Variable Oxidation States
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
what happens when adding zinc and acid to vanadium
can reduce vanadium step by step from vanadium (V) to vanadium (II).
what observations when zinc and acid is added to vanadium
we observe a series of colour changes known as the ‘vanadium rainbow’.
yellow (V(V)), blue (V(IV)), green (V(III)), and violet (V(II)).
the overall equation for the reaction for Vnadium reaction
2VO2++8H++3Zn→2V2++4H2O+3Zn3+
explain zinc and vanadium reaction usiing electrode potentials

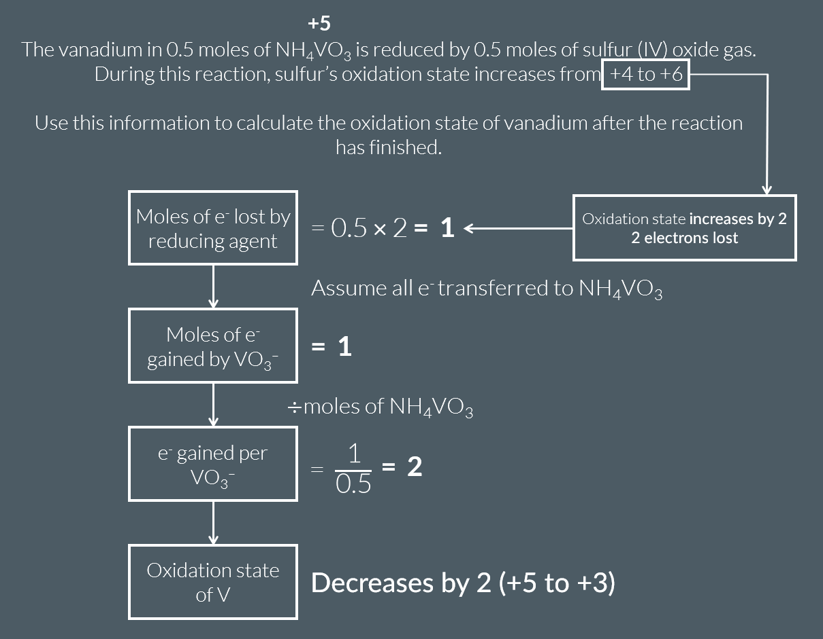
We can calculate the final oxidation state of vanadium during a reduction reaction by focussing on the number of electrons that are transferred from the reducing agent.
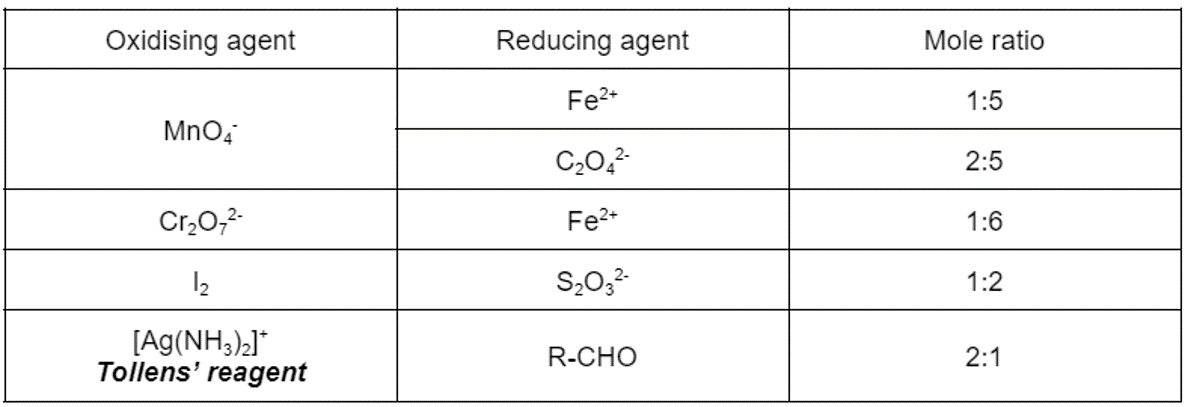
where does the highest oxidation state occur for Manganese
MnO4-
oxidation state +7
reaction of Manganate ion and Fe2+
MnO4−(aq)+5Fe2+(aq)+8H+(aq)→Mn2+(aq)+5Fe3+(aq)+4H2O (l)
reaction of Manganate ions and C2O42-
2MnO4−(aq)+5C2O42−(aq)+16H+(aq)→Mn2+(aq)+10CO2(aq)+8H2O (l)
Colour change in redox reaction for Manganate ions
Magnate ions purple in solution once fully used up change to colourless
How to work out redox titration calculations
same as acid-base reaction
They often involve taking samples, so you need to account for this in your calculations.
how to calculate % purity
%purity of substance x=( mass of x in the sample /total mass of the sample) ×100
mole ratio between reactants