ASTRONOMY FINAL!!!
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
187 Terms
What is the Maximum number of planets visible to the naked eye on a given night?
5
Planets…
move SLOWLY relative to the stars
The motion of the Earth around the sun is called…
Revolution
The number of seconds in a day is closest to
90,000
The celestial coordinate corresponding to latitude on Earth is called…
Declination
If Sirius the brightest star in the sky, rises at 10pm one night, the following night it will rise at…
9:56pm
Planet X has its rotation axis perpendicular to its orbital plane. Its seasons would be…
constant
At the Vernal equinox, an observer on the Equator will observe the sun to be ___ degrees above the horizon at noon.
90
Ptolemy…
wrote books summarizing astronomical knowledge of earlier cultures
True of False…An observer at a latitude of +27 degrees will have the Sun at its Zenith at least twice each year
False
Which of the following was NOT an important contribution of Brahe
discovery of the rings of Saturn
From his analysis of the motion of Mars, Kepler was able to conclude that…
the planets moves with varying orbital speed
You can tell that Jupiter is at opposition by noting that
it crosses the north-south line passing straight overhead at midnight
The latitude of Washington D.C. is 38 degrees. If the President were to look at Polaris one night, she would find that its altitude is…
38 degrees
Which planet below can never be seen at Midnight?
Venus, because it’s an inferior planet
Newtons law of gravity is…
F = GMm/r²
What force holds the planets in their orbits around the Sun?
Gravitational
The law of inertia states…
objects remain at rest or move in straight lines at constant velocity a net force acts on them.
The ability of a rocket to move through the vacuum of space by firing its engine demonstrates
Newton’s law that every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
Halley’s comet orbits the Sun with a period of 75 years. Write the letter of the equation below that would be used to calculate the the size (semi-major axis) of the orbit of that comet.
P² = a³
Rotation
turning a body about an axis running through it. Ex: Earth completes a ROTATION every 24 hours
Revolution
Motion about an external axis. Ex: Earth completes a REVOLUTION around the Sun once every 365 days
The Meridians
A series of lines passing through theNorth and South poles, that intersect the equator at a 90 degree angle. They specify the East West location of a coordinate.
The Latitude
The angle of a place measured along the Meridian from the equator to the place. Goes from 0 degrees to 90 degrees North or 0 degrees to 90 degrees South.
The Celestial Sphere
an imaginary sphere that astronomers use to describe the positions of celestial objects
Pythagorus (~500BC)
Observed that the moon is spherical and therefore theorized that the Earth must also be spherical
Aristotle (~350 BC)
Observed Lunar eclipses. Earths shadow is always round which meant Earth MUST be a Spherical
Eratosthenes (~200 BC)
made quantitative measurement of the size of the Earth using a stick and it’s shadow.
Motion of the Earth
Corresponds to the Celestial Sphere
Time
The measurement of this is based on the rotation of Earth. Earth’s is based off a Solar day which is why we have time zones.
Solar Day
Based off the Sun. About 1 degree longer meaning it’s 4 minutes longer than it’s counterpart.
Side real Day
Based off a Star. About 1 degree shorter and therefore 4 minutes shorter than it’s counterpart.
Claudius Ptolemy (~140 AD)
Gave a very mathematical description of the Earth centered universe. Predicted Planetary positions with great accuracy relative to his time period.
Earth’s orbit is NOT Circular it’s…
Elliptical
Elliptical (term)
oval shaped
Heliocentric Theory
Heliocentric Theory
the astronomical model that places the sun at the center of the solar system. It states that the Earth and other planets orbit around the sun.
Copernicus
The First Great Astronomer of the Renaissance
Tycho Brahe
Danish Nobleman & Astronomer. Constructed an Astronomical observatory, invented numerous devices for Astronomical measurement with the naked eye (before the telescope). For 20 years recored with great accuracy planetary postions (especially Mars. He also sought help from Kepler.
Johannes Kepler
Brilliant German Mathematician. Worked with Brahe. Established 3 laws for Planetary motion.
Keplers 1st Law
planets move in ellipses, with the sun at one focus
Keplers 2nd Law
The radius vector (the line joining the planet with the sun) sweeps out equal area in equal time.
