Music History Final
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Good luck, we're cooked
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
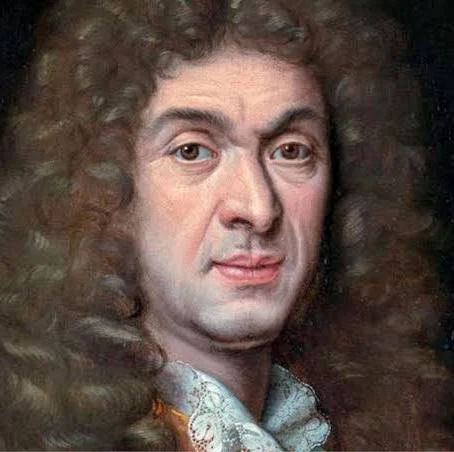

J. B. Lully
Made the French Armide

Who composed more than 550 one-movement keyboard sonatas?
Scarlatti
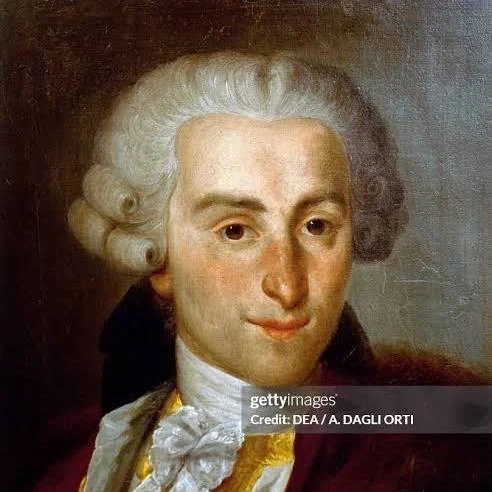

Who composed early symphonies in Italy during the 1730’s?
Giovanni Battista Sammartini
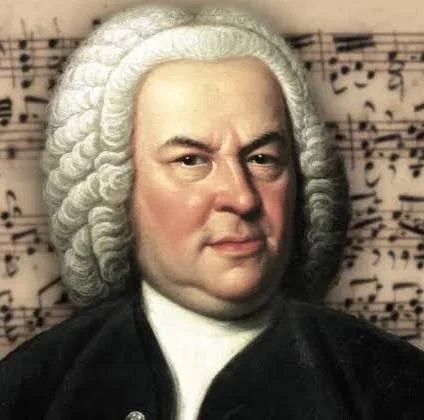

Who composed more than 300 cantatas for the Lutheran Service?
J. S. Bach
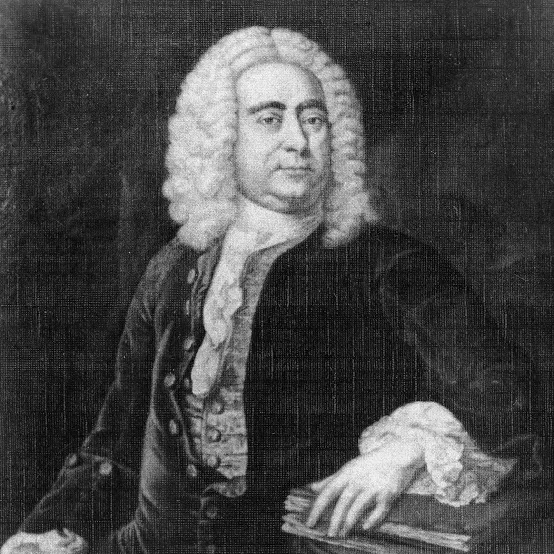

Who composed opera and oratorio in three countries and in three languages?
Handel
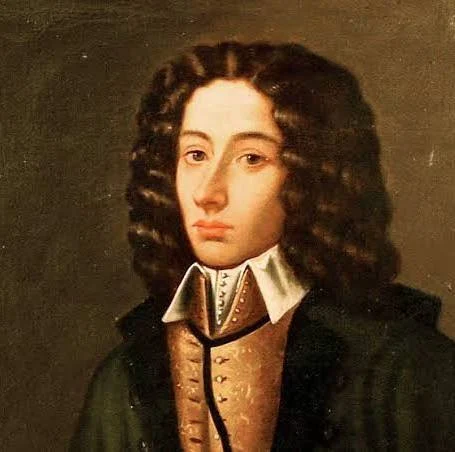

