Introduction to Clinical Health Psychology
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What is CHP rooted in?
a strong scientific evidence base and encompasses a breadth of inputs to support optimal healthcare provision and improve clinical outcomes
What does CHP aim to provide?
psychologically informed care pathways inc psych informed envs and trauma informed care
What may CHP offer?
certain inputs to achieve their aim
this inc providing specialist needs asm , care planning and delivery of interventions w/in a multidisciplinary care context to affect pos change for patients who may be facing distressing and chronic physical complaints/illness/brain changes
What does CHP look like?
a field which addresses psych, social, cultural and biological factors as applied to physical health and wb
applying knowledge in medicalised context
familirisation w/ psychosocial dimensions of health and health related bv
using knowledge of cog, social and clinical processes’ impacts on health bvs to understand/address illness, injury and disability - help them cope with it
What has there been growing evidence for?
over the least 4 decades that bv/thoughts/appraisals contb to health status and quality of life
What led to the dv of CHP?
skepticism abt mind body dualism and dissatisfaction w/ limits of biomedical approach
Whst did CHp cause a shift to?
indv respb and prevention
What is the biopsychosocial model?
a transdisciplinary model which examines the complex interactions bt bio, psych and social factors in health and disease
What do the factors in the BM encompass?
biological - physicology, genetics, biochem, neurobiology
social - economic factors, social support, cul, env
psych - emotional factors, bv patterns, coping mechanisms
biosocial - health, illness, mood
psychsocial - trauma, life events, adversity
How can we apply the BM to CHP physically?
physical problems sa unstable blood sugar, shortness of breath, visible scars etc can adversely impact psych wb and social integration - e.g. comorbid dpr/anx
tf patients w/ long term conditions may have unmet needs to psychotherapy/education and social support - leads to vicious cycle
How can we apply the BM psychosocially to CHP?
psychosocial problems sa dpr, anx and embarassment etc can adversely impact on physical health status directly sa psychoneuroimmunological pathways and indirectly sa by poor adherence to treatment and unwillingness to report symptoms and get help
by providing psychotherapy/edu and social support for patients w/ long term conditions might lead to improved physical health status
How is CHP typically delivered?
in acute settings and primary care, increasingly public health
services may specialise acc to age sa paediatrics or condition sa cardiology
What type of rubric do CHPs follow?
that psych principles, theory and practice are utliised to help those w/ physical health problems/disability
What can delivery focus on?
illness/symptoms
treatment
recovery/complications
quality of life
family/carers/staff
What are common responses to being diagnosed with a long term/chronic condition?
anger, anxiety, hopelessness and stress
What might affect the impact of responses?
diagnosis - how, when, meaning
point in life cycle - just got married, started uni, retired et
adjustments
treatments (or their absence)/concordance
side effects/comorbidities
Who might a CHP see?
clients w/ health anxiety or unexplained physical symptoms or diagnosed health problems
staff - delivering care and its impact
What do you want to do when working with adult clients who are ill?
help them make sense of the condition and accommodate change in the context of their time of life
acknowledge the impact on their self identity and their rs
look at any stigma asc with their condition and any losses/gains
How might you approach domains to explore?
share the story of illness and help reduce the pace
normalise the impact of illness and consider its emotional impact and on rs and lifestyle
what is the meaning of their illness and on their family
What is the process whilst working with patients?
respect their agency/family authoirty
address misunderstands and communication issues with/without family
identifying resources and prepare for future
What can be applied to working in clinical health settings?
all the main therapeutic models sa CBT and 3rd wave approaches sa compassion focused therapy and ACT but irrespective of theoretical orientation, psychoeducation is still imp
What should specific health psychology models do?
inform asm, formulation and interventions
What are illness perceptions?
a patient’s own implicit common-sense beliefs abt their illness ” (Leventhal et al., 1980, 2007a, 2007b; Leventhal and Nerenz 1985)
What do IPs provide?
patients w/ a framework/schema for coping w/ and understanding their illness
What are IPs influenced by?
info presented by healthcare professionals
prior experience w/ illness
info gained from social context
cultural beliefs
What type of beliefs are IPs?
beliefs that they have a sig impact on the bvs an indv uses to cope and manage their illness and tf on outcomes inc both clinical and quality of life (Dempster & McSharry, 2015)
What do IPs tend to be discussed in terms of?
