COMPSCI 1210 ( COMP ORG)
5.0(6)
5.0(6)
Card Sorting
1/115
Earn XP
Last updated 10:55 PM on 3/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
1
New cards
@@**UNIT 1 - SYSTEM CONCEPT**@@

2
New cards
is a system that @@**uses**@@ @@**information technology (IT)**.@@
INFORMATION SYSTEM
3
New cards
The ____@@**provides**@@ @@**services using a compute**@@**r**, and a computer operates with a combination of hardware and software.
INFORMATION SYSTEM
4
New cards
an INFORMATION SYSTEM used inside an enterprise, or provided as a service to users, requires the design and construction of IT infrastructures, such as)___ __and__ ___ design and development.
hardware & software
5
New cards
___ @@**designs the software components**@@ @@**and operations**@@, such as the connection of the software components and constraints based on software architecture.
Software
6
New cards
Just like software, ___@@**designs and develops the hardware architecture.**@@
hardware
7
New cards
refers to the @@**architecture for a system**@@ to
provide services, based on hardware and
software architecture.
provide services, based on hardware and
software architecture.
SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
8
New cards
In a broader definition, it refers to @@**all architecture**@@,
including the __*_, _, _,*__
for constructing an information system.
including the __*_, _, _,*__
for constructing an information system.
* application architecture (AA)
* data architecture (DA)
* technical architecture (TA)
* data architecture (DA)
* technical architecture (TA)
9
New cards
A narrow definition refers to the document that defines the ___ of hardware, such as a______ *,* _____,__ ___*and , and certain software parts, such as ___ and ___*
* configuration and relationship
* server, storage, network, and security
* Os and middleware
* server, storage, network, and security
* Os and middleware
10
New cards
A ____ is a document that @@**defines the structure of an information system**@@ provided to support the business process required to achieve the objective of an enterprise.
system architecture
11
New cards
A system architecture is divided into ___, , -__
* application architecture (AA)
* data architecture (DA)
* technical architecture (TA)
* data architecture (DA)
* technical architecture (TA)
12
New cards
it defines the @@**structure of hardware**@@, such as a @@**server, network, and security**@@, as well as the distributed structure of middleware operating on the hardware,
* technical architecture (TA)
13
New cards
it @@**defines the data structure to assure data integrity,**@@
* data architecture (DA)
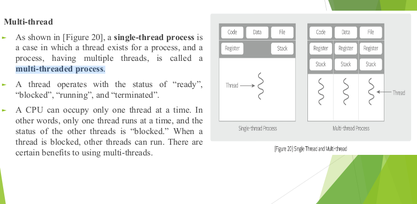
14
New cards
it defines the @@**software components**@@ and the relationship and constraints of said defined components.
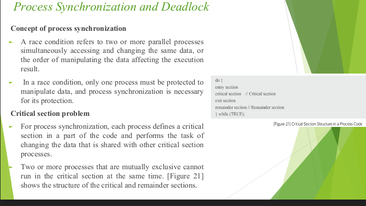
* application architecture (AA)
15
New cards
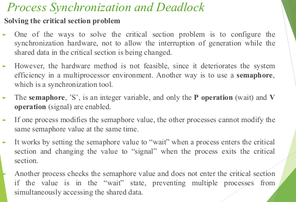
Narrow definition of
A ____ refers to the @@**structure of an information system**@@, which includes principles and guidelines that define the components, such as hardware, software, security, interactions, and constraints.
