3309 term 2 final week 10
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:00 PM on 4/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
1
New cards
what triggers ovulation
peak of LH in the middle of the menstrual cycle
2
New cards
graafian follicle right before ovulation
oocyte bursts out, polar body, secondary oocyte travels through oviduct to be fertilized, meiosis 2, second polar body
3
New cards
blastocyst cells in centre vs outside
centre cells are embryo cells, cells on outside become placenta
4
New cards
infundibulum
funnel shaped segment segment, end of oviduct
5
New cards
fimbriae
extensions of the infundibulum, extend towards ovary to catch secondary oocyte and bring it into the oviduct
6
New cards
ampulla
7-8cm, longest portion of oviduct, thinner walls, where fertilization occurs
7
New cards
isthmus
4cm, short thicker walls of oviduct
8
New cards
intramural segment
0\.6cm, connects the oviduct to the uterus
9
New cards
ampulla mucosa
* highly folded
* epithelium, basement membrane, highly cellular lamina propria with blood vessels
* epithelium, basement membrane, highly cellular lamina propria with blood vessels
10
New cards
why is the ampulla mucosa highly folded
for surface area in the lumen, so the secondary oocyte (fertilized embryo) is not lost on the way to the uterus
11
New cards
ampulla muscularis
* thick inner circular smooth muscle layer
* thin outer longitudinal smooth muscle layer
* thin outer longitudinal smooth muscle layer
12
New cards
ampulla serosa
mesothelium secretes serous lubricating fluid and supportive CT tissue layer
13
New cards
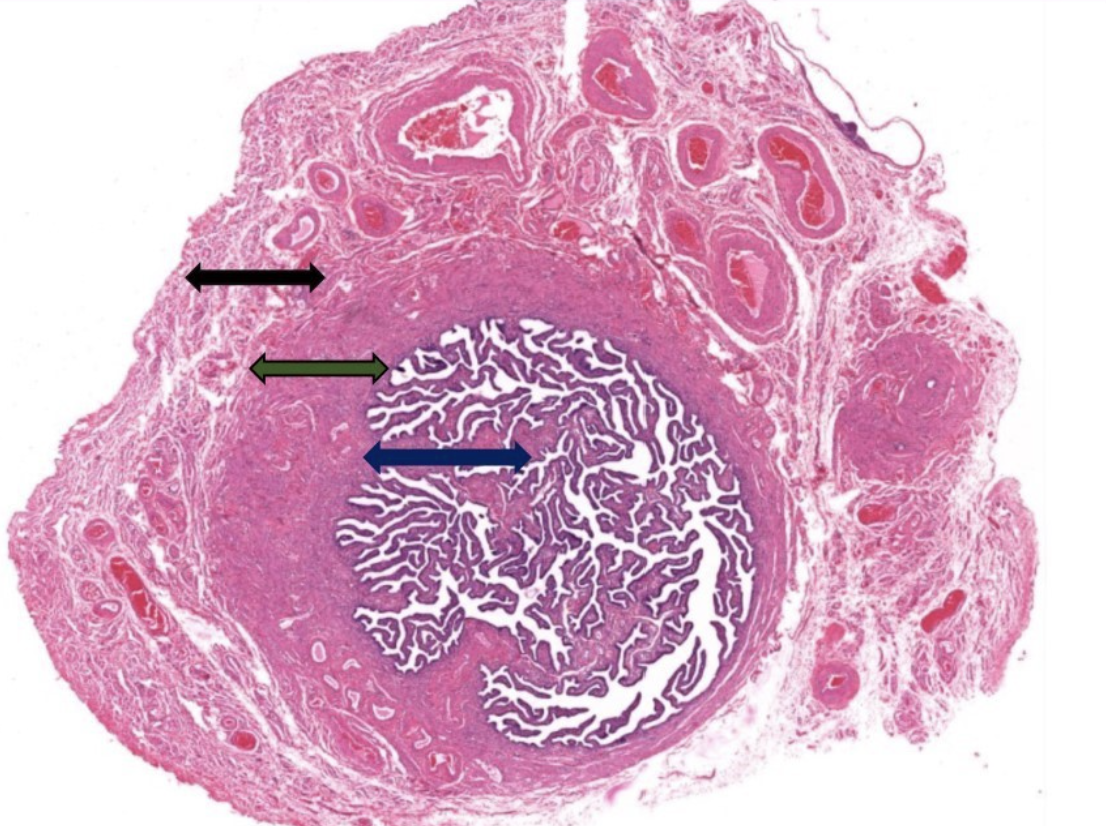