the self regulatory model - a dynamic process based on traditional models of problem solving in which an indv attempts to preserve the sense of self and solve the problem of what is happening to their health (Leventhal, 1980, 2007A)
Desc the SRM
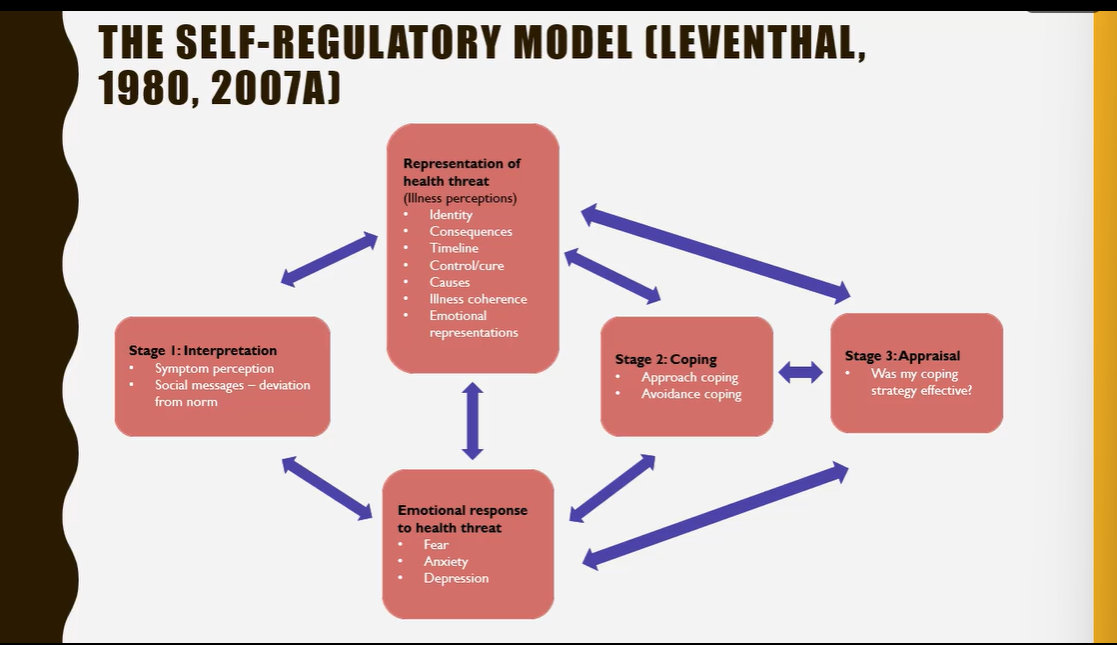
How long will the phases of the SRM last?
until coping strats are deemed successful and a state of equilibrium attained - any onset of illness interpreted as a problem and indv motivated to reestablish their state of health
How many IPs were there originally?
5 then 2 more (illness coherence and emotional representation added_
Desc the IPs
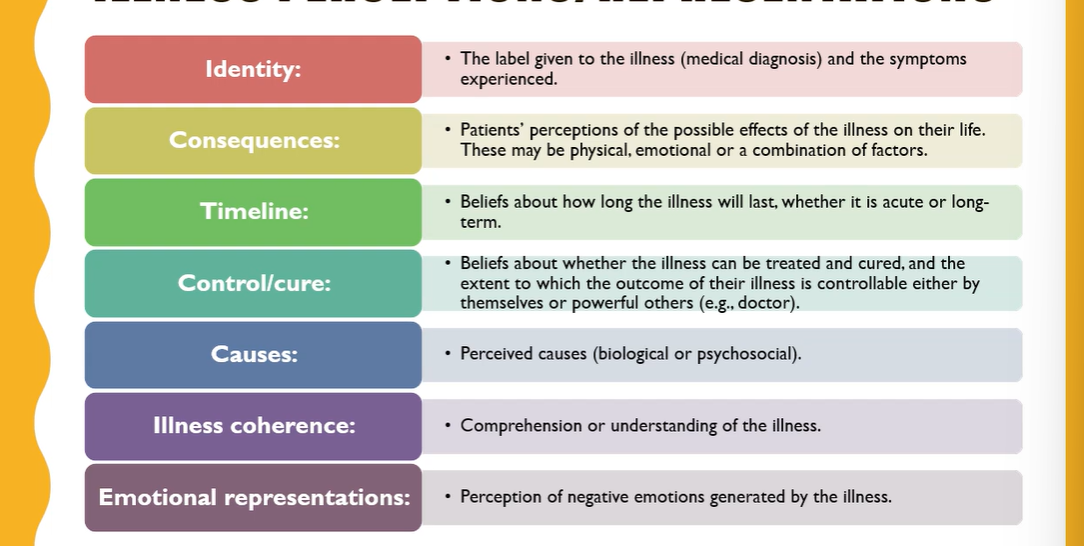
What did Lewin (1997) say?