Who composed intermezzi such as La Serva Padrona?
Giovanni Battista Pergolesi
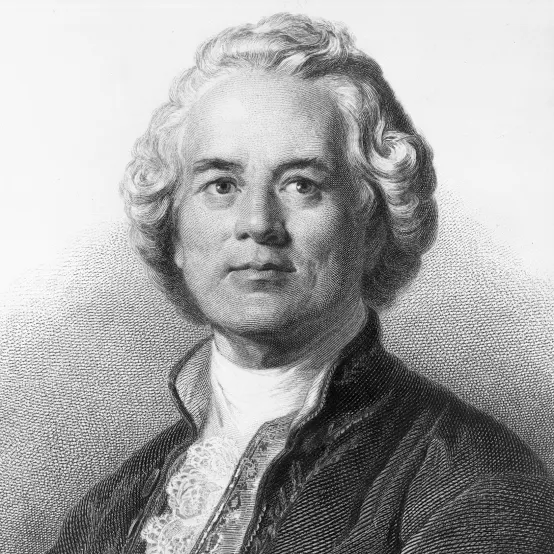

Who reformed opera to contain fewer arias and to be more natural?
Christoph Gluck
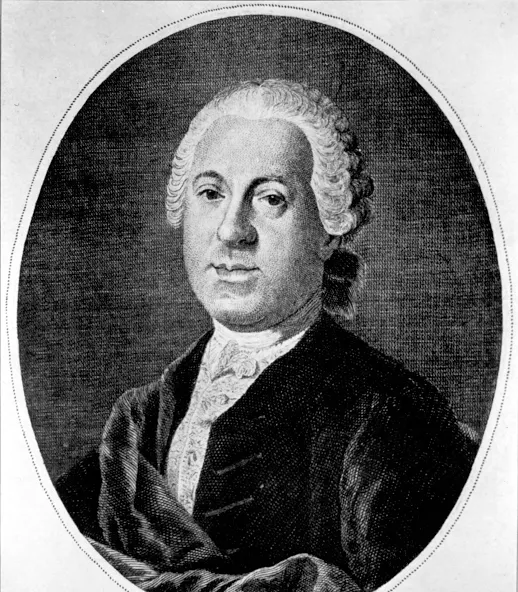

A german who composed Italian operas to Metastasian libertti?
Johann Adolph Hasse

Who invented and coposed works using the Manheim rocket and the Maniheim steamroller?
Johann Stamiitz

Who was a court poet in Vienna who composed more than 100 opera libertii?
Pietro Metastasio
Compser in all genres except opera?
Bach
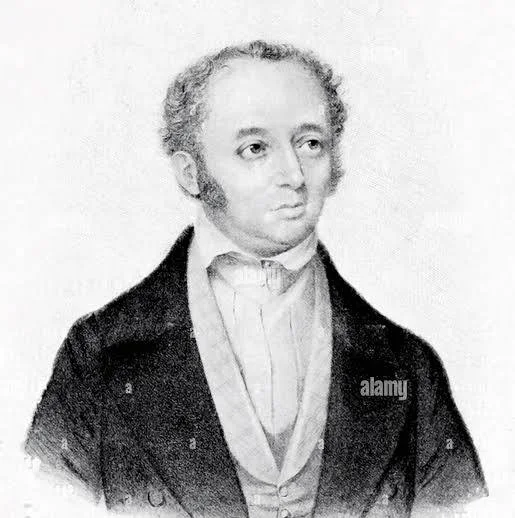