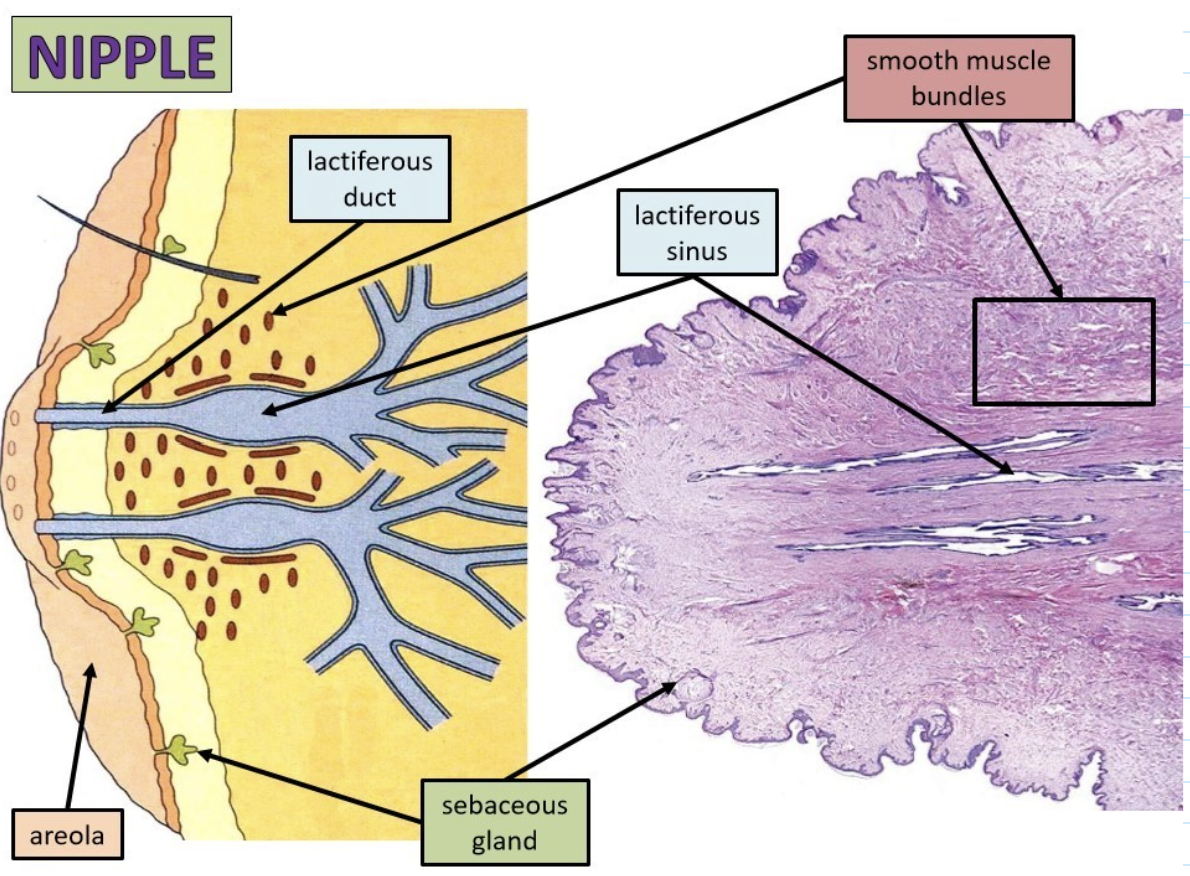
label this slide
ampulla of oviduct
14
New cards
mucosa of ampulla of oviduct epithelium
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
15
New cards
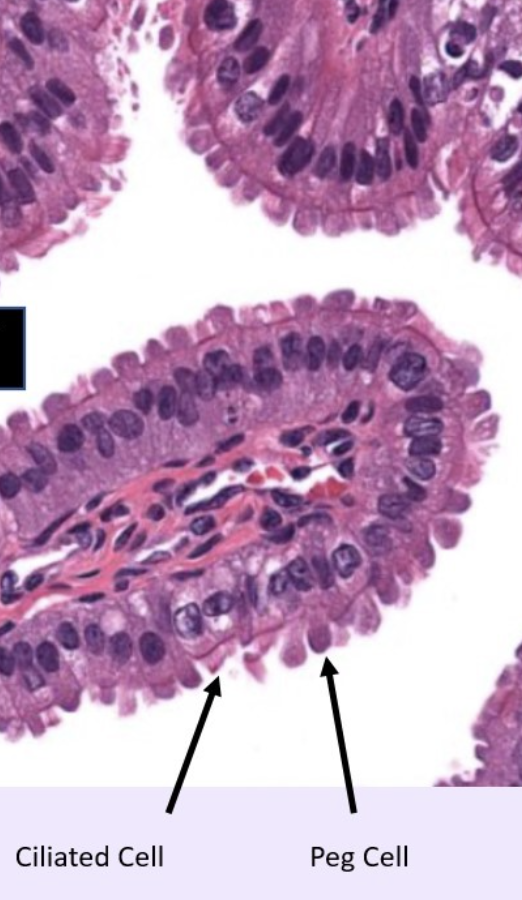
cells of mucosa of oviduct (ampulla)
ciliated cells and peg cells
16
New cards
ciliated cells
most numerous in infundibulum and ampulla, sweeps the zygote/embryo through the oviduct towards the uterus
17
New cards
peg cells
secretory cells for nutritive fluid for zygote/embryo
18
New cards
ciliated cell histology
can see basal body (dark line under cilia)
19
New cards
peg cell histology
no basal bodies, protrusions off apical surface
20
New cards
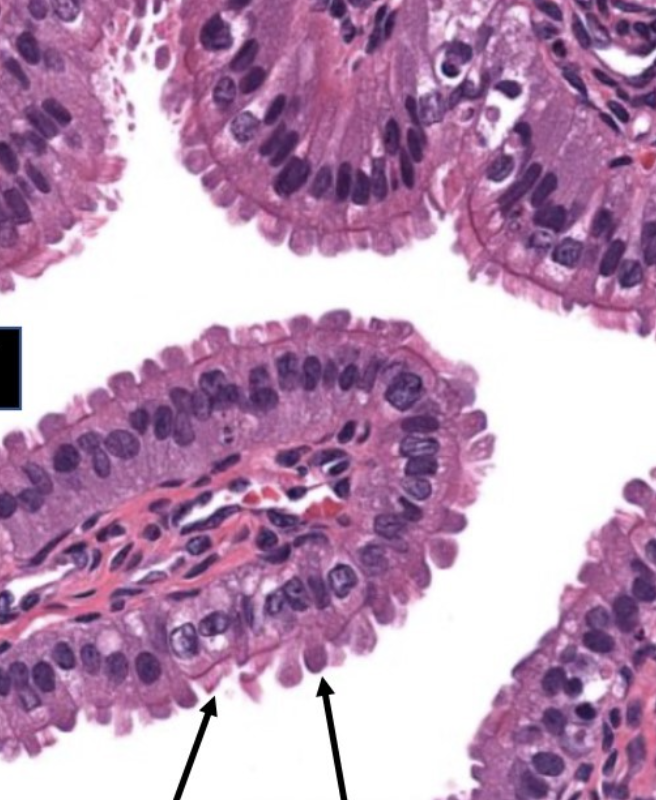
label this slide
mucosa of oviduct (ampulla)
21
New cards
mucosa of oviduct (ampulla) hormones
influenced by estrogen and progesterone
during the follicular phase, estrogen acts on ciliated cells to increase cilia
during ovulation, the corpus luteum produces progesterone that acts on secretory peg cells to increase its number (nutrients for embryo)
during the follicular phase, estrogen acts on ciliated cells to increase cilia
during ovulation, the corpus luteum produces progesterone that acts on secretory peg cells to increase its number (nutrients for embryo)
22
New cards
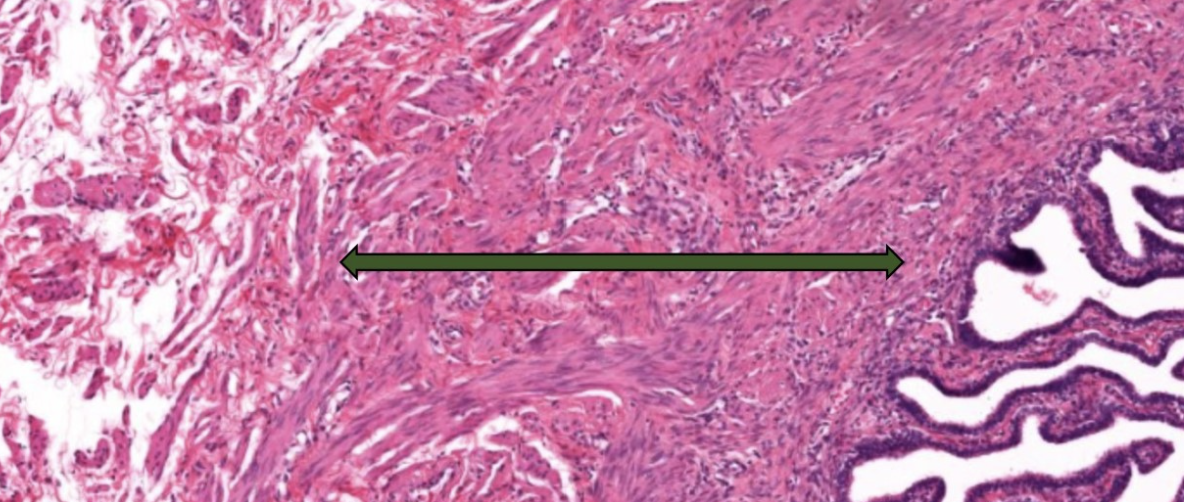
label this slide
muscularis of ampulla
23
New cards
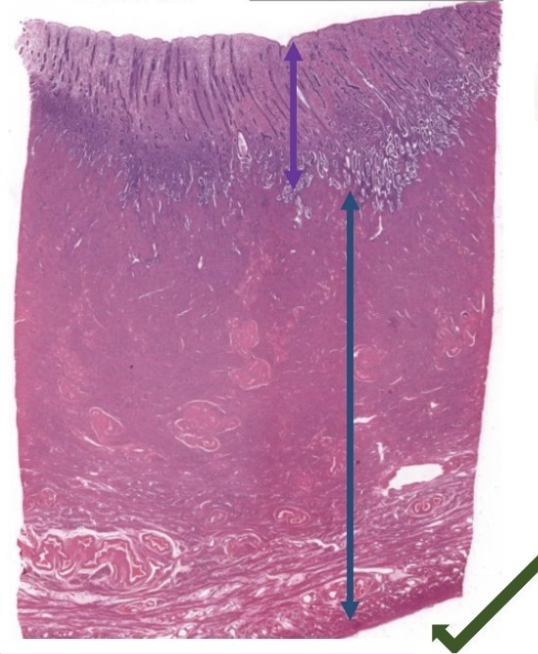
label this slide
uterus
purple = endometrium
blue = myometrium
green = perimetrium
purple = endometrium
blue = myometrium
green = perimetrium
24
New cards