A ____ refers to the @@**structure of an information system**@@, which includes principles and guidelines that define the components, such as hardware, software, security, interactions, and constraints.
system architecture
16
New cards
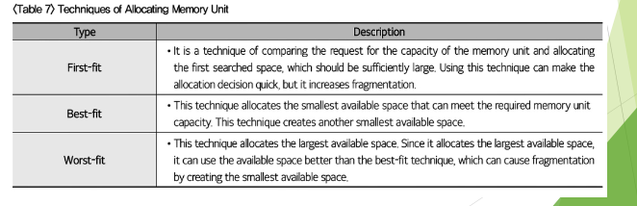
The following table shows the @@**types of detailed architecture defined in system architecture**@@. ( click to see)
* Server design Architecture
* Network Design Architecture
* storage design architecture
* Network Design Architecture
* storage design architecture
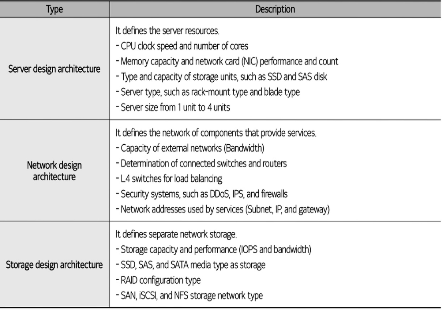
17
New cards
What are the Components of System Architecture
* **Server**
* **Network**
* **Storage**
* **Security**
\
* **Network**
* **Storage**
* **Security**
\
18
New cards
* It provides the @@**computing power of an information system.**@@ The information system uses this computing power to process the business logic and data by running the application programs.
* its components include the stacked structures of the computer's hardware, OS, middleware,
and application programs.
* its components include the stacked structures of the computer's hardware, OS, middleware,
and application programs.
Server
19
New cards
* it @@**connects the information system components for communication.**@@
* process communication between servers, between servers and
storage units, and between the enterprise's internal and external networks.
* process communication between servers, between servers and
storage units, and between the enterprise's internal and external networks.
Network
20
New cards
* @@**holds the data of an information system**@@.
The information system uses
this computing Power to process the business logic and data by running the application programs.
The information system uses
this computing Power to process the business logic and data by running the application programs.
Storage
21
New cards
Storage is categorized into 4 types according to how it stores data.
* Block storage
* File storage
* Object storage
* Direct Access Storage (DAS)
* File storage
* Object storage
* Direct Access Storage (DAS)
22
New cards
@@**saves data in fixed block units,**@@ like @@**16KB and 64KB.**@@ It stores the OS, such
as MS Windows, Linux, and Unix.
as MS Windows, Linux, and Unix.
* Block storage
23
New cards
@@**saves data in file units,**@@ instead of in fixed blocks. @@**Network Attached Storage
(NAS),**@@ widely used as the shared file repository, is a type of file storage.
(NAS),**@@ widely used as the shared file repository, is a type of file storage.
* File storage
24
New cards
@@**saves data in object units**@@, instead of in fixed blocks or files. @@**It is mostly
used in cloud storage**@@. Storage types can also be categorized by their connection method.
used in cloud storage**@@. Storage types can also be categorized by their connection method.
* Object storage
25
New cards
__@@**is mounted in each server**@@, NAS is connected through a network, and Storage Area Network (SAN) is connected through the network used exclusively for storage.
* Direct Access Storage (DAS)
26
New cards
@@**configured**@@ @@**through the network connection.**@@
* Security
27
New cards
System architecture @@**classification according to the system layout**@@
* Centralized architecture
* Multi-region
* Multi-region
28
New cards
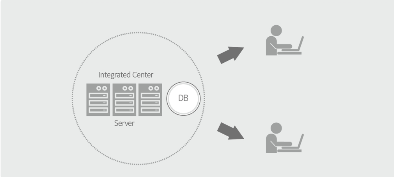
* arranges all the systems in a @@**centralized place**@@.
* stores and operates the system and data from an integrated center. It
configures an integrated database on a large-capacity server and it has a relatively simple system
configuration.
* stores and operates the system and data from an integrated center. It
configures an integrated database on a large-capacity server and it has a relatively simple system
configuration.
* Centralized architecture
29
New cards
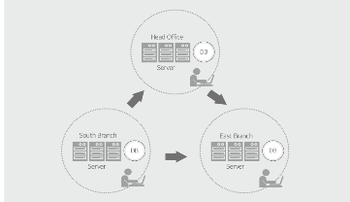
* distributed
architecture operates the system by distributing @@**regional**@@ and application systems regionally.
