AP Psychology Terms
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Psychodynamic perspective

How behavior is shaped by childhood experiences, conflicts, and unconscious drive
Cognitive perspective

Observes mental processes
Logic, memory, thinking, problem-solving
Biological perspective

Studies physiological bases of behavior in both humans and animals
Behavioral perspective

Focuses on observable behaviors
How they are learned through interaction and environment
Evolutionary perspective
How mental and behavior processes evolved
Adaptions for survival + reproduction
Sociocultural perspective

How culture, social norms, and social environment affects behavior
Humanistic perspective

Emphasizes free will and personal growth
Concept of self-actualization
Biopsychosocial perspective
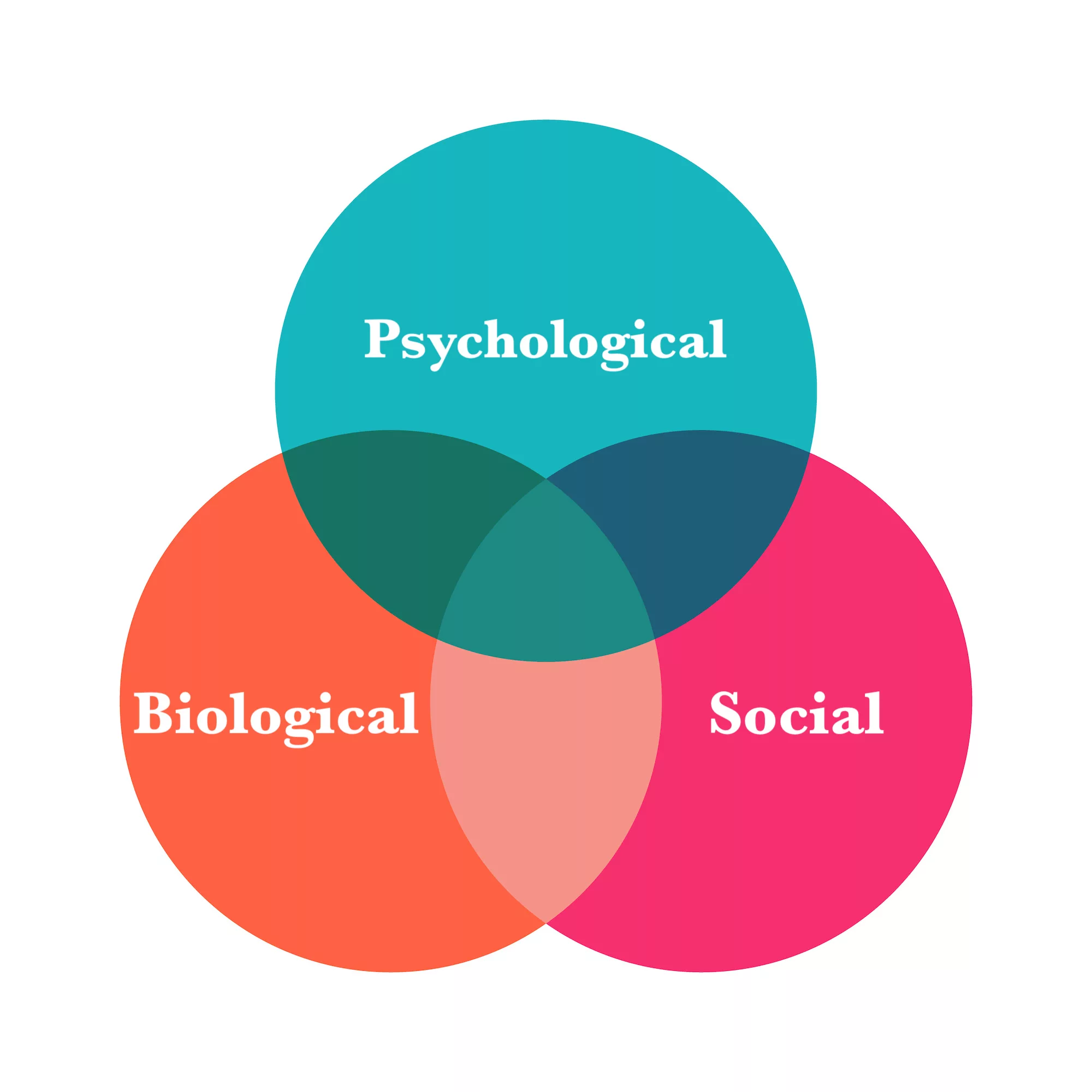
Combination of biological, psychological, and social factors
How all of these affect human behavior
Confirmation bias

People tend to look for information that already confirms their opinions/beliefs
Hindsight bias

People believe that they knew something was going to happen
Only after it has occurred
They did not predict it beforehand
“I knew it all along”
Overconfidence

People have too much faith in their own judgements and abilities
Think they know more than they actually do
Empirical evidence

Information obtained through research, experimentation, or measurement
Prevent cognitive bias
Objective data
Counteract natural tendencies to make biased decisions
Scientific method

Format to generate empirical evidence
Systemic approach to study
Includes hypotheses, data, experiments, groups, etc.
Conclusion based on evidence, not opinion
Hypothesis

An educated guess
Must be able to be proven false
Testable prediction
Based on previous research & observations
Falsifiable

Hypothesis that can be proven false
Proven false through examination + experimentation
Formulated in a way that allows for possibility of evidence to refute hypotheses
Peer review