Identified our earlist version of sonata form
Adolf Marx
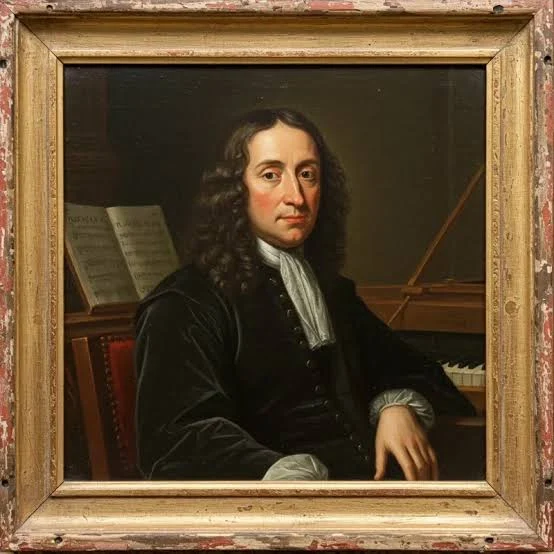

Who invented the first piano in the 1700
Cristofori
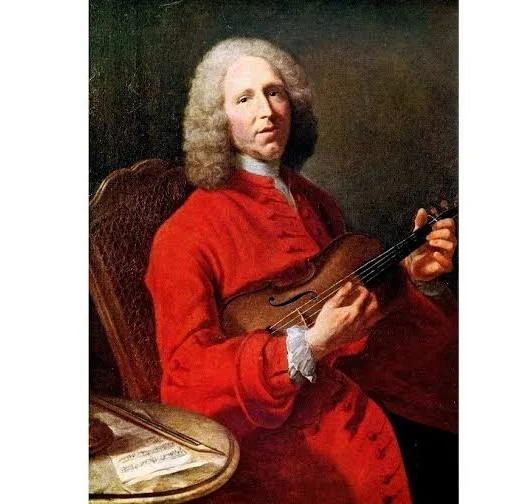

Who was the first practioner of our present music theory system?
J. P. Ramaeu
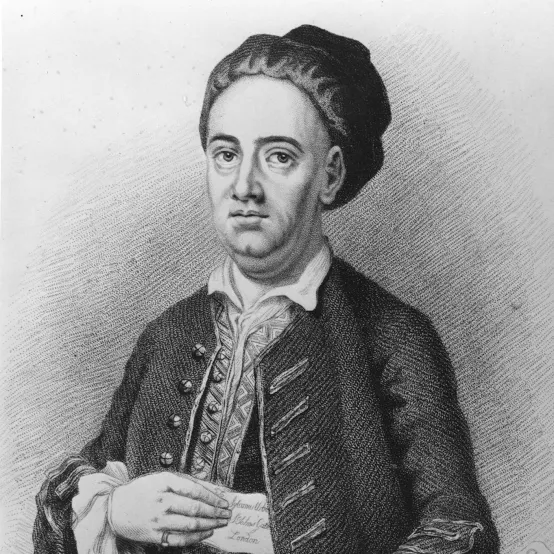

Composed Ballad Operas, such as tghe Beggar’s Opera
John Gay!
Who helped Mozart learn to compose piano Concertos
J. S. Bach

Who composed mostly keyboard works, with slow movement int he Empfindasm stil?
(C.P.E. Bach)
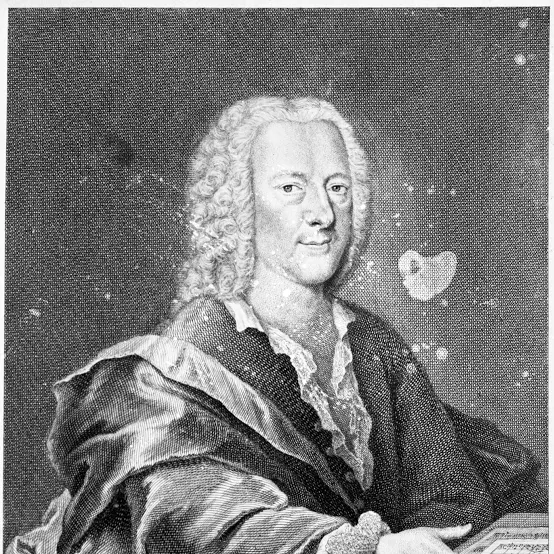

