Microbio Lecture 8 Environmental Sensing and Chemotaxis
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
1
New cards
What are the two component to two component regulatory systems?
Component 1: The Sensor Histidine Protein Kinase
Component 2: Response Regulator
Component 2: Response Regulator
2
New cards
Two Component Regulatory Systems
Important mediators of signal transduction that allows bacteria to detect physical/chemical changes and relay this signal to respond
3
New cards
Sensor Histidine Protein Kinase
\-Membrane associated or cytoplasmic
\-autophosphorylates a conserved histidine residue environmental signal
\-sensors consists of at least two domains:
a. variable response domain (why variable?)
b. conserved transmitter domain (histidine protein kinase); where they get phosphorylated
\
\-sensors usually form dimers and exhibit autokinase activity (ATP binds to one subunit and phosphorylates the other in a process known as transphosphorylation)
\-sensor transmits phospho-group from histidine residue to aspartate residue on response regulator
\-autophosphorylates a conserved histidine residue environmental signal
\-sensors consists of at least two domains:
a. variable response domain (why variable?)
b. conserved transmitter domain (histidine protein kinase); where they get phosphorylated
\
\-sensors usually form dimers and exhibit autokinase activity (ATP binds to one subunit and phosphorylates the other in a process known as transphosphorylation)
\-sensor transmits phospho-group from histidine residue to aspartate residue on response regulator
4
New cards
Transphosphorylation
Phosphate group is transferred to the receivor
5
New cards
Response Regulator
\-second part of 2 component regulatory system
\-consists of two domains: receiver domain with aspartate residue and variable regulator
\-different phosphorylated response regulators have different half lives; length of half life determines duration of response to changing environmental conditions
\-many dimerizes after phosphorylation and bind to DNA
\-consists of two domains: receiver domain with aspartate residue and variable regulator
\-different phosphorylated response regulators have different half lives; length of half life determines duration of response to changing environmental conditions
\-many dimerizes after phosphorylation and bind to DNA
6
New cards
What determines length of the duration of a response?
It depends on the half life of phosphorylated response regulators
7
New cards
Do all response regulators bind to DNA?
No not all of them do ex. CheY and CheB
8
New cards
CheY and CheB
two response regulators involved in chemotaxis; they dont bind to DNA at all but modulate activity of other proteins
9
New cards
EnvZ/OmpR System of E. Coli
\-Two Component Regulatory System
\-Has EnvZ sensor kinase and OmpR regulator
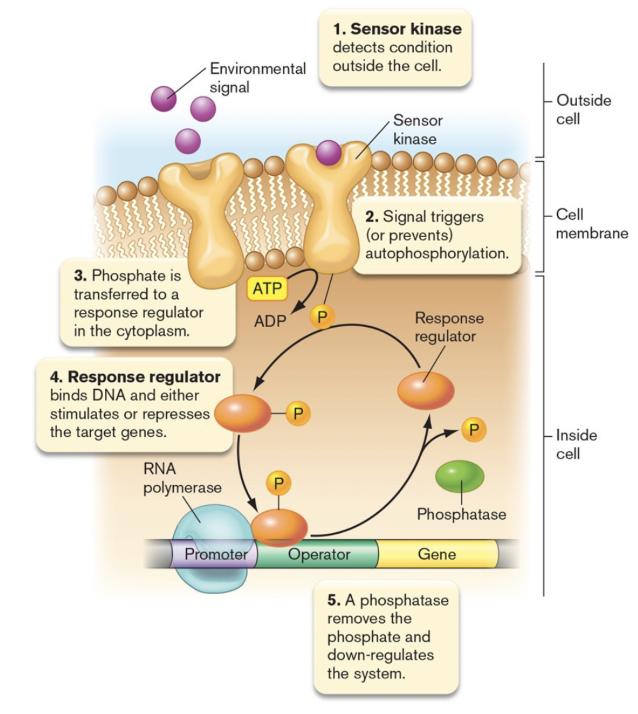
1\. Signal binding causes activation of the autokinase resulting in ATP hydrolysis and phosphorylation of the histidine on phosphotransfertase subdomain
2\. Phosphoryl group transferred to aspartyl group (D) on response regulator
\-Has EnvZ sensor kinase and OmpR regulator
1\. Signal binding causes activation of the autokinase resulting in ATP hydrolysis and phosphorylation of the histidine on phosphotransfertase subdomain
2\. Phosphoryl group transferred to aspartyl group (D) on response regulator
10
New cards
If ompF is upregulated by low osmolarity and ompC is upregulated by high osmolarity, which encodes a porin protein with a larger diameter?