three parts of the uterus
fundus, body, cervix
25
New cards
endometrium of uterus
* mucosal layer
* secretory uterine glands
* highly vascular
* 2 layers (stratum functionale and stratum basale)
* secretory uterine glands
* highly vascular
* 2 layers (stratum functionale and stratum basale)
26
New cards
epithelium of endometrium of uterus
simple columnar with ciliated cells and secretory cells
27
New cards
uterine glands
invaginations of endometrium made of secretory cells that secrete fluid
28
New cards
stratum functionale
upper layer of endometrium, lighter staining, sloughed off during menstruation
29
New cards
stratum basale
darker staining, maintained throughout menstrual cycle, rebuilds stratum functionale once lost
30
New cards
myometrium of uterus
* muscular layer
* 3 layers (middle stratum vascularis layer, outer and inner longitudinal layers)
* 3 layers (middle stratum vascularis layer, outer and inner longitudinal layers)
31
New cards
myometrium of uterus histology
eosinophilic, beneath endometrium, lots of arteries and arterioles
32
New cards
middle stratum vascularis layer of myometrium
circular smooth muscle, blood vessels, lymphatics
33
New cards
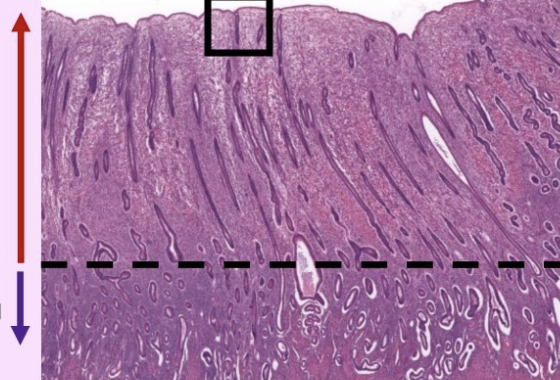
what is this slide
top = stratum functionale
bottom = stratum basale
endometrium of uterus
bottom = stratum basale
endometrium of uterus
34
New cards
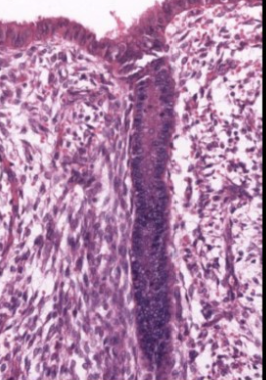
what is this slide
uterine gland
35
New cards
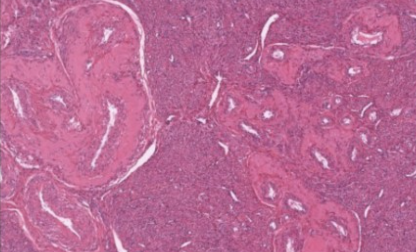
what is this slide
myometrium of uterus
36
New cards
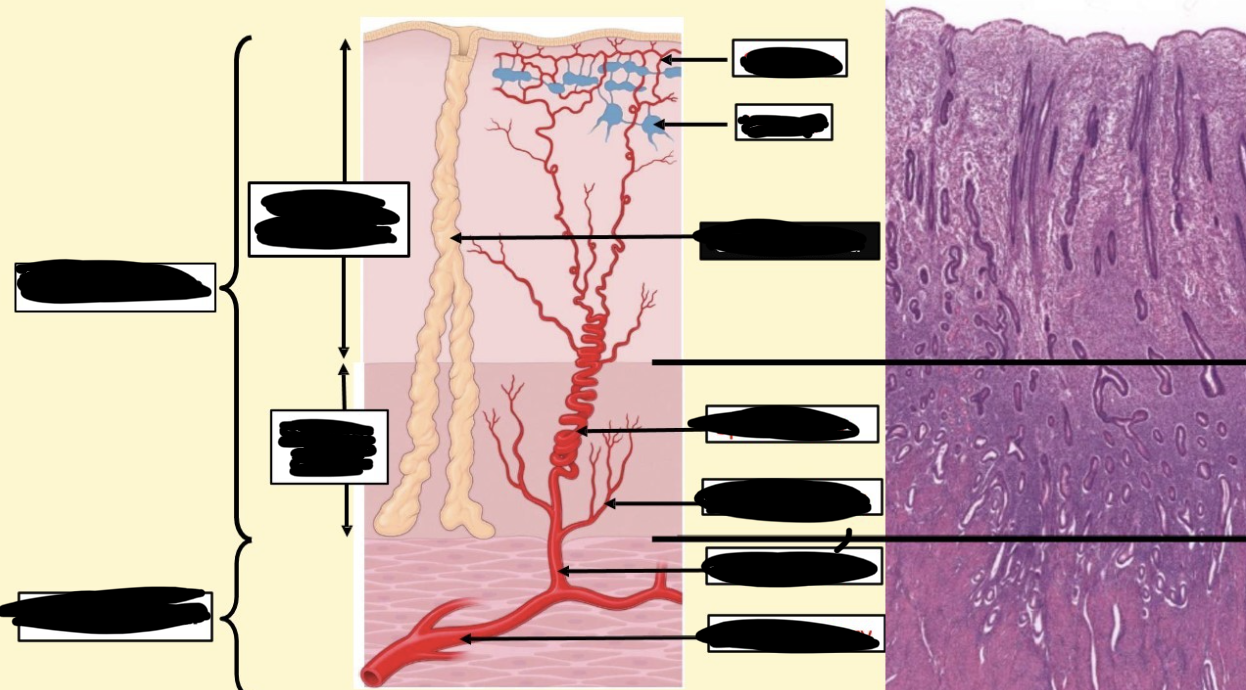
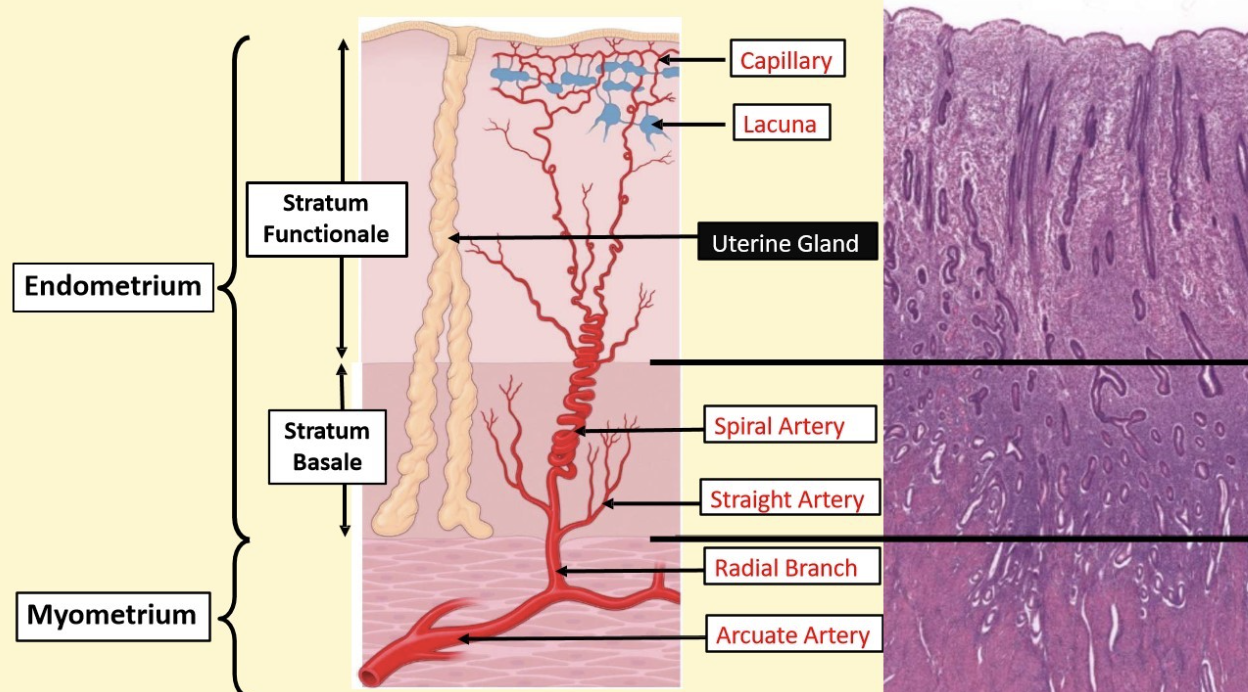