Extremely prolific German Baroque composer of sacred and secular vocal and instrumental works for all occasions?
Telemann

Who composed semi-operas for a girls boarding school in England
Purcell
Who had a patent on the production of all theatrical music in France during the late 17 century ?
Lully

Ventian composer of music for strings and other instruemnts?
Vivaldi
Cantata:
a medium-length narrative piece of music for voices with instrumental accompaniment, typically with solos, chorus, and orchestra.
Ritornello Form:
a Baroque musical structure featuring a recurring orchestral theme (ritornello, Italian for "little return") that alternates with contrasting solo passages (episodes), creating a "tutti-solo-tutti-solo" pattern, common in concertos and arias
Chorale
a Lutheran hymn tune, typically with a simple, memorable melody (often in the top voice) supported by rich four-part harmony
First-movement concerto form
a musical structure used for the opening movement of Classical and Romantic symphonies, sonatas, and quartets
Koch’s two-part sonata form:
based on the movement's plan of modulation and principal cadences, rather than on thematic groups, and consisted of two main sections (called zwey Theile).
Dry recitative
a speech-like vocal style in opera and vocal works, characterized by free rhythm following word accents, minimal, simple, chordal accompaniment (usually harpsichord/cello), and a focus on advancing the plot rather than showcasing melody, often sung by a vocalist with just the continuo group
Accompanied recitative
a style of singing in opera and oratorio where the vocal line is accompanied by the full orchestra, rather than just a continuo
Intermezzo:
a musical form that acts as an interlude, a short, light piece between acts of a larger work (like opera) or between movements in a longer composition
Stretto
in a fugue, it's when voices imitate a theme in rapid, overlapping succession for a climactic, hurried effect
Empfindsam Stil:
a German musical style from the mid-18th century that emphasized the expression of personal, heartfelt emotions
Stil Galant:
a light, elegant, and charming musical movement in the mid-18th century
Musical Period
a short, complete musical idea made of two balanced phrases (antecedent and consequent) that create a sense of question and answer, ending with a cadence
Suite
a collection of self-contained instrumental movements or pieces, often based on dances, that are performed together as a single, unified work
Fugue:
a complex, contrapuntal musical composition built on a main theme (the subject) that is introduced by one voice and then imitated, developed, and interwoven by other voices in a highly structured way, creating rich polyphony (multiple independent melodies)
Fortspinnung:
a Baroque musical technique where a short melodic idea (motif) is continuously developed into a longer, flowing melody, often using sequences, repetitions, and intervallic changes, creating a self-perpetuating, "spun-out" line rather than clear, balanced phrases
BWV
Bach-Werke-Verzeichnis, a German term meaning "Bach Works Catalogue
In which genre did J. S. Bach not compose?
Opera
Name at least one of Bach’s insturmental works
Fugue and prelude
Did Bach and Hendel both compose keyboard works
Yep
How many operas did Handel compose?
42
What is the most useful thematic catalog designation for locating Bach’s works
BWV
Who was the intended audience for the Beggar’s Opera?
Lower Class
Pergolesi’s “La Serva Padrona” is classified as which type of opera?
Intermezzo
In Opera seria of the eighteenth century, which type of revitative was used for moments of high drama?
accompanied recitative