Keplers 3rd Law
The square of the time revolution of each planet is proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of its orbit. (T² = Ka³)
Ellipse
a well known geometric shape conic section.
Eccentricity
E = f/m
Galiteo
Helped secure the acceptance of Heliocentric theory as with a telescope he discovered:
The moon has craters - not a perfect crystalline sphere
Sun spots
The phases of Venus, orbiting the Sun not the Earth
Saw the moons of Jupiter, another celestial
Sir Issac Newton
Established 3 laws of motion
Newtons 1st Law
A body at rest will stay at rest unless acted upon by an outside force
Newtons 2nd Law
Force = Mass x Acceleration
Newtons 3rd Law
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Contact Force
A force thats touching. Ex: push or pull
Field Forces
Forces not directly touching. Ex: Gravity, electric, magnetic
Orbits & Center of Mass
Objects (planets) orbit around a point between them called the Center Mass called the Fulcrum. The center of mass is always closer to the bigger object.
Tides
They depend on the difference in gravitational attraction between different locations i.e. where the Moon is located.
Mass of the Moon
~1/80 Mass of Earth
Density of the Moon
~7/10 Earth’s Density
Diameter of the Moon
3500 km
Moon’s Diameter
~ ¼ Earth’s Diameter
Distance from Earth to Moon
~240,000 miles
Why do we always see the same side of the Moon?
Because the Rotation (on it’s axis) and revolution around the Earth periods are the same
Moon’s Sidereal rotation period
27 days
Moon’s Synode period