blood supply to uterus
uterine arteries on either side give off arcuate arteries into myometrium and anastomose
37
New cards
radial branch
supply stratum basal consistently, give off straight arteries
38
New cards
spiral arteries
travel to stratum functionale, highly coiled, give off arterioles to make capillaries
39
New cards
lacuna
area where walls of blood vessels get wider and pooling of bloodu
40
New cards
stratum functionale lost during menstruation is due to
drop of hormones
41
New cards
stratum functionale lost during menstruation affect on blood supply
spiral arteries and stratum basale constrict causing stratum functionale to die off and slough
42
New cards
label this slide
43
New cards
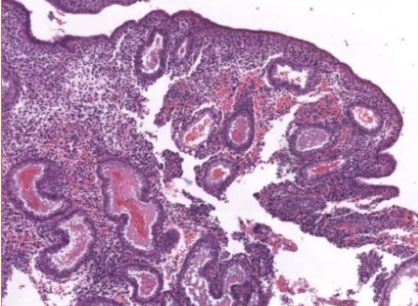
what phase of endometrial cycle
menstrual phase, loss of stratum functionale
44
New cards
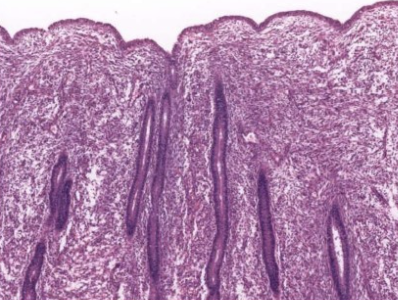
what phase of endometrial cycle
proliferative phase, stratum functionale rebuilt
45
New cards
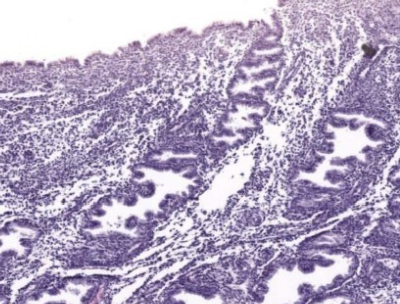
what phase of endometrial cycle
secretory phase, uterine glands form, epithelium fills with secretions in preparation for implantation
46
New cards
proliferative phase
* influenced by estrogen
* day 5-14
* day 5-14
47
New cards
estrogen affect on proliferative phase
* epithelial cells in basal portion of glands reconstitute the glands in the stratum functionale
* stromal cells proliferate and secrete collagen and ground substance
* spiral arteries lengthen
* stromal cells proliferate and secrete collagen and ground substance
* spiral arteries lengthen
48
New cards
secretory phase