In Opera Buffa, which class is often depicted as having more common sense?
Servant class
Which type of aria was the most popular aria type in opera seria of the 18th century?
da capo aria
True or False: Singspiel is a form of opera seria in German, and is tragic rather than comic?
False
True or Flase: English Ballad opera contains spoken dialogue rathe than recitative
True
True or False: Singspiel contains spoken dialogue rather than recitative
False
True or False: In Da capo arias, it is important to ornament the B. section of the aria
False
True or False: 18th century opera seria plots are about enlightended monarchs and beneficient rulers
True
True or False: Members of the nobility and upper classes only sponsored and attended Opera Seria productions
False
True or False: Members of the nobility and upper classes sponsored and attended both comic and serious productions of opera
True
True or False: The War of the Buffoons was about whether or not Italian comic opera was more pleasureable than French Lullian opera
True!
True or False: Opera did not utilize any of the emerging styles of the Classical period, such as the Stile Galant of the music period
False
What is the movement structure of the 1730’s symphony of Sammartini and Stamitz?
Sonata Form (Fast-slow-fast)
Of how many musicians were early orchestras of the classical period comprised?
25-35
The first movements of symphonies are generally in which standard form?
Sonata Form
True or False: Early symphonies were derived from concerto, the trio sonata, and the 3-part Italian opera overture
True
True or False: early symphonies were played as symphnoies are played today, with all of the movements performed together
False
True or False: Early symphonies were often shorter than ten mintues per symphony
True
True or False: Early symphonies were considered very serious forms of entertainment
False
Which instrumental genre is describes as a converstaion between instruments?
Concerto Grosso
What kinds of ensembles play divertimentos?
A. Small string ensembles
B. Small wind ensembles
C. small wind and string ensembles
D. All of the aboce
D. All of the above (small string, wind, and both)
When the piano was added to small ensembles of amateurs, what kind of role did it play?
A. IA leading role b/c keyboard players were more practiced than others
B. It served only as an accompaniment instrument, allowing the string players to be virtuosic
C. It played a role equal to the other players
A. It took a leading role b/c keyboard players were more practiced than others
Which statement is most correct about Classical chamber music?
A. Most composers did not compose accompanied solo sonatas
B. Chamber music consisted mostly of accompanied solo sonatas and string quartets
C. A wide varitety of ensemble combinations were utilized in Classical chamber music, such as quintets, trios, quartets, and duets.
D. Chamber groups of winds were extraordinarily popular
C. A wide variety of ensemble combinations were utilized in Classical chamber music, such as quintets, trios, quartets, and duets
The increased popularity of the fortepiano contributed to which of the following?
A. Ticket sales for public concerts
B. An increase in the co mposition of keybaord sonatas
C. An incrrease in amateur music-makig in middle class homes
D. Both B and C
D. (Both b and c)
The keyboarde sonata developed in which way?
A. From a one-movement work to a two-movement work
B. Froma one-movement work to a four-movement work
C. From a one-movement work to a three-movement work
D. Remained unstandardized
C. From a one-movement work to a three-movement work
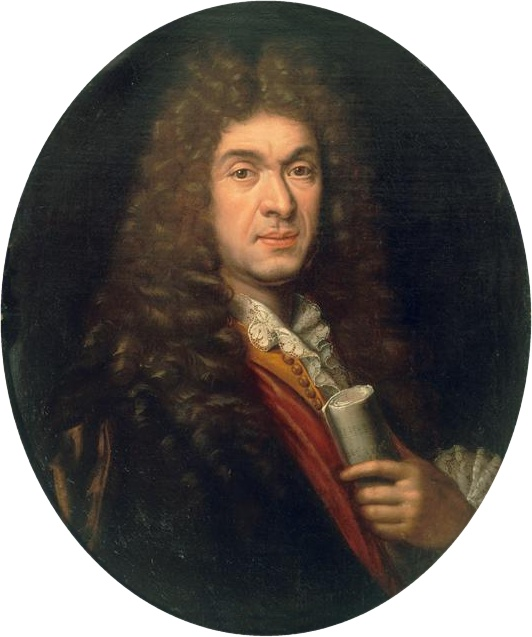