OmpF does
11
New cards
Sporulation Response of B. Subtilis
\-sensor kinase sends signal to series of proteins before it reaches to the response regulator where it interacts with DNA
12
New cards
Taxis
Oriented movement of motile organisms
13
New cards
What does taxis require?
motility and sensors
14
New cards
How does the sensor help the taxis?
It helps the bacteria know whether to go forward or which direction
15
New cards
What are taxis distinguished by?
They are distinguished by the basis of stimuli:
\- Chemotaxis (chemical substances)
\- Phototaxi (light)
\- scotophobotaxis (darkness)
\- Chemotaxis (chemical substances)
\- Phototaxi (light)
\- scotophobotaxis (darkness)
16
New cards
Chemotaxis
Prokaryotes have gradient sensing mechanism that allows them to compare concentration of a chemical over short time intervals rather than having to make instantaneous comparison in space
\-mechanism makes it possible for them to make spatial comparisons over many cell lengths rather than a single cell length
\-mechanism makes it possible for them to make spatial comparisons over many cell lengths rather than a single cell length
17
New cards
Bacterial Flagellum
Has a hook that helps it rotate via the motor switch (Fli proteins)
18
New cards
Fli Proteins
Motor switch for bacterial flagellum
19
New cards
What are some different types of flagella?
Peritrichous, polar, and lophotrichous
20
New cards
What modes of movements is chemotaxis based on?
Going forward or stop and tumble
21
New cards
What happens when bacteria rotates counterclockwise?
Moves forward
22
New cards
What happens when bacteria rotates clockwise?
They stop and tumble which can allow them to switch to a different direction
23
New cards
Random Walks
In absence of a chemical gradient, bacteria move in a random fashion that includes runs and tumbles
\-generates a random movement
\-generates a random movement
24
New cards
Biased Random Walk
\-can’t make conscientious decision to walk somewhere
\-in presence of gradient of attractant/repellant, bacteria bias their random walk to include longer runs and fewer tumbles up/down concentration gradient
\-in presence of gradient of attractant/repellant, bacteria bias their random walk to include longer runs and fewer tumbles up/down concentration gradient
25
New cards
What type of flagella does E. coli have?
\-Peritrichous
\-Counterclockwise Rotation → Smooth Swimming
\-Clockwise → Flagellar bundles fly apart resulting in tumbling
\-Counterclockwise Rotation → Smooth Swimming
\-Clockwise → Flagellar bundles fly apart resulting in tumbling
26
New cards
Clockwise Movement
Tumbling
27
New cards
Counterclockwise Movement
Smooth swimming
28
New cards
Bacterial Chemotaxis
A set of proteins that has a sensor histidine kinase that gets signals from attractants and then sends signals to response regulator to modulate the chemotaxis by alternating duration of periods of smooth swimming and tumbling
29
New cards
Sensory Proteins
Tar and Tsr proteins; methyl accepting chemotaxis proteins (MCPs) that act as the bacteria’s “nose”
30
New cards
MCP
methyl accepting chemotaxis proteins; acts as the bacteria “nose”
31
New cards
Tar
an MCP that senses aspartate and maltose as well as repellants cobalt and nickel; have multiple binding sites in sensor domains for attractants and repellants (each causes different conformational change)
32
New cards
What are the MCPs in contact with?
They are in contact with CheA and CheW
33
New cards
CheA
a sensor histidine kinase protein that is held by CheW
34
New cards
CheW
Protein that is in contact with MCP and CheA and helps alter rate of autophosphorylation of CheA
35
New cards
What does ligand binding to MCP result in?
Conformational changes that change rate of CheA autophosphorylation with help of CheW
36
New cards
What is the response regulator of CheA?
CheY; CheA transfers the phosphyl group to the aspartate residue of CheY
37
New cards
CheY
Response regulator of CheA; when phosphorylated it interacts with FliM to change rotation of bacteria from CCW to clockwise to cause tumbling
38
New cards
FliM
protein that is component of flagellar motor, responsible for changing direction of the bacteria movement
39
New cards
Does more attractant increase or slow the rate of autophosphorylation?
It slows the rate of autophosphorylation
40
New cards
What does phosphorylated CheA do?
It transfers its phosphate to aspartate residue on response regulator CheY
41
New cards
CheY
a response regulator
42
New cards
What does phosphorylated CheY do?
It interacts with FliM (part of the flagellar motor) to change direction of rotation from CCW to CW (results in tumbling)
43
New cards
What happens when an attractant is added to chemotaxis?