* influenced by progesterone produced by corpus luteum
* day 14-28
* day 14-28
49
New cards
progesterone acting on secretory phase
* glands enlarge to corkscrew or s shaped
* gland lumina becomes sacculated, epithelial secretory cells secrete fluid containing nutrients and glycogen
* increased vascularity, spiral arteries lengthen
* gland lumina becomes sacculated, epithelial secretory cells secrete fluid containing nutrients and glycogen
* increased vascularity, spiral arteries lengthen
50
New cards
pregnancy
fertilization in ampulla, blastocyst implants in endometrium cells making placenta (trophoblast cells) make hCG which acts on corpus luteum to keep it alive
51
New cards
menstruation
levels of LH drop, corpus luteum degenerates which leads to a drop in progesterone and estrogen, the drop of hormones trigger menstrual phase
52
New cards
menstrual phase
* day 28-5
* hormone levels decrease, uterine glands stop secreting, contraction of spiral arteries, stratum functionale becomes ischemic and vessels rupture, menstrual discharge
* hormone levels decrease, uterine glands stop secreting, contraction of spiral arteries, stratum functionale becomes ischemic and vessels rupture, menstrual discharge
53
New cards
menstrual discharge
blood, uterine fluid, stromal and epithelial cells
54
New cards
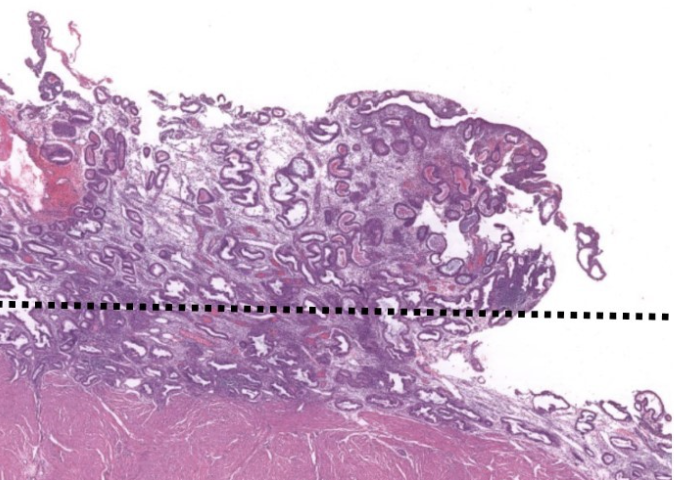
what phase is this
menstrual phase
55
New cards
cervix epithelium
simple columnar epithelium with branched mucous secreting glands
epithelium invaginates on itself making branches
epithelium invaginates on itself making branches
56
New cards
cervix histology
no spiral arteries, epithelial (nabothian) cyst