J. B. Lully
French opera, Louise XIV’s bitch

E. Jacquet De la Guerre
career under royal patronage (Louie XIV) and first woman in france to compose opera

F. Couperin
Born in paris and composed harpsichord works
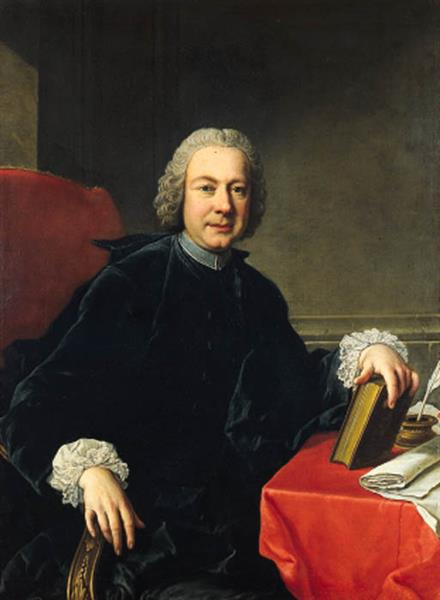

Pietro Metastasio
He was an opera liberttist
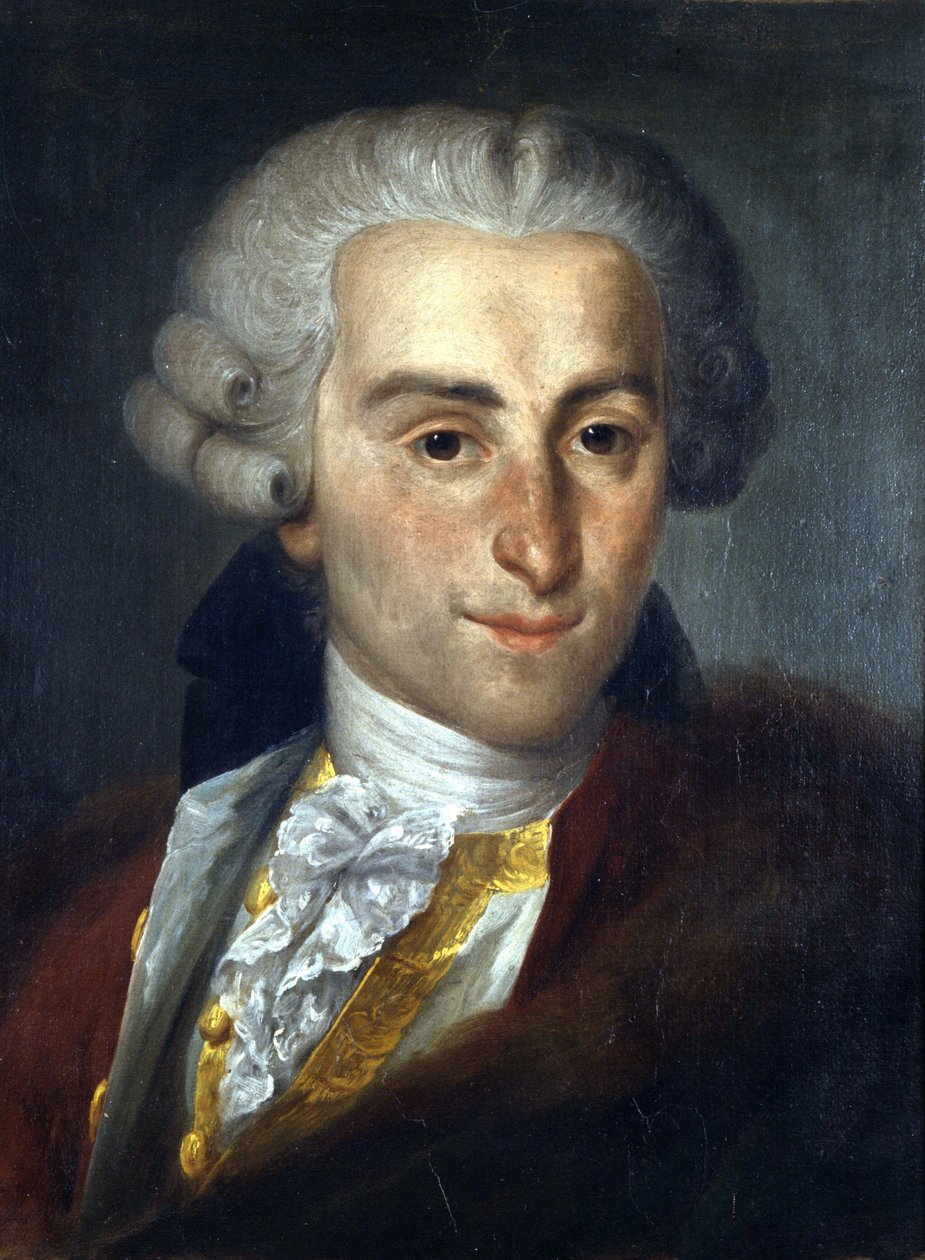