* Each region manages the distributed data using small or medium-sized
servers. This structure can reduce the load of each server, since it distributes the user load.
architecture operates the system by distributing @@**regional**@@ and application systems regionally.
* Each region manages the distributed data using small or medium-sized
servers. This structure can reduce the load of each server, since it distributes the user load.
Multi-region distributed system architecture
30
New cards
@@**Classification according to how the application programs are provided**@@
* Client-server architecture
* Web system architecture
\
* Web system architecture
\
31
New cards
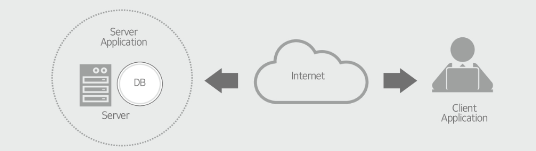
The architecture @@**places system functions in the servers and clients**@@ and configures them to use the
service, depending on the business size or environment.
service, depending on the business size or environment.
Client-server architecture
32
New cards
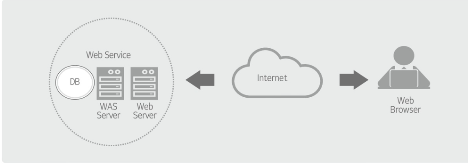
* The architecture runs the server's application programs, and the client uses the service with a @@**web browser.**@@ It generally consists of a web server, a web application server, and a database server.
* The ___@@**assures stable performance, and the program reusability is high.**@@
* The ___@@**assures stable performance, and the program reusability is high.**@@
* Web system architecture
* middleware
* middleware
33
New cards
@@**Classification by system layer**@@
* Two-tier architecture
* Three-tier architecture
* Three-tier architecture
34
New cards
The function and role of each system component are classified by __ __or__ ____
tier, or layer
35
New cards
The most @@**widely known layer**@@ is the___ which shows the network structure.
OSI 7 layer,
36
New cards
difference of layer and tier
* layers refer to structures from a logical point of view
* and tiers refer to structures from a physical perspective.
* and tiers refer to structures from a physical perspective.
37
New cards
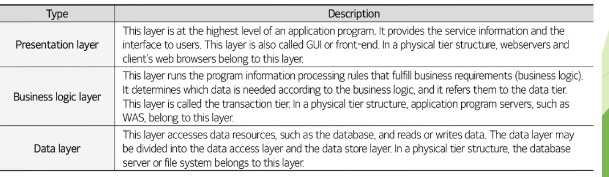
An information system is divided into a___
* presentation layer
* a business logic layer
* data layer
* a business logic layer
* data layer
38
New cards
different layer in Information System
39
New cards
* @@**stores and processes data in the server and processes
business logic and presentation for the client**.@@
* It is generally the @@**same structure
as the client-server**@@ architecture.
business logic and presentation for the client**.@@
* It is generally the @@**same structure
as the client-server**@@ architecture.
Two-tier architecture
40
New cards
* a structure created to @@**overcome the limitations of
two-tier architecture**@@,
* and it is also called @@**multi-tier architecture**@@.
* This structure has an @@**additional tier between the presentation tier and the data tier**@@, in order toprocess business logic to be flexible and scalable.
two-tier architecture**@@,
* and it is also called @@**multi-tier architecture**@@.
* This structure has an @@**additional tier between the presentation tier and the data tier**@@, in order toprocess business logic to be flexible and scalable.
Three-tier architecture
41
New cards
__refers to a computer or program that @@**provides information or services to users through a network**@@. It provides the computer power needed for the information system services.
“Server”
42
New cards
The concept of the server was created when __ started making a server called the mainframe.
IBM
43
New cards
* The term ___ refers to a @@**large steel enclosure**@@, like a cabinet, that ***houses the CPU and the main memory.***
\
\
mainframe
44
New cards
The mainframe began downsizing gradually in __when the attention to super Unix servers, such as HP. Sun, and Silicon Graphics, increased.