Research articles are evaluated by experts
Happens before publishing
Peers assess quality and validity of research
Provides feedback and recommendations
Replication

Process of repeating/reproducing research study
Meant to determine if findings can consistently be observed
Same study with new subjects
Similar conditions
Reliability
Test that produces consistent results
Must be repeated multiple times
Same premise + conditions
“RRR” → “repeated, reliable results”
Validity

Study accurately measures what it tends to measure
Valid if effectively assesses the construct or concept it is designed to measure
“VET” → “valid evidence, true”
American Psychological Association (APA)

Leading professional organization
Specializes in psychology
Advances field of psychology
Founded in 1892
Research design

Plan that outlines how a research study will be conducted
Addresses specific questions or objectives
Methodology

Techniques used to conduct research within a specific research design
“How will data be measured?”
Quantitative data
Number-based information
Gathered from surveys, tests, or experiments
Helps understand patterns/relationships in a precise way
Qualitative data

Not based on numbers
Focuses on description/quality
Deeper insight into complex subjects
Likert scales

Type of measurement tool
Captures attitudes and opinions in a quantitative way
“On a scale from 1-10…”
“Strongly agree (5)” or “Somewhat disagree (2)”
Structured interviews

Predetermined questions are asked to all participants in the same order
Allows for consistent data
Facilitates comparisons between participants
Survey technique

Collect data through self-report
Open-ended question about their attitudes/beliefs/opinions
Can result in both quantitative and qualitative data
Wording effect
Subtle changes in wording of questions
Can influences respondent’s responses
Can lead to biased/inaccurate data
Social desirability bias

Tendency of individuals to respond in a way that’s socially acceptable
Conform to social norms
Might skew research results
Naturalistic observation

Researchers observe and record behaviors in real-world scenarios
Do not intervene or manipulate
Deeper understanding of human behavior in its natural context
Case study
In-depth examination of a single individual, group, or phenomenon
May not be able to generalize to broader cases
Correlational research

Scientific method used to examine relationships
Between two or more variables
Do not manipulate variables
Focus on observing/measuring naturally occurring associations
Third Variable Problem
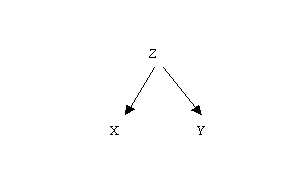
Possibility of a third, unmeasured variable may be influencing the relationship
Could imply that there are other factors at play
Explains the possibile correlation between varaible
Scatterplot
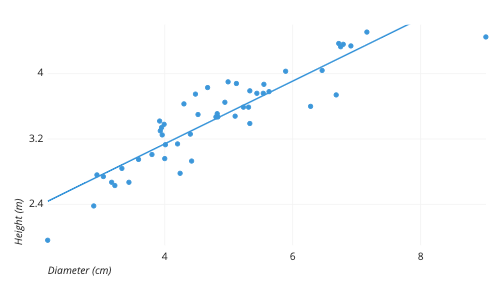
Visual representation used in correlational research
Graph for correlation
Assess strength & direction of correlation
Positive (+) or negative (-)
Correlation Coefficient

Represented by the letter ‘r’.
Strong is r = 1 / -1
Weak is 0.
Meant to display how strong relationships between variables are.
Positive Correlation
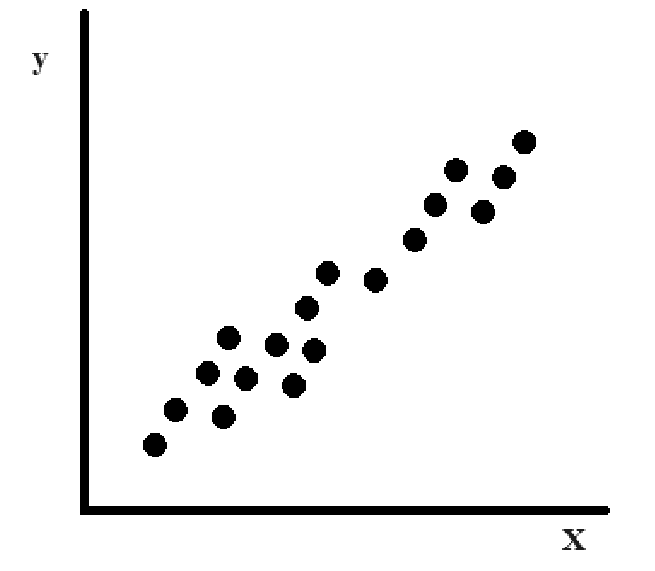
As one variable increases, the other variable also increases
Or as one variable decreases, the other variable also decreases
Variables moving in the same direction
Negative Correlation
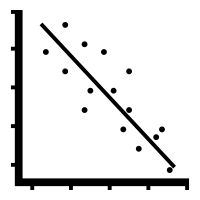
As one variable increases, the other decreases.
Variables move in opposite direction
Experimental Method
Research technique used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables
Manipulates one variable
Measures effect on other variable
Independent Variable

Variable that researcher changes/manipulates
Factor that possibly causes changes in outcomes
Affects other variable
Dependent Variable

Variablethat is observed/measured for changes in an experiment
Outcome may be changed by the independent variable
Confounding Variable

Variable that wasn’t accounted for in the study
But still affects the results
Can distort the true effects of the independent variable on dependent variable
Operational Definitions

How a researcher will measure and manipulate variables in a study
Outlines exact procedures
Ensures consistency and clarity in research