beliefs are imp and impacts us physically
How do we elicit IPs?
measure using IPQ-R (Moss-Morris et al., 2002)
ask questions during consultations sa what do you feel caused your condition or how is yr condition have an impact on you emotionally
How can we address IPs?
self management or rehab programmes
bv change techniques
CBT
providing psychoeducation
What are the 3 approaches to coping with the crisis of illness?
coping with the crisis of illness
adjustment to physical illness
benefit finding - post traumatic growth
What is crisis theory? (Moos & Schaefer, 1984)
relates to grief and mourning of change after crisis
crisis nature of illness can be exacerbated by the unpredictability and ambiguity of that illness
What 3 processes make up the crisis theory’s coping process?
cognitive appraisal - assessment of the seriousness and significance of the life change adaptation
adaptive tasks - learning to deal with pain and changes
coping skills - mental preparation
What did Taylor et al. 1984 look at?
examined ways indvs adjusted to threatening events and made cognitive adaptation theory which is a model based on interviews with rape victims and cardiac/cancer patients
What did Taylor et al. 1984 suggest?
that coping with threatening events inc illness consists of 3 process
search for meaning (why did this happen and what effect has it had on my life?), search for mastery (how can i prevent a similar event happening in the future and what can i do now?) and process of self enhancement (how can i rebuild my self esteem)
What did previous theories look at?
focus on return to normality but that is often something lost and has a neg focus
What is post traumatic growth?
based in positive psych and says although there are some neg consqs for lifestyle and quality of life, ppl can consider life to have improved
What did Sodergran et al. 2002 do?
made silver lining questionnaire and found that positivity can be improved by rehabilitation, the pos consqs of illness are varied and more common than realised
What makes ppl more likely to adhere to treatment?
perception of symptoms
belief of its seriousness and in treatment
family and social input
What is health?
a state of complete physical, mental and social wb and not merely the absence of disease/infirmity - WHO, 1946
What do recent definitions of health inc?
cultural, psychosocial and economic elements
What did Dahlgren & Whitehead, 1991 make?
determinants of health model which is used a lot in health psych and illustrates factors which infl health and its inequalities
What are the most dominant health issues rn?
dementia
heart diseases
cardiovascular diseases
respiratory diseases
lung cancer
covid
What are some risk factors for dementia?
physical inactivity
smoking and drinking
air pollution and head injury
What interventions help with adjustment?
CFT
What interventions help with managing stress and anxiety and dpr?
CBT, CFT, family therapy
What interventions help improve and maintain cog function?
cog stimulation theory and maintenance CST (also helps with maintaining quality of life, alongside life story work)
What is preventable?
upto 80% of premature CVD deaths are preventable
What explains the vast majority of CVD?
high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diet, obesity etc and in some cases exposure to these rfs is increasing
What increases the risk of several types of cancer?
obesity and alcohol - most imp nutritional factors contb to total burden of cancer worldwide (Key et al 2020)
What is the incidence of cancer also associated with?
deprivation, with greater prevalence in more deprived areas
How does smoking increase?
as SES diminishes, although reduction in overall prevalence, masks relative static use in socially disadvantaged groups
What should healthcare settings ensure?
that its able to preserve clients dignity, privacy, confidentiality and foster honest, trust and compassion
What is important to consider in sessions?
be flexible in timing and negotiate movement during session if discomfort/fatigue an issue
invite clients to let you know of discomfort and consider how/what you modify it at bedside
seek to structure and prioritise problems - physical and broader psychosocial issues