1\. In response to attractant binding to MCP, CheA slows its rate of autophosphorylation
2\. In absence of CheA\~P, CheY remains unphosphorylated and does not interact with FliM; CheZ helps keep CheY dephosphorylated in low levels of CheA\~P
3\. Disrupts CheY-FliM interaction switches flagellar to CCW rotation and continues to do smooth swimming
2\. In absence of CheA\~P, CheY remains unphosphorylated and does not interact with FliM; CheZ helps keep CheY dephosphorylated in low levels of CheA\~P
3\. Disrupts CheY-FliM interaction switches flagellar to CCW rotation and continues to do smooth swimming
44
New cards
CheZ
Protein that keeps CheY unphosphorylated in low levels of phosphorylated CheA
45
New cards
What happens when repellant is added to chemotaxis?
1\. Repellant binding by MCP leads to increase in CheA autophosphorylation
2\. CheA\~P transfer phosphate to CheY and stimulates its interaction with FliM
3\. CheY\~P-FliM interaction switches flagellar motor to clockwise movement and initiates tumbling
2\. CheA\~P transfer phosphate to CheY and stimulates its interaction with FliM
3\. CheY\~P-FliM interaction switches flagellar motor to clockwise movement and initiates tumbling
46
New cards
Adaptation of Chemotaxis
\-Adaptation allows resetting of signal state of MCP’s altho concentration of attraction remain the same
ex. cells bias their random walk up a gradient but can adapt to do random walk in high (but unchanging) conc. of the attractant
ex. cells bias their random walk up a gradient but can adapt to do random walk in high (but unchanging) conc. of the attractant
47
New cards
Sporulation
Process of bacteria asymmetrically dividing creating a spore that will break out of mother cell
Spore can survive in extreme environmental conditions
Spore can survive in extreme environmental conditions
48
New cards
Sporulation in B. Subtilis
49
New cards
What does B. Subtilis sporulation involve?
\-Quorum Sensing: Pheromones
\-Cell-cell signaling: -phosphorelay
\-Transcriptional regulation: sigma factors
\-Cell Type Specific Proteolysis - SigmaE and K
\-Cell-cell signaling: -phosphorelay
\-Transcriptional regulation: sigma factors
\-Cell Type Specific Proteolysis - SigmaE and K
50
New cards
B. Subtilis Endopore
\-they are remarkably resistant
\-can survive high temperatures, UV lights, and in organic solvents
\-can survive high temperatures, UV lights, and in organic solvents
51
New cards
What triggers sporulation?
\-Crowding
\-Starvation
\-Lack of options
* kind of a last ditch process that is irreversible once it started and requires a lot of energy
\-Starvation
\-Lack of options
* kind of a last ditch process that is irreversible once it started and requires a lot of energy
52
New cards
What is sporulation governed by?
By a cascade of transcriptional factors
53
New cards
Sigma F
Sigma F triggers the start of the mother cell tries to engulf the spores
54
New cards
Sigma E
Causes the mother cell to finish engulfing the spores
55
New cards
Sigma G
Triggered by the finishing of the mother cell engulfing the spores
Sends a signal via a transduction pathway to Sigma K in mother cell to process it from an inactive pro-protein into an active transcription factor
Sends a signal via a transduction pathway to Sigma K in mother cell to process it from an inactive pro-protein into an active transcription factor
56
New cards
Sigma K
Protein in the mother cell
\-gets activated by sigma G transduction
Add additional proteins in between the spore’s layers to make it more resistant to environmental conditions; adds the cortex
\-gets activated by sigma G transduction
Add additional proteins in between the spore’s layers to make it more resistant to environmental conditions; adds the cortex
57
New cards
Sigma H and Spo0A
\-activated during stationary phase via a two component regulatory system
\-trigger the process of asymmetric cell division
\-trigger the process of asymmetric cell division
58
New cards
What is the result of sporulation?
An endospore is formed and the mother cell degrades
59
New cards
What phase does sporulation occur?
It occurs during stationary phase
60
New cards
Spo0A
Response regulator activated at the end of a phosphorelay of a two component regulatory system
61
New cards
When does Spo0A and Sigma H get activated?