29.5 days
Why can we see the Moon at night?
Because the sunlight reflects off the Moon
How much of the Sun’s life light is reflected off the Moon?
7% of the incident sunlight
What is the Moon’s FIRST phase? What time of day is it at it’s highest point in the sky?
New Moon. 12 pm
What is the Moon’s SECOND phase? What time of day is it at it’s highest point in the sky?
Waxing Crescent. 3pm
What is the Moon’s THIRD phase? What time of day is it at it’s highest point in the sky?
First Quarter. 6pm
What is the Moon’s FOURTH phase? What time of day is it at it’s highest point in the sky?
Waxing Gibbous. 9pm
What is the Moon’s FIFTH phase? What time of day is it at it’s highest point in the sky?
Full Moon. 12am
What is the Moon’s SIXTH phase? What time of day is it at it’s highest point in the sky?
Waning Gibbous. 3am
What is the Moon’s SEVENTH phase? What time of day is it at it’s highest point in the sky?
Third Quarter. 6am
What is the Moon’s EIGHTH phase? What time of day is it at it’s highest point in the sky?
Waning Crescent. 9am
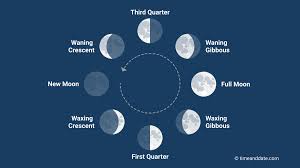
What is this?
The phases of the moon.
How much later does the Moon rise then the previous day?
50 minutes
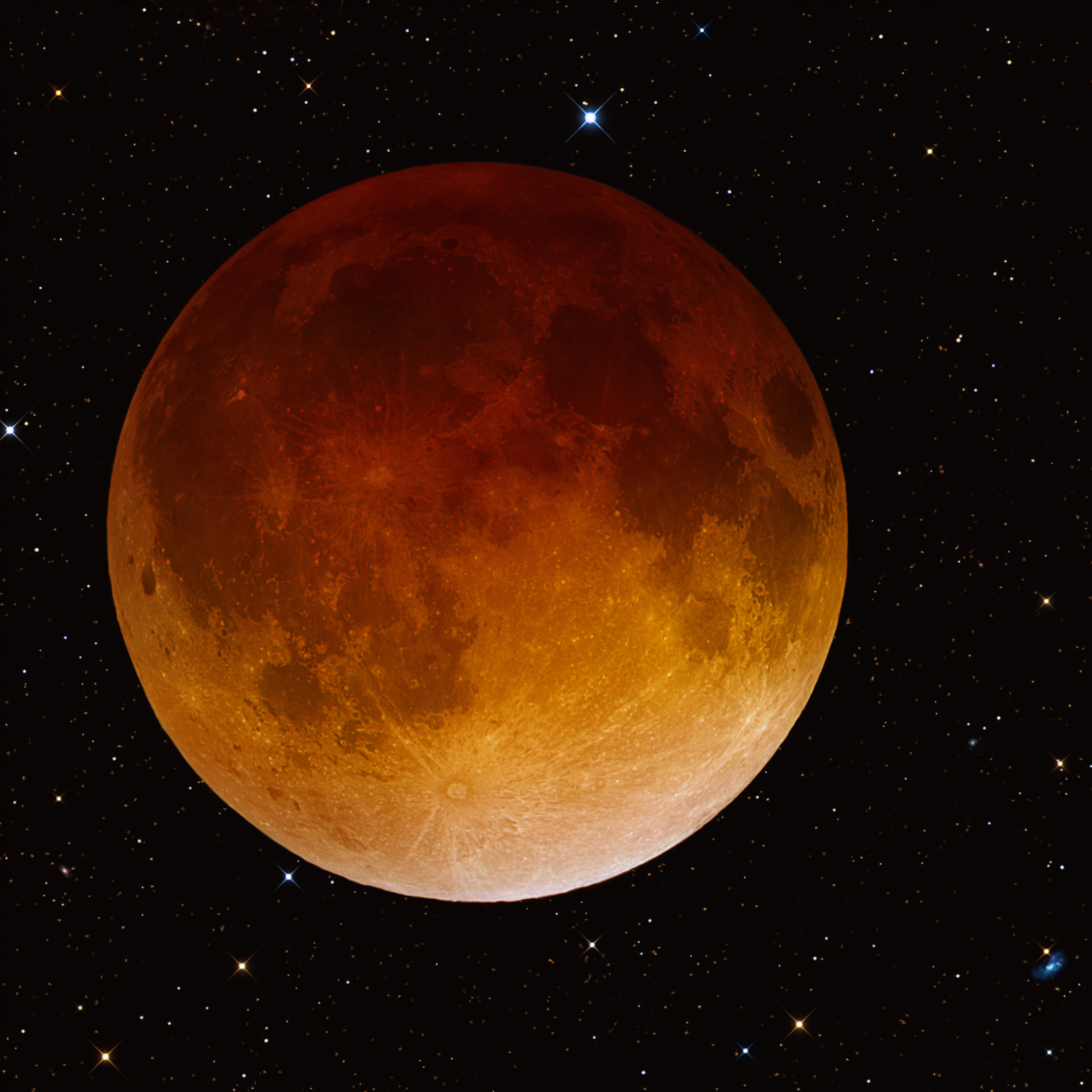

Lunar Eclipse
The Moon passes through the Earth's umbra, causing it to appear reddish or dim.
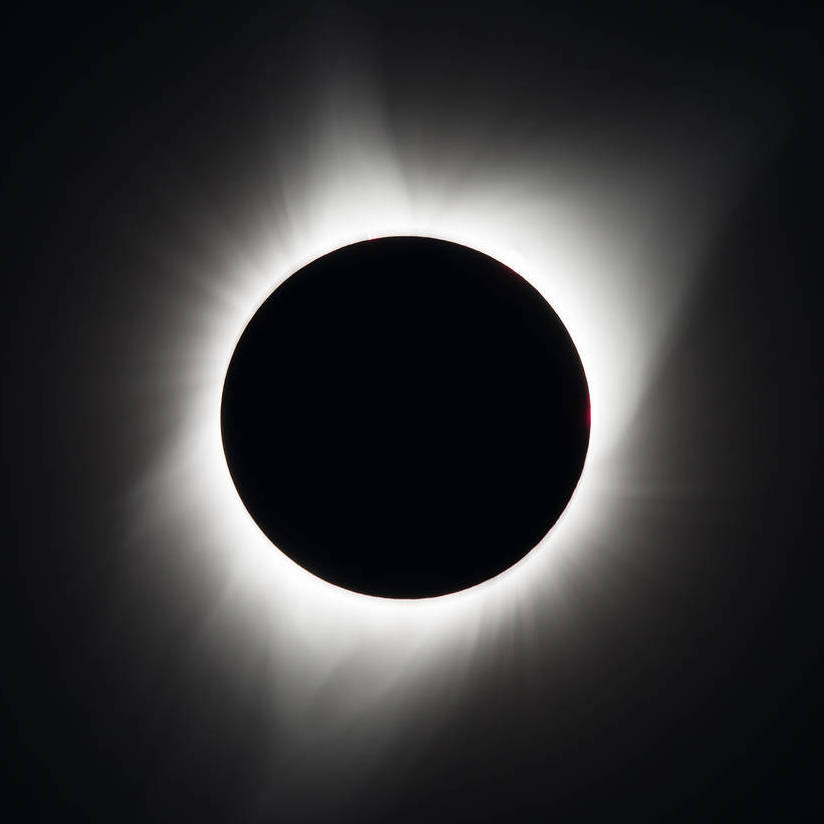

Solar Eclipse
The umbra of the Moon casts a path of totality where the Sun is completely blocked
Umbra
The region of total shadow, where a light source is completely blocked.