57
New cards
cervix during pregnancy
estrogen makes mucous is less viscous and less sticky
58
New cards
cervix not during pregnancy
progesterone makes mucous more viscous and sticky
59
New cards
epithelial (Nabothian) glands
blocked mucous glands
occurs when the cervix transitions from endocervix to exocervix
occurs when the cervix transitions from endocervix to exocervix
60
New cards
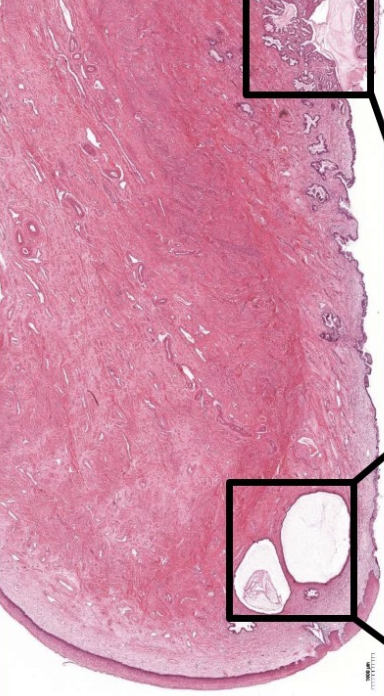
label this slide
cervix
61
New cards
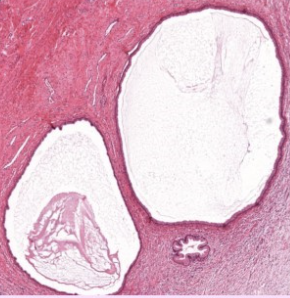
what is this
epithelial cyst
62
New cards
transformation zone
endocervix to exocervix transformation, towards stratified squamous non keratinized epithelium
63
New cards
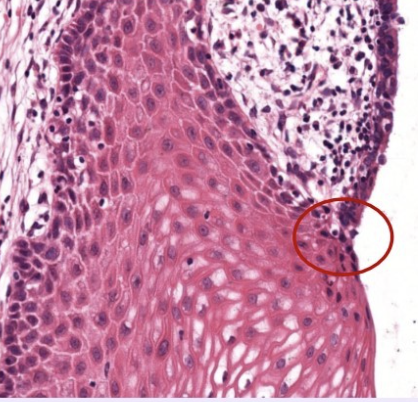
label this slide
transformation zone (to stratified squamous non keratinized epithelium)
64
New cards
vagina epithelium
stratified squamous non keratinized epithelium and lamina propria
65
New cards
vagina mucosa
estrogen influences the production and accumulation of glycogen by epithelial cells
66
New cards
vagina muscularis
indistinct thin inner circular and thick outer longitudinal layer
67
New cards
layers of vagina
mucosa, muscularis, adventitia
68
New cards
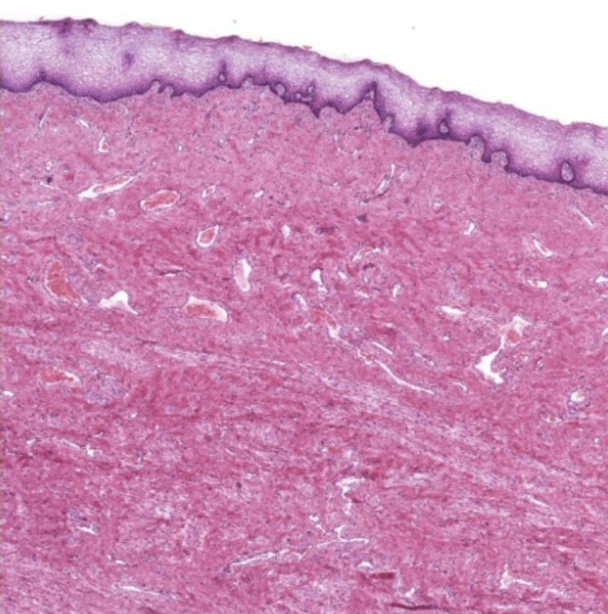
what is this a slide of
vagina
69
New cards
mammary gland organization
* modified apocrine sweat glands
* 15-20 lobes branching into lobules
* terminal duct lobular unit
* DICT and adipose tissue
* 15-20 lobes branching into lobules
* terminal duct lobular unit
* DICT and adipose tissue
70
New cards
what determines size of glands / breast