* 1997
45
New cards
@@**Downsizing**@@ refers to replacing a mainframe server with a ___
super Unix server.
46
New cards
regarded as
the beginning of modern computers.
the beginning of modern computers.
Turing Machine,
47
New cards
Who and When Turing Machine Invented
Allen Turing in 1936,
48
New cards
This Turing Machine proved the ___
mathematical concepts and calculation processes
49
New cards
known as the @@**first programmable general-purpose computer.**@@ Using 18,000 vacuum tubes, it weighed 30 tons and was literally as large as a house. And it was create in__
ENIAC, created in 1946,
50
New cards
the first computer that @@**embedded the program in a memory unit,**@@ it was proposed by __and developed in__
EDSAC.
John von Neumann in 1949
John von Neumann in 1949
51
New cards
**Unit II - Network
Concept**
Concept**
52
New cards
a @@**standardized communication rule**@@ for sending and receiving data through a network.
PROTOCOL
53
New cards
responsible for @@**most Internet-related standard protocols.**@@
IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force)
54
New cards
responsible for @@**wireless communication protocols**@@ such as GSM, CDMA, UMTS, LTE, and LTE-A.
3GPP (Third Generation Partnership Project) and 3GPP2
55
New cards
responsible for @@**protocols related to telephones.**@@
ITU-T (International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector)
56
New cards
commonly referred to when @@**dealing with networks.**@@
ISO's OSI reference model, or OSI layer
57
New cards
ISO is derived from the Greek word “__”?
ioo¢ (isos)
58
New cards
ISO is derived from the Greek word “ioo¢ (isos)’, meaning “__”,
identical
59
New cards
@@**IOS stands for?**@@
International Organization for
Standardization (IOS).
Standardization (IOS).
60
New cards
**OSI** is an abbreviation of?
Open Systems
Interconnection.
Interconnection.
61
New cards
The Internet protocol layer is based on the?
ARPANET reference model,
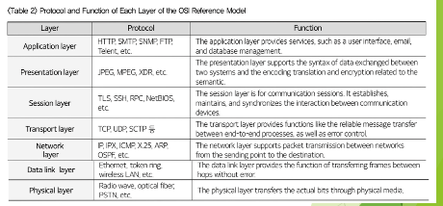
62
New cards
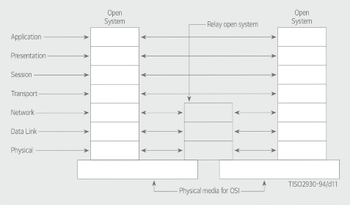
OSI Reference Model layers
1. Application layer
2. Presentation layer
3. Session layer
4. Transport layer
5. Network layer
6. Data link layer
7. Physical layer
63
New cards
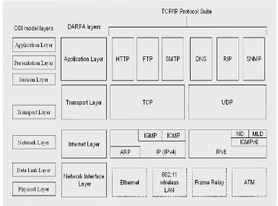
@@**Application programs**@@, such as web (HTTP), DNS, telnet, FTP, and email sending/receiving (SMTP/POP3/IMAP4), allow access to services on other layers.
APPLICATION LAYER
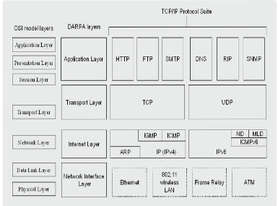
64
New cards
* @@**Also called the host-to-host transport layer**@@,
* It is @@**equivalent to the transport laye**r@@ in the OSI reference layer.
* It is @@**equivalent to the transport laye**r@@ in the OSI reference layer.
TRANSPORT LAYER
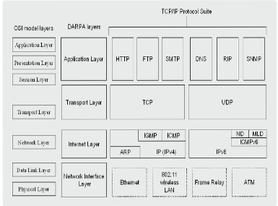
65
New cards
* Also @@**called the network layer**@@, it is responsible for addressing and routing functions.
* It is @@**equivalent to the network layer**@@ in the OSI reference layer.