Prenumbra
The region of partial shadow, where the light source is only partially blocked.
“Fission” Hypothesis
The Moon was flung away from the Equator of a very rapidly rotating
Proto-Earth.
Problem: The Moon is NOT in the Earth’s equatorial plane + there’s a difference in the chemical composition of the Earth’s crust & Moon’s crust.
“Capture” Hypothesis
Moon was formed elsewhere in the Solar system, ventured close to the Earth and was gravitationally captured
Problem: From a Sun centered orbit to an Earth centered orbit, the moon would have to lose a great deal of kinetic energy - highly improbable
Kinetic Energy of Motion Equation
½ Mass x Velocity²
“Co-Creation” Hypothesis
Earth & Moon were formed side by side at their present distance from the Sun
Problem: Very different chemical composition of high density (Fe) Earth, and Low Density
“Great Impact” Theory
the Moon formed from debris ejected into space after a Mars-sized object, named Theia, collided with the early Earth, which then coalesced to form our lunar companion
Current Favored explanation of the Moon
“Nebular” Hypothesis
Solar system began as Giant cloud of mostly Hydrogen and Helium and i-27 heavier elements
Fragment of solid material begin to form from collision of molecules and atoms
When too massive to be carried by the gas these fragments fall toward the central plane of the cloud where the density is the highest and gravitational anthem is the greatest.
Momentum Equation
Mass x Velocity
Angular Momentum
Mass x Velocity x Radius
Moment of Inertia
I = Σ (miri²)
How many planets are in our Solar System?
8 planets
What is the farthest Planet from the Sun?
Neptune as it’s 30 AU away.
What is the Closest Planet to the Sun?
Mercury as it’s 2/5 AU away
Total Mass of the Planets
~1/1000 Mass of Sun
What is the order of the Solar System?
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Astroid Belt, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
Terrestrial Planets
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars
Jovian Planets
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
Terrestrial Characteristics
4 closest planets to the sun
Composed mostly of Rocky Material + Fe
“Small in size”
Relatively dense
Short Revolution period
Slow Rotations on it’s Axis
High Surface Temperature
Few Satellites
Jovian (Gas Giants) Characteristics
Distant planets from the Sun
Mostly Hydrogen + Helium
Much Larger Diameter, much more massive
Much lower density (Saturn could float)
Long periods of Revolution
Rapid rotations on it’s axis (avg = 12hrs)
Low Surface Temperature
Many Moons
Astroids
Relics of rocky planetesimals that formed between Mars and Jupiter orbit
30,000 Astroids
Can have very Regular shapes
A day on an Astroid is only 9 hours long
More a tumble than a Spin
We measure rotation periods by watching changes in brightness
Main Astroid belt is between Mars and Jupiter
Comet
Icy Small bodies that orbit the sun, often leaving a visible tail of gas and dust as they approach the Sun
Come from:
Kuiper Belt - Flat disk shaped region begins beyond the orbit of Neptune extend s out several thousands Au’s tens of thousands of Icy planetesimals - too far from the Sun to be active
Oort Cloud - spherical distribution - 50,000 AU ~1/5 of way to the nearest star weakly held by the sun
Like Charges…
Repel
Unlike Charges…
Attract