adipose tissue, during pregnancy amount of glandular tissue increases
71
New cards
compound tubuloalveolar gland
tubules and alveoli at the end of the mammary duct system producing secretions
72
New cards
what separates lobes of mammary gland
CT septa
73
New cards
areola
pigmented region surrounding nipple
74
New cards
glandular portion of mammary gland
lobes divided into lobules, lobules form lactiferous ducts which form lactiferous sinus
75
New cards
development of mammary glands
* dermal mesenchymal cells induce formation of epithelial bud
* adipocytes stimulate branching of epithelial mammary cords
* mammary cords become hollow and epithelial cells differentiate
* adipocytes stimulate branching of epithelial mammary cords
* mammary cords become hollow and epithelial cells differentiate
76
New cards
luminal cells
line inner duct of mammary cord or secretory cells
77
New cards
cap cells of mammary cords
divide and differentiate into regular epithelial or myoepithelial cells
78
New cards
how is lumen of mammary cord created
apoptosis in middle of cord
79
New cards
what forms opening at nipple
lobes and lobules form lactiferous ducts and sinuses that open at nipple
80
New cards
epithelial tissue in mammary glands histology
basophilic regions
81
New cards
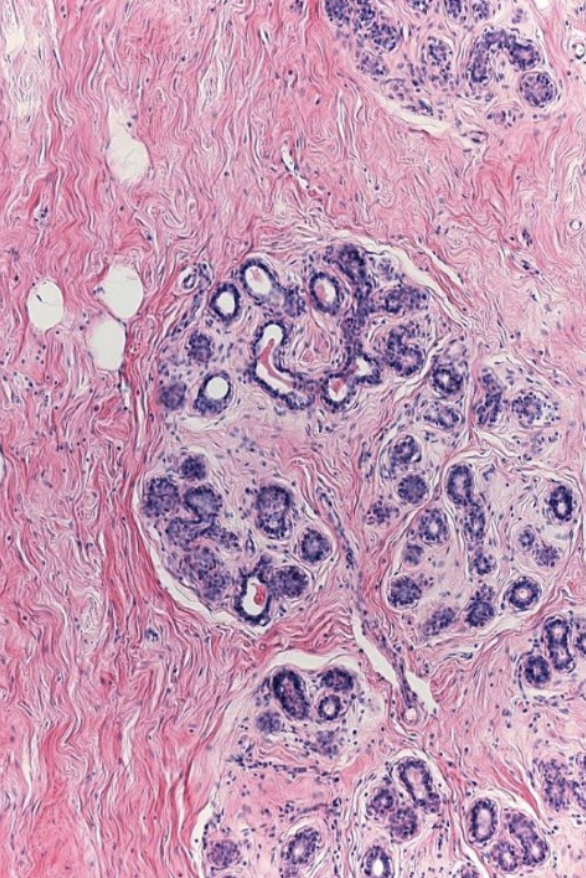
what is this slide
mammary gland
82
New cards
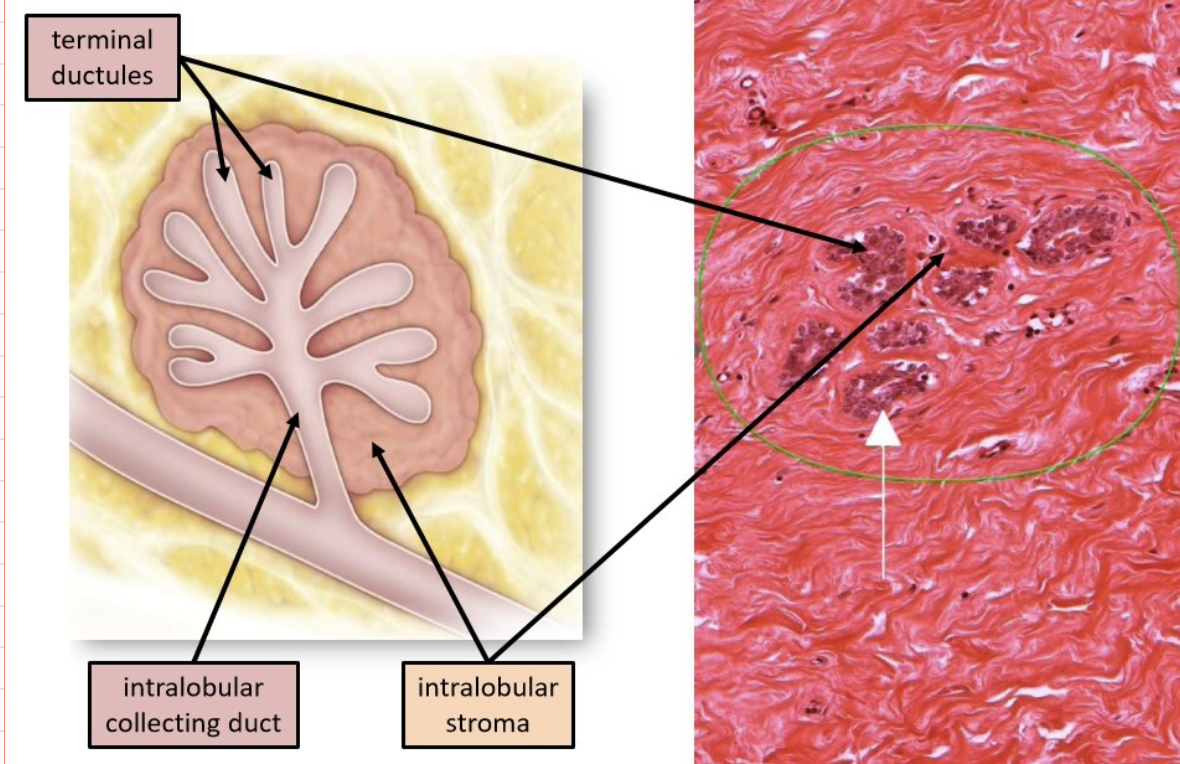
terminal duct lobular unit (TDLU)
terminal ductules, intralobular collecting duct, intralobular stroma
83
New cards
active mammary bland
alveoli bud off terminal ductules producing components of milk
84
New cards
lining of terminal duct lobular unit (TDLU) ducts