* It is @@**equivalent to the network layer**@@ in the OSI reference layer.
INTERNET LAYER
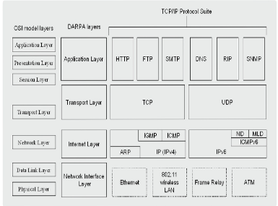
66
New cards
Also called the @@**network access layer**@@,
the network interface layer has the role of actually sending and receiving TCP/IP packets through physical media, such as IEEE 802.3 and IEEE 802.11 WIFI.
the network interface layer has the role of actually sending and receiving TCP/IP packets through physical media, such as IEEE 802.3 and IEEE 802.11 WIFI.
NETWORK INTERFACE LAYER
67
New cards
Internet users come across many terms related to numbers, such as a MAC address, an IP address,
and a port number.
and a port number.
Internet Address System
68
New cards
the address
system used by the data link layer, is @@**used to transfer frames between the physically connected
nodes.**@@
system used by the data link layer, is @@**used to transfer frames between the physically connected
nodes.**@@
MAC (MEDIUM ACCESS CONTROL)
69
New cards
* the address system of the network
layer to transfer datagram between two hosts/ routers.
* It @@**facilitates data to be transferred from the source node to the destination node, through multiple Internet networks.**@@
layer to transfer datagram between two hosts/ routers.
* It @@**facilitates data to be transferred from the source node to the destination node, through multiple Internet networks.**@@
INTERNET PROTOCOL
70
New cards
@@**transfer messages between two processes**@@ (running applications) is responsible for the connection between the web browser
PORT NUMBER
71
New cards
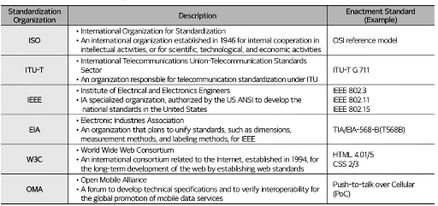
* is a @@**leading organization responsible for
Internet-related standards.**@@
* It defines the @@**basic protocols for Internet transmissions,**@@
Internet-related standards.**@@
* It defines the @@**basic protocols for Internet transmissions,**@@
IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force)
72
New cards
**Unit III – Operating
System**
System**
A. Operating System (OS)
B. Process and Thread
C. Process Synchronization and Deadlock
D. Memory Unit Management
E. Scheduling
F. Virtual Memory Unit
G. File System
H. Input/ Output System
B. Process and Thread
C. Process Synchronization and Deadlock
D. Memory Unit Management
E. Scheduling
F. Virtual Memory Unit
G. File System
H. Input/ Output System
73
New cards
**B. Process and Thread**
74
New cards
@@**refers to a running program,**@@ and in today’s concurrent multi-process
environment, it is a work unit of a time-sharing system.
environment, it is a work unit of a time-sharing system.
A process
75
New cards
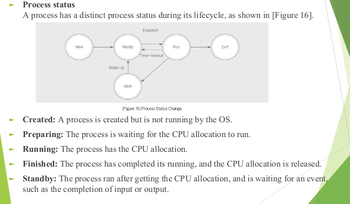
A @@**process has a distinct process status during its lifecycle**@@
Process status
* **Created:** A process is created but is not running by the OS.
* **Preparing**: The process is waiting for the CPU allocation to run.
* **Running:** The process has the CPU allocation.
* **Finished**: The process has completed its running, and the CPU allocation is released.
* **Standby:** The process ran after getting the CPU allocation, and is waiting for an event,
such as the completion of input or output.
* **Created:** A process is created but is not running by the OS.
* **Preparing**: The process is waiting for the CPU allocation to run.
* **Running:** The process has the CPU allocation.
* **Finished**: The process has completed its running, and the CPU allocation is released.
* **Standby:** The process ran after getting the CPU allocation, and is waiting for an event,
such as the completion of input or output.