G. B. Sammartini
Wrote and founded symphonies.
Bartolomeo Cristofori
Invented the piano and worded for the medii court in Florence

Johann Stamitz
Founded the Mannheim School shaping classical symphony
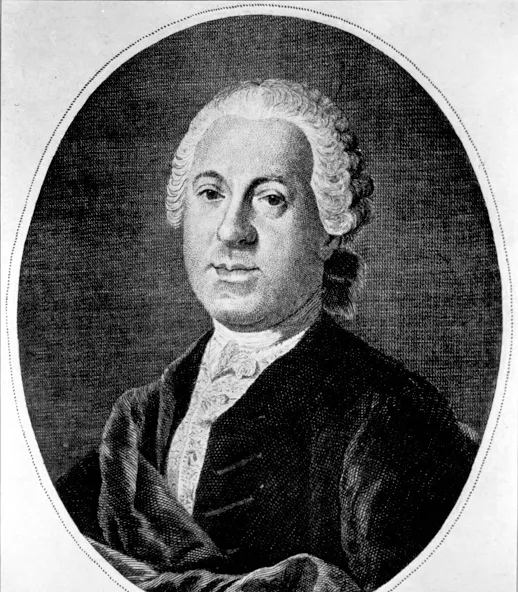

Johann Adolf Hasse
leading composer of opera seria, elegant vocal wirting and collaborations

Domenico Scarlatti
wrote over 500 keyboard sonatas
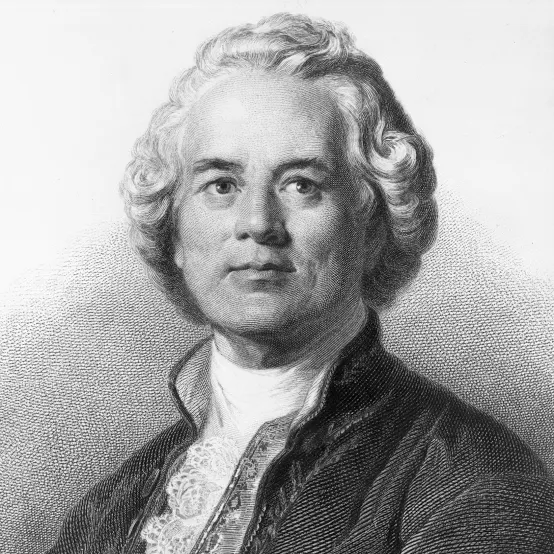

Christoph Willibald von Gluck
Refromed opera, more drama and expressiveness
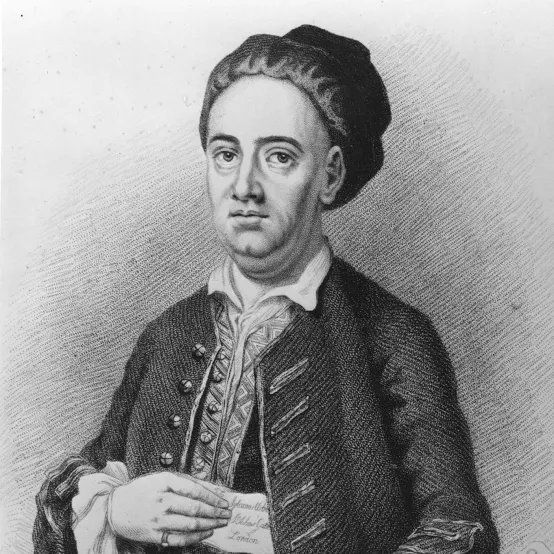