simple cuboidal epithelium
85
New cards
intralobular stroma
surrounds duct system, specialized LCT that is hormone sensitive
86
New cards
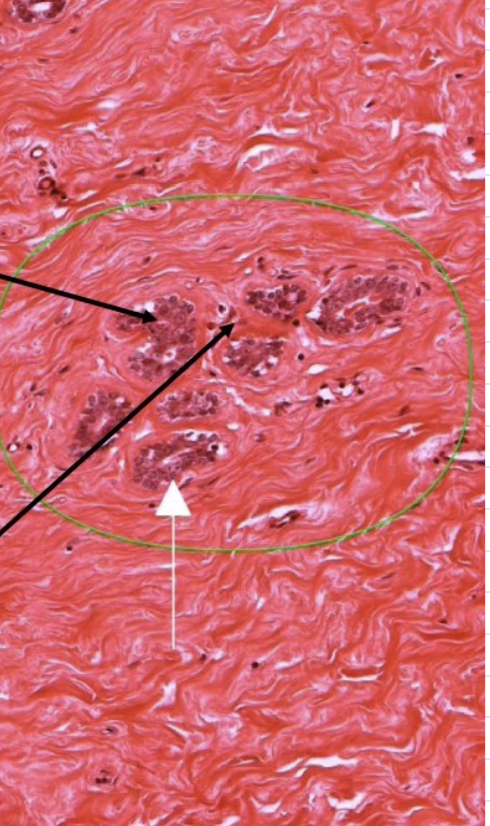
label this slide
terminal duct lobular unit (TDLU)
87
New cards
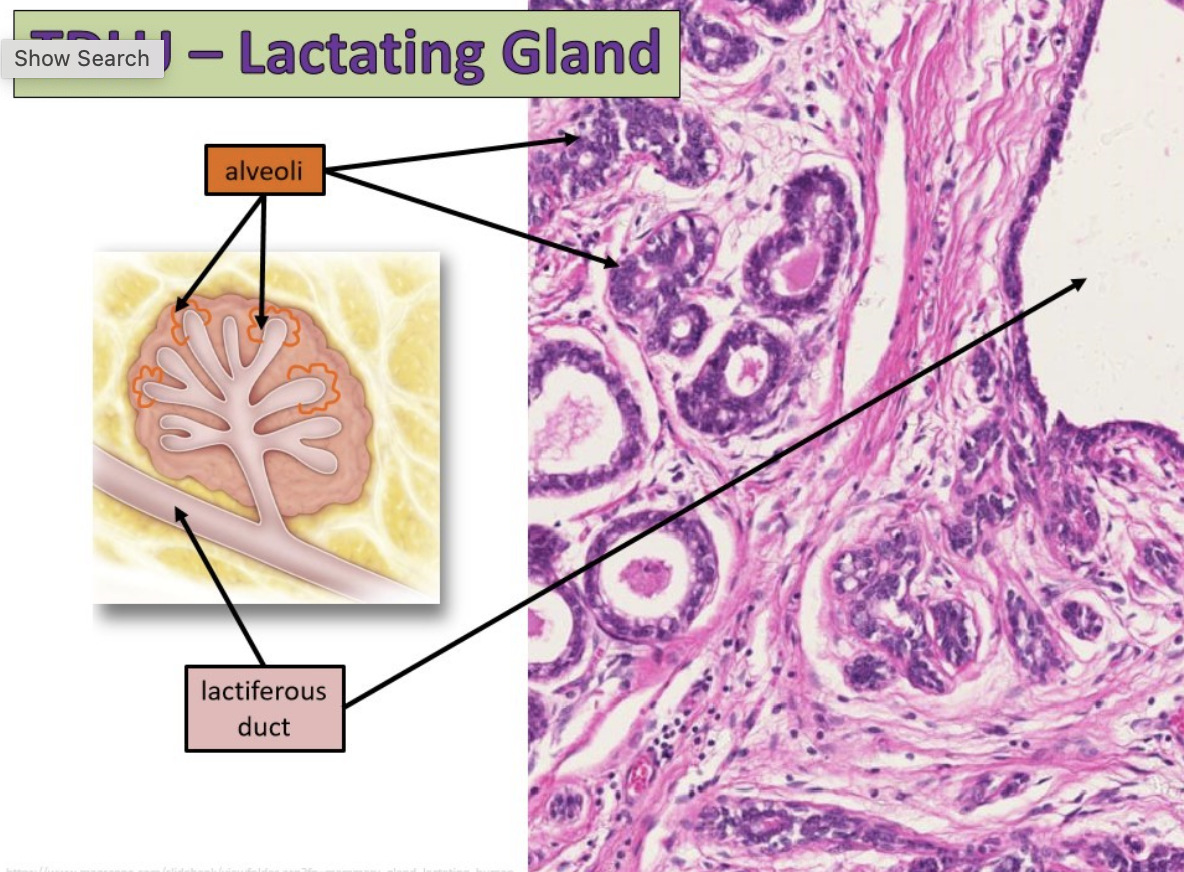
terminal ductules in a lactating gland
alveoli budding off
88
New cards
alveoli and ductule epithelium
simple cuboidal epithelium
89
New cards
CT of lactating gland
DCT
90
New cards
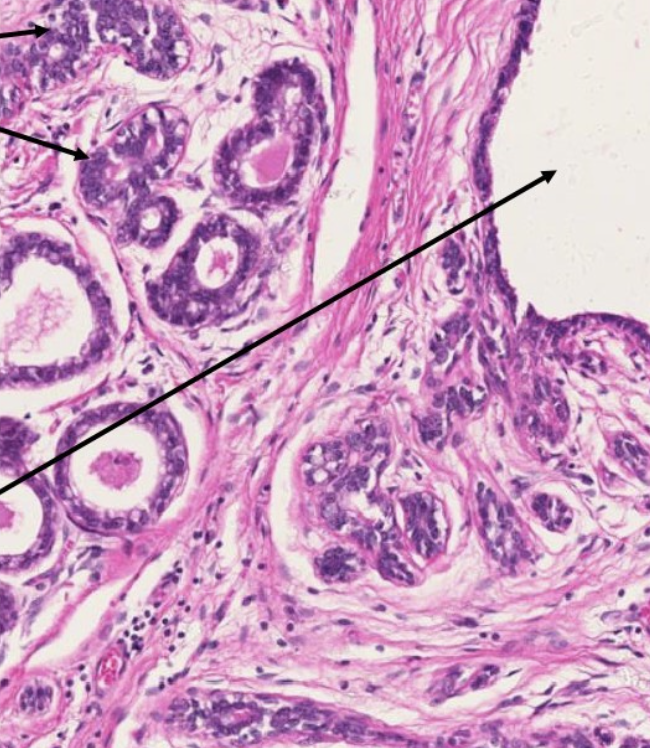
label this slide
lactating mammary gland
91
New cards
intralobular CT in stroma
extension of papillary layer of dermis, LCT
92
New cards
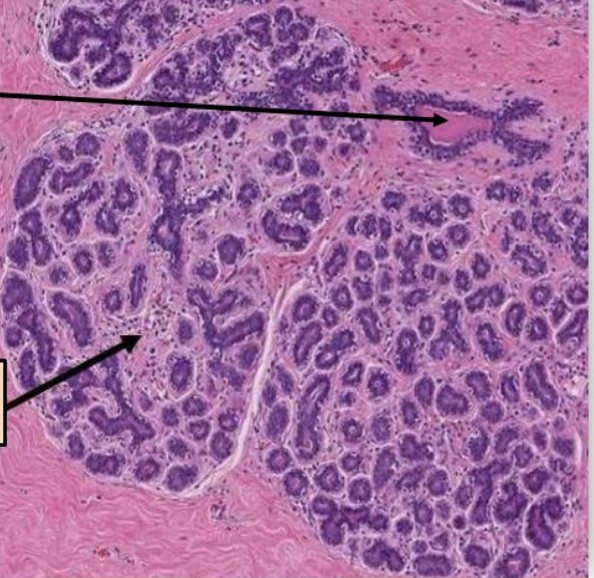
label this slide
lactiferous duct of terminal duct lobular unit (TDLU)
93
New cards
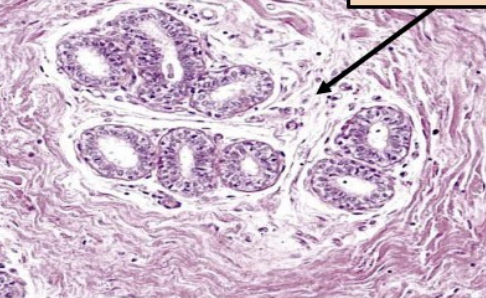
label this slide
intralobular stroma of terminal duct lobular unit (TDLU)
94
New cards
CT surrounding terminal duct lobular unit (TDLU)
DICT
95
New cards
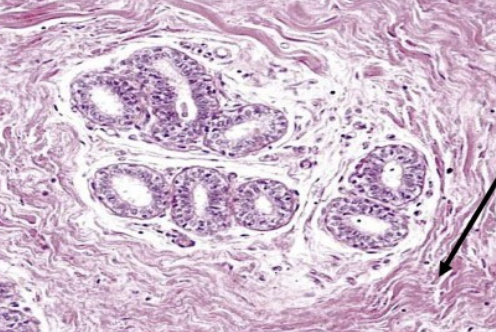
label this slide
interlobular DICT
96
New cards
lactiferous duct epithelium
simple cuboidal epithelium and transition to epithelium of skin (stratified squamous keratinized epithelium)
97
New cards
lactiferous sinus
swelling of lactiferous ducts, where milk collects, large empty epithelial lined spaces
98
New cards
smooth muscle bundles of nipple
surround ducts and sinuses, push secretions to surface, important for erections of nipple
99
New cards
sebaceous glands
modified, lubricate nipple and areola during suckling from baby
100
New cards
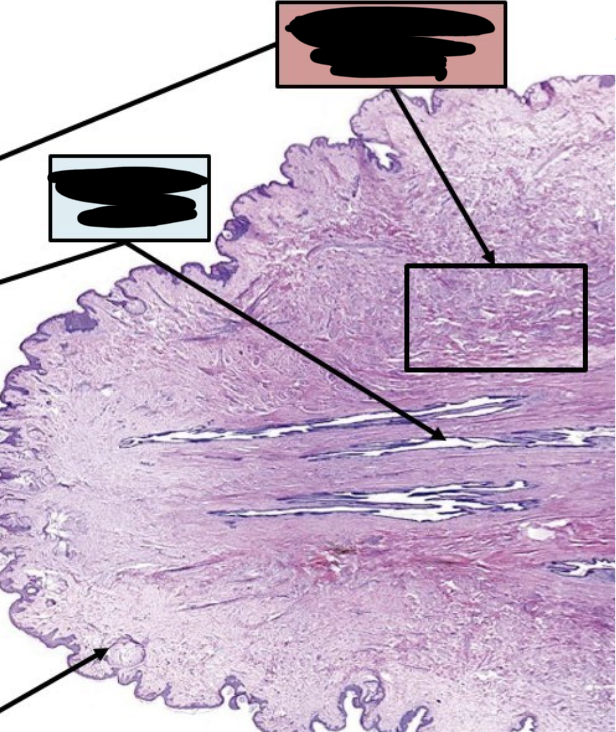
label this slide
nipple