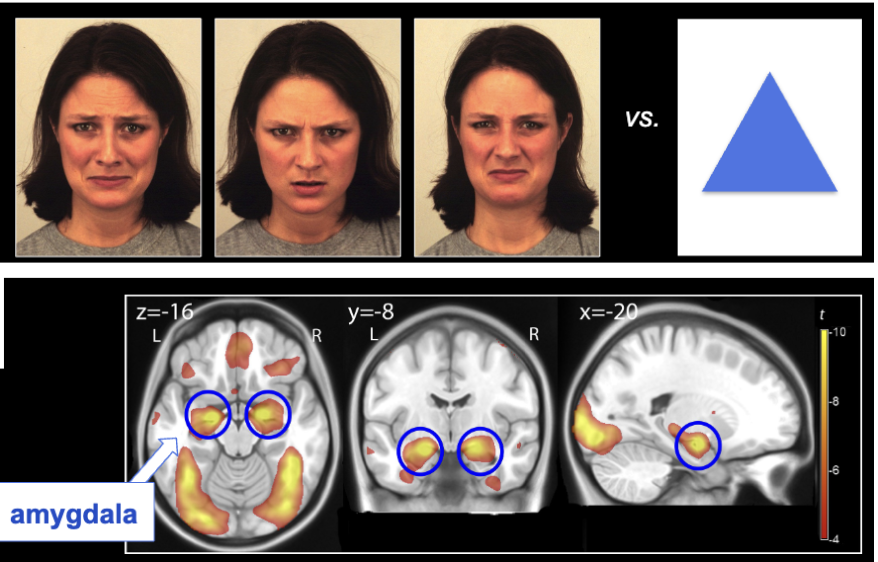
if we show people expressive faces, they respond with activity in the amygdala
→ not a great comparison between faces and shapes; lots of sites activated because faces are so different to shapes
fear conditioning paradigm
circle matched with mild electric shock on fingers
classical conditioning
when viewing shapes alon
e under the scanner after learning, the circle had significantly more activation in the amygdala compared to other shapes
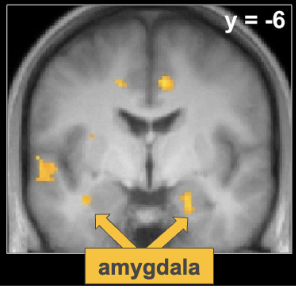
amygdala and memory
kensinger 2011
events eliciting higher amygdala activation in phase 1 were rated as more vivid in phase 2
BUT accuracy/details the same irrespective of amygdala activation
indicates that emotional valence enhances ability to remember, but only a more robust subjective experience
effects of damage on the amygdala
may fail to show normal fear conditioning
may fail to show a memory benefit for emotionally significant events
often poor at identifying facial expressions
SM
bilateral damage from urbach-wiethe disease
affected valence- missing negative emotions that perform a function e.g fear of snakes
overly positive & overly familiar
amygdala & story recall
phineas gage
left ventromedial prefrontal cortex damaged
impulsive, fearful, loss of control
behaviour changes around affect, inability to use good judgement for hot cognition
clinical featires of vmPFC damage
Emotional dysregulation, changes in emotional experience
philosophical calmness in high emotion situations
Diminished empathy, poor social awareness
Also true of damage to amygdala, but the problem here is somewhat higher up; can see it but cant interpret it
Poor decision-making, irresponsible behaviour, risk-taking
Specifically in hot context cases
vmPFC changes in emotional experience
increased impulsivity
increased aggression (some people get this with impulsivity, not all)
→ general disinhibition
diminished empathy / poor social awareness
NPI
neuropsychiatric inventory
designed to assess wether a person demonstrated increased impulsivity or reduced social awareness
head injury sample: significantly lower scores with right vmPFC damage
diminished empathy
tranel & damasio 1994
healthy participants; emotional picture evokes scr
damage; can describe picture in detail, but no scr
→ issue is making the perspective leap, understanding what the other person might be feeling
poor social awareness
patients score poorer than controls on the faux pas task
addresses higher level empathy than amygdala damage = perspective AND empathise
theory of mind, but for social rules and consequences
amygdala vs vmPFC
amygdala: ‘signals’ emotional valence, particularly negative valence
vmPFC: emotional regulation, cognition that relies strongly on emotion
poor decision making, irresponsibility, risk-taking
gambling game
vmPFC patients can explain the rule, but don’t act on it
difference between ability to rule detect, and ability to respond positively within the hot context
SCR: controls develop an anticipatory scr before selecting from a bad deck. patients get scr after the bad card, but don’t develop an anticipatory scr
cannot use emotional response in a proactive way to shape future decisions
left pfc crucial for this task
hot cognition
thinking and decising how to act when the emotional stakes are high
using emotional responses to guide decision making in complex high level decision making
gut instinct before verbal explanation
= winning poker
= trading on the stock market
= deciding wether or not to have cake
cold cognition
stroop task
thinking out a difficult mental problem
dividing a large goal into sub goals
gambling fMRI
people who did well on the iowa gambling task showed increasing activity in the left vmPFC as the trial progressed
right insula also activated= operate as a network
somatic marker hypothesis
vmPFC: binds memories and their emotional and physiological associations
creates an index of the way you’ve felt in similar situations in the past, which you can revoke in future to guide your actions
facilitates fast decision-making
limitations:
does it consider empathy or social awareness
does it consider causal vs association with bodily sensations
descartes error
damasio: we are not thinking machines that feel, we are feeling machines that think
it is not enough for us to be rational, that would be weird. we do a lot of things based on feeling and gut instinct