76
New cards
@@**stores information necessary for process
management.**@@
management.**@@
Process control block (PCB)

77
New cards
@@**The process that creates other processes**@@
parent process,
78
New cards
@@**newly created
process is called**@@
process is called**@@
child process.
79
New cards
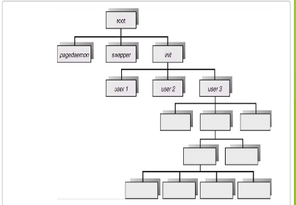
A @@**child process can create another child proces**@@**s**, and this relationship is formed in a___?
tree structure,
80
New cards
After completing the last code of the program, the
process requests the OS to delete the process with the
"exit()" system cal,
process requests the OS to delete the process with the
"exit()" system cal,
Process termination
81
New cards
* a @@**basic unit for using a CPU**@@
* @@**shares the memory unit,**@@ such as codes,
data, and files, and creates its own register and
stack.
* @@**shares the memory unit,**@@ such as codes,
data, and files, and creates its own register and
stack.
thread
82
New cards
thread is a @@**basic unit for using a CPU**@@ and is @@a**l called a?**@@
lightweight process.
83
New cards
a case in which a @@**thread exists for a process**@@, and a
process,
process,
single-thread process
84
New cards
* having @@**multiple threads**@@**,** is called a
multi-threaded process.
85
New cards
**C. Process Synchronization and Deadlock**
86
New cards
refers to @@**two or more parallel processes**@@
simultaneously accessing and changing the same data, or
the order of manipulating the data affecting the execution
result.
simultaneously accessing and changing the same data, or
the order of manipulating the data affecting the execution
result.
race condition
87
New cards
The part of the code that
@@**implements such a request**@@ is called the
@@**implements such a request**@@ is called the
entry section
88
New cards
The @@**exit section is after the critical section, and the rest of the code is collectively**@@ called the
remainder section

89
New cards
* the @@**hardware method is not feasible**@@, since it deteriorates the system efficiency in a multiprocessor environment.
* Another way is to use a__ which is @@**a synchronization tool.**@@
* Another way is to use a__ which is @@**a synchronization tool.**@@
s**emaphore**
90
New cards
The semaphore, ’S’, is an integer variable, and only the___@@**operation (wait)**@@ and__@@**operation (signal)**@@ are enabled.
P and V
91
New cards
There may be a case when the status of a process in @@**“standby”**@@ is never changed because the requested resource is allocated to other standby processes. This state is called the __
deadlock.
92
New cards
___ @@**cannot finish the running program**@@, and the system cannot start other tasks because the resource is tied to other processes.
deadlocked processes

93
New cards
**D. Memory Unit Management**
94
New cards
* technique of @@**running processes, even if they are not present in**@@
**the memory unit.**
* This technique a**llows a user program that is larger than the physical
memory unit to run.**
**the memory unit.**
* This technique a**llows a user program that is larger than the physical
memory unit to run.**
Virtual memory
95
New cards
@@**technique of searching for the best way
to allocate processes to the available main memory**@@ area when a process requests the
memory unit for a new use.
to allocate processes to the available main memory**@@ area when a process requests the
memory unit for a new use.
Memory unit allocation technique
96
New cards
@@**Memory space is allocated when the memory is
requested and recollected after use.**@@
requested and recollected after use.**@@
Fragmentation problem
97
New cards
@@**Using the first-fit, best-fit, and worst- fit techniques**@@ to allocate the memory unit can cause __,
external fragmentation
98
New cards
* __If the memory is @@**partitioned into a fixed size to provide multiple fixed-sized**@@ available spaces to processes, it may be slightly larger than the required space.
* The @@**remaining space**@@ is called the ___
\
* The @@**remaining space**@@ is called the ___
\
* Fragmentation problem
* internal fragmentation
* internal fragmentation
99
New cards
@@**merges small-sized available
memory,**@@
memory,**@@
Compaction technique
100
New cards
@@**merges spaces with adjacent addresses**@@ in the unused empty space list in order to create a larger space and to prevent multiple small spaces
Coalescing technique