During the stationary phase; they are activated via two component regulatory system
62
New cards
Quorum Sensing
\-Critical component of sporulation
\-helps sense that the area is crowded and sense if there is presence of food or not
\-helps sense that the area is crowded and sense if there is presence of food or not
63
New cards
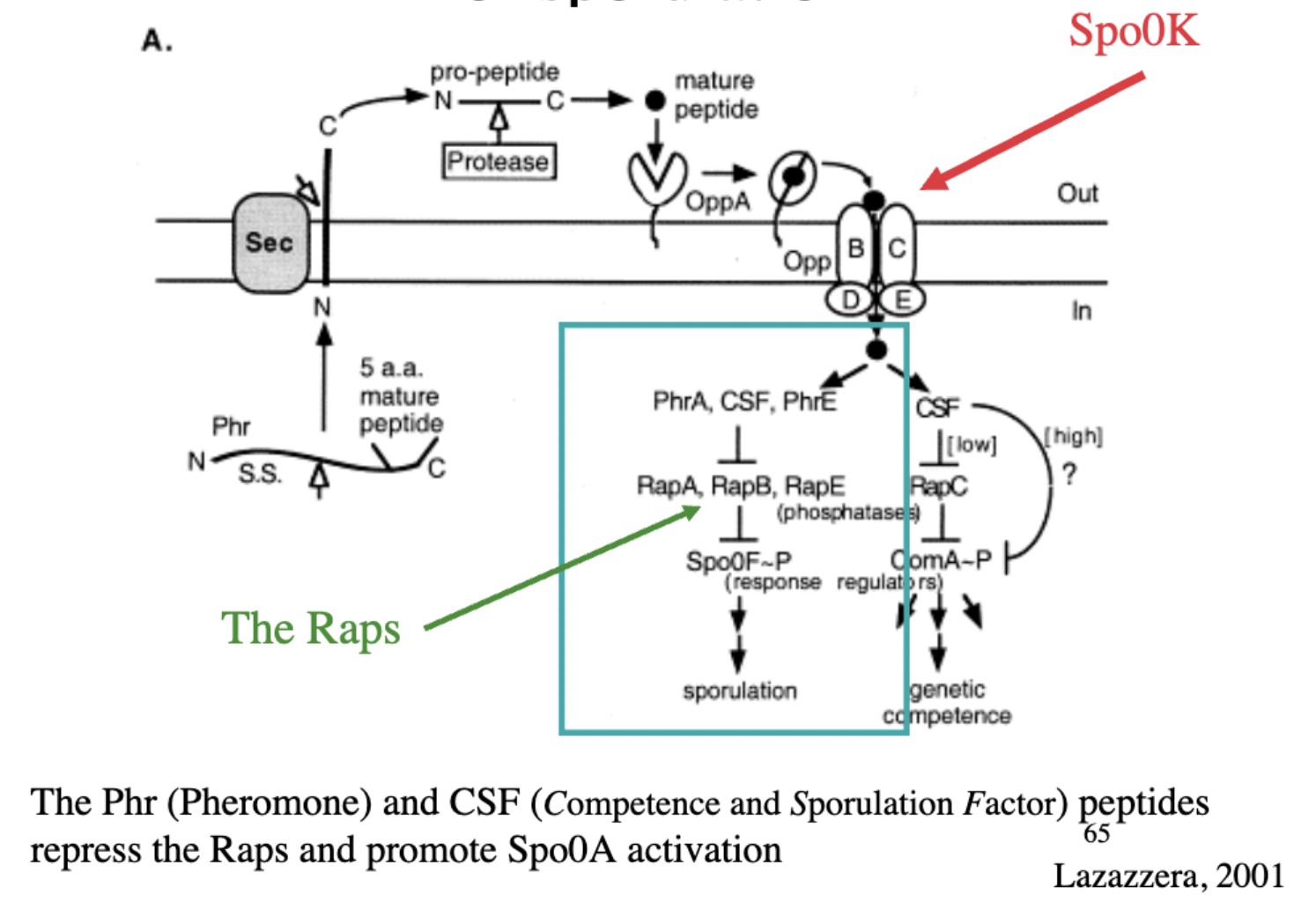
Rap Phosphatases
Proteins that can dephosphorylate Spo0F
\-block transfer of phosphyl group from Spo0F to Spo0A
\-activity dependent on quorum sensing
\-block transfer of phosphyl group from Spo0F to Spo0A
\-activity dependent on quorum sensing
64
New cards
What deactivates Rap Phosphatase?
Peptide signals
65
New cards
Quorum Sensing in B. Subtilis
cells secrete and respond to a set of small peptides via the ABC transporter Spo0K
66
New cards
Phr and CSF
peptides that repress Raps and promote Spo0A activation
67
New cards
What do you need to initiate sporulation?
Both Spo0A and Sigma H
68
New cards
How is Sigma H activated?
It’s activated in part by Spo0A\~P dependent transcription of the sigH gene
69
New cards
How would you test that Sigma H activation is related to Spo0A transcribing sigH gene?
Test this by creating a mutant that does not produce the sigH gene
70
New cards
Significance of Spo0A and SigmaH in Sporulation
Drive expression of genes responsible for the switch from medial to polar septation
71
New cards
What does Sigma E and Sigma F do in sporulation?
Required for mother cell engulfing the spore
72
New cards
What proteins are important for the engulfment in sporulation process
Sigma E and Sigma F
73
New cards
What is engulfment coupled to in the forespore?
Engulfment is coupled to Sigma G Activation in the forespore