John Gay
Wrote libretto and The Beggar’s Opera
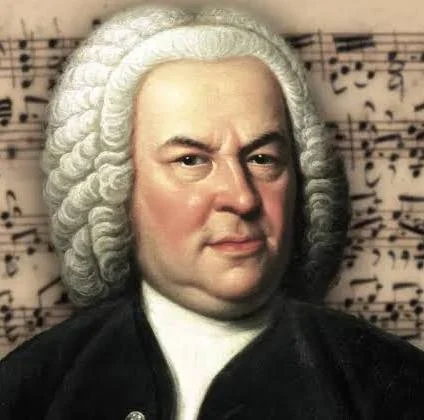

J. S. Bach
master of baroque composition, in fugues, cantatas, and keyboard workws
J. P. Rameau
Revolutionized French opera and harmony
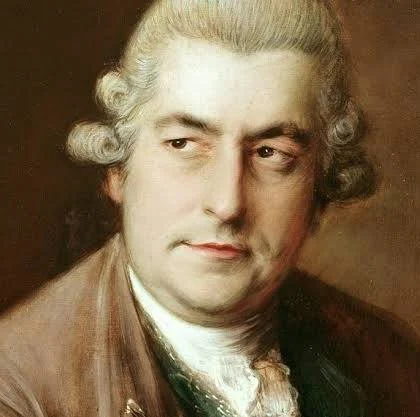

J. C. Bach
develped the classical style in symphonies and etc., “London Bach”
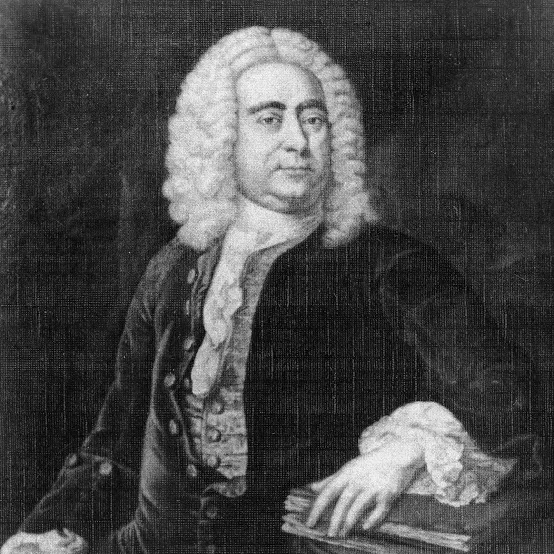

G. F. Handel
Huge operas, oratorios, and orchestral works, “Messiah”
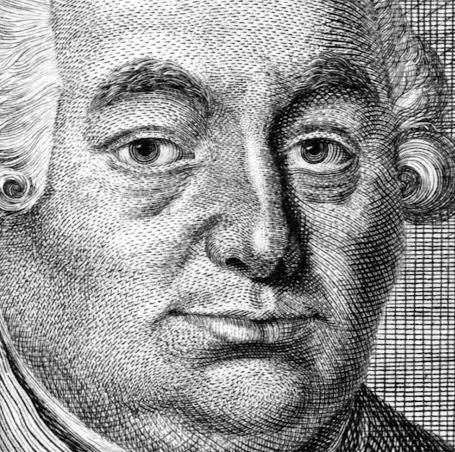

C. P. E. Bach
apart from the crazy name, he wrote “empfindsamer Stil” and influenced the transistion into the classical period.

Heinrich Christoph Koch (Cock)
yea this dude is cooked mb, some sonata form yadda yadda

G. F. Telemann
Church music, operas, instrumental works, “German Randmosoft”
Antonio Vivaldi
“Red Priest”, 500 concertos produced
H. Purcell
Master of english baroque music, and was known for his oepras “Dido and Aeneas”
Gioanni Perogolesi
Italian Baroque composer, intermezzi, comic opera